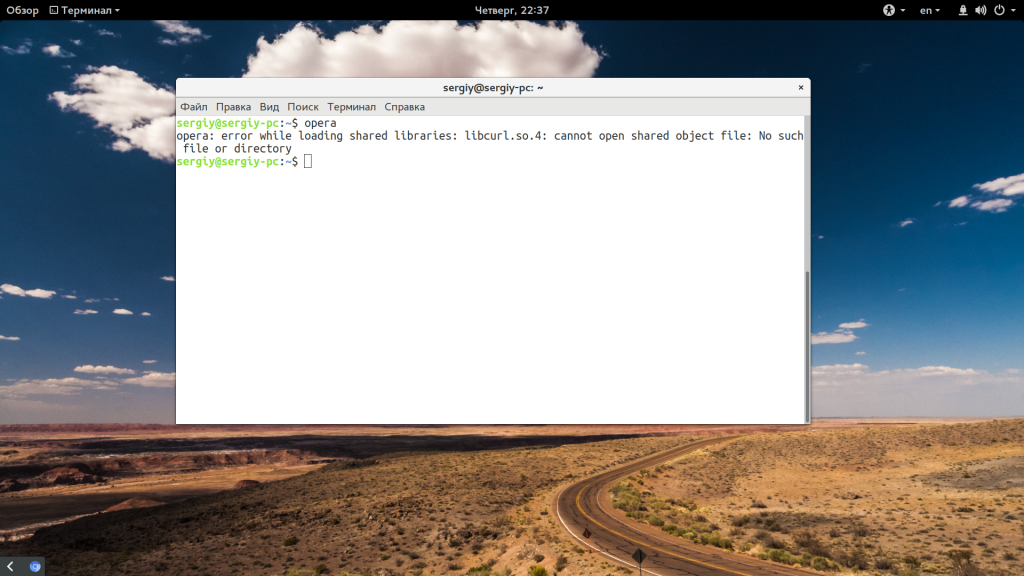
Новые и опытные пользователи Linux могут сталкиваться с ошибкой error loading shared libraries во время запуска программ, также с ней могут сталкиваться программисты и все желающие компилировать программное обеспечение в своей системе. Эта ошибка в дословном переводе означает что возникла проблема во время загрузки общей библиотеки. О том что такое библиотеки и зачем они нужны вы можете узнать из статьи библиотеки Linux.
В этой же статье мы рассмотрим что значит ошибка error while loading shared libraries более подробно, а главное, как ее решить.
Даже если вы не компилируете свои программы, то вы можете увидеть ошибку error while loading shared libraries: имя_библиотеки: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory достаточно часто во время установки новых программ не через пакетный менеджер или программ, предназначенных для другого дистрибутива. Как я уже говорил, она возникает потому, что система не может найти библиотеку.
А вот почему ее нельзя найти и загрузить, это уже интересно. Этому может быть несколько причин:
- Библиотека не установлена в системе;
- Библиотека установлена, но неизвестно куда;
- Библиотека установлена правильно, но имеет не ту версию.
При решении проблемы мы будем руководствоваться именно этими причинами и пытаться их решить.
Как исправить ошибку?
1. Библиотека не установлена
Первый вариант, тут все понятно, библиотеки просто нет в системе, поэтому мы и получаем такую ошибку. Верный способ ее решения — просто найти пакет библиотеки с помощью пакетного менеджера и установить ее. Обычно, пакеты с библиотеками называются так же, как и сами библиотеки с префиксом lib.
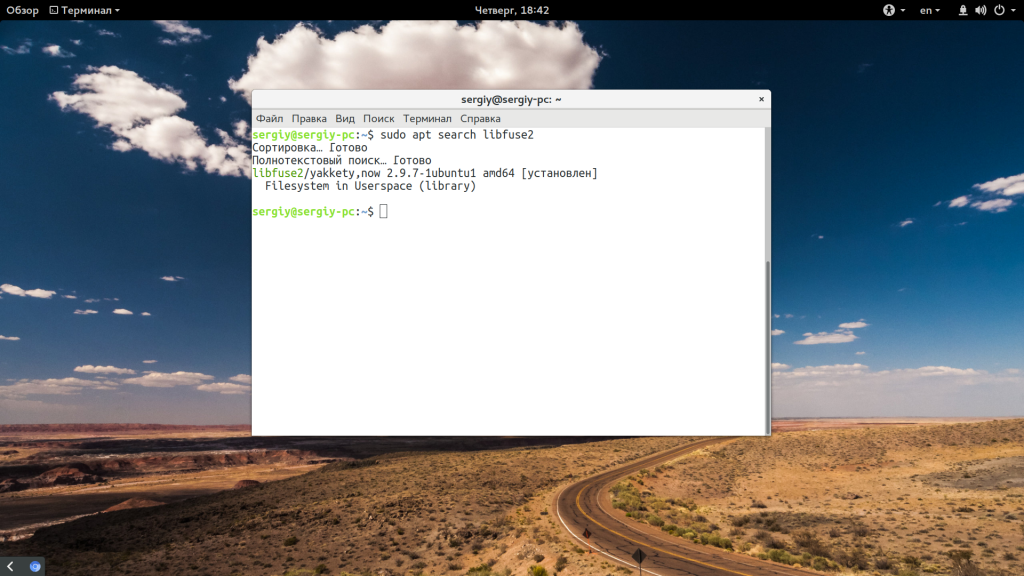
Например, если нам не хватает библиотеки libfuse2.so, то мы можем найти ее в Ubuntu такой командой:
sudo apt search libfuse2
Затем осталось только установить ее:
sudo apt install libfuse2
Если перед вами стоит задача собрать программу из исходников, то вам понадобится не только установить саму библиотеку, но и заголовочные файлы для нее:
sudo apt install libfuse-dev
И так для любой библиотеки. Но это не всегда помогает.
2. Библиотека находится не в том каталоге
Бывает что библиотека установлена, мы установили ее или она поставлялась вместе с программой, но ошибка как была, так и есть. Причиной этому может быть то, что загрузчик Linux не может найти библиотеку.
Поиск библиотек выполняется по всех папках, которые указаны в конфигурационных файлах /etc/ld.conf.d/. По умолчанию, это такие каталоги, как /usr/lib, /lib, /usr/lib64, /lib64. Если библиотека установлена в другой каталог, то, возможно, это и есть причина проблемы.
Вы можете посмотреть какие библиотеки сейчас доступны загрузчику с помощью команды:
ldconfig -p
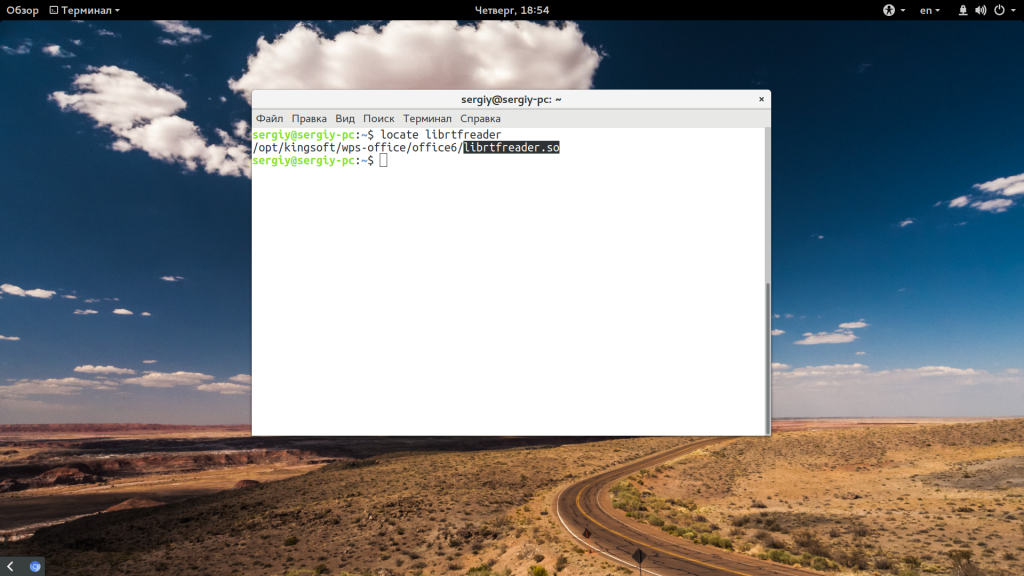
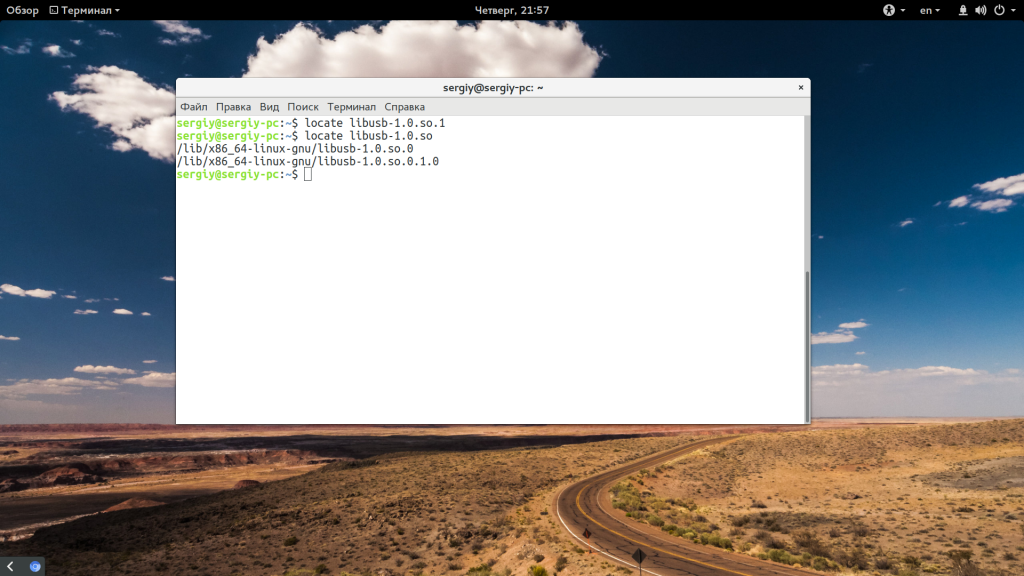
Найти, где находится ваша библиотека можно с помощью команды locate. Например, нас интересует библиотека librtfreader.so:
locate librtfreader
Теперь мы знаем, что она находится по адресу /opt/kingsoft/wps-office/office6/. А значит, для работы программы необходимо сделать чтобы загрузчик библиотек ее видел. Для этого можно добавить путь в один из файлов /etc/ld.so.conf.d/ или же в переменную LD_LIBRARY_PATH:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/kingsoft/wps-office/office6/
Опять же, так вы можете поставить с любой библиотекой, которая взывает ошибку. Еще один более простой метод — это просто создать символическую ссылку на нужную библиотеку в правильной папке:
ln -s /opt/kingsoft/wps-office/office6/librtfreader.so /usr/lib/librtfreader.so
3. Неверная версия библиотеки
Эта причина ошибки довольно часто встречается при использовании программ не для вашего дистрибутива. Каждая библиотека имеет дополнительную версию, так называемую ревизию, которая записывается после расширения .so. Например, libav.so.1. Так вот, номер версии меняется всякий раз, когда в библиотеку вносятся какие-либо исправления.
Часто возникает ситуация, когда в одном дистрибутиве программа собирается с зависимостью от библиотеки, например, libc.so.1, а в другом есть только libc.so.2. Отличия в большинстве случаев здесь небольшие и программа могла бы работать на второй версии библиотеки. Поэтому мы можем просто создать символическую ссылку на нее.
Например, библиотеки libusb-1.0.so.1 нет. Но зато есть libusb-1.0.so.0.1, и мы можем ее использовать:
Для этого просто создаем символическую ссылку на библиотеку:
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/libusb-1.0.so.0.1 /usr/lib/libusb-1.0.so.1
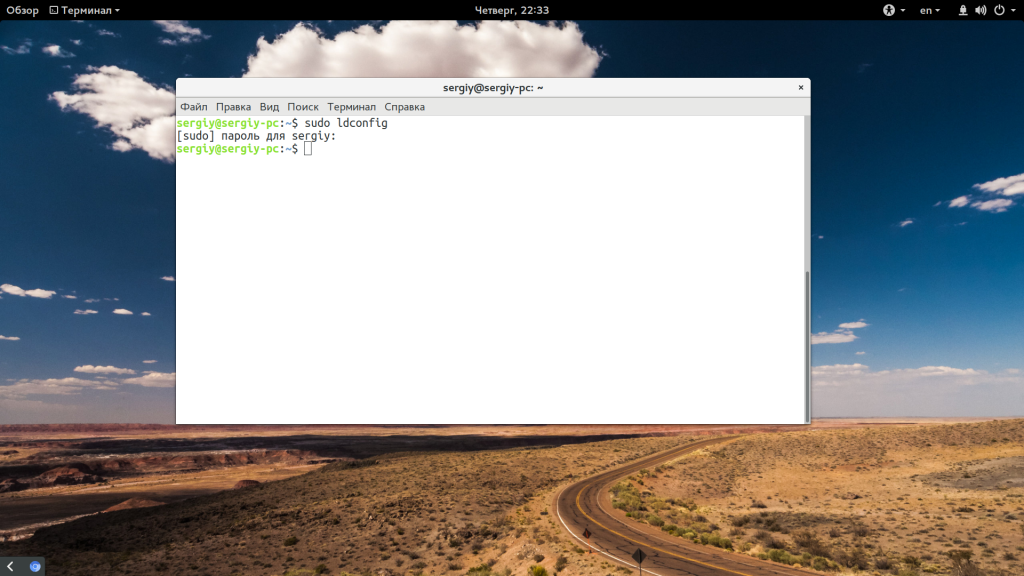
В большинстве случаев программа не заметит подмены и будет работать, как и ожидалось. Также для решения этой проблемы можно попытаться найти нужную версию библиотеки в интернете для своей архитектуры и поместить ее в папку /usr/lib/ или /usr/lib64/. Но после этого желательно обновить кэш:
sudo ldconfig
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели почему возникает ошибка Error while loading shared libraries, а также как ее решить. В большинстве случаев проблема решается довольно просто и вы получите работоспособную программу. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
There is a list of common errors I often see in Ubuntu. There is problem with merge list, then there is BADSIG error, and a number of common Ubuntu update errors.
One of such common errors which I often see while installing a program from its source code is error while loading shared libraries. The full error generally looks like this:
error while loading shared libraries:
cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
For example, I was trying to use FreeRADIUS server and it showed me this error:
radiusd: error while loading shared libraries:
libfreeradius-radius-2.1.10.so:
cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
The reason behind this error is that the libraries of the program have been installed in a place where dynamic linker cannot find it.
Let me show you how you can go about fixing this issue.
One quick way to fix this “error while loading shared libraries” automatically is to use ldconfig.
All you need to do is to open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and type the following command:
sudo /sbin/ldconfig -vThis one liner should solve the problem in most cases. However, if it doesn’t, I have discussed another method to handle this error. But before that, let me tell you what does the above command do.
What are shared object files? How does the above command fixes the issue?
You see, in C/C++, a .so (shared object) is a compiled library file. It is called shared object because this library file can be shared by several programs. These generated libraries are usually located in /lib or /usr/lib directories.
Now if you wonder how did this tiny command fixed this problem, you should read the man page of ldconfig which says:
ldconfig creates the necessary links and cache to the most recent shared libraries found in the directories specified on the command line, in the file /etc/ld.so.conf, and in the trusted directories (/lib and /usr/lib). The cache is used by the run-time linker, ld.so or ld-linux.so. ldconfig checks the header and filenames of the libraries it encounters when determining which versions should have their links updated.
I hope this quick fix helps you in eliminating the nasty error while loading shared libraries message in Ubuntu and other Linux.
If not, you can do some investigation and try to fix the issue the way it is mentioned in the next section.
The above discussed method fixes the issue if the library in question is available in your system. But that may not always be the case.
If you do not have the program installed on your system, you won’t have its library file. The ldconfig cannot do anything if there is no library file in the first place.
So, the alternate method is to install the required program and it should create the library automatically.
Let me show it to you by an example. Let’s say you see this error:
error while loading shared libraries: libgobject-2.0.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directoryThe problem is with libgobject version 2.0. The version number is important because some programs depend on a specific version of the library and if they don’t find, they complain about it.
Now, apt provides the search option that can be used for searching a package and knowing its version before installing it.
[email protected]:~$ apt search libgobject
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
librust-gobject-sys-dev/focal 0.9.0-2 amd64
FFI bindings to libgobject-2.0 - Rust source codeNow, this librust-gobject-sys-dev package could be what you need if you know that you were trying to run a Rust program. But what if it was a Python program you were running that complained about it?
You can widen your search by removing the lib from the package name while searching. The lib signifies library and libraries may be provided by a generic package that could be named gobject-xyz.
It would be a good idea to search for the string in the names of the package (instead of description) to get more concise results.
[email protected]:~$ apt search --names-only gobject
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
gobject-introspection/focal-updates 1.64.1-1~ubuntu20.04.1 amd64
Generate interface introspection data for GObject libraries
libavahi-gobject-dev/focal 0.7-4ubuntu7 amd64
Development headers for the Avahi GObject library
libavahi-gobject0/focal 0.7-4ubuntu7 amd64
Avahi GObject library
libcairo-gobject-perl/focal,now 1.005-2 amd64 [installed,automatic]
integrate Cairo into the Glib type system in Perl
libcairo-gobject2/focal,now 1.16.0-4ubuntu1 amd64 [installed,automatic]
Cairo 2D vector graphics library (GObject library)
libghc-gi-gobject-dev/focal 2.0.19-1build1 amd64
GObject bindings
libghc-gi-gobject-doc/focal,focal 2.0.19-1build1 all
GObject bindings; documentation
In the above truncated output, you’ll have to see if the package is related to the original program you were trying to run. You must also check the version of the library provided.
Once you have identified the correct package, install it like this:
sudo apt install package_nameOnce installed, you may run the ldconfig command again to update the cache:
sudo /sbin/ldconfig -vThis method requires some effort on your end but this is how the dependencies are handled.
Nothing works, what now?
If you are unfortunate enough, the above methods might not work for you. What can you do?
First, keep in mind that the shared libraries may be used from other packages in some cases. If you were trying to run XYZ program and ABC program installs the correct version of the shared library, it may (or may not) work for you. You can give it a hit and trial.
Second, if you are trying to run a program which is too old or too new, it may require a library version which is not available for your Linux distribution.
What you may do is to check if you can use some other version of the program. For example, using Eclipse version 3 instead of version 4. This may help your case.
The other way would be to check the developers website or forums and see if you can manually install the correct version of the library from its source code. That requires a lot of effort (in 2020) but you don’t have a lot of options.
Did it work for you?
I hope I have make things a bit more clear for you. Did you manage to fix the issue of shared libraries in your system? If you have questions, suggestions, feel free to drop a comment. Ciao 

Ошибка error while loading shared libraries означает, что программа, которую пользователь пытается запустить, не смогла найти необходимую для своего запуска библиотеку. Такое часто случается, если программа устанавливалась не из репозиториев, а вручную. Например, на скриншоте ниже мы видим, что свежая версия Mozilla Firefox требует для своей работы библиотеку libatomic.so.1, но не может её обнаружить.
При этом, кстати, совершенно не обязательно, что данная библиотека отсутствует в системе. Поэтому сперва выполним поиск библиотеки (подробнее о locate в статье по этой ссылке):
locate *libatomic*
Естественно, в Вашем случае библиотека может называться иначе. Смотрите, что упоминается в тексте ошибки.
Если команда ничего не выдаст, это значит, что библиотеки в системе нет (а вот если библиотека найдена, тогда об этом ниже).
Поищем библиотеку в репозиториях:
sudo apt search libatomic
В результате мы получим перечень пакетов, которые в названии содержат libatomic:
В моем случае речь идёт о стареньком ноутбуке с 32-битной системой, поэтому мой выбор пал на libatomic1. Если Вы собираете программу из исходников, то будет полезным поставить не только библиотеку, но и заголовочные файлы с приставкой -dev. Сама установка проста:
sudo apt install libatomic1
В результате — актуальная версия Firefox в уже не поддерживаемой разработчиками Ubuntu (подробнее об установке новых версий Firefox в старых релизах Ubuntu в статье по ссылке).
Кстати, иногда команда locate может не выдать Вам информацию о библиотеке, так как, на самом деле она не осуществляет поиск файлов или каталогов. Но это отдельный разговор. Посмотреть, установлена ли библиотека в системе, можно и при поиске пакетов в репозитории. Как видите, наш пакет libatomic1 теперь помечен как установленный.
Теперь о том, что делать, если библиотека есть в системе, но ошибка error while loading shared libraries всё равно появляется. Очень часто причиной этого является то, что загрузчик ОС не может найти библиотеку. По умолчанию поиск производится в каталогах: /usr/lib, /lib, /usr/lib64, /lib64. Не исключено, что библиотека просто лежит за пределами этих каталогов.
Вариантов тут несколько: переместить или скопировать библиотеку, ну или же указать загрузчику, где её искать. Последний способ более корректный, так как при нём Вы точно ничего не напортачите в системе.
Можно зайти в папку /etc/ld.so.conf.d/, открыть там любой конфигурационный файл и просто прописать местонахождение нужной библиотеки.
А можно сделать символьную (символическую) ссылку:
ln -s [путь_к_библиотеке/имя_библиотеки] /usr/lib/[имя_библиотеки]
Есть ещё одна причина ошибки while loading shared libraries даже когда нужна библиотека имеется в операционной системе. Библиотека может быть не той версии.
Версия библиотеки (или ещё её называют ревизией) пишется после расширения .so. В нашем примере нам требовалась библиотека libatomic.so.1, т.е. libatomic первой версии.
В разных дистрибутивах используются разные версии библиотек, а программы собираются под дистрибутив (и, как следствие, библиотеку конкретной версии). На практике же различия между версиями библиотек чаще всего минимальны. Поэтому для начала можно выдать библиотеку одной версии за библиотеку другой версии. В этом нам опять поможет символьная ссылка:
ln -s [путь_к_библиотеке/настоящее_имя_библиотеки] [путь_к_библиотеке/имя_библиотеки_с_нужной_версией]
Если этот способ не помог, то выход один — искать библиотеку нужной версии.
И последнее: после манипуляций с библиотеками желательно обновить кэш командой
sudo ldconfig
Вот, пожалуй, и всё, что нужно знать про ошибку error while loading shared libraries.
The program evince complains that it can’t find libfreetype.so.6; however I clearly have the file and its included in my LD_LIBRARY_PATH; furthermore I have another program which uses libfreetype6 and is able to run just fine. What’s going on here?
jbud@jb-pc ~> evince
evince: error while loading shared libraries: libfreetype.so.6: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
jbud@jb-pc ~> ldd /usr/bin/evince | grep freetype
libfreetype.so.6 => /usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6 (0x00007f912179d000)
jbud@jb-pc ~> file /usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6
/usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6: symbolic link to `libfreetype.so.6.11.1'
jbud@jb-pc ~> file /usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6.11.1
/usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6.11.1: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, BuildID[sha1]=0x21a4b8005e0c9a42af001b35fb984f4e25efc71c, not stripped
jbud@jb-pc ~> echo $LD_LIBRARY_PATH
/usr/lib/:/usr/lib64/:/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/:/usr/local/lib/
jbud@jb-pc ~> ldd jdrive/jstuff/work/personal/noengine/client | grep freetype
libfreetype.so.6 => /usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6 (0x00007feb5ac89000)
asked Jan 22, 2014 at 18:51
Creating a symbolic link to /usr/lib/libfreetype.so.6 should not be applied if the error was thrown by a 32-bit application on a 64-bit Linux distribution. The library could be left ‘broken’.
What you want on a 64-bit system is to install the necessary 32-bit dependencies around your 32-bit application, so that it will be able to detect and use the already existing libfreetype.so.6. This differs per application, but commonly missing are these:
sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-0:i386 libidn11:i386 libglu1-mesa:i386
And these may possibly fix the problem too:
sudo apt-get install libpangox-1.0-0:i386 libpangoxft-1.0-0:i386
Regards,
Albert Kok
answered Mar 5, 2014 at 10:59
I was able to fix this problem however I’m still not entirely sure why this was a problem in the first place.
After running strace, I saw open("/usr/local/lib/libfreetype.so.6", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 EACCES (Permission denied) which doesn’t quite make sense since other programs (without sudo powers) which depended on libfreetype were able to run, and the permissions are set for read/write for all, also running evince under sudo didn’t help either.
My apt-get of libfreetype placed the library in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libfreetype.so.6 but for some reason evince wasn’t checking that folder (even though it was added to LD_LIBRARY_PATH). However I created a symbolic link to a folder which it does check sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libfreetype.so.6.10.1 /usr/lib/libfreetype.so.6 and now evince runs fine.
answered Jan 23, 2014 at 15:44
glitchymeglitchyme
1911 gold badge1 silver badge5 bronze badges
For the past few days, I have been extensively testing PIP and Pipenv tools in my Arch Linux system. While testing these tools, I had to reinstall and downgrade Python2.x, Python 3.x packages and some other Python dependencies package many times. At some point, It broke my Arch Linux and pacman stopped working. Whenever I run pacman, I got an error that says «pacman: error while loading shared libraries: libidn2.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory».
pacman: error while loading shared libraries: libidn2.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
Not just pacman, some other applications, such as pacaur, yaourt, packer, virtualbox and transmission etc., also stopped working. When I try to open any one of these applications, I keep getting this message — «error while loading shared libraries: libidn2.so.0: cannot open shared object file».
Chances are that I may have uninstall something that I couldn’t remember. To my bad luck, It was my personal system and I don’t want to reinstall it because it has a lot of applications. So, reinstalling OS and all applications might took two or may be more days.
After vigorously searching on Arch Linux wiki and other Linux forums like a mad man, I finally managed to fixed it. If you ever run into a problem something like this, look nowhere, just download the source file and copy the missing file(s) to /usr/lib/ folder. As far as I searched on the web, this method seems very easiest one so far. Read on to know how I fixed this error.
Fix «pacman: error while loading shared libraries» Error In Arch Linux
As I said already, I kept getting this error — «pacman: error while loading shared libraries: libidn2.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory» when I run pacman command or any AUR helpers such as pacaur, packer, yaourt and I even can’t open VirtualBox application and Transmission client. So, the actual problem here is the file «libidn2.so.0» has gone missing. We need to find it out!
$ ls -la /usr/lib/libidn*
Sample output from my Arch Linux system:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 22 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkitlite.so -> libidnkitlite.so.1.0.2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 22 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkitlite.so.1 -> libidnkitlite.so.1.0.2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 276352 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkitlite.so.1.0.2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkit.so -> libidnkit.so.1.0.2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkit.so.1 -> libidnkit.so.1.0.2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 282368 Jul 22 2013 /usr/lib/libidnkit.so.1.0.2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Aug 15 19:00 /usr/lib/libidn.so -> libidn.so.11.6.16 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Aug 15 19:00 /usr/lib/libidn.so.11 -> libidn.so.11.6.16 -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 210872 Aug 15 19:00 /usr/lib/libidn.so.11.6.16
I had «libidn.so», but can’t find «libidn2.so.0». Since pacman and any other package manager didn’t work, there is no way to install, upgrade or downgrade any packages from official repository or local cache. So, I thought that the only way might be to download the package that has the missing file from Internet, extract it and finally copy the missing file(s) to /usr/lib/ directory. Let me create a directory to save libdin2 tar file:
$ mkdir libidn
$ cd libidn
Find and download the latest version of this package. A quick google search brought me here. Extract the file:
$ tar xf libidn2-2.0.4-2-x86_64.pkg.tar.xz
The above command extracted the contents of the file in a directory named «usr». Go to the usr/lib folder: (Note — It is usr/lib, not /usr/lib)
$ cd usr/lib
Finally copy the missing file, in our case it is libidn2.so.0, to /usr/lib/ directory of your Arch Linux system.
$ sudo cp libidn2.so.0 /usr/lib/
Then, I ran:
$ sudo pacman -syu
Update Arch Linux
Voila! Pacman works now!! Oops! Oh no, wait.. It didn’t work. I got this error after few minutes.
[....] (511/511) checking keys in keyring [######################] 100% (511/511) checking package integrity [######################] 100% (511/511) loading package files [######################] 100% (511/511) checking for file conflicts [######################] 100% error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files) libidn2: /usr/lib/libidn2.so.0 exists in filesystem Errors occurred, no packages were upgraded.
To fix this, I ran:
$ sudo pacman -S libidn2 --force
Then, I tried update again:
$ sudo pacman -Syu
Fixed!! All good now. So, if you guys ever run into an issue something like «error while loading shared libraries: .. cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory», one way to fix this is to find the the package that contains the missing files, download the latest version of that package, extract it and copy the missing files to /usr/lib/ directory. Of course, there could be many ways to fix such kind of issues. But this is the only working solution I could find and I find this much easier and faster. This trick might work on other Linux distros too.
Related read:
- How To Restore Broken Arch Linux To Previous Working State
- How To Fix “unable to lock database” Error In Arch Linux
- How To Fix “invalid or corrupted package (PGP signature)” Error In Arch Linux
- How To Solve “Starting full system upgrade… there is nothing to do” Issue In Arch Linux
- How To Solve “error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files)” In Arch Linux
sk
Senthilkumar Palani (aka SK) is the Founder and Editor in chief of OSTechNix. He is a Linux/Unix enthusiast and FOSS supporter. He lives in Tamilnadu, India.
Sometimes, when you try to install a program or a package from its source code, you might end up getting an error which looks like :
“error while loading shared libraries: cannot open shared object file No such file or directory”
In general, if the package shared library name is lib, the error sometimes shows the following :
“error while loading shared libraries: lib.so.X: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory “
Where X is a number.
These dynamically generated shared libraries, which are required by executables, are stored under /lib or /usr/lib directories.
The command below can help find out the libraries that are needed for a given executable :
ldd nw
As a quick workaround, you could try to fix the issue by running ldconfig command below :
sudo ldconfig -v
Now at runtime, the system would need to locate the ‘.so’ corresponding library file since the package or the program is linked with the library shared version.
To locate the library, invoke the command below :
sudo find / -name lib_file.so.x
or you could use apt search command. Jot down the path in which the lib_file.so.x is found, path_to_so_file.
Read: How to find the largest files on Linux
To include the folder in which the library is installed, the shell variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH has to be provided.
If LD_LIBRARY_PATH is not defined (run echo $LD_LIBRARY_PATH to find out), you could set it using the command (in the Bash shell) :
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib
Now using the path of the .so file that you found above, path_to_so_file, run the commands below :
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:path_to_so_file
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH $ ./your_package
You can find out more about shared libraries here.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.
Nikolaus Oosterhof
Nikolaus has a degree in software development. He is passionate about gadgets with a screen, nostalgic for phones, a retired gamer and open source programmer. He likes also to write about macOS and Windows. design web pages and debug long programs!