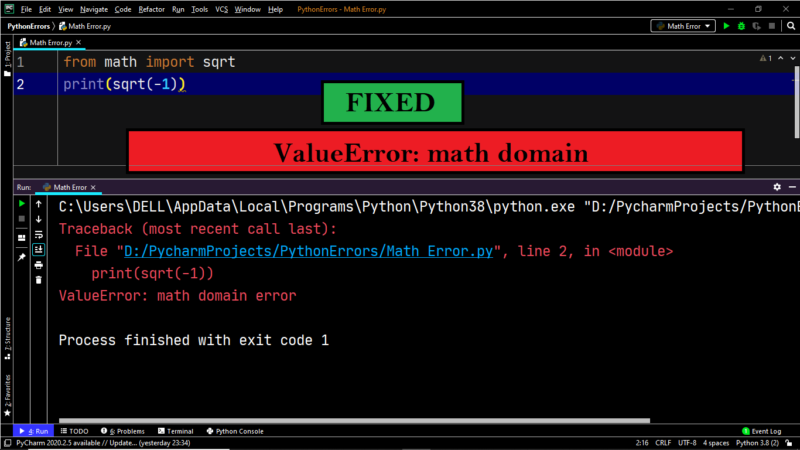
In mathematics, there are operations which do not work on negative numbers or zero numbers. Consider the square root, for example. You cannot find the square root of a negative number. Python recognizes that not all operations work with negative or zero numbers.
Python will raise an error when you try to use a negative number on an operation that does not support one. In this guide, we’re going to talk about the cause of the ValueError: math domain error. Toward the end of the guide, we’ll walk through a solution to this issue.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
ValueError: math domain error
The Python ValueError: math domain error is raised when you use a number that is not supported by a mathematical operation. This error is commonly raised with the sqrt() method and the log() method.
The ValueError is a type of error that indicates you are performing a mathematical operation on a value that does not work with that operation. In the case of the “math domain error”, we are using a negative number or a zero number where we should not be.
Let’s walk through an example of the ValueError: math domain error issue in action.
An Example Scenario
We are building a program that calculates the square root of a given number. This program is designed to help students revise their knowledge of square roots.
Let’s write a program that calculates the square root of a given number. We will start by importing the math library that we need to calculate a square root:
Next, we’re going to collect a number from the user:
number = input("Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: ")
We prompt the user to try finding the answer themselves, as our program is designed to help people check their answers. Next, we’re going to find the square root of the value the user inserts:
answer = math.sqrt(int(number))
We convert the value of “number”, which stores the number whose square root the user wants to find, into an integer. This is necessary because the input() method, which we used to collect the aforementioned number, returns a string. We cannot find the square root of a string value.
Finally, let’s print the answer to the console:
print("The square root of {} is {}.".format(number, answer))
We use a format() statement to add numbers to our string. Our string will show:
"The square root of [Number user inserted] is [The square root our program calculated]"
Let’s test our program with a negative number:
Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: -16 Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 5, in <module> answer = math.sqrt(int(number)) ValueError: math domain error
We inserted the value -16 into our program. Our code returned an error.
Let’s fix this error.
The Solution
To fix this error, we need to prompt the user that you cannot calculate the square root of a negative number before we execute the math.sqrt() function.
Let’s revise our code to make this happen:
import math
number = input("Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: ")
if int(number) >= 0:
answer = math.sqrt(int(number))
print("The square root of {} is {}.".format(number, answer))
else:
print("You cannot find the square root of a number less than 0.")
We use an if statement to check if the number the user inserts into the program is equal to or greater than zero. If the number meets this criterion, the contents of the if statement run. Otherwise, the else statement executes, presenting us with a message that we have inserted an invalid number.
Let’s run our program again. Our program returns:
Try solving the problem first using pencil and paper. Then, insert the number whose square root you want to verify: -16 You cannot find the square root of a number less than 0.
Our code works successfully.
Conclusion
The ValueError: math domain error is raised when you perform a mathematical function on a negative or zero number which cannot be computed. To solve this error, make sure you are using a valid number for the mathematical function you are using.
If you want to learn more about coding in Python, check out our How to Learn Python guide. This guide contains a number of learning resources, courses, and books designed for people who are learning the Python programming language.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- ⚠️What Is a Math Domain Error in Python?
- ➥ Fixing “ValueError: math domain error”-sqrt
- 💡 Solution 1: Using “cmath” Module
- 💡 Solution 2: Use Exception Handling
- ➥ “ValueError: math domain error” Examples
- ✰ Scenario 1: Math Domain Error While Using pow()
- ✰ Scenario 2: Python Math Domain Error While Using log()
- ✰ Scenario 3: Math Domain Error While Using asin()
- 📖 Exercise: Fixing Math Domain Error While Using Acos()
- Conclusion
Introduction
So, you sit down, grab a cup of coffee and start programming in Python. Then out of nowhere, this stupid python error shows up: ValueError: math domain error. 😞
Sometimes it may seem annoying, but once you take time to understand what Math domain error actually is, you will solve the problem without any hassle.
To fix this error, you must understand – what is meant by the domain of a function?
Let’s use an example to understand “the domain of a function.”
Given equation: y= √(x+4)
- y = dependent variable
- x = independent variable
The domain of the function above is x≥−4. Here x can’t be less than −4 because other values won’t yield a real output.
❖ Thus, the domain of a function is a set of all possible values of the independent variable (‘x’) that yield a real/valid output for the dependent variable (‘y’).
If you have done something that is mathematically undefined (not possible mathematically), then Python throws ValueError: math domain error.
➥ Fixing “ValueError: math domain error”-sqrt
Example:
|
from math import * print(sqrt(—5)) |
Output:
|
Traceback (most recent call last): File «D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/Math Error.py», line 2, in <module> print(sqrt(—5)) ValueError: math domain error |
Explanation:
Calculating the square root of a negative number is outside the scope of Python, and it throws a ValueError.
Now, let’s dive into the solutions to fix our problem!
💡 Solution 1: Using “cmath” Module
When you calculate the square root of a negative number in mathematics, you get an imaginary number. The module that allows Python to compute the square root of negative numbers and generate imaginary numbers as output is known as cmath.
Solution:
|
from cmath import sqrt print(sqrt(—5)) |
Output:
2.23606797749979j
💡 Solution 2: Use Exception Handling
If you want to eliminate the error and you are not bothered about imaginary outputs, then you can use try-except blocks. Thus, whenever Python comes across the ValueError: math domain error it is handled by the except block.
Solution:
|
from math import * x = int(input(‘Enter an integer: ‘)) try: print(sqrt(x)) except ValueError: print(«Cannot Compute Negative Square roots!») |
Output:
Enter an integer: -5
Cannot Compute Negative Square roots!
Let us have a look at some other scenarios that lead to the occurrence of the math domain error and the procedure to avoid this error.
➥ “ValueError: math domain error” Examples
✰ Scenario 1: Math Domain Error While Using pow()
Cause of Error: If you try to calculate a negative base value raised to a fractional power, it will lead to the occurrence of ValueError: math domain error.
Example:
|
import math e = —1.7 print(math.pow(—3, e)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/Math Error.py”, line 3, in
print(math.pow(-3, e))
ValueError: math domain error
Solution: Use the cmath module to solve this problem.
- Note:
- Xy = ey ln x
Using the above property, the error can be avoided as follows:
|
from cmath import exp,log e = —1.7 print(exp(e * log(—3))) |
Output:
(0.0908055832509843+0.12498316306449488j)
✰ Scenario 2: Python Math Domain Error While Using log()
Consider the following example if you are working on Python 2.x:
|
import math print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “main.py”, line 2, in
print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2))
ValueError: math domain error
Explanation: In Python 2.x, 2/3 evaluates to 0 since division floors by default. Therefore you’re attempting a log 0, hence the error. Python 3, on the other hand, does floating-point division by default.
Solution:
To Avoid the error try this instead:
from __future__ import division, which gives you Python 3 division behaviour in Python 2.7.
|
from __future__ import division import math print(2/3*math.log(2/3,2)) # Output: -0.389975000481 |
✰ Scenario 3: Math Domain Error While Using asin()
Example:
|
import math k = 5 print(«asin(«,k,«) is = «, math.asin(k)) |
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “D:/PycharmProjects/PythonErrors/rough.py”, line 4, in
print(“asin(“,k,”) is = “, math.asin(k))
ValueError: math domain error
Explanation: math.asin() method only accepts numbers between the range of -1 to 1. If you provide a number beyond of this range, it returns a ValueError – “ValueError: math domain error“, and if you provide anything else other than a number, it returns error TypeError – “TypeError: a float is required“.
Solution: You can avoid this error by passing a valid input number to the function that lies within the range of -1 and 1.
|
import math k = 0.25 print(«asin(«,k,«) is = «, math.asin(k)) #OUTPUT: asin( 0.25 ) is = 0.25268025514207865 |
📖 Exercise: Fixing Math Domain Error While Using Acos()
Note: When you pass a value to math.acos() which does not lie within the range of -1 and 1, it raises a math domain error.
Fix the following code:
|
import math print(math.acos(10)) |
Answer:
Conclusion
I hope this article helped you. Please subscribe and stay tuned for more exciting articles in the future. Happy learning! 📚
You may encounter a special ValueError when working with Python’s math module.
ValueError: math domain error
Python raises this error when you try to do something that is not mathematically possible or mathematically defined.
To understand this error, have a look at the definition of the domain:
“The domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable. Roughly speaking, the domain is the set of all possible (input) x-values which result in a valid (output) y-value.” (source)
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values. If Python throws the ValueError: math domain error, you’ve passed an undefined input into the math function. Fix the error by passing a valid input for which the function is able to calculate a numerical output.
Here are a few examples:
The math domain error appears if you pass a negative argument into the math.sqrt() function. It’s mathematically impossible to calculate the square root of a negative number without using complex numbers. Python doesn’t get that and throws a ValueError: math domain error.
Here’s a minimal example:
from math import sqrt
print(sqrt(-1))
'''
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 2, in <module>
print(sqrt(-1))
ValueError: math domain error
'''
You can fix the math domain error by using the cmath package that allows the creation of complex numbers:
from cmath import sqrt print(sqrt(-1)) # 1j
Python Math Domain Error Log
The math domain error for the math.log() function appears if you pass a zero value into it—the logarithm is not defined for value 0.
Here’s the code on an input value outside the domain of the logarithm function:
from math import log print(log(0))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(log(0))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value into the math.log() function:
from math import log print(log(0.000001)) # -13.815510557964274
This error can sometimes appear if you pass a very small number into it—Python’s float type cannot express all numbers. To pass a value “close to 0”, use the Decimal module with higher precision, or pass a very small input argument such as:
math.log(sys.float_info.min)
Python Math Domain Error Acos
The math domain error for the math.acos() function appears if you pass a value into it for which it is not defined—arccos is only defined for values between -1 and 1.
Here’s the wrong code:
import math print(math.acos(2))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.acos(2))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value between [-1,1] into the math.acos() function:
import math print(math.acos(0.5)) # 1.0471975511965979
Python Math Domain Error Asin
The math domain error for the math.asin() function appears if you pass a value into it for which it is not defined—arcsin is only defined for values between -1 and 1.
Here’s the erroneous code:
import math print(math.asin(2))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.asin(2))
ValueError: math domain error
You can fix this error by passing a valid input value between [-1,1] into the math.asin() function:
import math print(math.asin(0.5)) # 0.5235987755982989
Python Math Domain Error Pow
The math domain error for the math.pow(a,b) function to calculate a**b appears if you pass a negative base value into it and try to calculate a negative power of it. The reason it is not defined is that any negative number to the power of 0.5 would be the square number—and thus, a complex number. But complex numbers are not defined by default in Python!
import math print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
The output is the math domain error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:UsersxcentDesktopFinxterBlogcode.py", line 3, in <module>
print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
ValueError: math domain error
If you need a complex number, ab must be rewritten into eb ln a. For example:
import cmath print(cmath.exp(0.5 * cmath.log(-2))) # (8.659560562354932e-17+1.414213562373095j)
You see, it’s a complex number!
NumPy Math Domain Error — np.log(x)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plotting y = log(x) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set(xlim=(-5, 20), ylim=(-4, 4), title='log(x)', ylabel='y', xlabel='x') x = np.linspace(-10, 20, num=1000) y = np.log(x) plt.plot(x, y)
This is the graph of log(x). Don’t worry if you don’t understand the code, what’s more important is the following point. You can see that log(x) tends to negative infinity as x tends to 0. Thus, it is mathematically meaningless to calculate the log of a negative number. If you try to do so, Python raises a math domain error.
>>> math.log(-10) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: math domain error
Where to Go From Here?
Enough theory. Let’s get some practice!
Coders get paid six figures and more because they can solve problems more effectively using machine intelligence and automation.
To become more successful in coding, solve more real problems for real people. That’s how you polish the skills you really need in practice. After all, what’s the use of learning theory that nobody ever needs?
You build high-value coding skills by working on practical coding projects!
Do you want to stop learning with toy projects and focus on practical code projects that earn you money and solve real problems for people?
🚀 If your answer is YES!, consider becoming a Python freelance developer! It’s the best way of approaching the task of improving your Python skills—even if you are a complete beginner.
If you just want to learn about the freelancing opportunity, feel free to watch my free webinar “How to Build Your High-Income Skill Python” and learn how I grew my coding business online and how you can, too—from the comfort of your own home.
Join the free webinar now!
While working as a researcher in distributed systems, Dr. Christian Mayer found his love for teaching computer science students.
To help students reach higher levels of Python success, he founded the programming education website Finxter.com. He’s author of the popular programming book Python One-Liners (NoStarch 2020), coauthor of the Coffee Break Python series of self-published books, computer science enthusiast, freelancer, and owner of one of the top 10 largest Python blogs worldwide.
His passions are writing, reading, and coding. But his greatest passion is to serve aspiring coders through Finxter and help them to boost their skills. You can join his free email academy here.
The domain of a mathematical function is the set of all possible input values. If you pass an undefined input to a function from the math library, you will raise the ValueError: math domain error.
To solve this error, ensure that you use a valid input for the mathematical function you wish to use. You can put a conditional statement in your code to check if the number is valid for the function before performing the calculation.
You cannot use functions from the math library with complex numbers, such as calculating a negative number’s square root. To do such calculations, use the cmath library.
This tutorial will go through the error in detail and solve it with the help of some code examples.
Table of contents
- ValueError: math domain error
- What is a ValueError?
- Example #1: Square Root of a Negative Number
- Solution #1: Use an if statement
- Solution #2: Use cmath
- Example #2: Logarithm of Zero
- Solution
- Summary
ValueError: math domain error
What is a ValueError?
In Python, a value is the information stored within a particular object. You will encounter a ValueError in Python when you use a built-in operation or function that receives an argument with the right type but an inappropriate value.
The ValueError: math domain error occurs when you attempt to use a mathematical function with an invalid value. You will commonly see this error using the math.sqrt() and math.log() methods.
Example #1: Square Root of a Negative Number
Let’s look at an example of a program that calculates the square root of a number.
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')We import the math library to use the square root function in the above code. We collect the number from the user using the input() function. Next, we find the square root of the number and print the result to the console using an f-string. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: -4---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
3 number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
4
----> 5 sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
6
7 print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')
ValueError: math domain errorWe raise the ValueError because a negative number does not have a real square root.
Solution #1: Use an if statement
To solve this error, we can check the value of the number before attempting to calculate the square root by using an if statement. Let’s look at the revised code:
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number > 0:
sqrt_number = math.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')
else:
print('The number you input is less than zero. You cannot find the real square root of a negative number.')In the above code, we check if the user’s number is greater than zero. If it is, we calculate the number’s square root and print it to the console. Otherwise, we print a statement telling the user the number is invalid for the square root function. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: -4
The number you input is less than zero. You cannot find the real square root of a negative number.Go to the article: Python Square Root Function for further reading on calculating the square root of a number in Python.
Solution #2: Use cmath
We can also solve the square root math domain error using the cmath library. This library provides access to mathematical functions for complex numbers. The square root of a negative number is a complex number with a real and an imaginary component. We will not raise a math domain error using the square root function from cmath on a negative number. Let’s look at the revised code:
import cmath
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
sqrt_number = cmath.sqrt(number)
print(f' The square root of {number} is {sqrt_number}')Let’s run the code to get the result:
Enter a number: -4
The square root of -4 is 2jExample #2: Logarithm of Zero
Let’s look at an example of a program that calculates the natural logarithm of a number. The log() method returns the natural logarithm of a number or to a specified base. The syntax of the math.log() method is:
math.log(x, base)Parameters:
- x: Required. The value to calculate the number logarithm for.
- base: Optional. The logarithmic base to use. The default is e.
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')We import the math library to use the natural logarithm function in the above code. We collect the number from the user using the input() function. Next, we find the natural logarithm of the number and print the result to the console using an f-string. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Enter a number: 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
3 number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
4
----> 5 print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')
ValueError: math domain errorWe raise the ValueError because you cannot calculate the natural logarithm of 0 or a negative number. The log(0) means that the exponent e raised to the power of a number is 0. An exponent can never result in 0, which means log(0) has no answer, resulting in the math domain error.
Solution
We can put an if statement in the code to check if the number we want to use is positive to solve this error. Let’s look at the revised code:
import math
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number > 0:
print(f'The log of {number} is {math.log(number)}.')
else:
print(f'The number you provided is less than or equal to zero. You can only get the logarithm of positive real numbers')Now we will only calculate the natural logarithm of the number if it is greater than zero. Let’s run the code to get the result:
Enter a number: 0
The number you provided is less than or equal to zero. You can only get the logarithm of positive real numbersSummary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! ValueError: math domain error occurs when you attempt to perform a mathematical function with an invalid number. Every mathematical function has a valid domain of input values you can choose. For example, the logarithmic function accepts all positive, real numbers. To solve this error, ensure you use input from the domain of a function. You can look up the function in the math library documentation to find what values are valid and which values will raise a ValueError.
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about coding in Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!
ValueError: math domain error
While working with mathematical functions in Python, you might come across an error called «ValueError math domain error«. This error is usually encountered when you are trying to solve quadratic equations or finding out the square root of a negative number.
You can avoid this error by providing the correct values to the math functions. Avoiding the use of negative values will be ideal.
Let us look at some examples where the error might be encountered.
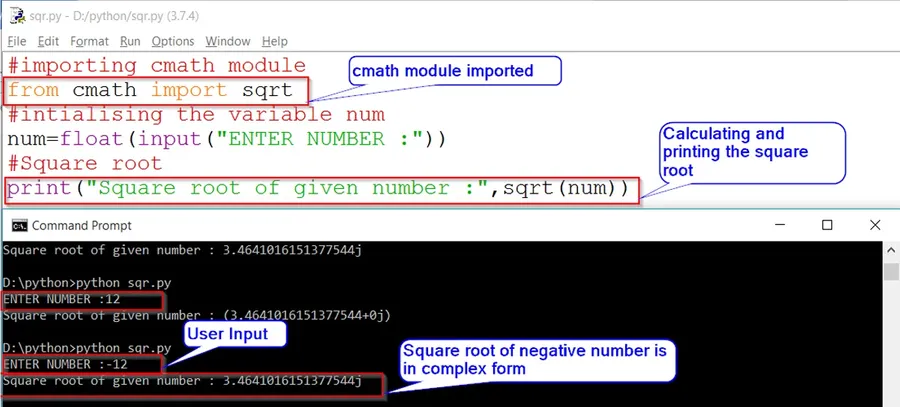
Example 1: Square Root of Negative Number
We can calculate the square root of a number in python by importing the sqrt method from the math module. But what if a user entered a negative number?
Will it throw an error or will we get the desired output? let’s understand it with a few examples.
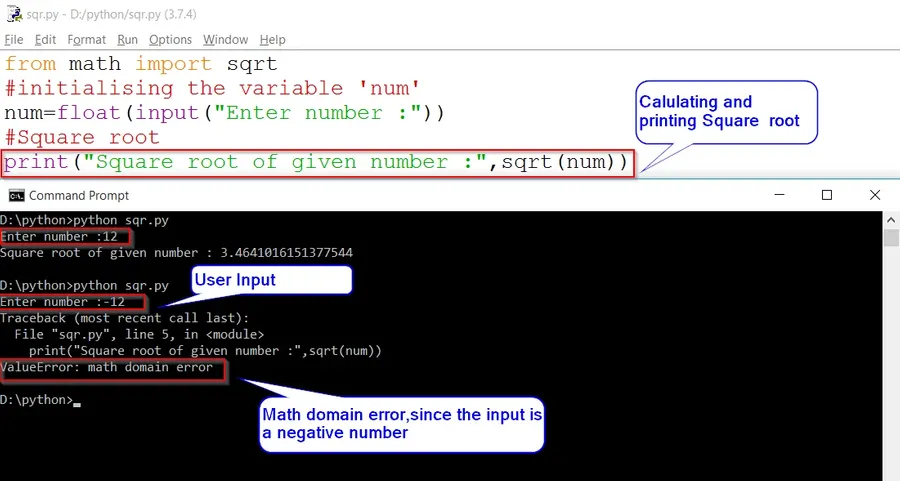
from math import sqrt
# Initialising the variable 'num'
num=float(input("Enter number :"))
#Square root of num
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))Output:
Enter number :12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544
Enter number :-12
File "sqr.py", line 5, in <module>
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))
ValueError: math domain errorIf num less then 0 or negative number then this code throws a math domain error as mentioned above.
Solution:
We can either handle the ValueError by raising an exception or by importing sqrt method from cmath library lets discuss both of them.
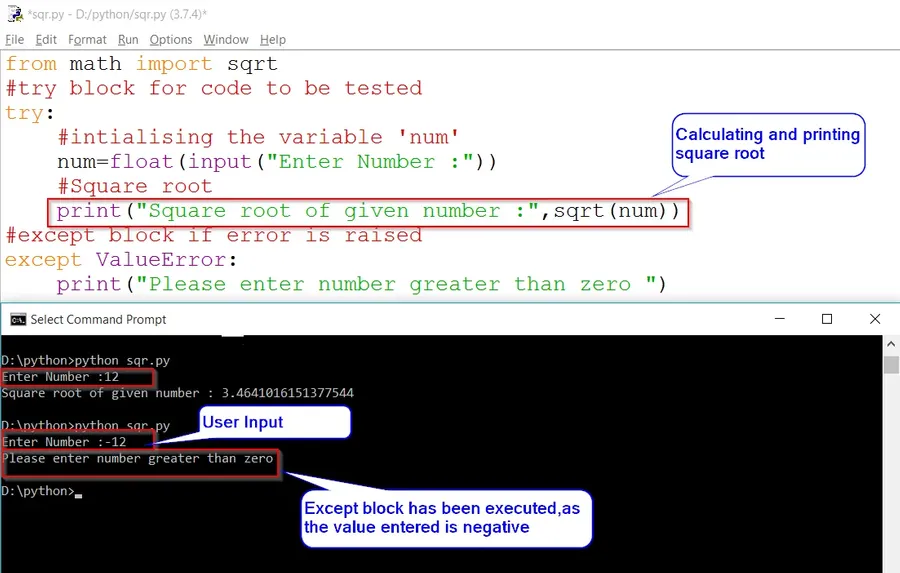
Method 1: Using Try and Except Block for Handling the Error.
from math import sqrt
#try block for code to be tested
try:
#intialising the variable 'num'
num=float(input("Enter Number :"))
#Square root
print("Square root of given number :",sqrt(num))
#except block if error is raised
except ValueError:
print("Please enter a number greater than zero ")OUTPUT :
Enter Number : 12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544
Enter Number : -12
Please enter a number greater than zeroIn the above code, when we enter a positive value we will get the desired output. But, when we will enter a negative value it’ll throw an error i.e «ValueError: math domain error«.
And to handle the ValueError we use try and except block.
The try block includes the code to be tested.
The Except block handles the error by displaying the desired message. Which in this case is «Please enter the number greater than zero«.
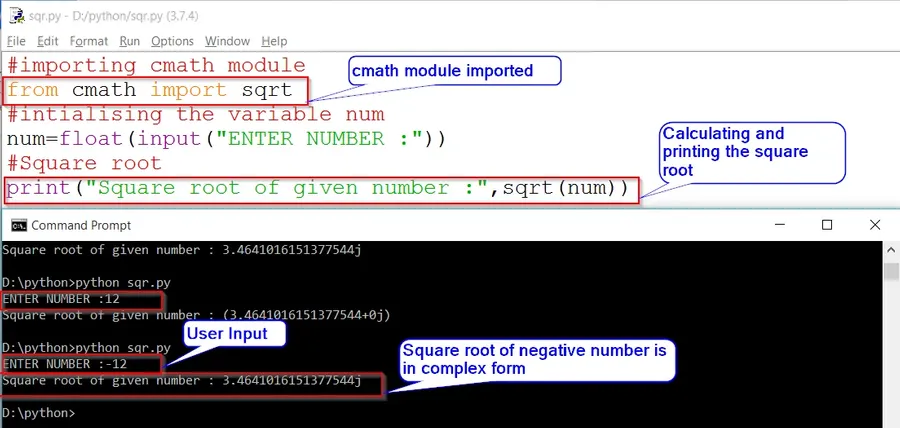
Method2: Importing Sqrt From «cmath» Which Will Return Square Root of Negative Number in Complex/Imaginary Form.
# Importing cmath module
from cmath import sqrt
# Input from user
num=float(input("Enter Number: "))
#Square root
print("Square root of given number : ", sqrt(num))OUTPUT:
Enter Number : 12
Square root of given number : (3.4641016151377544+0j)
Enter Number : -12
Square root of given number : 3.4641016151377544jIn Method 1 we did not get the result instead we raised an exception. But what if we want the square root of a negative index in complex form.
To solve this issue import «sqrt» from cmath module. Which shows the result in complex/imaginary form as in mathematics.
When we import the cmath module the result which we will get will be in the complex form as shown in the output of «Method 2«.
Example 2: Log of a Negative Number
#importing log from math module
from math import log
#Intialising the variable 'num'
num= float(input("Enter Number :"))
#Natural logarithm of num
print("Natural logarithm of provided number :",log(num))OUTPUT:
Enter Number :12
Natural logarithm of provided number : 2.4849066497880004
Enter Number :-12
File "sqr.py", line 6, in <module>
print("Natural logarithm of provided number :",log(num))
ValueError: math domain errorIn the above code, When we try to find the log of the positive value we get the desired output. But when we try to find the log of the negative index it throws an error «ValueError: math domain error«.
This is because the negative of the log is not defined in python.
- Understand the Root Cause of the
ValueError: math domain errorin Python - Replicate the
ValueError: math domain errorin Python - Solve the
ValueError: math domain errorin Python

In this tutorial, we aim to explore different methods to resolve the ValueError: math domain error in Python.
This article tackles the following topics.
- Understanding the root cause of the problem.
- Replicating the issue.
- Resolving the issue.
Understand the Root Cause of the ValueError: math domain error in Python
A ValueError: math domain error is generally raised in Python whenever there is an inherent flaw in the usage of Mathematics (Basic or Advanced) in the coding aspect.
Dividing any integer or floating point value by zero, taking the logarithm of any non-positive number or multiplying any integer by infinity are some examples that generally lead to the ValueError: math domain error.
Replicate the ValueError: math domain error in Python
Now that we understand the reason behind the issue let us try replicating it. This can be done in Python with the help of the following block of code.
from numpy import zeros, array
from math import sin, log
def f(x):
f= log(-3) - 7.0
return "Executed successfully"
x = array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
a = f(x)
print(a)
Here, we are trying to calculate a simple expression that subtracts the result of log(-3) and 7. The code above gives us the error below.
line 5, in f
f = log(-3) - 7.0
ValueError: math domain error
This error is because we are trying to calculate the log of a negative number, which is impossible.
Similarly, we get the ValueError: math domain error if we use the sqrt function with a negative number in Python.
This error can be replicated with the help of the following block of code.
from math import sqrt
print(sqrt(-4))
The output of the above code can be illustrated as follows.
line 2, in print(srqt(-4))
ValueError: math domain error
The primary reason is that a negative integer’s square root is a complex number.
Similarly, while using the pow function in Python, we can get the ValueError: math domain error with the following code block.
import math
print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
The output of the above code block can be illustrated as:
line 2, in print(math.pow(-2, 0.5))
ValueError: math domain error
The primary reason is that a negative number cannot be raised to a fractional power in Python.
Solve the ValueError: math domain error in Python
We can use the absolute operator abs in Python to resolve the above issues. The following block of code can help us eliminate the error mentioned.
from numpy import zeros, array
from math import sin, log
def f(x):
f= log(abs(-3)) - 7.0
return "Executed successfully"
x = array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
a = f(x)
print(a)
The output of the above code can be illustrated as follows.
Similarly, if we ever want to take the square root of a negative number, we can also use abs. This can be understood better with the help of the following block of code.
from math import sqrt
print(sqrt(abs(-4)))
The output of the above code can be illustrated as follows.
The same logic can be used to calculate a negative number’s power.
import math
print(math.pow(abs(-2), 0.5))
The output of the above code can be illustrated as follows.
Thus, with the help of this tutorial, we have managed to get rid of the ValueError: math domain error in Python.