In python, lists are mutable as the elements of a list can be modified. But if you try to modify a value whose index is greater than or equal to the length of the list then you will encounter an Indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Example
If ‘fruits’ is a list, fruits=[‘Apple’,’ Banana’,’ Guava’]and you try to modify fruits[5] then you will get an index error since the length of fruits list=3 which is less than index asked to modify for which is 5.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Type is", type(fruits))
fruits[5] = 'Mango'
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/example.py", line 3, in <module> fruits[5]='Mango' IndexError: list assignment index out of range
So, as you can see in the above example, we get an error when we try to modify an index that is not present in the list of fruits.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
Method 1: Using insert() function
The insert(index, element) function takes two arguments, index and element, and adds a new element at the specified index.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the list of fruits on index 1.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.insert(1, "Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Guava']
It is necessary to specify the index in the insert(index, element) function, otherwise, you will an error that the insert(index, element) function needed two arguments.
Method 2: Using append()
The append(element) function takes one argument element and adds a new element at the end of the list.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the end of the list using the append(element) function.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.append("Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava', 'Mango']
An IndexError is nothing to worry about. It’s an error that is raised when you try to access an index that is outside of the size of a list. How do you solve this issue? Where can it be raised?
In this article, we’re going to answer those questions. We will discuss what IndexErrors are and how you can solve the “list assignment index out of range” error. We’ll walk through an example to help you see exactly what causes this error.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
The Problem: indexerror: list assignment index out of range
When you receive an error message, the first thing you should do is read it. An error message can tell you a lot about the nature of an error.
Our error message is: indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
IndexError tells us that there is a problem with how we are accessing an index. An index is a value inside an iterable object, such as a list or a string.
The message “list assignment index out of range” tells us that we are trying to assign an item to an index that does not exist.
In order to use indexing on a list, you need to initialize the list. If you try to assign an item into a list at an index position that does not exist, this error will be raised.
An Example Scenario
The list assignment error is commonly raised in for and while loops.
We’re going to write a program that adds all the cakes containing the word “Strawberry” into a new array. Let’s start by declaring two variables:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = []
The first variable stores our list of cakes. The second variable is an empty list that will store all of the strawberry cakes. Next, we’re going to write a loop that checks if each value in “cakes” contains the word “Strawberry”.
for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry[c] = cakes[c] print(strawberry)
If a value contains “Strawberry”, it should be added to our new array. Otherwise, nothing will happen. Once our for loop has executed, the “strawberry” array should be printed to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 6, in <module> strawberry[c] = cakes[c] IndexError: list assignment index out of range
As we expected, an error has been raised. Now we get to solve it!
The Solution
Our error message tells us the line of code at which our program fails:
The problem with this code is that we are trying to assign a value inside our “strawberry” list to a position that does not exist.
When we create our strawberry array, it has no values. This means that it has no index numbers. The following values do not exist:
strawberry[0] strawberry[1] …
We are trying to assign values to these positions in our for loop. Because these positions contain no values, an error is returned.
We can solve this problem in two ways.
Solution with append()
First, we can add an item to the “strawberry” array using append():
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let’s run our code: [‘Strawberry Tart’, ‘Strawberry Cheesecake’].
Our code works!
Solution with Initializing an Array
Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our “strawberry” array.
To initialize an array, you can use this code:
This will create an array with 10 empty values. Our code now looks like this:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] * 10 for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
Let’s try to run our code:
['Strawberry Tart', 'Strawberry Cheesecake']
Our code successfully returns an array with all the strawberry cakes.
This method is best to use when you know exactly how many values you’re going to store in an array.
«Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!»
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Our above code is somewhat inefficient because we have initialized “strawberry” with 10 empty values. There are only a total of three cakes in our “cakes” array that could possibly contain “Strawberry”. In most cases, using the append() method is both more elegant and more efficient.
Conclusion
IndexErrors are raised when you try to use an item at an index value that does not exist. The “indexerror: list assignment index out of range” is raised when you try to assign an item to an index position that does not exist.
To solve this error, you can use append() to add an item to a list. You can also initialize a list before you start inserting values to avoid this error.
Now you’re ready to start solving the list assignment error like a professional Python developer!
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
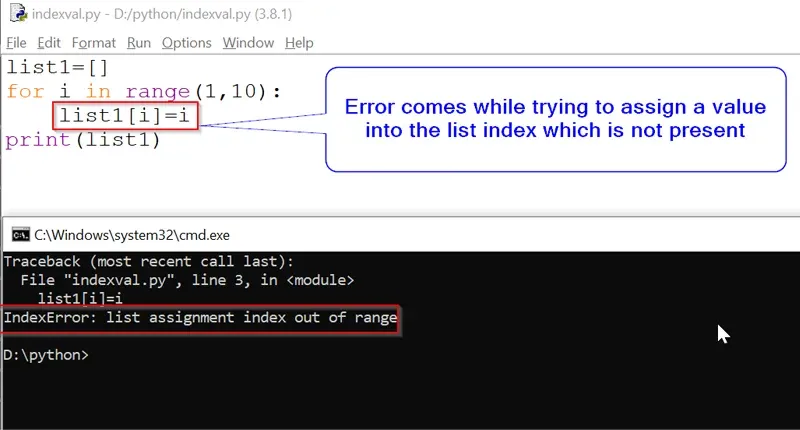
List elements can be modified and assigned new value by accessing the index of that element. But if you try to assign a value to a list index that is out of the list’s range, there will be an error. You will encounter an IndexError list assignment index out of range. Suppose the list has 4 elements and you are trying to assign a value into the 6th position, this error will be raised.
Example:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1[i]=i
print(list1)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeIn the above example we have initialized a “list1“ which is an empty list and we are trying to assign a value at list1[1] which is not present, this is the reason python compiler is throwing “IndexError: list assignment index out of range”.
We can solve this error by using the following methods.
Using append()
We can use append() function to assign a value to “list1“, append() will generate a new element automatically which will add at the end of the list.
Correct Code:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.append(i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is empty and instead of assigning a value to list, we append the list with new value using append() function.
Using insert()
By using insert() function we can insert a new element directly at i’th position to the list.
Example:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1.insert(i,i)
print(list1)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]In the above example we can see that “list1” is an empty list and instead of assigning a value to list, we have inserted a new value to the list using insert() function.
Example with While loop
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num[i] = I
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeCorrect example:
num = []
i = 1
while(i <= 10):
num.append(i)
i=i+1
print(num)Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]Conclusion:
Always check the indices before assigning values into them. To assign values at the end of the list, use the append() method. To add an element at a specific position, use the insert() method.
- Python
IndexError: list assignment index out of range - Fix the
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangein Python - Fix
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeUsingappend()Function - Fix
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeUsinginsert()Function - Conclusion

In Python, the IndexError: list assignment index out of range is raised when you try to access an index of a list that doesn’t even exist. An index is the location of values inside an iterable such as a string, list, or array.
In this article, we’ll learn how to fix the Index Error list assignment index out-of-range error in Python.
Python IndexError: list assignment index out of range
Let’s see an example of the error to understand and solve it.
Code Example:
# error program --> IndexError: list assignment index out of range
i = [7,9,8,3,7,0] # index range (0-5)
j = [1,2,3] # index range (0-3)
print(i,"n",j)
print(f"nLength of i = {len(i)}nLength of j = {len(j)}" )
print(f"nValue at index {1} of list i and j are {i[1]} and {j[1]}")
print(f"nValue at index {3} of list i and j are {i[3]} and {j[3]}") # error because index 3 isn't available in list j
Output:
[7, 9, 8, 3, 7, 0]
[1, 2, 3]
Length of i = 6
Length of j = 3
Value at index 1 of list i and j are 9 and 2
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
The reason behind the IndexError: list assignment index out of range in the above code is that we’re trying to access the value at the index 3, which is not available in list j.
Fix the IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python
To fix this error, we need to adjust the indexing of iterables in this case list. Let’s say we have two lists, and you want to replace list a with list b.
Code Example:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
b[k] = l # indexError --> because the length of b is 0
k += 1
print(f"{a}n{a}")
Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
You cannot assign values to list b because the length of it is 0, and you are trying to add values at kth index b[k] = I, so it is raising the Index Error. You can fix it using the append() and insert().
Fix IndexError: list assignment index out of range Using append() Function
The append() function adds items (values, strings, objects, etc.) at the end of the list. It is helpful because you don’t have to manage the index headache.
Code Example:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
# use append to add values at the end of the list
j.append(l)
k += 1
print(f"List a: {a}nList b: {a}")
Output:
List a: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
List b: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Fix IndexError: list assignment index out of range Using insert() Function
The insert() function can directly insert values to the k'th position in the list. It takes two arguments, insert(index, value).
Code Example:
a = [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
# use insert to replace list a into b
j.insert(k, l)
k += 1
print(f"List a: {a}nList b: {a}")
Output:
List a: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
List b: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
In addition to the above two solutions, if you want to treat Python lists like normal arrays in other languages, you can pre-defined your list size with None values.
Code Example:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = [None] * len(i)
print(f'Length of a: {len(a)}')
print(f'Length of b: {len(b)}')
print(f"n{a}n{b}")
Output:
Length of a: 6
Length of b: 6
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[None, None, None, None, None, None]
Once you have defined your list with dummy values None, you can use it accordingly.
Conclusion
There could be a few more manual techniques and logic to handle the IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python. This article overviews the two common list functions that help us handle the Index Error in Python while replacing two lists.
We have also discussed an alternative solution to pre-defined the list and treat it as an array similar to the arrays of other programming languages.
In this article, we’ll talk about the IndexError: list index out of range error in Python.
In each section of the article, I’ll highlight a possible cause for the error and how to fix it.
You may get the IndexError: list index out of range error for the following reasons:
- Trying to access an index that doesn’t exist in a list.
- Using invalid indexes in your loops.
- Specifying a range that exceeds the indexes in a list when using the
range()function.
Before we proceed to fixing the error, let’s discuss how indexing work in Python lists. You can skip the next section if you already know how indexing works.
How Does Indexing Work in Python Lists?
Each item in a Python list can be assessed using its index number. The first item in a list has an index of zero.
Consider the list below:
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
print(languages[1])
# JavaScriptIn the example above, we have a list called languages. The list has three items — ‘Python’, ‘JavaScript’, and ‘Java’.
To access the second item, we used its index: languages[1]. This printed out JavaScript.
Some beginners might misunderstand this. They may assume that since the index is 1, it should be the first item.
To make it easier to understand, here’s a breakdown of the items in the list according to their indexes:
Python (item 1) => Index 0
JavaScript (item 2) => Index 1
Java (item 3) => Index 2
As you can see above, the first item has an index of 0 (because Python is «zero-indexed»). To access items in a list, you make use of their indexes.
What Will Happen If You Try to Use an Index That Is Out of Range in a Python List?
If you try to access an item in a list using an index that is out of range, you’ll get the IndexError: list index out of range error.
Here’s an example:
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
print(languages[3])
# IndexError: list index out of rangeIn the example above, we tried to access a fourth item using its index: languages[3]. We got the IndexError: list index out of range error because the list has no fourth item – it has only three items.
The easy fix is to always use an index that exists in a list when trying to access items in the list.
How to Fix the IndexError: list index out of range Error in Python Loops
Loops work with conditions. So, until a certain condition is met, they’ll keep running.
In the example below, we’ll try to print all the items in a list using a while loop.
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
i = 0
while i <= len(languages):
print(languages[i])
i += 1
# IndexError: list index out of rangeThe code above returns the IndexError: list index out of range error. Let’s break down the code to understand why this happened.
First, we initialized a variable i and gave it a value of 0: i = 0.
We then gave a condition for a while loop (this is what causes the error): while i <= len(languages).
From the condition given, we’re saying, «this loop should keep running as long as i is less than or equal to the length of the language list».
The len() function returns the length of the list. In our case, 3 will be returned. So the condition will be this: while i <= 3. The loop will stop when i is equal to 3.
Let’s pretend to be the Python compiler. Here’s what happens as the loop runs.
Here’s the list: languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']. It has three indexes — 0, 1, and 2.
When i is 0 => Python
When i is 1 => JavaScript
When i is 2 => Java
When i is 3 => Index not found in the list. IndexError: list index out of range error thrown.
So the error is thrown when i is equal to 3 because there is no item with an index of 3 in the list.
To fix this problem, we can modify the condition of the loop by removing the equal to sign. This will stop the loop once it gets to the last index.
Here’s how:
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
i = 0
while i < len(languages):
print(languages[i])
i += 1
# Python
# JavaScript
# Java
The condition now looks like this: while i < 3.
The loop will stop at 2 because the condition doesn’t allow it to equate to the value returned by the len() function.
How to Fix the IndexError: list index out of range Error in When Using the range() Function in Python
By default, the range() function returns a «range» of specified numbers starting from zero.
Here’s an example of the range() function in use:
for num in range(5):
print(num)
# 0
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4As you can see in the example above, range(5) returns 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
You can use the range() function with a loop to print the items in a list.
The first example will show a code block that throws the IndexError: list index out of range error. After pointing out why the error occurred, we’ll fix it.
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
for language in range(4):
print(languages[language])
# Python
# JavaScript
# Java
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# File "<string>", line 5, in <module>
# IndexError: list index out of rangeThe example above prints all the items in the list along with the IndexError: list index out of range error.
We got the error because range(4) returns 0, 1, 2, 3. Our list has no index with the value of 3.
To fix this, you can modify the parameter in the range() function. A better solution is to use the length of the list as the range() function’s parameter.
That is:
languages = ['Python', 'JavaScript', 'Java']
for language in range(len(languages)):
print(languages[language])
# Python
# JavaScript
# JavaThe code above runs without any error because the len() function returns 3. Using that with range(3) returns 0, 1, 2 which matches the number of items in a list.
Summary
In this article, we talked about the IndexError: list index out of range error in Python.
This error generally occurs when we try to access an item in a list by using an index that doesn’t exist within the list.
We saw some examples that showed how we may get the error when working with loops, the len() function, and the range() function.
We also saw how to fix the IndexError: list index out of range error for each case.
Happy coding!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
[SOLVED] List Index Out of Range Meaning, How to Fix | Python Program.
If you are frequent in Python programming, you will definitely come across this error message, “indexerror: list index out of range“. You might want to ask, what does list index out of range mean? and how to fix the list index out of range in python?
Well, in this article, I will share with you everything you need to know about this common list assignment index out of range error in Python. Here, you will follow this guide and fic the error once and for all. After reading this post, you will find yourself at a position where you can even teach others on how to fix this error message.
Why do you have “List Index Out of Range” Error?
Table of Contents
- Why do you have “List Index Out of Range” Error?
- See other explanations here:
- List Index Out of Range Meaning
- 2 Ways to Fix List Index Out of Range Error
- You May Also Like:
If you write a simple python program, as follow;
l=[1,2,3,0,0,1]
for i in range(0,len(l)):
if l[i]==0:
l.pop(i)This will give you an error message ‘list index out of range’ on line if l[i]==0:
And you will observe that i is getting incremented and the list is getting reduced.
However, you may have a loop termination condition i < len(l).
See other explanations here:
check out the following code in python
- >>> even = [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ]
- >>> even[1]
- 4
- >>> even[3]
- 8
- >>> even[5]
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File “<pyshell#7>”, line 1, in <module>
- even[5]
- IndexError: list index out of range
So in the above code, we have defined an even list that contains 4 elements with starting index 0 and last index 3.
clearly, this means you can’t access any elements in even list if you go beyond your last index value.
And if u try, then u will get a list index out of range error.
List index out of range means that you are providing an index for which a list element does not exist. Index out of range means that the code is trying to access a matrix or vector outside of its bounds.
In python list is mutable, so the size is not fixed.
Due to size is not fixed, the available index is greater than the assigned index for a list(available index > assigned index).
2 Ways to Fix List Index Out of Range Error
See how to handle indexerror list index out of range in python here. You are reducing the length of your list l as you iterate over it, so as you approach the end of your indices in the range statement, some of those indices are no longer valid.
It looks like what you want to do is:
l = [x for x in l if x != 0]which will return a copy of l without any of the elements that were zero (that operation is called a list comprehension, by the way). You could even shorten that last part to just if x, since non-zero numbers evaluate to True.
There is no such thing as a loop termination condition of i < len(l), in the way you’ve written the code, because len(l) is precalculated before the loop, not re-evaluated on each iteration. You could write it in such a way, however:
i = 0
while i < len(l):
if l[i] == 0:
l.pop(i)
else:
i += 1If you try to access the empty or None element by pointing available index of list, Then you will get the List index out of range error.
open python and dirty your hands with this below code, to have a better understanding.
>> x = list(‘1234’)
>> x
[‘1’ , ‘2’ , ‘3’, ‘4’]
>> length = len(x)
4
>> x[length]
Index Error: list index out of range
Final Answer [SOLVED]: If you have a list with 53 items, the last one is thelist[52] because indexing starts at 0 (zero).
AD! Click here to Get the Highest Paying Work from Home Jobs in USA
======================
The content on this site is posted with good intentions. If you own this content & believe your copyright was violated or infringed, make sure you contact us at [easyinfoblog@gmail.com] to file a complaint and actions will be taken immediately.
You May Also Like:
Author: Simon RobertEasyInfoBlog is a multi-author blog. We have experts and professionals in various fields who share their ideas and expert knowledge to help you with your daily information needs. Thanks for reading!


![List Index Out of Range – Python Error [Solved]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2022/08/kelly-sikkema--1_RZL8BGBM-unsplash--3-.jpg)