[This article was first published on stevenmortimer.com, and kindly contributed to R-bloggers]. (You can report issue about the content on this page here)
Want to share your content on R-bloggers? click here if you have a blog, or here if you don’t.
The R community is a diverse and inclusive group. About a month ago (June 2020)
GitHub announced it would start to remove references to ‘master’ across its
sites and I’m surprised the R community hasn’t jumped on the opportunity to
be on the bleeding edge of this change. I think we can all take a very quick and
very small step forward in removing divisive language in tech by changing the default
branch name in R package repositories to ‘main’ instead of ‘master’. There are a
wealth of other posts/tutorials that others have written. Here is a small sampling
listed in order of publishing date:
- Easily rename your Git default branch from master to main by Scott Hanselman
- Git: Renaming the “master” branch by Richard Walters
- How To: Safely Rename master Branch on GitHub by Jake Jarvis
Eugene Shen even made a small web app to automate the entire process for you that is
available at: (https://eyqs.ca/tools/rename/).
I thought I’d share the 5 simple steps that I tested and used to make the change in under 1
minute. Yes, you can do this in under a minute, so what’s stopping you? If you
are concerned about compatibility, GitHub is providing updates on their
renaming efforts here: https://github.com/github/renaming.
Below are screenshots to walk you through each step. In addition, there is a block
of code with all Terminal commands in one place at the end of this post
here and GitHub repo here:
https://github.com/StevenMMortimer/master-to-main.
- Step 1 – Move the master branch to ‘main’
- Step 2 – Push ‘main’ to remote repo
- Step 3 – Point HEAD to ‘main’ branch
- Step 4 – Change default branch to ‘main’ on GitHub site
- Step 5 – Delete ‘master’ branch on the remote repo
Step 1 – Move the ‘master’ branch to ‘main’
Run the following command which creates a branch called ‘main’ using the history
from ‘master’. Using the argument -m will transfer all of the commit history on
the ‘master’ branch to your new ‘main’ branch so nothing gets lost.
git branch -m master main
Step 2 – Push ‘main’ to remote repo
Remember that git is version control software on your local machine and GitHub
is the remote server that stores your code. For this reason, you’ll have to push
your new ‘main’ branch up to GitHub and tell the local branch to start tracking
the remote branch with the same name.
git push -u origin main
Step 3 – Point HEAD to ‘main’ branch
At this stage if ‘master’ was your default branch you cannot remove it without
first changing HEAD, the pointer to the current branch reference. This following
command will point it to ‘main’.
git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD refs/remotes/origin/main
All three steps are shown in the screenshot below:
At this point you can take a breather. You’re on the home stretch! If you want
to check that things are going as planned then you’re welcome to run the following
that should show the HEAD is pointing to main which now frees you up to delete ‘master’.
Note: When you enter this command in your Terminal you will have to type :q to
exit it. Not CTRL+C, ESC, etc.
git branch -a
Step 4 – Change default branch to ‘main’ on GitHub site
At this point you’ve succesfully transitioned everything to the ‘main’ branch, but
you can’t delete the ‘master’ branch without changing the default branch in GitHub
to something other than ‘master’. This is the only step that requires you to leave
the Terminal and navigate in your browser to your GitHub repository. From there,
click "Settings" -> "Branches" on the left rail and change the default branch to
‘main’. I’ve included some screenshots below and GitHub provides instructions for
doing this here: https://docs.github.com/en/github/administering-a-repository/setting-the-default-branch.
Step 5 – Delete ‘master’ branch on the remote repo
Now that the local ‘master’ is gone and there’s nothing pointing to it on Github
you can delete it with the following command:
git push origin --delete master
That’s it! You’re done! You should no longer see “master” or “remotes/origin/master” locally
or on your GitHub repository. If you want to check, you can always run the following:
git branch -a
Feel free to let me know if this worked for you or if you had issues! Note:
I take no responsibility for messing up your git repo. In case this wasn’t clear
enough, all instructions are available in its own repo here: https://github.com/StevenMMortimer/master-to-main.
All commands
# Step 1 # create main branch locally, taking the history from master git branch -m master main # Step 2 # push the new local main branch to the remote repo (GitHub) git push -u origin main # Step 3 # switch the current HEAD to the main branch git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD refs/remotes/origin/main # Step 4 # change the default branch on GitHub to main # https://docs.github.com/en/github/administering-a-repository/setting-the-default-branch # Step 5 # delete the master branch on the remote git push origin --delete master
I found the following info, but didn’t find where to go to access it. Didn’t find it in account settings. Is there a repo settings page? Do you have to be the repo owner?
https://github.com/blog/421-pick-your-default-branch
How to set the default branch on github.com when I go to browse commits.
CharlesB
84.4k27 gold badges189 silver badges214 bronze badges
asked Jul 4, 2012 at 18:37
Do you have to be the repo owner?
Yes you do.
How to set the default branch on github.com when I go to browse commits.
If you fork the repository, you can change the default branch of your fork, by clicking on the Settings button (see below).
This will allow you to pick your favorite branch as the default one for your own fork, but you’ll have to keep your forked repository in sync with the upstream repository by yourself.
Or you can directly jump to the following url https://github.com/{:user}/{:repo}/settings
answered Jul 4, 2012 at 18:42
nulltokennulltoken
62.8k20 gold badges135 silver badges130 bronze badges
2
Just log into your GitHub account and on the far right side in the navigation menu choose Settings, in the Settings Tab choose Default Branch and return back to main page of your repository.
Here’s a visual for the answer:
mkrieger1
16.9k4 gold badges51 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Jan 27, 2013 at 19:48
MatijaMatija
17.4k2 gold badges47 silver badges42 bronze badges
1
2021 Update
The current GitHub UI has changed quite a bit — what used to be buttons are now tabs across the top of the repo’s home page:
Click the Settings tab then, on the left, click Branches:
Mousing over the switch branch icon (right/left arrow, bottom right of pic) pops up a hint. [or click the pencil icon to give the default branch a new name]:
Clicking on switch branch pops up a list of branches:
Select the new default branch (I chose master), click Update, and acknowledge that you know what you’re doing:
Voila!
mkrieger1
16.9k4 gold badges51 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Feb 4, 2021 at 2:51
cb4cb4
5,5395 gold badges43 silver badges54 bronze badges
Initially, I confirmed the «Default Branch» was ‘master’ even though clones were defaulting to another branch ‘stackato’. Here’s what I tried…
Change and change back
- The main/top option in the settings is titled «Options» and I changed my «Default Branch» from ‘master’ (what I wanted) to a third branch name that I did not want, but different from ‘stackato’ that was appearing when I cloned
- I selected «Collaborators» from the menu on the left
- I selected «Options» again from the menu on the left and confirmed that my selection from #1 was still active (telling me it had presumably auto-saved)
- I changed my «Default Branch» back to ‘master’
- I selected «Collaborators» again from the menu on the left
- I selected «Options» one last time from the menu on the left and confirmed that my ‘master’ was still active (telling me it had presumably auto-saved)
and/or Wait a while
I cannot rule out the possibility that it just took some time for my change to ‘propagate’.
answered Dec 31, 2013 at 6:44
sagesage
4,7002 gold badges42 silver badges47 bronze badges
This is pretty easy from the github interface. You just need to go into the repository where you want to change de default branch and click on settings on the right side of the page:
and then, inside there you just need to change the branch as you would like to:
answered Feb 23, 2015 at 11:26
Introduction
In my previous article, we have discussed Gitignore with its uses to ignore files without committing to Git or Github. Also, we have discussed the steps to customize the .gitignore file of the GitHub repo and steps to add .gitignore file manually to GitHub.
In this article, I will describe the below-mentioned points in detail,
- What is git default branch
- Use of default branch
- How to change the default branch
- Check default branch using Git Bash
Learn About Git Default Branch
When we create a new repository on GitHub, there is a branch created by default as shown below,

So, all the developers clone this repository as shown in the above image. They will be connected to the master branch and whatever modifications they do those changes will be committed to this master branch also. In my previous article, I have described the steps to create and manage the Git branch in detail. If I will create a new branch named Satya and after refresh the repository, the branch will be selected as master by default as shown below,

Let’s see what happens after refreshing the GitHub repository as shown below,

Here we can see the master branch is selected as the default branch instead of a new branch called Satya after refreshing the SatyaThreeEmptyRepo GitHub repository. It happens because the master branch is the default branch.
Now we check these branch details that I have created along with the default branch master as shown below,
Steps To Create New Branch As Default Branch
Here I will create a new branch called Development and make this branch the default branch instead of the master branch in this GitHub repository.
Now go to these branches’ details as shown below,
Step 1
Step 2

Step 3
Step 4

Step 5

Step 6
After these previous steps are completed, we can set our default branch called Development as shown below,

Now, we check branch details for checking the default branch as shown below,

Also, we can check as shown below,

Uses Of Default Branch After Cloning The Repository
Let me clone this repository under Development as the default branch using Git Bash as shown below.

Using Git Bash to clone the repo as shown below,

Let’s check the default branch using Git Bash.

Also, we can check the default branch or currently connected branch using a command called git branch as shown below,
So, now all developers will connect this default branch and commit the code to this branch. We have described the steps to move code from one branch to other in my previous article link as given above. So, in this article, we have 3 branches in the GitHub repository as shown below.

Describe The Uses Of These 3 Branches In Short
- Development
This branch is used for developers to commit code. After successful sanity testing in this branch, the code moved to the Satya branch. - Satya
This branch is used for testing purposes or QA purposes by the Testing team. After successful testing, the same code moves to the master branch. - master
Finally, the code moves from Satya to the master branch for deployment purposes to the production/prod server.
Like above we follow different branching strategies in GitHub.
Summary
In this write-up, we have learned the below details,
- What is git default branch
- Use of default branch
- How to change the default branch
- Check default branch using Git Bash
Thank You & Stay Tuned For More

Scott covered this nicely with links to topics that show how master originated from BitKeeper. There is evidence to strongly suggest it does pertain to the outdated, oppressive and perverse master/slave metaphor, rather than master-copy.
Edited 17th October 2020 (a bit late, I know!), Git now lets you set a default branch for init, and GitHub now defaults to main.
But if you have an older repository, some of these steps remain relevant.
So, here are the steps I followed:
Move Master to Main
# maintain refs
git branch --move master main
# push to remote
git push -u origin main
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Change the Default on Remote
Now depending on your remote tool, this might differ.
GitHub
- Assuming you’ve pushed
mainfrom the steps above. - Go to your Settings
- Go to the Branches section
- Change «Default branch» from
mastertomain
GitLab
- Assuming you’ve pushed
mainfrom the steps above. - Go to your Settings
- Go to the Repository section
- Change «Default Branch» from
mastertomain
BitBucket
- Assuming you’ve pushed
mainfrom the steps above. - Go to your Repository settings
- Go to the Repository details section
- Change «Main branch» from
mastertomain
then…
- Go to the Branching model section
- Change «Development branch» from
mastertomain
Git Now Lets You Name a Default Branch
Git Init Doesn’t Let You Name a Default Branch
Edited 17th October 2020 Since git 2.28, you’ve been able to change your default branch using built-in git features.
git config --global init.defaultBranch main
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Summary
Sort of past the point about caring which side you fall on here. The evidence is there. Be your own teacher, make the world a better place.
If you’ve been using Git for a while, you’ve probably come across the term master. You might’ve seen it when you run git status or git branch.
It’s a somewhat old-fashioned phrase and you may well be wondering where it comes from or how you can change it. Whether you’re a command-line user or a fan of GitHub, you can change branch names and even set the default branch name to something appropriate to your needs.
What Is the Default Branch?
Every brand new Git repository has a default branch, even if it doesn’t really branch off anything! Branches are simply commit references, and there’s always a HEAD reference pointing to the current branch.
Historically, Git has named that default branch master. Although you can rename it, many people stick with the default, so you’ll see lots of projects using master as their default branch.
Branch Naming and Why Master Is Being Phased Out
Recent versions of Git (2.28 and later) produce the following hint when you create a new repository using git init:
Using ‘master’ as the name for the initial branch. This default branch name is subject to change. To configure the initial branch name to use in all of your new repositories, which will suppress this warning, call: git config —global init.defaultBranch <name> Names commonly chosen instead of ‘master’ are ‘main’, ‘trunk’ and ‘development’. The just-created branch can be renamed via this command: git branch -m <name>
The master/slave terminology has a long history in computing, especially in reference to hardware such as disk drives. Other version control systems such as BitKeeper, a predecessor to Git, have also used the term. However, the term has become somewhat outdated for its association with colonialism.
The Git maintainers have worked with the wider development community to address these concerns. Aside from any offense it may cause, master isn’t a particularly descriptive name anyway. It implies a relationship with some other, unnamed entity, but it doesn’t represent the unique status of the initial branch. Many people consider the name main to do a better job of describing this branch and its typical usage.
The name main is short, translates easily, and is in common use. The fact that it begins with the same two letters as master may help if you need to retrain your muscle memory.
How to Make the Change Using Command Line Git
As Git itself explains, you can configure the default branch name with the following command:
git config --global init.defaultBranch main
The —global ensures this setting applies to all repositories created by the current user.
Once set, new repositories will use the new default name:
$ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in /private/tmp/bar/.git/
$ git status -sb
## No commits yet on main
Note that you can also rename a branch at any time using the -m option, e.g.
git branch -m main
One day, Git may make this change for you, by using the name main by default, for all new repositories. It’s still useful to know how to change it yourself, and you may have a personal or team preference for a name other than main.
How to Set the Default Branch Name in GitHub
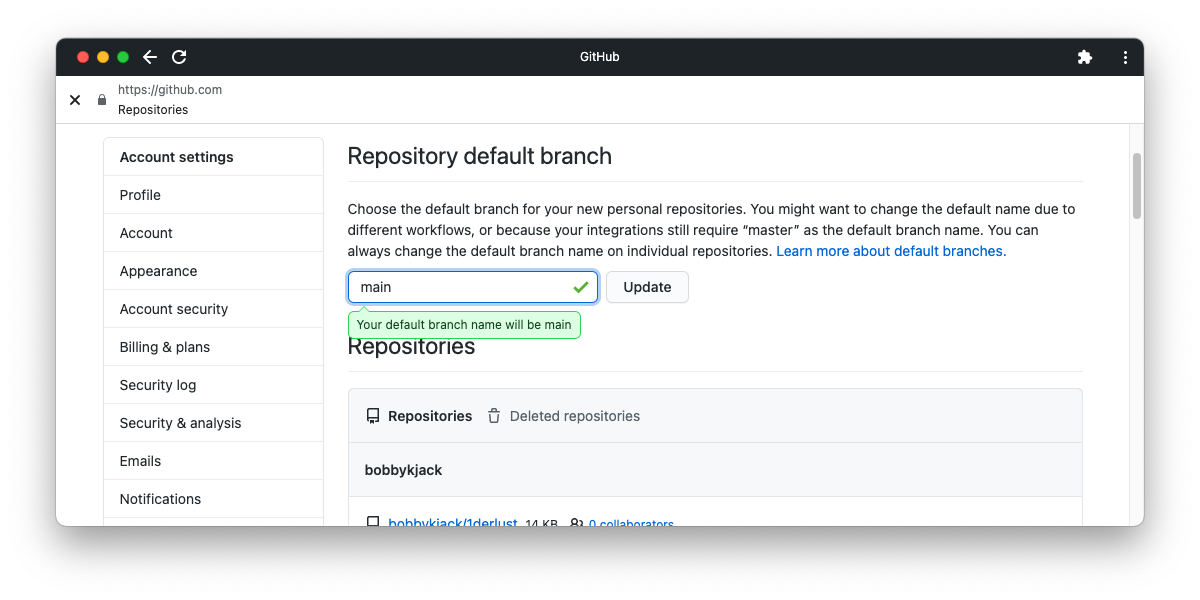
Branches created on GitHub are now automatically named main instead of master. However, you can still change the name of this default by following these steps:
- Open Settings via your profile photo in the top-right.
- Click Repositories in the left-hand menu.
- Under the Repository default branch section, choose an alternative name.
- Click Update.
Take Control of Git’s Default Branch Name
Git has historically named its default branch master, but you don’t have to keep it that way!
Whether you think an alternative is more inclusive, easier to understand, or simply shorter to type, it’s easy to change. The default branch is just one tiny part of Git’s enormous repertoire. To take your Git skill from beginner to advanced, check out our comprehensive guide next.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) points out that «Master-slave is an oppressive metaphor that will and should never become fully detached from history» as well as «In addition to being inappropriate and arcane, the master-slave metaphor is both technically and historically inaccurate.» There’s lots of more accurate options depending on context and it costs me nothing to change my vocabulary, especially if it is one less little speed bump to getting a new person excited about tech.
You might say, «I’m all for not using master in master-slave technical relationships, but this is clearly an instance of master-copy, not master-slave.»
UPDATE: There is Good analysis of the whole main branch convo in the Git Rev News: Edition 65. Git likely uses master in the context of «master copy» or «master recording.»
So we see that while the word master doesn’t always connote slave, for many, it’s evocative via basic word-association and they just don’t want to look at the word on their prompt all day. Choice is cool.
I have had dozens of git repositories that have ‘master’ as the main branch. Changing that would be a hassle right?

Let’s see. I’ll just «git branch -m master main» and then push it back! Remember that -m is —move so your history isn’t changed! Even better I can «git push -u origin main» to set the upstream at the same time.
D:githubWindowsTerminalHere [master]
> git branch -m master main
D:githubWindowsTerminalHere [main]
> git push -u origin main
Total 0 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote:
remote: Create a pull request for 'main' on GitHub by visiting:
remote: https://github.com/shanselman/WindowsTerminalHere/pull/new/main
remote:
To https://github.com/shanselman/WindowsTerminalHere.git
* [new branch] HEAD -> main
That was easy.
NOTE: Changing the default branch to «main» also has the benefit of starting with «ma» so that autocomplete <TAB> muscle memory still works. Another great option for your main github branch is «latest.» The goal is to just be unambiguous.
Now I just need to change my default branch in my GitHub settings for my repository.
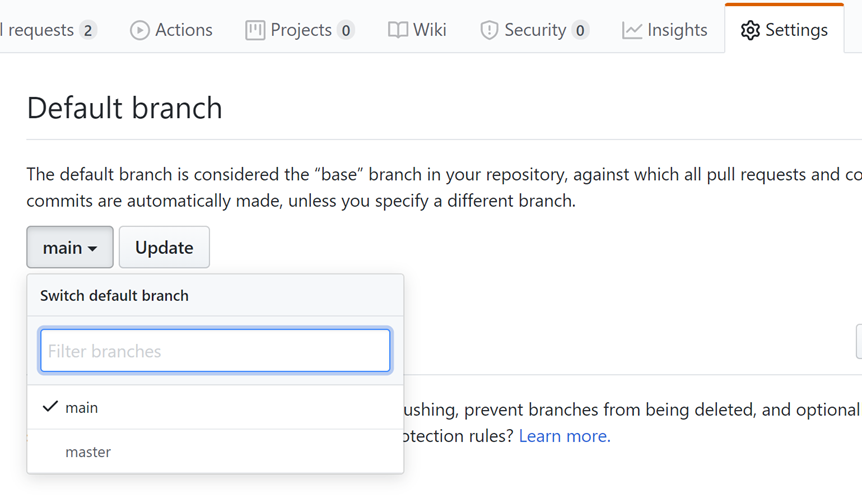
I can also update the tracking branch manually as seen here, but if you use git push -u origin main it’ll do both.
git branch -u origin/main main
The last thing to think about is if you have a CI/CD, GitHub Action, Azure DevOps pipeline or some other build system that pulls a specific branch. You’ll just change that to main. However, usually unless your CI explicitly calls for a branch by name, changing master to main will «just work!»
NOTE: For more complex repos also check your protected branch rules.

This is because -m is —move and all your reflog is unchanged!
TL;DR in conclusion:
git branch -m master main
git push -u origin main
Updating local clones
If someone has a local clone, then can update their locals like this:
$ git checkout master
$ git branch -m master main
$ git fetch
$ git branch --unset-upstream
$ git branch -u origin/main
$ git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD refs/remotes/origin/main
From the tweet above (Thanks Brad from XUnit.net!), these steps
- Go to the master branch
- Rename master to main locally
- Get the latest commits from the server
- Remove the link to origin/master
- Add a link to origin/main
- Update the default branch to be origin/main
You can add an alias «git new» that will default to whatever starting branch you like. (NOTE: This is no longer needed, set below)
git config --global alias.new '!git init && git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/main'
UPDATE! As of Git 2.28 you don’t need an alias as above, as there is a new config option called init.DefaultBranch. Just set it and forget it.
git config --global init.defaultBranch main
Hope this helps! Other good names are latest, trunk, and stable!
Sponsor: Have you tried developing in Rider yet? This fast and feature-rich cross-platform IDE improves your code for .NET, ASP.NET, .NET Core, Xamarin, and Unity applications on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
About Scott
Scott Hanselman is a former professor, former Chief Architect in finance, now speaker, consultant, father, diabetic, and Microsoft employee. He is a failed stand-up comic, a cornrower, and a book author.
About Newsletter
Hosting By

Hey there! I’m Srebalaji. You are receiving this email because you have subscribed to level up your game in Git.

Recently, there are many suggestions about renaming the default branch master to some other name. This was mainly due to the master-slave metaphor that some people are talking about.
There is evidence that states it was intended to mention master-copy or master recording. And it is not intended to master-slave.
But I think it’s people’s perspective and if some think that they are not cool with that they can change the default branch.
So let’s see how to change the default git branch master to default (you can use your preferred name)
Before starting I have to tell you that I have tried this in multiple repos and its working fine without any breaking changes. If you are not confident enough then fork your repo and try it first.
-
Make sure your CI/CD flow doesn’t get interrupted.
-
Make sure you have merged all the PRs targeting master. Other PRs are fine
-
Change the branch name
-
Set remote upstream tracking for the new branch
-
Change the new branch name in repo host (Github, Gitlab)
git branch -m master defaultThe above command just renames the default branch to the name default.
-m attribute is used to rename the branch name without affecting the branch’s history.
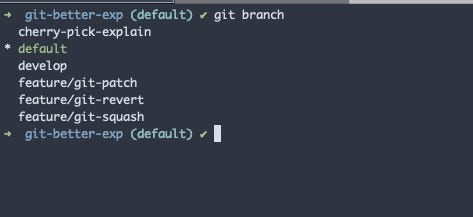
Now the default branch is changed in the local but not in the remote.
git push -u origin defaultThe above command will push the new branch to the remote.
-u attribute is used to set the upstream tracking for the branch.
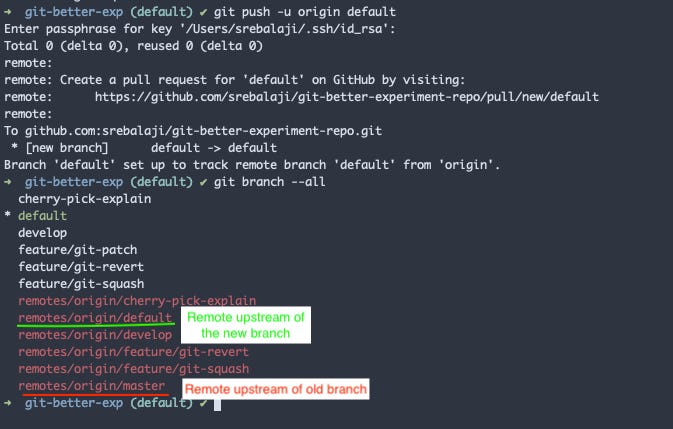
As you can see that the upstream is set for the new branch. But still, the reference to the old upstream is present in the local.
In this tutorial, let’s consider Github. But the same option is also available in Gitlab, Bitbucket.
In Github, go to settings -> branches. You can change the default branch there.
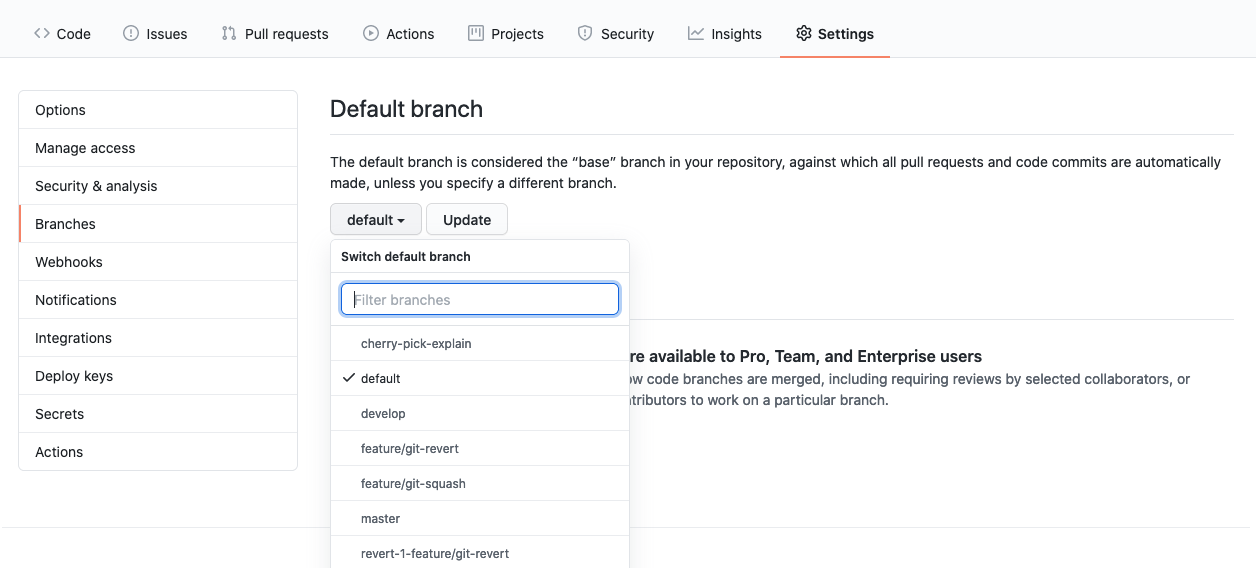
That’s it you are done.
But remember that the old branch’s upstream is still present. It won’t affect your workflow. But you should delete it to keep your repo clean.
To delete the old branch’s upstream you can use
git push origin --delete master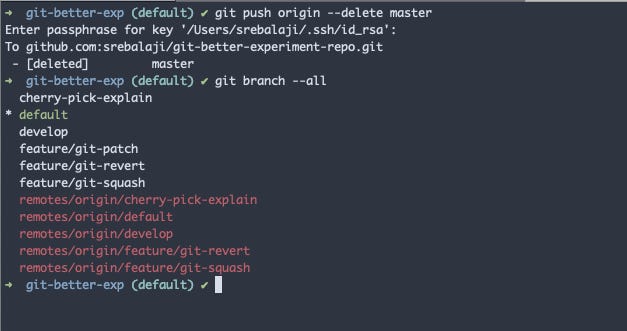
As you can see the old remote stream is deleted.
Now the changes are done in your local and in the remote host. Let’s see how to bring those to other people who are already using the repo.
I mean there will be other people who will be using this repo. They have to do few changes to complete the flow.
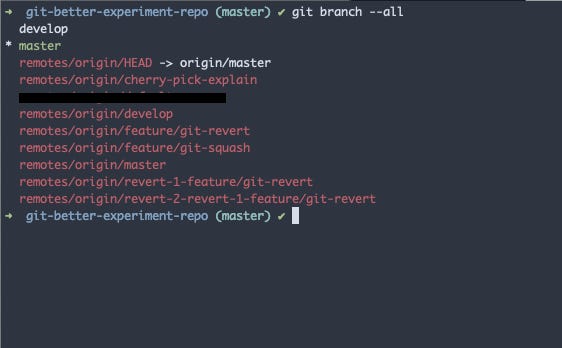
As you can see still the branch master is present in the local of others who are already using the repo.
-
Fetch all the branches
-
Update the upstream remote’s HEAD
-
Rename the default branch
git fetchThe above command will just fetch all the remote branches to your local.
git remote set-head origin -aThe above command will query the remote host for the HEAD upstream and it updates that upstream in the local.
git branch -m master defaultThis is the same as the old one. We are just moving the branch without affecting the history of the branch.
As we have already set the remote upstream in the previous step, the new branch is changed and is in sync with the remote.
Now the person can work with the default branch.
As I said earlier, I have tried this is in multiple repos of mine and it’s working fine without any breaking changes. This may seem to be confusing at first, but if you understand the process and read it multiple times you will get familiar.
If you got any doubts or stuck somewhere, you can contact me.
That’s it for today
See you next week 





























