В статье:
-
Что такое LCP — показатель Largest Contentful Paint
-
Как измерить LCP: инструменты веб-мастера
-
Как улучшить показатель LCP:
-
Ускорить время ответа сервера
-
Решить блокировку рендеринга JavaScript и CSS
-
Ускорить загрузку ресурсов
-
Оптимизировать рендеринг на стороне клиента
-
В мае Google определил новый способ оценки пользовательского опыта. Показатель называется Google Core Vitals, он связан со скоростью загрузки сайта и появления на нем контента.
Google Core Vitals состоит из трех метрик:
- FID — First Input Delay — время между первым взаимодействием пользователя со страницей и ответом бразуера.
- CLS — Cumulative Layout Shift — показатель смещения элементов во время загрузки страницы.
- LCP — Largest Contentful Paint — определяет время, за которое браузер отрисовывает самый крупный видимый объект в области просмотра.
Про CLS у нас есть подробный материал «Как оптимизировать CLS: сдвиги макета страницы, которые мешают пользователям», в этой статье поговорим о показателе LCP и способах его улучшить.
Что такое LCP — показатель Largest Contentful Paint
Largest Contentful Paint — время рендеринга самого большого элемента, видимого в области просмотра пользователем — изображения, текстового блока, видео или другого контента. Учитываются те размеры элементов, которые видны пользователю. Если элемент частично скрыт за областью просмотра, эти невидимые части не берутся в расчет.
Самый аккуратный способ определить время отображения основного содержимого страницы — использовать API Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
Как это происходит:
При загрузке страницы контент может меняться, поэтому каждый раз, когда появляется новый большой элемент, браузер отправляет PerformanceEntry c типом largest-contentful-paint. Когда пользователь начинает взаимодействовать со страницей, отправка метрики прекращается. Нужное значение — время самого последнего отправленного события.
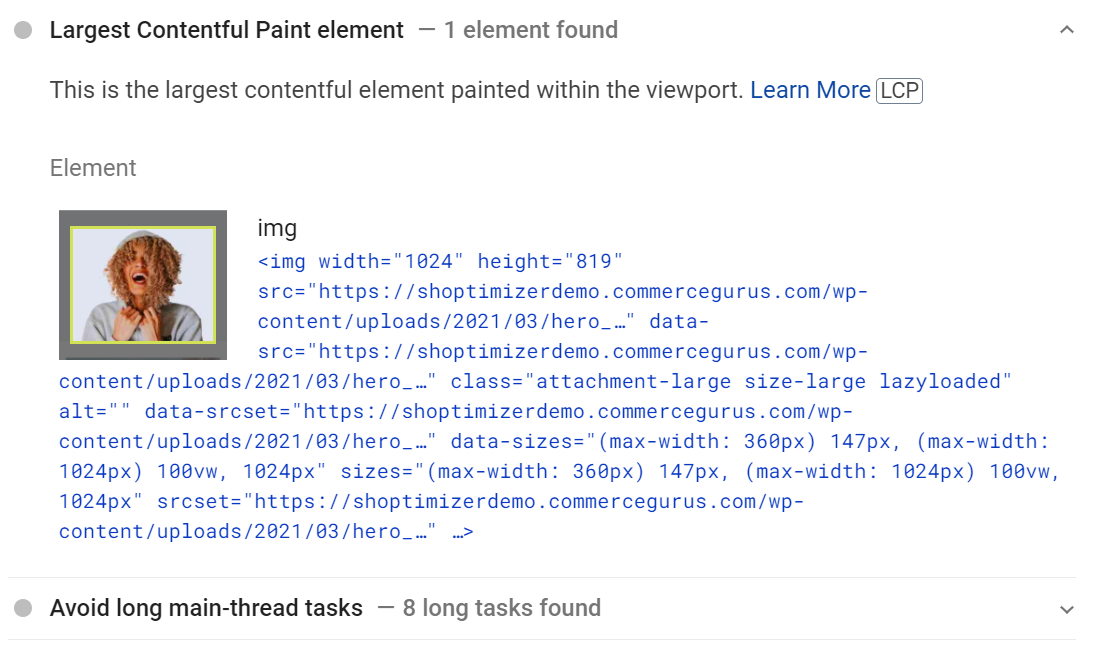
Отрисовка самого большого элемента может происходить и до полной загрузки страницы. К примеру, логотип Instagram — самый большой элемент, он загружается относительно рано и остается самым большим элементом, пока постепенно отображается остальной контент.
В следующем примере самый большой элемент изменяется по мере загрузки содержимого — сначала им был текст, потом самым большим объектом стала картинка.
Инструменты, которые позволяют измерить показатель LCP:
- Отчет Core Web Vitals в Search Console, он находится в Отчете об основных интернет-показателях
- PageSpeed Insights
Проверка скорости сайта от PR-CY бесплатно анализирует загрузку страницы по ключевым параметрам, проверяет десктопное и мобильное отображение. Сервис дает рекомендации и прикидывает, сколько можно сэкономить, если их внедрить на сайте.
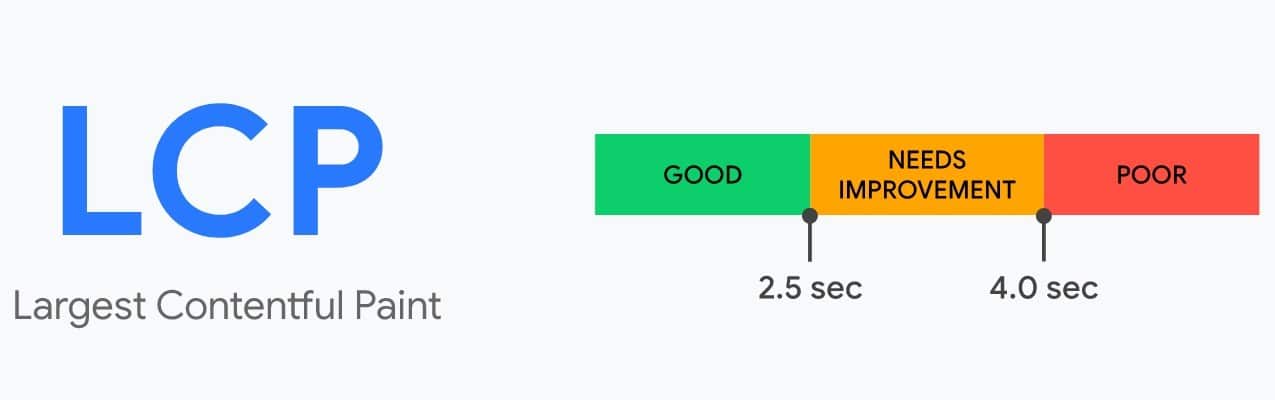
Какой показатель LCP считается хорошим
Нужно стремиться, чтобы отрисовка самого большого контента происходила не дольше, чем за 2,5 секунды после начала загрузки страницы. Тогда пользователям будет удобно работать на сайте.
Инструменты для измерения показывают сводный показатель LCP для 75 % посещений URL.
Как улучшить показатель LCP
На LCP влияют четыре фактора:
- время ответа сервера;
- JavaScript и CSS с блокировкой рендеринга;
- время загрузки ресурса;
- рендеринг на стороне клиента.
Рассмотрим эти факторы, сопутствующие им проблемы и способы оптимизировать показатели.
Медленный ответ сервера
Чем быстрее браузер получает контент с сервера, тем быстрее загрузка страницы и тем лучше показатель LCP.
Вы можете улучшить TTFB — время до первого байта. Какие есть способы:
- Обратитесь к рекомендациям по производительности сервера.
Многие веб-фреймворки, работающие на сервере, имеют такие рекомендации, нужные для ускорения. Как исправить перегруженный сервер - Используйте CDN (Content Delivery Network).
CDN хранят контент и быстро отдают его клиентам из разных географических точек. Подробнее есть в нашей статье. По выводам из исследования, использование CDN коррелировало с улучшением показателей скорости загрузки TTFB, особенно на десктопах. - Кэшируйте страницы.
Статичный HTML, который редко изменяется, можно закэшировать в браузере пользователя, чтобы при каждом визите не загружать контент заново. О кэшировании, сжатии gzip и brotli и других способах оптимизации есть отдельный материал. - Попробуйте сервис-воркеры
Service Worker могут перехватывать запросы с сервера и управлять кэшем — например, кэшировать только часть страницы или обновлять кэш только при изменении содержимого. - Устанавливайте сторонние подключения на раннем этапе.
На LCP могут влиять запросы сервера к сторонним источникам. Можно дать сигнал браузеру, что страница как можно скорее собирается установить соединение, для этого есть rel=» preconnect «.
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://site.ru>Другой вариант — dns-prefetch для ускорения поиска DNS, подходит для браузеров, которые не поддерживают preconnect.
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="https://site.ru">Можно использовать оба варианта для разных браузеров.
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://site.ru">
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="https://site.ru">
Блокировка рендеринга JavaScript и CSS
Браузер преобразовывает разметку HTML в дерево DOM, а потом уже отображает контент. Он не сможет продолжать работу, если обнаружит ресурсы, блокирующие рендеринг: внешние таблицы стилей link rel=»stylesheet» и сценарии JavaScript script src=»main.js». Чтобы ускорить загрузку содержимого страницы, нужно отложить все некритические JavaScript и CSS.
Неиспользуемый JavaScript и CSS можно найти с помощью Chrome DevTools на вкладке Coverage.
Найденный неиспользуемый CSS можно вообще удалить или переместить в другую таблицу стилей, если он нужен на других страницах сайта.
Если CSS не нужен для начального рендеринга, можно использовать loadCSS для асинхронной загрузки файлов, который использует rel=»preload» и onload.
<link rel="preload" href="stylesheet.css" as="style" onload="this.rel='stylesheet'">Критический CSS можно включить в head, если он нужен для верхней части страницы. Встраивание стилей таким образом позволит не делать двусторонний запрос для получения критического CSS.
Как автоматизировать добавление встроенных стилей на сайт:
- Critical, CriticalCSS и Penthouse извлекают и встраивают верхний CSS;
- Critters встраивает критический CSS и загружает остальные в отложенном режиме.
Для JavaScript также можно использовать асинхронную загрузку.
Еще полезна минификация или минимизация кода CSS и JavaScript — удаление символов, которые не нужны браузеру для чтения кода. Минификаторы удаляют отступы, интервалы, разделители и комментарии, файл по сути не меняется, но становится легче.
Список бесплатных инструментов для минимизации CSS, JS, HTML-файлов есть в статье.
Долгая загрузка ресурсов
Время, которое требуется контенту для загрузки, влияет на LCP, так что имеет смысл поработать с элементами на странице.
Что можно сделать:
- Оптимизировать изображения.
Если на сайте много больших по размеру изображений, которые замедляют загрузку страниц, попробуйте lazy loading картинок — постепенную подгрузку, которая обычно зависит от действий пользователя на странице. Еще можно сжать изображения, если они много весят, попробовать новый формат WebP, обратиться к CDN. - Загрузить важное сначала
Критически важные ресурсы, например, шрифты, изображения или видеозаписи, нужно загрузить первым делом. Для придания ресурсу приоритета есть < link rel = «preload» >. - Использовать сервис-воркеры
В предыдущем пункте упоминали сервис-воркеры для выборочного кэширования, их можно использовать и для изображений и других элементов, которые редко обновляют на странице. - Использовать gzip или brotli
Эти виды сжатия могут значительно уменьшить размер файлов HTML, CSS и JavaScript при их передаче между сервером и браузером. Об настройке в статье «Как ускорить сайт с помощью gzip, brotli, минификации и других способов».
Рендеринг на стороне клиента
Есть сайты, которые работают через рендеринг на стороне клиента (CSR) — то есть рендеринг страниц происходит в браузере с использованием JavaScript, все обрабатывается на стороне клиента, а не на сервере.
Основной недостаток такого подхода в том, что по мере роста сайта, добавления новых библиотек и кода начинает страдать скорость загрузки и отображения контента для пользователя.
Что можно сделать:
- минифицировать код JavaScript — сократить и сжать файл;
- выявить неиспользуемые элементы JavaScript, удалить или отложить их;
- минимизировать неиспользуемые полифиллы, которые используют для работы сайта в старых браузерах. Сведите к минимуму неиспользуемые полифилы и ограничьте их использование средами, где они необходимы.
В некоторых случаях можно использовать предварительный рендеринг. В таком способе рендер выполняется в headless браузере типа Chrome, который генерирует статические файлы HTML, а их уже подставляют в ответ сервера.
Предварительный рендеринг не нагружает реальный сервер и позволяет улучшить показатель LCP, но не подходит для страниц с изменяемым или с введенным пользователем контентом.
Скорость загрузки ресурса на компьютере и мобильных устройствах можно проверить в Анализе сайта от PR-CY. Он проверяет сайт по 70+ параметрам, включая скорость загрузки и отображения контента, анализирует, что реализовано на сайте для ускорения, и дает советы, что еще можно улучшить.
Некоторые подробные тесты и графики, а также проверка внутренних страниц и отслеживание позиций доступны на платных тарифах. Но мы даем новым пользователям неделю на бесплатный тест сервиса — оставайтесь, если понравится!
Подключить
Подробнее о LCP в статьях «Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)» и «Optimize LCP».
В комментариях напишите, о чем еще вам было бы интересно почитать по теме оптимизации и работы с техническими характеристиками сайта.
Picture this: you visit a website and instead of seeing a well-crafted homepage you find no content, just a blank screen. This can happen due to largest contentful paint element issues. In simple words, this means that if the largest element on the page isn’t loaded completely, visitors will not be able to see anything except a blank page.
This not only damages the user experience on your website but can also make visitors bounce off your website immediately.
In this article, we’ll take a look at what largest contentful paint means, how to calculate it, and what causes it. We’ll also go over some ways you can fix largest contentful paint element issues on your website.
What does largest contentful paint mean?
Largest contentful paint or LCP is one of the Core Web Vitals metrics that measure how long it takes for the largest content element to display on your screen. With recent updates, LCP is also included in Google’s Page Experience update which makes it even more important if you want to improve your website’s ranking and enhance the user experience on your website.
If the largest contentful paint element doesn’t load in time, visitors may not see anything on the web page until it fully loads up. LCP is always above the fold or at the top of the webpage.
Largest contentful paint elements may include images, text blocks, videos, animations, or elements with background images loaded through URL instead of CSS. In addition to this, block-level elements such as <h1>, <h2>, <ul>, and <table> on your site can be largest contentful paint elements.
It’s important to note that the largest contentful paint element can be different between mobile and desktop versions of your website. For example, the desktop view of your website might have an image as the LCP but the mobile view may not because everything collapses. The mobile view of your website may have an h1 as the LCP. The h1 on mobile view will be faster to load as compared to an image on the desktop view. Core Web Vitals prioritize the mobile view which is why it’s an important consideration when designing pages.
The first contentful paint or FCP is a metric used to measure how long it takes initial DOM content to render on your webpage. This is different from largest contentful paint as it does not measure how long it takes for the largest content element to load on the webpage. Knowing how long it takes LCP content to load on your webpage is crucial for improving the user experience on your website.
How does largest contentful paint affect page speed?
Largest contentful paint can affect your website’s page speed and can cause a poor user experience on your site. It accounts for 25% of the Page Speed Insights score. By fixing the largest contentful paint element issues, you can improve your website’s ranking and page speed.
Since it’s the “largest” element on your webpage that won’t load up, it’s the most important for impacting the user experience and load times on your site. If your webpage’s largest element doesn’t load up, it will display a blank page. This means that visitors will not be able to see the content they wanted to and bounce off your site.
These couple of seconds may not seem like much but they make a huge difference for website visitors. Ideally, you want to let visitors see content on your site without having to deal with the largest contentful paint element issues. Poor LCP drastically reduces the user experience on your website and can cause slower page load times.
What causes poor largest contentful paint?
Before we start fixing largest contentful paint element issues, we first need to understand what a good LCP score is.
- Ideally, you want to aim for an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less, which is considered a good LCP score.
- If your largest contentful paint score is between 2.5 seconds and 4.0 seconds, you need to improve LCP on your website.
- And an LCP score of 4.0 seconds or above is poor and can cause major largest contentful paint element issues on your website.
Now with a better understanding of how LCP scores work, you can determine if your website’s LCP score needs improvement or not.
Poor largest contentful paint can be caused by many reasons including slower server response times, render-blocking JavaScript and CSS, slower resource load times, and client-side rendering.
It’s almost certain that the longer it takes for content to be requested by the server, the longer it will take to load anything on the screen, especially for first-time visitors. Improving server response times is a great way to speed up page load times and improve LCP on your site.
If JavaScript and CSS on your site are render-blocking resources, it can cause poor largest contentful paint. It’s important to make sure there’s no “extra” code for any non-critical JavaScript and CSS. This is great for improving your site’s page load time speeds.
Additionally, if JavaScript and CSS are not being loaded quickly, it can cause other resources on your webpage to load slower, as well. You can optimize images, compress text files, or preload important resources to reduce slower resource load times that can cause poor largest contentful paint on your webpage.
If you’re working with a client-side rendered site, you need to make sure to minimize any critical JavaScript, pre-render important resources, and use server-side rendering. This makes sure the LCP score won’t be affected by using large JavaScript bundles. These optimizations can help users view content on your webpage. Once the critical JavaScript is done loading, users will be able to view and consume content on your site.
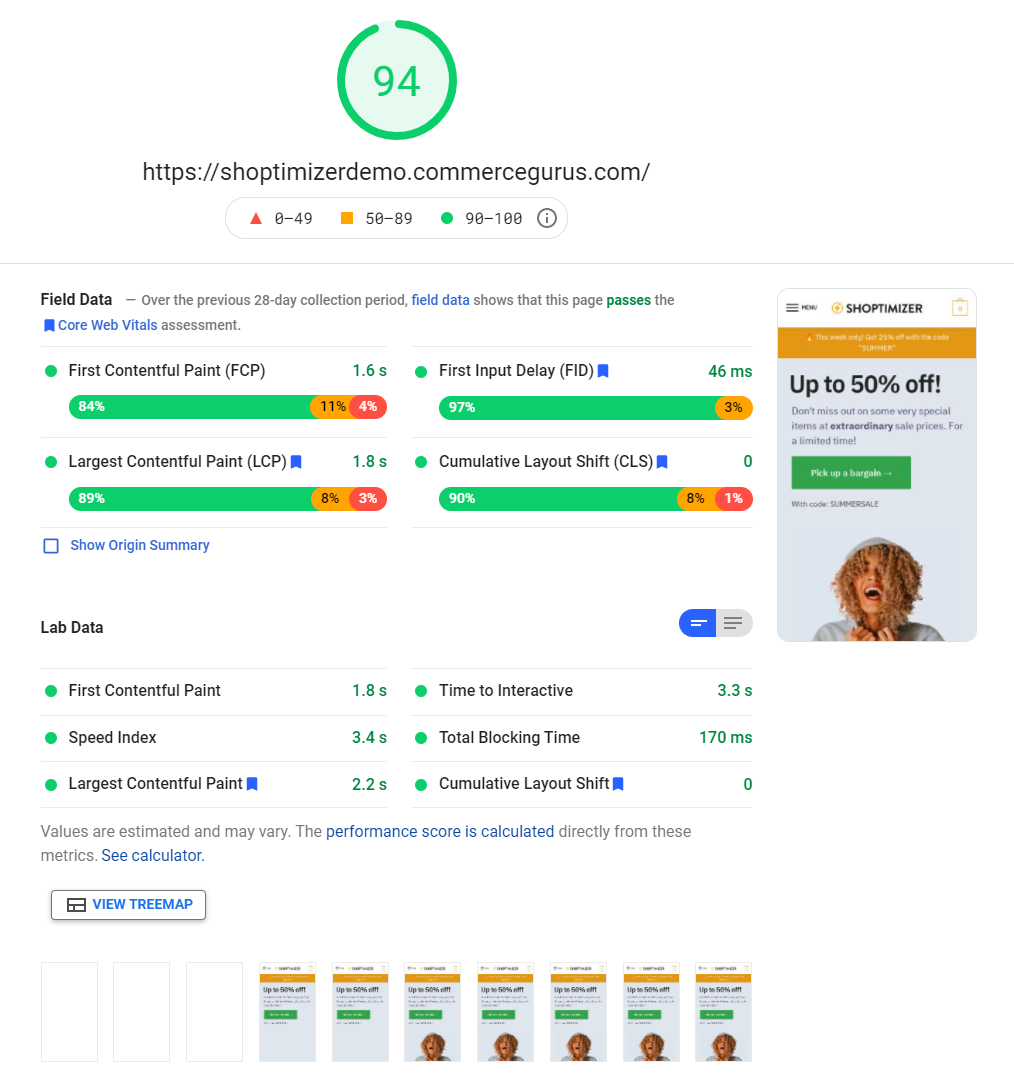
Using the Chrome DevTools, you can monitor LCP on your website easily. Just navigate to the Timings section of the Performance panel from the Inspect menu. This will include a LCP marker that shows you detailed information about LCP on your webpage.
You can also use Google PageSpeed Insights to see what your website’s LCP time is and figure out which element is the largest contentful paint.
Next, let’s step through some different ways to fix largest contentful paint element issues:
Reduce server response times
Reducing the server response times is one of the best ways to fix largest contentful paint element issues on your website. Your hosting plan can be the biggest reason resources are not loading quickly on web pages. For most online stores, a shared hosting plan won’t give you lighting fast server response times. It’s not possible to have a quick, responsive website using a slow host server. Other than hosting, optimizing your server to withstand traffic spikes is a great way to avoid LCP element issues.
For an immediate improvement look at switching to a faster host. We recommend examining the offerings at Nexcess and Cloudways.
Using third party plugins and tools can also cause a slow server response time. It adds to your code, increasing the amount of resources your site needs to completely load web pages. Enabling page cache on your website is one of the best ways to ensure LCP scores stay low. Catch elements that aren’t used frequently on a day-to-day basis. This frees up resources and space for other important elements that need to be loaded when a visitor opens the webpage. In addition to this, you can also cache your HTML if it’s static and reduce time to first byte (TTFB).
A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of servers that are spread out in many different geological locations. Instead of hosting your website on a single server, you can host it on many servers around the world. This helps users that are geographically farther away from the single server to quickly process their browser requests. Put simply, a CDN reduces the distance between your content and visitors as they don’t have to wait for network requests from a server on the other side of the globe.
Optimize your images
If the LCP element is an image, you need to make sure it’s optimized enough to load quickly without causing any LCP issues. For instance, you can compress images to make them load faster for all types of visitors and their internet connections. That means that going from a 300 KB image file to a 150 KB image file can reduce the LCP score on your webpage. There are two types of compression: one for JPEG and GIF files and the other for RAW and PNG image files. JPEG and GIF files images are lossy image types. This means that during compression it removes parts from the image data that reduces image quality. Though it does make it a smaller sized image than before, it’s not good for maintaining image quality. For RAW and PNG image files, you can use lossless compression. This type of compression maintains almost the same image quality since it doesn’t take out image data. It’s best for producing high-quality images that look the best on most devices.
Finding the right compressional ratio comes down to individual needs and business requirements. You can find the right compression for your website by using tools such as Optimizilla or Imagify.
Different formats can result in different image qualities and loading times. A high-quality, bulky image will look really good but will load a lot slower than a lower-quality image. For some businesses, it’s important to use the right format to stand out and help boost engagement. For example, eCommerce stores need to use higher-quality images to best showcase their products.
Additionally, one mistake most website owners make when dealing with images is using one large image for all different screen sizes. Large images need to be optimized so that no extra resources are being used. Let the browser decide which image size to use after providing various image sizes of the same image. You can use the srcset attribute and specify the dimensions of the image. Doing this lets the browser know that it has many options for image sizes according to the user’s screen size.
Optimize CSS and Javascript elements
Before your browser loads your webpage, it needs to render all critical CSS and JavaScript files. This can slow down page load speeds and cause a poor LCP score if CSS and JavaScript files are not optimized within your code.
Minifying and compressing code is one of the best ways to remove unnecessary “junk” code to reduce file size and improve page loading speeds on your website. It removes parts from the code such as comments, whitespace, and line-breaks that aren’t important to reduce file size. Then you can compress the code file by applying various algorithms.
Another great way of improving response times and page speed is by removing any non-critical CSS and implementing only critical CSS resources. Once you’re able to find the critical CSS resources above the fold, you can try removing or reducing any unused CSS from the code. In addition to this, inline any critical CSS used for above-the-fold content. This gets rid of the need to request critical CSS and reduces the CSS blocking time by removing any unused CSS from the code.
Similarly, you can only provide the necessary amounts of JavaScript payloads to visitors on your website. This not only helps reduce LCP scores but also improves the overall page response speed on your website.
Preload high-priority resources
Pre-loading important resources can help you improve page loading times and lower LCP scores for your website. You can preload above-the-fold images, videos, critical CSS, or fonts on your website so that the high-priority resources can be used later whenever it’s needed, without causing a delay. To do this, use rel=preload for important resources that should be prioritized on your website.
Reducing the file size of text files such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript can help improve LCP scores for your website. It also improves loading times as text files are transferred between the servers and the browser.
Using third-party tools and services can negatively affect page loading speeds and eventually, LCP scores. By using the rel=preconnect attribute, you can speed up the loading times by establishing crucial third-party connections beforehand. So when visitors open your website, the content will already be loaded and ready to go.
Bonus: What else can you do to avoid largest contentful paint element issues?
- Use server-level compression. Reducing the size of your site further can help improve response times and loading speeds for your website. You can use a server compression algorithm such as Gzip to do this.
- Page caching. Using a caching plugin can help you speed up LCP and improve page speeds. It makes it easier for you to deliver content quickly and without any largest contentful paint element issues.
- Server-side rendering. Using server-side rendering is a great way to improve LCP by ensuring content loads on the server first rather than just loading on the client.
- Pre-rendering. Pre-rendering is less complex than server-side rendering. It uses a browser without a user interface used to generate static HTML files. These files can then later be used along with JavaScript bundles to improve server response times and reduce the page loading time on your website.
Conclusion
LCP is the most important metric used for measuring page speed and response time on your website.
Reducing server times and optimizing servers can help lower LCP scores on your website. Choose a faster hosting service and enable page caching to improve page speeds. In addition to this, using a CDN can also help deliver content to visitors much quicker. You should also optimize images, CSS, and JavaScript elements on your web pages to fix largest contentful paint element issues.
By going through the different steps we covered to fix largest contentful paint element issues, you can aim for a lower LCP score.
Also, be sure to check out our tutorial on How to Avoid Large Layout Shifts and How to solve the “Avoid an excessive DOM size” warning to learn more about how you can improve your Core Web Vitals score.
You can get our Shoptimizer WooCommerce theme for low LCP scores from the get-go.
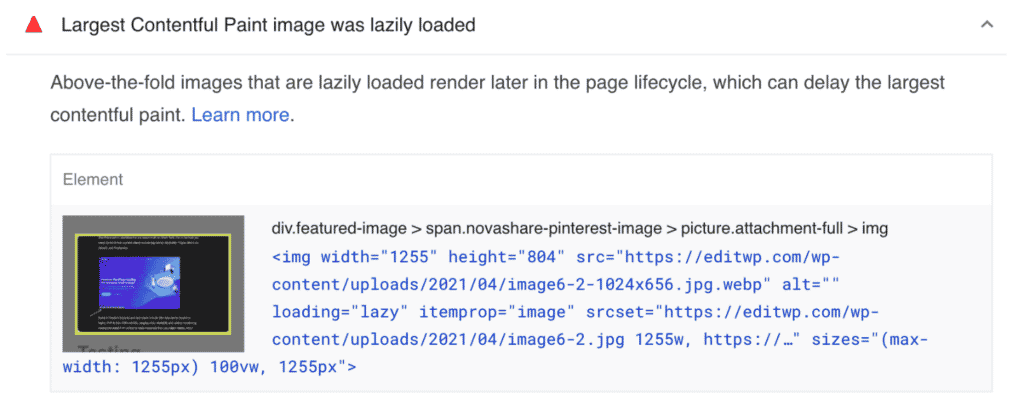
Lazy loading is standard practice these days and one of the easiest ways to speed up your WordPress site. By lazy loading images, you ensure they don’t load until they are needed as a user scrolls down the page. Also, if you don’t, you’ll get the “Defer offscreen images” warning from PageSpeed Insights.
With that being said, it doesn’t mean that every image should always be lazy loaded. Generally, you don’t want to lazy load images that appear above the fold; otherwise, it can cause higher Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). It might also generate the warning in Google PageSpeed Insights: “Largest Contentful Paint image was lazily loaded.”
There are a couple of ways you can fix this warning, which we’ll dive into below. This tutorial assumes you’re using lazy loading in Perfmatters.
- Manually exclude image from lazy loading
- Automatically exclude leading images
Manually exclude image from lazy loading
The easiest way to fix the “Largest Contentful Paint image was lazily loaded” warning is to simply manually exclude the image from lazy loading.
Step 1
Click into the Perfmatters plugin settings.
Step 2
Click on the “Lazy Loading” tab.
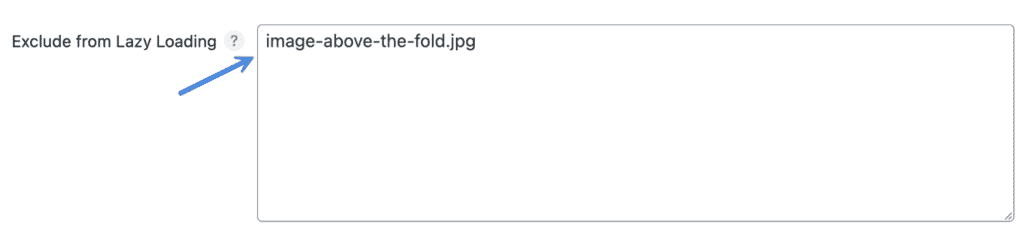
Step 3
In the “Exclude from Lazy Loading” box, enter the URL of the image you want to exclude from lazy loading. You can also add any unique portion of its attribute string (class=”example”).
Step 4
Scroll down and click “Save Changes.”
Automatically exclude leading images
An alternative to a manual exclusion is to use the Exclude Leading Images feature in Perfmatters. This allows you to automatically exclude a certain number of images starting from the top of the page (above the fold).
Step 1
Click into the Perfmatters plugin settings.
Step 2
Click on the “Lazy Loading” tab.
Step 3
Under “Exclude Leading Images” choose how many images you want to be automatically excluded from lazy loading, starting from the top of the page (above the fold).
Step 4
Scroll down and click “Save Changes.”
What is the largest contentful paint? The largest contentful paint is a metric that shows when the browser starts to paint its content. This article will introduce you to fixing the largest contentful paint step by step.
The largest-contentful-paint (LCP) determines how long it takes for the web page’s largest contentful (DOM) element to be displayed on its visible portion of the browser window once the web page is requested.
The LCP is an indicator of user experience and web page performance, but most importantly, it’s a visual cue that the page is “ready to be read.”
There are three events in the largest contentful painting. The contentful elements contain:
- HTML-like images (including background images).
- SVG or canvas.
- No div or background color.
The browser performs several “paint” operations while rendering a web page. The LCP measures the largest paint on the page above the fold.
Do search engines give credit to the Largest Contentful Paint for ranking websites?
Yes, it is. The LCP is one of the essential on-page factors for search engines like Google. Everybody who knows about contentful paint sees that it can be imperative for a website to appear in search results, and it is one of the most important factors that search engines like Google look at when ranking a site. The contentful paint is also significant for mobile sites because Google has a mobile-friendly algorithm that punishes sites that are not mobile-friendly. So, how much of the contentful color is needed to rank well in search results?
Why is Contentful Paint important for your visitors?
While surfing the internet, speed is a crucial factor. A recent study by Google found that the probability of leaving the site doubles with a loading time of 3 seconds. The result doesn’t come as a surprise: most internet users feel that slow-loading websites are highly annoying and thus abandon them shortly after surfacing on them.
The Best LCP According to Google
Google says that getting the first byte of a web page should be less than 2.5 seconds. A latency between 2.5 and 4 seconds is considered moderate and more than 4 seconds is very slow. For latency, lower is always better.
First Meaningful Paint
The First Meaningful Paint metric is all about website render performance and specifically on how long it takes to display the first pixels of your site.
TIP: TIP stands for Time To Interactive Page, which means that the page has been fully rendered and can be used by the user instantly without waiting for additional resources to load.
The FMP metric is calculated as the point in time when 50% of the critical resources are received and processes are executed, which means that it’s enough for your page to be rendered completely.
The FMP tests how quickly a page loads and paints on the screen and is measured in the time it takes for half of the above-the-fold content to be displayed.
What are render-blocking resources? And how do they impact “Largest Contentful Paint”?
Render blocking resources are HTML elements that block the browser from printing the content. If a resource is considered render-blocking, it will delay displaying content to the user until it has been downloaded and processed. For example:
When an image is requested, it will be blocked from displaying until downloaded. It’sIt’s a bit like when the images on a web page are blue with an icon that says, “Loading.” Then, once all photos have finished downloading and processing, they will be displayed (the blue loading icons will disappear).
CSS and JavaScript are two types of render-blocking resources, and CSS is used for presentation—styling. JavaScript is used to enhance functionality — interactions.
When you optimize the LCP, you can reduce the time it takes for the page to render. Optimization strategies include removing generated resources from the critical rendering path, deferring non-critical resources, and removing unnecessary JS.
How to Improve LCP
With this knowledge, we will examine the concept of LCP timing and how one can improve it.
If you don’t feel confident about making this improvement by yourself, contact a professional to get help.
Image Optimization can Improve LCP.
Always use the most miniature images possible. To reduce image size, use an optimization plugin like SSmush or Hummingbird. You can also minimize LCP load by using a CDN.
Choose a Good Hosting Service
Choosing a good hosting service is as essential as selecting a suitable domain for your website. The two services are intertwined and need to be in sync. If you choose an average hosting service, your site will have average performance and average loading times. If you select an excellent hosting service, you will enjoy top performance and quick loading times.
The core web vitals of the site include page load speed, server uptime, disk space, database storage, bandwidth limits, security features, and customer support. It’sIt’s vital that your web host meets or exceeds these standards, or else your site will not have a good start in life.
USE CDN
The browser waits for the server to send back a file, which takes too long to send. You’ll fix the issue by speeding up your site, using a CDN, and establishing an excellent third-party connection. In other words, load time is slow, and the LCP score isn’t great. You’ll fix the issue by using a content delivery network, establishing third-party connections, and improving your Time To First Byte.
Faster Server Response Time
Reducing the time for the browser to render a page can significantly reduce the largest contentful paint. According to new research by Google, this is especially true for pages with heavy use of JavaScript and CSS. The study found that faster server response time can reduce the largest contentful paint by up to 94%. It means that even if a page is slow to render, it’s still possible to have a fast first paint if the server responds quickly.
Slashing server response times get top billing in PageSpeed Insights.
Here’sHere’s a list of steps you can take to solve this problem:
Upgrade Your Hosting
If you’re on a cheap, shared hosting plan, you need to upgrade. It’s impossible to have a fast website with a slow host server. Even if your site is getting traffic from thousands of visitors every day, it will be dead if your web host doesn’t have enough bandwidth capacity. Using managed WordPress or cloud hosting can save money on expensive dedicated servers.
Optimize Server
You’ve done the hard part: you wrote a blog post and published it. Now your work is done. Not so fast! It would help if you still did several things to ensure that your post is optimized for search and delivers the best possible user experience to your readers. The most important thing you can do after publishing is to optimize your server.
Reduce the amount of third-party code on the site.
One of the easiest ways to reduce the amount of code to be executed on the server and thus improve metrics like Time to First Byte, First Contentful Paint, and LCP is to minimize the site’s reliance on 3rd party plugins, tools, and libraries. Free resources abound, so take advantage of them. But there is also a substantial amount of paid products that can help you build a fast, lightweight site, and we recommend using them.
Make the Most of Caching
Make sure to take advantage of caching whenever possible. Caching can help make your site load more quickly. Many types of assets, such as images and logos, can be cached for long periods, which can help make your website’s performance even better. In addition, if you make all the HTML on your site static, you could potentially cache it, too. It will likely lessen the time it takes for your pages to load–especially when visitors come to one page on your site from another.
Utilize Service Workers
To reduce the size of HTML payloads, use service workers. Service workers let you avoid the repetition of common elements. Once installed, they request the bare minimum of data from the server and transform it into a complete HTML doc.
JavaScript and CSS Optimization
Remove Unnecessary CSS
Remove unnecessary CSS from your site by finding unused classes, deleting code that isn’t necessary, and optimizing what you have left. Your loading times will increase if you strip your website of these unnecessary CSS elements.
Optimize CSS delivery
Some cache plugins, such as WP Rocket, have an option to optimize CSS delivery. No caching plugin can guarantee that every visitor always downloads the most optimized version of a stylesheet. Still, it’s worth checking whether your cache plugin is optimizing the delivery of your stylesheets. If not, you can set a fallback for all visitors so that a critical stylesheet is always available, generate a necessary stylesheet and clear your cache.
Third-party JavaScript
Code from external domains—can reduce your page load speed, causing a higher largest contentful paint if it’s loading above the fold. Use the Lighthouse report to identify third-party code that can move to a local server. You can also optimize web fonts using plugins like OMGF, Flying Analytics, and WP User Avatar.
Manification HTML, JavaScript, and CSS
When minifying HTML, JavaScript, and CSS code for your website, you can decrease the load time by removing all characters that aren’t needed. Minification is a process of removing extra spaces and characters to reduce the number of bytes your site takes up and improve First contentful paint timing.
Load JavaScript While Needed
You can harness the power of JavaScript to load the JavaScript files only when needed. For example, you can use Perfmatters and Assets Cleanup to load the JavaScript files only on the pages on which they are required. Perfmatters and Assets Cleanup are plugins that can help you with this aspect.
Delay JavaScript
Delay the loading of JavaScript files until a user interaction is made. This way, neither Google PageSpeed Insights nor Lighthouse will report that specific JavaScript files should be delayed. To address this PageSpeed audit, we’ll be delayed loading some JavaScript files. It will not solve the recommendation, but it’ll help us improve our LCP score.
Deferring JavaScript
By deferring JavaScript, the browser will load and execute the JavaScript files only after the HTML document is fully parsed and the DOM tree has been built. Since there won’t be anything to block the process, rendering will be much faster, and users will experience a better experience — resulting in an improved LCP metric.
By using the defer attribute in JavaScript files, browsers can detect and load resources in the background while loading the HTML document without interruption.
Example of deferring attribute:
<script defer src=”/example-js-script”></script>