I have a table in Oracle which has following schema:
City_ID Name State Country BuildTime Time
When I declared the table my primary key was both City_ID and the BuildTime, but now I want to change the primary key to three columns:
City_ID BuildTime Time
How can I change the primary key?
Nathan
7,8127 gold badges47 silver badges72 bronze badges
asked Feb 22, 2010 at 11:34
Mohit BAnsalMohit BAnsal
1,5615 gold badges16 silver badges13 bronze badges
1
Assuming that your table name is city and your existing Primary Key is pk_city, you should be able to do the following:
ALTER TABLE city
DROP CONSTRAINT pk_city;
ALTER TABLE city
ADD CONSTRAINT pk_city PRIMARY KEY (city_id, buildtime, time);
Make sure that there are no records where time is NULL, otherwise you won’t be able to re-create the constraint.
answered Feb 22, 2010 at 11:50
Peter LangPeter Lang
53.7k27 gold badges149 silver badges161 bronze badges
1
You will need to drop and re-create the primary key like this:
alter table my_table drop constraint my_pk;
alter table my_table add constraint my_pk primary key (city_id, buildtime, time);
However, if there are other tables with foreign keys that reference this primary key, then you will need to drop those first, do the above, and then re-create the foreign keys with the new column list.
An alternative syntax to drop the existing primary key (e.g. if you don’t know the constraint name):
alter table my_table drop primary key;
answered Feb 22, 2010 at 11:51
Tony AndrewsTony Andrews
129k21 gold badges221 silver badges258 bronze badges
3
Sometimes when we do these steps:
alter table my_table drop constraint my_pk;
alter table my_table add constraint my_pk primary key (city_id, buildtime, time);
The last statement fails with
ORA-00955 «name is already used by an existing object»
Oracle usually creates an unique index with the same name my_pk. In such a case you can drop the unique index or rename it based on whether the constraint is still relevant.
You can combine the dropping of primary key constraint and unique index into a single sql statement:
alter table my_table drop constraint my_pk drop index;
check this:
ORA-00955 «name is already used by an existing object»
answered Mar 25, 2020 at 14:26
Primary Key refers to the column of a table that uniquely identifies a row in a table. It contains unique values and can not contain NULL values. For the purpose of the demonstration, we will be creating geeks for geeks table in a database called “geeks“.
Step 1: Creating the database
The database is created in SQL Server using the following command
Query:
CREATE DATABASE geeks;
Step 2: Using the Database
Use the below SQL statement to switch the database context to geeks:
Query:
USE geeks;
In SQL Server, the Primary key constraint is defined by the syntax:
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE tablename ( column_name datatype NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY);
We can also define the primary key after making the table, but make sure the column has the NOT NULL constraint on it. The syntax for declaring primary key after defining the table:
Syntax:
Alter table table_name add primary key (column_name);
To change the Primary key column in the SQL Server, follow these steps:
- Drop already defined primary key.
- Add a new column as the primary key.
Step 1: Table creation
We have the following geeks for geeks table in the geeks database
Query:
CREATE TABLE geeksforgeeks( ID int PRIMARY KEY, FIRSTNAME varchar(30), LASTNAME varchar(30), CITY varchar(18), EmpID int NOT NULL );
Step 2: Insert data into the table
Query:
INSERT INTO geeksforgeeks VALUES (1,'Romy', 'Kumari', 'Delhi',1900089), (2,'Avinav', 'Pandey', 'Delhi',1909089), (3,'Nikhil', 'Kalra', 'Punjab',1000089), (4,'Mansi', 'Lal', 'Uttarpradesh',1905689), (5,'Rinkle', 'Arora', 'Haryana',1900989), (6,'Sakshi', 'Kumari', 'Delhi',1700089), (7,'Soumya', 'Shriya', 'Bihar',1660089), (8,'Mitu', 'Kumari', 'Rajasthan',1340089);
Step 3: Check the content of table
Query:
SELECT * FROM geeksforgeeks;
Output:
Check which column is set as Primary key, we can use following command:
Query:
SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CONSTRAINT_COLUMN_USAGE ;
Output:
In the above figure, you can see ID column is the primary key. We can drop this primary key by using the CONSTRAINT_NAME mentioned in the image. From here copy CONSTRAINT_NAME to drop the primary key.
Command to drop primary key:
Query:
ALTER TABLE geeksforgeeks DROP CONSTRAINT PK__geeksfor__3214EC275032BA6D;
Add EmpID as new Primary key (always check NOT NULL constraint is specified, otherwise, an error will be thrown)
Query:
ALTER TABLE geeksforgeeks ADD PRIMARY KEY (EmpID);
Now check the primary key of the table using ‘SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CONSTRAINT_COLUMN_USAGE ‘ command
Output:
In the above image, you can see EMPID is the primary key.
- Update Primary Key in MySQL Tables
- Drop the Existing Primary Key and Make a New Primary Key Using a Different Column in MySQL
- Update the Number of Columns Involved in Constructing the Primary Key in MySQL
- Update MySQL Primary Key By Changing Its Data Type

This tutorial teaches how to update the primary key in MySQL tables. We’ll be using the ALTER command to make any change in the primary key.
Update Primary Key in MySQL Tables
There are various scenarios where we can update the primary key in MySQL Tables. Let’s see each of them below.
- Drop the existing primary key and make a new primary key using a different column.
- Update the number of columns involved in constructing the primary key.
- Change the data type of the primary key.
We can use the ALTER command that will be practically demonstrated later in this tutorial to change the primary key.
Drop the Existing Primary Key and Make a New Primary Key Using a Different Column in MySQL
Suppose we have a users table in the test database whose primary key is the ID attribute. For some reason, we want to drop it and construct a new primary key using the USERNAME column.
Create users Table:
#create a table named 'users' in 'test' database
CREATE TABLE `test`.`users` (
`ID` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`USERNAME` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`EMAIL` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`));
Use the following query to check the table definition.
SHOW CREATE TABLE test.users;
It will show the following output; your results may differ if you use a different table.
Output:
To update the primary key from ID to the USERNAME field, we must drop the AUTO_INCREMENT from the ID attribute first; otherwise, it will generate an error.
Drop AUTO_INCREMENT for ID field:
# Disable foreign key check
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
# Modify the `ID` attribute
ALTER TABLE test.users MODIFY COLUMN ID INT NOT NULL;
# Enable foreign key check
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=1;
Use SHOW CREATE TABLE test.users; to confirm that AUTO_INCREMENT is dropped.
Output:
Update Primary Key:
ALTER TABLE test.users DROP PRIMARY KEY, ADD PRIMARY KEY(USERNAME);
Use SHOW CREATE TABLE test.users; again to ensure that the primary key is USERNAME.
Output:
Update the Number of Columns Involved in Constructing the Primary Key in MySQL
We are moving ahead with the users table we created in the previous section. The primary key was the USERNAME column which can be easily checked using the following query.
SHOW CREATE TABLE test.users;
We use the ALTER command to update the primary key that will consist of two columns now, ID and USERNAME.
ALTER TABLE test.users DROP PRIMARY KEY, ADD PRIMARY KEY(ID, USERNAME);
We can confirm the updated primary key by using the following query.
SHOW CREATE TABLE test.users;
Output:
Update MySQL Primary Key By Changing Its Data Type
Here, we create another table and name it user where the primary key is the ID field of the INT type.
CREATE TABLE `test`.`user` (
`ID` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`USERNAME` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`EMAIL` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`));
We can use the following queries to update the data type from INT to BIGINT of an existing primary key.
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
ALTER TABLE test.users MODIFY COLUMN ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=1;
Confirm the changes by using a query which is given below.
SHOW CREATE TABLE test.user;
Output:
Updating the primary key in the MySQL table is not difficult before making relationships in the database but highly discouraged after establishing the relationships in the database for the following basic reasons.
-
If you got the idea to change the primary key in the running database, you probably have chosen the incorrect field for the primary key. So be extra careful about selecting the fields as a primary key.
-
You will be required to drop that record on which you are trying to change the primary key. You may have to lose all the relationships for that particular record.
If you change the primary key, you have to add that record and create relationships again.
-
If you change the primary key from one column to three columns, the new primary key (consisting of three columns) must be used as a foreign key in all other related tables. Remember, this can impact storage, performance, and design.
-
Any change in the primary key is never encouraged within the database except if you re-construct the database during MIGRATION or FILE RE-ORGANIZATION. But, you have to be extra careful because these primary keys might be used as foreign keys in other tables.
Here you will learn how to modify or delete an existing primary key in a table.
Delete Primary Key using T-SQL
Use the ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT command to delete a primary key from a table.
The following T-SQL script deletes a primary key PK_Employee_EmployeeID from the Employee table.
ALTER TABLE Employee
DROP CONSTRAINT PK_Employee_EmployeeID;
Delete a Primary Key using SSMS
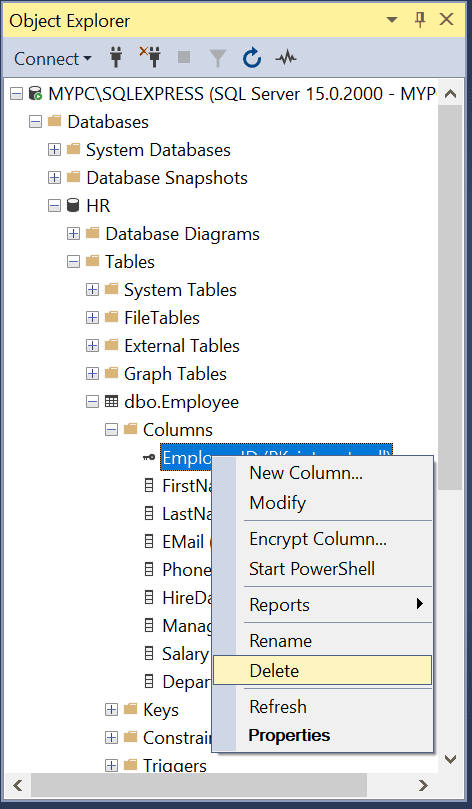
In the Object Explorer, expand the table that contains the primary key to be deleted.
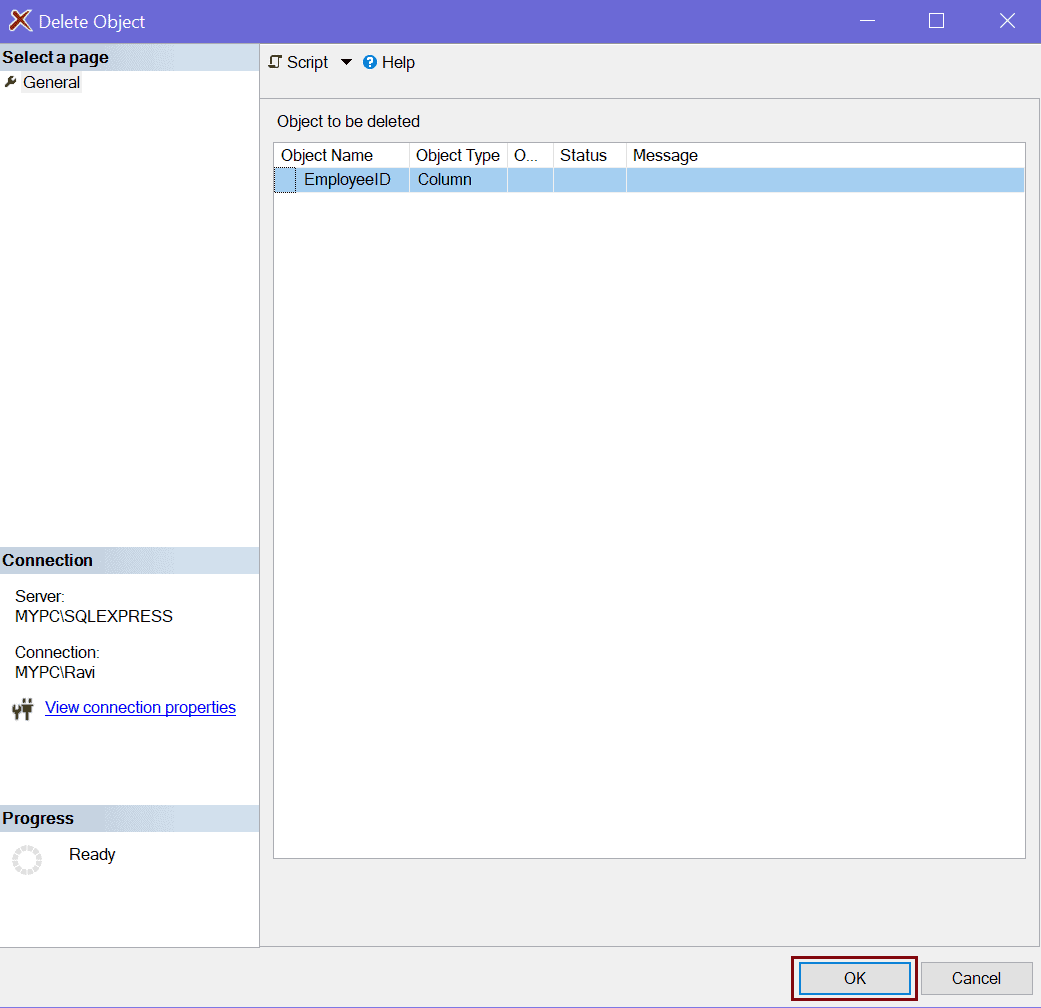
Expand Keys node and Right-click on the key, and select Delete.
In the Delete Object dialog box, verify the correct key is specified and select OK.
Delete Primary Key using Table Designer
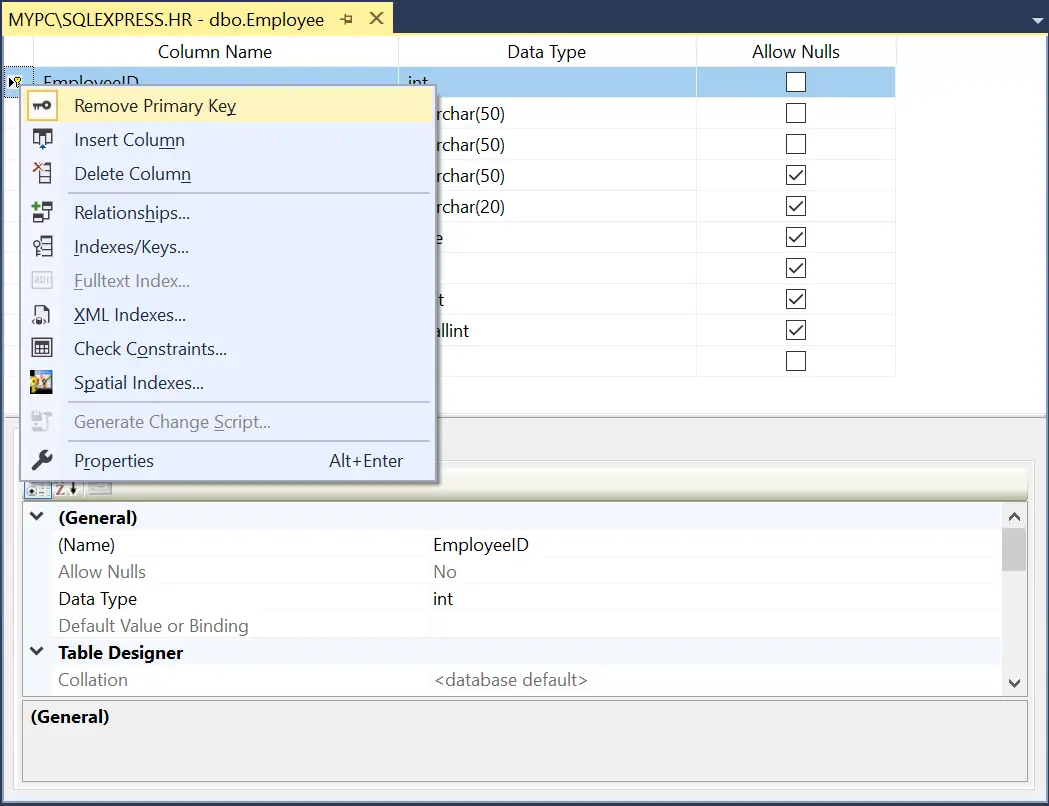
In Object Explorer, right-click the table whose primary key has to be deleted. Select Design.
In the table designer, right-click on the row with the primary key and choose Remove Primary Key.
Save the table to reflect the changes.
Modify Primary Key Using SSMS
You can modify the primary key of a table by changing the key name, columns order, clustered option, or fill factor.
To modify a primary key using T-SQL, you must first delete the existing primary key constraint and then re-create it with the new definition.
To modify or delete a primary key using SSMS
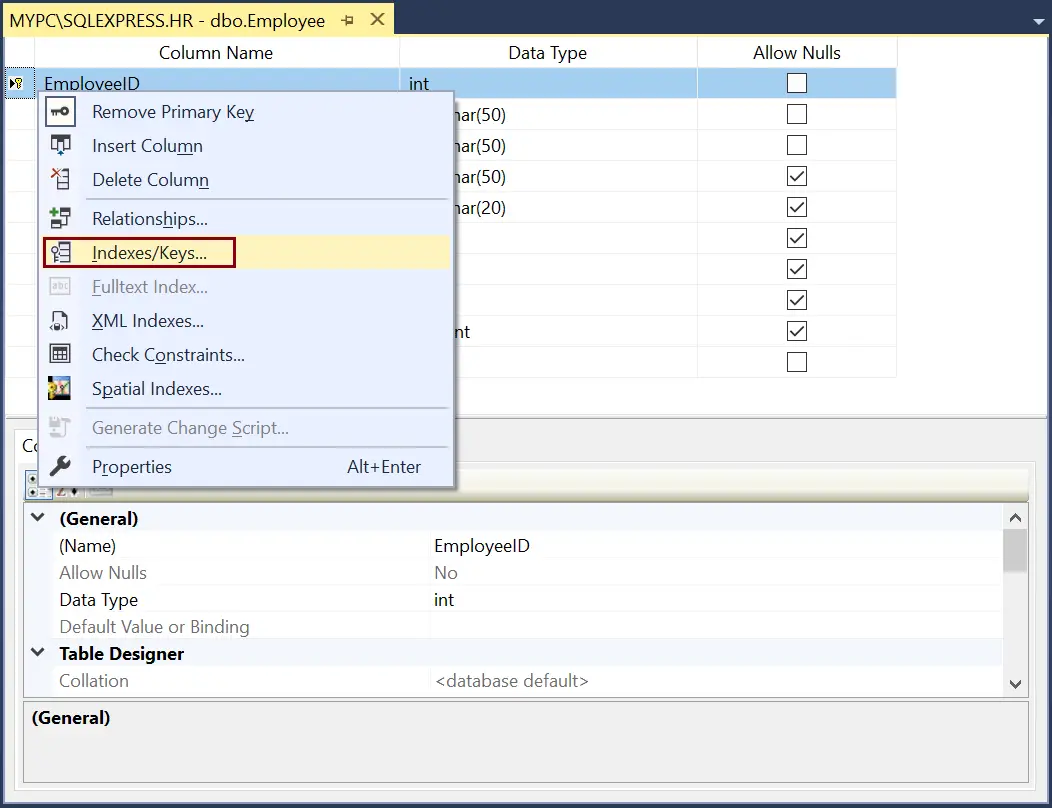
right-click on the table for which you want to modify the primary key and click on Design option to open a table in the design mode.
Now, right-click in the table designer and choose Indexes/Keys from the menu, as shown below.
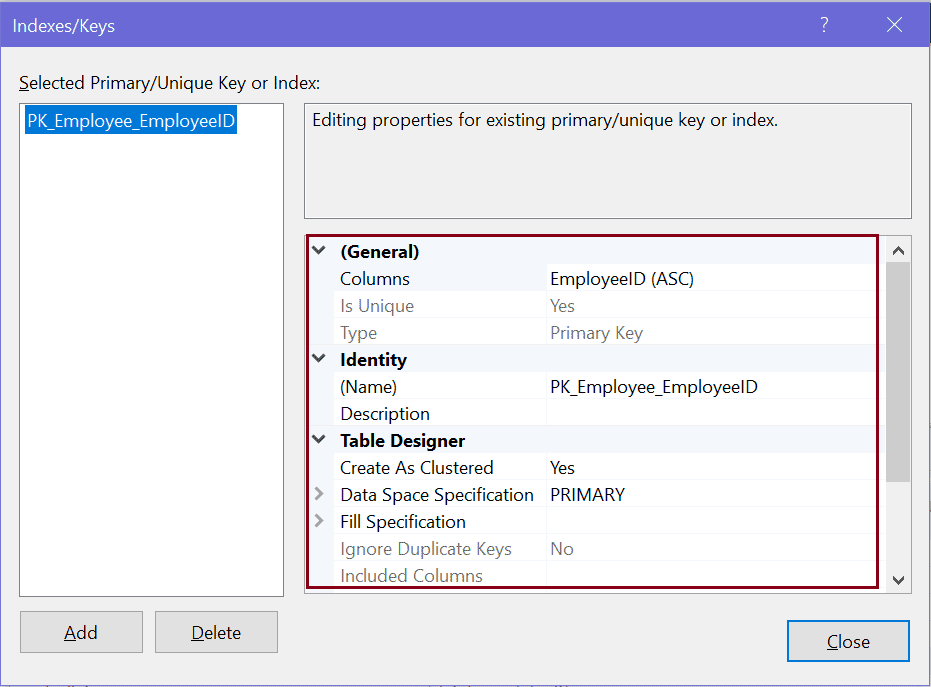
In the Indexes/Keys dialog box, select the primary key index, as shown below.
In the Indexes/Keys dialog box, you can rename a primary key, set the clustered option, set the fill factor, change the primary key column or change the column order in case of the composite primary key.
Click on the Add button to add a new index or primary key.
Click on the Delete button to delete the selected index or primary key.
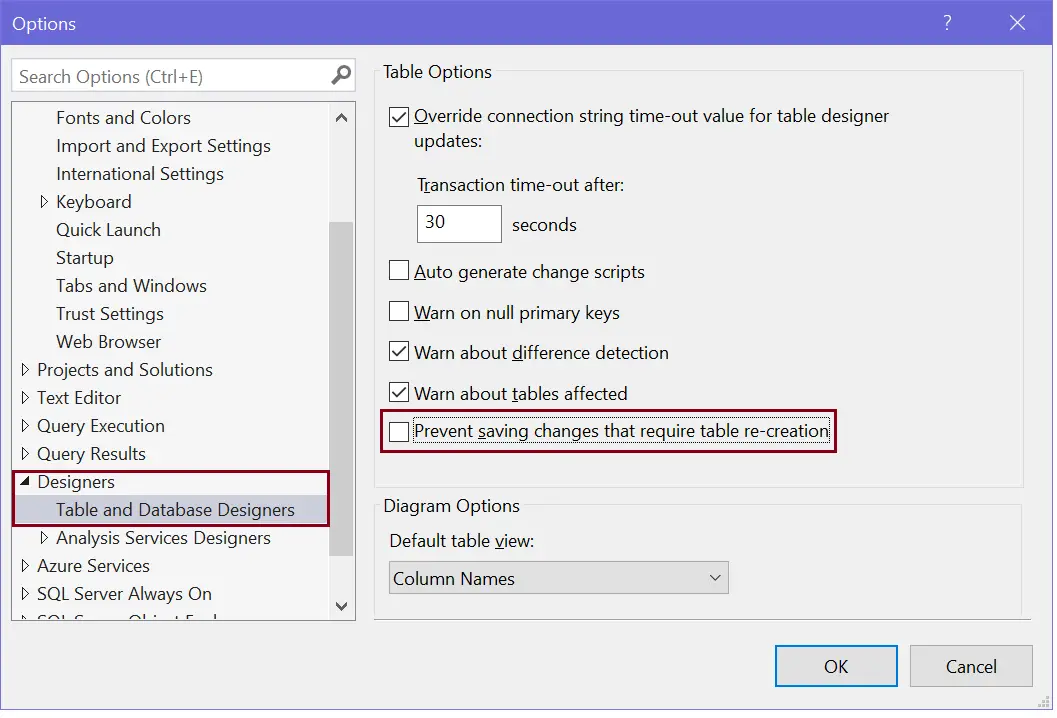
Save the changes by pressing Ctrl + s. If it prevents saving and display a message to re-create a table, then go to Tools menu, click Options, expand Designers, and then click Table and Database Designers.
Clear the Prevent saving changes that require the table to be re-created check box, as shown below.
Want to check how much you know SQL Server?