| title | description | author | ms.author | ms.reviewer | ms.date | ms.service | ms.subservice | ms.topic | helpviewer_keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MSSQLSERVER_18456 |
A connection attempt is rejected due to a failure with a bad password or username in SQL Server. See an explanation of the error and possible resolutions. |
MashaMSFT |
mathoma |
pijocoder, randolphwest |
01/16/2023 |
sql |
supportability |
reference |
18456 (Database Engine error) |
MSSQLSERVER_18456
[!INCLUDE SQL Server]
Details
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | SQL Server |
| Event ID | 18456 |
| Event Source | MSSQLSERVER |
| Component | SQLEngine |
| Symbolic Name | LOGON_FAILED |
| Message Text | Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’.%.*ls |
Explanation
You get this error message when a connection attempt is rejected because of an authentication failure. User logins can fail for many reasons, such as invalid credentials, password expiration, and enabling the wrong authentication mode. In many cases, error codes include descriptions.
User action
The following examples are some of the common login failures. Select the exact error that you’re experiencing to troubleshoot the issue:
-
Login failed for user ‘<username>’ or login failed for user ‘<domain><username>’
-
Login failed for user ‘NT AUTHORITYANONYMOUS’ LOGON
-
Login failed for user ’empty’
-
Login failed for user ‘(null)’
Login failed for user ‘<username>’ or login failed for user ‘<domain><username>’
If the domain name isn’t specified, the problem is a failing SQL Server login attempt. If the domain name is specified, the problem is a failing Windows user account login. For potential causes and suggested resolutions, see:
| Potential cause | Suggested resolution |
|---|---|
| You’re trying to use SQL Server Authentication, but the SQL server instance is configured for Windows Authentication mode. | Verify that SQL Server is configured to use SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode. You can review and change the authentication mode for your SQL Server instance on the Security page under Properties for the corresponding instance in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). For more information, see Change server authentication mode. Alternatively, you can change your application to use Windows Authentication mode to connect to SQL Server. Note: You can see a message like the following one in the SQL Server Error log for this scenario: Login failed for user '<UserName>'. Reason: An attempt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Windows authentication only. |
| Login doesn’t exist on the SQL Server instance you’re trying to connect to. | Verify that the SQL Server login exists and that you’ve spelled it properly. If the login doesn’t exist, create it. If it’s present but misspelled, correct that in the application connection string. The SQL Server Errorlog will have one of the following messages: — Login failed for user 'username'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided.— Login failed for user 'Domainusername'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided.This can be a common issue if you deploy an application that uses a DEV or QA server into production and you fail to update the connection string. To resolve this issue, validate that you are connecting to the appropriate server. If not, correct the connection string. If it is, grant the login access to your SQL Server. Or if it’s a windows login grant access directly or add it to a local or domain group that is allowed to connect to the database server. For more information, see Create a Login. |
| You’re using SQL Server Authentication, but the password you specified for SQL Server login is incorrect. | Check the SQL error log for messages like «Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided» to confirm the cause. To fix the issue, use the correct password in your application or use a different account if you can’t remember the password. Alternatively, work with your SQL Server administrator to reset the password for the account. If the application is SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), there may be multiple levels of a Configuration file for the job, which may override the Connection Manager settings for the package. If the application was written by your company and the connection string is programmatically generated, engage the development team to resolve the issue. As a temporary workaround, hard-code the connection string and test. Use a UDL file or a script to prove a connection is possible with a hard-coded connection string. |
| Server name is incorrect. | Ensure you’re connecting to the correct server. |
| You’re trying to connect using Windows authentication but are logged into an incorrect domain. | Verify that you’re properly logged into the correct domain. The error message usually displays the domain name. |
| You aren’t running your application (for example, SSMS) as an administrator. | If you’re trying to connect using your administrator credentials, start your application by using the Run as Administrator option. When connected, add your Windows user as an individual login. |
| Login is deleted after a migration to a contained database user. | If the Database Engine supports contained databases, confirm that the login wasn’t deleted after migration to a contained database user. For more information, see Contained Database Authentication: Introduction. |
| Login’s default database is offline or otherwise not available. | Check with your SQL Server administrator and resolve issues related to database availability. If the login has permissions to other databases on the server and you don’t need to access the currently configured default database in your application, use one of the following options: — Request the administrator to change the default database for the login using ALTER LOGIN statement or SSMS. — Explicitly specify a different database in your application connection string. Or if you’re using SSMS switch to the Connection Properties tab to specify a database that is currently available.Applications like SSMS may show an error message like the following one: Cannot open user default database. Login failed.Login failed for user <user name>. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 4064)SQL Server Errorlog will have an error message like the following one: Login failed for user '<user name>'. Reason: Failed to open the database '<dbname>' specified in the login properties [CLIENT: <ip address>]For more information, see MSSQLSERVER_4064. |
| The database explicitly specified in the connection string or in SSMS is incorrectly spelled, offline, or otherwise not available. | — Fix the database name in the connection string. Pay attention to case sensitivity if using a case sensitive collation on the server. — If the database name is correct, check with your SQL Server administrator and resolve issues related to database availability. Check if the database is offline, not recovered, and so on. — If the login has been mapped to users with permissions to other databases on the server and you don’t need to access the currently configured database in your application, then specify a different database in your connection string. Or if you’re connecting with SSMS, use the Connection Properties tab to specify a database that is currently available. SQL Server Errorlog will have an error message like the following one: Login failed for user <UserName>. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database 'dbname'. [CLIENT: <ip address>]Note: If the login’s default database is available, SQL Server allows the connection to succeed. For more information, see MSSQLSERVER_4064. |
| The user doesn’t have permissions to the requested database. | — Try connecting as another user that has sysadmin rights to see if connectivity can be established. — Grant the login access to the database by creating the corresponding user (for example, CREATE USER [<UserName>] FOR LOGIN [UserName]) |
Also, check the extensive list of error codes at Troubleshooting Error 18456.
For more troubleshooting help, see Troubleshooting SQL Client / Server Connectivity Issues.
Login failed for user NT AUTHORITYANONYMOUS LOGON
There are at least four scenarios for this issue. In the following table, examine each applicable potential cause, and use the appropriate resolution:
See the note below the table for an explanation of the term double hop.
| Potential causes | Suggested resolutions |
|---|---|
| You’re trying to pass NT LAN Manager (NTLM) credentials from one service to another service on the same computer (for example: from IIS to SQL server), but a failure occurs in the process. | Add the DisableLoopbackCheck or BackConnectionHostNames registry entries. |
| There are double-hop (constraint delegation) scenarios across multiple computers. The error could occur if the Kerberos connection fails because of Service Principal Names (SPN) issues. | Run SQLCheck on each SQL Server and the web server. Use the troubleshooting guides: 0600 Credential Delegation Issue and 0650 SQL Server Linked Server Delegation Issues. |
| If no double-hop (constraint delegation) is involved, then likely duplicate SPNs exist, and the client is running as a LocalSystem or another machine account that gets NTLM credentials instead of Kerberos credentials. | Use SQLCheck or Setspn.exe to diagnose and fix any SPN-related issues. Also review Overview of the Kerberos Configuration Manager for SQL Server. |
| Windows Local Security policy may have been configured to prevent the use of the machine account for remote authentication requests. | Navigate to Local Security Policy > Local Policies > Security Options > Network security: Allow Local System to use computer identity for NTLM, select the Enabled option if the setting is disabled, and then select OK. Note: As detailed on the Explain tab, this policy is enabled in Windows 7 and later versions by default. |
| Intermittent occurrence of this issue when using constrained delegation can indicate presence of an expired ticket that can’t be renewed by middle tier. This is an expected behavior with either linked server scenario or any application that is holding a logon session for more than 10 hours. | Change delegation settings on your middle-tier server from Trust this computer for delegation to specified services only – Use Kerberos Only to Trust this computer for delegation to specified services only — Use any protocol. For more information review Intermittent ANONYMOUS LOGON of SQL Server linked server double hop. |
[!NOTE]
A double-hop typically involves delegation of user credentials across multiple remote computers. For example, assume you have a SQL Server instance named SQL1 where you created a linked server for a remote SQL Server named SQL2. In linked server security configuration, you selected the option Be made using the login’s current security context. When using this configuration, if you execute a linked server query on SQL1 from a remote client computer named Client1, the windows credentials will first have to hop from Client1 to SQL1 and then from SQL1 to SQL2 (hence, it’s called a double-hop). For more information, see Understanding Kerberos Double Hop and Kerberos Constrained Delegation Overview
Login failed for user (empty)
This error occurs when a user tries unsuccessfully to log in. This error might occur if your computer isn’t connected to the network. For example, you may receive an error message that resembles the following one:
Source: NETLOGON
Date: 8/12/2012 8:22:16 PM
Event ID: 5719
Task Category: None
Level: Error
Keywords: Classic
User: N/A
Computer: <computer name>
Description: This computer was not able to set up a secure session with a domain controller in domain due to the following: The remote procedure call was cancelled.
This may lead to authentication problems. Make sure that this computer is connected to the network. If the problem persists, please contact your domain administrator.
An empty string means that SQL Server tried to hand off the credentials to the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) but couldn’t because of some problem. Either LSASS wasn’t available, or the domain controller couldn’t be contacted.
Check the event logs on the client and the server for any network-related or Active Directory-related messages that were logged around the time of the failure. If you find any, work with your domain administrator to fix the issues.
Login failed for user ‘(null)’
An indication of «null» could mean that LSASS can’t decrypt the security token by using the SQL Server service account credentials. The main reason for this condition is that the SPN is associated with the wrong account.
To fix the issue, follow these steps:
-
Use the SQLCheck or Setspn.exe to diagnose and fix SPN-related issues.
-
Use SQLCheck to check whether the SQL Service account is trusted for delegation. If the output indicates that the account isn’t trusted for delegation, work with your Active Directory administrator to enable delegation for the account.
-
Diagnose and fix Domain Name System (DNS) name resolution issues. For example:
-
Ping IP address by using PowerShell scripts:
ping -a <your_target_machine>(use-4for IPv4 and-6IPv6 specifically)ping -a <your_remote_IPAddress>
-
Use NSLookup to enter your local and remote computer name and IP address multiple times.
-
-
Look for any discrepancies and mismatches in the returned results. The accuracy of the DNS configuration on the network is important for a successful SQL Server connection. An incorrect DNS entry could cause numerous connectivity issues later.
-
Make sure that firewalls or other network devices don’t block a client from connecting to the domain controller. SPNs are stored in Active Directory. If the clients can’t communicate with the directory, the connection can’t succeed.
Additional error information
To increase security, the error message that is returned to the client deliberately hides the nature of the authentication error. However, in the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] error log, a corresponding error contains an error state that maps to an authentication failure condition. Compare the error state to the following list to determine the reason for the login failure.
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Error information isn’t available. This state usually means you don’t have permission to receive the error details. Contact your [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] administrator for more information. |
| 2 | User ID isn’t valid. |
| 5 | User ID isn’t valid. |
| 6 | An attempt was made to use a Windows login name with SQL Server Authentication. |
| 7 | Login is disabled, and the password is incorrect. |
| 8 | The password is incorrect. |
| 9 | Password isn’t valid. |
| 11 | Login is valid, but server access failed. One possible cause of this error is when the Windows user has access to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] as a member of the local administrators’ group, but Windows isn’t providing administrator credentials. To connect, start the connecting program using the Run as administrator option, and then add the Windows user to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] as a specific login. |
| 12 | Login is valid login, but server access failed. |
| 18 | Password must be changed. |
| 38, 46 | Couldn’t find database requested by user. |
| 58 | When SQL Server is set to use Windows Authentication only, and a client attempts to log in using SQL authentication. Another cause is when SIDs don’t match. |
| 102 — 111 | Azure AD failure. |
| 122 — 124 | Failure due to empty user name or password. |
| 126 | Database requested by user doesn’t exist. |
| 132 — 133 | Azure AD failure. |
Other error states exist and signify an unexpected internal processing error.
More rare possible cause
The error reason An attempt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Windows authentication only. can be returned in the following situations.
-
When the server is configured for mixed mode authentication, and an ODBC connection uses the TCP protocol, and the connection doesn’t explicitly specify that the connection should use a trusted connection.
-
When SQL server is configured for mixed mode authentication, and an ODBC connection uses named pipes, and the credentials the client used to open the named pipe are used to automatically impersonate the user, and the connection string doesn’t explicitly specify the use of a trusted authentication.
To resolve this issue, include TRUSTED_CONNECTION = TRUE in the connection string.
Examples
In this example, the authentication error state is 8. This indicates that the password is incorrect.
| Date | Source | Message |
|---|---|---|
| 2007-12-05 20:12:56.34 | Logon | Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8. |
| 2007-12-05 20:12:56.34 | Logon | Login failed for user ‘<user_name>’. [CLIENT: <ip address>] |
[!NOTE]
When [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] is installed using Windows Authentication mode and is later changed to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] and Windows Authentication mode, the sa login is initially disabled. This causes the state 7 error: «Login failed for user ‘sa’.» To enable the sa login, see Change Server Authentication Mode.
See also
- 0420 Reasons for Consistent Auth Issues
Вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой SQL Server 18456, если сервер не может аутентифицировать соединение, и это может быть вызвано недоступностью прав администратора для SQL-сервера или если протокол TCP / IP отключен в настройках SQL-сервера.
Проблема возникает, когда пользователь пытается подключиться к серверу SQL (локальному или удаленному), но обнаруживает ошибку 18456 (с разными состояниями).
Ошибка Microsoft SQL Server 18456
Вы можете исправить ошибку SQL-сервера 18456, попробовав приведенные ниже решения, но перед этим проверьте, решает ли проблему перезагрузка сервера, клиентского компьютера и сетевых компьютеров. Кроме того, убедитесь, что вы вводите правильное имя пользователя и пароль (а не копируете адрес).
Также проверьте, правильно ли вы вводите имя базы данных (без опечаток), и убедитесь, что вы соответствующим образом обновили файл конфигурации. Кроме того, проверьте, решает ли проблему разблокировка учетной записи (с помощью запроса ALTER LOGIN WITH PASSWORD = UNLOCK). Если вы видите ошибки в журнале ошибок SQL, убедитесь, что ваш SQL-сервер не атакован. И последнее, но не менее важное: убедитесь, что часы сервера и клиентского компьютера установлены правильно.
Вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой 18456, если SQL-сервер не имеет повышенных разрешений на выполнение своей операции, и запуск его от имени администратора (или отключение элементов управления UAC на сервере) может решить проблему.
Откройте SQL Server от имени администратора
- Щелкните Windows и введите SQL Server Management Studio.
- Теперь щелкните правой кнопкой мыши SMSS и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Запустите Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio от имени администратора.
- Затем нажмите Да (если получено приглашение UAC) и проверьте, не содержит ли SQL-сервер ошибки 18456.
- Если нет, проверьте, решает ли проблему отключение UAC на сервере.
Запуск SQL Server в однопользовательском режиме
- Щелкните Windows, введите и откройте диспетчер конфигурации SQL Server.
- Теперь щелкните правой кнопкой мыши службу SQL Server (на вкладке «Службы SQL Server») и выберите «Свойства».
Откройте свойства SQL Server
- Затем перейдите на вкладку Параметры запуска и в поле Укажите параметр запуска введите: -m
- Теперь нажмите «Добавить» и примените изменения.
Добавьте параметр «-m» к параметрам запуска SQL Server.
- Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши службу SQL Server и выберите «Перезагрузить».
Перезапустите службу SQL Server.
- Теперь щелкните Windows, введите: SQL Server Management Studio, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши SMSS и выберите Запуск от имени администратора.
- Теперь проверьте, можете ли вы подключиться к SQL Server от имени администратора.
- Если это так, добавьте учетную запись домена на SQL-сервер и назначьте ей роль SysAdmin.
- Теперь вернитесь в окно диспетчера конфигурации SQL Server и удалите параметр -m на вкладке Параметры запуска.
- Затем перезапустите службу SQL Server (шаг 3) и проверьте, нормально ли работает SQL-сервер.
Если проблема не исчезнет, проверьте, правильно ли настроены параметры запуска или сведения о пути. Если проблема все еще существует, убедитесь, что ваша учетная запись пользователя имеет необходимые разрешения для служб базы данных / отчетов, а затем проверьте, решена ли проблема.
Включите протокол TCP / IP в диспетчере конфигурации сервера.
Код ошибки 18456 на сервере SQL означает, что серверу не удалось аутентифицировать соединение, и это может произойти, если протокол TCP / IP, необходимый для доступа к базе данных в сети, отключен в диспетчере конфигурации сервера. В этом контексте включение TCP / IP в диспетчере конфигурации SQL Server может решить проблему.
- Щелкните Windows и разверните Microsoft SQL Server, указав год, например, 2008 (вам может потребоваться немного прокрутить, чтобы найти параметр).
- Теперь откройте диспетчер конфигурации SQL Server и нажмите Да (если получено приглашение UAC).
- Затем разверните сетевую конфигурацию SQL Server и выберите Протоколы для (имя сервера / базы данных) на левой панели.
- Теперь на правой панели дважды щелкните TCP / IP и выберите Да в раскрывающемся списке Включено.
Откройте TCP / IP в протоколах конфигурации сети SQL Server
- Затем примените изменения и щелкните Windows.
Включить TCP / IP в SQL
- Теперь введите «Службы», щелкните правой кнопкой мыши результат «Службы» и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Откройте службы в качестве администратора
- Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши SQL Server (с именем сервера) и выберите «Перезагрузить».
Перезапустите службу SQL в окне служб.
- Теперь проверьте, очищен ли SQL-сервер от ошибки 18456.
Если это не помогло, убедитесь, что вы подключаетесь к правильному порту SQL-сервера (особенно, если вы используете сервер в многосерверной среде).
Измените режим аутентификации SQL Server
Сервер SQL может отображать ошибку 18456, если метод аутентификации сервера SQL не настроен должным образом (например: вы пытаетесь войти в систему с использованием аутентификации сервера SQL, тогда как сервер настроен на использование аутентификации Windows). В этом случае изменение метода аутентификации SQL-сервера может решить проблему. Прежде чем двигаться дальше, убедитесь, что для текущего пользователя включен статус входа в систему (например, SA).
- В обозревателе объектов Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio щелкните правой кнопкой мыши свой сервер и выберите «Свойства».
- Теперь на левой панели выберите Безопасность, а на правой панели выберите SQL Server и проверку подлинности Windows (или наоборот).
Включить SQL Server и проверку подлинности Windows
- Затем примените изменения и в обозревателе объектов щелкните правой кнопкой мыши сервер.
- Теперь выберите «Перезагрузить» и после перезапуска проверьте, можете ли вы подключиться к базе данных без ошибки 18456.
Если вы не можете войти в SQL, вы можете установить MS Power Tools и выполнить следующую команду с повышенными привилегиями:
psexec.exe -i -s ssms.exe
После этого вы можете использовать учетную запись установки SQL, чтобы внести изменения, а также убедиться, что учетная запись SA не отключена:
Включите учетную запись SA и сбросьте пароль учетной записи
Если вы не можете подключиться к SQL Server, то включение учетной записи SA SQL-сервера и сброс его пароля может решить проблему.
- Запустите Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (возможно, вам придется использовать учетную запись администратора домена) и разверните Безопасность.
- Затем дважды щелкните Logins и откройте SA.
Откройте учетную запись SA в Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
- Теперь введите новый пароль и подтвердите его (убедитесь, что вы используете надежный пароль).
- Затем перейдите на вкладку Server Roles и убедитесь, что выбраны следующие роли: Public Sysadmin
Включение ролей общедоступного сервера и сервера системного администратора для учетной записи SA
- Теперь перейдите на вкладку «Статус» и на правой панели выберите «Включено» (в разделе «Вход»).
Включение учетной записи SA в SQL
- Затем примените изменения и нажмите кнопку Windows.
- Теперь введите Services и щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши.
- Затем выберите «Запуск от имени администратора» и перейдите к службе SQL Server.
- Теперь щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Перезагрузить».
- После перезапуска службы проверьте, устранена ли ошибка 18456 SQL-сервера.
Создайте новый логин и перезапустите службы Reporting Services
Если вы не можете использовать какую-либо учетную запись для подключения к базе данных, то создание новой учетной записи и перезапуск служб отчетов может решить проблему.
- Запустите Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio и разверните вкладку «Безопасность».
- Затем разверните Логины и щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши.
- Теперь выберите «Новый вход» и введите учетные данные (в имени входа выберите учетную запись компьютера), если используется проверка подлинности SQL Server.
Создать новый логин в SQL Server
- Затем не забудьте снять флажок «Пользователь должен сменить пароль при следующем входе в систему» и выберите базу данных.
- Теперь перейдите на вкладку Server Roles и выберите роль Public.
- Затем на вкладке «Сопоставление пользователей» обязательно выберите базу данных и выберите db_owner.
Выберите db_owner для базы данных в SQL
- Теперь примените ваши изменения и щелкните Windows.
- Затем введите Services и щелкните правой кнопкой мыши результат Services. Затем выберите Запуск от имени администратора.
- Теперь щелкните правой кнопкой мыши службу отчетов SQL Server и выберите «Перезагрузить».
Перезапустите службу отчетов SQL Server.
- Затем повторно подключитесь к базе данных и проверьте, очищен ли сервер SQL от ошибки 18456.
Если это так, убедитесь, что вы создали пользователя в BUILTIN administrators, и затем вы можете использовать этого пользователя для управления SQL Server. Если вы восстановили базу данных из резервной копии, будет лучше удалить и повторно добавить пользователей, чтобы удалить все старые записи пользователей. Если вы хотите запустить SQL-сервер от имени другого пользователя, введите Microsoft SQL Server в поиске Windows, Shift + щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на SQL Server и выберите «Запуск от имени другого пользователя». И последнее, но не менее важное: проверьте, решает ли проблема использование Azure Data Studio с сервером SQL.
Sql server error 18456 is common issue appear during login process on Microsoft SQL Server. This error can happen when you try to login with local administrator, as well as under the domain administrator and under the sa. Microsoft SQL Server login failed error can be encountered due to varied reasons. Most of the time, an error code comes up with a description that gives a hint about what has gone wrong. But I some cases the error come without any description. In this article, we’ll take a look at the typical reasons of the error 18456 appear on SQL Server during login process and show different ways to solve this error.
The view of error:
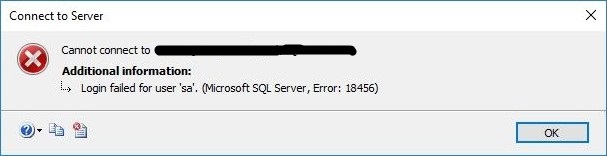
“Login failed for user ‘<user_name>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456)”.
How To FIX SQL Server Error 18456
Troubleshoot with Short Solutions
Here, you have some possible reasons:
- The login does not exist or was not typed correctly
- Make sure that the username or password are correct
- The password is incorrect
- The user forgot the password or login
- The Windows Authentication is not in Mixed mode
- A virus resets all the passwords
- A malicious hacker reset the password
- The logins were damaged or the master database is damaged
- The database was migrated, but the logins were not migrated
- The administrator modified the passwords by mistake
- Restart the SLQ Server service
Troubleshoot with State of the Microsoft SQL error 18456
Most of the time the SQL error 18456 come with the severity and state number. A state number might not mean much, yet it can offer more details as to what is wrong and where to look next.
To get a more detailed info about Microsoft SQL Server Error 18456 reason, you need to open the SQL Server error log file – ERROR.LOG. This is plain text file located under folder MSSQLLog. Below are some states of the error 18456 sql server. The descriptions and potential solutions offer a quick explanation and potential troubleshooting guide.
| State | Error Description |
| 1 | Error information is not available. This state usually means you do not have permission to receive the error details |
| 2 | Invalid user ID |
| 5 | User ID is not valid. |
| 6 | Attempt to use a Windows login name with SQL Authentication |
| 7 | Login disabled |
| 8 | Password is incorrect |
| 9 | Password is not valid |
| 11-12 | Valid login but server access failure |
| 13 | SQL Server service paused |
| 16 | Authorization is correct, but access to the selected database is not allowed |
| 18 | Change password required |
| 27 | Initial database not found |
| 38 | Could not find database requested by user |
|
102 – 111 |
AAD failure. |
| 122 – 124 | Failure due to empty user name or password. |
| 126 | Database requested by user does not exist. |
| 132 – 133 | AAD failure. |
Common Solution for Error 18456
If the issue cannot be resolved from with short solutions above, read below for additional information:
Read also other SQL Server Helping Posts:
- SQL Server Error 233
- Fix SQL server error 26 and error 40
- Restore Master Database
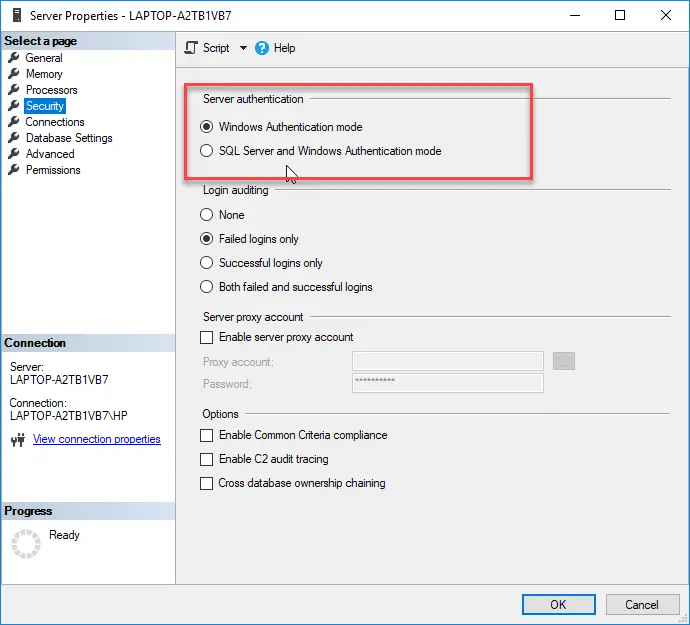
Checking the Server Authentication Mode
In this case you are trying to login on SQL Server using sql user. Once we login to SSMS using Windows Authentication, we need to check the security settings to confirm whether MSSQL is set up to allow both Windows and SQL Authentication.
Check and Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from GUI:
- In SSMS, right-click the Server Name at the top of the Object Explorer window and choose Properties.
- Next, click the Security page.
- If you find Windows Authentication is the only mode configured, this is the likely cause of sql server error 18456, Login failed for user ‘’.
- Setting the Server authentication mode to allow SQL Server and Windows Authentication, you will be able to login to MS-SQL with a SQL user and password or a Windows user and password. After making this change, you will need to restart the SQL Server service.
Server Authentication Mode
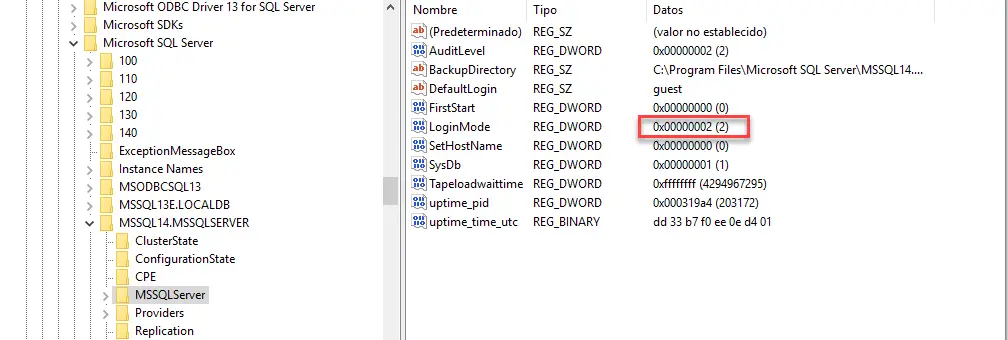
Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from regedit
You can use the registry to modify the authentication mode. Use the regedit to change the registry:
Image (regedit)
- machineHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQLXX.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLServer
- Change the login mode value.
- 2 is mixed mode.
- 1 is Windows Authentication.
Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from regedit
Checking pass expired or login disabled
Check out that the password is not expired.
- Open SSMS, Instance – Security – Logins and find the user that have issue
- On general tab check if the Enforce password expiration and enforce password policy are checked
- Un-check them
Check out that the login is enabled.
- Open SSMS, Instance – Security – Logins and find the user that have issue
- On status tab and check if is selected the “Enabled” option
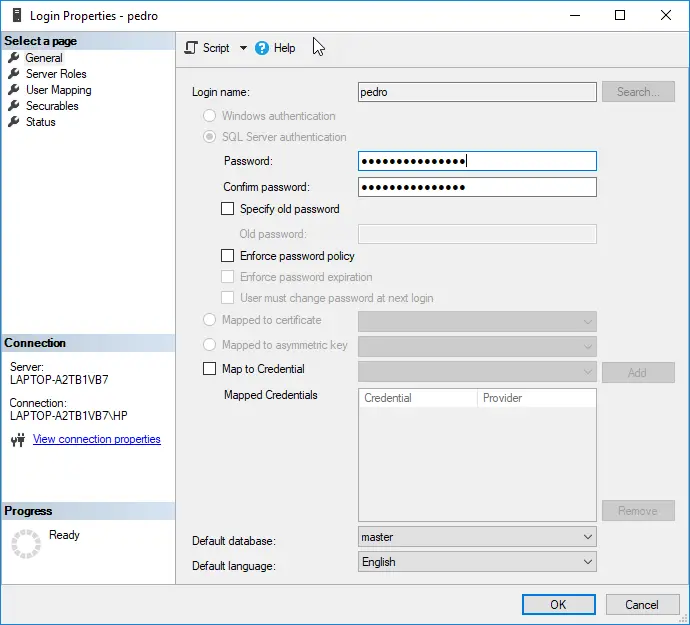
Reset the Password of the user
If you forget your password, you can ask your DBA to reset your account. The easiest way to reset the password is by using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
- Go to security and Logins:
- Select the login and you can change the password:
Checking pass expired or login disabled
- If you do not like to use SSMS, you can use T-SQL to create users and change the password:
USE [master] GOALTER LOGIN [Test] WITH ‘newpasswordtest’GOChange Windows Authentication
So we hope that you fixed the issue with the sql server error 18456.
Input : select * from sys.sysmessages where error = 18456
Output: Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’.%.*ls%.*ls
This is one of the infamous error message (and number) that most of the DBAs and developers have come across while working on SQL server. This message simply denotes that the client call was able to reach the SQL server and then an ACCESS was denied to the particular login for a reason. To figure out the exact reason, this error number 18456 with its STATE number is logged into the SQL server error log file, if SQL server was allowed or configured to capture the failed logins.
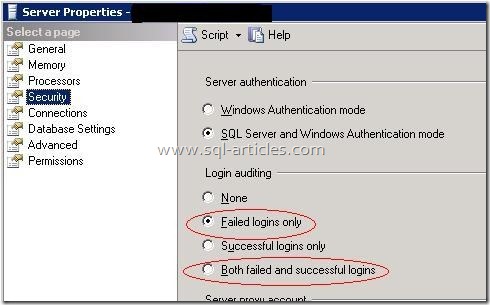
Configuring SQL server for capturing login failures:
By default, SQL server is configured to capture only failed logins but it can be changed to any of the options as mentioned in this books online link http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188470.aspx
Below figure shows these options to have login failed messages written into error log
Accessing Error log:
Now that, we know SQL server logs all login failed messages into its error log and windows event viewer but how do I access them?
Windows event viewer:
GO to start –> Run –> Eventvwr –> open up the application logs, and now we could see the login failed error message with computer name, instance name, date and time and finally the reason for the login failed
SQL Error log:
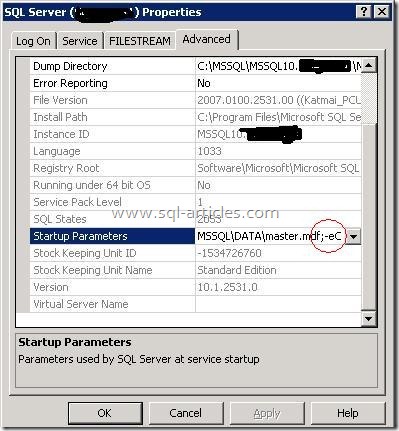
SQL server error log can be viewed from multiple places
- If we have gained access or can gain access to SQL server with different logon credentials then always use sp_readerrorlog, xp_readerrorlog or use the GUI option of opening up Management node –> SQL server Logs –> View –> SQL server log. Same sample shown above looks like
- In a case where we cannot gain access to SQL server, then we may use the actual error log path and open the txt file physically from the file system. Use SQL server configuration manager to find the error log path and from there you could open the file. Get the value next to –e parameter and that gives the actual error log file location
Typically the error log files are available in install directory for SQL server.
SQL server 2005:
C:MSSQLMSSQL.1MSSQLLOGErrorlog
SQL server 2008:
C:MSSQLMSSQL10.instanceIDMSSQLLogErrorlog
InstanceID – MSSQLSERVER for default instance and for named instance it’s the name of the instance
STATES of 18456
State 1:
This is a very generic error message that is sent to the client tools to deliberately hide the nature of the login failure issue. However, the SQL Server error log, a corresponding error contains an error state that maps to an authentication failure condition with its state number.
State 2 and 5:
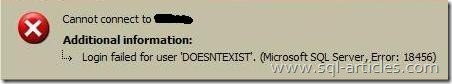
This state occurs when a SQL server login logs in with the name that doesn’t exist in sql server. This error mostly comes in when users specify wrong user name or misspell the login name. I am logging in to my instance with a login name called DOESNTEXIST that really doesn’t exist and let’s see what the error state in error log is.
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 5.
Login failed for user ‘DOESNT EXIST’. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. [CLIENT: ]
State 6:
This state occurs when a user tries to login with a WINDOWS account but specifying that as a sql server account. I have a windows account test (domaintest) but I am specifying it as a sql account and trying to login into SQL server, let’s see what state the error log has
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 6.
Login failed for user ‘domaintest’. Reason: Attppting to use an NT account name with SQL Server Authentication. [CLIENT: ]
State 7:
This state occurs when a wrong password is specified for a login which is disabled too. In this case, my SQL server user ‘Leks’ is disabled and I’m mentioning a wrong password for the connection
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 7.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. Reason: An error occurred while evaluating the password. [CLIENT: ]
For the accounts (logins) that are disabled and if you specify the correct password, the error log is logged with 18470
Error: 18470, Severity: 14, State: 1.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. Reason: The account is disabled. [CLIENT:]
State 8:
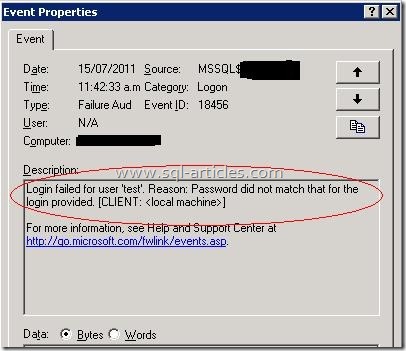
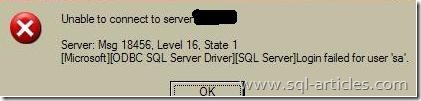
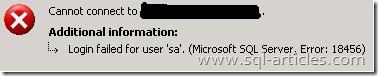
This state occurs when password is not correct in the connection string for any SQL server authenticated logins. I’m logging into SQL server using ‘sa’ account with wrong password
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8.
Login failed for user ‘sa’. Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided. [CLIENT:]
State 9:
This state means that the password was rejected by the password policy check as an invalid one. The policy API has rejected the password with error NERR_BadPassword. See more info on this error and visit http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/enus/netmgmt/netmgmt/net_validate_output_arg.asp
State 10:
This is one of the rare state and is very well documented here – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/925744
State 11 & 12:
This state means the login was valid but server access failed. One such example is when a windows login in trying to access sql server that wasn’t explicitly added to sql server (at least starting from 2008). To overcome this error, you can add that domainwindows account to sql logins explicitly.
Other reasons for this to happen are when a login is denied access (revoking connect permissions to SQL) to SQL server and UAC issues.SQL server product team covered this state extensively here –http://blogs.msdn.com/b/sqlserverfaq/archive/2010/10/27/troubleshooting-specific-login-failed-error-messages.aspx
Windows account which do not have access
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 11.
Login failed for user ‘domainuser’. Reason: Token-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Check for previous errors. [CLIENT:]
SQL account that was denied access
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 12.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. Reason: Login-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Check for previous errors. [CLIENT:]
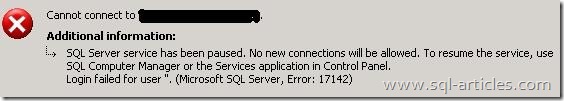
State 13:
This state occurs when any login tries to access to sql server with services paused on it. But for this reason, there will also be other error number 17142 logged along with 18456.
Error: 17142, Severity: 14, State: 0.
SQL Server service has been paused. No new connections will be allowed. To resume the service, use SQL Computer Manager or the Services application in Control Panel.
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 13.
Login failed for user ”. Reason: SQL Server service is paused. No new connections can be accepted at this time. [CLIENT:]
State 16:
This state occurs for logins that do not have access to the target database or the database doesn’t exist anymore with the same name or offline. We always specify the database in the connection string as initial catalog or using -d parameter.
This can be fixed by granting access to the database and sometimes orphan users existing in the database. Orphan users can be fixed by sp_change_users_login
This state occurs in SQL server 2005 and same is changed to 40 in SQL server 2008 and above
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 16.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. [CLIENT: <local machine>]
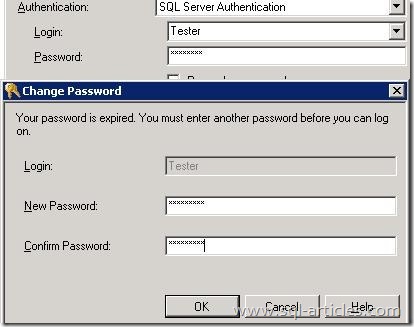
State 18:
This state occurs when a sql login is added with USER MUST CHANGE THEIR PASSORD ON FIRST LOGON or a login that needs to have its password changed as per the domain or windows password policy ; this state gets in to error log when the new password box prompts up.
This error is logged with state 18488
Error: 18488, Severity: 14, State: 1.
Login failed for user ‘Tester’. Reason: The password of the account must be changed. [CLIENT: ]
State 23:
This state can happen due to couple reasons; first being simultaneous action of shutting down SQL SERVER and any incoming logins to sql server takes place. The other one is documented here as an issue http://support.microsoft.com/kb/937745
State 38:
This is similar to state 16 but this was introduced from SQL server 2008 and above.
Database doesn’t exist or login doesn’t have access to the database.
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 38.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database. [CLIENT: ]
State 40:
This state occurs when the login’s default database doesn’t exist in SQL server or offline or the login doesn’t have access to the default database. This state is always logged alongside with error 4064
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 40.
Login failed for user ‘Leks’. Reason: Failed to open the database specified in the login properties. [CLIENT: ]
State 58:
This state occurs when a SQL server login is used for accessing SQL server when SQL server is installed with windows authentication mode.
You may have to use only windows login or change the authentication to mixed authentication for this to work – http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188670.aspx. The authentication mode change always requires a SQL restart to come into effect.
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 58.
Login failed for user ‘sa’. Reason: An attppt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Windows authentication only. [CLIENT: <local machine>]
I have tried and covered most of the states that I know of, and if you find states that I haven’t discussed happy to hear and add to this list. Apart from the error 18456, there are other login failure errors that you might have to keep an eye on
|
18451 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Only administrators may connect at this time.%.*ls |
|
18452 |
Login failed. The login is from an untrusted domain and cannot be used with Windows authentication.%.*ls |
|
18458 |
Login failed. The number of simultaneous users already equals the %d registered licenses for this server. To increase the maximum number of simultaneous users, obtain additional licenses and then register them through the Licensing item in Control Panel.% |
|
18459 |
Login failed. The workstation licensing limit for SQL Server access has already been reached.%.*ls |
|
18460 |
Login failed. The number of simultaneous users has already reached the limit of %d licenses for this ‘%ls’ server. Additional licenses should be obtained and installed or you should upgrade to a full version.%.*ls |
|
18461 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Reason: Server is in single user mode. Only one administrator can connect at this time.%.*ls |
|
18462 |
The login failed for user “%.*ls“. The password change failed. The password for the user is too recent to change. %.*ls |
|
18463 |
The login failed for user “%.*ls“. The password change failed. The password cannot be used at this time. %.*ls |
|
18464 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Reason: Password change failed. The password does not meet Windows policy requirements because it is too short.%.*ls |
|
18465 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Reason: Password change failed. The password does not meet Windows policy requirements because it is too long.%.*ls |
|
18466 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Reason: Password change failed. The password does not meet Windows policy requirements because it is not complex enough.%.*ls |
|
18467 |
The login failed for user “%.*ls“. The password change failed. The password does not meet the requirements of the password filter DLL. %.*ls |
|
18468 |
The login failed for user “%.*ls“. The password change failed. An unexpected error occurred during password validation. %.*ls |
|
18470 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘. Reason: The account is disabled.%.*ls |
|
18471 |
The login failed for user “%.*ls“. The password change failed. The user does not have permission to change the password. %.*ls |
|
18482 |
Could not connect to server ‘%.*ls’ because ‘%.*ls’ is not defined as a remote server. Verify that you have specified the correct server name. %.*ls. |
|
18483 |
Could not connect to server ‘%.*ls’ because ‘%.*ls’ is not defined as a remote login at the server. Verify that you have specified the correct login name. %.*ls. |
|
18485 |
Could not connect to server ‘%.*ls’ because it is not configured to accept remote logins. Use the remote access configuration option to allow remote logins.%.*ls |
|
18486 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’ because the account is currently locked out. The system administrator can unlock it. %.*ls |
|
18487 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘.Reason: The password of the account has expired.%.*ls |
|
18488 |
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls‘.Reason: The password of the account must be changed.%.*ls |
|
18489 |
The dedicated administrator connection is in use by “%.*ls” on “%.*ls“.%.*ls |
Happy “login failure “troubleshooting