How to rename a MySQL database?
The MySQL online manual has said about the RENAME DATABASE command (this documentation page has been removed by Oracle some time ago):
This statement was added in MySQL 5.1.7 but was found to be dangerous and
was removed in MySQL 5.1.23.
So, how to proceed? The rationale: We started with a code name for the project and want the database name now to reflect the definitive name of the project.
asked Oct 27, 2010 at 7:35
3
From this blog post by Ilan Hazan:
In MySQL there is no support for database renaming.
In order to rename a MySQL database you can do one of the following:
-
Create new database and rename all tables in the old database to be in the new database:
CREATE database new_db_name; RENAME TABLE db_name.table1 TO new_db_name.table1, db_name.table2 TO new_db_name.table2; DROP database db_name; -
In Linux shell, use mysqldump to back up the old database, then restore the dumped database under a new name using the MySQL utility. Finally, use the drop database command to drop the old database. This option can perform badly for large database.
mysqldump -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx db_name > db_name_dump.sql mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx -e "CREATE DATABASE new_db_name" mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx new_db_name < db_name_dump.sql mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx -e "DROP DATABASE db_name" -
Write a simple Linux script (my favorite solution)
#!/bin/bash dbuser=xxxx dbpass=xxxx olddb=xxxx newdb=xxxx mysqlconn="mysql -u $dbuser -p$dbpass -h localhost" $mysqlconn -e "CREATE DATABASE `$newdb`" params=$($mysqlconn -N -e "SELECT TABLE_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE table_schema='$olddb'") for name in $params; do sql="RENAME TABLE `$olddb`.`$name` to `$newdb`.`$name`" echo "$sql"; $mysqlconn -e "$sql"; echo "Renamed $olddb.$name to $newdb.$name"; done; #$mysqlconn -e "DROP DATABASE `$olddb`" -
If all your tables are MyISAM, you can rename the old database folder name:
- Shut down the MySQL server,
- Rename the database folder name to the new name,
- Start the MySQL server.
5
MySQL kinda sucks for this. The only solid reliable solution is to use phpMyAdmin.
Login —> click Scheme —> click Operations —> find Rename database to: —> write NewName > click Go.
As simple as that. All permissions are carried over.
HopelessN00b
53.6k32 gold badges134 silver badges208 bronze badges
answered Sep 27, 2012 at 15:40
1
I tend to create a new database, and then dump the tables out of the old one, into a .sql file (with mysqldump), edit the file, do some kind of s/old_database/new_database/g and then reimport it into the new db.
Probably not the best way to do it, but it does work.
answered Oct 27, 2010 at 7:42
Tom O’ConnorTom O’Connor
27.5k10 gold badges72 silver badges148 bronze badges
I used following method to rename the database
-
take backup of the file using mysqldump or any DB tool eg heidiSQL,mysql administrator etc
-
Open back up (eg backupfile.sql) file in some text editor.
-
Search and replace the database name and save file.
-
Restore the edited sql file
answered Sep 11, 2013 at 5:26
If you have chance to use a MySQL Management-Tool (e.g. phpMyAdmin) then you can rename it easily as they create the query for you.
In phpMyAdmin they also create each table and insert the data by «INSERT INTO… SELECT * FROM…». So by chaining they copy the data over.
If you can’t do this I would recommend to make a dump and re-import the sql-File into a new database.
Good luck!
Regards,
Ben.
answered Oct 27, 2010 at 8:53
Well there are 2 methods:
Method 1: A well-known method for renaming database schema is by dumping the schema using Mysqldump and restoring it in another schema, and then dropping the old schema (if needed).
From Shell
mysqldump emp > emp.out
mysql -e "CREATE DATABASE employees;"
mysql employees < emp.out
mysql -e "DROP DATABASE emp;"
Although the above method is easy, it is time and space consuming. What if the schema is more than a 100GB? There are methods where you can pipe the above commands together to save on space, however it will not save time.
To remedy such situations, there is another quick method to rename schemas, however, some care must be taken while doing it.
Method 2: MySQL has a very good feature for renaming tables that even works across different schemas. This rename operation is atomic and no one else can access the table while its being renamed. This takes a short time to complete since changing a table’s name or its schema is only a metadata change. Here is procedural approach at doing the rename:
Create the new database schema with the desired name.
Rename the tables from old schema to new schema, using MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” command.
Drop the old database schema.
If there are views, triggers, functions, stored procedures in the schema, those will need to be recreated too. MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” fails if there are triggers exists on the tables. To remedy this we can do the following things :
1) Dump the triggers, events and stored routines in a separate file. This done using -E, -R flags (in addition to -t -d which dumps the triggers) to the mysqldump command. Once triggers are dumped, we will need to drop them from the schema, for RENAME TABLE command to work.
$ mysqldump <old_schema_name> -d -t -R -E > stored_routines_triggers_events.out
2) Generate a list of only “BASE” tables. These can be found using a query on information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE';
3) Dump the views in an out file. Views can be found using a query on the same information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW';
$ mysqldump <database> <view1> <view2> … > views.out
4) Drop the triggers on the current tables in the old_schema.
mysql> DROP TRIGGER <trigger_name>;
...
5) Restore the above dump files once all the “Base” tables found in step #2 are renamed.
mysql> RENAME TABLE <old_schema>.table_name TO <new_schema>.table_name;
...
$ mysql <new_schema> < views.out
$ mysql <new_schema> < stored_routines_triggers_events.out
Intricacies with above methods : We may need to update the GRANTS for users such that they match the correct schema_name. These could fixed with a simple UPDATE on mysql.columns_priv, mysql.procs_priv, mysql.tables_priv, mysql.db tables updating the old_schema name to new_schema and calling “Flush privileges;”. Although “method 2″ seems a bit more complicated than the “method 1″, this is totally scriptable. A simple bash script to carry out the above steps in proper sequence, can help you save space and time while renaming database schemas next time.
The Percona Remote DBA team have written a script called “rename_db” that works in the following way :
[root@dba~]# /tmp/rename_db
rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>
To demonstrate the use of this script, used a sample schema “emp”, created test triggers, stored routines on that schema. Will try to rename the database schema using the script, which takes some seconds to complete as opposed to time consuming dump/restore method.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
[root@dba ~]# time /tmp/rename_db localhost emp emp_test
create database emp_test DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1
drop trigger salary_trigger
rename table emp.__emp_new to emp_test.__emp_new
rename table emp._emp_new to emp_test._emp_new
rename table emp.departments to emp_test.departments
rename table emp.dept to emp_test.dept
rename table emp.dept_emp to emp_test.dept_emp
rename table emp.dept_manager to emp_test.dept_manager
rename table emp.emp to emp_test.emp
rename table emp.employees to emp_test.employees
rename table emp.salaries_temp to emp_test.salaries_temp
rename table emp.titles to emp_test.titles
loading views
loading triggers, routines and events
Dropping database emp
real 0m0.643s
user 0m0.053s
sys 0m0.131s
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp_test |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
As you can see in the above output the database schema “emp” was renamed to “emp_test” in less than a second. Lastly, This is the script from Percona that is used above for “method 2″.
#!/bin/bash
# Copyright 2013 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates
set -e
if [ -z "$3" ]; then
echo "rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>"
exit 1
fi
db_exists=`mysql -h $1 -e "show databases like '$3'" -sss`
if [ -n "$db_exists" ]; then
echo "ERROR: New database already exists $3"
exit 1
fi
TIMESTAMP=`date +%s`
character_set=`mysql -h $1 -e "show create database $2G" -sss | grep ^Create | awk -F'CHARACTER SET ' '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}'`
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
STATUS=$?
if [ "$STATUS" != 0 ] || [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Error retrieving tables from $2"
exit 1
fi
echo "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
mysql -h $1 -e "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
TRIGGERS=`mysql -h $1 $2 -e "show triggersG" | grep Trigger: | awk '{print $2}'`
VIEWS=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW'" -sss`
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
mysqldump -h $1 $2 $VIEWS > /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
mysqldump -h $1 $2 -d -t -R -E > /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
for TRIGGER in $TRIGGERS; do
echo "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
done
for TABLE in $TABLES; do
echo "rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
done
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
echo "loading views"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
echo "loading triggers, routines and events"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
if [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Dropping database $2"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop database $2"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.columns_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
COLUMNS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.columns_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.procs_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
PROCS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.procs_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.tables_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
TABLES_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.tables_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.db where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
DB_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.db set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then
echo "IF YOU WANT TO RENAME the GRANTS YOU NEED TO RUN ALL OUTPUT BELOW:"
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$COLUMNS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$PROCS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ]; then echo "$TABLES_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then echo "$DB_PRIV"; fi
echo " flush privileges;"
fi
How to rename a MySQL database?
The MySQL online manual has said about the RENAME DATABASE command (this documentation page has been removed by Oracle some time ago):
This statement was added in MySQL 5.1.7 but was found to be dangerous and
was removed in MySQL 5.1.23.
So, how to proceed? The rationale: We started with a code name for the project and want the database name now to reflect the definitive name of the project.
asked Oct 27, 2010 at 7:35
3
From this blog post by Ilan Hazan:
In MySQL there is no support for database renaming.
In order to rename a MySQL database you can do one of the following:
-
Create new database and rename all tables in the old database to be in the new database:
CREATE database new_db_name; RENAME TABLE db_name.table1 TO new_db_name.table1, db_name.table2 TO new_db_name.table2; DROP database db_name; -
In Linux shell, use mysqldump to back up the old database, then restore the dumped database under a new name using the MySQL utility. Finally, use the drop database command to drop the old database. This option can perform badly for large database.
mysqldump -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx db_name > db_name_dump.sql mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx -e "CREATE DATABASE new_db_name" mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx new_db_name < db_name_dump.sql mysql -uxxxx -pxxxx -h xxxx -e "DROP DATABASE db_name" -
Write a simple Linux script (my favorite solution)
#!/bin/bash dbuser=xxxx dbpass=xxxx olddb=xxxx newdb=xxxx mysqlconn="mysql -u $dbuser -p$dbpass -h localhost" $mysqlconn -e "CREATE DATABASE `$newdb`" params=$($mysqlconn -N -e "SELECT TABLE_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE table_schema='$olddb'") for name in $params; do sql="RENAME TABLE `$olddb`.`$name` to `$newdb`.`$name`" echo "$sql"; $mysqlconn -e "$sql"; echo "Renamed $olddb.$name to $newdb.$name"; done; #$mysqlconn -e "DROP DATABASE `$olddb`" -
If all your tables are MyISAM, you can rename the old database folder name:
- Shut down the MySQL server,
- Rename the database folder name to the new name,
- Start the MySQL server.
5
MySQL kinda sucks for this. The only solid reliable solution is to use phpMyAdmin.
Login —> click Scheme —> click Operations —> find Rename database to: —> write NewName > click Go.
As simple as that. All permissions are carried over.
HopelessN00b
53.6k32 gold badges134 silver badges208 bronze badges
answered Sep 27, 2012 at 15:40
1
I tend to create a new database, and then dump the tables out of the old one, into a .sql file (with mysqldump), edit the file, do some kind of s/old_database/new_database/g and then reimport it into the new db.
Probably not the best way to do it, but it does work.
answered Oct 27, 2010 at 7:42
Tom O’ConnorTom O’Connor
27.5k10 gold badges72 silver badges148 bronze badges
I used following method to rename the database
-
take backup of the file using mysqldump or any DB tool eg heidiSQL,mysql administrator etc
-
Open back up (eg backupfile.sql) file in some text editor.
-
Search and replace the database name and save file.
-
Restore the edited sql file
answered Sep 11, 2013 at 5:26
If you have chance to use a MySQL Management-Tool (e.g. phpMyAdmin) then you can rename it easily as they create the query for you.
In phpMyAdmin they also create each table and insert the data by «INSERT INTO… SELECT * FROM…». So by chaining they copy the data over.
If you can’t do this I would recommend to make a dump and re-import the sql-File into a new database.
Good luck!
Regards,
Ben.
answered Oct 27, 2010 at 8:53
Well there are 2 methods:
Method 1: A well-known method for renaming database schema is by dumping the schema using Mysqldump and restoring it in another schema, and then dropping the old schema (if needed).
From Shell
mysqldump emp > emp.out
mysql -e "CREATE DATABASE employees;"
mysql employees < emp.out
mysql -e "DROP DATABASE emp;"
Although the above method is easy, it is time and space consuming. What if the schema is more than a 100GB? There are methods where you can pipe the above commands together to save on space, however it will not save time.
To remedy such situations, there is another quick method to rename schemas, however, some care must be taken while doing it.
Method 2: MySQL has a very good feature for renaming tables that even works across different schemas. This rename operation is atomic and no one else can access the table while its being renamed. This takes a short time to complete since changing a table’s name or its schema is only a metadata change. Here is procedural approach at doing the rename:
Create the new database schema with the desired name.
Rename the tables from old schema to new schema, using MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” command.
Drop the old database schema.
If there are views, triggers, functions, stored procedures in the schema, those will need to be recreated too. MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” fails if there are triggers exists on the tables. To remedy this we can do the following things :
1) Dump the triggers, events and stored routines in a separate file. This done using -E, -R flags (in addition to -t -d which dumps the triggers) to the mysqldump command. Once triggers are dumped, we will need to drop them from the schema, for RENAME TABLE command to work.
$ mysqldump <old_schema_name> -d -t -R -E > stored_routines_triggers_events.out
2) Generate a list of only “BASE” tables. These can be found using a query on information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE';
3) Dump the views in an out file. Views can be found using a query on the same information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW';
$ mysqldump <database> <view1> <view2> … > views.out
4) Drop the triggers on the current tables in the old_schema.
mysql> DROP TRIGGER <trigger_name>;
...
5) Restore the above dump files once all the “Base” tables found in step #2 are renamed.
mysql> RENAME TABLE <old_schema>.table_name TO <new_schema>.table_name;
...
$ mysql <new_schema> < views.out
$ mysql <new_schema> < stored_routines_triggers_events.out
Intricacies with above methods : We may need to update the GRANTS for users such that they match the correct schema_name. These could fixed with a simple UPDATE on mysql.columns_priv, mysql.procs_priv, mysql.tables_priv, mysql.db tables updating the old_schema name to new_schema and calling “Flush privileges;”. Although “method 2″ seems a bit more complicated than the “method 1″, this is totally scriptable. A simple bash script to carry out the above steps in proper sequence, can help you save space and time while renaming database schemas next time.
The Percona Remote DBA team have written a script called “rename_db” that works in the following way :
[root@dba~]# /tmp/rename_db
rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>
To demonstrate the use of this script, used a sample schema “emp”, created test triggers, stored routines on that schema. Will try to rename the database schema using the script, which takes some seconds to complete as opposed to time consuming dump/restore method.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
[root@dba ~]# time /tmp/rename_db localhost emp emp_test
create database emp_test DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1
drop trigger salary_trigger
rename table emp.__emp_new to emp_test.__emp_new
rename table emp._emp_new to emp_test._emp_new
rename table emp.departments to emp_test.departments
rename table emp.dept to emp_test.dept
rename table emp.dept_emp to emp_test.dept_emp
rename table emp.dept_manager to emp_test.dept_manager
rename table emp.emp to emp_test.emp
rename table emp.employees to emp_test.employees
rename table emp.salaries_temp to emp_test.salaries_temp
rename table emp.titles to emp_test.titles
loading views
loading triggers, routines and events
Dropping database emp
real 0m0.643s
user 0m0.053s
sys 0m0.131s
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp_test |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
As you can see in the above output the database schema “emp” was renamed to “emp_test” in less than a second. Lastly, This is the script from Percona that is used above for “method 2″.
#!/bin/bash
# Copyright 2013 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates
set -e
if [ -z "$3" ]; then
echo "rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>"
exit 1
fi
db_exists=`mysql -h $1 -e "show databases like '$3'" -sss`
if [ -n "$db_exists" ]; then
echo "ERROR: New database already exists $3"
exit 1
fi
TIMESTAMP=`date +%s`
character_set=`mysql -h $1 -e "show create database $2G" -sss | grep ^Create | awk -F'CHARACTER SET ' '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}'`
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
STATUS=$?
if [ "$STATUS" != 0 ] || [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Error retrieving tables from $2"
exit 1
fi
echo "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
mysql -h $1 -e "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
TRIGGERS=`mysql -h $1 $2 -e "show triggersG" | grep Trigger: | awk '{print $2}'`
VIEWS=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW'" -sss`
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
mysqldump -h $1 $2 $VIEWS > /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
mysqldump -h $1 $2 -d -t -R -E > /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
for TRIGGER in $TRIGGERS; do
echo "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
done
for TABLE in $TABLES; do
echo "rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
done
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
echo "loading views"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
echo "loading triggers, routines and events"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
if [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Dropping database $2"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop database $2"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.columns_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
COLUMNS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.columns_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.procs_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
PROCS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.procs_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.tables_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
TABLES_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.tables_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.db where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
DB_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.db set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then
echo "IF YOU WANT TO RENAME the GRANTS YOU NEED TO RUN ALL OUTPUT BELOW:"
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$COLUMNS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$PROCS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ]; then echo "$TABLES_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then echo "$DB_PRIV"; fi
echo " flush privileges;"
fi
Well there are 2 methods:
Method 1: A well-known method for renaming database schema is by dumping the schema using Mysqldump and restoring it in another schema, and then dropping the old schema (if needed).
From Shell
mysqldump emp > emp.out
mysql -e "CREATE DATABASE employees;"
mysql employees < emp.out
mysql -e "DROP DATABASE emp;"
Although the above method is easy, it is time and space consuming. What if the schema is more than a 100GB? There are methods where you can pipe the above commands together to save on space, however it will not save time.
To remedy such situations, there is another quick method to rename schemas, however, some care must be taken while doing it.
Method 2: MySQL has a very good feature for renaming tables that even works across different schemas. This rename operation is atomic and no one else can access the table while its being renamed. This takes a short time to complete since changing a table’s name or its schema is only a metadata change. Here is procedural approach at doing the rename:
Create the new database schema with the desired name.
Rename the tables from old schema to new schema, using MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” command.
Drop the old database schema.
If there are views, triggers, functions, stored procedures in the schema, those will need to be recreated too. MySQL’s “RENAME TABLE” fails if there are triggers exists on the tables. To remedy this we can do the following things :
1) Dump the triggers, events and stored routines in a separate file. This done using -E, -R flags (in addition to -t -d which dumps the triggers) to the mysqldump command. Once triggers are dumped, we will need to drop them from the schema, for RENAME TABLE command to work.
$ mysqldump <old_schema_name> -d -t -R -E > stored_routines_triggers_events.out
2) Generate a list of only “BASE” tables. These can be found using a query on information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE';
3) Dump the views in an out file. Views can be found using a query on the same information_schema.TABLES table.
mysql> select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where
table_schema='<old_schema_name>' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW';
$ mysqldump <database> <view1> <view2> … > views.out
4) Drop the triggers on the current tables in the old_schema.
mysql> DROP TRIGGER <trigger_name>;
...
5) Restore the above dump files once all the “Base” tables found in step #2 are renamed.
mysql> RENAME TABLE <old_schema>.table_name TO <new_schema>.table_name;
...
$ mysql <new_schema> < views.out
$ mysql <new_schema> < stored_routines_triggers_events.out
Intricacies with above methods : We may need to update the GRANTS for users such that they match the correct schema_name. These could fixed with a simple UPDATE on mysql.columns_priv, mysql.procs_priv, mysql.tables_priv, mysql.db tables updating the old_schema name to new_schema and calling “Flush privileges;”. Although “method 2″ seems a bit more complicated than the “method 1″, this is totally scriptable. A simple bash script to carry out the above steps in proper sequence, can help you save space and time while renaming database schemas next time.
The Percona Remote DBA team have written a script called “rename_db” that works in the following way :
[root@dba~]# /tmp/rename_db
rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>
To demonstrate the use of this script, used a sample schema “emp”, created test triggers, stored routines on that schema. Will try to rename the database schema using the script, which takes some seconds to complete as opposed to time consuming dump/restore method.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
[root@dba ~]# time /tmp/rename_db localhost emp emp_test
create database emp_test DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1
drop trigger salary_trigger
rename table emp.__emp_new to emp_test.__emp_new
rename table emp._emp_new to emp_test._emp_new
rename table emp.departments to emp_test.departments
rename table emp.dept to emp_test.dept
rename table emp.dept_emp to emp_test.dept_emp
rename table emp.dept_manager to emp_test.dept_manager
rename table emp.emp to emp_test.emp
rename table emp.employees to emp_test.employees
rename table emp.salaries_temp to emp_test.salaries_temp
rename table emp.titles to emp_test.titles
loading views
loading triggers, routines and events
Dropping database emp
real 0m0.643s
user 0m0.053s
sys 0m0.131s
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| emp_test |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
As you can see in the above output the database schema “emp” was renamed to “emp_test” in less than a second. Lastly, This is the script from Percona that is used above for “method 2″.
#!/bin/bash
# Copyright 2013 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates
set -e
if [ -z "$3" ]; then
echo "rename_db <server> <database> <new_database>"
exit 1
fi
db_exists=`mysql -h $1 -e "show databases like '$3'" -sss`
if [ -n "$db_exists" ]; then
echo "ERROR: New database already exists $3"
exit 1
fi
TIMESTAMP=`date +%s`
character_set=`mysql -h $1 -e "show create database $2G" -sss | grep ^Create | awk -F'CHARACTER SET ' '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}'`
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
STATUS=$?
if [ "$STATUS" != 0 ] || [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Error retrieving tables from $2"
exit 1
fi
echo "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
mysql -h $1 -e "create database $3 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET $character_set"
TRIGGERS=`mysql -h $1 $2 -e "show triggersG" | grep Trigger: | awk '{print $2}'`
VIEWS=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='VIEW'" -sss`
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
mysqldump -h $1 $2 $VIEWS > /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
mysqldump -h $1 $2 -d -t -R -E > /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
for TRIGGER in $TRIGGERS; do
echo "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop trigger $TRIGGER"
done
for TABLE in $TABLES; do
echo "rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; rename table $2.$TABLE to $3.$TABLE"
done
if [ -n "$VIEWS" ]; then
echo "loading views"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_views${TIMESTAMP}.dump
fi
echo "loading triggers, routines and events"
mysql -h $1 $3 < /tmp/${2}_triggers${TIMESTAMP}.dump
TABLES=`mysql -h $1 -e "select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.tables where table_schema='$2' and TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE'" -sss`
if [ -z "$TABLES" ]; then
echo "Dropping database $2"
mysql -h $1 $2 -e "drop database $2"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.columns_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
COLUMNS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.columns_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.procs_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
PROCS_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.procs_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.tables_priv where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
TABLES_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.tables_priv set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ `mysql -h $1 -e "select count(*) from mysql.db where db='$2'" -sss` -gt 0 ]; then
DB_PRIV=" UPDATE mysql.db set db='$3' WHERE db='$2';"
fi
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ] || [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then
echo "IF YOU WANT TO RENAME the GRANTS YOU NEED TO RUN ALL OUTPUT BELOW:"
if [ -n "$COLUMNS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$COLUMNS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$PROCS_PRIV" ]; then echo "$PROCS_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$TABLES_PRIV" ]; then echo "$TABLES_PRIV"; fi
if [ -n "$DB_PRIV" ]; then echo "$DB_PRIV"; fi
echo " flush privileges;"
fi
Introduction
As an administrator, you may need to change the name of a database. However, for security, the command to rename a database directly was removed in MySQL 5.1.23.
This guide provides three options to rename a MySQL database.
Prerequisites
- The cPanel server management software (optional)
- An SSH login to the server, if working remotely
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
- Access to the command line/terminal window
- A user account and password for the MySQL database
Rename a MySQL Database Using cPanel
Servers configured with cPanel offer the easiest way to rename a MySQL database.
1. Log in to cPanel.
2. In the Databases section, click MySQL Databases.
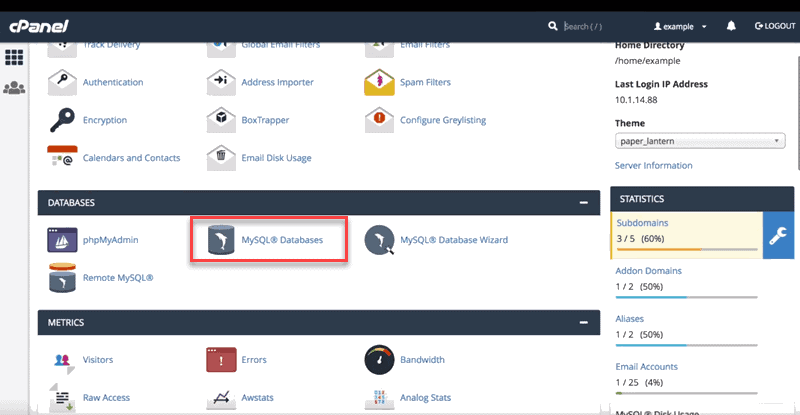
3. A new page will open. Scroll down to the database you want to rename and select the Rename link under the Actions column.
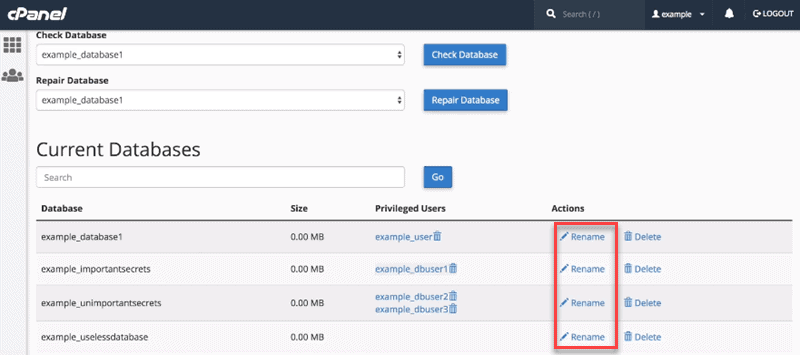
4. Type the new database name, then click Proceed.
Rename MySQL Database from Command Line
If you’re working on a server that doesn’t support cPanel, you’ll need to create a new database and import the data.
1. Log into the server, and open a command line / terminal window. (If you’re working remotely, connect to the server via SSH.)
2. Create a dump file for the database:
mysqldump -u [UserName] -p[Password] -R [DB_Name] > [DB_Name].sqlReplace [UserName] and [Password] with the actual credentials for the database, and replace [DB_Name] with the exact name of the database you’re changing. There should be no space between -p and the password. The -R flag indicates that the dump file should retain all stored procedures and functions.
You may want to copy this file to a different location as a backup.
3. Create a new blank database by using the mysqladmin command:
mysqladmin -u [UserName] -p[Pasword] create [New_DB_Name]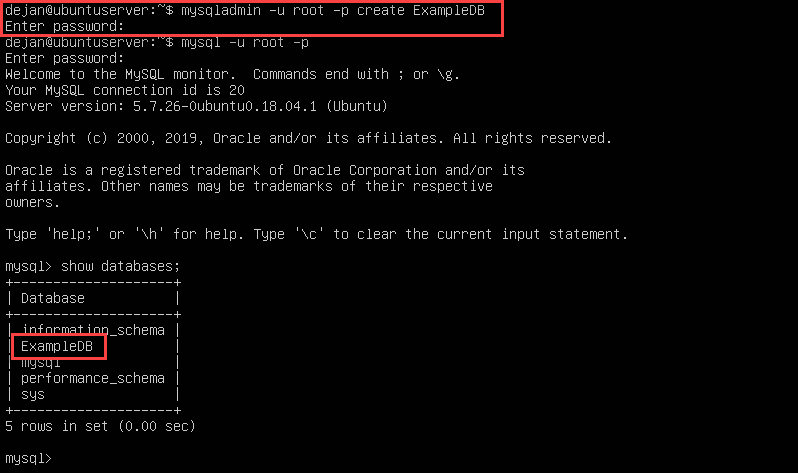
Note: Make sure the database name isn’t already in use.
4. Import the dump file into the new database you created:
mysql -u [UserName] -p[Password] [New_DB_Name] < [DB_Name].sql5. Delete the old MySQL database name (optional):
mysqladmin -u [Username] -p[Password] drop [DB_Name]It won’t hurt if you skip this step. However, it can help you keep a clean database environment.
Renaming Tables with InnoDB
The InnoDB storage engine is a feature included in all versions of MySQL since MySQL 5.5. It can be used to create a new database, then rename each table from the old database to the new database.
1. Start by creating a new database:
mysql -u [UserName] -p[Password] create [New_DB_Name]Replace [UserName] with the database username, and [Password] with the password for that account. Replace [New_DB_Name] with any name you’d like.
2. Use a script to rename all the tables in the database:
mysql -u [UserName] -p[Password] [DB_Name] -sNe
'show tables' | while read table; do mysql -u [UserName] -p
[PassWord] -sNe "RENAME TABLE [DB_Name].$table TO
[New_DB_Name].$table"; doneThe script above cycles through each table in the database and renames it. Provide your password in the script to avoid having to enter it for each cycle.
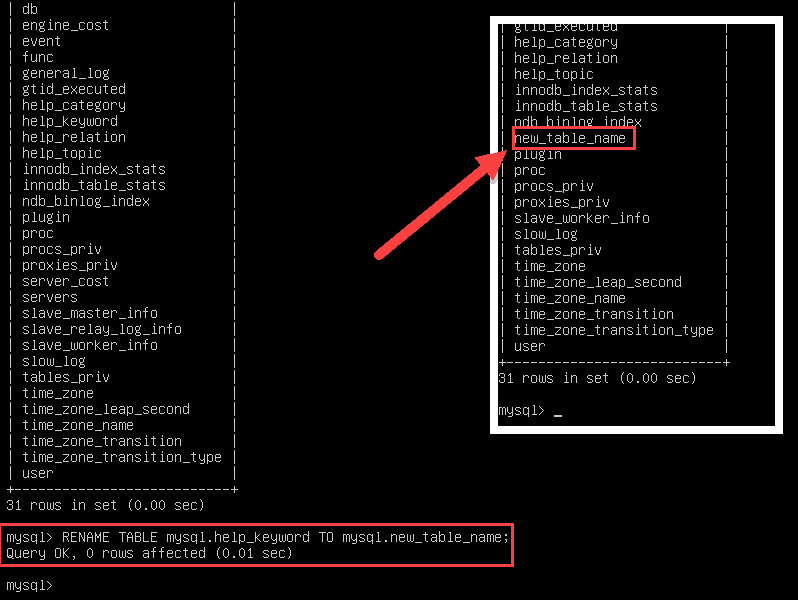
3. If you have a very small database, you can move the tables manually. This can be less intimidating than running a script, but time-consuming. Start by logging into the MySQL shell:
mysql -u [UserName] -p[Password]Use the RENAME TABLE command to rename a table:
RENAME TABLE [DB_Name].[Table1] TO New_DB_Name.Table1;Instead [Table1], type the name of a table in the existing [DB_Name] database. If you have more than one table in this database, you’ll need to repeat this action for each table.
Conclusion
By following this guide, you should now know how to rename a MySQL database.
When working with an older version of MySQL (5.1.7 and older), you may have the ability to use the RENAME DATABASE command. It is strongly recommended that you update your database for security and stability, and use the renaming methods in this guide.
Introduction to MySQL rename database
Sometimes, the database administrator may feel a necessity to change the name of the database that is present on a database server such as, when the project is to be deployed to the client-side or new project needs to share the same database and now, you feel that the existing name of the database is not that relevant or meaningful as per the new context. The older versions of MySQL that is versions before MySQL 5.1.23 had provided the simple method to rename the database using the RENAME DATABASE command. But this proved to be dangerous concerning the security and hence it was removed in all the new versions of MySQL starting from 5.1.23. In this article, we will learn about some of the techniques that can be used to change the name of the database safely and effectively.
How to Rename the database?
Many methods can be followed to rename the database. Out of them, which method is to be used depends on the context like how big is your database, what type of tables are present in your database, and so on. If your MYSQL version is older than MySQL 5.1.23, you can make the use of following commands:
RENAME DATABASE existing_DB_name TO name_Of_new_DB
or
ALTER DATABASE existing_DB_name MODIFY NAME = name_Of_new_DB
Methods of Renaming the database
However, this method is not supported in the latest versions of MySQL for security reasons. Below is the list of some of the methods that can be followed to rename the database in the latest versions of MySQL:
Create a new database with the name that you wish the older database to be changed. Rename all the tables of the old database to new database names and then drop the old database.
Dump the existing database to generate backup and restore the backup with a new name of the database.
Write the script in case you are using the Linux platform that will contain the code to get all the tables from the database and renaming all the tables to the database to the new database name. tablename format.
If all the tables present in your existing database are of type MyISAM then you can use one trick. Just close your MySQL server and then rename the directory of your database i.e the folder of the database then that will automatically lead to a changed database name with the changed directory name.
Let us see each of the methods in detail one by one:
1. Renaming the tables
Step 1: The first step that we need to perform is to create a new database with the name with which we wanted to rename the existing database. For that, you can simply execute the following statement.
Code:
CREATE database new_Name_Of_DB;
Explanation: where new_Name_Of_DB is the name of the new database.
Step 2: The next step is to rename the names of tables of the existing database. As we know that the table is completely referred to by using the name of the database in which it resides then dot operator and then the actual table name. So here we will rename it to the new database name then dot and then the table name that will lead the table to be placed and belong to the new database. This can be done in the following manner.
Code:
RENAME TABLE old_Name_Of_DB.presentTable1 TO new_Name_Of_DB.presentTable1, old_Name_Of_DB.presentTable2 TO new_Name_Of_DB.presentTable2;
Step 3: The last thing to do is to drop the old database that existed and you wanted to rename. But before that, you can make sure that all your tables are present in the new database and the old database is empty to avoid data loss. Then you can execute the DROP DATABASE statement in the following manner:
Code:
DROP database old_Name_Of_DB;
Explanation: where old_Name_Of_DB is the name of your old database that existed and you wanted to rename.
2. Dump and restore the database
One of the methods that can be followed to rename the database for small databases easily and effectively is to dump the database to create a backup file. Then to restore the backup file with the new name of the database that you wished to have. But note that this method works well only with small databases as it creates a problem if the data is sufficiently big and large while backup and restoration.
Step 1: The first step is to create a new database for which you can make the use of the following query:
Code:
mysql -u uname -p "pass" -e "CREATE DATABASE new_Name_Of_DB"
Explanation: where new_Name_Of_DB is the name which you wanted to assign to the existing name and uname is the username of MySQL and pass is the password of your user login if set.
Step 2: The next step is to export the backup file that dumps the existing database with the name old_Name_Of_DB.
Code:
mysqldump -u uname -p "pass" old_Name_Of_DB > exportedDatabaseFile.sql
Step 3: Now. You will have to import the database backup that restores the data from the exported file, in my case exportedDatabaseFile.sql to the new database named new_Name_Of_DB in my case using the following query statement:
Code:
mysql -u uname -p "pass" new_Name_Of_DB < exportedDatabaseFile.sql
Step 4: Finally, you can drop the old database using the following query statement.
Code:
mysql -u uname -p "pass" -e "DROP DATABASE old_Name_Of_DB"
3. script to be executed on command-line
You can even execute the following one-line script instead of converting each table’s name as in the first method. The script statement is somewhat like the following where you can replace the old_Name_Of_DB and new_Name_Of_DB with your existing and new database names.
Code:
$ mysql -u uname -p "pass" old_Name_Of_DB -sNe 'show tables' | while read table; do mysql -u uname -p "pass" -sNe "RENAME TABLE old_Name_Of_DB.$table TO new_Name_Of_DB.$table";
Conclusion
We cannot make use of the RENAME DATABASE command in the newer versions of MySQL for renaming the database. However, there are different alternatives available that can be followed to rename the database. Some of them are renaming the names of tables to new database names, while another method suggests dumping the database to create the backup file and then restoring it with another name that is the new name of the database. One of the techniques that can be used if all of the tables inside your database are of MyISAM type is to shut down the MySQL server, rename the database folder name to a new name with which you wish to rename the database, and the restart MySQL server.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the MySQL rename database. Here we an introduction to MySQL rename database, how to do it, methods with an explanation. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Table in MySQL
- MySQL Queries
- Data Definition Language
- SQL Keywords

