- Remove From My Forums

Opening Word document in VFP7 — Error 1429, not enough memory???
-
Question
-
Hello anybody,
When trying to open a Word document from our VFP7 application, we get an error message like:
Error number: 1429 = OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Word: Er is onvoldoende geheugen. Sla het document nu op.
The last italic sentences are in Dutch and mean something like: There is not enough memory. Save the document now.The most frustrating thing is that it happens only once in a while, and trying to open the same document again immediately after is succesful most of the time.
We retrieved LINENO(1) when the error occurred, the statement causing the message appears to be:
oDoc = oApp.Documents.Open(sFileToOpen)
preceding statements are:
oApp = CREATEOBJECT( ‘Word.Application’)
= KickStartOfficeAddIns(nAppType, oApp)
oApp.Run(‘Save_Init’) && Set Save button(s) and initialize event handler.
oApp.WindowState = 1 && Maximized( = not normal or minimized)
oApp.Activate()Extra info:
— The statement ‘= KickStartOfficeAddIns(…)’ is executed because the auto_exec macros of all the Add-ins that are currently installed for Word will not fire automatically when starting Word with the CREATEOBJECT-statement. The procedure KickStartOfficeAddIns ‘kicks’ each add-in into action (e.g. initializing a command bar) by explicitly calling the auto_exec macro with a statement oApp.Run(…) for each add-in.
— The statement oApp.Run(‘Save_Init’) runs a (VB-)macro in a Word add-in we developed to handle save actions for the benefit of our application.
— The document seems to be opened by Word, it is visible, the message occurs immediately after it is opened, without the user trying to save the document.
— The document is opened in Word 2003.Any enlightenment on this problem would be greatly appreciated!
Thanx in advance,
Answers
-
May be some «macros» are not supported…You may try to run without macros, then add one by one to see if still have the error….
Содержание
- Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429
- Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429
- Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429
- Answered by:
- Question
- 14.2 The war of 1426-1429
Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429

Невозможно получить свойство Open класса Workbooks..
Класс создается и другие его методы доступны и работают нормально, например loXLS.WorkBooks.Add()
Причем наблюдается только в exe, из фокса эта процедура отрабатывает нормально.
Убил полдня на эксперименты .
vfp9 sp1, server 2008
Равиль

Невозможно получить свойство Open класса Workbooks..
Класс создается и другие его методы доступны и работают нормально, например loXLS.WorkBooks.Add()
Причем наблюдается только в exe, из фокса эта процедура отрабатывает нормально.
Убил полдня на эксперименты .
vfp9 sp1, server 2008
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| pioner-v
Сообщений: 1656 |
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Равиль Автор |
Сообщений: 6478
Откуда: Уфа
Дата регистрации: 01.08.2003
к сожалению до имени файла дело не доходит — т.к. не обнаружен метод open .
Но что любопытно — скомпилировал в vfp7 — косяка нет ))
Попробую дробить этот модуть — часть на 7-ке, часть на 9-ке ))
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| pioner-v
Сообщений: 1656 |
Антивирус или вирус?
Как получена ссылка loXLS? Права «запускающего» IDE и exe, были ли запросы UAC-а?
Макро тут совсем не при чём — это вредный совет, сбивает с правильного пути поиска причин проблемы
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Igor Korolyov
Сообщений: 34580 |
Для начала, я бы разбил на «слагаемые»
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Владимир Максимов
Сообщений: 13997 |
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Равиль Автор |
Сообщений: 6478
Откуда: Уфа
Дата регистрации: 01.08.2003
Igor Korolyov
Антивирус или вирус?
Как получена ссылка loXLS? Права «запускающего» IDE и exe, были ли запросы UAC-а?
Макро тут совсем не при чём — это вредный совет, сбивает с правильного пути поиска причин проблемы

осталась проблема при запуске EXE из планировщика (хотя с теми же правами от имени того же пользователя)
Для начала, я бы разбил на «слагаемые»
loBooks = loXLS.Workbooks
loBook = loBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile)
Довольно часто Com-объекты не могут «переварить» «многочлены». А по одному члену за раз — вполне стабильно работают. Но даже если это не поможет, подобное разбиение позволит точнее определить, на каком члене иерархии произошел сбой.

Исправлено 1 раз(а). Последнее : Равиль, 16.12.10 18:26
Источник
Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429

Невозможно получить свойство Open класса Workbooks..
Класс создается и другие его методы доступны и работают нормально, например loXLS.WorkBooks.Add()
Причем наблюдается только в exe, из фокса эта процедура отрабатывает нормально.
Убил полдня на эксперименты .
vfp9 sp1, server 2008
Равиль

Невозможно получить свойство Open класса Workbooks..
Класс создается и другие его методы доступны и работают нормально, например loXLS.WorkBooks.Add()
Причем наблюдается только в exe, из фокса эта процедура отрабатывает нормально.
Убил полдня на эксперименты .
vfp9 sp1, server 2008
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| pioner-v
Сообщений: 1656 |
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Равиль Автор |
Сообщений: 6478
Откуда: Уфа
Дата регистрации: 01.08.2003
к сожалению до имени файла дело не доходит — т.к. не обнаружен метод open .
Но что любопытно — скомпилировал в vfp7 — косяка нет ))
Попробую дробить этот модуть — часть на 7-ке, часть на 9-ке ))
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| pioner-v
Сообщений: 1656 |
Антивирус или вирус?
Как получена ссылка loXLS? Права «запускающего» IDE и exe, были ли запросы UAC-а?
Макро тут совсем не при чём — это вредный совет, сбивает с правильного пути поиска причин проблемы
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Igor Korolyov
Сообщений: 34580 |
Для начала, я бы разбил на «слагаемые»
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Владимир Максимов
Сообщений: 13997 |
| Re: loXLS.WorkBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile) — err 1429 |
|---|
| Равиль Автор |
Сообщений: 6478
Откуда: Уфа
Дата регистрации: 01.08.2003
Igor Korolyov
Антивирус или вирус?
Как получена ссылка loXLS? Права «запускающего» IDE и exe, были ли запросы UAC-а?
Макро тут совсем не при чём — это вредный совет, сбивает с правильного пути поиска причин проблемы

осталась проблема при запуске EXE из планировщика (хотя с теми же правами от имени того же пользователя)
Для начала, я бы разбил на «слагаемые»
loBooks = loXLS.Workbooks
loBook = loBooks.Open(m.lcXlsFile)
Довольно часто Com-объекты не могут «переварить» «многочлены». А по одному члену за раз — вполне стабильно работают. Но даже если это не поможет, подобное разбиение позволит точнее определить, на каком члене иерархии произошел сбой.

Исправлено 1 раз(а). Последнее : Равиль, 16.12.10 18:26
Источник
Microsoft visual foxpro error 1429
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
When trying to open a Word document from our VFP7 application, we get an error message like:
Error number: 1429 = OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Word: Er is onvoldoende geheugen. Sla het document nu op.
The last italic sentences are in Dutch and mean something like: There is not enough memory. Save the document now.
The most frustrating thing is that it happens only once in a while, and trying to open the same document again immediately after is succesful most of the time.
We retrieved LINENO(1) when the error occurred, the statement causing the message appears to be:
preceding statements are:
oApp = CREATEOBJECT( ‘Word.Application’)
= KickStartOfficeAddIns(nAppType, oApp)
oApp.Run(‘Save_Init’) && Set Save button(s) and initialize event handler.
oApp.WindowState = 1 && Maximized( = not normal or minimized)
oApp.Activate()
Extra info:
— The statement ‘= KickStartOfficeAddIns(. )’ is executed because the auto_exec macros of all the Add-ins that are currently installed for Word will not fire automatically when starting Word with the CREATEOBJECT-statement. The procedure KickStartOfficeAddIns ‘kicks’ each add-in into action (e.g. initializing a command bar) by explicitly calling the auto_exec macro with a statement oApp.Run(. ) for each add-in.
— The statement oApp.Run(‘Save_Init’) runs a (VB-)macro in a Word add-in we developed to handle save actions for the benefit of our application.
— The document seems to be opened by Word, it is visible, the message occurs immediately after it is opened, without the user trying to save the document.
— The document is opened in Word 2003.
Any enlightenment on this problem would be greatly appreciated!
Thanx in advance,
Источник
14.2 The war of 1426-1429
The war of 1426 1429
No, we re not talking about a centuries-old battle here, we re talking about a series of error numbers. But we re certain you ll battle these four errors frequently while writing Automation code. These four errors are raised by the Automation server sending back an error code. Which one you get depends on how much information the server is willing to provide. This is the frustrating part: there isn t any categorical difference between these errors, and each error has a variety of meanings. These four errors return every possible problem from every Automation server; in contrast, FoxPro has hundreds of error messages!
Before you think that this is an awful design, remember that FoxPro is receiving the errors in a standard COM/Automation interface. There isn t any way to assign a unique error number to every possible error in every possible server even if we could ensure the errors are unique across servers, we d have error numbers larger than GUIDs, which would cause other problems.
So why is it so frustrating to work with these four errors? You can t tell the difference between a fatal error (the server has disconnected), a syntax error, and an error that can be fixed (like a divide by zero error) by the number. Yes, it is possible to keep a meticulous database of the text and number of each error for each server, but because of the volume of errors, it s very hard to track every error you come across and stay on-track with your development efforts.
As we said before, the difference between these errors is in the quantity of information the server is willing to provide. Error 1426, «OLE error code 0x,»is the most simplistic. It returns only a character string containing the hexadecimal number and a short message, for example: «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.» In your error handler, ERROR() returns 1426, and MESSAGE() returns «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.»
Errors 1427, 1428, and 1429 all appear to return similar information: an exception code followed by the message. While FoxPro sees them as different errors, their messages seem eerily similar. The differences may lie in what is returned in the AERROR() function.
Visual FoxPro s AERROR() function returns more information for an error. It builds an array with seven columns containing various information, depending on whether it is a FoxPro, OLE, or ODBC error. Help indicates that most FoxPro errors return nulls for most of the entries, with the exception of OLE errors 1427 and 1429, and ODBC error 1526. In fact, OLE errors 1426 and 1428 also make good use of AERROR().
Table 2 lists the contents of the resulting AERROR() array. Error 1426 sets only the first three values; the remaining four are set to null values. Errors 1427, 1428, and 1429 use up to seven columns of the array.
Table 2 . The contents of the AERROR() array, using a 1429 error generated by Excel. The described positions reflect those for OLE errors only; not general FoxPro errors or ODBC errors, which have different descriptions.
Position
Contents
The error number. Same as ERROR().
Text of the VFP error message. Same as MESSAGE(). Note that this is a concatenation of some of the other information in this array.
«OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Excel: Unable to set the Bold property of the Font class»
The text of the OLE message.
«Unable to set the Bold property of the Font class»
The application sending the message.
«Microsoft Excel»
The application s Help file, if available (.Null. if not).
«c:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice1033xlmain9.chm»
The Help context ID, if available (.Null. if not).
The OLE 2.0 exception number.
Error 1426 sets the first three columns. The first is the error number, which is the same as querying ERROR(). The second is the VFP error message the one that s displayed in the error dialog box, as in: «OLE error code 0x80020026: Unknown name.» This is the same string that is returned from the MESSAGE() function. The third column contains only a portion of the text string; it is the string returned from the OLE server. VFP adds some standard text to clarify the message; in the case of 1426, it s «OLE error code 0x.» While you can parse that out of the string, it s probably easier just to check the third column of the array, which contains the error code followed by the message: «80020026: Unknown name.» Actually, it s even easier to check SYS(2018), the most recent error message parameter function. The remaining AERROR() array columns are .Null., like any other VFP error.
Errors 1427 1429 fill all columns of the array (if the Help file and Help Context ID are available). As you can see from Table 1, the VFP message is a concatenation of a standard message («OLE IDispatch exception code «), the exception number (column 7), the application name (column 4), and finally the text of the OLE message (column 3). The text of the message (column 3) is also the value returned by SYS(2018), the most recent error message parameter, which is different from error 1426, which returns just the text (as in column 3). Actually, SYS(2018) returns only the first 255 characters of the message, which can be significant in longer messages, as we ll see later on.

Some interesting error observations
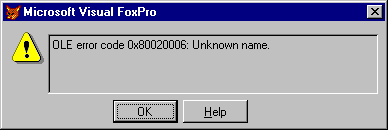
To really see how frustrating handling these errors can be, a few examples are in order. The first example shows the range of how informative these errors can be. For example, imagine the following line of code (yes, it has a typo in it, to illustrate our point):
xlColumn, 6, xlColumns, 1, 1, 1, «», «», «Assets», «»)
The resulting error message is shown in Figure 1 .
Figure 1 . A sample error, 1426, obtained by a misspelled method name. While its conciseness is admirable, a bit of help on exactly what the unknown name is would be helpful.
Just a bit brief, no? Especially since our example has no fewer than five names in it: the references to oExcel, oChart, the ChartWizard method (which is the culprit here), the Sheets object, and the Range object. To be fair, VFP is reporting what it received from the server, so we can blame the server for its omission of one small, but very helpful, piece of information.
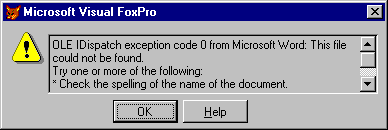
On the flip side, there s this error that comes from the following line of code. This line references a file that doesn t exist:
This error, number 1429, is shown in Figure 2 .
Figure 2 . Another error, 1429, offers a lot of information. There s so much information, it even has a scroll bar!
This message is so unusually long and informative, the error message box actually has a scroll bar to allow you to read the full text of the message! The full text of the error message is as follows:
OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Word: This file could not be found.
Try one or more of the following:
* Check the spelling of the name of the document.
* Try a different file name.
It was while testing this error that we found that SYS(2018) contains only the first 255 characters.
Another situation is that the same error number gives different kinds of errors that need to be handled differently. One kind of error is the syntax error, those pesky typos that the compiler usually catches, or the run-time notification that informs you that you ve reversed those two parameters. Another kind of error is when the user is notified that their system is improperly configured, or they ve made a mistake. Almost all FoxPro errors fall into one category or the other, so it s much easier to handle each individual error.
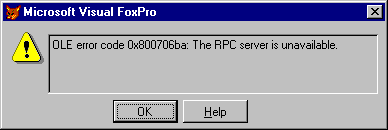
Errors 1426 1429 return errors in both of these categories (and any other category you can think of). To illustrate, let s pick on error 1426. We ve already talked about «OLE error code 0x80020026: Unknown name,» shown in Figure 1, which generally means there s a misspelled method or property in the code and the developer needs to fix the code. The error handler can gracefully skip this line, shut down the module, or whatever action is appropriate (ideally, the developer fixes this before it gets to the user!). In contrast to that situation, Figure 3 shows a different error: «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.» This error can show up on two occasions: when you re opening the server and it doesn t start up correctly (or doesn t start up all), or later, after your program opens the server, and the user closes it before your program is finished with it. Another 1426 classic is «OLE error code 0x80080005: Server execution failed.» This means that the server is registered, but the actual EXE file isn t found (usually due to the user uninstalling by deleting the folder instead of using the Uninstall routine). These last two errors are handled a bit differently than a syntax error! Who knows how many other errors are returned as 1426.
Figure 3 . Another error 1426, this one indicating the server is unavailable. Automation errors can return nearly any kind of error (including syntax errors, run-time errors, and configuration errors), which makes programming your error handler a bit tricky.
Copyright 2000 by Tamar E. Granor and Della Martin All Rights Reserved
Источник
Click here follow the steps to fix Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 and related errors.
|
|
|
|
To Fix (Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429) error you need to |
|
|
Step 1: |
|
|---|---|
| Download (Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429) Repair Tool |
|
|
Step 2: |
|
| Click the «Scan» button | |
|
Step 3: |
|
| Click ‘Fix All‘ and you’re done! | |
|
Compatibility:
Limitations: |
Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 Error Codes are caused in one way or another by misconfigured system files
in your windows operating system.
If you have Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 errors then we strongly recommend that you
Download (Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429) Repair Tool.
This article contains information that shows you how to fix
Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429
both
(manually) and (automatically) , In addition, this article will help you troubleshoot some common error messages related to Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error code that you may receive.
Note:
This article was updated on 2023-02-03 and previously published under WIKI_Q210794
Contents
- 1. What is Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error?
- 2. What causes Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error?
- 3. How to easily fix Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 errors
What is Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error?
The Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error is the Hexadecimal format of the error caused. This is common error code format used by windows and other windows compatible software and driver vendors.
This code is used by the vendor to identify the error caused. This Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error code has a numeric error number and a technical description. In some cases the error may have more parameters in Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 format .This additional hexadecimal code are the address of the memory locations where the instruction(s) was loaded at the time of the error.
What causes Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error?
The Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error may be caused by windows system files damage. The corrupted system files entries can be a real threat to the well being of your computer.
There can be many events which may have resulted in the system files errors. An incomplete installation, an incomplete uninstall, improper deletion of applications or hardware. It can also be caused if your computer is recovered from a virus or adware/spyware
attack or by an improper shutdown of the computer. All the above actives
may result in the deletion or corruption of the entries in the windows
system files. This corrupted system file will lead to the missing and wrongly
linked information and files needed for the proper working of the
application.
How to easily fix Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 error?
There are two (2) ways to fix Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429 Error:
Advanced Computer User Solution (manual update):
1) Start your computer and log on as an administrator.
2) Click the Start button then select All Programs, Accessories, System Tools, and then click System Restore.
3) In the new window, select «Restore my computer to an earlier time» option and then click Next.
4) Select the most recent system restore point from the «On this list, click a restore point» list, and then click Next.
5) Click Next on the confirmation window.
6) Restarts the computer when the restoration is finished.
Novice Computer User Solution (completely automated):
1) Download (Microsoft Visual Foxpro Error 1429) repair utility.
2) Install program and click Scan button.
3) Click the Fix Errors button when scan is completed.
4) Restart your computer.
How does it work?
This tool will scan and diagnose, then repairs, your PC with patent
pending technology that fix your windows operating system registry
structure.
basic features: (repairs system freezing and rebooting issues , start-up customization , browser helper object management , program removal management , live updates , windows structure repair.)
https://help.myob.com/wiki/x/zQR3AQ
Close
How satisfied are you with our online help?*
Just these help pages, not phone support or the product itself
Very dissatisfied
Very satisfied
Why did you give this rating?
It’s hard to find information
Instructions are hard to follow
Content isn’t detailed enough
It doesn’t fix my software problems
These instructions require technical expertise
Make sure you know what you’re doing and are using one of the products listed. If you’re not sure, ask your IT professional or MYOB.
Article ID: 23409
ARTICLE LAST UPDATED: 30/01/2013 2:23:00 PM
In MYOB Accountants Office Classic you may experience the error «1429/OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Word: Word was unable to open the data source» when attempting to use templates.
This error can occur if an incorrect version of the Microsoft Visual Fox Pro driver is installed.
This error may also occur when using or creating templates on a computer running an installed program that uses the Borland Database Engine (BDE). Examples of programs that we have found to require the BDE are, BGL — Corporate Affairs System, CashManager and Visiplan, but undoubtedly there are others.
Please follow the following suggestions in the recommended order as displayed.
2. Modify the Registry
The procedure below contains information about modifying the registry. Before you modify the registry, make sure to back it up and make sure that you understand how to restore the registry if a problem occurs. For information about how to back up, restore, and edit the registry, refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base article Q256986 Description of the Microsoft Windows Registry.
-
Exit from any open programs.
-
From the Start menu, select Run. The Run window appears.
-
Type regedit in the Open field and click OK. The Registry Editor window appears.
-
Double-click the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE folder.
-
Double-click the Software folder.
-
Double-click the Microsoft folder.
-
Double-click the Jet folder.
-
Double-click the 4.0 folder.
-
Double-click the Engines folder.
-
Double-click the Xbase folder.
- If you see the BDE value in the right window pane, go to step 15, otherwise continue with the next step.
-
From the Edit menu, select New, and choose DWORD Value. A new value with the temporary name of New Value #1 appears in the right window pane.
-
Click the New Value #1 value, and select Rename from the Edit menu.
-
Change the name to BDE.
-
Double-click BDE to open it. The Edit DWORD Value window appears
-
Click the Decimal radio-button at the Base section.
-
Type 2 in the Value data field and click OK.
- From the Registry menu, select Exit.
3. Relocate the IDAPI Driver
If the procedure above doesn’t resolve the issue, follow the procedure below.
If the BDE-based program isn’t required, uninstalling it will resolve the issue. If the BDE-based program is required, move the file named IDR20009.DLL, which is located in the C:WindowsIDAPI folder, to the appropriate BDE-based program folder. For example:
- If BGL — Corporate Affairs System is the only BDE-based program, move the IDR20009.DLL file from the C:WindowsIDAPI folder to the BGL — Corporate Affairs System program folder.
-
If BGL Simple Fund is installed in addition to the BGL — Corporate Affairs System, copy the IDR20009.DLL file into the BGL Simple Fund program folder and move the IDR20009.DLL file from the C:WindowsIDAPI folder to the BGL — Corporate Affairs System folder.
-
If CashManager is the only BDE-based program, move the IDR20009.DLL file from the C:WindowsIDAPI folder to the CashManager program folder, with the default folder being C:Cashwin.
If you have previously moved the IDR20009.DLL file and the BDE-based program is upgraded, another IDR20009.DLL file is installed in the C:WindowsIDAPI folder. In this instance, delete the IDR20009.DLL file from the C:WindowsIDAPI folder.
MYOB INTERNAL STAFF ONLY
INTERNAL NOTES
This may still be relevant with Microsoft Vista and Word 2007.
Reinstalling the Microsoft Visual Fox Pro driver 5 may also resolve.
INTELLIGENT WORK FORUMS
FOR COMPUTER PROFESSIONALS
Contact US
Thanks. We have received your request and will respond promptly.
Log In
Come Join Us!
Are you a
Computer / IT professional?
Join Tek-Tips Forums!
- Talk With Other Members
- Be Notified Of Responses
To Your Posts - Keyword Search
- One-Click Access To Your
Favorite Forums - Automated Signatures
On Your Posts - Best Of All, It’s Free!
*Tek-Tips’s functionality depends on members receiving e-mail. By joining you are opting in to receive e-mail.
Posting Guidelines
Promoting, selling, recruiting, coursework and thesis posting is forbidden.
Students Click Here
ERROR: 1429 — OLE IDispacth exception code 0 from WSDLR ReaderERROR: 1429 — OLE IDispacth exception code 0 from WSDLR Reader(OP) 9 Sep 13 09:20
we have a Visual FoxPro Desktop the Visual Foxpro Application is calling a .NET Web Service some user are getting the following messages as the Visual FoxPRO Application calls the .NET Web service ERROR: 1429 — OLE IDISPATCH Exception code 0 from WSDLReader: SDLReader: XML Parser failed at linenumber 0, lineposition 0, Reason is: Access denied HRESULT=0X1: Incorrect function. -WSDLReader: Loading the WSDL file failed HRESULT=0x80070057: The parameter is incorrect. -Client: One of the parameters supplied is invalid. HRESULT=0x80070057: the parameter is incorrect. Any Ideas jhhaidar@sbcglobal.net Red Flag SubmittedThank you for helping keep Tek-Tips Forums free from inappropriate posts. |
Join Tek-Tips® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet’s largest technical computer professional community.
It’s easy to join and it’s free.
Here’s Why Members Love Tek-Tips Forums:
Talk To Other Members
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More…
Register now while it’s still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close
The war of 1426 1429
No, we re not talking about a centuries-old battle here, we re talking about a series of error numbers. But we re certain you ll battle these four errors frequently while writing Automation code. These four errors are raised by the Automation server sending back an error code. Which one you get depends on how much information the server is willing to provide. This is the frustrating part: there isn t any categorical difference between these errors, and each error has a variety of meanings. These four errors return every possible problem from every Automation server; in contrast, FoxPro has hundreds of error messages!
Before you think that this is an awful design, remember that FoxPro is receiving the errors in a standard COM/Automation interface. There isn t any way to assign a unique error number to every possible error in every possible server even if we could ensure the errors are unique across servers, we d have error numbers larger than GUIDs, which would cause other problems.
So why is it so frustrating to work with these four errors? You can t tell the difference between a fatal error (the server has disconnected), a syntax error, and an error that can be fixed (like a divide by zero error) by the number. Yes, it is possible to keep a meticulous database of the text and number of each error for each server, but because of the volume of errors, it s very hard to track every error you come across and stay on-track with your development efforts.
Subtle differences
As we said before, the difference between these errors is in the quantity of information the server is willing to provide. Error 1426, «OLE error code 0x,»is the most simplistic. It returns only a character string containing the hexadecimal number and a short message, for example: «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.» In your error handler, ERROR() returns 1426, and MESSAGE() returns «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.»
Errors 1427, 1428, and 1429 all appear to return similar information: an exception code followed by the message. While FoxPro sees them as different errors, their messages seem eerily similar. The differences may lie in what is returned in the AERROR() function.
Visual FoxPro s AERROR() function returns more information for an error. It builds an array with seven columns containing various information, depending on whether it is a FoxPro, OLE, or ODBC error. Help indicates that most FoxPro errors return nulls for most of the entries, with the exception of OLE errors 1427 and 1429, and ODBC error 1526. In fact, OLE errors 1426 and 1428 also make good use of AERROR().
Table 2 lists the contents of the resulting AERROR() array. Error 1426 sets only the first three values; the remaining four are set to null values. Errors 1427, 1428, and 1429 use up to seven columns of the array.
Table 2. The contents of the AERROR() array, using a 1429 error generated by Excel. The described positions reflect those for OLE errors only; not general FoxPro errors or ODBC errors, which have different descriptions.
|
Position |
Contents |
Example |
|
1 |
The error number. Same as ERROR(). |
1429 |
|
2 |
Text of the VFP error message. Same as MESSAGE(). Note that this is a concatenation of some of the other information in this array. |
«OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Excel: Unable to set the Bold property of the Font class» |
|
3 |
The text of the OLE message. |
«Unable to set the Bold property of the Font class» |
|
4 |
The application sending the message. |
«Microsoft Excel» |
|
5 |
The application s Help file, if available (.Null. if not). |
«c:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice1033xlmain9.chm» |
|
6 |
The Help context ID, if available (.Null. if not). |
0 |
|
7 |
The OLE 2.0 exception number. |
0 |
Error 1426 sets the first three columns. The first is the error number, which is the same as querying ERROR(). The second is the VFP error message the one that s displayed in the error dialog box, as in: «OLE error code 0x80020026: Unknown name.» This is the same string that is returned from the MESSAGE() function. The third column contains only a portion of the text string; it is the string returned from the OLE server. VFP adds some standard text to clarify the message; in the case of 1426, it s «OLE error code 0x.» While you can parse that out of the string, it s probably easier just to check the third column of the array, which contains the error code followed by the message: «80020026: Unknown name.» Actually, it s even easier to check SYS(2018), the most recent error message parameter function. The remaining AERROR() array columns are .Null., like any other VFP error.
Errors 1427 1429 fill all columns of the array (if the Help file and Help Context ID are available). As you can see from Table 1, the VFP message is a concatenation of a standard message («OLE IDispatch exception code «), the exception number (column 7), the application name (column 4), and finally the text of the OLE message (column 3). The text of the message (column 3) is also the value returned by SYS(2018), the most recent error message parameter, which is different from error 1426, which returns just the text (as in column 3). Actually, SYS(2018) returns only the first 255 characters of the message, which can be significant in longer messages, as we ll see later on.

Some interesting error observations
To really see how frustrating handling these errors can be, a few examples are in order. The first example shows the range of how informative these errors can be. For example, imagine the following line of code (yes, it has a typo in it, to illustrate our point):
oChart.ChartWizrd(oExcel.Sheets(cSheetName).Range(cGraphRange), ;
xlColumn, 6, xlColumns, 1, 1, 1, «», «», «Assets», «»)
The resulting error message is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A sample error, 1426, obtained by a misspelled method name. While its conciseness is admirable, a bit of help on exactly what the unknown name is would be helpful.
Just a bit brief, no? Especially since our example has no fewer than five names in it: the references to oExcel, oChart, the ChartWizard method (which is the culprit here), the Sheets object, and the Range object. To be fair, VFP is reporting what it received from the server, so we can blame the server for its omission of one small, but very helpful, piece of information.
On the flip side, there s this error that comes from the following line of code. This line references a file that doesn t exist:
oWord.Documents.Open(«Test.Doc»)
This error, number 1429, is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Another error, 1429, offers a lot of information. There s so much information, it even has a scroll bar!
This message is so unusually long and informative, the error message box actually has a scroll bar to allow you to read the full text of the message! The full text of the error message is as follows:
OLE IDispatch exception code 0 from Microsoft Word: This file could not be found.
Try one or more of the following:
* Check the spelling of the name of the document.
* Try a different file name.
(Test.Doc).
It was while testing this error that we found that SYS(2018) contains only the first 255 characters.
Another situation is that the same error number gives different kinds of errors that need to be handled differently. One kind of error is the syntax error, those pesky typos that the compiler usually catches, or the run-time notification that informs you that you ve reversed those two parameters. Another kind of error is when the user is notified that their system is improperly configured, or they ve made a mistake. Almost all FoxPro errors fall into one category or the other, so it s much easier to handle each individual error.
Errors 1426 1429 return errors in both of these categories (and any other category you can think of). To illustrate, let s pick on error 1426. We ve already talked about «OLE error code 0x80020026: Unknown name,» shown in Figure 1, which generally means there s a misspelled method or property in the code and the developer needs to fix the code. The error handler can gracefully skip this line, shut down the module, or whatever action is appropriate (ideally, the developer fixes this before it gets to the user!). In contrast to that situation, Figure 3 shows a different error: «OLE error code 0x800706ba: The RPC server is unavailable.» This error can show up on two occasions: when you re opening the server and it doesn t start up correctly (or doesn t start up all), or later, after your program opens the server, and the user closes it before your program is finished with it. Another 1426 classic is «OLE error code 0x80080005: Server execution failed.» This means that the server is registered, but the actual EXE file isn t found (usually due to the user uninstalling by deleting the folder instead of using the Uninstall routine). These last two errors are handled a bit differently than a syntax error! Who knows how many other errors are returned as 1426.
Figure 3. Another error 1426, this one indicating the server is unavailable. Automation errors can return nearly any kind of error (including syntax errors, run-time errors, and configuration errors), which makes programming your error handler a bit tricky.
Copyright 2000 by Tamar E. Granor and Della Martin All Rights Reserved




 Talk To Other Members
Talk To Other Members