Чтение файла: file_get_contents()
С помощью функции file_get_contents() можно получить содержимое файла:
<?php
# Получение информации из файла
$data = file_get_contents('data.txt');
var_dump($data);Также мы можем получить html-код какой-либо страницы в интернете:
<?php
echo '<textarea>';
echo file_get_contents('https://ya.ru');
echo '</textarea>';Но работает это далеко не для всех сайтов, у многих есть защита от такого примитивного парсинга.
Чтение файла: file()
Функция file() позволяет получить содержимое файла в виде массива. Разделителем элементов является символ переноса строки.
Создадим в корне сайта файл data.txt со следующим содержимым:
Vasya
Petya
GoshaТеперь запустим скрипт index.php со следующим кодом:
<?php
$arr = file('data.txt');
echo '<pre>';
var_dump($arr);При запуске этого скрипта мы получим в браузере:
array(3) {
[0]=>
string(7) "Vasya
"
[1]=>
string(7) "Petya
"
[2]=>
string(5) "Gosha"
}Заметили, что у первых двух строк длина 7 символов вместо пяти? Это из-за того, что каждая строка содержит в конце символы переноса строки.
Чаще всего они нам не нужны, поэтому их можно убрать, передав вторым параметром константу FILE_IGNORE_NEW_LINES:
<?php
$arr = file('data.txt', FILE_IGNORE_NEW_LINES);
echo '<pre>';
var_dump($arr);Теперь у всех строк будет по 5 символов.
Если нам необходимо получить только заполненные строки в файле и пропустить пустые, можно передать вторым параметром константу FILE_SKIP_EMPTY_LINES:
<?php
$arr = file('data.txt', FILE_SKIP_EMPTY_LINES);Разумеется, мы можем передать сразу две константы:
<?php
$arr = file('data.txt', FILE_IGNORE_NEW_LINES | FILE_SKIP_EMPTY_LINES);Создание файла и запись в файл: file_put_contents()
Функция file_put_contents() позволяет создать файл и заполнить его данными.
Первым параметром функция принимает путь к файлу, вторым — строку с данными. Для создания пустого файла нужно передать вторым параметром пустую строку.
<?php
// Создаём файл и записываем в него строку 'Vasya'
file_put_contents('data.txt', 'Vasya');
// Создаём пустой файл
file_put_contents('data.txt', '');Если файла не существует — он будет создан. Если существует — данные в файле будут перезаписаны.
Чтобы не перезаписывать данные, а добавить их в конец файла, нужно передать третьим параметром константу FILE_APPEND:
<?php
file_put_contents('data.txt', 'Данные', FILE_APPEND);Также вторым параметром можно передать массив:
<?php
file_put_contents('data.txt', ['Один', 'Два', 'Три'], FILE_APPEND);Но этот вариант не очень удобен, поскольку все элементы массива запишутся подряд, без каких-либо разделителей. Чтобы их добавить, можно использовать функцию implode:
<?php
$arr = ['Один', 'Два', 'Три'];
// Разделим элементы запятой
$str = implode(',', $arr);
// Или можно разделить их символом переноса строки
$str = implode("n", $arr);
file_put_contents('data.txt', $str);Создание папки или структуры папок
Создать папку можно с помощью функции mkdir() (make directory):
<?php
mkdir('new_folder');Вторым параметром указываются права доступа к файлу в виде восьмеричного числа, по-умолчанию это 0777, что означает самые широкие права. Для Windows этот аргумент игнорируется.
<?php
mkdir('new_folder', 0755);Кроме этого, второй параметр может игнорироваться при заданной umask (пользовательская маска (user mask), которая нужна для определения конечных прав доступа). В этом случае принудительно сменить права можно функцией chmod():
<?php
mkdir('new_folder', 0777, true);
chmod('new_folder', 0777);Также мы можем создать структуру папок рекурсивно, для этого нужно третьим параметром передать true:
<?php
mkdir('folder1/folder2/folder3', 0755, true);Но в этом случае права доступа будут заданы только для конечной папки. Для изменения прав у каждой из папок придётся указывать права вручную:
<?php
mkdir('folder1/folder2/folder3', 0755, true);
chmod('folder1', 0755);
chmod('folder1/folder2', 0755);
chmod('folder1/folder2/folder3', 0755); // Если нужно проигнорировать umaskПрава доступа — это отдельная объёмная тема, поэтому сейчас мы её пока рассматривать не будем.
Проверка существования файла или папки
Проверить существование папки или файла можно с помощью функции file_exists():
<?php
if(file_exists('data.txt'))
echo 'Файл или папка существует';Если вы хотите проверить существование только папки или только файла, для этого есть специальные функции is_dir() и is_file():
<?php
$path = 'data.txt';
if(is_file($path))
echo 'Это файл';
elseif(is_dir($path))
echo 'Это папка';
else
echo 'Не найдено';Проверка прав доступа
Функции is_readable() и is_writable() проверяют, есть ли у пользователя, от имени которого запущен PHP, права на чтение и запись файла или папки:
<?php
$path = 'data.txt';
if(is_readable($path))
echo 'Есть права на чтение.';
if(is_writable($path))
echo 'Есть права на запись.';Копирование, перенос и удаление файла
Для удаления файлов используется функция unlink():
<?php
unlink('data.txt');Чтобы скопировать файл, используем функцию copy():
<?php
copy('data.txt', 'new_data.txt');Для переименования и переноса файла в другую папку используется функция rename():
<?php
rename('data.txt', 'new_data.txt');Работа с файлами с помощью fopen()
Функций file(), file_get_contents() и file_put_contents() достаточно для решения большинства задач, связанных с управлением файлами.
Но иногда возникают ситуации, когда нам необходимы более продвинутые инструменты. Например, если у нас есть большой текстовый файл и мы хотим читать его построчно, а не весь сразу, для экономии оперативной памяти.
Итак, открыть (или создать и открыть) файл можно с помощью функции fopen():
<?php
# Если файла нет - он будет создан
$f = fopen('data.txt', 'w');Функция fopen() возвращает так называемый лескриптор. Это ссылка, указатель на файл, его мы будем передавать в другие функции. Кстати, тип данных этого дескриптора — resource.
Первым параметром мы передаём путь к файлу, вторым — модификатор доступа к файлу. Ниже перечислены наиболее популярные модификаторы:
- r — открытие для чтения, указатель переходит в начало файла.
- r+ — открытие для чтения и записи, указатель переходит в начало файла.
- w — открытие для записи, указатель переходит в начало файла. Если файла нет — создаётся, если есть — очищается от данных.
- w+ — открытие для чтения и записи, в остальном аналогичен w.
- a — открытие для записи, указатель переходит в конец файла. Если файла нет — создаётся.
- a+ — открытие для чтения и записи, в остальном аналогичен a.
- x — создание и открытие для записи, указатель переходит в начало файла. Если файл существует — PHP покажет ошибку.
- x+ — создание и открытие для чтения и записи, в остальном аналогичен x.
Указатель — это нечто вроде курсора. Вы можете переместить его в любое место файла, чтобы добавить или отредактировать определённые данные.
Для записи данных в файл существует функция fwrite(). Давайте попробуем создать файл и записать в него какие-нибудь данные:
<?php
# Если файла нет - создастся, если есть - удалит старые данные
$f = fopen('data.txt', 'w');
# Добавим что-нибудь в файл
fwrite($f, 'Первая запись');
# Добавим что-нибудь ещё
fwrite($f, 'Вторая запись');
# Закроем соединение с файлом
fclose($f);
# Теперь в файле лежит текст "Первая записьВторая запись"Заметьте, из-за модификатора w при каждом запуске скрипта данные в файле стираются и добавляются заново. Если модификатор заменить на a, данные будут не перезаписываться, а добавляться в конец файла.
Для построчного чтения файла используется функция fgets():
<?php
$f = fopen("data.txt", "r");
while($line = fgets($f, 4096))
echo $line, '<br>';
fclose($f);При каждом запуске fgets получает следующую строку и возвращает её в $line. Вторым параметром передаётся максимальная длина строки. Это означает, что если строка слишком длинная, она будет обрезана.
Также в PHP существует множество других полезных функций, работающих с дескриптором файла. Почитать о них можно в документации.
Прежде чем создавать PHP-файл, нужно понимать, что он собой представляет. На самом деле php-файл – это обычный текстовый документ, но этот текстовый документ имеет расширение php. Благодаря расширению компьютер, на котором установлен и настроен веб-сервер, может понять, какой программой этот файл нужно обрабатывать.
Исходя из этого, предлагаю два основных способа, благодаря которым вы можете этот php-файл создать.
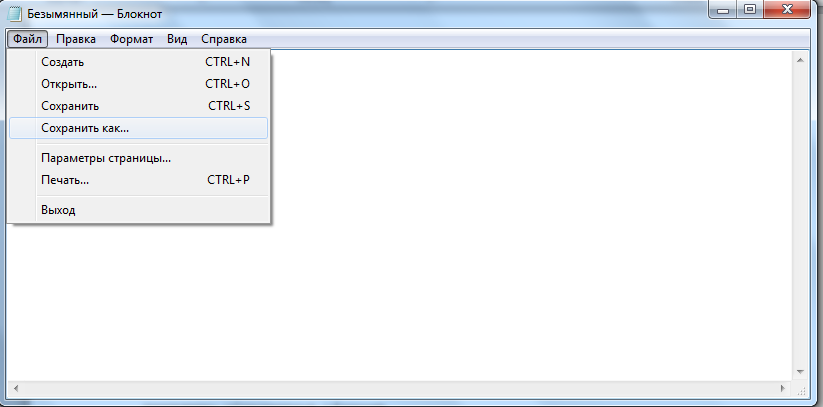
Способ 1. Создание файла PHP, меняя расширение текстового файла.
В главном меню программы выбираем «Файл-Сохранить как».
И сохраняем текстовый файл с расширением *.txt.
Теперь нужно поменять расширение этого файла с *.txt на *.php.
Если у вас расширение файлов не отображается, то советую почитать эту заметку.
После того, как вы выполните инструкции из этой заметки, рядом с названием файла будет отображаться его расширение.
Теперь, для создания файла php нужно просто переименовать файл, изменив его расширение на php.
Больше моих уроков по PHP для начинающих здесь.
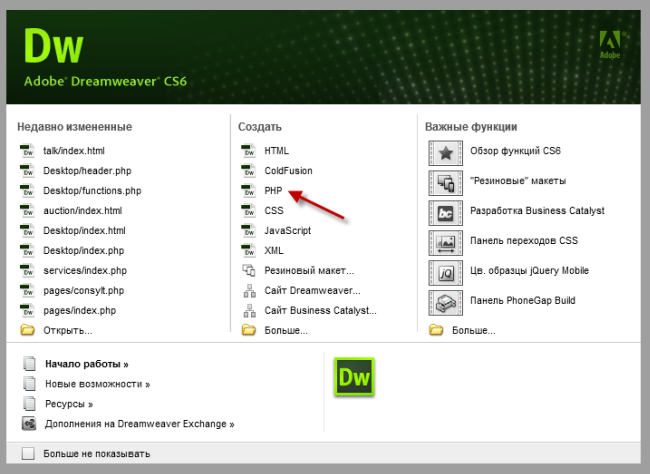
Способ 2. Создание файла PHP с помощью универсальных редакторов кода (например, Dreamweaver)
Давайте посмотрим, как это можно сделать в редакторе Dreamweaver.
После открытия программы появляется главное меню, в котором можно выбрать создание файла PHP.
Кроме того, это меню можно вызвать через меню «Файл – Создать».
После того, как файл будет создан, его можно будет сохранить через главное меню «Файл-сохранить как…».
Аналогичный процесс создания файлов PHP есть и в других редакторов кода.
Больше моих уроков по PHP для начинающих здесь.
Чтобы оставить сообщение, зарегистрируйтесь/войдите на сайт через:
Или зарегистрируйтесь через социальные сети:
Источник
Запись и вывод данных из файла TXT в PHP
Пишу бота для группы в ВК…
Как реализовать функцию при которой при получении сообщения «Подписка» и если его ID не занесён в список он заносит его ID в файл user_id.txt.
А при получении сообщения «Отписка» и если его ID занесен в этот список он убирает ID пользователя из данного списка.
PS. Так же буду благодарен если кто-то скажет как можно перечислять переменные (Например: Привет, привет, хай, ку и т.д.) и он будет понимать что на все эти команды ему нужно отвечать одним сообщением.
1 ответ 1
Текстовый файл, возможно, не лучшее хранилище, но для обучения сойдёт.
Далее, чтобы искать в уже записанных id, их значения надо прочитать:
Однако у такого способа много недостатков.
Эти проблемы хорошо известны и решения для них давно придуманы. Для обеспечения согласованности данных используются блокировки (пока один работает с файлом, остальные ждут). Для ускорения поиска используются индексы (это как алфавитный указатель в книге, позволяет не листать всё сначала, а сразу открыть нужную страницу).
Реализация блокировок и индексов может оказаться достаточно сложной задачей для новичка и достаточно скучной для многоопытного разработчика, но есть готовое решение! Это базы данных. Самым простым вариантом может стать SQLite, для работ с ней надо освоить PDO. Умение работать с базами данных не только поможет вам в задаче с ботом, но и очень пригодится в будущем.
Источник
Конвертер TXT в HTML
Конвертируйте TXT в HTML онлайн бесплатно с любого устройства.
Хотите сообщить об этой ошибке на форуме Aspose, чтобы мы могли изучить и решить проблему? Когда ошибка будет исправлена, вы получите уведомление на email. Форма отчета
Приложение для просмотра документов на Android
Конвертировать TXT в HTML онлайн
Используйте форматы Текст и HTML по максимуму. Мы предоставляем бесплатный Конверте TXT в HTML. Наше онлайн-приложение создает HTML из TXT с высокой скоростью и профессиональным качеством. Алгоритм преобразования позволяет конвертировать TXT во многие популярные файловые форматы.
Лучший бесплатный конвертер TXT в HTML
Конвертировать TXT в HTML высочайшего качества в любом браузере. Вам не нужно устанавливать какое-либо дополнительное программное обеспечение, такое как Microsoft Word, OpenOffice или Acrobat Reader. Попробуйте прямо сейчас конвертировать TXT в HTML онлайн. Вы можете использовать его совершенно бесплатно.
Сохранить TXT как HTML с высокой скоростью
Преобразование TXT выполняется быстро и легко. Выполните следующие простые шаги, чтобы преобразовать TXT файл в HTML формат. Чтобы преобразовать TXT в HTML, перетащите Текст в поле загрузки, укажите параметры преобразования и нажмите кнопку КОНВЕРТИРОВАТЬ. Посмотрите, как ваше TXT превратится в HTML в течение минуты. Выходное содержимое и форматирование будут идентичны исходному документу.
Программная платформа Aspose Words
Онлайн-приложение Conversion создано на базе программной платформы Aspose Words. Наша компания разрабатывает современные высокопроизводительные решения обработки документов для различных ОС и языков программирования.
Источник
Конвертируйте ваши документы в текст
Конвертер TXT
Конвертируйте документы или электронную книгу в обычный текст с помощью бесплатного он-лайн конвертера. Просто загрузите свои файлы и нажмите на «Преобразовать файл». Спустя определенное время вы сможете загрузить полученный файл. Если в вашем файле PDF содержатся отсканированные изображения или текст, выберите функцию распознавания текста.
Ошибка: количество входящих данных превысило лимит в 3.
Чтобы продолжить, вам необходимо обновить свою учетную запись:
Ошибка: общий размер файла превысил лимит в 100 MB.
Чтобы продолжить, вам необходимо обновить свою учетную запись:
Ошибка: общий размер файла превысил абсолютный лимит в 8GB.
Для платных аккаунтов мы предлагаем:
- Вплоть до 8GB общего размера файла за один сеанс конвертирования 200 файлов на одно конвертирование Высокий приоритет и скорость конвертирования Полное отсутствие рекламы на странице Гарантированный возврат денег
- До 100 Мб общего размера файла за один сеанс конвертирования 5 файлов на одно конвертирование Обычный приоритет и скорость конвертирования Наличие объявлений
Мы не может загружать видео с Youtube.
В настоящий момент доступны следующие направления конвертации: DOCX в TXT, DOC в TXT, ODT в TXT, PDF в TXT, SXW в TXT, WPD в TXT, RTF в TXT и HTML в TXT (тестовая версия конвертирования).
TXT (Raw text file)
Источник
Файлы PHP – для чего нужны, как открыть или конвертировать
Файл с расширением PHP представляет собой файл исходного кода PHP, который содержит код препроцессора гипертекста. Они часто используются в качестве файлов веб-страниц, которые генерируют HTML-код из движка PHP, работающего на веб-сервере.
Содержимое HTML, которое движок PHP создает из кода, – это то, что видно в вашем веб-браузере. Поскольку на веб-сервере выполняется код PHP, доступ к странице PHP не дает вам доступа к коду, а предоставляет контент HTML, который генерирует сервер.
Как открыть файлы PHP
Файлы PHP – это просто текстовые документы, поэтому вы можете открыть их в любом текстовом редакторе или веб-браузере. Блокнот в Windows – один из примеров, но подсветка синтаксиса настолько полезна при кодировании на PHP, что обычно предпочитают более специализированные редакторы PHP.
Некоторые текстовые редакторы включают подсветку синтаксиса. Вот некоторые популярные редакторы PHP: Adobe Dreamweaver, Eclipse PHP Development Tools, Zend Studio, phpDesigner, EditPlus и WeBuilder.
Однако, хотя эти программы позволяют вам редактировать или изменять файлы PHP, они не позволяют вам фактически запускать сервер PHP. Для этого вам нужно что-то вроде веб-сервера Apache.
Как конвертировать файл PHP
См. документацию по jason_encode на PHP.net, чтобы узнать, как преобразовать массивы PHP в код Javascript в формате JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). Это доступно только в PHP 5.2 и выше.
Чтобы сгенерировать PDF-файлы из PHP, смотрите FPDF или dompdf.
Переименование файла таким образом не выполняет реальное преобразование файла, а просто позволяет правильной программе открыть файл. Реальные преобразования обычно происходят либо в инструменте преобразования файлов, либо в меню «Сохранить как» или «Экспорт» программы.
Как заставить PHP работать с HTML
Код PHP, встроенный в файл HTML, понимается как PHP, а не HTML, если он заключен в эти теги вместо общего тега HTML:
Иногда можно увидеть, что веб-страница использует PHP, посмотрев её URL, например, когда файл PHP по умолчанию называется index.php. В этом примере это может выглядеть как http://www.examplesite.com/index.php
Дополнительная информация о PHP
PHP был портирован почти на все операционные системы и полностью бесплатен для использования. Официальный сайт PHP – это PHP.net. Есть целый раздел документации, который служит онлайн-руководством по PHP, если вам нужна помощь, чтобы узнать больше о том, что вы можете делать с PHP или как всё это работает. Ещё один хороший источник – W3Schools.
Первая версия PHP была выпущена в 1995 году и называлась Personal Home Page Tools (инструменты PHP). Изменения проводились на протяжении многих лет, новые версии выпускались каждые несколько месяцев.
Скрипты на стороне сервера – наиболее распространенное применение PHP. Как описано выше, это работает с синтаксическим анализатором PHP, веб-сервером и веб-браузером, где браузер обращается к серверу, на котором выполняется программное обеспечение PHP, так что браузер может отображать всё, что производит сервер.
Другой сценарий командной строки, где не используются ни браузер, ни сервер. Эти типы реализаций PHP полезны для автоматизированных задач.
Источник
Во время работы иногда возникает необходимость изменить расширение файла. Это может потребоваться для файлов, с которыми можно работать в разных программах. Например, расширение текстового файла можно изменить с TXT на CFG, INI, BAT, REG, HTML, PHP, XML, VBS, CSV или CMD. Это позволит продолжить работу в другой программе.
Если вы столкнулись с подобной задачей, то этот материал должен вам помочь. Здесь вы узнаете, как изменить расширение файла в операционных системах Windows 11 или Windows 10.
Что такое расширение файла в Windows 10

В операционных системах Windows 11 и Windows 10 расширение файла используется для определения программы, которую нужно использовать для открытия этого файла. Например, если документ называется «filename.TXT», то он будет открываться с помощью текстового редактора, а если «filename.BAT», то с помощью интерпретатора командной строки. Связь между суфиксом и программой задается в реестре Windows и при необходимости ее можно изменить.
Изменение расширения файла позволяет изменить программу, с помощью которой он будет открываться. Например, вы можете создать текстовый документ «filename.TXT» в программе «Блокнот» и потом переименовать его в «filename.REG». После такого переименования созданный документ начнет открываться уже не в «Блокноте» в редакторе реестра Windows 11 или Windows 10.
Нужно отметить, что изменение расширения никак не изменяет тип файла или его содержимое, изменяется только имя. Изменение с «AVI» в «MP3» не превратит видео в аудио. Для решения таких задач нужно использовать конвертацию с помощью специального софта.
Как поменять расширение файла в Windows 10
Для того чтобы изменить расширение файла нужно сначала включить его отображение в Проводнике.
В Windows 10 для этого нужно открыть любую папку и перейти на вкладку «Вид».
После чего нужно нажать на кнопку «Параметры», которая находится на вкладке «Вид» в правой части окна.
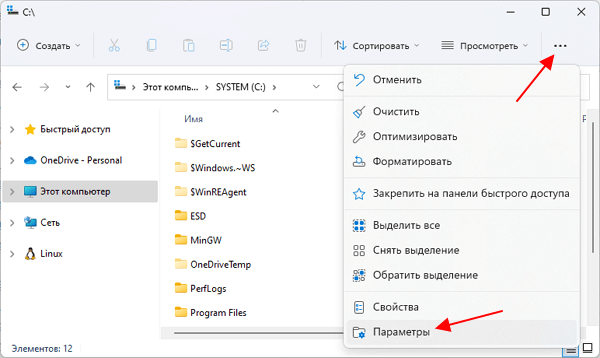
В случае Windows 11 нужно октрыть любую папку и нажать на кнопку с тремя точками. После этого в появившемся меню нужно выбрать пункт «Параметры».
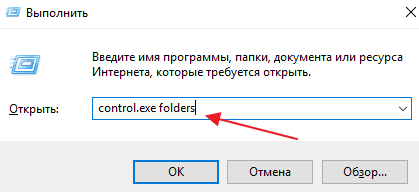
Если с этим возникают какие-то проблемы, то «Параметры» можно открыть с помощью команды. Для этого нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win-R и введите команду «control.exe folders».
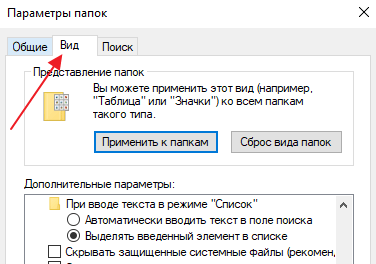
В результате перед вами появится окно «Параметры папок». В данном окне можно изменить многие настройки, которые касаются отображения файлов и папок в проводнике Windows 10. Для того чтобы включить отображение расширений файлов перейдите на вкладку «Вид».
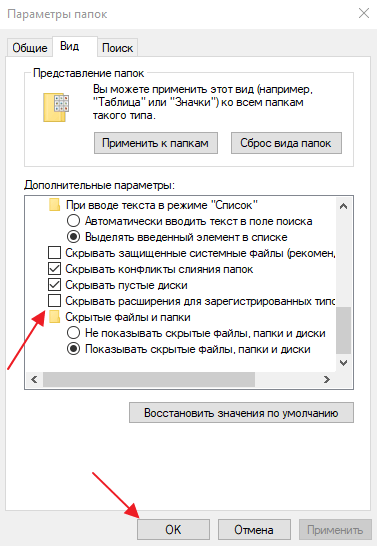
На этой вкладке будет доступен список параметров. Пролистайте данный список в самый конец, найдите там параметр «Скрывать расширения» и отключите его. Для этого достаточно снять отметку и сохранить изменения с помощью кнопки «ОК».
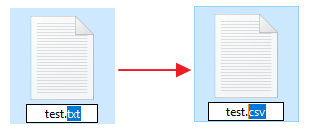
После этого рядом с названием файла всегда будет отображаться и его расширение. Например, на картинке внизу показаны файлы DOCX и TXT.
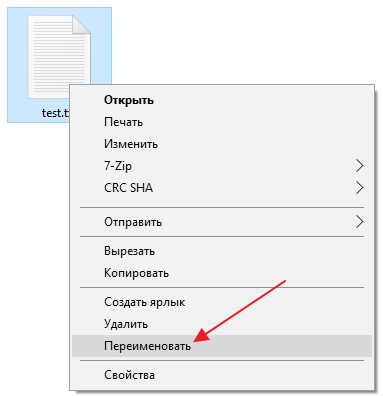
Теперь можно изменить расширение файла. Для этого кликните по нему правой кнопкой мышки и выберите вариант «Переименовать».
Теперь, когда скрытие окончаний отключено, вы сможете не только переименовать файл, но и изменить его расширение.
Например, вместо TXT можно указать CSV или наоборот.
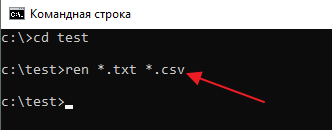
Как изменить расширение для большого количества файлов
Если у вас много файлов, расширение которых нужно изменить, то вы можете воспользоваться командной строкой и тем самым значительно ускорить процесс. Для этого запустите командную строку и перейдите в папку, где находятся нужные вам файлы (для перехода между папками используйте команду cd).
Находясь в нужной папке выполните команду «ren *.txt *.csv». Данная команда изменит расширение с TXT на CSV для всех файлов, которые находятся в этой папке.
Еще раз отметим, что изменение расширения не влияет на содержимое, оно всего лишь указывает операционной системе Windows 11 или Windows 10 какой программой открывать данный документ.
Посмотрите также:
- Чем открыть DJVU формат в Windows 7 и Windows 10
- Чем открыть PDF файл в Windows 7 или Windows 10
- Чем открыть MDF файл в Windows 7 или Windows 10
- Чем открыть mkv
- Чем открыть fb2
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
After I’ve read a lot of similar problems with the edit/update function on a file and none of it worked I would like to ask for some help.
I am trying to edit a .txt document from php. I have tried these things:
-
This was the last code which I’ve read here and didn’t work.
$data_to_write = "$_POST[subject]"; $file_path = "text/" + $row['name']; $file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'w'); fwrite($file_handle, $data_to_write); fclose($file_handle); -
And this is my previous try:
$new_contents = "$_POST[subject]n"; $path = "text/$row[name]"; file_put_contents($path, $new_contents);
I hope someone would explain me how to do this the right way. Thank you.
This is all of my code:
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id']))
{
$edit = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM text_area WHERE text_id=$_GET[id]");
$row = mysql_fetch_assoc($edit);
$contents = file_get_contents($row['content']);
?>
<form action="" name="form" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo $row['text_id']; ?>" /><br />
<label for="">Заглавие:</label><br />
<input type="text" name="title" style="width:500px;" value="<?php echo $row['subject'] ?>" /><br />
<select name="opt">
<option value="0"></option>
<?php
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM image_area");
while ($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo "<option value=" . $row['path'] . ">" . $row['name'] . "</option>
";
}
?>
</select><input type="button" name="sumbitP" value="Choose" onclick="addtext();" /><a href="../image_list.php" target="_blank">Image list</a><br />
<textarea rows="10" cols="50" name="text" id="markItUp"><?php echo $contents ?></textarea><br />
<input type="submit" name="sumbitT" value="Update" />
<input type="reset" value="Reset" />
</form>
<?php
}
?>
<?php
if(isset($_POST['id']))
{
if(mysql_query("UPDATE text_area SET title='$_POST[subject]' WHERE text_id ='$_POST[id]'"))
{
$data_to_write = "" . $_POST['text'];
$file_path = "text/$row[name]";
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'w');
fwrite($file_handle, $data_to_write);
fclose($file_handle);
echo '<br><br><p align="center">Everything is ok</p>';
} else {
echo '<br><br><p align="center">Everything is not ok</p>' ;
}
?>
Just to add something which might be useful:
I am getting this error which I can’t manage to find an answer for with Google.
Warning: fopen(text/) [function.fopen]: failed to open stream: Is a directory in
Sam
3713 silver badges15 bronze badges
asked Sep 18, 2013 at 6:46
3
You just need to change :
$file_path = "text/" + $row['name'];
to this :
$file_path = "text/" . $row['name'];
The concatenation operator in PHP is . (not +)
And make sure the directory text exists, otherwise its better to check and then write :
$data_to_write = $_POST['subject'];
$file_path = "text/" . $row['name'];
if ( !file_exists("text") )
mkdir("text");
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'w');
fwrite($file_handle, $data_to_write);
fclose($file_handle);
answered Sep 18, 2013 at 7:15
Nikhil PatelNikhil Patel
1,74112 silver badges23 bronze badges
4
You can also open file in append mode using fopen() and put whatever you have at the end like
$path = dirname(__FILE__).'/newfile.txt';
$fp = fopen($path, 'a');
if(!$fp){
echo 'file is not opend';
}
fwrite($fp, 'this is simple text written');
fclose($fp);
answered Jul 7, 2016 at 13:48
You need to use file_get_contents to get the text of your file.
$file_path= "text/" . $row['name'];
// Open the file to get existing content
$current = file_get_contents($file_path);
// Append a new person to the file
$data_to_write.= $_POST[subject]."n";
// Write the contents back to the file
file_put_contents($file_path, $data_to_write);
See Documentation
answered Sep 18, 2013 at 7:02
Moeed FarooquiMoeed Farooqui
3,5841 gold badge16 silver badges23 bronze badges
1
I prefer to use file_put_contents and set flags in order to add text instead of overwrite the whole file. With flags you can also lock the file if you have multiple script accessing the same file simultaneously.
Here is how:
$file_name = 'text.txt';
$line= "This is a new linen";
// use flag FILE_APPEND to append the content to the end of the file
// use flag LOCK_EX to prevent other scripts to write to the file while we are writing
file_put_contents($file_name , $line, FILE_APPEND | LOCK_EX);
Here is the full documentation: https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.file-put-contents.php
answered Oct 27, 2020 at 9:45
PinonirvanaPinonirvana
8301 gold badge8 silver badges11 bronze badges
I think the problem may be the first line :
$data_to_write = "$_POST[subject]";
Replace it with the following :
$data_to_write = "" . $_POST['subject'];
And i highly recommand to protect this with hmtlentities or anything else as it’s a direct user input.
answered Sep 18, 2013 at 6:52
2
I just put the code into a compiler, you are missing a } at the end.
answered Oct 5, 2017 at 8:30
(PHP 5, PHP 7, PHP 
file_put_contents — Пишет данные в файл
Описание
file_put_contents(
string $filename,
mixed $data,
int $flags = 0,
?resource $context = null
): int|false
Если filename не существует, файл будет
создан. Иначе, существующий файл будет перезаписан, за исключением
случая, если указан флаг FILE_APPEND.
Список параметров
-
filename -
Путь к записываемому файлу.
-
data -
Записываемые данные. Может быть типа string,
array или ресурсом потока.Если
dataявляется потоковым ресурсом
(stream), оставшийся буфер этого потока будет скопирован
в указанный файл. Это похоже на использование функции stream_copy_to_stream().Также вы можете передать одномерный массив в качестве параметра
data. Это будет эквивалентно вызову
file_put_contents($filename, implode('', $array)). -
flags -
Значением параметра
flagsможет быть
любая комбинация следующих флагов, соединённых бинарным
оператором ИЛИ (|).Доступные флаги
Флаг Описание FILE_USE_INCLUDE_PATHИщет filenameв подключаемых директориях.
Подробнее смотрите директиву include_path.FILE_APPENDЕсли файл filenameуже существует, данные
будут дописаны в конец файла вместо того, чтобы его перезаписать.LOCK_EXПолучить эксклюзивную блокировку на файл на время записи. Другими словами,
между вызовами fopen() и fwrite() произойдёт
вызов функции flock(). Это не одно и то же, что вызов
fopen() с флагом «x». -
context -
Корректный ресурс контекста, созданный с помощью функции
stream_context_create().
Возвращаемые значения
Функция возвращает количество записанных байт в файл, или
false в случае возникновения ошибки.
Внимание
Эта функция может возвращать как логическое значение false, так и значение не типа boolean, которое приводится к false. За более подробной информацией обратитесь к разделу Булев тип. Используйте оператор === для проверки значения, возвращаемого этой функцией.
Примеры
Пример #1 Пример простого использования
<?php
$file = 'people.txt';
// Открываем файл для получения существующего содержимого
$current = file_get_contents($file);
// Добавляем нового человека в файл
$current .= "John Smithn";
// Пишем содержимое обратно в файл
file_put_contents($file, $current);
?>
Пример #2 Использование флагов
<?php
$file = 'people.txt';
// Новый человек, которого нужно добавить в файл
$person = "John Smithn";
// Пишем содержимое в файл,
// используя флаг FILE_APPEND для дописывания содержимого в конец файла
// и флаг LOCK_EX для предотвращения записи данного файла кем-нибудь другим в данное время
file_put_contents($file, $person, FILE_APPEND | LOCK_EX);
?>
Примечания
Замечание: Эта функция безопасна для обработки данных в двоичной форме.
Подсказка
Для этой функции вы можете использовать URL в качестве имени файла, если была включена опция fopen wrappers. Смотрите более подробную информацию об определении имени файла в описании функции fopen(). Смотрите также список поддерживаемых обёрток URL, их возможности, замечания по использованию и список предопределённых констант в разделе Поддерживаемые протоколы и обёртки.
Смотрите также
- fopen() — Открывает файл или URL
- fwrite() — Бинарно-безопасная запись в файл
- file_get_contents() — Читает содержимое файла в строку
- stream_context_create() — Создаёт контекст потока
TrentTompkins at gmail dot com ¶
14 years ago
File put contents fails if you try to put a file in a directory that doesn't exist. This creates the directory.
<?php
function file_force_contents($dir, $contents){
$parts = explode('/', $dir);
$file = array_pop($parts);
$dir = '';
foreach($parts as $part)
if(!is_dir($dir .= "/$part")) mkdir($dir);
file_put_contents("$dir/$file", $contents);
}
?>
justin dot carlson at gmail dot com ¶
11 years ago
It should be obvious that this should only be used if you're making one write, if you are writing multiple times to the same file you should handle it yourself with fopen and fwrite, the fclose when you are done writing.
Benchmark below:
file_put_contents() for 1,000,000 writes - average of 3 benchmarks:
real 0m3.932s
user 0m2.487s
sys 0m1.437s
fopen() fwrite() for 1,000,000 writes, fclose() - average of 3 benchmarks:
real 0m2.265s
user 0m1.819s
sys 0m0.445s
maksam07 at gmail dot com ¶
3 years ago
A slightly simplified version of the method: http://php.net/manual/ru/function.file-put-contents.php#84180
<?php
function file_force_contents( $fullPath, $contents, $flags = 0 ){
$parts = explode( '/', $fullPath );
array_pop( $parts );
$dir = implode( '/', $parts );
if( !
is_dir( $dir ) )
mkdir( $dir, 0777, true );file_put_contents( $fullPath, $contents, $flags );
}file_force_contents( ROOT.'/newpath/file.txt', 'message', LOCK_EX );
?>
deqode at felosity dot nl ¶
12 years ago
Please note that when saving using an FTP host, an additional stream context must be passed through telling PHP to overwrite the file.
<?php
/* set the FTP hostname */
$user = "test";
$pass = "myFTP";
$host = "example.com";
$file = "test.txt";
$hostname = $user . ":" . $pass . "@" . $host . "/" . $file;
/* the file content */
$content = "this is just a test.";
/* create a stream context telling PHP to overwrite the file */
$options = array('ftp' => array('overwrite' => true));
$stream = stream_context_create($options);
/* and finally, put the contents */
file_put_contents($hostname, $content, 0, $stream);
?>
chris at ocportal dot com ¶
9 years ago
It's important to understand that LOCK_EX will not prevent reading the file unless you also explicitly acquire a read lock (shared locked) with the PHP 'flock' function.
i.e. in concurrent scenarios file_get_contents may return empty if you don't wrap it like this:
<?php
$myfile=fopen('test.txt','rt');
flock($myfile,LOCK_SH);
$read=file_get_contents('test.txt');
fclose($myfile);
?>
If you have code that does a file_get_contents on a file, changes the string, then re-saves using file_put_contents, you better be sure to do this correctly or your file will randomly wipe itself out.
Anonymous ¶
5 years ago
Make sure not to corrupt anything in case of failure.
<?phpfunction file_put_contents_atomically($filename, $data, $flags = 0, $context = null) {
if (file_put_contents($filename."~", $data, $flags, $context) === strlen($contents)) {
return rename($filename."~",$filename,$context);
}
@
unlink($filename."~", $context);
return FALSE;
}?>
egingell at sisna dot com ¶
16 years ago
In reply to the previous note:
If you want to emulate this function in PHP4, you need to return the bytes written as well as support for arrays, flags.
I can only figure out the FILE_APPEND flag and array support. If I could figure out "resource context" and the other flags, I would include those too.
<?
define('FILE_APPEND', 1);
function file_put_contents($n, $d, $flag = false) {
$mode = ($flag == FILE_APPEND || strtoupper($flag) == 'FILE_APPEND') ? 'a' : 'w';
$f = @fopen($n, $mode);
if ($f === false) {
return 0;
} else {
if (is_array($d)) $d = implode($d);
$bytes_written = fwrite($f, $d);
fclose($f);
return $bytes_written;
}
}
?>
aidan at php dot net ¶
18 years ago
This functionality is now implemented in the PEAR package PHP_Compat.
More information about using this function without upgrading your version of PHP can be found on the below link:
http://pear.php.net/package/PHP_Compat
gurjindersingh at SPAM dot hotmail dot com ¶
8 years ago
File put contents fails if you try to put a file in a directory that doesn't exist. This function creates the directory.
i have updated code of "TrentTompkins at gmail dot com". thanks
<?php
/**
* @param string $filename <p>file name including folder.
* example :: /path/to/file/filename.ext or filename.ext</p>
* @param string $data <p> The data to write.
* </p>
* @param int $flags same flags used for file_put_contents.
* more info: http://php.net/manual/en/function.file-put-contents.php
* @return bool <b>TRUE</b> file created succesfully <br> <b>FALSE</b> failed to create file.
*/
function file_force_contents($filename, $data, $flags = 0){
if(!is_dir(dirname($filename)))
mkdir(dirname($filename).'/', 0777, TRUE);
return file_put_contents($filename, $data,$flags);
}
// usagefile_force_contents('test1.txt','test1 content'); // test1.txt createdfile_force_contents('test2/test2.txt','test2 content');
// test2/test2.txt created "test2" folder. file_force_contents('~/test3/test3.txt','test3 content');
// /path/to/user/directory/test3/test3.txt created "test3" folder in user directory (check on linux "ll ~/ | grep test3").
?>
Brandon Lockaby ¶
11 years ago
Calling file_put_contents within a destructor will cause the file to be written in SERVER_ROOT...
error at example dot com ¶
12 years ago
It's worth noting that you must make sure to use the correct path when working with this function. I was using it to help with logging in an error handler and sometimes it would work - while other times it wouldn't. In the end it was because sometimes it was called from different paths resulting in a failure to write to the log file.
__DIR__ is your friend.
ravianshmsr08 at gmail dot com ¶
12 years ago
To upload file from your localhost to any FTP server.
pease note 'ftp_chdir' has been used instead of putting direct remote file path....in ftp_put ...remoth file should be only file name
<?php
$host = '*****';
$usr = '*****';
$pwd = '**********';
$local_file = './orderXML/order200.xml';
$ftp_path = 'order200.xml';
$conn_id = ftp_connect($host, 21) or die ("Cannot connect to host");
ftp_pasv($resource, true);
ftp_login($conn_id, $usr, $pwd) or die("Cannot login");
// perform file upload
ftp_chdir($conn_id, '/public_html/abc/');
$upload = ftp_put($conn_id, $ftp_path, $local_file, FTP_ASCII);
if($upload) { $ftpsucc=1; } else { $ftpsucc=0; }
// check upload status:
print (!$upload) ? 'Cannot upload' : 'Upload complete';
print "n";
// close the FTP stream
ftp_close($conn_id);
?>
Anonymous ¶
9 months ago
A more simplified version of the method that creates subdirectories:
function path_put_contents($filePath, $contents, $flags = 0) {
if (! is_dir($dir = implode('/', explode('/', $filePath, -1))))
mkdir($dir, 0777, true);
file_put_contents($filePath, $contents, $flags);
}
daniel at garcianoriega dot com ¶
4 years ago
I faced the problem of converting a downloaded csv file that had Windows-1252 encoding, so to convert it to UTF-8 this worked for me:
$from = 'Windows-1252';
$to = 'UTF-8';
$content = file_get_contents($this->path());
file_put_contents($this->path(), mb_convert_encoding($content, $to, $from));
where "$this->path()" has the path of the file... Using this the file is converted from Windows-1252 to UTF-8.
With this you can import it with mysqlimport with no problems.
briethings at gmail dot com ¶
4 years ago
Here is a stupid pitfall I just fell into.
I think it may happen rather frequently, so I report it.
A common situation is that the $filename argument is built from two variables:
file_put_contents($path . $file, $content);
Say that $path = 'path/to' and $file = 'file.txt': you see that $path lacks its ending "/", so the resulting full path is 'path/tofile.txt'.
Then you look at 'path/to' and don't see any 'file.txt', although no warning or notice was thrown!
And may be (like for me :D) it'll take time before you realize that a bad 'tofile.txt' was created in the *parent* directory of the one where you were looking for your file.
vaneatona at gmail dot com ¶
5 years ago
I'm updating a function that was posted, as it would fail if there was no directory. It also returns the final value so you can determine if the actual file was written.
public static function file_force_contents($dir, $contents){
$parts = explode('/', $dir);
$file = array_pop($parts);
$dir = '';
foreach($parts as $part) {
if (! is_dir($dir .= "{$part}/")) mkdir($dir);
}
return file_put_contents("{$dir}{$file}", $contents);
}
aabaev arroba gmail coma com ¶
6 years ago
I suggest to expand file_force_contents() function of TrentTompkins at gmail dot com by adding verification if patch is like: "../foo/bar/file"
if (strpos($dir, "../") === 0)
$dir = str_replace("..", substr(__DIR__, 0, strrpos(__DIR__, "/")), $dir);
vahkos at mail dot ru ¶
11 years ago
file_put_contents does not issue an error message if file name is incorrect(for example has improper symbols on the end of it /n,/t)
that is why use trim() for file name.
$name=trim($name);
file_put_contents($name,$content);
John Galt ¶
13 years ago
I use file_put_contents() as a method of very simple hit counters. These are two different examples of extremely simple hit counters, put on one line of code, each.
Keep in mind that they're not all that efficient. You must have a file called counter.txt with the initial value of 0.
For a text hit counter:
<?php
$counter = file_get_contents("counter.txt"); $counter++; file_put_contents("counter.txt", $counter); echo $counter;
?>
Or a graphic hit counter:
<?php
$counter = file_get_contents("counter.txt"); $counter++; file_put_contents("counter.txt", $counter); for($i = 0; $i < strlen($counter); $i++) echo "<img src="counter/".substr($counter, $i, 1).".gif" alt="".substr($counter, $i, 1)."" />";
?>
wjsams at gmail dot com ¶
13 years ago
file_put_contents() strips the last line ending
If you really want an extra line ending at the end of a file when writing with file_put_contents(), you must append an extra PHP_EOL to the end of the line as follows.
<?php
$a_str = array("these","are","new","lines");
$contents = implode(PHP_EOL, $a_str);
$contents .= PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL;
file_put_contents("newfile.txt", $contents);
print("|$contents|");
?>
You can see that when you print $contents you get two extra line endings, but if you view the file newfile.txt, you only get one.
caiofior at gmail dot com ¶
11 years ago
I had some troubles using file_put_contents with an absolute but no canonicalized path (eg. w:/htdocs/pri/../test/log.txt): on windows environment php was unable to create the file also using the realpath function .
I had to use fopen and frwite functions to write the data.
kola_lola at hotmail dot com ¶
14 years ago
I wrote this script implementing the file_put_contents() and file_get_contents() functions to be compatible with both php4.* and php 5.*. It is a PHP Command line interface script which searches and replaces a specific word recursively through all files in the supplied directory hierarchy.
Usage from a Linux command line: ./scriptname specifieddirectory searchString replaceString
#!/usr/bin/php
<?php
$argc = $_SERVER['argc'];
$argv = $_SERVER['argv'];
if(
$argc != 4)
{
echo "This command replaces a search string with a replacement stringn for the contents of all files in a directory hierachyn";
echo "command usage: $argv[0] directory searchString replaceStringn";
echo "n";
exit;
}
?><?phpif (!function_exists('file_put_contents')) {
function file_put_contents($filename, $data) {
$f = @fopen($filename, 'w');
if (!$f) {
return false;
} else {
$bytes = fwrite($f, $data);
fclose($f);
return $bytes;
}
}
}
function
get_file_contents($filename)/* Returns the contents of file name passed
*/
{
if (!function_exists('file_get_contents'))
{
$fhandle = fopen($filename, "r");
$fcontents = fread($fhandle, filesize($filename));
fclose($fhandle);
}
else
{
$fcontents = file_get_contents($filename);
}
return $fcontents;
}
?><?phpfunction openFileSearchAndReplace($parentDirectory, $searchFor, $replaceWith)
{
//echo "debug here- line 1an";
//echo "$parentDirectoryn";
//echo "$searchForn";
//echo "$replaceWithn";if ($handle = opendir("$parentDirectory")) {
while (false !== ($file = readdir($handle))) {
if (($file != "." && $file != "..") && !is_dir($file)) {
chdir("$parentDirectory"); //to make sure you are always in right directory
// echo "$filen";
$holdcontents = file_get_contents($file);
$holdcontents2 = str_replace($searchFor, $replaceWith, $holdcontents);
file_put_contents($file, $holdcontents2);
// echo "debug here- line 1n";
// echo "$filen";}
if(is_dir($file) && ($file != "." && $file != ".."))
{
$holdpwd = getcwd();
//echo "holdpwd = $holdpwd n";
$newdir = "$holdpwd"."/$file";
//echo "newdir = $newdir n"; //for recursive call
openFileSearchAndReplace($newdir, $searchFor, $replaceWith);
//echo "debug here- line 2n";
//echo "$filen";
}
}
closedir($handle);
}
}$parentDirectory2 = $argv[1];
$searchFor2 = $argv[2];
$replaceWith2 = $argv[3];//Please do not edit below to keep the rights to this script
//Free license, if contents below this line is not edited
echo "REPLACEDn'$searchFor2' with '$replaceWith2' recursively through directory listed belownFor all files that current user has write permissions fornDIRECTORY: '$parentDirectory2'n";
echo "command written by Kolapo Akande :) all rights reserved :)n";$holdpwd = getcwd();
//echo "$holdpwdn";
chdir($parentDirectory2);
openFileSearchAndReplace($parentDirectory2, $searchFor2, $replaceWith2);
exit;
?>
Curtis ¶
16 years ago
As to the previous user note, it would be wise to include that code within a conditional statement, as to prevent re-defining file_put_contents and the FILE_APPEND constant in PHP 5:
<?php
if ( !function_exists('file_put_contents') && !defined('FILE_APPEND') ) {
...
}
?>
Also, if the file could not be accessed for writing, the function should return boolean false, not 0. An error is different from 0 bytes written, in this case.
moura dot kadu at gmail dot com ¶
11 years ago
I made a ftp_put_contents function.
hope you enjoy.
<?phpfunction ftp_put_contents($fpc_path_and_name, $fpc_content) {//Temporary folder in the server
$cfg_temp_folder = str_replace("//", "/", $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']."/_temp/");//Link to FTP
$cfg_ftp_server = "ftp://ftp.com";//FTP username
$cfg_user = "user";//FTP password
$cfg_pass = "password";//Document Root of FTP
$cfg_document_root = "DOCUMENT ROOT OF FTP";//Link to the website
$cfg_site_link = "Link to the website";//Check if conteins slash on the path of the file
$cotains_slash = strstr($fpc_path_and_name, "/");//Get filename and paths
if ($cotains_slash) {
$fpc_path_and_name_array = explode("/", $fpc_path_and_name);
$fpc_file_name = end($fpc_path_and_name_array);
}
else {
$fpc_file_name = $fpc_path_and_name;
}//Create local temp dir
if (!file_exists($cfg_temp_folder)) {
if (!mkdir($cfg_temp_folder, 0777)) {
echo "Unable to generate a temporary folder on the local server - $cfg_temp_folder.<br />";
die();
}
}//Create local file in temp dir
if (!file_put_contents(str_replace("//", "/", $cfg_temp_folder.$fpc_file_name), $fpc_content)) {
echo "Unable to generate the file in the temporary location - ".str_replace("//", "/", $cfg_temp_folder.$fpc_file_name).".<br />";
die();
}//Connection to the FTP Server
$fpc_ftp_conn = ftp_connect("$cfg_ftp_server");//Check connection
if (!$fpc_ftp_conn) {
echo "Could not connect to server <b>$cfg_ftp_server</b>.<br />";
die();
}
else {// login
// check username and password
if (!ftp_login($fpc_ftp_conn, "$cfg_user", "$cfg_pass")) {
echo "User or password.<br />";
die();
}
else {//Document Root
if (!ftp_chdir($fpc_ftp_conn, $cfg_document_root)) {
echo "Error to set Document Root.<br />";
die();
}//Check if there are folders to create
if ($cotains_slash) {//Check if have folders and is not just the file name
if (count($fpc_path_and_name_array) > 1) {//Remove last array
$fpc_remove_last_array = array_pop($fpc_path_and_name_array);//Checks if there slashs on the path
if (substr($fpc_path_and_name,0,1) == "/") {
$fpc_remove_first_array = array_shift($fpc_path_and_name_array);
}//Create each folder on ftp
foreach ($fpc_path_and_name_array as $fpc_ftp_path) {
if (!@ftp_chdir($fpc_ftp_conn, $fpc_ftp_path)) {
if (!ftp_mkdir($fpc_ftp_conn, $fpc_ftp_path)) {
echo "Error creating directory $fpc_ftp_path.<br />";
}
else {
if (!ftp_chdir($fpc_ftp_conn, $fpc_ftp_path)) {
echo "Error go to the directory $fpc_ftp_path.<br />";
}
}
}
}
}
else {
}
}
//Check upload file
if (!ftp_put($fpc_ftp_conn, $fpc_file_name, str_replace("//", "/", $cfg_temp_folder.$fpc_file_name), FTP_ASCII)) {
echo "File upload <b>$fpc_path_and_name</b> failed!<br />";
die();
}
else {
if (!unlink(str_replace("//", "/", $cfg_temp_folder.$fpc_file_name))) {
echo "Error deleting temporary file.<br />";
die();
}
else {
echo "File upload <a href='$cfg_site_link".str_replace("//", "/", "/$fpc_path_and_name")."'><b>$cfg_site_link".str_replace("//", "/", "/$fpc_path_and_name")."</a></b> successfully performed.<br />";
}
}//Close connection to FTP server
ftp_close($fpc_ftp_conn);
}
}
}#Sample$content_file = "<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Test</p>
</body>
</html>";ftp_put_contents("test.php", $content_file);
?>
the geek man at hot mail point com ¶
15 years ago
I use the following code to create a rudimentary text editor. It's not fancy, but then it doesn't have to be. You could easily add a parameter to specify a file to edit; I have not done so to avoid the potential security headaches.
There are still obvious security holes here, but for most applications it should be reasonably safe if implemented for brief periods in a counterintuitive spot. (Nobody says you have to make a PHP file for that purpose; you can tack it on anywhere, so long as it is at the beginning of a file.)
<?php
$random1 = 'randomly_generated_string';
$random2 = 'another_randomly_generated_string';
$target_file = 'file_to_edit.php';
$this_file = 'the_current_file.php';
if (
$_REQUEST[$random1] === $random2) {
if (isset($_POST['content']))
file_put_contents($target_file, get_magic_quotes_qpc() ? stripslashes($_POST['content']) : $_POST['content']);
die(
'<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en">
<head>
<title>Editing...</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="' . $this_file . '" />
<input type="hidden" name="' . $random1 . '" value="' . $random2 . '" />
<textarea name="content" rows="50" cols="100">' . file_get_contents($target_file) . '</textarea><br />
<input type="submit" value="Save Changes" />
</form>
</body>
</html>');
}
?>
Then simply browse to hxxp://www.example.com/{$this_file}?{$random1}={$random2}, with the appropriate values substituted for each bracketed variable. Please note that this code assumes the target file to be world writable (-rw-rw-rw- or 666) and will fail to save properly without error if it is not.
Once again, this is by no means secure or permanent, but as a quick fix for brief edits to noncritical files it should be sufficient, and its small size is a definite bonus.
marc at gutt dot it ¶
5 years ago
This php.net example could be confusing:
<?php
file_put_contents($file, $person, FILE_APPEND | LOCK_EX);
?>
You do not need LOCK_EX if you write only to a file (like log files). Multiple writing processes are already queued. Test it on your own by calling this script 4 times simultaneously:
<?php
function string_rand($len, $split="n") {
return substr(chunk_split(bin2hex(openssl_random_pseudo_bytes(ceil($len / 2))), 1023, $split), 0, $len);
}ini_set('memory_limit', '200M');
if (!
file_put_contents('../cache4/file.txt', string_rand(102400000), FILE_APPEND)) {
exit('file_put_contents() error!');
}clearstatcache();
echo 'filesize: ' . filesize('../cache4/file.txt') . PHP_EOL;$fp = fopen('../cache4/file.txt', 'r');
if ($fp) {
while (($line = fgets($fp)) !== false) {
if (strlen($line) != 1024) {
exit('Line length error!');
}
}
fclose($fp);
}
?>
You will not see an error, the last called script needs the longest time (as it is the last one in the queue) and the final size will be 409600000 bytes as it should be.
vilhar at hotmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
This should also handle $filename from other than root and also $filename without path.
function file_force_contents($filename, $data, $per = 0755, $flags = 0) {
$fn = "";
if(substr($filename, 0, 1) === "/") $fn .= "/";
$parts = explode("/", $filename);
$file = array_pop($parts);
foreach($parts as $part) {
if(!is_dir($fn .= "$part")) mkdir($fn, $per, true);
$fn .= "/";
}
file_put_contents($fn.$file, $data, $flags);
}
michel kollenhoven ¶
9 years ago
egingell at sisna dot com ¶
15 years ago
There is a better way. www.php.net/touch
Since you're not adding anything to the file,
<?php
function updateFile($filename) {
if (!file_exists($filename)) return;
touch($filename);
}
?>
Nadeem ¶
8 years ago
Log custom or error messages to a file.
<?phpclass Logger{
protected
$file;
protected
$content;
protected
$writeFlag;
protected
$endRow;
public function
__construct($file,$endRow="n",$writeFlag=FILE_APPEND) { $this->file=$file;$this->writeFlag=$writeFlag;$this->endRow=$endRow;
}
public function
AddRow($content="",$newLines=1){
for (
$m=0;$m<$newLines;$m++)
{$newRow .= $this->endRow;
}
$this->content .= $content . $newRow;
}
public function
Commit(){
return
file_put_contents($this->file,$this->content,$this->writeFlag);
}
public function
LogError($error,$newLines=1)
{
if ($error!=""){$this->AddRow($error,$newLines);
echo $error;
}
}
}
$logFileDirectoryAndName="/yourDirectory/yourFileName.xxx";$logger = new Logger($logFileDirectoryAndName);$logger->AddRow("Your Log Message");#log a system error and echo a message
$logger->LogError(mysql_error($conn));$logger->Commit();
?>
klunker dot roox at gmail dot com ¶
8 years ago
if path to the file not exist function file_put_contents can't create it. This simple function make it on UNIX-based and Windows servers.
<?php
function file_put_contents_force(){
$args = func_get_args();
$path = str_replace(array('/','\'), DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR, $args[0]);
$parts = explode(DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR, $path);
array_pop($parts);
$directory = '';
foreach($parts as $part):
$check_path = $directory.$part;
if( is_dir($check_path.DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR) === FALSE) {
mkdir($check_path, 0755);
}
$directory = $check_path.DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR;
endforeach;
call_user_func_array('file_put_contents',$args);
}
?>
hilton at allcor dot com dot br ¶
12 years ago
NOTE : file_put_contents create files UTF-8
<?php
$myFile = 'test.txt';
$myContent = 'I love PHP'; file_put_contents($myFile, utf8_encode($myContent));
?>
clement dot delmas at gmail dot com ¶
12 years ago
NOTE : file_put_contents doesn't add a valid BOM while creating the file
<?php
$myFile = 'test.txt';
$myContent = 'I love PHP';
file_put_contents($myFile, "xEFxBBxBF".$myContent);
?>
Abe ¶
4 years ago
If you need to read a file, process the contents, and then write the contents back, all inside a lock so that no other process can interfere, then you probably can't use file_put_contents in lock mode.
As a work around, you can consider trying the following code to do a file write (fwrite) inside of a file lock.
Play with the $overwriting= setting to switch from simply appending to completely overwriting.
<?php
// Tested in PHP7.0.18$trackErrors = ini_get('track_errors');
ini_set('track_errors', 1);$filename="c:/temp/test.txt";
if ( !
file_exists($filename) ) {
touch($filename);
}$mode="r+";
$fh=fopen($filename, $mode);
if ( ! $fh ) {
echo "<LI style='color:red'>Failed to open $filename in $mode";
die();
}
if (
1==1 ) {
flock($fh, LOCK_EX);
if (
1==1 ) {
if (filesize($filename) > 0) {
$txt = fread($fh, filesize($filename));
echo "BEFORE:<OL>$txt</OL>";
}
else {
$txt = "empty";
}$txt = "<LI>Date is now " . gmdate("Y-m-d H:i:s", time());
echo
"<HR>WRITING:<OL>";
if ( 1==1 ) {$overwrite = false;
if ($overwrite) {
echo "(Overwrite)<BR><BR>";
ftruncate($fh, 0);
// ftruncate is here as rewind will move the pointer
// to the beginning of the file and allow overwrite,
// but it will not remove existing content that
// extends beyond the length of the new write
rewind($fh);
}
else {
echo "(Appending)<BR><BR>";
}
if (
fwrite($fh, $txt) == FALSE) {
echo "<LI style='color:red'>Failed to write to $filename";
die();
}
else {
echo "$txt";
}
fflush($fh);
}
echo
"</OL>";
}
flock($fh, LOCK_UN);
}
fclose($fh);// -------------------------------------------------------------------echo "<HR>AFTER:<OL>";
if ( 1==2 ) {
// I've noticed that this block fails to pick up the newly
// written content when run with fread, but does work with
// the fgets logic below - possibly there is caching going on.
$mode = "r";
$fh2 = fopen($filename, $mode);
$contents = fread($fh2, filesize($filename));
echo "$contents";
fclose($fh2);
}
else {
$fh3 = fopen($filename, "r");
while (!feof($fh3)) {
$line = fgets($fh3);
echo $line;
}
fclose($fh3);
}
echo "</OL>";
echo
"<HR>Fin";
?>
josemiguel at likeik dot com ¶
6 years ago
Under PHP7.0, I have seen that using an empty string as $data, the function returns FALSE instead of 0 as it should:
$data = ''
$size = file_put_contents($filename, $data, FILE_APPEND);
if ($size == FALSE)
{
echo "error writing file"
}
Code will give error when $data is an empty string even using == operator.
Hope it helps somebody...
jul dot rosset at gmail dot com ¶
2 years ago
This function doesn't return False if all data isn't write, especially when data is a stream resource
You must check yourself using return value.
<?php
$url = 'https://monsite.fr/image.png';
$size = filesize($url);
$written = file_put_contents('image.png', fopen($url, 'r'));
if ($size === false || $size != $written) {
die('Download failed');
}
?>
admin at nabito dot net ¶
14 years ago
This is example, how to save Error Array into simple log file
<?php
$error
[] = 'some error';
$error[] = 'some error 2';
@
file_put_contents('log.txt',date('c')."n".implode("n", $error),FILE_APPEND);?>
I have tried everything, and multiple different source codes, I have tried creating the file so all the PHP had to do was write in it, and still unable to do it.
This is my HTML on index.html
<form name="userinput" action="usersave.php" method="post">
Your name: <input type="text" name="username><br>
Your email: <input type="text" name="useremail"><br>
Your story: <textarea rows="3" cols="50" name="userstory"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit!" name="submit">
</form>
And this is my PHP on usersave.php
<header>
<?php
$file = 'output.txt';
$buffer = $_POST['userstory'];
if (file_exists($file)) {
$buffer = file_get_contents($file) . "n" . $buffer;
}
$success = file_put_contents($file, $buffer);
?>
</header>
any help is appreciated, please and thank you.
asked Apr 5, 2013 at 23:09
4
edit: You’ll need to install some sort of server environment to get started.
I recommend WAMP
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:13
castiscastis
8,1124 gold badges44 silver badges63 bronze badges
3
If you are not using any host what soever, then there isn’t a server to run the php, the browser doesn’t parse PHP, the server does, so if there isn’t a server, none of the PHP gets parsed.
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:17
3
<?php
$file_path = "text_file.txt";
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'r'); // OPEN FILE READY FOR 'R'eading!
$text_data = fread($file_handle, filesize($file_path)); //Read actual data in file
print $text_data; // print the data you can use echo if you like
fclose($file_handle); // Close the file read / buffer
$data_to_write = "This is the data that will be written to disk!";
$file_path = "new_file.txt";
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'w'); // OPEN FILE READY FOR 'W'riting!
fwrite($file_handle, $data_to_write);
fclose($file_handle);
?>
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:19
GrmnGrmn
5322 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
I am not using any host whatsoever and am opening the files directly from my PC into Chrome.
You cannot run PHP files without a server (e.g. Apache). PHP files are ‘server-side’ scripts; the script is executed on the server, and the resulting output is send to the browser by the server.
See this question:
Parsing PHP content in HTML without Webserver
Or try searching Google
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:21
thaJeztahthaJeztah
26.8k9 gold badges69 silver badges91 bronze badges
0
I have tried everything, and multiple different source codes, I have tried creating the file so all the PHP had to do was write in it, and still unable to do it.
This is my HTML on index.html
<form name="userinput" action="usersave.php" method="post">
Your name: <input type="text" name="username><br>
Your email: <input type="text" name="useremail"><br>
Your story: <textarea rows="3" cols="50" name="userstory"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit!" name="submit">
</form>
And this is my PHP on usersave.php
<header>
<?php
$file = 'output.txt';
$buffer = $_POST['userstory'];
if (file_exists($file)) {
$buffer = file_get_contents($file) . "n" . $buffer;
}
$success = file_put_contents($file, $buffer);
?>
</header>
any help is appreciated, please and thank you.
asked Apr 5, 2013 at 23:09
4
edit: You’ll need to install some sort of server environment to get started.
I recommend WAMP
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:13
castiscastis
8,1124 gold badges44 silver badges63 bronze badges
3
If you are not using any host what soever, then there isn’t a server to run the php, the browser doesn’t parse PHP, the server does, so if there isn’t a server, none of the PHP gets parsed.
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:17
3
<?php
$file_path = "text_file.txt";
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'r'); // OPEN FILE READY FOR 'R'eading!
$text_data = fread($file_handle, filesize($file_path)); //Read actual data in file
print $text_data; // print the data you can use echo if you like
fclose($file_handle); // Close the file read / buffer
$data_to_write = "This is the data that will be written to disk!";
$file_path = "new_file.txt";
$file_handle = fopen($file_path, 'w'); // OPEN FILE READY FOR 'W'riting!
fwrite($file_handle, $data_to_write);
fclose($file_handle);
?>
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:19
GrmnGrmn
5322 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
I am not using any host whatsoever and am opening the files directly from my PC into Chrome.
You cannot run PHP files without a server (e.g. Apache). PHP files are ‘server-side’ scripts; the script is executed on the server, and the resulting output is send to the browser by the server.
See this question:
Parsing PHP content in HTML without Webserver
Or try searching Google
answered Apr 5, 2013 at 23:21
thaJeztahthaJeztah
26.8k9 gold badges69 silver badges91 bronze badges
0
Главная » Основы PHP » Работа с файлами-2 (удаление, копирование, переименование и перемещение файлов). Основы PHP с нуля. Урок №20
Работа с файлами-2 (удаление, копирование, переименование и перемещение файлов). Основы PHP с нуля. Урок №20
Всем привет!
Продолжаем изучать основы PHP с нуля! В этом уроке я расскажу вам, как при помощи кода php Вы сможете удалить любой файл, а также копировать, переименовывать или перемещать файл.
Не буду тянуть кота за хвост, а приступим к изучению.
Удаление файлов
Для удаления файлов воспользуйтесь функцией unlink().
Синтаксис:
unlink(имя_файла);
— имя_файла – здесь укажите имя файла, который нужно удалить (либо переменная, которой присвоили название файла).
Пример:
unlink("file.txt");
или так:
$stepkinblog = "file.txt"; unlink($stepkinblog);
Если файл «file.txt» существовал, то после запуска этого скрипта файл будет полностью удален.
Копирование файлов на php
Если вам нужно перекопировать содержимое с одного файла в другой, можно воспользоваться замечательной функцией php — copy().
Синтаксис:
copy("файл1", "файл2");
— файл1 – имя файла, откуда будет копироваться текст
— файл2 – имя файла, куда будет копироваться текст
Пример:
<?php
// копируем текст с файла file1.txt в файл file2.txt
copy("file1.txt", "file2.txt");
?>
Вот полный пример.
Создайте на локальном сервере или на хостинге пустой файл «file2.txt». Рядом создаем файл «file.php» с таким кодом и запускаем его:
<?php
// строка, которую будем записывать
$text = "Я рад видеть вас на блоге StepkinBLOG.RU";
// открываем файл, если файл не существует,
//делается попытка создать его
$fp = fopen("file1.txt", "w");
// записываем в файл текст
fwrite($fp, $text);
// закрываем файл
fclose($fp);
// копируем текст с файла file1.txt в файл file2.txt
copy("file1.txt", "file2.txt");
// выводим содержание файла на экран браузера
readfile("file2.txt");
?>
После запуска в браузере отобразится содержимое файла «file2.txt» и при открытии файла «file2.txt» через блокнот мы увидим, что он не пустой, а вся информация с файла «file1.txt» перекопировалась в файл «file2.txt»:
Переименование файлов на php
Если вам нужно переименовать файлы, воспользуйтесь функцией php — rename().
Синтаксис:
rename("файл1", "файл2");
— файл1 – название файла, которое нужно заменить (переименовать)
— файл2 – здесь нужно дать новое название файла
Пример:
rename("file2.txt", "stepkinblog-ru.php");
Файл «file2.txt» переименован в файл «stepkinblog-ru.php».
Перемещение файлов
Если вам нужно переместить файл, воспользуйтесь верхней функцией php по переименованию — rename().
Синтаксис:
rename("файл1", "путь/файл1");
— файл1 – название файла, которое нужно переместить
— путь/файл1 – здесь нужно указать путь перемещения файла с его названием.
Пример:
rename("file.txt", "111/file.txt");
Файл «file.txt» переместится в папку «111».
На сегодня все!
Подписывайтесь на обновления блога, если не хотите пропустить уроки по основам PHP!