- Прозрачность картинки
- Прозрачность при наведении
- Прозрачность фона
Прозрачность картинки
Для создания эффекта прозрачности в CSS используется свойство opacity.
Браузер IE8 и более ранние его версии поддерживают альтернативное свойство — filter:alpha(opacity=x), где «x» может принимать значение от 0 до 100, чем меньше значение, тем прозрачнее будет элемент.
Все остальные браузеры поддерживают стандартное CSS свойство opacity, которое может принимать в качестве значения числа от 0.0 до 1.0, чем меньше значение, тем прозрачнее будет элемент:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Название документа</title>
<style>
.myClass {
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
opacity: 0.4;
filter: alpha(opacity=40); /*для IE8 и более ранних версий*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="klematis.jpg" class="myClass">
<img src="klematis.jpg">
</body>
</html>
Попробовать »
Прозрачность при наведении
Псевдо-класс :hover позволяет изменять внешний вид элементов при наведении на них курсора мыши. Мы воспользуемся этой возможностью, чтобы изображение при наведении мыши теряло свою прозрачность:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Название документа</title>
<style>
img {
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
opacity: 0.4;
filter: alpha(opacity=40); /*для IE8 и более ранних версий*/
}
img:hover {
opacity: 1.0;
filter: alpha(opacity=100);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="klematis.jpg">
<img src="klematis2.jpg">
</body>
</html>
Попробовать »
Прозрачность фона
Есть два возможных способа сделать элемент прозрачным: свойство opacity, описанное выше, и указание цвета фона в RGBA формате.
Возможно вы уже знакомы с моделью представления цвета в формате RGB. RGB (Red, Green, Blue — красный, зеленый, синий) — цветовая система, определяющая оттенок путем смешивания красного, зеленого и синего цветов. Например, для задания желтого цвета для текста можно воспользоваться любым из следующих объявлений:
color: rgb(255,255,0); color: rgb(100%,100%,0);
Цвета, заданные с помощью RGB, будут отличаться от шестнадцатеричных значений, используемых нами до этого тем, что позволяют использовать альфа-канал прозрачности. Это значит, что сквозь фон элемента с альфа-прозрачностью будет видно то, что располагается под ним.
Объявление цвета RGBA схоже по синтаксису со стандартными правилами RGB. Однако, кроме всего прочего, нам потребуется объявить значение как RGBA (вместо RGB) и задать дополнительное десятичное значение прозрачности после значения цвета в промежутке от 0.0 (полная прозрачность) до 1 (полная непрозрачность).
color: rgba(255,255,0,0.5); color: rgba(100%,100%,0,0.5);
Разница между свойством opacity и RGBA заключается в том, что свойство opacity применяет прозрачность ко всему элементу целиком, то есть все содержимое элемента становится прозрачным. А RGBA позволяет задать прозрачность отдельным частям элемента (например, только тексту или фону):
body { background-image: url(img.jpg); }
.prim1 {
width: 400px;
margin: 30px 50px;
background-color: #ffffff;
border: 1px solid black;
font-weight: bold;
opacity: 0.5;
filter: alpha(opacity=70); /*для IE8 и более ранних версий*/
text-align: center;
}
.prim2 {
width: 400px;
margin: 30px 50px;
background-color: rgba(255,255,255,0.5);
border: 1px solid black;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
}
Попробовать »
Примечание: значения RGBA не поддерживаются в браузере IE8 и более ранних версиях. Для объявления резервного варианта цвета для старых браузеров, не поддерживающих значения цветов с альфа-каналами, следует указать его первым до значения RGBA:
background: rgb(255,255,0); background: rgba(255,255,0,0.5);
Transparency plays an important role in front end development. It lets you choose how transparent the elements on your web pages appear.
You can adjust transparency in several ways – because of course, in CSS, there are multiple ways to do the same thing.
The CSS opacity property is the first way that might come to your mind to change transparency. But this property can’t come to the rescue all the time, especially when there is a background image with text in it that you want to make transparent.
So in this article, I’m going to show you the various ways you can adjust transparency so you can start implementing it in your coding projects.
Image Transparency with the CSS Opacity Property
To make an image transparent, you can use the CSS opacity property, as I mentioned above. The basic syntax of the opacity property is shown in the code snippet below:
selector {
opacity: value;
}
The opacity property takes values from 0.0 to 1.0, with 1 being the default value for all elements. The lower the value, the more transparent. So if an element is given an opacity of 0, it would be invisible.
You can find examples of different opacity values in the code snippets below:
<img src="freecodecamp.png" alt="freecodecamp-logo" />
I have added some CSS to center everything on the page:
body {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin: 0 auto;
height: 100vh;
}
img {
opacity: 1;
}
An opacity value of 1 is the default, so the image appears like this:
img {
opacity: 0.5;
}
This code gives us 50% opacity, and you can see that the logo has faded a bit:
img {
opacity: 0;
}
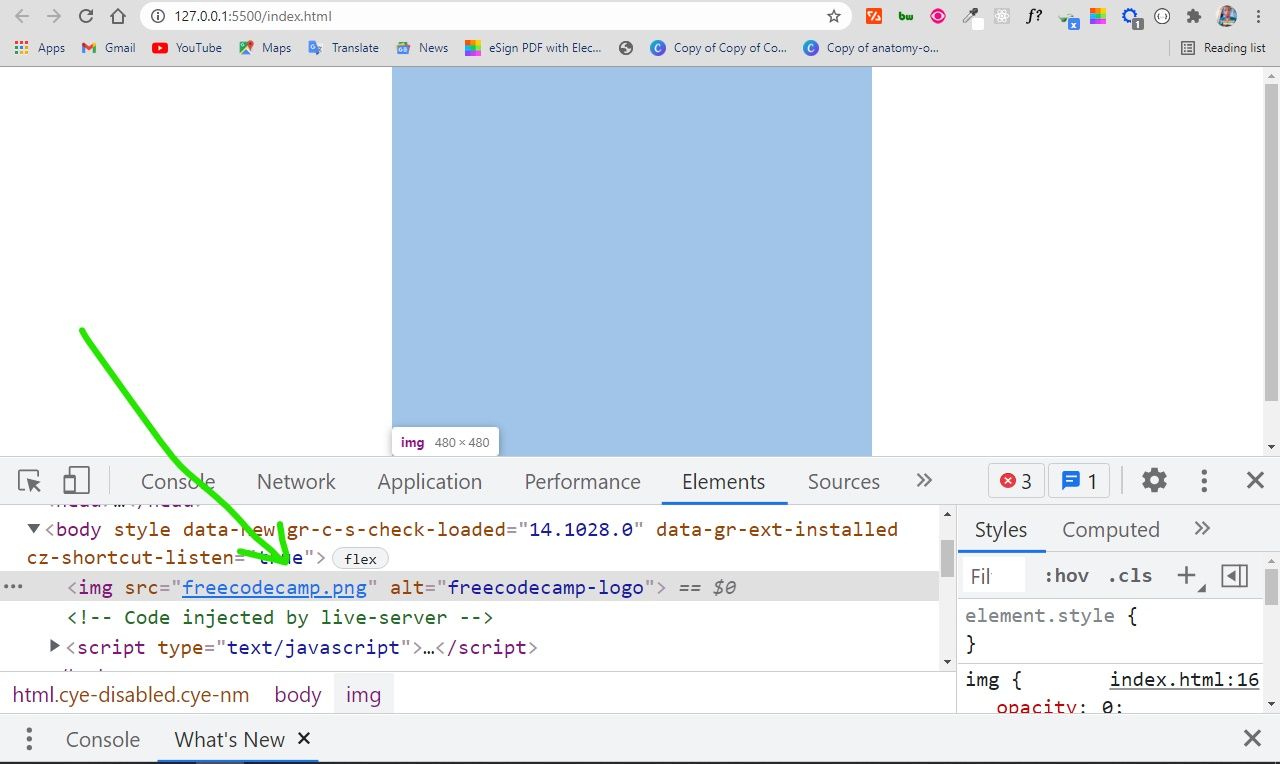
With an opacity of 0, the image is 100% transparent, so it becomes invisible:
The only way to be sure the image is on the page is to inspect it with your browser devtools:
You can use this opacity value to do a lot of things – for example, you can use it to include text over a hero image on a website.
You might be wondering why you would want to make content invisible with an opacity value of 0. Well, it can be useful in animations, and in building HTM + CSS + JavaScript games as well.
You’ll definitely want to use CSS positioning to help you align things. I’ll discuss this in the next parts of the article.
Background Image Transparency in HTML and CSS
CSS offers a way to set the background image for a container element with the background-image property, so you don’t necessarily have to do it with the CSS. This means you can also place text in the container as well.
<div class="showcase">
<h1>A group of ring-tailed lemurs</h1>
</div>
body {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin: 0 auto;
height: 100vh;
}
.showcase {
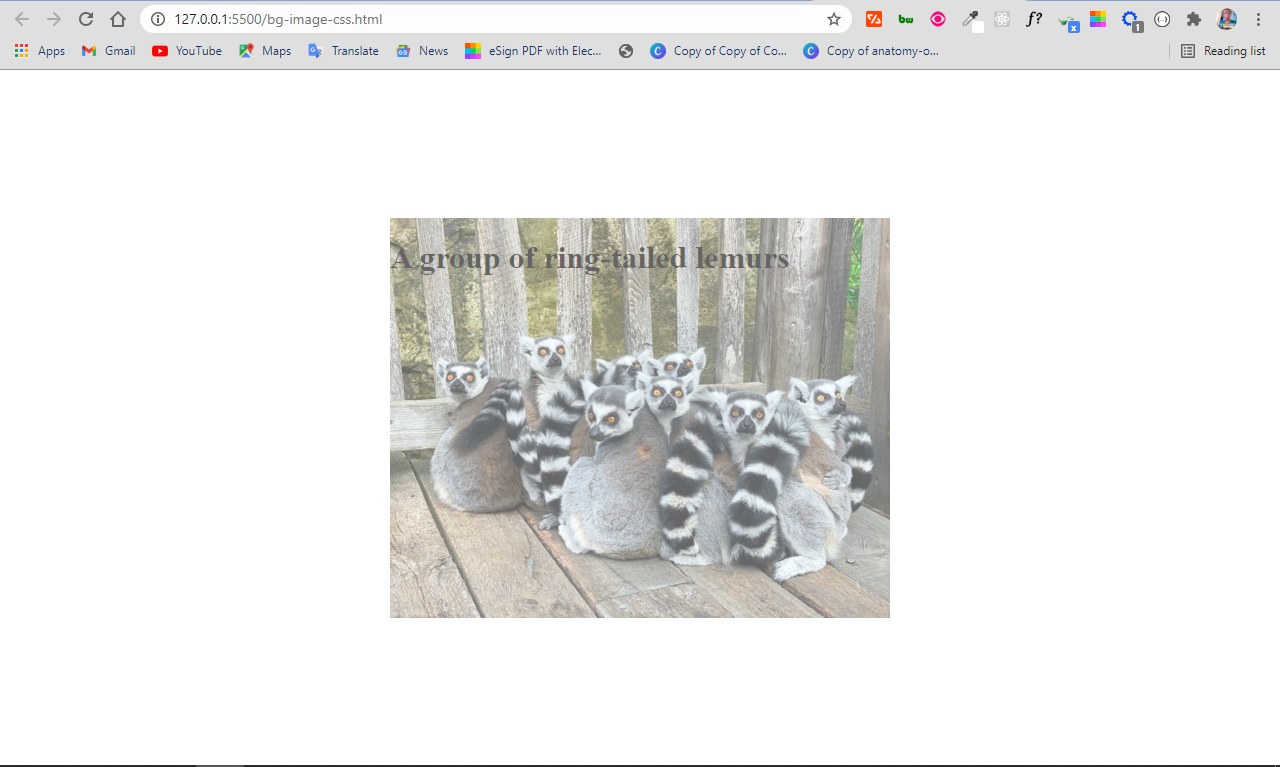
background-image: url("ring-tailed-lemurs.jpeg");
height: 400px;
width: 500px;
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
opacity: 0.6;
}
The downside of this approach is that the opacity is set for the container where the image and text are. So, the opacity affects the text as well, not only the image. This is probably not what you want!
The solution
By default, when you apply an opacity to a container, the descendants inherit it as well.
A workaround in this situation is to set the background image in the HTML. This makes it easy to apply the opacity to the image only, instead of setting the background image for the container in the CSS.
This time around, the image and the text will be separated, so the text will not inherit the value set for the opacity.
This means you also have to use CSS positioning to align the text within the image.
<div class="showcase">
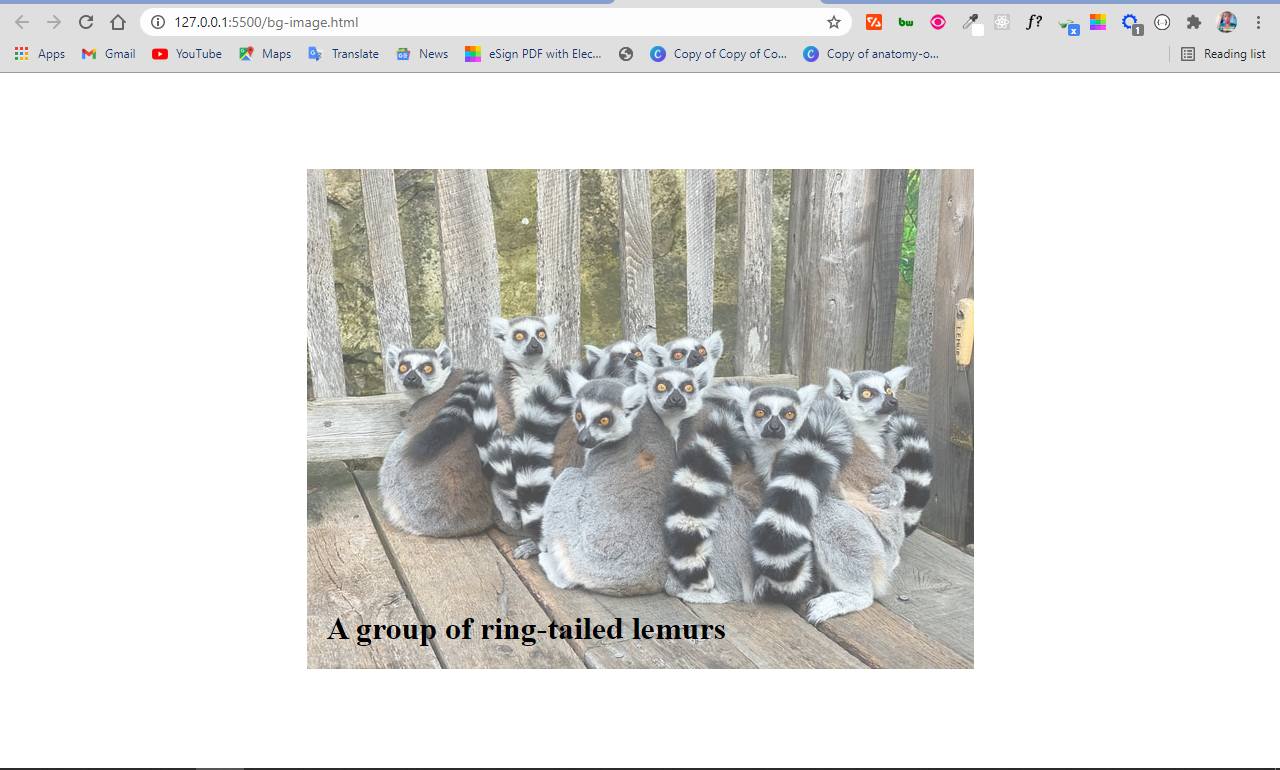
<img src="ring-tailed-lemurs.jpeg" alt="lemurs" class="bg-image" />
<h1 class="bg-img-title">A group of ring-tailed lemurs</h1>
</div>
body {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin: 0 auto;
height: 100vh;
}
.showcase {
position: relative;
}
.bg-image {
opacity: 0.7;
}
.bg-img-title {
position: absolute;
top: 420px;
left: 20px;
}
In the CSS code snippet above, I use flexbox to center everything on the page.
The container div element with the class of showcase is positioned relative, so you can position the h1 text absolute within it. This will push the h1 text to the top-left corner of the image. The top and left properties are then used to push the text to the bottom-left corner of the image.
If you are wondering what the top and left properties are, they are the properties you get access to when you use the display property.
In addition to these two, you also get access to the right and bottom properties. They let you position an element anywhere.
In the end, the image is opaque and the text is not affected:
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to use the opacity property of CSS to make images transparent.
As CSS remains tricky and a bit weird, it’s helpful to combine the opacity property with other CSS features such as positioning in order to put it into proper use.
Apart from CSS positioning, you can also use the opacity property with CSS pseudo-elements such as ::before and ::after, which is sort of a hacky way of doing things.
Thank you for reading, and keep coding.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
For a simple semi-transparent background color, the above solutions (CSS3 or bg images) are the best options. However, if you want to do something fancier (e.g. animation, multiple backgrounds, etc.), or if you don’t want to rely on CSS3, you can try the “pane technique”:
.pane, .pane > .back, .pane > .cont { display: block; }
.pane {
position: relative;
}
.pane > .back {
position: absolute;
width: 100%; height: 100%;
top: auto; bottom: auto; left: auto; right: auto;
}
.pane > .cont {
position: relative;
z-index: 10;
}
<p class="pane">
<span class="back" style="background-color: green; opacity: 0.6;"></span>
<span class="cont" style="color: white;">Hello world</span>
</p>
The technique works by using two “layers” inside of the outer pane element:
- one (the “back”) that fits the size of the pane element without affecting the flow of content,
- and one (the “cont”) that contains the content and helps determine the size of the pane.
The position: relative on pane is important; it tells back layer to fit to the pane’s size. (If you need the <p> tag to be absolute, change the pane from a <p> to a <span> and wrap all that in a absolutely-position <p> tag.)
The main advantage this technique has over similar ones listed above is that the pane doesn’t have to be a specified size; as coded above, it will fit full-width (normal block-element layout) and only as high as the content. The outer pane element can be sized any way you please, as long as it’s rectangular (i.e. inline-block will work; plain-old inline will not).
Also, it gives you a lot of freedom for the background; you’re free to put really anything in the back element and have it not affect the flow of content (if you want multiple full-size sub-layers, just make sure they also have position: absolute, width/height: 100%, and top/bottom/left/right: auto).
One variation to allow background inset adjustment (via top/bottom/left/right) and/or background pinning (via removing one of the left/right or top/bottom pairs) is to use the following CSS instead:
.pane > .back {
position: absolute;
width: auto; height: auto;
top: 0px; bottom: 0px; left: 0px; right: 0px;
}
As written, this works in Firefox, Safari, Chrome, IE8+, and Opera, although IE7 and IE6 require extra CSS and expressions, IIRC, and last time I checked, the second CSS variation does not work in Opera.
Things to watch out for:
- Floating elements inside of the cont layer will not be contained. You’ll need to make sure they are cleared or otherwise contained, or they’ll slip out of the bottom.
- Margins go on the pane element and padding goes on the cont element. Don’t do use the opposite (margins on the cont or padding on the pane) or you’ll discover oddities such as the page always being slightly wider than the browser window.
- As mentioned, the whole thing needs to be block or inline-block. Feel free to use
<div>s instead of<span>s to simplify your CSS.
A fuller demo, showing off the flexibility of this technique by using it in tandem with display: inline-block, and with both auto & specific widths/min-heights:
.pane, .pane > .back, .pane > .cont { display: block; }
.pane {
position: relative;
width: 175px; min-height: 100px;
margin: 8px;
}
.pane > .back {
position: absolute; z-index: 1;
width: auto; height: auto;
top: 8px; bottom: 8px; left: 8px; right: 8px;
}
.pane > .cont {
position: relative; z-index: 10;
}
.debug_red { background: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5); border: 1px solid rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.75); }
.debug_green { background: rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.5); border: 1px solid rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.75); }
.debug_blue { background: rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5); border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.75); }<p class="pane debug_blue" style="float: left;">
<span class="back debug_green"></span>
<span class="cont debug_red">
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.
</span>
</p>
<p class="pane debug_blue" style="float: left;">
<span class="back debug_green"></span>
<span class="cont debug_red">
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.
</span>
</p>
<p class="pane debug_blue" style="float: left; display: inline-block; width: auto;">
<span class="back debug_green"></span>
<span class="cont debug_red">
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.
</span>
</p>
<p class="pane debug_blue" style="float: left; display: inline-block; width: auto; min-height: auto;">
<span class="back debug_green"></span>
<span class="cont debug_red">
Pane content.<br/>
Pane content.
</span>
</p>And here’s a live demo of the technique being used extensively:
Способы создания прозрачных фонов
Вы хотите научиться создавать страницы с оригинальным и ярким современным дизайном? Применение полупрозрачных элементов способно помочь Вам в решении этой непростой задачи. Сегодня мы рассмотрим основные практические способы задания прозрачности структурных элементов.
Как задать прозрачность?
Если рассматривать данную тему сквозь призму исторического развития веб-технологий, то можно выделить следующие подходы:
- Свойство opacity.
- Использование PNG -картинки
- Формат системы RGBA
- Ну, и наконец, древность или клетчатые изображения.
CSS свойство Opacity
Применение стилевого CSS свойства оpacity позволяет задать прозрачность того элемента, к которому применяется. Значения, которые можно использовать в качестве аргумента изменяются в пределах от 0 до 1.
Рассмотрим пример.
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>TODO supply a title</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" media="all" type="text/css" href="css/style2.css" /> </head> <body> <div class=" prozrachen "> Тут будет много Вашего текста </div> </body> </html>
CSS:
body { background: url(./vaden-pro-logo.png); /* Фон для тела страницы */ } . prozrachen { padding: 10px; /*Отступы для текста*/ background: darkturquoise; /* Задаем цвет фона */ margin: 0 auto; /* Центрируем блок */ width: 50%; /* Задаем ширину блока */ opacity: 0.7; /* Задаем прозрачность */ font: 48px/64px Times New Roman; text-align: justify; }
В результате мы получили полупрозрачный блок:
Важно!!!
- Opacity принимает значения из диапазона: 0 (полная прозрачность) — 1 (непрозрачность).
- Кросс-браузерность. В IE до седьмой версии включительно Opacity не поддерживается. Добиться одинакового отображения элемента поможет следующая строчка:
filter: alpha(Opacity=70);
Стоит принимать во внимание то, что свойство filter отсутствует в html спецификациях, изменяет значения от 1 до 100 и может применяться только к элементам:
- с абсолютным позиционированием (position: absolute)
- с фиксированным линейным размером (height или width).
- Степень прозрачности наследуется дочерними элементами, при чем дочернему элементу можно увеличить прозрачность, но сделать меньше — нельзя. Т. е. на полупрозрачном фоне НЕ ПРОЗРАЧНОГО текста не сделать.
Для лучшего понимания материала последнего пункта, в предыдущем примере зададим тексту белый цвет
и рассмотрим его под микроскопом:
Как видим, контент нашего блока (текст) тоже стал полупрозрачным. Но что делать, если на практике прозрачность содержимого вас не интересует, а интересует лишь прозрачность фона? В таком случае, переходим к следующему пункту.
Использование PNG -картинки
Интересной особенностью формата PNG является то, что он имеет 256 уровней прозрачности. Думаю, Вы уловили ход мыслей, и наверняка уже построили алгоритм работы такого подхода. Мне остается только его озвучить.
- Создаем в Photoshop, однотонную полупрозрачную картинку (назовем ее transparent) и сохраняем в формате png.
- Используем ее в качестве бэкграунда:
body { background: url(./vaden-pro-logo.png); } .prozrachen { padding: 10px; background: url(./transparent.png); margin: 0 auto; width: 50%; font: 48px/64px Times New Roman; color: white;</li> text-align: justify; }
В результате мы получили блок с прозрачным фоном и непрозрачным содержимым:
Важно!!!
- В отличии от свойства opacity прозрачность задается только для фона
- Кросс-браузерность. Работает почти во всех браузерах, и это плюс. Но прозрачность PNG не поддерживается в IE6. Если вы оптимизируете свой сайт под такую древность — придется применять другие методы или скрипты.
- При отключении отображения картинок, ваш фон пропадет (учтите этот момент при оптимизации отображения на мобильных устройствах, ведь безлимитный интернет не всегда есть под рукою).
- Для изменения цвета и/или степени прозрачности вам нужно создать новую картинку и перезалить ее на серв.
Формат системы RGBA
Одним из самых современных методов изменения транспарантности фона является применение системы RGBA.
RGBA – система представления цвета при помощи трех стандартных каналов RGB (красный, зеленый, синий), и четвертого, так называемого Alpha-канала, характеризующего степень прозрачности.
background: rgba(r, g, b, a);
В уже известном нам примере, заменим содержимое в CSS файле на следующее:
body { background: url(./vaden-pro-logo.png); /* Фоновый рисунок */ } .prozrachen { padding: 10px; background: rgba(0, 206, 209, 0.7); margin: 0 auto; width: 50%; font: 48px/64px Times New Roman; color: white; text-align: justify; }
Важно!!!
- В отличии от свойства opacity прозрачность задается только фону
- В отличии от метода PNG картинки, для изменения цвета или степени транспарентности нам нужно просто поменять значения rgba.
- Кросс-браузерность. Работает во всех современных браузерах (начиная с IE9, Op10, Fx3,Sf3.2).Для более старых браузеров придется либо пожертвовать прозрачностью, либо применять opacity, png методы.
Клетчатые изображения, или с уважением к истории
Этот метод стоял у истоков веб-дизайна, и видел старые-старые браузеры, которые ничего толком не умели. Он заключается в создании клетчатого фона, в котором цветные квадратики чередовались с прозрачными.
В результате применения такой картинки в качестве background получали псевдо-прозрачный фон.
Важно!!!
- При просмотре текста на таком фоне могут быстро уставать глаза (особенно давит рябь при прокрутке).
- В остальном особенности применения аналогичны с методом «PNG -картинки».
Подытожим?
Напоследок, несколько общих рекомендаций по использованию прозрачности в своих проектах:
- Под прозрачным блоком должна находиться яркая не однообразная картинка. На однотонном фоне изюминка прозрачности теряется.
- При выборе конкретного практического подхода, ориентируйтесь на то, какими браузерами пользуется ваша целевая аудитория. Кросс-браузерность — вещь важная.
Успехов!!!
Уровень сложности:
Средний
Как установить изображение полупрозрачным?
| Internet Explorer | Chrome | Opera | Safari | Firefox | Android | iOS |
| 5.5+ | 3.0+ | 9.2+ | 3.1+ | 3.0+ | 2.0+ | 1.0+ |
Задача
Изменить значение прозрачности изображения.
Решение
За управление прозрачностью элемента на странице отвечает стилевое свойство opacity, которое относится к CSS3. В качестве значения применяются дробные числа от 0 до 1, где ноль соответствует полной прозрачности, а единица, наоборот, непрозрачности объекта.
Старые версии Internet Explorer не поддерживает opacity, поэтому для этого браузера следует использовать специфическое свойство filter со значением alpha(Opacity=X), где под X подразумевается целое число от 0 до 100. Это значение определяет уровень прозрачности: 0 — полная прозрачность; 100 — наоборот, непрозрачность объекта.
Соединяя воедино два свойства, получим универсальный код, который устанавливает заданную прозрачность для изображений (пример 1).
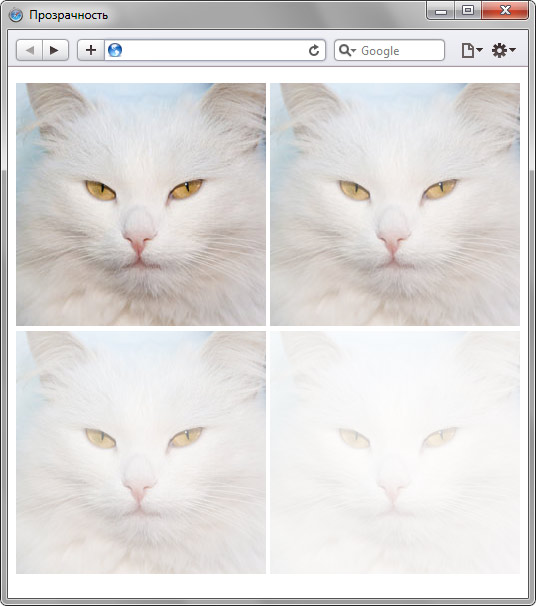
Пример 1. Полупрозрачное изображение
HTML5CSS 2.1CSS3IECrOpSaFx
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Прозрачность</title>
<style>
.transparent75 {
filter: alpha(Opacity=75); /* Полупрозрачность для IE */
opacity: 0.75; /* Полупрозрачность для других браузеров */
}
.transparent50 {
filter: alpha(Opacity=50);
opacity: 0.5;
}
.transparent25 {
filter: alpha(Opacity=25);
opacity: 0.25;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<img src="images/cat.jpg" alt="Оригинальное изображение"
width="250" height="243">
<img src="images/cat.jpg" alt="Непрозрачность 75%"
width="250" height="243" class="transparent75">
<img src="images/cat.jpg" alt="Непрозрачность 50%"
width="250" height="243" class="transparent50">
<img src="images/cat.jpg" alt="Непрозрачность 25%"
width="250" height="243" class="transparent25">
</p>
</body>
</html>Результат примера показан на рис. 1.
Рис. 1. Фотография с различными значениями прозрачности
В данном примере вначале приводится исходная фотография, к которой не применяются настройки прозрачности, последующие фотографии отображаются с уровнем непрозрачности 75%, 50% и 25%.