In this article, we are going to learn how to change the font size of the text in Tkinter. Font size refers to how large the characters displayed on the screen are. It is crucial to use proper font size in order to gain the reader’s attention wherever needed. So let’s see the different ways using which we can change the font size of text using Tkinter.
Method 1: Changing Tkinter font size using the font as a tuple
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
#main window
root = Tk()
#title of the window
root.title("Tkinter Font Size")
#adding a label
l = Label(root, text="This is a sample line with font size 15.", width=40,
height=5, font=('Times New Roman', 15, 'bold'))
l.pack()
root.mainloop()
Output:
In the above code, we have created a very basic GUI and added a label to it. Label widgets have an inbuilt property of font(‘font family’, size, ‘font style’). Font acts as a parameter in the code above. If not mentioned explicitly, the parameters will have their default values. In the above code, we have only used the size property and set the size to 15.
Method 2: Changing tkinter font size using the font as an object
Recommended Read: Tkinter Font Class Tutorial
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
import tkinter.font as tkFont
#main window
root = tk.Tk()
#title of the window
root.title("Tkinter Font Size")
#creating a font object
fontObj = tkFont.Font(size=28)
#adding a label
l = Label(root, text="This is a sample line with font size 28.",
width=40, height=5, font=fontObj)
l.pack()
root.mainloop()
Output:
Here, we have created an object of the Font class named fontObj and set the font size to 28. Later, in the label, we assigned the value of parameters for the font to be equal to the font object (fontObj) and hence, in the output, the font size is 28. In addition to size, we can also mention the font family and style as required.
Method 3: Using changing fonts using a custom class
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkinter.font import Font
#creating a custom class
class cl:
def __init__(self, master) -> None:
self.master = master
#setting the font size to be 40
self.customFont = Font(size=40)
Label(self.master, text="Font size in the custom class is 40.",
font=self.customFont).pack()
#end of custom class
if __name__ == "__main__":
#main window
root = tk.Tk()
#title of the window
root.title("Tkinter Font Size")
#adding a label
l = Label(root, text="This is a sample line with default font size.",
width=40, height=5)
l.pack()
#calling our class object
customSize = cl(root)
root.mainloop()
Output:
In the above example, we have defined a custom class (cl), inside which we have a constructor where we assign the font size to 40. A label is also created with the font parameter being equal to the customFont.
In the main function, we first created a label with no explicit mention of the size of the text. Hence, it has the default size. After this, we call the cl class by creating its object customSize. On creating a new instance or object, the label with font size 40 is also displayed in the output along with the default size label.
Every time a new instance of the class is created, the label with font size 40 will be displayed as it is a part of the constructor of the class here. We can also set the font family and style inside the class itself.
Summary
In this way, we have understood how to change the font size in Tkinter in multiple ways. It is an easy topic to understand and implement. Please check out our other Tkinter tutorials here.
Tkinter Label is used to display one or more lines, it can also be used to display bitmap or images. In this article, we are going to change the font-size of the Label Widget. To create Label use following:
Syntax: label = Label(parent, option, …)
Parameters:
parent: Object of the widget that will display this label, generally a root object
text: To display one or more lines of text.
image: To display a static image
compound: To display both Text and Image. It accepts TOP, BOTTOM, LEFT, RIGHT, CENTER. For example, if you write compound=TOPimage will displayed to the top of Text.
We can do this using different methods:
Method 1: By using Label’s font property.
Python3
from tkinter import Tk
from tkinter.ttk import Label
class App:
def __init__(self, master) -> None:
self.master = master
Label(self.master, text="I have default font-size").pack(pady=20)
Label(self.master,
text="I have a font-size of 25",
font=("Arial", 25)
).pack()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
root.title("Change font-size of Label")
root.geometry("400x250")
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Output:
Method 2: By using Style class. In this method, we will use our custom style otherwise all the Label widgets will get the same style.
Python3
from tkinter import Tk
from tkinter.ttk import Label, Style
class App:
def __init__(self, master) -> None:
self.master = master
Label(self.master, text="I have default font-size").pack(pady=20)
self.style = Style(self.master)
self.style.configure("My.TLabel", font=('Arial', 25))
Label(
self.master,
text="I have a font-size of 25",
style="My.TLabel").pack()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
root.title("Change font-size of Label")
root.geometry("400x250")
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Output:
Note: In the above method, TLabel is the name of the default style. So if you want to create your own style name then always use below syntax
my_style_name.default_style_name
Example:
New.TButton # To override Button Widget’s styles
My.TLabel # To override Label Widget’s Styles
Abc.TEntry # To override Entry Widget’s Styles
If you use only the default style name then it will apply to all the corresponding widgets i.e if I use TLabel instead of My.TLabel then both the label will have font-size of 25. And importantly, if you use the default style name then you don’t need to provide style property.
Extra: Changing font size using the Default Style Name.
Python3
from tkinter import Tk
from tkinter.ttk import Label, Style
class App:
def __init__(self, master) -> None:
self.master = master
Label(self.master, text="I have default font-size").pack(pady=20)
self.style = Style(self.master)
self.style.configure("TLabel", font=('Arial', 25))
Label(self.master, text="I have a font-size of 25").pack()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
root.title("Change font-size of Label")
root.geometry("400x250")
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Notice in the above program that we have not provided style or font property to any of the Label still both of them got the same font-size and same font-family.
Output:
Method 3: By using the Font class. In this method, we will create a Font object and then use this to change Font style of any widget. Benefit of this
Font class consist of following property:
root: Object of toplevel widget.
family: The font family name as a string.
size: The font height as an integer in points.
weight: ‘bold’/BOLD for boldface, ‘normal’/NORMAL for regular weight.
slant: ‘italic’/ITALIC for italic, ‘roman’/ROMAN for unslanted.
underline: 1/True/TRUE for underlined text, 0/False/FALSE for normal.
overstrike: 1/True/TRUE for overstruck text, 0/False/FALSE for normal.
Python3
from tkinter import Tk
from tkinter.font import BOLD, Font
from tkinter.ttk import Label
class App:
def __init__(self, master) -> None:
self.master = master
Label(self.master, text="I have default font-size").pack(pady=20)
self.bold25 = Font(self.master, size=25, weight=BOLD)
Label(self.master, text="I have a font-size of 25",
font=self.bold25).pack()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
root.title("Change font-size of Label")
root.geometry("400x250")
app = App(root)
root.mainloop()
Output:
Tkinter actually has a variety of ways in which we may change the font type and size. Tkinter has several built in fonts, which can complicate things, especially when you realize that Each widget only uses one of these fonts. However, this also gives us the option to individually change the font type and size for different types of widgets.
We’ll start off with a general way of changing the font size and type that effects everything in the tkinter window.
Technique 1
The following code will only change the Font.
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.option_add('*Font', '19')
root.geometry("200x150")
label = tk.Label(root, text = "Hello World")
label.pack(padx = 5, pady = 5)
root.mainloop()

The following code changes only the font type. Tip:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.option_add('*Font', 'Times')
root.geometry("200x150")
label = tk.Label(root, text = "Hello World")
label.pack(padx = 5, pady = 5)
root.mainloop()

Tip: If you want a list of font families, you can use the following code. It will return a list of different font types.
from tkinter import Tk, font root = Tk() print(font.families())
Finally, you can change both simultaneously by writing both at the same time.
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.option_add('*Font', 'Times 19')
root.geometry("200x150")
label = tk.Label(root, text = "Hello World")
label.pack(padx = 5, pady = 5)
root.mainloop()
Note, however, that option_add only affects widgets created after you’ve called option_add, so you need to do it before creating any other widgets.
Technique 2
Here narrow down our area of effect from the whole tkinter program to certain segments of it. As mentioned earlier, tkinter has several built in fonts which different widgets use. We can change each one of these individually.
import tkinter as tk import tkinter.font as tkFont root = tk.Tk() print(tkFont.names())
('fixed', 'oemfixed', 'TkDefaultFont', 'TkMenuFont', 'ansifixed', 'systemfixed', 'TkHeadingFont', 'device', 'TkTooltipFont', 'defaultgui', 'TkTextFont', 'ansi', 'TkCaptionFont', 'system', 'TkSmallCaptionFont', 'TkFixedFont', 'TkIconFont')Above we can notice several font types like TkHeadingFont and TkMenuFont. These appear to be the fonts that determine the font type and size for headings and Menu’s respectively. Let’s try to change the TkDefaultFont. Any widget that uses the TkDefaultFont type will automatically change to the new settings.
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("200x150")
def_font = tk.font.nametofont("TkDefaultFont")
def_font.config(size=24)
label = tk.Label(root, text = "Hello World")
label.pack(padx = 5, pady = 5)
root.mainloop()
The tricky part however is figuring out which widgets are affected by which Font types. Due to a lack of material, this information is currently unavailable. Though you are free to search for it on your own.
This marks the end of the change font type and size in Tkinter article. Any suggestions or contributions for CodersLegacy are more than welcome. Any questions can be asked in the comments section below.
See more Tkinter related tit bits below.
How to improve Tkinter screen resolution?
How to prevent resizing in Tkinter Windows?
Using Lambda with Tkinter “command” option
- HowTo
- Python Tkinter Howtos
- Change the Tkinter Label Font Size
Jinku Hu
Mar 16, 2022
Nov 21, 2019
- Change the Tkinter Label Font Size
- Change the Tkinter Label Font Family
This tutorial guide demonstrates how to change the Tkinter label font size. We create two buttons Increase and Decrease to increase/decrease the Tkinter label font size.
Change the Tkinter Label Font Size
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
app = tk.Tk()
fontStyle = tkFont.Font(family="Lucida Grande", size=20)
labelExample = tk.Label(app, text="20", font=fontStyle)
def increase_label_font():
fontsize = fontStyle['size']
labelExample['text'] = fontsize+2
fontStyle.configure(size=fontsize+2)
def decrease_label_font():
fontsize = fontStyle['size']
labelExample['text'] = fontsize-2
fontStyle.configure(size=fontsize-2)
buttonExample1 = tk.Button(app, text="Increase", width=30,
command=increase_label_font)
buttonExample2 = tk.Button(app, text="Decrease", width=30,
command=decrease_label_font)
buttonExample1.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
buttonExample2.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
labelExample.pack(side=tk.RIGHT)
app.mainloop()
fontStyle = tkFont.Font(family="Lucida Grande", size=20)
We specify the font to be font family Lucida Grande with size of 20, and assign it to be the font of label labelExample.
def increase_label_font():
fontsize = fontStyle['size']
labelExample['text'] = fontsize+2
fontStyle.configure(size=fontsize+2)
The font size is updated with tkinter.font.configure() method. The widget that uses this specific font will be updated automatically as you could see from the gif animation.
labelExample['text'] = fontsize+2
We also update the label text to be same with font size to make the animation more intuitive.
Change the Tkinter Label Font Family
We will also introduce how to change the Tkinter label font family by clicking the button.
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.font as tkFont
app = tk.Tk()
fontfamilylist = list(tkFont.families())
fontindex = 0
fontStyle = tkFont.Font(family=fontfamilylist[fontindex])
labelExample = tk.Label(app, text=fontfamilylist[fontindex], font=fontStyle)
def increase_label_font():
global fontindex
fontindex = fontindex + 1
labelExample.configure(font=fontfamilylist[fontindex], text=fontfamilylist[fontindex])
buttonExample1 = tk.Button(app, text="Change Font", width=30,
command=increase_label_font)
buttonExample1.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
labelExample.pack(side=tk.RIGHT)
app.mainloop()
fontfamilylist = list(tkFont.families())
It gets the available Tkinter font families list.
labelExample.configure(font=fontfamilylist[fontindex], text=fontfamilylist[fontindex])
The font property of labelExample will change to the next font in the font.families list, and the label text is also updated to the font name.
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
Related Article — Tkinter Label
- Hide, Recover and Delete Tkinter Widgets
- Change the Tkinter Label Text
- Get the Tkinter Label Text
- Set Border of Tkinter Label Widget
Related Article — Tkinter Font
- Set Font of Tkinter Text Widget
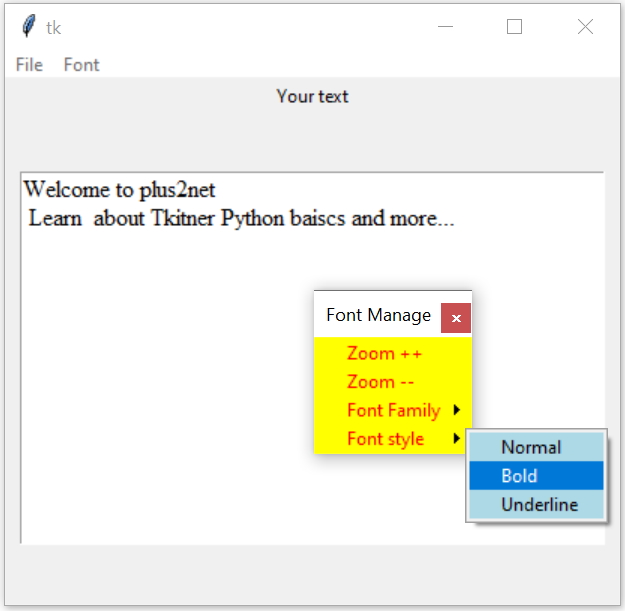
Tkinter Text Menu
Tkinter managing font family, size and style of text widget from menu bar
my_font_family(f_type) |
Receives font family name and set it |
my_font_size(dir) |
Receives direction and accordingly increase or decrease font size |
my_font_style() |
Reads the radio button selected value and set the style accordingly. |
font option of text widget
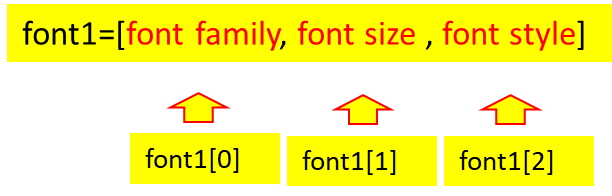
The font option of text widget takes three inputs, we will prepare one list and use it to add / update the font option.
font1=['Times',12,'normal'] # default font details
my_font_family(f_type)
Our Font menu item has one sub-menu menu_sub_family which can be used to select one of the font family. There is a command option to trigger the my_font_family() function with name of the font family passed as parameter. Here more font family can be added by extending the submenu menu_sub_family.
menu_sub_family.add_command(label='Times',command=lambda:my_font_family('Times'))
menu_sub_family.add_command(label='Arial Black',command=lambda:my_font_family('Arial Black'))Inside the function my_font_family() we receive the font family name and update the first element of the font1 ( list ) with this name. After updating, we used config to change the font option of the text widget.
def my_font_family(f_type): # select font family
font1[0]=f_type # set the font family
t1.config(font=font1) # config the fontmy_font_size(dir)
We have two commands to in our font menu, both runs the same function my_font_size() with different parameters ( increase or decrease ) to give direction as parameter for changing the font size.
menu_font.add_command(label="Zoom ++",command=lambda:my_font_size('increase')) #
menu_font.add_command(label="Zoom --",command=lambda:my_font_size('decrease'))Inside the function my_font_size() we receive the direction as per the user click of the menu option. Here font size is 2nd element of the list font1. We are increasing or decreasing based on the parameter ( dir ) value.
def my_font_size(dir): # font size is increased or decreased
if(dir=='increase'):
font1[1]=font1[1]+2 # increase font size
elif(dir=='decrease'):
font1[1]=font1[1]-2 # decrease font size
t1.config(font=font1) # configure the font def my_font_style()
We will use radio buttons for this in our menu. One common IntVar() ( r1_v )is used for the radio buttons and it holds the value based on the user selection of radio button. For the three options Normal, Bold and Underline the variable r1_v holds the value 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
r1_v = tk.IntVar(my_w) # for radio buttons menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Normal',value=1,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())
menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Bold',value=2,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())
menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Underline',value=3,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())Here user can select one of the three available options and on click of the radio buttons the function my_font_style() is executed. Inside this function we read the value of the variable r1_v and accourdingly the style for the font list is updated. Note that here the 3rd element of the list font1 is the style for the font list.
def my_font_style(): # selection of sub menu for style
if(r1_v.get()==1): # reading the value of r1_v
font1[2]='normal'
elif(r1_v.get()==2):
font1[2]='bold'
elif(r1_v.get()==3):
font1[2]='underline'
t1.config(font=font1) # configure the fontYou can read more about the menu and its sub-menu here.
Full code is here .
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import BOTH, END, LEFT
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("700x450")
my_frame = Frame(my_w, width=600, height=400)
my_frame.pack(fill="both", expand=1)
my_frame.pack_propagate(0)
l1 = tk.Label(my_frame,text='Your text', width=10) #add Label
l1.pack(fill="both", expand=0,padx=10)
#l1.grid(row=0,column=0,sticky='W')
font1=['Times',12,'normal'] # default font details
t1 = tk.Text(my_frame,height=4,font=font1) #text box
t1.pack(fill="both", expand=1,padx=10,pady=40)
#t1.grid(row=1,column=0,columnspan=2,padx=5,pady=10)
my_str="Welcome to plus2net n Learn "
my_str = my_str + " about Tkitner Python baiscs and more..."
t1.insert(tk.END, my_str) # add default string to text widget
def my_font_family(f_type): # select font family
font1[0]=f_type # set the font family
t1.config(font=font1) # config the font
def my_font_size(dir): # font size is increased or decreased
if(dir=='increase'):
font1[1]=font1[1]+2 # increase font size
elif(dir=='decrease'):
font1[1]=font1[1]-2 # decrease font size
t1.config(font=font1) # configure the font
def my_font_style(): # selection of sub menu for style
if(r1_v.get()==1): # reading the value of r1_v
font1[2]='normal'
elif(r1_v.get()==2):
font1[2]='bold'
elif(r1_v.get()==3):
font1[2]='underline'
t1.config(font=font1) # configure the font
r1_v = tk.IntVar(my_w) # for radio buttons
menubar = tk.Menu(my_w)
menu_font = tk.Menu(menubar,title='my title' ,
tearoff=1,fg='red',bg='yellow') # file
menu_file=tk.Menu(menubar,tearoff=0) # edit menu
menu_sub_family=tk.Menu(menu_font,tearoff=0,bg='lightgreen')
menu_sub_style=tk.Menu(menu_font,tearoff=0,bg='lightblue')
menu_font.add_command(label="Zoom ++",command=lambda:my_font_size('increase')) #
menu_font.add_command(label="Zoom --",command=lambda:my_font_size('decrease')) #
menu_font.add_cascade(label='Font Family',menu=menu_sub_family ) # add sub
menu_font.add_cascade(label='Font style',menu=menu_sub_style ) # add sub
menu_sub_family.add_command(label='Times',command=lambda:my_font_family('Times'))
menu_sub_family.add_command(label='Arial Black',command=lambda:my_font_family('Arial Black'))
menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Normal',value=1,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())
menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Bold',value=2,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())
menu_sub_style.add_radiobutton(label='Underline',value=3,variable=r1_v,command=lambda:my_font_style())
menubar.add_cascade(label="File", menu=menu_file) # Top Line
menubar.add_cascade(label="Font", menu=menu_font) # Top Line
menu_file.add_command(label="New") # Item 1 of file
menu_file.add_command(label="Open..") # Item 2
menu_file.add_separator()
menu_file.add_command(label="Exit", command=my_w.quit) # Item 3
my_w.config(menu=menubar) # adding menu to window
my_w.mainloop() Tkinter Text
Python Tkinter Entry How to Validate user entered data