In this article you’ll see how to style a button using CSS.
My goal here is mostly to showcase how different CSS rules and styles are applied and used. We won’t see much design inspiration nor will we discuss ideas for styling.
Instead, this will be more of an overview of how the styles themselves work, what properties are commonly used, and how they can be combined.
You’ll first see how to create a button in HTML. Then you’ll learn how to override the default styles of buttons. Lastly, you’ll get a glimpse of how to style buttons for their three different states.
Here’s an Interactive Scrim of CSS Button Style
Table of Contents
- Create a button in HTML
- Change default styling of buttons
- Change the background color
- Change text color
- Change the border style
- Change the size
- Style button states
- Style hover state
- Style focus state
- Style active state
- Conclusion
Let’s get started!
How to Create a Button in HTML
To create a button, use the <button> element.
This is a more accessible and semantic option compared to using a generic container which is created with the <div> element.
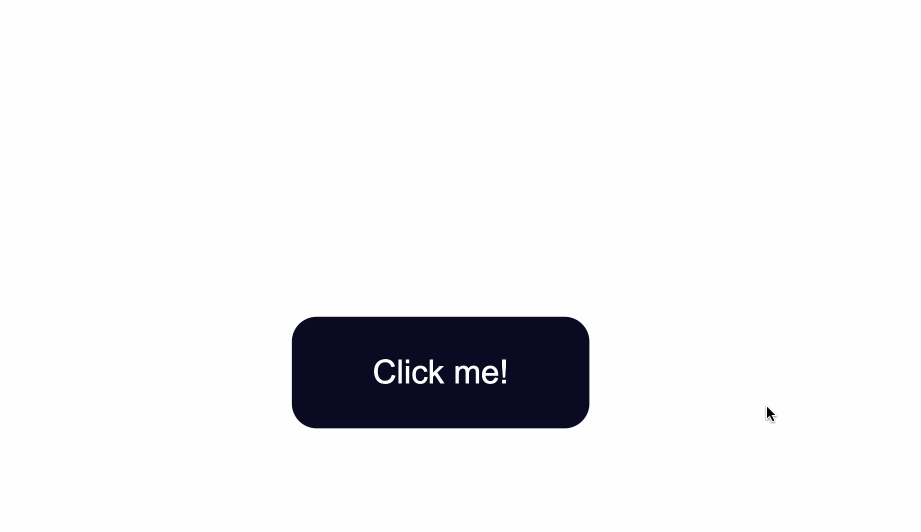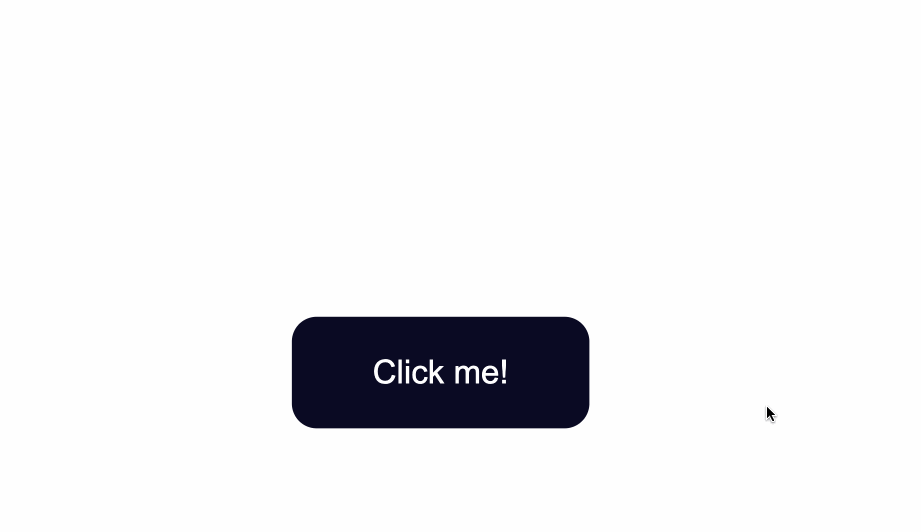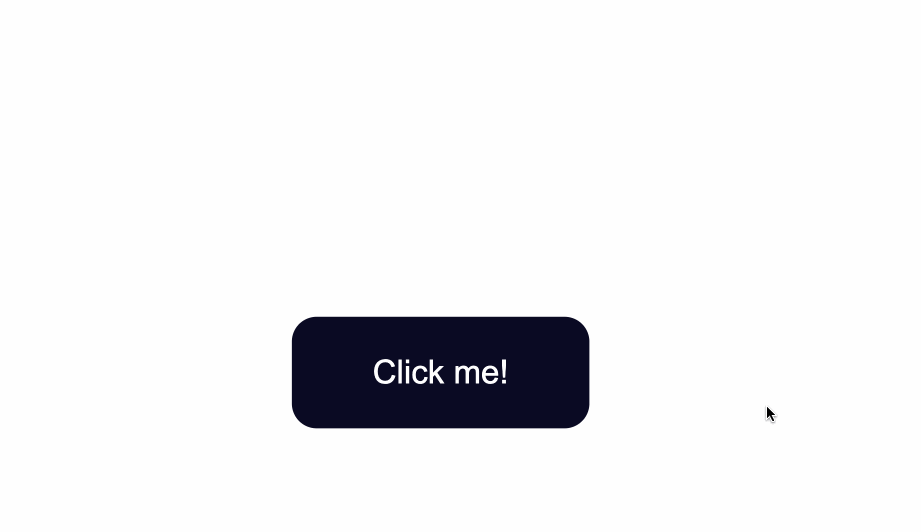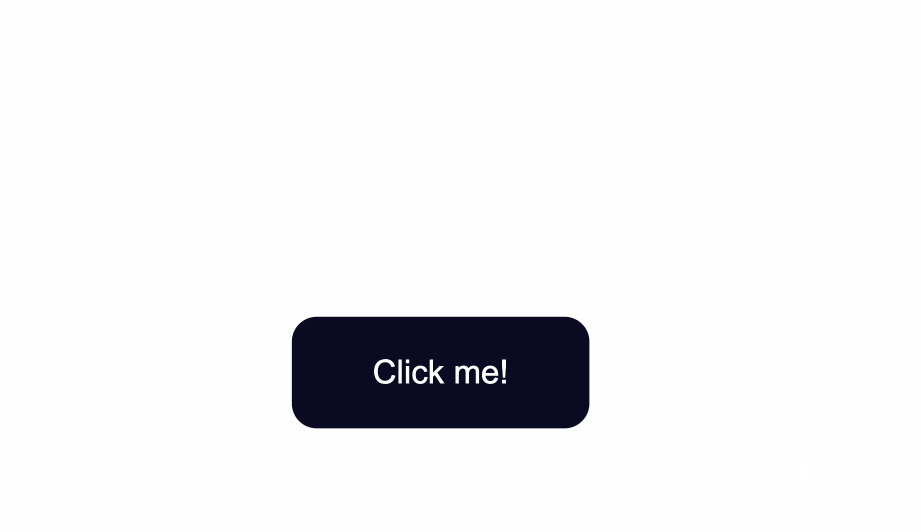
In the index.html file below, I’ve created the basic structure for a webpage and added a single button:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>CSS Button Style</title>
</head>
<body>
<button type="button" class="button">Click me!</button>
</body>
</html>
Let’s break down the line <button type="button" class="button">Click me!</button>:
- You first add the button element, which consists of an opening
<button>and closing</button>tag. - The
type="button"attribute in the opening<button>tag explicitly creates a clickable button. Since this particular button is not used for submitting a form, it is useful for semantic reasons to add it in order to make the code clearer and not trigger any unwanted actions. - The
class="button"attribute will be used to style the button in a separate CSS file. The valuebuttoncould be any other name you choose. For example you could have usedclass="btn". - The text
Click me!is the visible text inside the button.
Any styles that will be applied to the button will go inside a spearate style.css file.
You can apply the styles to the HTML content by linking the two files together. You do this with the <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> tag which was used in index.html.
In the style.css file, I’ve added some styling which only centers the button in the middle of the browser window.
Notice that the class="button" is used with the .button selector. This is a way to apply styles directly to the button.
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display:flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
margin:50px auto;
}
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%
}
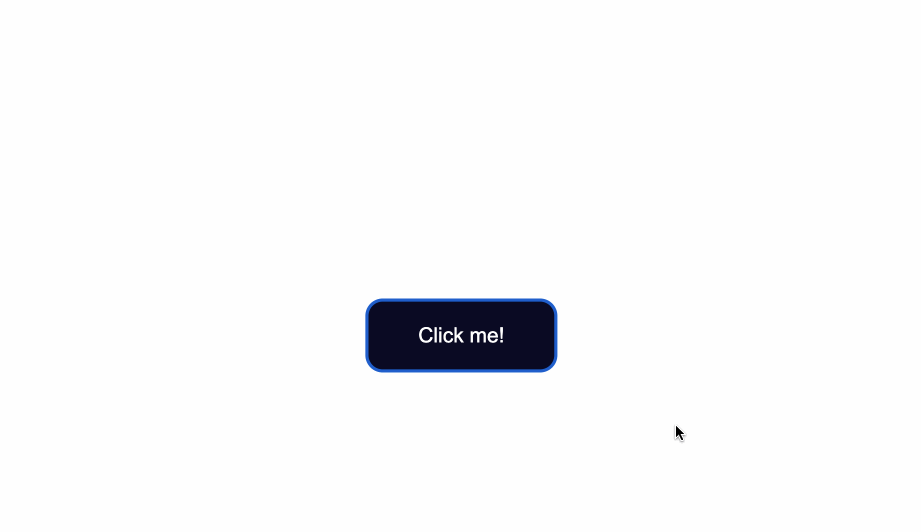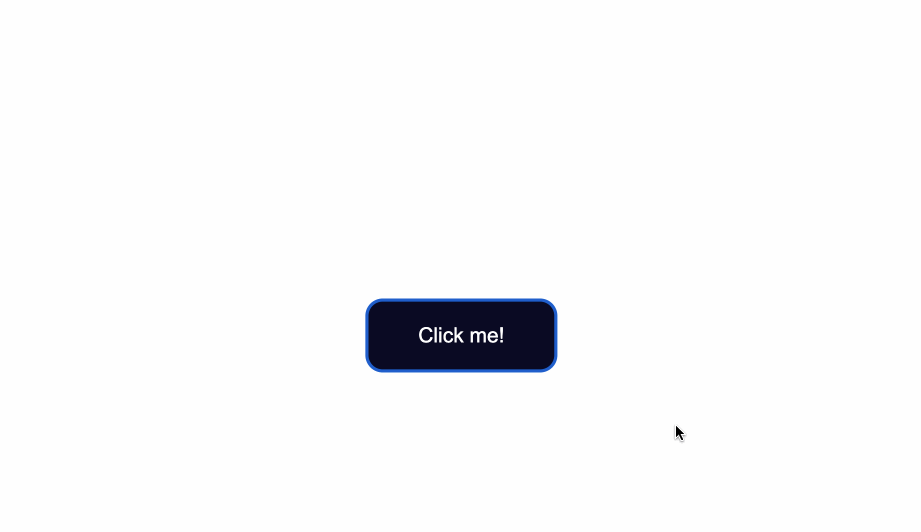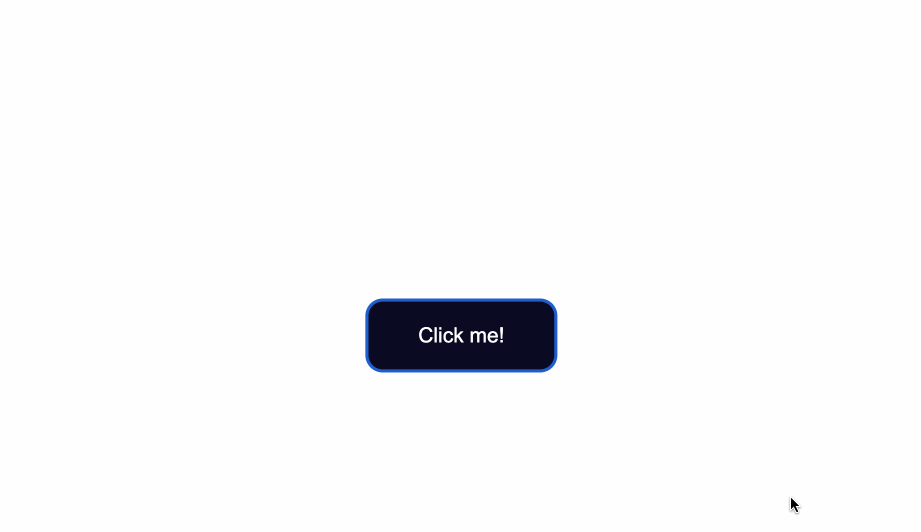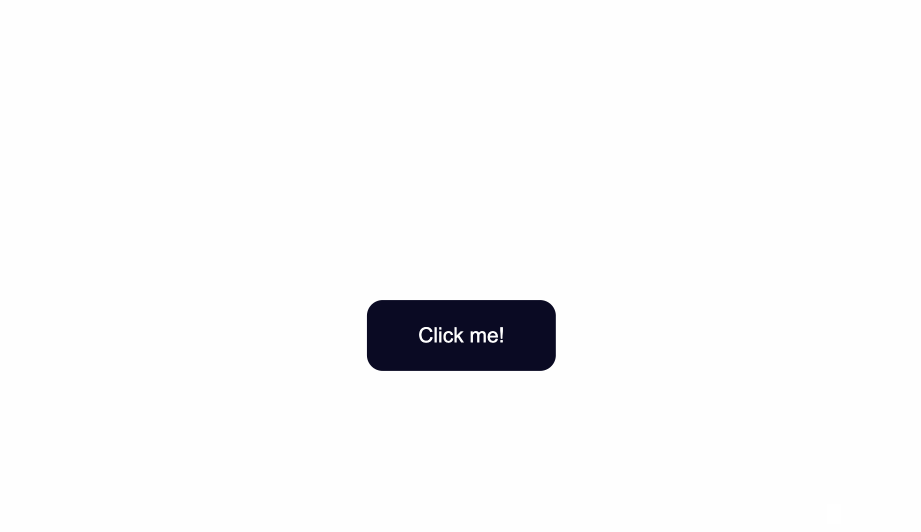
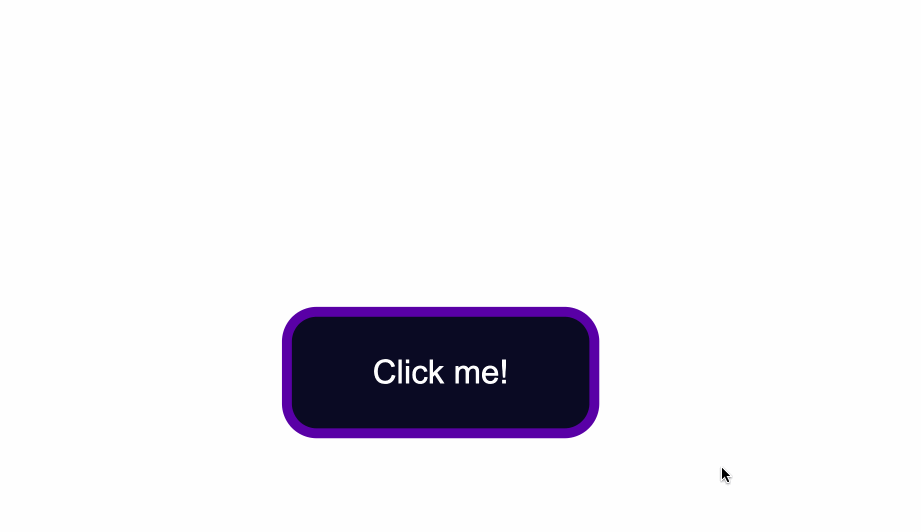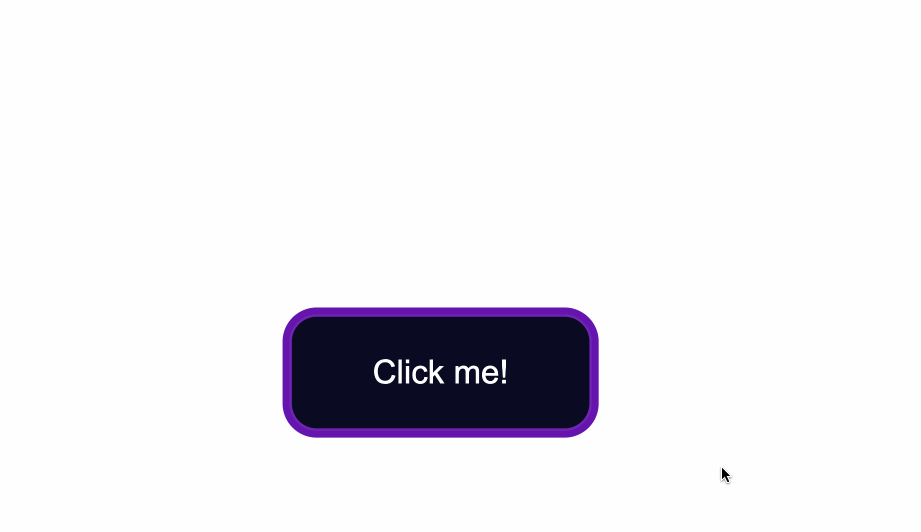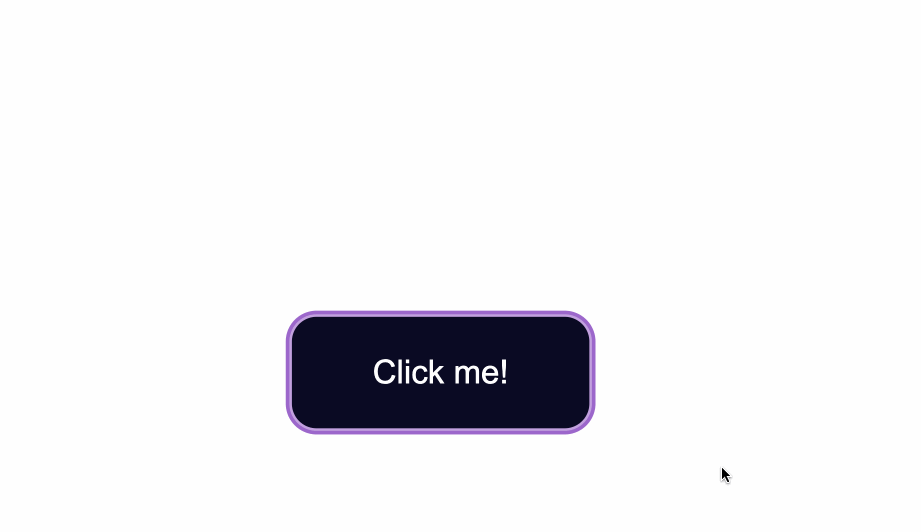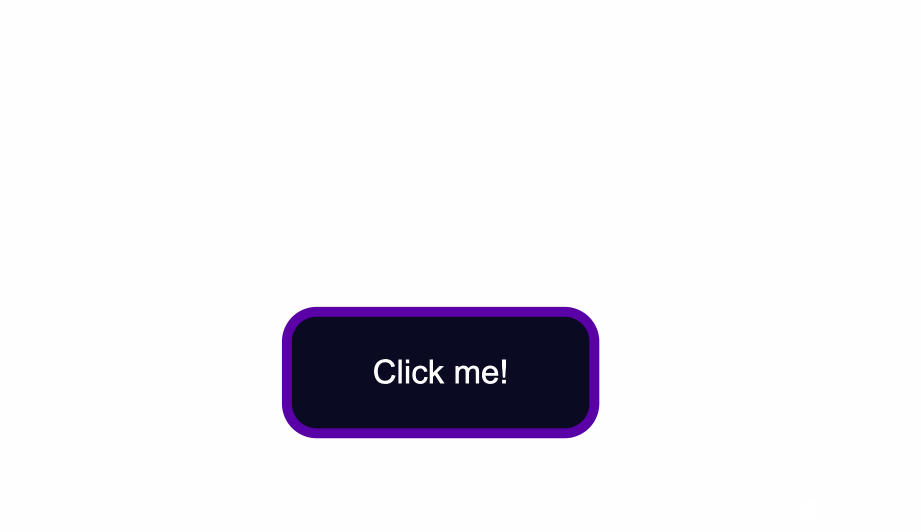
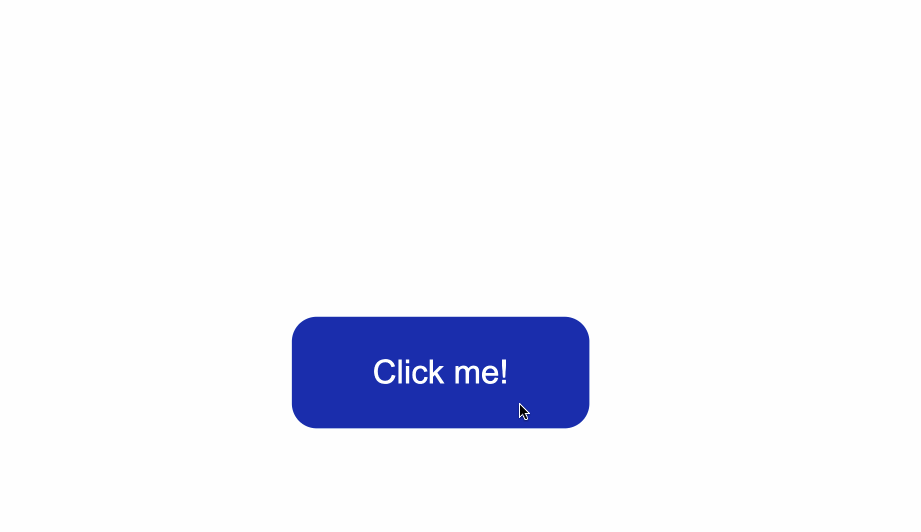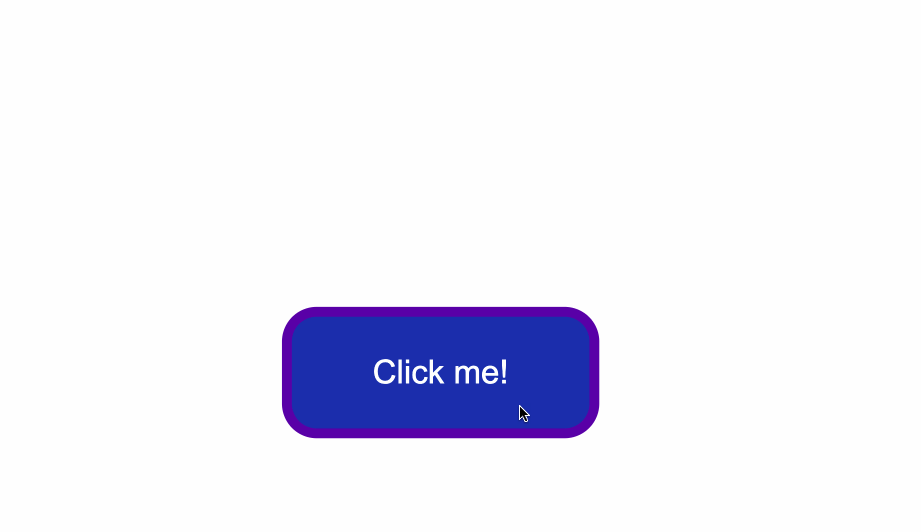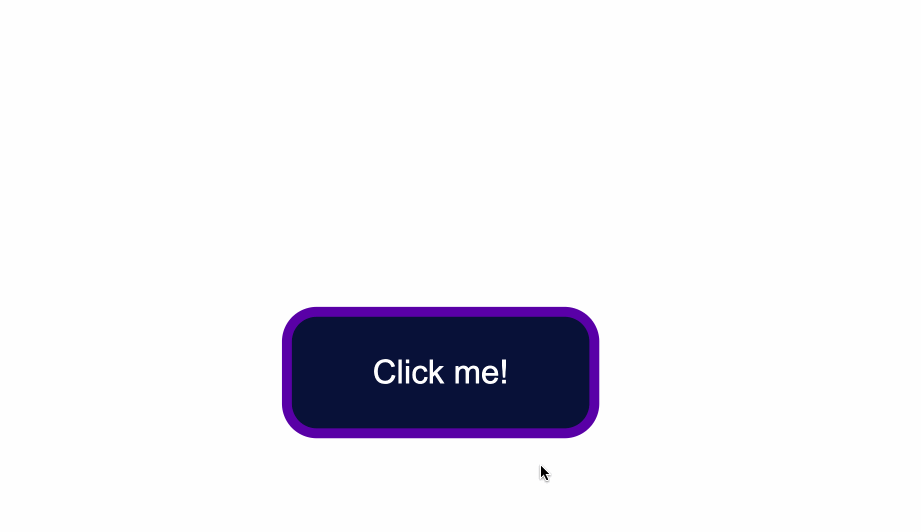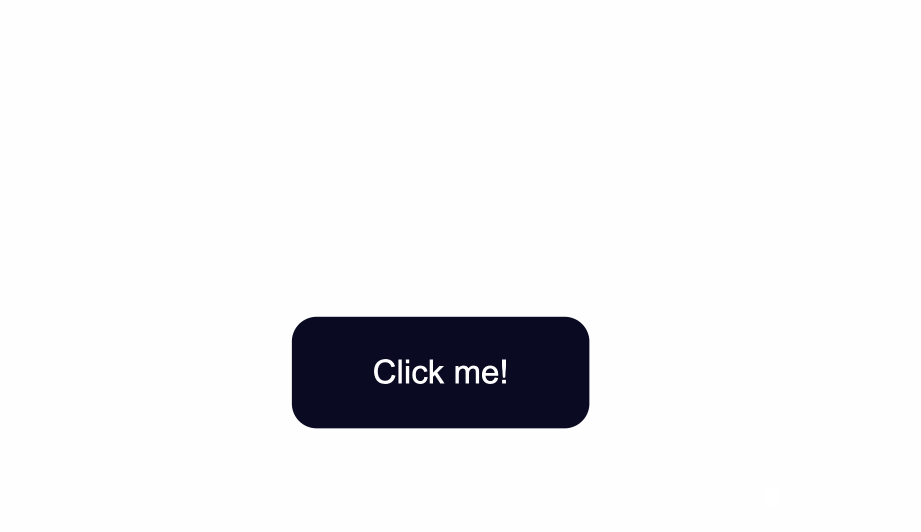
The code from above will result in the following:
The default styling of buttons will vary depending on the browser you’re using.
This is an example of how the native styles for buttons look on the Google Chrome browser.
How to Change the Default Styling of Buttons
How to Change the Background Color of Buttons
To change the background color of the button, use the CSS background-color property and give it a value of a color of your taste.
In the .button selector, you use background-color:#0a0a23; to change the background color of the button.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
}
How to Change the Text Color of Buttons
The default color of text is black, so when you add a dark background color you will notice that the text has disappeared.
Another thing to make sure of is that there is enough contrast between the button’s background color and text color. This helps make the text more readable and easy on the eyes.
Next, use the color property to change the color of text:
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
}
How to Change the Border Style of Buttons
Notice the grey around the edges of the button? That is the default color of the button’s borders.
One way to fix this is to use the border-color property. You set the value to be the same as the value of background-color. This makes sure the borders have the same color as the background of the button.
Another way would be to remove the border around the button entirely by using border:none;.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
}
Next, you can also round-up the edges of the button by using the border-radius property, like so:
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
}
You could also add a slight dark shadow effect around the button by using the box-shadow property:
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 2px 2px rgb(0,0,0);
How to Change the Size of Buttons
The way to create more space inside the button’s borders is to increase the padding of the button.
Below I added a value of 15px for the top, bottom, right, and left padding of the button.
I also set a minimum height and width, with the min-height and min-width properties respectively. Buttons need to be large enough for all different kind of devices.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
padding:15px;
min-height:30px;
min-width: 120px;
}
How to Style Button States
Buttons have three different states:
:hover:focus:active
It’s best that the three states are styled differently and don’t share the same styles.
In the following sections I’ll give a brief explanation on what each one of the states mean and what triggers them. You’ll also see some ways you can style the button for each separate state.
Here’s an interactive scrim about styling button states:
How to Style :hover States
The :hover state becomes present when a user hovers over a button, by bringing their mouse or trackpad over it, without selecting it or clicking on it.
To change the button’s styles when you hover over it, use the :hover CSS
pseudoclass selector.
A common change to make with :hover is switching the background-color of the button.
To make the change less sudden, pair :hover with the transition property.
The transition property will help make the transition from no state to a :hover state much smoother.
The change of background color will happen a bit slower than it would without the transition property. This will also help make the end result less jarring for the user.
.button:hover {
background-color:#002ead;
transition: 0.7s;
}
In the example above, I used a Hex color code value to make the background color a lighter shade for when I hover over the button.
With the help of the transition property I also caused a delay of 0.7s when the transition from no state to a :hover state happens. This caused a slower transition from the original #0a0a23 background color to the #002ead background color.
Keep in mind that the :hover pseudoclass does not work for mobile device screens and mobile apps. Choose to use hover effects only for desktop web applications and not touch screens.
How to Style :focus States
The :focus state takes effect for keyboard users — specifically it will activate when you focus on a button by hitting the Tab key (⇥).
If you’re following along, when you focus on the button after pressing the Tab key, you’ll see the following:
Notice the slight light blue outline around the button when it’s gained focus?
Browsers have default styling for the :focus pseudoclass, for accessibility keyboard navigation purposes. It’s not a good idea to remove that outline altogether.
You can however create custom styles for it and make it easily detectable.
A way to do so is by setting the outline color to first be transparent.
Following that, you can maintain the outline-style to solid. Lastly, using the box-shadow property, you can add a color of your liking for when the element is focused on:
.button:focus {
outline-color: transparent;
outline-style:solid;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 4px #5a01a7;
}
You can also again pair these styles with the transition property, depending on the effect you want to achieve:
.button:focus {
outline-color: transparent;
outline-style:solid;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 4px #5a01a7;
transition: 0.7s;
}
How to Style for the :active State
The :active state gets activated when you click on the button by either clicking the computer’s mouse or pressing down on the laptop’s trackpad.
That being said, look at what happens when I click the button after I’ve applied and kept the styles for the :hover and :focus states:
The :hover state styles are applied before clicking when I hover over the button.
The :focus state styles are applied also, because when a button is clicked it also gains a :focus state alongside an :active one.
However, keep in mind that they are not the same thing.
:focus state is when an element is being focused on and :active is when a user clicks on an element by holding and pressing down on it.
To change the style for when a user clicks a button, apply styles to the :active CSS pseudoselector.
In this case, I’ve changed the background color of the button when a user clicks on it
.button:active {
background-color: #ffbf00;
}
Conclusion
And there you have it! You now know the basics of how to style a button with CSS.
We went over how to change the background color and text color of buttons as well as how to style buttons for their different states.
To learn more about web design, check out freeCodeCamp’s Responsive Web Design Certification. In the interactive lessons, you’ll learn HTML and CSS by building 15 practice projects and 5 certification projects.
Note that the above cert is still in beta — if you want the latest stable version, check here.
Thanks for reading and happy coding!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
In this article you’ll see how to style a button using CSS.
My goal here is mostly to showcase how different CSS rules and styles are applied and used. We won’t see much design inspiration nor will we discuss ideas for styling.
Instead, this will be more of an overview of how the styles themselves work, what properties are commonly used, and how they can be combined.
You’ll first see how to create a button in HTML. Then you’ll learn how to override the default styles of buttons. Lastly, you’ll get a glimpse of how to style buttons for their three different states.
Here’s an Interactive Scrim of CSS Button Style
Table of Contents
- Create a button in HTML
- Change default styling of buttons
- Change the background color
- Change text color
- Change the border style
- Change the size
- Style button states
- Style hover state
- Style focus state
- Style active state
- Conclusion
Let’s get started!
How to Create a Button in HTML
To create a button, use the <button> element.
This is a more accessible and semantic option compared to using a generic container which is created with the <div> element.
In the index.html file below, I’ve created the basic structure for a webpage and added a single button:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>CSS Button Style</title>
</head>
<body>
<button type="button" class="button">Click me!</button>
</body>
</html>
Let’s break down the line <button type="button" class="button">Click me!</button>:
- You first add the button element, which consists of an opening
<button>and closing</button>tag. - The
type="button"attribute in the opening<button>tag explicitly creates a clickable button. Since this particular button is not used for submitting a form, it is useful for semantic reasons to add it in order to make the code clearer and not trigger any unwanted actions. - The
class="button"attribute will be used to style the button in a separate CSS file. The valuebuttoncould be any other name you choose. For example you could have usedclass="btn". - The text
Click me!is the visible text inside the button.
Any styles that will be applied to the button will go inside a spearate style.css file.
You can apply the styles to the HTML content by linking the two files together. You do this with the <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> tag which was used in index.html.
In the style.css file, I’ve added some styling which only centers the button in the middle of the browser window.
Notice that the class="button" is used with the .button selector. This is a way to apply styles directly to the button.
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display:flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
margin:50px auto;
}
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%
}
The code from above will result in the following:
The default styling of buttons will vary depending on the browser you’re using.
This is an example of how the native styles for buttons look on the Google Chrome browser.
How to Change the Default Styling of Buttons
How to Change the Background Color of Buttons
To change the background color of the button, use the CSS background-color property and give it a value of a color of your taste.
In the .button selector, you use background-color:#0a0a23; to change the background color of the button.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
}
How to Change the Text Color of Buttons
The default color of text is black, so when you add a dark background color you will notice that the text has disappeared.
Another thing to make sure of is that there is enough contrast between the button’s background color and text color. This helps make the text more readable and easy on the eyes.
Next, use the color property to change the color of text:
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
}
How to Change the Border Style of Buttons
Notice the grey around the edges of the button? That is the default color of the button’s borders.
One way to fix this is to use the border-color property. You set the value to be the same as the value of background-color. This makes sure the borders have the same color as the background of the button.
Another way would be to remove the border around the button entirely by using border:none;.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
}
Next, you can also round-up the edges of the button by using the border-radius property, like so:
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
}
You could also add a slight dark shadow effect around the button by using the box-shadow property:
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 2px 2px rgb(0,0,0);
How to Change the Size of Buttons
The way to create more space inside the button’s borders is to increase the padding of the button.
Below I added a value of 15px for the top, bottom, right, and left padding of the button.
I also set a minimum height and width, with the min-height and min-width properties respectively. Buttons need to be large enough for all different kind of devices.
.button {
position: absolute;
top:50%;
background-color:#0a0a23;
color: #fff;
border:none;
border-radius:10px;
padding:15px;
min-height:30px;
min-width: 120px;
}
How to Style Button States
Buttons have three different states:
:hover:focus:active
It’s best that the three states are styled differently and don’t share the same styles.
In the following sections I’ll give a brief explanation on what each one of the states mean and what triggers them. You’ll also see some ways you can style the button for each separate state.
Here’s an interactive scrim about styling button states:
How to Style :hover States
The :hover state becomes present when a user hovers over a button, by bringing their mouse or trackpad over it, without selecting it or clicking on it.
To change the button’s styles when you hover over it, use the :hover CSS
pseudoclass selector.
A common change to make with :hover is switching the background-color of the button.
To make the change less sudden, pair :hover with the transition property.
The transition property will help make the transition from no state to a :hover state much smoother.
The change of background color will happen a bit slower than it would without the transition property. This will also help make the end result less jarring for the user.
.button:hover {
background-color:#002ead;
transition: 0.7s;
}
In the example above, I used a Hex color code value to make the background color a lighter shade for when I hover over the button.
With the help of the transition property I also caused a delay of 0.7s when the transition from no state to a :hover state happens. This caused a slower transition from the original #0a0a23 background color to the #002ead background color.
Keep in mind that the :hover pseudoclass does not work for mobile device screens and mobile apps. Choose to use hover effects only for desktop web applications and not touch screens.
How to Style :focus States
The :focus state takes effect for keyboard users — specifically it will activate when you focus on a button by hitting the Tab key (⇥).
If you’re following along, when you focus on the button after pressing the Tab key, you’ll see the following:
Notice the slight light blue outline around the button when it’s gained focus?
Browsers have default styling for the :focus pseudoclass, for accessibility keyboard navigation purposes. It’s not a good idea to remove that outline altogether.
You can however create custom styles for it and make it easily detectable.
A way to do so is by setting the outline color to first be transparent.
Following that, you can maintain the outline-style to solid. Lastly, using the box-shadow property, you can add a color of your liking for when the element is focused on:
.button:focus {
outline-color: transparent;
outline-style:solid;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 4px #5a01a7;
}
You can also again pair these styles with the transition property, depending on the effect you want to achieve:
.button:focus {
outline-color: transparent;
outline-style:solid;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 4px #5a01a7;
transition: 0.7s;
}
How to Style for the :active State
The :active state gets activated when you click on the button by either clicking the computer’s mouse or pressing down on the laptop’s trackpad.
That being said, look at what happens when I click the button after I’ve applied and kept the styles for the :hover and :focus states:
The :hover state styles are applied before clicking when I hover over the button.
The :focus state styles are applied also, because when a button is clicked it also gains a :focus state alongside an :active one.
However, keep in mind that they are not the same thing.
:focus state is when an element is being focused on and :active is when a user clicks on an element by holding and pressing down on it.
To change the style for when a user clicks a button, apply styles to the :active CSS pseudoselector.
In this case, I’ve changed the background color of the button when a user clicks on it
.button:active {
background-color: #ffbf00;
}
Conclusion
And there you have it! You now know the basics of how to style a button with CSS.
We went over how to change the background color and text color of buttons as well as how to style buttons for their different states.
To learn more about web design, check out freeCodeCamp’s Responsive Web Design Certification. In the interactive lessons, you’ll learn HTML and CSS by building 15 practice projects and 5 certification projects.
Note that the above cert is still in beta — if you want the latest stable version, check here.
Thanks for reading and happy coding!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
- CSS кнопка вверх
- Крупные кнопки-изображения
Простая HTML кнопка для сайта
Есть несколько типов input для создания кнопки и тег button [ type=»button | reset | submit» ]. Внешне и функционально они абсолютно одинаковы.
<input type="button" value="input"/> <button type="button">button</button>
Когда использовать тег button?
- button имеет открывающий и закрывающий тег, а значит он может содержать дочерние теги,
- когда текст на кнопке один, а значение value при клике должно передаваться другое.
Как сделать кнопку на CSS
Из ссылки, тега span или div можно сделать с помощью CSS очень даже симпатичную кнопку.
Посмотреть описание
<a href="#" class="knopka">кнопка</a>
Создание кнопки: «А нужно ли изменять вид кнопки при наведении или делать кнопку с эффектом нажатия?»
Динамические эффекты реализуются благодаря псевдоклассам:
- :hover — при наведении. С появлением сенсорных экранов необходимость в :hover отпала. Для остальных же нужно как минимум изменение вида курсора мышки, чтобы дать понять, что элемент не является декорацией.
- :active — в момент нажатия кнопки. Когда на странице тут же что-то явно происходит, например, переход по ссылке, загрузка модального окна, появляется значок обработки формы, то :active можно опустить.
- :focus — пока кнопка в фокусе, то есть когда пользователь нажал на кнопку, но ещё не щёлкнул курсором мышки в другое место окна браузера. Без :focus невозможно объединить visibility: hidden; и transition. Если слишком быстро убрать мышку, то элемент повиснет в «половинном» состоянии, например, ссылка будет прозрачна, но по ней можно делать переход.
Надо признать, что сложнее всего придумать как будет вести себя кнопка во время нажатия.
Код кнопки для сайта
Иногда самый простой внешний вид может выглядеть более стильно, чем навороченная с крутыми эффектами кнопка. Взгляните, как она тут [cssdeck.com] смотрится.
Добавить в корзину
<a href="#" class="button7">кнопка</a>
<a href="#" class="button7">кнопка</a>
Как у Сбербанка
<a href="#" class="button24">кнопка</a>
Кнопка с градиентом
Градиенты плохо поддаются анимации, плавной смене цвета фона. Что же делать? Ответ: box-shadow [перейдите по ссылке, там есть суперская форма входа].
Купить
<a href="#" class="button10">кнопка</a>
А вот всякие перемещения работают на ура.
Забронировать
<a href="#" class="button12" tabindex="0">кнопка</a>
Довольно популярно разделение кнопки на два цвета
Положить в корзину
<a href="#" class="button25">кнопка</a>
Красивые кнопки CSS
10 999 р.
<a href="#" class="button11">кнопка</a>
Как у Google
<a href="#" class="button15">кнопка</a>
<a href="#" class="button17" tabindex="0">кнопка</a>
Заказать
<a href="#" class="button21">Заказать</a>
<a href="#" class="button28">Установить</a>
Кнопки «Скачать» CSS
Скачать
бесплатно первые 30 дней Автор
<a href="#" class="button13">Скачать бесплатно первые 30 дней</a>
скачать
<a href="#" class="button14">Скачать</a>
Стилизация кнопок с помощью CSS
Анимированная кнопка: «свечение текста»
<input type="button" class="button4" value="Купить">
<input type="button" class="knopka01" value="запись">
Стиль кнопок с бликами
Глянцевая кнопка
<a href="#" class="button1">кнопка</a>
<a href="#" class="button9">кнопка</a>
Заказать билеты
<a href="#" class="knopka01">кнопка</a>
<a href="#" class="button5" data-twitter>twitter</a>
<a href="#" class="button16">кнопка</a>
<a href="#" class="button18" tabindex="0">кнопка</a>
1 2 3
<a href="#" class="button27">1</a>
Объёмная кнопка CSS
Объёмная
<a href="#" class="button19">кнопка</a>
кнопка Автор
<a href="#" class="button">кнопка</a>
сделать
заказ Автор
<a href="#" class="button20">Объёмная</a>
положить в корзину
<a href="#" class="button23">Объёмная</a>
Вдавленная кнопка
Оформить
<a href="#" class="button22">Заказать</a>
Выпуклая кнопка HTML
<a href="#" class="boxShadow4">Заказать</a>
Круглые CSS кнопки
<a href="#" class="button29"></a>
+
<a href="#" class="button30">+</a>
Анимированная кнопка CSS
Анимированное заполнение происходит так (тут нет лишнего кода, связанного с кнопкой). Другие интересные эффекты загрузки можно найти тут [tympanus.net].
<a href="#" class="button26" tabindex="0"><span></span></a>
<a href="#" class="button31" tabindex="0"></a>
3d кнопка CSS
<a href="#" class="button2" tabindex="0">кнопка</a>
Оформление кнопок
Кнопки сайта следует выполнять в едином стиле, чтобы не оставалось сомнений, что если здесь нажать, то произойдёт какое-то действо.
Кнопка с главным действием должна выделяться из общего содержания, быть контрастной. Тут главное не переусердствовать. Так, например, у интернет магазина e5 это приятно для глаза:
А тут с оранжевым явный перебор, даже на изображении сложно остановить взгляд:

Именно поэтому у Google второстепенные кнопки сначала плоские, а после наведения мышки обретают объём.
Также нужно победить желание сделать кнопку величиной со слона, чтобы не стать объектом баннерной слепоты.
В этой статье мы расскажем о том как сделать кнопку в CSS?. Но понимание разницы между Flat UI и Material Design не имеет смысла, если вы не знаете, какие компоненты нужно применять. Давайте быстро пробежимся по основам создания кнопок с помощью CSS.
- Основы CSS кнопок
- Цвет
- Тени
- Время плавного перехода
- Сброс стилей кнопки
- Три стиля кнопок
- Простой черный и белый
- Кнопки Flat UI
- Material Design
- В заключение
Существует несколько «нетехнических» стандартов кнопок:
- Доступность – имеет первостепенное значение. Пользователи с ограниченными возможностями и старыми браузерами должны иметь простой доступ к кнопкам;
- Простой текст – пишите на кнопках простой и короткий текст. Пользователи должны сразу понять назначение кнопки и то, куда она их приведет.
Почти все кнопки в интернете используют эффекты с изменением цвета рамок и теней. Это можно сделать реализовать с помощью псевдоклассов. Мы остановимся на двух из них: :hover и :active. Псевдокласс :hover отвечает за поведение CSS при наведении курсора мыши. Код :active, когда пользователь нажал кнопку мыши, но еще ее не отпустил.
С помощью псевдоклассов можно полностью изменить внешний вид кнопки, но это неудобный подход. Новичкам лучше редактировать основные стили кнопки, почти полностью сохраняя ее внешний вид. В реализации данного элемента управления можно выделить три основных аспекта – цвет, тени и время перехода.
Изменить цвет CSS buttons можно с помощью различных свойств: color, background-color и border. Сначала разберемся, как выбрать цвет кнопки:
- Комбинации цветов – используйте цвета, которые дополняют друг друга. Colorhexa – отличный инструмент для поиска сочетающихся цветов;
- Соблюдение палитры — если вы ищете палитру цветов, зайдите на lolcolors.
С помощью box-shadow можно добавить тень вокруг объекта. Эта идея реализована в Flat UI и Material Design. Более подробно о свойстве box-shadow можно почитать на MDN.
Свойство transition-duration добавляет временные рамки CSS изменениям. Стили кнопки без плавного перехода моментально меняются на стили псевдокласса :hover, что может отпугнуть пользователя. В следующем примере стиль кнопки плавно меняется (за 0.5 с): на :hover:
.color-change {
border-radius: 5px;
font-size: 20px;
padding: 14px 80px;
cursor: pointer;
color: #fff;
background-color: #00A6FF;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: 'Roboto';
font-weight: 100;
border: 1px solid #fff;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 5px #AFE9FF;
transition-duration: 0.5s;
-webkit-transition-duration: 0.5s;
-moz-transition-duration: 0.5s;
}
.color-change:hover {
color: #006398;
border: 1px solid #006398;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 20px #AFE9FF;
}
А смотрится это так:
Код для плавных переходов сложный и старые браузеры по-разному выполняют анимацию. Поэтому нужно добавить префиксы для старых браузеров:
transition-duration: 0.5s /* Обычная запись, работает во всех современных браузерах*/ -webkit-transition-duration: 0.5s; /* Помогает некоторым версиям safari, chrome и android */ -moz-transition-duration: 0.5s; /* для firefox */
Чтобы браузер установил значение по умолчанию для CSS button style, можно установить пользовательские стили:
button.your-button-class {
-webkit-appearance: none;
-moz-appearance: none;
}
Лучше применять это к классам элементов кнопки, а не к каждой кнопке по отдельности.
Такие кнопки хорошо сочетаются с множеством различных стилей. Этот эффект основан на контрасте черного и белого.
Рассмотрим код черной кнопки с белым фоном. Чтобы перекрасить кнопку в другой цвет, поменяйте в button стилях CSS все значения white и black местами:
.suit_and_tie {
color: white;
font-size: 20px;
font-family: helvetica;
text-decoration: none;
border: 2px solid white;
border-radius: 20px;
transition-duration: .2s;
-webkit-transition-duration: .2s;
-moz-transition-duration: .2s;
background-color: black;
padding: 4px 30px;
}
.suit_and_tie:hover {
color: black;
background-color: white;
transition-duration: .2s;
-webkit-transition-duration: .2s;
-moz-transition-duration: .2s;
}
В приведенных выше стилях видно, что свойства font и background-color меняют свои значения со свойством transition-duration.2s. Можно взять цвета своих любимых брендов и создать свою кнопку. Цвета брендов можно найти на BrandColors.
Flat UI делает упор на минимализм в HTML button CSS – больше действий, меньше движений. Обычно я перехожу от черно-белых кнопок на Flat UI, когда мой проект начинает обретать форму. Кнопки Flat UI имеют минималистичный вид и подходят под большинство дизайнов.
Улучшим нашу кнопку, добавив ей движения для имитации 3D эффекта.
Мы рассмотрим первую кнопку:
.turquoise {
margin-right: 10px;
width: 100px;
background: #1abc9c;
border-bottom: #16a085 3px solid;
border-left: #16a085 1px solid;
border-right: #16a085 1px solid;
border-radius: 6px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
float: left;
font-size: 12px;
font-weight: 800;
}
.turquoise:hover {
opacity: 0.8;
}
.turquoise:active {
width: 100px;
background: #18B495;
border-bottom: #16a085 1px solid;
border-left: #16a085 1px solid;
border-right: #16a085 1px solid;
border-radius: 6px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
margin-top: 3px;
]]
float: left;
}
У button CSS три состояния: обычное, :hover и :active.
:hover содержит всего одну строку кода с уменьшением прозрачности, чтобы сделать кнопку немного светлее, поэтому нам не нужно подбирать более светлый цвет.
Вместо того чтобы указать сплошную рамку border, тут используются свойства border-bottom, border-left и border-right, которые создают 3D-эффект глубины.
Псевдокласс :active часто используется в Flat UI кнопках. Когда наша кнопка становится :active происходит две вещи:
- :border-bottom меняется с 3px на 1px. Тень под кнопкой уменьшается, а кнопка опускается на пару пикселей. Это изменение позволяет пользователю почувствовать, что он нажал кнопку;
- Цвет фона темнеет, имитируя смещение кнопки от пользователя к экрану. Что также напоминает пользователю о том, что он нажал кнопку.
Во Flat UI ценятся минималистичные движения кнопок, «рассказывающие большую историю». Многие имитируют сдвиг кнопки с помощью :border-bottom. Стоит отметить, что во Flat UI есть кнопки, которые вообще не двигаются, а только меняют цвет.
Material Design – подход к дизайну, который продвигает идею передачи информации в виде карточек с различной анимацией для привлечения внимания. Google перечислил на странице Material Design Homepage три основных принципа:
- Слово «Материальный» — это метафора;
- Монотонность, графика, агрессивность;
- Движение передает значение.
Чтобы лучше понять три этих принципа, взглянем на Material Design в действии:
Эти CSS buttons реализуют две основные идеи – свойство box-shadow и Polymer.
Polymer – фреймворк для создания сайтов. С его помощью эффект распространяющейся волны на кнопках добавляется всего одной строкой кода:
<div class="button"> <div class="center" fit>SUBMIT</div> <paper-ripple fit></paper-ripple> /* эта строка добавляет эффект */ </div>
<paper-ripple fit></paper-ripple> — компонент Polymer. Подключив фреймворк в самом начале HTML, мы получаем доступ к его компонентам. Более подробно ознакомиться с возможностями фреймворка можно на сайте Polymer project.
Теперь поговорим о CSS коде, который реализует принципы Material Design:
body {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
font-family: RobotoDraft, 'Helvetica Neue';
}
/* Button */
.button {
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
width: 120px;
height: 32px;
line-height: 32px;
border-radius: 2px;
font-size: 0.9em;
background-color: #fff;
color: #646464;
margin: 20px 10px;
transition: 0.2s;
transition-delay: 0.2s;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
}
.button:active {
box-shadow: 0 8px 17px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
transition-delay: 0s;
}
/* Misc */
.button.grey {
background-color: #eee;
}
.button.blue {
background-color: #4285f4;
color: #fff;
}
.button.green {
background-color: #0f9d58;
color: #fff;
}
.center {
text-align: center;
}
Во всех button CSS используется свойство box-shadow. Удалим весь неменяющийся CSS код и посмотрим, как box-shadow работает:
.button {
transition: 0.2s;
transition-delay: 0.2s;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
}
.button:active {
transition-delay: 0s;
box-shadow: 0 8px 17px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
Свойство box-shadow используется в button стилях CSS для добавления тонкой темной тени слева и снизу у каждой кнопки. При нажатии тень немного увеличивается и становится светлее. Это движение имитирует эффект 3D тени, которая как бы подпрыгивает от страницы к пользователю. Эффект прописан в стилях Material Design и его принципах.
Кнопки в стиле Material Design можно создать путем совмещения Polymer и box-shadow эффектов.
- Слово «материальный» – метафора – с помощью свойства box-shadow мы имитируем эффект 3D тени, создаем аналог настоящей тени;
- Монотонность, графика, агрессивность – больше относится к ярко-голубым и зеленым кнопкам;
- Значение передается при помощи движений – с помощью Polymer и анимации свойства box-shadow можно создавать множество различных движений, когда пользователь нажимает на кнопку.
Черно-белые кнопки довольно просты и понятны. Flat UI кнопки тоже простые и используют мелкие движения и цвета, чтобы «рассказать большую историю». Material Design использует крупномасштабные сложные движения, имитирующие реальную тень, чтобы привлечь внимание пользователя.
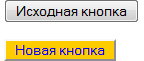
Стандартные кнопки, созданные через тег <button> или <input type=»button»>, выглядят, конечно, хорошо, но попытка изменить их вид через стили приводит к ужасному результату. Кнопки становятся приветом интерфейсам десятилетней давности с их угловатостью (рис. 1). Разумеется, такая метаморфоза возникает только при использовании свойств background и border, иными словами, нельзя изменить цвет фона кнопки и рамку вокруг нее.
Рис. 1. Исходная и измененная кнопка
Чтобы кардинально поменять вид кнопки можно воспользоваться изображениями, но по сравнению с возможностями CSS 3 этот вариант теперь кажется доморощенным.
За основу возьму оригинальную кнопку в браузере, которая содержит линейный вертикальный градиент и скругленные края.
Самое простое сделать закругление уголков, для чего используем свойство border-radius, задавая ему нужный радиус скругления. Как обычно, работает не во всех браузерах, поэтому придется добавлять полный комплект. В итоге получается следующее.
-moz-border-radius: 5px; /* Firefox */
-webkit-border-radius: 5px; /* Safari 4 */
border-radius: 5px; /* IE 9, Safari 5, Chrome */Вид кнопок в разных браузерах показан на рис. 2.
Рис. 2. Кнопки со скругленными уголками
В общем, все ожидаемо. Старые версии IE не поддерживают CSS 3, остальные корректно делают нужные мне уголки. Опера почему-то не отображает фон по умолчанию, как это делают другие браузеры, но про Оперу еще зайдет особый разговор.
Теперь самое интересное, делаем вертикальный линейный градиент. Для этого опять в ход пойдут индивидуальные стили для каждого браузера.
Firefox
background: -moz-linear-gradient(#00BBD6, #EBFFFF);
В градиенте указывается исходная точка, угол градиента, начальный и конечный цвет. В нашем случае, когда градиент идет вертикально сверху вниз, достаточно задать только цвета, остальные параметры используются по умолчанию.
Chrome, Safari
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 0 100%, from(#00BBD6), to(#EBFFFF));
Здесь указывается тип градиента (linear), стартовая точка приложения градиента (левый верхний угол), финальная точка (левый нижний угол), а также начальный и конечный цвет.
Internet Explorer
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr=’#00BBD6′, endColorstr=’#EBFFFF’);
Браузер IE идет своим путем и для разных эффектов применяет свойство filter, в том числе и для градиента. Здесь все тривиальнее, пишется только начальный и конечный цвет градиента.
Опера отдыхает, в ней градиенты еще не реализованы.
Собираем воедино все свойства для браузеров, уголков и градиентов (пример 1).
Пример 1. Кнопки с линейным градиентом
HTML 5CSS 2.1CSS 3IE 9CrOpSaFx
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Кнопки</title>
<style type="text/css">
button.new {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(#00BBD6, #EBFFFF);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 0 100%, from(#00BBD6), to(#EBFFFF));
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#00BBD6', endColorstr='#EBFFFF');
padding: 3px 7px;
color: #333;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
border: 1px solid #666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<p><button>Исходная кнопка</button></p>
<p><button class="new">Новая кнопка</button></p>
</form>
</body>
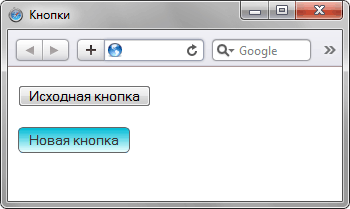
</html>Получилось довольно симпатично (рис. 3), но есть и явные отличия от первоначальной кнопки — она выглядит плоской, как доска.
Рис. 3. Вид кнопки с градиентом
Сделать кнопку нужной формы можно опять же градиентом, «играя» цветами. Двумя значениями градиента уже не обойтись, к счастью, Firefox и Safari предлагают решение.
Firefox
background: -moz-linear-gradient(#D0ECF4, #5BC9E1, #D0ECF4);
Вместо двух значений вставляем желаемое количество цветов, градиент будет плавно переходить от одного цвета к другому.
Chrome, Safari
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 0 100%, from(#D0ECF4), to(#D0ECF4), color-stop(0.5, #5BC9E1));
Параметр color-stop указывает точку приложения нового цвета. Значение варьируется от 0 до 1.
Пример 2. Кнопки с улучшенным градиентом
HTML 5CSS 2.1CSS 3IE 9CrOpSaFx
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Кнопки</title>
<style type="text/css">
button.new {
background: -moz-linear-gradient(#D0ECF4, #5BC9E1, #D0ECF4);
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, 0 0, 0 100%, from(#D0ECF4), to(#D0ECF4), color-stop(0.5, #5BC9E1));
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#00BBD6', endColorstr='#EBFFFF');
padding: 3px 7px;
color: #333;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
border: 1px solid #666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<p><button>Исходная кнопка</button></p>
<p><button class="new">Новая кнопка</button></p>
</form>
</body>
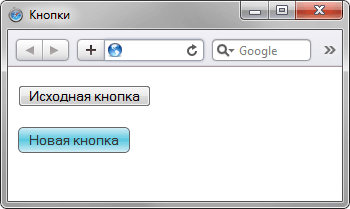
</html>Результат примера показан на рис. 4.
Рис. 4. Градиент, какой надо градиент
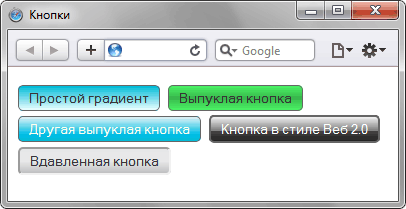
Аналогично можно создавать любые другие градиенты на кнопке или другом элементе (рис. 5). Но это уже сделайте самостоятельно, для чего в практикум добавил соответствующую задачу.
Рис. 5. Такие разные кнопки
Подведу итоги. Кнопку с градиентом и скругленными уголками без изображений сделать можно. Однако с браузерами разброд и шатание. Опера вообще не умеет работать с градиентами, в IE 9 наблюдается неприятный баг при сочетании градиента с уголками (рис. 6).
Рис. 6. Наложение фона на уголки в IE 9
Что ж, пока будем делать «красивости» для браузеров Firefox, Safari и Chrome.
Узнайте, как стиль кнопок с помощью CSS.
Основные стили кнопок
Пример
.button {
background-color: #4CAF50; /* Green */
border: none;
color: white;
padding: 15px 32px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
}
Цвета кнопок
Используйте свойство background-color для изменения цвета фона кнопки:
Пример
.button1 {background-color: #4CAF50;} /* Green */
.button2
{background-color: #008CBA;} /* Blue */
.button3 {background-color:
#f44336;} /* Red */
.button4 {background-color: #e7e7e7; color: black;} /* Gray */
.button5
{background-color: #555555;} /* Black */
Размеры кнопок
Используйте свойство font-size для изменения размера шрифта кнопки:
Пример
.button1 {font-size: 10px;}
.button2 {font-size: 12px;}
.button3
{font-size: 16px;}
.button4 {font-size: 20px;}
.button5 {font-size: 24px;}
Используйте свойство padding для изменения заполнения кнопки:
Пример
.button1 {padding: 10px
24px;}
.button2 {padding: 12px 28px;}
.button3 {padding: 14px 40px;}
.button4 {padding: 32px 16px;}
.button5 {padding: 16px;}
Закругленные кнопки
Используйте свойство border-radius для добавления скругленных углов к кнопке:
Пример
.button1 {border-radius: 2px;}
.button2 {border-radius: 4px;}
.button3
{border-radius: 8px;}
.button4 {border-radius: 12px;}
.button5 {border-radius: 50%;}
Цветные границы кнопок
Используйте свойство border, чтобы добавить цветную рамку к кнопке:
Пример
.button1 {
background-color: white;
color: black;
border: 2px solid #4CAF50; /* Green */
}
…
Наведите кнопки
Используйте селектор :hover для изменения стиля кнопки при наведении на нее указателя мыши.
Совет: Используйте свойство transition-duration для определения скорости эффекта «Hover»:
Пример
.button {
-webkit-transition-duration: 0.4s; /* Safari */
transition-duration: 0.4s;
}
.button:hover {
background-color: #4CAF50; /* Green */
color: white;
}
…
Кнопки теней
Use the box-shadow property to add shadows to a button:
Пример
.button1 {
box-shadow: 0 8px 16px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.2), 0 6px 20px 0
rgba(0,0,0,0.19);
}
.button2:hover {
box-shadow: 0 12px
16px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.24), 0 17px 50px 0 rgba(0,0,0,0.19);
}
Отключенные кнопки
Используйте свойство opacity для добавления прозрачности к кнопке (создает «отключенный» вид).
Совет: Вы также можете добавить свойство cursor со значением «not-allowed», которое будет отображать «нет парковки знак» при наведении указателя мыши на кнопку:
Пример
.disabled {
opacity: 0.6;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
Ширина кнопки
По умолчанию размер кнопки определяется по ее текстовому содержимому (так же широко, как и ее содержимое). Используйте свойство width для изменения ширины кнопки:
Пример
.button1 {width: 250px;}
.button2 {width: 50%;}
.button3 {width:
100%;}
Группы кнопок
Удалите поля и добавьте float:left к каждой кнопке, чтобы создать группу кнопок:
Пример
.button {
float: left;
}
Группа кнопок на границе
Используйте свойство border для создания группы кнопок с рамками:
Пример
.button {
float: left;
border: 1px
solid green;
}
Вертикальная группа кнопок
Используйте display:block вместо float:left для группирования кнопок ниже друг друга, вместо того, чтобы бок о бок:
Пример
.button {
display: block;
}
Кнопка на картинке
Анимированные кнопки
Пример
Добавить стрелку на наведении:
Пример
Добавить «нажатия» эффект на кнопку:
Пример
Исчезать при наведении:
Пример
Добавить эффект «рябь» при щелчке:
Стилизация ссылок и кнопок на примере разных сайтов с поддержкой разными состояний – наведение курсора, нажатие, попадание в фокус и заблокированное состояние элемента.
1
Скругленная кнопка
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 25px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #fff;
border-radius: 50px;
height: 46px;
line-height: 46px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 600;
text-decoration: none;
color: #444;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgb(65 132 144 / 10%), 0 1px 3px rgb(0 0 0 / 8%);
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
vertical-align: top;
transition: box-shadow 0.2s;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
border: 1px solid #4c51f9;
outline: none;
}
.btn:hover {
transition: all 0.2s;
box-shadow: 0 7px 14px rgb(65 132 144 / 10%), 0 3px 6px rgb(0 0 0 / 8%);
}
.btn:active {
background-color: #808080;
}
.btn:disabled {
background-color: #eee;
border-color: #eee;
color: #444;
cursor: not-allowed;
}CSS
Результат:
2
Двойная рамка
<a class="btn" href="##"><span>Link</span></a>
<button class="btn"><span>Button</span></button>
<button class="btn" disabled><span>Disabled</span></button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 1px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #F18230;
border-radius: 25px;
height: 46px;
line-height: 0;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #fff;
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
vertical-align: top;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn span {
display: block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 25px;
height: 42px;
line-height: 38px;
border: 1px solid #F18230;
border-radius: 25px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #FFFFFF;
background: linear-gradient(180deg, rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.25) 0%, rgba(255, 255, 255, 0) 100%), #F18230;
text-align: center;
font-weight: 600;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:hover span {
background-color: #fba768
}
.btn:active span {
background-color: #c17237 !important;
}
.btn:disabled {
opacity: 0.65;
pointer-events: none;
}CSS
Результат:
3
Yahoo
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 20px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
height: 32px;
line-height: 32px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #3775dd;
box-shadow: 0 2px #21487f;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
vertical-align: top;
}
.btn:hover {
background-color: #002fed;
}
.btn:active {
background-color: #2f599e !important;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:disabled {
background-color: #6c87b5;
pointer-events: none;
}CSS
Результат:
4
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
const buttons = document.querySelectorAll(".btn");
buttons.forEach((button) => {
button.onclick = function(e){
let x = e.clientX - e.target.offsetLeft;
let y = e.clientY - e.target.offsetTop;
let ripple = document.createElement("span");
ripple.style.left = `${x}px`;
ripple.style.top = `${y}px`;
this.appendChild(ripple);
setTimeout(function(){
ripple.remove();
}, 600);
}
});JS
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #1a73e8;
position: relative;
overflow:hidden;
vertical-align: top;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
z-index: 1;
}
.btn span{
position: absolute;
background: #fff;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
border-radius: 50%;
pointer-events: none;
animation: btn_ripples 0.6s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes btn_ripples {
0% {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
opacity: 0.5;
}
100% {
width: 1000px;
height: 1000px;
opacity: 0;
}
}
.btn:hover {
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgb(26 115 232 / 45%), 0 1px 3px 1px rgb(26 115 232 / 30%);
background-color: #297be6;
}
.btn:active {
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgb(26 115 232 / 45%), 0 2px 6px 2px rgb(26 115 232 / 30%);
background-color: #1a73e8 !important;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}CSS
Результат:
5
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>
<a class="btn-2" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn-2" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn-2">Button</button>
<button class="btn-2" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 24px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 3px;
height: 37px;
line-height: 37px;
font-size: 14px;
text-transform: uppercase;
font-weight: normal;
text-decoration: none;
color: #07bc4c;
background-color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
transition: box-shadow .18s ease-out,background .18s ease-out,color .18s ease-out;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:hover {
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px 0 #cfcfcf, 0 2px 5px 0 #cfcfcf;
}
.btn:active {
background-color: #efefef !important;
}
.btn:disabled {
background-color: #eee;
color: #444;
pointer-events: none;
}
.btn-2 {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 24px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 3px;
height: 37px;
line-height: 37px;
font-size: 14px;
text-transform: uppercase;
font-weight: normal;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #05cd51;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
transition: box-shadow .18s ease-out,background .18s ease-out,color .18s ease-out;
}
.btn-2:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn-2:hover {
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px 0 #cfcfcf, 0 2px 5px 0 #cfcfcf;
}
.btn-2:active {
background-color: #058c38 !important;
}
.btn-2:disabled {
background-color: #aed2bc;
color: #444;
pointer-events: none;
}CSS
Результат:
6
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 20px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 6px;
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
font-size: 17px;
font-weight: 600;
text-decoration: none;
color: #385898;
background-color: #e7f3ff;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 2px #666;
}
.btn:hover {
background-color: #DBE7F2;
}
.btn:active {
transform: scale(0.96);
}
.btn:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}CSS
Результат:
7
Вконтакте
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>
<a class="btn-2" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn-2" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn-2">Button</button>
<button class="btn-2" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 16px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
font-size: 12.5px;
font-weight: normal;
text-decoration: none;
vertical-align: top;
color: #55677d;
background-color: #dfe6ed;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
overflow: hidden;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:hover {
opacity: 0.88;
}
.btn:active {
line-height: 32px;
}
.btn:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}
.btn-2 {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 16px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
font-size: 12.5px;
font-weight: normal;
text-decoration: none;
vertical-align: top;
color: #fff;
background-color: #5181b8;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
overflow: hidden;
}
.btn-2:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn-2:hover {
opacity: 0.88;
}
.btn-2:active {
line-height: 32px;
}
.btn-2:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}CSS
Результат:
8
Habr
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>
<a class="btn-2" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn-2" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn-2">Button</button>
<button class="btn-2" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 13px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #a4afba;
border-radius: 3px;
height: 32px;
line-height: 32px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
text-decoration: none;
color: #838a92;
background-color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn:hover {
border-color: #65a3be;
color: #4e879c;
}
.btn:active {
border-color: #78a2b7 !important;
color: #3a728b !important;
}
.btn:disabled {
background-color: #eee;
color: #444;
pointer-events: none;
}
.btn-2 {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 13px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 3px;
height: 32px;
line-height: 32px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #65a3be;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn-2:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px lightskyblue;
}
.btn-2:hover {
border-color: transparent;
background-color: #4986a1;
color: #fff;
}
.btn-2:active {
border-color: #6f9cbc !important;
background-color: #367089 !important;
}
.btn-2:disabled {
background-color: #558cb7;
color: #fff;
pointer-events: none;
}CSS
Результат:
9
Bootstrap
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>
<a class="btn-2" href="##">Link</a>
<input class="btn-2" type="button" value="Input">
<button class="btn-2">Button</button>
<button class="btn-2" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
.btn {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #6c757d;
border-radius: 5px;
height: 38px;
line-height: 38px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 600;
text-decoration: none;
color: #6c757d;
background-color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn:focus {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgb(108 117 125 / 50%);
}
.btn:hover {
color: #fff;
background-color: #6c757d;
border-color: #6c757d;
}
.btn:active {
color: #fff;
background-color: #6c757d;
border-color: #6c757d;
}
.btn:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}
.btn-2 {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 0 15px;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #7952b3;
border-radius: 5px;
height: 38px;
line-height: 38px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 600;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
background-color: #7952b3;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn-2:focus {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgb(121 82 179 / 25%);
}
.btn-2:hover {
background-color: #61428f;
border-color: #61428f;
}
.btn-2:active {
background-color: #61428f !important;
border-color: #61428f !important;
}
.btn-2:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
opacity: 0.65;
}CSS
Результат:
10
<a class="btn" href="##">Link</a>
<button class="btn">Button</button>
<button class="btn" disabled>Disabled</button>HTML
body {
padding: 15px 0;
}
.btn {
text-decoration: none;
color: #6b5770;
background-image: linear-gradient(90deg, #fd7f34, #bd155b);
display: inline-block;
padding: 14px 30px;
border: 1px solid;
position: relative;
z-index: 0;
border-radius: 5px;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0 15px 15px 0;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
appearance: none;
touch-action: manipulation;
}
.btn:before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
left: -2px;
top: -2px;
width: calc(100% + 4px);
height: calc(100% + 4px);
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #fd7f34, #bd155b);
z-index: -2;
transition: .4s;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.btn:after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #fff, #fff);
z-index: -1;
transition: .4s;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn:hover {
color: #fff;
transition: .3s;
}
.btn:hover:after {
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #fd7f34, #bd155b);
}
.btn:active:after {
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #d96d2d, #760f3a);
}
.btn:focus-visible {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px #fd7f34;
}
.btn:disabled {
pointer-events: none;
}
.btn:disabled:before {
filter: grayscale(100%);
}CSS
Результат:
От автора: кнопки – самые важные компоненты любой веб-страницы, они могут принимать множество различных состояний и функций, которые должны подходить под предыдущее дизайнерское решение. В этой статье мы расскажем про три способа проектирования кнопок, а также покажем специальные CSS инструменты и код, дабы помочь начинающим разработчикам научиться создавать кнопки.
Сначала нам нужно освежить в памяти парочку основных моментов по CSS кнопкам. То, что вы понимаете разницу между Flat UI и Material Design, не имеет смысла, если вы не знаете, какие компоненты CSS нужно менять. Быстренько пробежимся по основам CSS кнопок.
Основы CSS кнопок
Для всех сайтов хорошая кнопка это понятие субъективное, но существует парочка общих нетехнических стандартов:
Доступность – Самое важное. Люди с ограниченными возможностями и старыми браузерами должны иметь простой доступ к кнопкам. Открытость интернета для всех и каждого это прекрасно, не разрушайте ее своим ленивым кодом.
Простой текст – Внутри кнопок пишите простой и короткий текст. Пользователи должны сразу понять назначение кнопки и куда она их приведет.
Практический курс по верстке адаптивного сайта с нуля!
Изучите курс и узнайте, как верстать современные сайты на HTML5 и CSS3
Узнать подробнее
Почти все кнопки, которые вы видите в интернете, используют какие-либо смены цветов, рамок и теней. Сделать это можно через различные CSS псевдоклассы. Мы остановимся на двух, :hover и :active. Псевдокласс :hover отвечает за поведение CSS при наведении курсора мыши над объектом. :active по большей части выполняется в момент, когда пользователь нажал кнопку мыши, но еще ее не отпустил.
С помощью псевдоклассов можно полностью изменить внешний вид кнопки, но это не user-friendly подход. Новичкам хорошо добавлять небольшие изменения в основные стили кнопки, почти полностью сохраняя ее внешний вид. В кнопках можно выделить 3 основные момент – цвет, тени и время перехода.
Основной момент 1 – Цвет
Данный параметр меняют чаще всего. Сменить цвет можно с помощью различных свойств, самые простые color, background-color и border. Перед показом примеров давайте разберем, как выбрать цвет кнопки:
Комбинации цветов – Используйте дополняющие друг друга цвета. Colorhexa – замечательный инструмент, там вы сможете найти сочетающиеся цвета. Если вы еще ищите цвета, загляните на Flat UI color picker.
Соблюдайте цвета палитры – Соблюдать цветовую палитру – хорошая практика. Если вы ищите палитры цветов, зайдите на lolcolors.
Основной момент 2 – Тени
С помощью box-shadow объекту можно добавить тень. Каждой стороне можно создать свою собственную тень. Идея реализована как в обоих дизайнах Flat UI и Material Design. Более подробно о свойстве box-shadow можно почитать на MDN box-shadow docs.
Основной момент 3 – Время плавного перехода
Свойство transition-duration добавляет к вашим CSS изменениям временную шкалу. В кнопке без времени плавного перехода стили моментально меняются на стили псевдокласса :hover, что может оттолкнуть пользователя. В этом руководстве много кнопок используют время перехода для того, чтобы кнопки выглядели натуральнее. В примере ниже в состоянии :hover стили кнопки меняются медленно (за 0.5 секунды):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
.color—change { border—radius: 5px; font—size: 20px; padding: 14px 80px; cursor: pointer; color: #fff; background—color: #00A6FF; font—size: 1.5rem; font—family: ‘Roboto’; font—weight: 100; border: 1px solid #fff; box—shadow: 2px 2px 5px #AFE9FF; transition—duration: 0.5s; —webkit—transition—duration: 0.5s; —moz—transition—duration: 0.5s; } .color—change:hover { color: #006398; border: 1px solid #006398; box—shadow: 2px 2px 20px #AFE9FF; } |
А смотрится это так:
Код для плавных переходов сложный, и старые браузеры немного по-разному выполняют анимацию. Поэтому нам нужно добавить вендорные префиксы для старых браузеров:
|
transition—duration: 0.5s /* Обычная запись, работает во всех современных браузерах */ —webkit—transition—duration: 0.5s; /* Помогает некоторым версиям safari, chrome и android */ —moz—transition—duration: 0.5s; /* для firefox */ |
Есть множество сложных и интересных способов изменять поведение свойства transition, демо выше лишь показали основные моменты.
Три стиля кнопок
1 – Простые черные и белые
Обычно, такие кнопки я добавляю в первую очередь в свои сторонние проекты, так как они просто работают с множеством различных стилей. Данный стиль работает на контрасте черного и белого. Оба варианта одинаковы, поэтому мы рассмотрим код только для черной кнопки с белым фоном. Чтобы перекрасить кнопку в другой цвет, просто поменяйте все white и black местами.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
.suit_and_tie { color: white; font—size: 20px; font—family: helvetica; text—decoration: none; border: 2px solid white; border—radius: 20px; transition—duration: .2s; —webkit—transition—duration: .2s; —moz—transition—duration: .2s; background—color: black; padding: 4px 30px; } .suit_and_tie:hover { color: black; background—color: white; transition—duration: .2s; —webkit—transition—duration: .2s; —moz—transition—duration: .2s; } |
В стилях выше видно, что свойства font и background-color меняют свои значения со свойством transition-duration: .2s. Это простой пример. Вы можете взять цвета своих любимых брендов и создать свою кнопку. Цвета брендов можно найти на BrandColors.
2- Кнопки Flat UI
Flat UI делает упор на минимализм – больше действий, меньше движений. Как правило, я перехожу с просто черно-белых кнопок на Flat UI, когда проект начинает обретать форму. Кнопки Flat UI имеют минималистичный вид и подходят под большинство дизайнов. Исправим нашу кнопку сверху и добавим ей движения, имитируя 3D эффект.
В демо пять кнопок, но так как у всех меняется только цвет, мы рассмотрим первую.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
.turquoise { margin—right: 10px; width: 100px; background: #1abc9c; border—bottom: #16a085 3px solid; border—left: #16a085 1px solid; border—right: #16a085 1px solid; border—radius: 6px; text—align: center; color: white; padding: 10px; float: left; font—size: 12px; font—weight: 800; } .turquoise:hover { opacity: 0.8; } .turquoise:active { width: 100px; background: #18B495; border—bottom: #16a085 1px solid; border—left: #16a085 1px solid; border—right: #16a085 1px solid; border—radius: 6px; text—align: center; color: white; padding: 10px; margin—top: 3px; float: left; } |
Практический курс по верстке адаптивного сайта с нуля!
Изучите курс и узнайте, как верстать современные сайты на HTML5 и CSS3
Узнать подробнее
У кнопки 3 состояния: обычное (без состояния), :hover и :active. Обратите внимание, что состояние :hover содержит всего одну строку с уменьшением прозрачности. Полезный трюк – кнопка становится чуть светлее, и вам не нужно подбирать более светлый цвет.
Переменные в CSS уже не самая новая функция, но некоторые из них тут используются по-другому. Вместо того, чтобы указать сплошную рамку border, тут указываются свойства border-bottom, border-left и border-right, которые создают 3D эффект глубины. Псевдокласс :active часто используется в Flat UI. Когда наша кнопка становится :active происходит 2 вещи:
:border-bottom меняется с 3px до 1px. Тень под кнопкой уменьшается, а кнопка опускается на пару пикселей. Вроде бы просто, но так пользователь чувствует, что он «вдавил» кнопку в страницу.
Изменение цвета. Фон темнеет, имитируя смещение кнопки от пользователя к экрану. И опять, такой простой эффект показывает пользователю, что он нажал кнопку.
Во Flat UI ценятся простые и минималистичные движения кнопок, «рассказывающие большую историю». Многие имитирует сдвиг кнопки с помощью :border-bottom. Стоит также сказать, что во Flat UI есть кнопки, которые вообще не двигаются, а только лишь меняют цвет.
3 — Material Design
Material Design – стиль дизайна, который продвигает идею передачи информации в виде карточек с различной анимацией для привлечения внимания. Material Design создал Google, на странице Material Design Homepage они описали 3 основных принципа:
Слово Материальный не переводится буквально, это метафора
Монотонность, графика, агрессивность
Значение передается при помощи движений
Чтобы лучше понять 3 этих принципа, взгляните на демо MD ниже:
Эти кнопки используют две основные идеи – свойство box-shadow и Polymer. Polymer – фреймворк компонентов и инструментов для создания, упрощающий процесс проектирования веб-сайтов. Если вы работали с Bootstrap, Polymer не сильно отличается. Эффект распространяющейся волны на кнопках выше добавляется всего одной строкой кода.
|
<div class=«button»> <div class=«center» fit>SUBMIT</div> <paper—ripple fit></paper—ripple> /*вот эта строка добавляет эффект */ </div> |
<paper-ripple fit></paper-ripple> — компонент Polymer. Подключив фреймворк в самом начале HTML кода, мы получаем доступ к его компонентам. Подробнее ознакомиться можно на домашней странице Polymer project. Мы разобрались с тем, что такое polymer, и как получить эффект волны (как он работает это тема для другой статьи), теперь поговорим о CSS коде, который с помощью эффекта подпрыгивания исполняет описанные выше принципы.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
body { background—color: #f9f9f9; font—family: RobotoDraft, ‘Helvetica Neue’; } /* Кнопка */ .button { display: inline—block; position: relative; width: 120px; height: 32px; line—height: 32px; border—radius: 2px; font—size: 0.9em; background—color: #fff; color: #646464; margin: 20px 10px; transition: 0.2s; transition—delay: 0.2s; box—shadow: 0 2px 5px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26); } .button:active { box—shadow: 0 8px 17px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2); transition—delay: 0s; } /* Прочее */ .button.grey { background—color: #eee; } .button.blue { background—color: #4285f4; color: #fff; } .button.green { background—color: #0f9d58; color: #fff; } .center { text—align: center; } |
Во всех дизайнах кнопок выше используется свойство box-shadow. Давайте удалим весь неменяющийся CSS код и посмотрим, как box-shadow изменяется и вообще работает:
|
.button { transition: 0.2s; transition—delay: 0.2s; box—shadow: 0 2px 5px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26); } .button:active { transition—delay: 0s; box—shadow: 0 8px 17px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2); } |
Свойство box-shadow используется для добавления тонкой темной тени слева и снизу у каждой кнопки. По клику тень немного увеличивается и становится светлее – имитируется эффект 3D тени под кнопкой, когда кнопка как бы подпрыгивает от страницы к пользователю. Это движение прописано в стилях Material Design и его принципах. Кнопки в стиле Material Design можно создать с помощью Polymer и box-shadow эффектов.
Слово материальный – метафора – с помощью свойства box-shadow мы имитируем эффект 3D тени, создаем аналог настоящей тени.
Монотонность, графика, агрессивность – больше относится к ярко-голубым и зеленым кнопкам и к остальным, соблюдающим данный принцип.
Значение передается при помощи движений – С помощью Polymer и анимации свойства box-shadow мы можем создавать множество различных движений, когда пользователь кликает на кнопку.
В статье описано, как создавать кнопки по трем разным методологиям. Если вы хотите спроектировать свой собственный дизайн кнопок, рекомендую воспользоваться сервисом CSS3 Button Generator.
В заключение
Черно-белые кнопки довольно просты и понятны. Измените цвета на цвета ваших любимых брендов и вы получите кнопки для вашего сайта. Flat UI кнопки тоже простые: маленькие движения и цвета «рассказывают большую историю». Material Design для привлечения внимания пользователей имитирует крупномасштабные сложные движения, как реальная тень.
Надеюсь, это руководство помогло новичкам в CSS разобраться со строительными кирпичиками, которые делают кнопки популярными и очень мощными компонентами веб-страницы.
Редакция: Jack Rometty
Источник: //www.sitepoint.com/
Редакция: Команда webformyself.
Практический курс по верстке адаптивного сайта с нуля!
Изучите курс и узнайте, как верстать современные сайты на HTML5 и CSS3
Узнать подробнее
PSD to HTML
Практика верстки сайта на CSS Grid с нуля
Смотреть
Styled buttons help you create cool websites. There are a lot of styles that you can apply to the buttons. Here is the guide to styling buttons.
At first, create a <button> element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Styling Buttons</title>
</head>
<body>
<button type="button">Submit</button>
</body>
</html>So, it is time to apply styles to your button. Let’s do it step by step.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Styling Buttons</title>
<style>
button {
display: inline-block;
background-color: #7b38d8;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button type="button">Submit</button>
</body>
</html>We’re starting by adding these styles:
- display: inline-block to enable the ability to add width and height to our button
- background-color: #7b38d8 a fancy background color for the button
- padding: 20px makes a bit more room for our button in all four sides
- width: 200px gives a 200px width
- color: #ffffff makes our Submit text white
- text-align: center; puts our text in the center
Let’s see what we’ve got so far:
Now, we’re going to round our borders and use the border property. Also, let’s make our text a bit larger. So add these lines to the code:
button {
display: inline-block;
background-color: #7b38d8;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
border: 4px double #cccccc; /* add this line */
border-radius: 10px; /* add this line */
font-size: 28px; /* add this line */
}Here’s the result
Much better, right?
Let’s add cursor: pointer to have the handicon while bringing our cursor to the button and give it a bit margin of 5px, so :
button {
display: inline-block;
background-color: #7b38d8;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
border: 4px double #cccccc;
border-radius: 10px;
font-size: 28px;
cursor: pointer; /* add this line */
margin: 5px; /* add this line */
}Here’s the updated result, try to move your cursor towards the button!
You need to be aware of a tiny difference here. In the previous example, when we move the cursor to the Submit text, it’ll be turned to a hand. But now the whole button will turn to a hand as soon as we move the mouse towards it!
3. Style the hover state
Your third step is to style the hover state to give visual feedback to the user when the button’s state changes.
button:hover {
background-color: green;
}Here’s the result, but we have a problem!
Changing the colour on hover is too fast, and it’s not so pleasant!
So let’s add transition and be careful that we have to use it in the button element, not in its hover state.
button {
display: inline-block;
background-color: #7b38d8;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
border: 4px double #cccccc;
border-radius: 10px;
font-size: 28px;
cursor: pointer;
margin: 5px;
-webkit-transition: all 0.5s; /* add this line, chrome, safari, etc */
-moz-transition: all 0.5s; /* add this line, firefox */
-o-transition: all 0.5s; /* add this line, opera */
transition: all 0.5s; /* add this line */
}
button:hover {
background-color: green;
}I like it! So much better!
Now, as the last step, let’s add functionality to our beautiful button. We want to open an alert whenever clicking on this button.
So click on the button below, and let’s greet!
We just used onclick event of javascript and alert something on the screen after clicking the button!
<button type="button" onclick="alert('Hi from W3Docs!')">Submit</button>Now let’s see an interesting example using the <button> element.
Example of styling a button created with the <button> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
button {
display: inline-block;
background-color: #7b38d8;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 4px double #cccccc;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
padding: 20px;
width: 200px;
transition: all 0.5s;
cursor: pointer;
margin: 5px;
}
button span {
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
transition: 0.5s;
}
button span:after {
content: '0bb';
position: absolute;
opacity: 0;
top: 0;
right: -20px;
transition: 0.5s;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #f7c2f9;
}
button:hover span {
padding-right: 25px;
}
button:hover span:after {
opacity: 1;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Style buttons</h2>
<button>
<span>Submit</span>
</button>
</body>
</html>The codes you see here are similar to what we’ve done in the previous example.
Here, we used a span tag inside of the button. We can later use the :after pseudo-class to create a creative hover effect.
We’ll place the arrow sign » on our button, which will show it on the hover effect of the mouse, with a smooth transition.
Here’s the essential part of the above code:
button span:after {
content: "0bb"; /* HTML code of » sign */
position: absolute; /* its parent (button) is relative */
opacity: 0;
top: 0;
right: -20px;
transition: 0.5s;
}Here’s the result:
Example of styling a button created with the <span> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
body {
background: #560059;
color: #eeeeee;
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 16px;
}
.wrapper {
margin: 80px auto;
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
position: relative;
}
.button {
padding: 15px 100px;
margin: 10px 4px;
color: #ffffff;
font-family: sans-serif;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid;
}
.button::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
display: block;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
z-index: -1;
-webkit-transform: scaleY(0.1);
transform: scaleY(0.1);
transition: all 0.4s;
}
.button:hover {
color: #b414ba;
}
.button:hover::before {
opacity: 1;
background-color: #f7c2f9;
-webkit-transform: scaleY(1);
transform: scaleY(1);
transition: -webkit-transform 0.6s cubic-bezier(0.08, 0.35, 0.13, 1.02), opacity 0.4s;
transition: transform 0.6s cubic-bezier(0.08, 0.35, 0.13, 1.02), opacity;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<span class="button">Button 1</span>
<span class="button">Button 2</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>The code above is the final code, and you can see the result in the «Try it Yourself» section.
Now let’s break down the code and explain the tricky parts to make you understand it well. We explain that parts in snippets below as comments in front of each line.
We applied some general styles on body, and then we have a wrapper class which acts like a wrapper parent for two tags which in this example will be treated like buttons.
You can read the comments below for more explanation.
.button::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
display: block;
width: 100%; /* use 100% width of the button */
height: 100%; /* use 100% height of the button */
z-index: -1; /* make the hover effect behind the text in the button */
-webkit-transform: scaleY(0.1); /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transform: scaleY(0.1); /* move the hover effect a bit in Y axis*/
transition: all 0.4s;
}
.button:hover {
color: #b414ba;
}
.button:hover::before {
opacity: 1;
background-color: #f7c2f9;
-webkit-transform: scaleY(1); /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transform: scaleY(1); /* move the hover effect a bit in Y axis*/
transition: -webkit-transform 0.6s cubic-bezier(0.08, 0.35, 0.13, 1.02), opacity 0.4s; /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transition: transform 0.6s cubic-bezier(0.08, 0.35, 0.13, 1.02), opacity;
}Example of styling a button created with the <a> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
body {
background: #3b0044;
color: #6098ff;
font-family: sans-serif;
font-size: 16px;
}
.wrapper {
margin: 80px auto;
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
position: relative;
}
.button {
padding: 15px 100px;
margin: 10px 4px;
color: #ffffff;
font-family: sans-serif;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
}
.button {
border: 1px solid transparent;
-webkit-transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1);
transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1);
}
.button::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
bottom: 0px;
z-index: -1;
width: 0%;
height: 1px;
background: #003177;
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 0px #b6cdef;
display: block;
-webkit-transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1);
transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1);
}
.button:hover::before {
width: 100%;
}
.button::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
top: 0px;
z-index: -1;
width: 0%;
height: 1px;
background: #a9c1e8;
-webkit-transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.7, 0.25, 0, 1);
transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.7, 0.25, 0, 1);
}
.button:hover::after {
width: 100%;
}
.button:hover {
border-left: 1px solid #b6cdef;
border-right: 1px solid #6098ff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<a href="#" class="button">Button 1</a>
<a href="#" class="button">Button 2</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>Let’s learn what happens here in the essential parts of the code.
.button::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
bottom: 0px;
z-index: -1; /* make it behind the button */
width: 0%; /* first let it to be 0% of width */
height: 1px;
background: #003177;
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 0px #b6cdef;
display: block;
-webkit-transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1); /* code for webkit engine browsers like safari and chrome */
transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.5, 0.24, 0, 1); /* add transition for the width change to be smooth */
}
.button:hover::before {
width: 100%; /* then on the hover effect, bring the width higher up to 100% */
}Example of styling the <button> element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
.container {
position: absolute;
top: 10%;
}
.button {
border: none;
display: block;
text-align: center;
cursor: pointer;
text-transform: uppercase;
outline: none;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: 600;
font-size: 15px;
background-color: #153f00;
padding: 15px 50px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.button span {
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
}
.button:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
height: 470%;
width: 140%;
background: #52b71f;
-webkit-transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
transition: all .5s ease-in-out;
-webkit-transform: translateX(-100%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
transform: translateX(-100%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
}
.button:hover:after {
-webkit-transform: translateX(-9%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
transform: translateX(-9%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Style button</h2>
<div class="container">
<button type="button" class="button">
<span>Hover!</span>
</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>Let’s break down the tricky parts of the code!
But before that, please note that these examples just give you a hint or a whole idea of being creative with buttons to build or use on your web journey!
The best way to understand them is to open it in the demo section (Try it Yourself!) and play with the properties or have it in your code editor and check them.
We give you the hints and necessary tips and explanations that you may need along the way to understand it better.
So with that being said, let’s explain some essential parts of the above code:
.button {
border: none;
display: block;
text-align: center;
cursor: pointer;
text-transform: uppercase;
outline: none; /* removes the default outline of button element */
overflow: hidden; /* hidden the part that's outside of the container div */
position: relative;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: 600;
font-size: 15px;
background-color: #153f00;
padding: 15px 50px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.button span {
position: relative;
z-index: 1; /* bring it in front of the button */
}
.button:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
height: 470%; /* change the value in demo to see the difference */
width: 140%; /* change the value in demo to see the difference */
background: #52b71f;
-webkit-transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out; /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
-webkit-transform: translateX(-100%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg); /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transform: translateX(-100%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
}
.button:hover:after {
-webkit-transform: translateX(-9%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg); /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
transform: translateX(-9%) translateY(-25%) rotate(45deg);
}Example of styling some <button> elements:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
body {
font-size: 60%;
background: #00abb7;
}
.container {
padding: 50px;
}
button,
button::after {
-webkit-transition: all 0.3s;
-moz-transition: all 0.3s;
-o-transition: all 0.3s;
transition: all 0.3s;
}
button {
background: none;
border: 4px solid #fff;
border-radius: 10px;
color: #ffffff;
display: block;
font-size: 1.6em;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 10px auto;
padding: 2em 6em;
position: relative;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
button::before,
button::after {
background: #fff;
content: "";
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
}
button:hover {
color: #29f2e4;
}
.button1::after {
height: 0;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
}
.button1:hover:after {
height: 100%;
}
.button2::after {
height: 100%;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 0;
}
.button2:hover:after {
width: 100%;
}
.button3::after {
height: 0;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
width: 0;
}
.button3:hover:after {
height: 100%;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<button type="button" class="button1">Button 1</button>
<button type="button" class="button2">Button 2</button>
<button type="button" class="button3">Button 3</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>And here’s another example, let’s explain some tricky parts of it down below:
button,
button::after {
-webkit-transition: all 0.3s; /* for webkit engine browsers like chrome and safari */
-moz-transition: all 0.3s; /* for moz engine browsers like firefox */
-o-transition: all 0.3s; /* for opera browser */
transition: all 0.3s;
}
button::before,
button::after {
background: #fff;
content: "";
position: absolute;
z-index: -1; /* make it behind its container */
}Example of styling a button created with the <input> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
input {
padding: 15px 100px;
margin: 10px 4px;
cursor: pointer;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
}
input:hover {
opacity: 0.5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Button" />
</body>
</html>This example is pretty straight forward!
We just added a hover effect with the opacity of 0.5 , which is a simple but a good practice in web development world.
Thanks fro joining us, and hope to see you again soon!