Если у вас сайт на PHP, даже самый простой, время от времени в его скриптах могут возникать ошибки. Это может привести к различным неприятным последствиям, от некорректной работы некоторых компонентов сайта (например, формы обратной связи), до недоступности сайта целиком. Как самостоятельно распознать тип ошибки PHP и понять, что с ней делать дальше?
Этот материал поможет вам, во-первых, самостоятельно оценить ситуацию (и, возможно, даже решить ее), а во-вторых, точно ускорит диагностику и решение проблемы при обращении в службу поддержки. Самые ценные советы по устранению наиболее частых ошибок PHP, связанных с лимитами оперативной памяти, вы найдете в конце статьи.
Как обнаружить ошибку PHP на сайте
1. Встроенными средствами браузера
Итак, если на сайте вместо привычной страницы ничего не отображается (вы видите “пустую страницу”), то, вероятнее всего, в одном из скриптов возникла ошибка. В этом можно убедиться, воспользовавшись встроенными «Инструментами разработчика» вашего браузера. В каждом браузере они могут называться немного по-разному, но суть от этого не меняется.
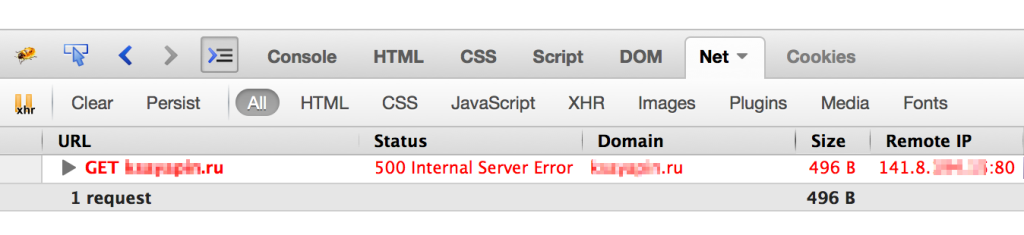
Например, в браузере Google Chrome это вкладка Dev Tools (или «Инструменты разработчика»). В Mozilla Firefox — это расширение Firebug (его нужно установить отдельно в меню Adds On) или же вкладка Developer.
Внутри «Инструментов разработчика» нас интересует вкладка, которая называется Network (или Net, или каким-то похожим образом).
Если на странице сайта присутствует ошибка, в этой вкладке вы увидите код ответа 500 (“Internal Server Error”).
2. Если вывод сообщений об ошибках в браузер отключен
Случается, что вывод сообщений об ошибках в браузер отключён. Чтобы сообщение об ошибке отображалось в браузере, достаточно добавить в файл .htaccess в корневой директории сайта следующую строку:
php_value display_errors on
Файл .htaccess вы найдете по адресу: /home/login/domains/domain.ru/public_html/, где вместо login следует подставить логин вашего аккаунта, а вместо domain.ru — домен вашего сайта.
После сохранения файла .htaccess и обновления страницы вы сможете увидеть ошибку.
Если сайтом используется, например, CMS WordPress, то отображение ошибок можно также включить, заменив в файле wp-config.php:
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, false);
на:
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, true);
3. С помощью журнала ошибок PHP
Иногда по различным причинам отображать ошибки в браузере нежелательно. В этом случае лучше всего сохранять их в какой-нибудь файл, например errors.log — журнал ошибок PHP. Для этого достаточно в файле .htaccess добавить следующую строку:
php_value error_log /home/login/domains/domain.ru/log/errors.log
Здесь /home/login/domains/domain.ru/log/errors.log — это полный путь до файла, в который будут записываться ошибки PHP (если файла с таким именем нет, он будет создан автоматически при появлении ошибки).
Теперь, если мы снова зайдем на сайт с ошибкой (либо обновим страницу с ошибкой), то в errors.log будут записаны сообщения об ошибках.
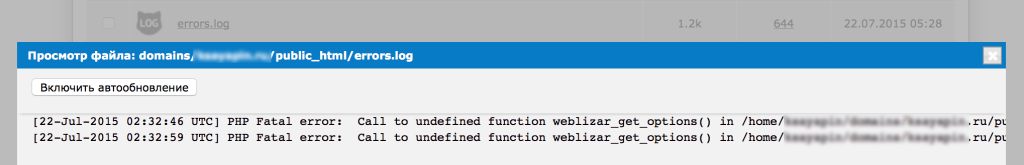
Журнал ошибок PHP можно просмотреть, например, с помощью файлового менеджера в Панели управления, открыв файл errors.log:
Также можно открыть файл с ошибками и нажать кнопку “Включить автообновление”. Таким образом, новые записи в журнале можно просматривать в реальном времени.
Расшифровка ошибок PHP
Как правило, в сообщении об ошибке достаточно подробно указано где именно и при выполнении какой части кода она возникла. Например:
Здесь ошибка заключается в следующем:
Fatal error: Call to undefined function weblizar_get_options() in /home/login/domains/domain.ru/public_html/wp-content/themes/enigma/header.php on line 14
“Вызов неопределенной функции weblizar_get_options() в файле используемой на сайте темы enigma”.
Вероятнее всего, был поврежден один из файлов темы, поэтому можно восстановить только директорию темы ./wp-content/themes/enigma/ , а не всего сайта.
Что делать, в зависимости от типа ошибки PHP
Условно ошибки PHP можно разбить на 4 уровня:
- PARSE ERROR
- FATAL ERROR
- WARNING
- NOTICE
Parse Error
Возникают, если уже на этапе проверки кода интерпретатором PHP найдена ошибка. Чаще всего это синтаксические ошибка (например, пропущенная точка с запятой). Скорее всего, такая ошибка возникла в результате последних внесенных на сайт изменений.
Что делать?
1. Если вы НЕ специалист в PHP, восстановите сайт из последней резервной копии на тот момент, когда сайт работал без ошибок.
2. Если вы специалист и самостоятельно вносили правки в код сайта, вы наверняка сможете отследить синтаксическую ошибку и исправить ее. Но проще все же воспользоваться пунктом 1.
Fatal Error и Warning
Возникают, если при выполнении кода какой-то его участок не может быть выполнен (например, попытка открыть несуществующий файл). Разница между 2-ым и 3-им уровнем в том, что при получении “критической ошибки” (FATAL ERROR) выполнение скрипта завершится, а при получении “предупреждения” (WARNING) — нет.
Что делать?
Восстановите сайт из последней доступной резервной копии на тот момент, когда он работал без ошибок.
Notice
К этому уровню ошибок относятся различные “замечания”, суть которых обычно отображена в тексте ошибки.
Что делать?
Если замечание самостоятельно исправить не получается, обратитесь в службу поддержки или же восстановите сайт из последней доступной резервной копии на тот момент, когда он работал без ошибок.
Частые ошибки PHP и их решение
Fatal Error: Allowed Memory
Означает, что для выполнения какой-либо части кода PHP не хватает выделенной оперативной памяти. При этом лимит памяти ограничен какими-то директивами «изнутри» сайта (то есть где-либо в скриптах сайта, либо директивой memory_limit в файле .htaccess). Чтобы исправить это, измените данный лимит в большую сторону, например, в файле .htaccess.
Для этого найдите в .htaccess такую директиву:
php_value memory_limit 128M
Вместо 128M укажите желаемый размер ограничения. Обратите внимание, что символ «M» (латинская M) указывается слитно со значением.
Помните, что есть максимальные значения памяти, отведенной на выполнение скриптов PHP, предусмотенные вашим тарифом хостинга (например, на тарифах виртуального хостинга это 512 Мб, премиум — 1024 Мб). Уточните эти значения у вашего провайдера, если они не указаны явно.
Fatal Error: Out of memory
То же самое, что и предыдущая ошибка, с той разницей, что достигнут лимит памяти, заданный “снаружи”. Обратите внимание на параметр “Памяти на процесс, Мб, не более“ в условиях пользования нашим сервисом.
Для решения вопроса в данном случае, скорее всего, потребуется либо оптимизация скриптов, чтобы они потребляли меньше памяти, либо разбиение процессов на части. Например, объемную загрузку или выгрузку данных, если она упирается в данный лимит, имеет смысл производить частями.
Также в этом случае мы советуем попробовать отключить акселераторы PHP, если они у вас подключены.
Unable to allocate memory for pool
Сайтам на аккаунте не хватает выделенной на тарифном плане памяти для акселераторов PHP.
Для решения проблемы вы можете отключить использование акселераторов в Панели управления хостингом, в разделе «Управление персональным веб-сервером».
Также, например, можно отключить акселератор APC для определенного сайта, добавив в файл .htaccess корневой директории следующую директиву:
php_value apc.cache_by_default off
Обычно имеет смысл оставлять APC для использования на самом посещаемом из ваших сайтов — это позволит использовать именно на нем преимущества акселератора, не заполняя его память данными с других, менее посещаемых сайтов.
В случаях, когда акселератор объективно необходим для корректной и комфортной работы сайтов и его отключение нежелательно, напишите в службу поддержки.
Мы постараемся предложить возможные варианты решения.
Желаем вам приятной работы!
Вчера всё работало, а сегодня не работает / Код не работает как задумано
или
Debugging (Отладка)
В чем заключается процесс отладки? Что это такое?
Процесс отладки состоит в том, что мы останавливаем выполнения скрипта в любом месте, смотрим, что находится в переменных, в функциях, анализируем и переходим в другие места; ищем те места, где поведение отклоняется от правильного.
Важное замечание:
Есть много IDE и редакторов кода, которые позволяют производить отладку. Процесс настройки в них у всех различается. Поэтому стОит обратиться к документации по настройке отладки для непосредственно той среды разработки и той версии, в которой работаете именно ВЫ.
На текущий момент будет рассмотрен пример с PHPStorm 2017.
Подготовка
Для начала необходимо, чтобы в PHP имелась библиотека для отладки под названием xdebug. Если её еще нет, то надо установить.
ВАЖНО! Для очень новых версий PHP (например 8), требуется и новый xdebug, а он, в свою очередь, работает на порту 9003. Не пропустите указание правильного порта в IDE!! (Примерно в разделе PHP -> Debug -> Debug Port . Где точно — зависит от конкретной IDE)
Для WINDOWS:
скачать dll, например на xdebug.org.
Обычно все библиотеки лежат в папке ext внутри папки PHP. Туда и надо поместить dll.
Далее в php.ini прописываем настройки:
[Xdebug]
zend_extension="C:/server/php/ext/php_xdebug.dll" // <!-- тут свой путь до dll!!! Это для среды Windows.
; Для Linux путь должен быть что-то типа zend_extension=/usr/lib/php/20151012/xdebug.so
xdebug.default_enable = 1
xdebug.remote_enable = 1
xdebug.remote_handler = "dbgp"
xdebug.remote_host = "localhost"
xdebug.remote_port = 9000
xdebug.auto_trace = 0
Перезагружаем сервер, на всякий случай.
Для UBUNTU:
-
sudo apt updateИЛИsudo apt-get update -
sudo apt install php-xdebugили если нужнен отладчик для конкретной версии PHP, тоsudo apt install php7.0-xdebugгде7.0указывается версия PHP -
sudo nano /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/xdebug.iniвписываем строки:
zend_extension=/usr/lib/php/20151012/xdebug.so xdebug.remote_autostart = 1 xdebug.remote_enable = 1 xdebug.remote_handler = dbgp xdebug.remote_host = 127.0.0.1 xdebug.remote_log = /tmp/xdebug_remote.log xdebug.remote_mode = reqПримечание: каталог
20151012, скорее всего, будет другим.cdв/usr/lib/phpи проверьте, в каком каталоге в этом формате находится файлxdebug.so, и используйте этот путь.7.0— тоже отличается, в зависимости от того, какая версия у вас используется -
Перезагружаем сервер, на всякий случай.
Теперь если в файле .php написать phpinfo(); то можно будет увидеть в самом низу такую картину:
Открываем PHPStorm
- нажимаем
create project from existing files - выбираем
Web server is installed locally, source files are located under its document root - выбираем папку с файлами, и нажав вверху кнопку «Project Root» помечаем папку как корень проекта
- нажимаем «Next»
- нажимаем Add new local server
- вводим имя сервера любое и
Web Server root URL. В рассматриваемом примере этоhttp://localhost/testy2
- нажимаем «Next» и затем «Finish»
Запуск
Для начала в левой части панели с кодом на любой строке можно кликнуть ЛКМ, тем самым поставив точку останова (breakpoint — брейкпойнт). Это то место, где отладчик автоматически остановит выполнение PHP, как только до него дойдёт. Количество breakpoint’ов не ограничено. Можно ставить везде и много.
Если кликнуть ПКМ и во всплывающем меню выбрать Debug (или в верхнем меню — Run → Debug), то при первом запуске PHPStorm попросит настроить интерпретатор. Т.е. надо выбрать версию PHP из папки, где он лежит, чтобы шторм знал, какую версию он будет отлаживать.
Теперь можно нажать Debug!!!
В данном случае, т.к. функция вызывается сразу на той же странице, то при нажатии кнопки Debug — отладчик моментально вызовет функцию, выполнение «заморозится» на первом же брейкпойнте. В ином случае, для активации требуется исполнить действие, при котором произойдет исполнение нужного участка кода (клик на кнопку, передача POST-запроса с формы с данными и другие действия).
Цифрами обозначены:
- Стэк вызовов, все вложенные вызовы, которые привели к текущему месту кода.
- Переменные. На текущий момент строки ниже номера 3 ещё не выполнились, поэтому определена лишь
$data - Показывает текущие значения любых переменных и выражений. В любой момент здесь можно нажать на
+, вписать имя любой переменной и посмотреть её значение в реальном времени. Например:$dataили$nums[0], а можно и$nums[i]иitem['test']['data'][$name[5]][$info[$key[1]]]и т.д. На текущий момент строки ниже номера 3 ещё не выполнились, поэтому$sumи$outputобозначены красным цветом с надписью «cannot evaluate expression».
Процесс
Для самого процесса используются элементы управления (см. изображение выше, выделено зеленым прямоугольником) и немного из дополнительно (см. изображение выше, выделено оранжевым прямоугольником).
Show Execution Point (Alt+F10) — переносит в файл и текущую линию отлаживаемого скрипта. Например, если файлов много, решили посмотреть что в других вкладках, а потом забыли где у вас отладка 
Step Over (F8) — делает один шаг, не заходя внутрь функции. Т.е. если на текущей линии есть какая-то функция, а не просто переменная со значением, то при клике данной кнопки, отладчик не будет заходить внутрь неё.
Step Into (F7) — делает шаг. Но в отличие от предыдущей, если есть вложенный вызов (например функция), то заходит внутрь неё.
Step Out (Shift+F8) — выполняет команды до завершения текущей функции. Удобно, если случайно вошли во вложенный вызов и нужно быстро из него выйти, не завершая при этом отладку.
Rerun (Ctrl+F5) — перезапускает отладку.
Resume Program(F9) — продолжает выполнение скрипта с текущего момента. Если больше нет других точек останова, то отладка заканчивается и скрипт продолжает работу. В ином случае работа прерывается на следующей точке останова.
Stop (Ctrl+F2) — завершает отладку.
View Breakpoints (Ctrl+Shift+F8) — просмотр всех установленных брейкпойнтов.
Mute Breakpoints — отключает брейкпойнты.
…
Итак, в текущем коде видно значение входного параметра:
$data = "23 24 11 18"— строка с данными через пробел$nums = (4) ["23", "24", "11", "18"]— массив, который получился из входной переменной.
Если нажмем F8 2 раза, то окажемся на строке 7; во вкладках Watches и Variables и в самой странице с кодом увидим, что переменная $sum была инициализирована и её значение равно 0.
Если теперь нажмем F8, то попадем внутрь цикла foreach и, нажимая теперь F8, пока не окончится цикл, можно будет наблюдать на каждой итерации, как значения $num и $sum постоянно изменяются. Тем самым мы можем проследить шаг за шагом весь процесс изменения любых переменных и значений на любом этапе, который интересует.
Дальнейшие нажатия F8 переместят линию кода на строки 11, 12 и, наконец, 15.
Дополнительно
Если нажать на View Breakpoints в левой панели, то можно не только посмотреть все брейкпойнты, но в появившемся окне можно еще более тонко настроить условие, при котором на данной отметке надо остановиться.
В функции выше, например, нужно остановиться только когда $sum превысит значение 20.
Это удобно, если останов нужен только при определённом значении, а не всегда (особенно в случае с циклами).
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors occurred in the same file — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
Note that above recommentdtion is only suitable for the dev environment. On a live site display_errors must be set to 0, while log_errors to 1. And then you’ll be able to see all errors in the error log.
In case of AJAX call, on a dev server open DevTools (F12), then Network tab.
Then initiate the request which result you want to see, and it will appear in the Network tab. Click on it and then the Response tab. There you will see the exact output.
While on a live server just check the error log all the same.
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
Fancy JohnFancy John
37.5k3 gold badges26 silver badges25 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors in the same file where error output is enabled at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
53.8k7 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.4k28 gold badges80 silver badges89 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,5951 gold badge9 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5594 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Warning: the below answer is factually incorrect. Nothing has been changed in error handling, uncaught exceptions are displayed just like other errors. Suggested approach must be used with caution, because it outputs errors unconditionally, despite the display_error setting and may pose a threat by revealing the sensitive information to an outsider on a live site.
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,89518 silver badges18 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,3001 gold badge32 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,7152 gold badges32 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5674 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5895 silver badges3 bronze badges
In order to display a parse error, instead of setting display_errors in php.ini you can use a trick: use include.
Here are three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
When running this file directly, it will show nothing, given display_errors is set to 0 in php.ini.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
Now run tst2.php which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,24319 silver badges32 bronze badges
4
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0571 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 0);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 0);
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // Mechanism to log errors
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.1k12 gold badges98 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,8592 gold badges23 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7319 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
XakiruXakiru
2,4481 gold badge14 silver badges11 bronze badges
3
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3591 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,19014 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
17.8k19 gold badges69 silver badges108 bronze badges
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
NVRMNVRM
10.6k1 gold badge82 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
If you are on a SharedHosting plan (like on hostgator)… simply adding
php_flag display_errors 1
into a .htaccess file and uploading it to the remote folder may not yield the actual warnings/errors that were generated on the server.
What you will also need to do is edit the php.ini
This is how you do it via cPanel (tested on hostgator shared hosting
plan)
After logging into your cPanel, search for MultiPHP INI Editor.
It is usually found under the SOFTWARE section in your cPanel list of items.
On the MultiPHP INI Editor page …you can stay on the basic mode tab and just check the button on the line that says display_errors.
Then click the Apply button to save.
IMPORTANT: Just remember to turn it back off when you are done debugging; because this is not recommended for public servers.
answered Mar 13, 2022 at 17:21
Really Nice CodeReally Nice Code
1,0141 gold badge12 silver badges21 bronze badges
As it is not clear what OS you are on these are my 2 Windows cents.
If you are using XAMPP you need to manually create the logs folder under C:xamppphp. Not your fault, ApacheFriends ommitted this.
To read and follow this file do.
Get-Content c:xamppphplogsphp_error_log -Wait
To do this in VSCode create a task in .vscodetasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Monitor php errors",
"type": "shell",
"command": "Get-Content -Wait c:\xampp\php\logs\php_error_log",
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
}
]
and have it run on folder load.
answered Dec 3, 2022 at 14:40
theking2theking2
1,8101 gold badge24 silver badges30 bronze badges
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors occurred in the same file — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
Note that above recommentdtion is only suitable for the dev environment. On a live site display_errors must be set to 0, while log_errors to 1. And then you’ll be able to see all errors in the error log.
In case of AJAX call, on a dev server open DevTools (F12), then Network tab.
Then initiate the request which result you want to see, and it will appear in the Network tab. Click on it and then the Response tab. There you will see the exact output.
While on a live server just check the error log all the same.
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
Fancy JohnFancy John
37.5k3 gold badges26 silver badges25 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors in the same file where error output is enabled at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
53.8k7 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.4k28 gold badges80 silver badges89 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,5951 gold badge9 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5594 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Warning: the below answer is factually incorrect. Nothing has been changed in error handling, uncaught exceptions are displayed just like other errors. Suggested approach must be used with caution, because it outputs errors unconditionally, despite the display_error setting and may pose a threat by revealing the sensitive information to an outsider on a live site.
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,89518 silver badges18 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,3001 gold badge32 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,7152 gold badges32 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5674 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5895 silver badges3 bronze badges
In order to display a parse error, instead of setting display_errors in php.ini you can use a trick: use include.
Here are three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
When running this file directly, it will show nothing, given display_errors is set to 0 in php.ini.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
Now run tst2.php which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,24319 silver badges32 bronze badges
4
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0571 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 0);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 0);
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // Mechanism to log errors
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.1k12 gold badges98 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,8592 gold badges23 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7319 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
XakiruXakiru
2,4481 gold badge14 silver badges11 bronze badges
3
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3591 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,19014 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
17.8k19 gold badges69 silver badges108 bronze badges
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
NVRMNVRM
10.6k1 gold badge82 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
If you are on a SharedHosting plan (like on hostgator)… simply adding
php_flag display_errors 1
into a .htaccess file and uploading it to the remote folder may not yield the actual warnings/errors that were generated on the server.
What you will also need to do is edit the php.ini
This is how you do it via cPanel (tested on hostgator shared hosting
plan)
After logging into your cPanel, search for MultiPHP INI Editor.
It is usually found under the SOFTWARE section in your cPanel list of items.
On the MultiPHP INI Editor page …you can stay on the basic mode tab and just check the button on the line that says display_errors.
Then click the Apply button to save.
IMPORTANT: Just remember to turn it back off when you are done debugging; because this is not recommended for public servers.
answered Mar 13, 2022 at 17:21
Really Nice CodeReally Nice Code
1,0141 gold badge12 silver badges21 bronze badges
As it is not clear what OS you are on these are my 2 Windows cents.
If you are using XAMPP you need to manually create the logs folder under C:xamppphp. Not your fault, ApacheFriends ommitted this.
To read and follow this file do.
Get-Content c:xamppphplogsphp_error_log -Wait
To do this in VSCode create a task in .vscodetasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Monitor php errors",
"type": "shell",
"command": "Get-Content -Wait c:\xampp\php\logs\php_error_log",
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
}
]
and have it run on folder load.
answered Dec 3, 2022 at 14:40
theking2theking2
1,8101 gold badge24 silver badges30 bronze badges
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Как быстро показать все ошибки PHP
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
(PHP 4, PHP 5, PHP 7, PHP 
error_reporting — Sets which PHP errors are reported
Description
error_reporting(?int $error_level = null): int
Parameters
-
error_level -
The new error_reporting
level. It takes on either a bitmask, or named constants. Using named
constants is strongly encouraged to ensure compatibility for future
versions. As error levels are added, the range of integers increases,
so older integer-based error levels will not always behave as expected.The available error level constants and the actual
meanings of these error levels are described in the
predefined constants.
Return Values
Returns the old error_reporting
level or the current level if no error_level parameter is
given.
Changelog
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| 8.0.0 |
error_level is nullable now.
|
Examples
Example #1 error_reporting() examples
<?php// Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);// Report simple running errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);// Reporting E_NOTICE can be good too (to report uninitialized
// variables or catch variable name misspellings ...)
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE);// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(-1);// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);?>
Notes
Tip
Passing in the value -1 will show every possible error,
even when new levels and constants are added in future PHP versions. The
behavior is equivalent to passing E_ALL constant.
See Also
- The display_errors directive
- The html_errors directive
- The xmlrpc_errors directive
- ini_set() — Sets the value of a configuration option
info at hephoz dot de ¶
14 years ago
If you just see a blank page instead of an error reporting and you have no server access so you can't edit php configuration files like php.ini try this:
- create a new file in which you include the faulty script:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include("file_with_errors.php");
?>
- execute this file instead of the faulty script file
now errors of your faulty script should be reported.
this works fine with me. hope it solves your problem as well!
dave at davidhbrown dot us ¶
16 years ago
The example of E_ALL ^ E_NOTICE is a 'bit' confusing for those of us not wholly conversant with bitwise operators.
If you wish to remove notices from the current level, whatever that unknown level might be, use & ~ instead:
<?php
//....
$errorlevel=error_reporting();
error_reporting($errorlevel & ~E_NOTICE);
//...code that generates notices
error_reporting($errorlevel);
//...
?>
^ is the xor (bit flipping) operator and would actually turn notices *on* if they were previously off (in the error level on its left). It works in the example because E_ALL is guaranteed to have the bit for E_NOTICE set, so when ^ flips that bit, it is in fact turned off. & ~ (and not) will always turn off the bits specified by the right-hand parameter, whether or not they were on or off.
jcastromail at yahoo dot es ¶
2 years ago
Under PHP 8.0, error_reporting() does not return 0 when then the code uses a @ character.
For example
<?php
$a
=$array[20]; // error_reporting() returns 0 in php <8 and 4437 in PHP>=8?>
Fernando Piancastelli ¶
18 years ago
The error_reporting() function won't be effective if your display_errors directive in php.ini is set to "Off", regardless of level reporting you set. I had to set
display_errors = On
error_reporting = ~E_ALL
to keep no error reporting as default, but be able to change error reporting level in my scripts.
I'm using PHP 4.3.9 and Apache 2.0.
lhenry at lhenry dot com ¶
3 years ago
In php7, what was generally a notice or a deprecated is now a warning : the same level of a mysql error … unacceptable for me.
I do have dozen of old projects and I surely d'ont want to define every variable which I eventually wrote 20y ago.
So two option: let php7 degrade my expensive SSDs writing Gb/hours or implement smthing like server level monitoring ( with auto_[pre-ap]pend_file in php.ini) and turn off E_WARNING
Custom overriding the level of php errors should be super handy and flexible …
ecervetti at orupaca dot fr ¶
13 years ago
It could save two minutes to someone:
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE integer value is 6135
luisdev ¶
4 years ago
This article refers to these two reporting levels:
// Report all PHP errors (see changelog)
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(-1);
What is the difference between those two levels?
Please update this article with a clear explanation of the difference and the possible use cases.
qeremy ! gmail ¶
7 years ago
If you want to see all errors in your local environment, you can set your project URL like "foo.com.local" locally and put that in bootstrap file.
<?php
if (substr($_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'], -6) == '.local') {
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
// or error_reporting(E_ALL);
}
?>
Rash ¶
8 years ago
If you are using the PHP development server, run from the command line via `php -S servername:port`, every single error/notice/warning will be reported in the command line itself, with file name, and line number, and stack trace.
So if you want to keep a log of all the errors even after page reloads (for help in debugging, maybe), running the PHP development server can be useful.
chris at ocproducts dot com ¶
6 years ago
The error_reporting() function will return 0 if error suppression is currently active somewhere in the call tree (via the @ operator).
keithm at aoeex dot com ¶
12 years ago
Some E_STRICT errors seem to be thrown during the page's compilation process. This means they cannot be disabled by dynamically altering the error level at run time within that page.
The work-around for this was to rename the file and replace the original with a error_reporting() call and then a require() call.
Ex, rename index.php to index.inc.php, then re-create index.php as:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~(E_STRICT|E_NOTICE));
require('index.inc.php');
?>
That allows you to alter the error reporting prior to the file being compiled.
I discovered this recently when I was given code from another development firm that triggered several E_STRICT errors and I wanted to disable E_STRICT on a per-page basis.
kevinson112 at yahoo dot com ¶
4 years ago
I had the problem that if there was an error, php would just give me a blank page. Any error at all forced a blank page instead of any output whatsoever, even though I made sure that I had error_reporting set to E_ALL, display_errors turned on, etc etc. But simply running the file in a different directory allowed it to show errors!
Turns out that the error_log file in the one directory was full (2.0 Gb). I erased the file and now errors are displayed normally. It might also help to turn error logging off.
https://techysupport.co/norton-tech-support/
adam at adamhahn dot com ¶
5 years ago
To expand upon the note by chris at ocproducts dot com. If you prepend @ to error_reporting(), the function will always return 0.
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
var_dump(
error_reporting(), // value of E_ALL,
@error_reporting() // value is 0
);
?>
vdephily at bluemetrix dot com ¶
17 years ago
Note that E_NOTICE will warn you about uninitialized variables, but assigning a key/value pair counts as initialization, and will not trigger any error :
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);$foo = $bar; //notice : $bar uninitialized$bar['foo'] = 'hello'; // no notice, although $bar itself has never been initialized (with "$bar = array()" for example)$bar = array('foobar' => 'barfoo');
$foo = $bar['foobar'] // ok$foo = $bar['nope'] // notice : no such index
?>
fredrik at demomusic dot nu ¶
17 years ago
Remember that the error_reporting value is an integer, not a string ie "E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE".
This is very useful to remember when setting error_reporting levels in httpd.conf:
Use the table above or:
<?php
ini_set("error_reporting", E_YOUR_ERROR_LEVEL);
echo ini_get("error_reporting");
?>
To get the appropriate integer for your error-level. Then use:
php_admin_value error_reporting YOUR_INT
in httpd.conf
I want to share this rather straightforward tip as it is rather annoying for new php users trying to understand why things are not working when the error-level is set to (int) "E_ALL" = 0...
Maybe the PHP-developers should make ie error_reporting("E_ALL"); output a E_NOTICE informative message about the mistake?
rojaro at gmail dot com ¶
12 years ago
To enable error reporting for *ALL* error messages including every error level (including E_STRICT, E_NOTICE etc.), simply use:
<?php error_reporting(-1); ?>
j dot schriver at vindiou dot com ¶
22 years ago
error_reporting() has no effect if you have defined your own error handler with set_error_handler()
[Editor's Note: This is not quite accurate.
E_ERROR, E_PARSE, E_CORE_ERROR, E_CORE_WARNING, E_COMPILE_ERROR and E_COMPILE_WARNING error levels will be handled as per the error_reporting settings.
All other levels of errors will be passed to the custom error handler defined by set_error_handler().
Zeev Suraski suggests that a simple way to use the defined levels of error reporting with your custom error handlers is to add the following line to the top of your error handling function:
if (!($type & error_reporting())) return;
-zak@php.net]
kc8yds at gmail dot com ¶
14 years ago
this is to show all errors for code that may be run on different versions
for php 5 it shows E_ALL^E_STRICT and for other versions just E_ALL
if anyone sees any problems with it please correct this post
<?php
ini_set('error_reporting', version_compare(PHP_VERSION,5,'>=') && version_compare(PHP_VERSION,6,'<') ?E_ALL^E_STRICT:E_ALL);
?>
misplacedme at gmail dot com ¶
13 years ago
I always code with E_ALL set.
After a couple of pages of
<?php
$username = (isset($_POST['username']) && !empty($_POST['username']))....
?>
I made this function to make things a little bit quicker. Unset values passed by reference won't trigger a notice.
<?php
function test_ref(&$var,$test_function='',$negate=false) {
$stat = true;
if(!isset($var)) $stat = false;
if (!empty($test_function) && function_exists($test_function)){
$stat = $test_function($var);
$stat = ($negate) ? $stat^1 : $stat;
}
elseif($test_function == 'empty') {
$stat = empty($var);
$stat = ($negate) ? $stat^1 : $stat;
}
elseif (!function_exists($test_function)) {
$stat = false;
trigger_error("$test_function() is not a valid function");
}
$stat = ($stat) ? true : false;
return $stat;
}
$a = '';
$b = '15';test_ref($a,'empty',true); //False
test_ref($a,'is_int'); //False
test_ref($a,'is_numeric'); //False
test_ref($b,'empty',true); //true
test_ref($b,'is_int'); //False
test_ref($b,'is_numeric'); //false
test_ref($unset,'is_numeric'); //false
test_ref($b,'is_number'); //returns false, with an error.
?>
Alex ¶
16 years ago
error_reporting() may give unexpected results if the @ error suppression directive is used.
<?php
@include 'config.php';
include 'foo.bar'; // non-existent file
?>
config.php
<?php
error_reporting(0);
?>
will throw an error level E_WARNING in relation to the non-existent file (depending of course on your configuration settings). If the suppressor is removed, this works as expected.
Alternatively using ini_set('display_errors', 0) in config.php will achieve the same result. This is contrary to the note above which says that the two instructions are equivalent.
teynon1 at gmail dot com ¶
11 years ago
It might be a good idea to include E_COMPILE_ERROR in error_reporting.
If you have a customer error handler that does not output warnings, you may get a white screen of death if a "require" fails.
Example:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
function
myErrorHandler($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline) {
// Do something other than output message.
return true;
}$old_error_handler = set_error_handler("myErrorHandler");
require
"this file does not exist";
?>
To prevent this, simply include E_COMPILE_ERROR in the error_reporting.
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE | E_COMPILE_ERROR);
?>
Daz Williams (The Northeast) ¶
13 years ago
Only display php errors to the developer...
<?php
if($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']=="00.00.00.00")
{
ini_set('display_errors','On');
}
else
{
ini_set('display_errors','Off');
}
?>
Just replace 00.00.00.00 with your ip address.
forcemdt ¶
9 years ago
Php >5.4
Creating a Custom Error Handler
set_error_handler("customError",E_ALL);
function customError($errno, $errstr)
{
echo "<b>Error:</b> [$errno] $errstr<br>";
echo "Ending Script";
die();
}
huhiko334 at yandex dot ru ¶
4 years ago
If you get a weird mysql warnings like "Warning: mysql_query() : Your query requires a full tablescan...", don't look for error_reporting settings - it's set in php.ini.
You can turn it off with
ini_set("mysql.trace_mode","Off");
in your script
http://tinymy.link/mctct
DarkGool ¶
17 years ago
In phpinfo() error reporting level display like a bit (such as 4095)
Maybe it is a simply method to understand what a level set on your host
if you are not have access to php.ini file
<?php
$bit = ini_get('error_reporting');
while ($bit > 0) {
for($i = 0, $n = 0; $i <= $bit; $i = 1 * pow(2, $n), $n++) {
$end = $i;
}
$res[] = $end;
$bit = $bit - $end;
}
?>
In $res you will have all constants of error reporting
$res[]=int(16) // E_CORE_ERROR
$res[]=int(8) // E_NOTICE
...
&IT ¶
2 years ago
error_reporting(E_ALL);
if (!ini_get('display_errors')) {
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
}
На чтение 11 мин Просмотров 1.2к. Опубликовано 16.10.2021
PHP существует довольно давно и разработал свои особенности и особенности. Он также разработал свой собственный вид отчетов об ошибках, который довольно прост. В этом посте мы покажем вам, как легко добавить мониторинг ошибок для PHP.
Содержание
- Что такое ошибка PHP?
- Какие бывают типы ошибок в PHP?
- Ошибки синтаксического анализа или синтаксиса
- Фатальные ошибки
- Предупреждение об ошибках
- Уведомление об ошибках
- Как включить отчеты об ошибках в PHP
- Сколько уровней ошибок доступно в PHP?
- Ошибки отображения PHP
- Что такое предупреждение PHP?
- Как помогают отчеты о сбоях
- Завершение отчета об ошибках PHP
Что такое ошибка PHP?
Ошибка PHP — это структура данных, представляющая что-то, что пошло не так в вашем приложении. В PHP есть несколько конкретных способов вызова ошибок. Один из простых способов имитировать ошибку — использовать die()функцию:
die("something bad happened!");
Это завершит программу PHP и сообщит об ошибке. Когда программа завершается, это то, что мы называем фатальной ошибкой. Позже вы увидите, что мы можем контролировать, как именно обрабатывается ошибка, в случае, если нам нужно вызвать некоторую логику очистки или перенаправить сообщение об ошибке. Вы также можете смоделировать это с помощью trigger_error()функции:
<?php trigger_error("something happened"); //error level is E_USER_NOTICE //You can control error level trigger_error("something bad happened", E_USER_ERROR); ?>
По умолчанию это вызовет в системе некритическое уведомление. Вы можете переопределить уровень ошибки, если вам нужна более серьезная ошибка.
На самом деле в PHP есть две формы ошибок: стандартные обычные ошибки и исключения.
Исключения были введены в PHP 5. Они дают вам легче семантику, как try, throwи catch. Исключение легко создать. Это следует из большого успеха языков со статической типизацией, таких как C # и Java.
throw new Exception("Yo, something exceptional happened);
Перехват и выдача исключений, как правило, более упрощены, чем более традиционная обработка ошибок PHP. Вы также можете иметь более локализованную обработку ошибок, а не только глобальную обработку ошибок с помощью set_error_handler (). Вы можете окружить конкретную логику блоками try / catch, которые заботятся только о конкретных исключениях:
<?php try { doSystemLogic(); } catch (SystemException $e) { echo 'Caught system exception '; } try { doUserLogic(); } catch (Exception $e) { echo 'Caught misc exception '; } ?>
Какие бывают типы ошибок в PHP?
Ошибка PHP — это не одно и то же, но бывает четырех разных типов:
- синтаксические или синтаксические ошибки
- фатальные ошибки
- предупреждения об ошибках
- замечать ошибки
Ошибки синтаксического анализа или синтаксиса
Первая категория ошибок в PHP — это ошибки синтаксического анализа, также называемые синтаксическими ошибками. Они просто означают, что в вашем скрипте есть один или несколько неправильных символов. Возможно, вы пропустили точку с запятой или неправильно поставили скобку. Взгляните на следующий пример:
<?php $age = 25; if ($age >= 18 { echo 'Of Age'; } else { echo 'Minor'; } ?>
Запустив приведенный выше сценарий, я получаю следующую ошибку:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected '{' in <path> on line 4
С помощью сообщения об ошибке легко увидеть, что в операторе if отсутствует закрывающая скобка. Давайте исправим это:
<?php $age = 25; if ($age >= 18) { echo 'Of Age'; } else { echo 'Minor'; } ?>
Фатальные ошибки
Неустранимые ошибки, как следует из их названия, — это те, которые способны убить — или привести к сбою — приложение. Другими словами, фатальные ошибки — это критические ошибки, означающие, что произошло что-то катастрофическое, и приложение не может продолжать работу.
Часто причиной фатальных ошибок является неопределенный класс, функция или другой артефакт. Если сценарий пытается использовать несуществующую функцию, PHP не знает, что делать, и сценарий необходимо остановить.
Рассмотрим следующий сценарий:
<?php function add($a, $b) { return $a + $b; } echo '2 + 2 is ' . sum(2, 2); ?>
Как видите, сценарий определяет функцию с именем add, а затем пытается вызвать ее с неправильным именем. Эта ситуация приводит к фатальной ошибке:
Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function sum() in F:xampphtdocstest.php:7 Stack trace: #0 {main} thrown in <path> on line 7
Все, что нужно для решения ошибки, — это изменить вызов функции на правильное имя, добавить:
echo '2 + 2 is ' . add(2, 2);
Предупреждение об ошибках
Предупреждающие ошибки — это ошибки, которые не приводят к завершению работы скрипта. Подобно тому, что происходит на других языках, предупреждение в PHP обычно представляет собой что-то, что еще не является серьезной проблемой — или, по крайней мере, не критичной, — но может стать серьезной проблемой в будущем, поэтому вам лучше сохранить глаз на это.
Взгляните на следующий код:
<?php $components = parse_url(); var_dump($components); ?>
После выполнения приведенного выше кода мы получаем следующее предупреждение:
Warning: parse_url() expects at least 1 parameter, 0 given in <path> on line 2
Предупреждение вызывает тот факт, что мы не предоставили параметр функции parse_url. Давайте исправим это:
<?php $components = parse_url('https://example.com'); var_dump($components); ?>
Это устраняет предупреждение:
array(2) { ["scheme"]=> string(5) "https" ["host"]=> string(11) "example.com" }
Уведомление об ошибках
Уведомления об ошибках похожи на предупреждения в том, что они также не останавливают выполнение скрипта. Вы также должны думать об ошибках уведомления как о том, что PHP предупреждает вас о том, что может стать проблемой в будущем. Однако уведомления обычно считаются менее важными или менее важными, чем предупреждения.
Рассмотрим следующий фрагмент кода, который представляет собой измененную версию сценария, использованного в предыдущих разделах:
<?php $numbers = "1,2,5,6"; $parts = explode(",", $integers); echo 'The first number is ' . $parts[0]; ?>
Как видите, сценарий определяет переменную $ numbers, а затем пытается передать переменную с именем $ inteers в функцию explode.
Неопределенные переменные действительно являются одной из основных причин уведомлений в PHP. Чтобы ошибка исчезла, достаточно изменить переменную $ inteers на $ numbers.
Как включить отчеты об ошибках в PHP
Включить отчеты об ошибках в PHP очень просто. Вы просто вызываете функцию в своем скрипте:
<?php error_reporting(E_ALL); //You can also report all errors by using -1 error_reporting(-1); //If you are feeling old school ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL); ?>
Здесь сказано: «Пожалуйста, сообщайте об ошибках всех уровней». Мы рассмотрим, какие уровни есть позже, но считаем это категорией ошибок. По сути, он говорит: «Сообщайте обо всех категориях ошибок». Вы можете отключить отчет об ошибках, установив 0:
<?php error_reporting(0); ?>
Параметр метода в error_reporting()действительности является битовой маской. Вы можете указать в нем различные комбинации уровней ошибок, используя эту маску, как видите:
<?php error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE); ?>
В нем говорится: «сообщать о фатальных ошибках, предупреждениях и ошибках синтаксического анализатора». Вы можете просто разделить их знаком «|» чтобы добавить больше ошибок. Иногда вам могут потребоваться более расширенные настройки отчетов об ошибках. Вы можете использовать операторы битовой маски для составления отчетов по различным критериям:
<?php // Report all errors except E_NOTICE error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE); ?>
Как видите, вы можете гибко определять, о каких ошибках сообщать. Возникает вопрос: о каких типах ошибок и исключений следует сообщать?
Сколько уровней ошибок доступно в PHP?
В PHP 5 целых 16 уровней ошибок. Эти ошибки представляют категорию, а иногда и серьезность ошибки в PHP. Их много, но многочисленные категории позволяют легко определить, где отлаживать ошибку, исходя только из ее уровня. Итак, если вы хотите сделать что-то конкретное только для ошибок пользователя, например, проверку ввода, вы можете определить обработчик условий для всего, что начинается с E_USER. Если вы хотите убедиться, что вы закрыли ресурс, вы можете сделать это, указав на ошибки, оканчивающиеся на _ERROR.
Ошибки в PHP по большей части классифицируются по степени серьезности (предупреждение об ошибке, уведомление) и источнику (пользователь, компилятор, среда выполнения).
Я хочу остановиться на нескольких популярных из них.
Во-первых, у нас есть общие ошибки:
- E_ERROR (значение 1): это типичная фатальная ошибка. Если вы видите этого плохого парня, ваше приложение готово. Перезагрузите и попробуйте еще раз.
- E_WARNING (2): это ошибки, которые не приводят к сбою вашего приложения. Похоже, что большинство ошибок находятся на этом уровне.
Далее у нас есть пользовательские ошибки:
- E_USER_ERROR (256): созданная пользователем версия указанной выше фатальной ошибки. Это часто создается с помощью trigger_error ().
- E_USER_NOTICE (1024): созданная пользователем версия информационного события. Обычно это не оказывает неблагоприятного воздействия на приложение, как и log.info ().
Последняя категория, на которую следует обратить внимание, — это ошибки жизненного цикла приложения, обычно с «core» или «compile» в названии:
- EE_CORE_ERROR (16): Подобно фатальным ошибкам выше, эта ошибка может возникнуть только при запуске приложения PHP.
- EE_COMPILE_WARNING (128): нефатальная ошибка, которая возникает только тогда, когда скрипт PHP не компилируется.
Есть еще несколько ошибок. Вы можете найти их полный список здесь.
Ошибки отображения PHP
Отображение сообщений об ошибках в PHP часто сбивает с толку. Просто погуглите «Отображение сообщения об ошибке PHP» и посмотрите. Почему так?
В PHP вы можете решить, отображать ли ошибки или нет. Это отличается от сообщения о них. Сообщение о них гарантирует, что ошибки не будут проглочены. Но отображение их покажет их пользователю. Вы можете настроить отображение всех ошибок PHP с помощью директив display_errors и display_startup_errors:
<?php ini_set('display_errors', 1); ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1); ?>
Их включение гарантирует, что они будут отображаться в теле веб-ответа пользователю. Обычно рекомендуется отключать их в среде, не связанной с разработкой. Целочисленный параметр метода также является битовой маской, как в error_reporting(). Здесь также применяются те же правила и параметры для этого параметра.
Что такое предупреждение PHP?
Выше вы заметили, что одним из уровней ошибок является E_WARNING. Вы также могли заметить, что многие уровни ошибок имеют версии предупреждений. Я хочу немного в этом разобраться. Основное различие между предупреждением и ошибкой в PHP заключается в том, завершает ли оно приложение. В PHP большинство ошибок фактически не останавливают выполнение скрипта.
Вот пример:
<?php $x = 1; trigger_error("user warning!", E_USER_WARNING); $x = 3; echo "$x is ${$x}"; ?>
Вы все равно будете видеть, $x is 3несмотря на срабатывание предупреждения. Это может быть полезно, если вы хотите собрать список ошибок проверки. Я лично предпочитаю использовать исключения в наши дни, но ваш опыт может отличаться.
Конечно, вы можете настроить отображение предупреждений PHP или нет. Для этого вы должны использовать конфигурацию display_errors, которую вы видели в предыдущем разделе.
Как помогают отчеты о сбоях
PHP упрощает настройку внешних инструментов отчетов об ошибках, подобных тем, которые предлагает Raygun. Он предоставляет несколько различных ловушек для своей среды выполнения, чтобы обрабатывать ошибки и отправлять их по сети. См. Этот пример, взятый со страницы PHP Raygun :
namespace { // paste your 'requires' statement $client = new Raygun4phpRaygunClient("apikey for your application"); function error_handler($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline ) { global $client; $client->SendError($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline); } function exception_handler($exception) { global $client; $client->SendException($exception); } set_exception_handler('exception_handler'); set_error_handler("error_handler"); }
Сначала мы объявляем клиента, используя ключ API для безопасности:
$client = new Raygun4phpRaygunClient("apikey for your application");
Затем мы создаем пару функций, которые обрабатывают наши ошибки и исключения:
function error_handler($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline ) { global $client; $client->SendError($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline); } function exception_handler($exception) { global $client; $client->SendException($exception); }
Обратите внимание, что мы вызываем SendError()функцию, передавая некоторые важные сведения о структуре данных ошибки. Это сделает удаленный вызов Raygun.
Наконец, мы подключаем их к среде выполнения PHP, глобально обрабатывая как традиционные ошибки, так и новые исключения:
set_exception_handler('exception_handler'); set_error_handler("error_handler");
Вот и все. Имея все это на месте, мы можем получить красиво отформатированный отчет об ошибках, который может выглядеть следующим образом:
Завершение отчета об ошибках PHP
Как видите, отчеты об ошибках PHP просты. Вы можете инициировать исключения с помощью специальных функций. Вы также можете запускать исключения, как и в других типизированных языках.
Также вы можете легко подключить свои собственные обработчики и управлять отчетностью и отображением ошибок. Это позволяет нам подключить инструмент Raygun без особых усилий — не стесняйтесь подписаться на пробную версию Raygun и добавить ее в свое приложение за считанные минуты.
- Способы включения и отключения вывода ошибок PHP
- Через .htaccess
- Через логи PHP
- Через файл php.ini
Как правило, хостинг-провайдеры отключают или блокируют показ ошибок PHP. Подобные ограничения вводятся потому что информацией об ошибках могут воспользоваться злоумышленники. Поэтому на рабочих серверах нежелательно включать вывод ошибок на экран.
При разработке сайтов и скриптов крайне важно отслеживать возникающие проблемы. Также эта информация нужна и системным администраторам, чтобы своевременно предотвращать сбои в работе сайта и сервера.
Лучшим вариантом будет отключить вывод ошибок на экран и настроить отображение ошибок в логах. Так вы сможете отслеживать возникающие проблемы, не подвергая сервер угрозе.
В статье мы расскажем, как отключить или включить отображение ошибок PHP при помощи .htaccess, через скрипт PHP и с помощью файла php ini.
Обратите внимание: в некоторых случаях изменить настройки вывода можно только через обращение в техническую поддержку.
Способы включения и отключения вывода ошибок PHP
Через .htaccess
Перейдите в корневую папку сайта. Путь к корневой папке можно посмотреть в разделе «Хостинг» > «Сайты» в колонке «Папка»:
Открыть папку можно в разделе «Хостинг» > «Файловый менеджер». Другой способ перейти к папке: в разделе «Хостинг» > «Сайты» в колонке «Операции» нажмите Открыть папку.
В корневой папке откройте файл .htaccess. Если файла не существует, создайте его.
Чтобы вывести ошибки, добавьте в файл следующие строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
Чтобы отключить ошибки PHP, добавьте в файл строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
Так же отключить отображение PHP error можно используя строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
php_value docref_root 0
php_value docref_ext 0
Через логи PHP
Проверить или скрыть ошибки в определенных файлах можно при помощи вызова PHP-функций.
Способ 1. Для вывода ошибок используйте функцию error_reporting. Пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие ошибки вы хотите увидеть.
- Функция для вывода всех ошибок:
error_reporting(E_ALL)
- Функция для вывода всех ошибок, за исключением типа Notice:
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)
- Отключение вывода:
error_reporting(0)
- Отключение логирования повторяющихся ошибок:
# disable repeated error logging
php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on
php_flag ignore_repeated_source on
Способ 2. Этот метод подойдет для проверки конкретной части кода. Пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие типы ошибок вы хотите увидеть.
Команда для вывода всех ошибок выглядит следующим образом:
ini_set(‘display_errors’, ‘On’)
error_reporting(E_ALL)
После этого добавьте:
ini_set(‘display_errors’, ‘Off’)
Способ 3. Другой вариант включения вывода ошибок через скрипт:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
Для отключения добавьте строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
Способ 4. Для подключения вывода с логированием через конфигурацию веб-сервера введите:
- для Apache:
ErrorLog «/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log»,
- для Nginx:
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log.
Подробнее о других аргументах вы можете прочитать в документации PHP на официальном сайте php.net.
Через файл php.ini
Включить отслеживание ошибок можно с помощью файла php.ini. Такой способ подойдет тем, кто хочет отобразить или скрыть ошибки для всего сайта или кода.
Важно! Настройка отслеживания ошибок через файл php.ini есть не у всех, так как некоторые хостинг-провайдеры частично или полностью закрывают доступ к файлу.
Способ 1. Показать все ошибки можно добавив в php.ini строку:
display_errors = on
После этого перезагрузите сервер:
sudo apachectl -k graceful
Способ 2. Включить вывод ошибок можно при помощи error_reporting. После знака «=» пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие типы ошибок вы хотите увидеть.
Чтобы вывести все ошибки, добавьте следующие строки:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors On
После перезагрузите веб-сервер:
sudo apachectl -k graceful
Чтобы скрыть отображение ошибок, добавьте строки:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors Off
Теперь вы знаете, как можно включить и отключить вывод ошибок PHP.