WRITE FOR US
The MySQL server has gone away error, which means that the MySQL server (mysqld) timed out and closed the connection. By default, MySQL will close connections after eight hours (28800 seconds) if nothing happens. However, in some cases, your web host, DBA, or app developer may have decreased this timeout setting, as discussed below.
MySQL server has gone away, can be a frustrating error to solve. This is partly because, to solve this error, sometimes the solution involves multiple layers, application, or service config changes. This article includes solutions I’ve seen for this MySQL server general error. If you’ve found a solution not listed or linked to on this page, please send me a note or leave a comment.
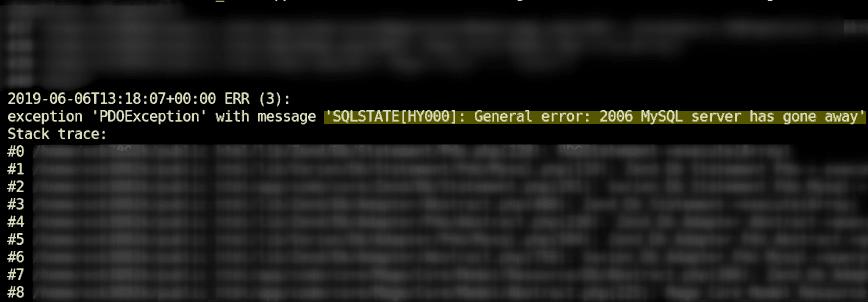
MySQL server has gone away error log examples.
Keep in mind that this error can be logged in a few ways, as listed below. In addition, at times, the error is only an indication of a deeper underlying issue. Meaning the error could be due to a problem or bug in your connecting application or remote service. In this case, you need to check ALL related error logs with the same timestamp to determine whether another issue may be to blame. Application Performance Monitoring solutions and PHP Stack trace tools can be of help. With this in mind, here are error log examples of the MySQL server has gone away error:
General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away
Error Code: 2013. Lost connection to MySQL server during query
Warning: Error while sending QUERY packet
PDOException: SQLSTATE[HY000]: General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away
Sponsored: Datadog – View query metrics and explain plans from all of your databases in a single place.
Datadog is a unified monitoring, analytics, and security platform that offers end-to-end monitoring for all of your databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more! Quickly pinpoint costly, slow queries and troubleshoot performance issues faster with key database metrics and patterns in one place. Easily search, compare, and filter your queries on execution plans to quickly identify areas for performance and cost improvements. Utilize our integrations for MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and more to visualize key system performance metrics on an out-of-the-box dashboard alongside query and host-level metrics. Datadog Database Monitoring is closely integrated with the rest of the Datadog platform; further improve your Database performance with other key features such as SLO tracking, monitors & alerts, Security Monitoring, and more!
Cost: Free plan, or starting at $70.
MySQL wait_timeout
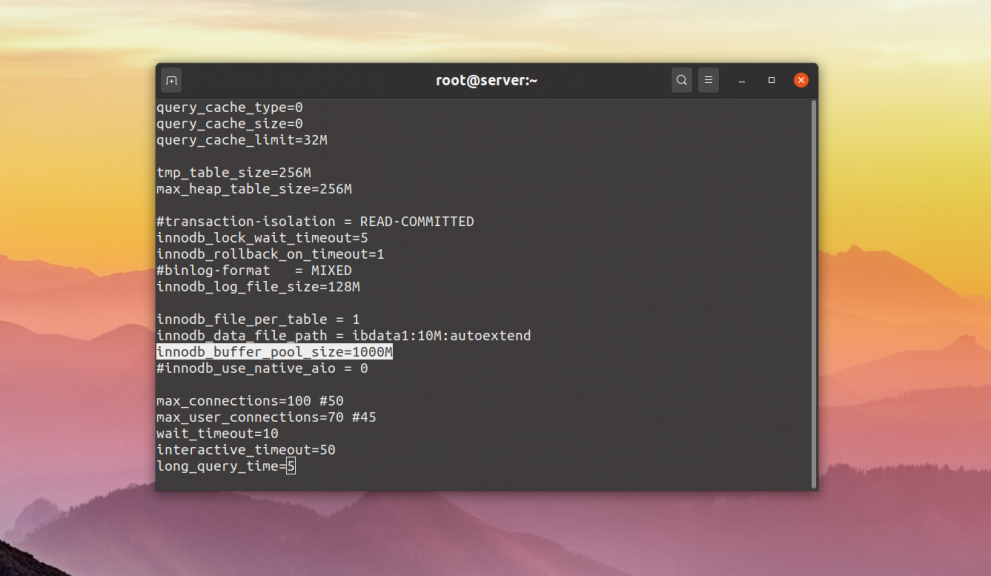
The reason for MySQL server has gone away error is often because MySQL’s wait_timeout was exceeded. MySQL wait_timeout is the number of seconds the server waits for activity on a non-interactive connection before closing it. You should make sure the wait_timeout is not set too low. The default for MySQL wait_timeout is 28800 seconds. Often, it gets lowered arbitrarily. That said, the lower you can set wait_timeout without affecting database connections, can be a good sign of MySQL database efficiency. Also, check the variables: net_read_timeout, net_write_timeout and interactive_timeout. Adjust or add the following lines in my.cnf to meet your requirements:
wait_timeout=90 net_read_timeout=90 net_write_timeout=90 interactive_timeout=300 connect_timeout=90
MySQL connect timeout in PHP config.
Have a look at your php.ini config file. You’ll find MySQL configuration options. Make sure the mysql.connect_timeout setting isn’t set lower than MySQL wait_timeout, discussed above. The PHP option mysql.connect_timeout is not only used for connect timeout. It’s also when waiting for the first response from the MySQL server. Try increasing mysql.connect_timeout to match or exceed your MySQL wait_timeout and make sure that mysql.allow_persistent is on (default = enabled).
mysql.connect_timeout=90 mysql.allow_persistent=1
IMPORTANT: Read first about PHP Persistent Database Connections to understand the benefits and caveats.
Also, adjust PHP’s default_socket_timeout. For example, a PHP script could be running a slow query. Creating a wait that utilizes the default_socket_timeout. Eventually, it quits with the “MySQL server has gone away” error. Before you send hate mail, please read here first. Here’s an excerpt:
“PHP, by default, sets a read timeout of 60s for streams. This is set via php.ini, default_socket_timeout. This default applies to all streams that set no other timeout value. mysqlnd does not set any other value and therefore connections of long running queries can be disconnected after default_socket_timeout seconds resulting in an error message 2006 – MySQL Server has gone away
.”
default_socket_timeout=90
To be throughout, also adjust max_execution_time and max_input_time still in php.ini, if necessary. If PHP’s execution time is longer than max_execution_time, then MySQL server might disconnect.
max_execution_time = 90 max_input_time = 90
MySQL max_allowed_packet
max_allowed_packet is the maximum size of one packet. The default size of 4MB helps the MySQL server catch large (possibly incorrect) packets. As of MySQL 8, the default has been increased to 16MB. If mysqld receives a packet that is too large, it assumes that something is wrong and closes the connection. To fix this, you should increase the max_allowed_packet in my.cnf, then restart MySQL. The max for this setting is 1GB. For example:
max_allowed_packet = 512M
MySQL innodb_log_file_size
You may need to increase the innodb_log_file_size MySQL variable in your my.cnf configuration. MySQL’s innodb_log_file_size should be 25% of innodb_buffer_pool_size (if possible, no less than 20%). Remember that the larger this value, the longer it will take to recover from a database crash. (Source: Phpmyadmin Advisor)
This means for example: if your buffer pool size is set to innodb_buffer_pool_size=16G and your innodb_log_files_in_group setting is still set to the recommended default of 2 files (innodb_log_files_in_group=2), then your innodb_log_file_size should be set to 2G. This will create two (2) log files at 2GB each, which equals 25% of innodb_buffer_pool_size=16G.
WARNING: You must stop MySQL server in order to change innodb_log_file_size or innodb_log_files_in_group. If you don’t, you risk catastrophe! (Read: MySQL Log Redo instructions.)
Other causes of MySQL server has gone away
Remote MySQL connections
Remember earlier I mentioned that the error, at times, is only an indication of a deeper underlying issue. For example, remote MySQL connections to 3rd party services. Using a 3rd party payment processing plugin for osCommerce, Magento, etc.
MySQL database charset and collation
Changing default database charset to latin1 and default collation to latin1_general_ci seemed to have solved MySQL server has gone away for some.
Exceeding MySQL max_connections setting
Max_connections set the maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections. Be careful with this setting!! Exhaustion of memory and other resources can occur when set too large and scheduling overhead also increases. As a guide, set max_connections to approximately double the previous number of maximum simultaneous client connections. E.g., if after a month of uptime, the maximum simultaneous client connections were 114, then set to max_connections=250. Before you go crazy with this setting, please read: How MySQL Handles Client Connections.
Still unresolved? See MySQL’s help page.
Oracle has put together a nice self-help page for MySQL server has gone away errors. On that page, they also suggest that you make sure MySQL didn’t stop/restart during the query. Excerpt:
“You can check whether the MySQL server died and restarted by executing mysqladmin version and examining the server’s uptime. If the client connection was broken because mysqld crashed and restarted, you should concentrate on finding the reason for the crash.”
# mysqladmin version mysqladmin Ver 9.1 Distrib 10.1.40-MariaDB, for Linux on x86_64 Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Server version 10.1.40-MariaDB Protocol version 10 Connection Localhost via UNIX socket UNIX socket /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock Uptime: 20 days 11 hours 49 min 40 sec Threads: 5 Questions: 1030744326 Slow queries: 3343 Opens: 3585 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 2564 Queries per second avg: 582.150
# mysqladmin status Uptime: 1770590 Threads: 4 Questions: 1030752268 Slow queries: 3343 Opens: 3585 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 2564 Queries per second avg: 582.151
I hope this helps!
Related articles:
- MySQL Performance Tuning: Tips, Scripts and Tools
- Tuning MySQL: my.cnf, avoid this common pitfall!
- MySQL Performance: Stop hoarding. Drop unused MySQL databases
Published: June 7th, 2019 | Last updated: Nov 10th, 2022
Tags: apm, linux, mariadb, mysql, performance, server, sysadmins
Эта ошибка означает, что MySQL сервер запущен, но он отказывает вам в соединении. Это может произойти по нескольким причинам. Самых основных и часто встречающихся причин три: сервер перегружен, и у вас истекло время ожидания ответа, ваш клиент отправил слишком большой пакет или сервер был не до конца проинициализирован.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим более подробно, почему возникает ошибка 2006: MySQL server has gone away, а также — как её исправить.
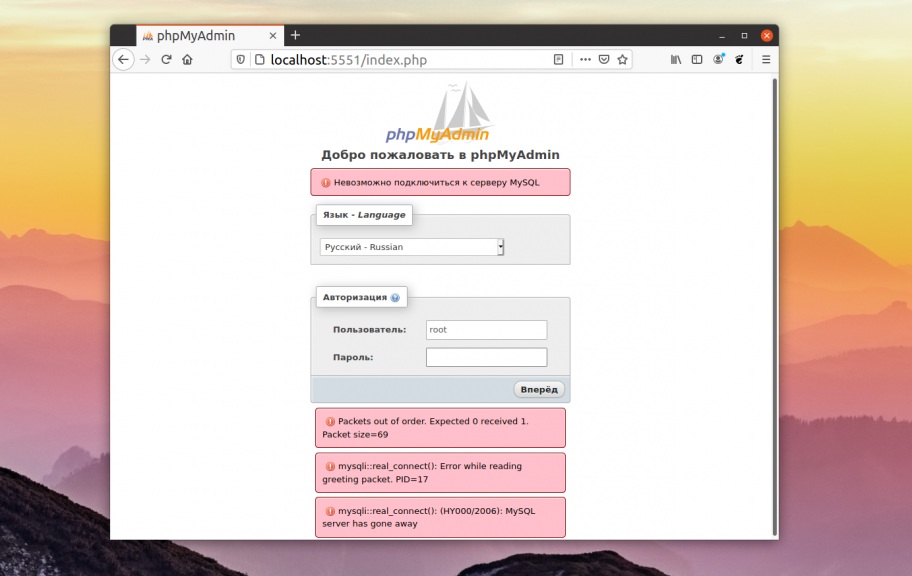
Такую ошибку вы можете увидеть во время подключения к базе данных с помощью PHP, консольного клиента или, например, в PhpMyAdmin:
1. Истекло время ожидания
Как я уже писал выше, одной из причин может быть таймаут ожидания соединения. Возможно, сервер баз данных перегружен и не успевает обрабатывать все соединения. Вы можете подключиться к серверу с помощью консольного клиента, если вам это удастся, и попытаться выполнить какой-либо запрос, чтобы понять, действительно ли запросы выполняются слишком долго. Если это так, можно оптимизировать производительность MySQL с помощью скрипта MySQLTuner.
В большинстве случаев надо увеличить размер пула движка InnoDB с помощью параметра innodb_buffer_pool_size. Какое значение лучше поставить, можно узнать с помощью указанного выше скрипта. Например, 800 мегабайт:
sudo vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
innodb_buffer_pool_size=800M
Есть и другой путь решения этой проблемы. Если такая скорость обработки запросов считается нормальной, можно увеличить время ожидания ответа от сервера. Для этого измените значение параметра wait_timeout. Это время в секундах, на протяжении которого надо ждать ответа от сервера. Например:
wait_timeout=600
После любых изменений не забудьте перезапустить MySQL сервер:
sudo systemctl restart mysql
или:
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
2. Слишком большой пакет
Если ваш клиент MySQL создаёт слишком большие пакеты с запросами к серверу, это тоже может стать причиной такой ошибки. Максимально доступный размер пакета можно увеличить с помощью параметра max_allowed_packet. Например:
sudo vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
max_allowed_packet=128M
Обратите внимание, что если вы из своей программы отправляете большие пакеты, то, скорее всего, вы делаете что-то не так. Не надо генерировать запросы к MySQL с помощью циклов for. SQL — это отдельный язык программирования, который многое может сделать сам, без необходимости писать очень длинные запросы.
3. Сервер неверно проинициализирован
Такая проблема может возникать при разворачивании контейнера MySQL или MariaDB в Docker. Дело в том, что на первоначальную инициализацию контейнера нужно много времени: около нескольких минут. Если вы не дадите контейнеру завершить инициализацию, а остановите его и потом снова запустите, то база данных будет всегда возвращать такую ошибку.
Вам нужно полностью удалить данные контейнера с базой данных. Например, с помощью docker-compose:
docker-compose down
или вручную:
docker rm mysql-container
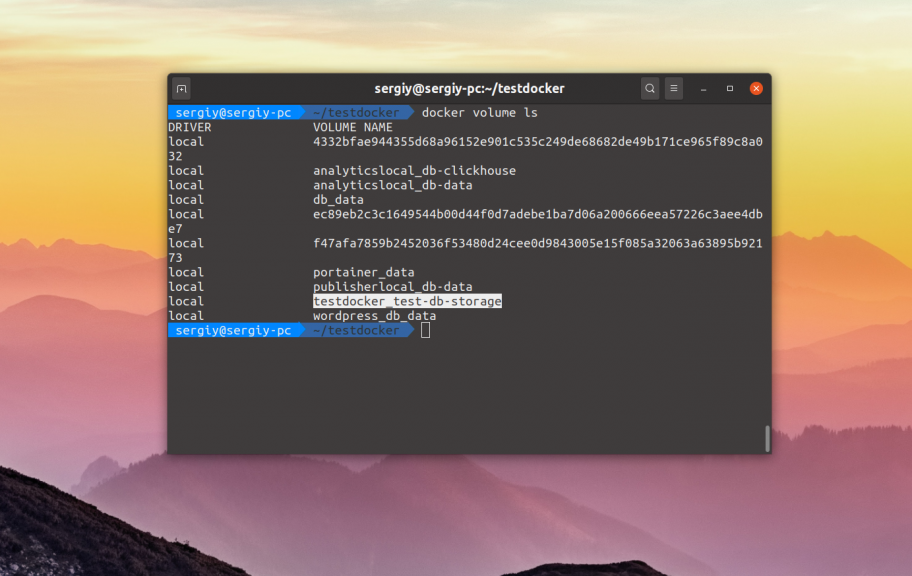
Здесь mysql-container — это имя контейнера с базой данных. А затем надо удалить хранилище (volume) с некорректно проинициализированной базой. Сначала посмотрите список всех хранилищ:
docker volume ls
Затем удалите нужное:
docker volume rm имя_хранилища
После этого можете снова запускать инициализацию приложения, только на этот раз дождитесь, пока сервер баз данных сообщит, что он готов, и вы сможете к нему подключиться.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели, что значит ошибка MySQL Server has gone away, а также как её исправить на сервере или в контейнере Docker. Вы знаете ещё другие причины и решения этой проблемы? Пишите в комментариях!
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
This article provides the solution to the following MySQL error:
ERROR 2006 (HY000): MySQL server has gone away
We generally get this kind of error when we try to import or insert a large volume of data into the MySQL database.
To solve this error, we can:
– either update the MySQL’s configuration file:
my.cnf
– or, update the global variables directly by logging into the MySQL server
Update my.cnf file
- Open terminal
- Find the
my.cnffile by running the following command:
mysql --help | grep my.cnf
- This should output something like this:
order of preference, my.cnf, $MYSQL_TCP_PORT,
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf /usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf
- Open your
my.cnffile in any editor and add/update the value of the following variables:
[mysqld]
max_allowed_packet= 1024M
- In your
my.cnffile, you may also try increasing the wait_timeout value:
[mysqld]
max_allowed_packet= 1024M
wait_timeout= 60000
- Restart MySQL server
LINUX
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
//OR
sudo service mysqld restart
//OR
sudo service mysql restart
MACOS
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restart
Now, you should be able to work fine with large MySQL datasets.
Update the global variables directly by logging into the MySQL server
First of all, you need to restart the MySQL server. You can run the commands listed above to restart the MySQL server.
After that, you can check the list of all the MySQL Global Variables and their values with the following command:
$> mysqladmin variables -u YourMysqlUsername -p
You can also check for these variables value by first logging into MySQL server:
$> mysql -u YourMysqlUsername -p
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES;
To check specific variable value:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'max_allowed_packet';
To solve MySQL Server Gone Away error, you need to increase the value of max_allowed_packet variable. To do so, you have to run the following command:
mysql> SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet=1072731894;
After that, quit MySQL login:
mysql> quit
Now, when you again login to MySQL and check for the max_allowed_packet value, you should see the updated value.
$> mysql -u YourMysqlUsername -p
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'max_allowed_packet';
+--------------------+------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------+------------+
| max_allowed_packet | 1072731136 |
+--------------------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Now, you should be able to work fine with large MySQL datasets.
Hope this helps. Thanks.