During the startup of SQL Server, a process called database recovery occurs for every database residing on the instance which includes system databases as well. In a scenario where for multiple reasons the recovery process fails, the SQL Server would report an error 3414 in the ERRORLOG and the Windows Application Event Log. The error indicates would look like this:
“An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘YourDB’ (database ID 11) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support)”
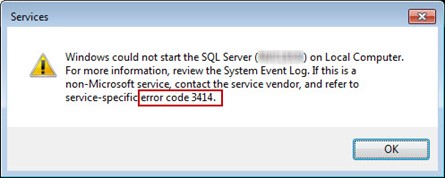
A similar error is shown below from the Services Manager when starting SQL Server fails to start with error code 3414.
As mentioned earlier, there are several reasons that could be the root cause for this error. Until the error is resolved you will be restricted in working with the database. In order to resolve issue, you need to examine the error preceding this error in the ERRORLOG or Event Log to determine the underlying issue. In majority of cases, the database is set to ‘Suspect’ mode and may incur additional errors on further usage. The Error message 926 usually appears on your screen when you try to access the SQL database marked as ‘Suspect’.
One typical example of error 3414 is when recovery of a database fails and encounters a checksum error while attempting to read a block in the transaction log file. For such an example, you would see similar errors in your SQL error log below:
2018-08-20 14:30:37.68 spid15s Error: 824, Severity: 24, State: 4. 2018-08-20 14:30:37.68 spid15s SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error: (bad checksum). It occurred during a read of page (0:-1) in database ID 14 at offset 0x0000000000b900 in file ‘C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL12.SQL2K14MSSQLDATAmydata_log.LDF’. Additional messages in the SQL Server error log or system event log may provide more detail. This is a severe error condition that threatens database integrity and must be corrected immediately. Complete a full database consistency check (DBCC CHECKDB). This error can be caused by many factors; for more information, see SQL Server Books Online. 2018-08-20 14:30:37.81 spid15s Error: 3414, Severity: 21, State: 1. 2018-08-20 14:30:37.81 spid15s An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘mydata’ (database ID 14) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support
How to Resolve the SQL Server Error 3414?
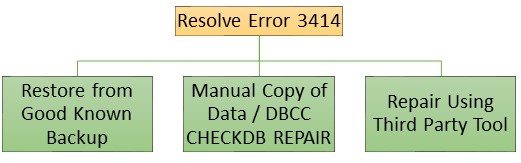
There are 3 ways of rectifying this error code 3414 when the database recovery fails. The chart below shows what options are available to help resolve this issue.
Method 1: Restore from Good Known Backup
The most recommended option is restoring from a good known backup. The database curator needs to utilize the most current backup file for restoring the suspect database. To learn more about restoring a backup for a suspect SQL database, click this link.
Method 2: Manual Copy of Data / DBCC CHECKDB REPAIR
The next method of a resolution would be executing DBCC CHECKDB command. This manual intervention will be best to retrieve back your database in an online and accessible mode. However, due to the recovery failure, consistency of transactions is not guaranteed after a repair. It is almost impossible to track the transactions, which have been rolled back or forward but, were not completed. The commands below would attempt to repair the suspect database using the DBCC CHECKDB feature:
This set of commands would put the database in ethe mergency state.
EXEC sp_resetstatus 'db_name'; ALTER DATABASE db_name SET EMERGENCY
Perform an integrity and consistency check on the database.
DBCC CHECKDB ('database_name')
The check would recommend the minimal repair level. Set database to single user to allow repair.
ALTER DATABASE database_name SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
Run the repair command as shown below
DBCC CHECKDB ('database_name', REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS)
Once the repair is complete, set database back to multi-user to allow connections.
ALTER DATABASE database_name SET MULTI_USER
In some cases, the steps provided using DBCC CHECKDB fails to repair and recover the suspect database. You can attempt to COPY OUT as much data as possible from the suspect database. In order to do that, you would need to put the database back into EMERGENCY mode. This would allow you to access the content of the database. At this point try to copy as much as possible out of the database into a new database. Use the following command below to put the database into EMERGENCY:
EXEC sp_resetstatus 'db_name'; ALTER DATABASE db_name SET EMERGENCY
Methods 3: Repair Using SQL Recovery Software
Finally, if you find yourself in the worst-case scenario where all the above solutions did not work out, then the Stellar Repair for MS SQL software can help you perform a SQL error 3414 repairs. The software has dedicated and easy-to-use mechanism to effectively repair corrupt SQL databases and safely recover all the database objects like tables, views, indexes, keys, constraints, etc. stored in the database. The renowned tool enables you to efficiently resolve error 3414 which saves you from the risk of looming data loss. The software supports all the latest SQL Server versions, from SQL Server 2019, 2017, 2016 to 7.0.
About The Author
Priyanka
Priyanka is a technology expert working for key technology domains that revolve around Data Recovery and related software. She got expertise on SQL Database. Loves to write on different technology and data recovery subjects on regular basis. Technology freak who always found exploring neo-tech subjects, when not writing, research is something that keeps her going in life.
As we all know, Microsoft released MS SQL Server 29 years ago i.e. SQL Server 1.0 and for ages, it has reached many milestones with its ease of use and security. It has grabbed its own space in online markets with lightning speed over the years. The latest version was released in 2017 i.e. SQL Server 2017 which also supports Linux platforms as well such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise & Docker Engine.
MS SQL Server is a management system for storing and extracting data from the connected application. Though the most widely used secure and safe database server, it is also prone to unexpected errors. One such error is “SQL Error 3414” –
SYMPTOMS of the Error 3414:
The error is caused when the SQL Server service does not start during login or startup of database recovery. Hence, the database fails to retrieve causing MSSQL error code 3414.
The extended form of the error written to ERRORLOG or Windows Application Event Log with EvenetID-3414 with SQL Server is as follows:
“Error: 3414, Severity: 21, State: 1.
An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘mydb’ (database ID 13) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support)”
Usually, an error that precedes Error 3414 in the ERRORLOG or Event Log is the reason for SQL database recovery failure.
Also, the status of the database is set to SUSPECT. The SUSPECT status is reflected in SQL Server Management Studio and sys.databases.state_desc. If you try to operate the database in this state you might encounter “SQL suspect database error 926” as follows:
“Msg 926, Level 14, State 1, Line 1
Database ‘mydb’ cannot be opened. It has been marked SUSPECT by recovery. See the SQL Server errorlog for more information”
Understand the Primary Cause of the Error 3414
The basic cause of the occurrence of error 3414 is due to the same SPID value in the server log file with the failure in the recovery of the database file. Go through the following checksum error that occurred during the time of the “read page” operation in the database to roll forward a transaction.
“2010-03-31 17:33:13.00 spid15s Error: 824, Severity: 24, State: 4.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.00 spid15s SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error: (bad checksum). It occurred during a read of page (0:-1) in database ID 13 at offset 0x0000000000b800 in file ‘C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQL2008MSSQLDATAmydb_log.LDF’. Additional messages in the SQL Server error log or system event log may provide more detail. This is a severe error condition that threatens database integrity and must be corrected immediately. Complete a full database consistency check (DBCC CHECKDB). This error can be caused by many factors; for more information, see SQL Server Books Online.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.16 spid15s Error: 3414, Severity: 21, State: 1.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.16 spid15s An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘mydb’ (database ID 13) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support”
Resolution to Fix “Error Code 3414” in SQL Server?
The best possible solution to resolve the SQL Server error 3414 is to restore the database from a backup (if available) using SQL Server Management Studio. It is a good practice to take timely backups for handling unexpected disastrous situations. But, there are times when it is not possible to recover from a backup of the database or incomplete data is restored from your available backup. Here are the following methods to fix the error:
Method 1: Use DBCC CHECDB for emergency repair
Executing DBCC CHECDB should be your first step to get back the database to running state.
DBCC CHECKDB
[ ( database_name | database_id | 0
[ , NOINDEX
| , { REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS | REPAIR_FAST | REPAIR_REBUILD } ]
) ]
[ WITH
{
[ ALL_ERRORMSGS ]
[ , EXTENDED_LOGICAL_CHECKS ]
[ , NO_INFOMSGS ]
[ , TABLOCK ]
[ , ESTIMATEONLY ]
[ , { PHYSICAL_ONLY | DATA_PURITY } ]
[ , MAXDOP = number_of_processors ]
}
]
]
However, it the best method but transactional consistency is not guaranteed since recovery failed. There are no ways to find out which transactions were rolled back or rolled forward and not allowed due to recovery failure.
Method 2: Copy Entire (healthy or recoverable data) Database to another Database
If the first workaround method fails to work, then you must try to copy all the possible data that is in the healthy or recoverable state to another database. To do this, set the database in emergency mode with the help of the given command:
ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET EMERGENCY
After setting emergency mode, you can try to copy or move all the data to another database.
Resolve with Automated Method – SQL Database Recovery
In case the above-mentioned methods fail to fix and recover the database, then we recommend you immediately choose SQL Database Recovery software. This SQL Recovery is the most trustworthy software that serves the purpose of resolving SQL Server error code 3414. The software is specially designed for the recovery of corrupt and inaccessible SQL database files of any SQL server version.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have completely analyzed one of the common SQL Server errors which occur during the database recovery. Along with symptoms, primary cause, three potential manual solutions, a complete SQL Database Recovery software for quick and fine recovery of data from corrupted SQL Server database file is proposed in the end.
Содержание
- How to Resolve Error Code 3414 MS SQL Server 2008-r2?
- How to Fix SQL Server 2008-R2 Error with Code 3414?
- What to do if this method did not work?
- How manual solutions are not completely reliable?
- Alternative Option – Third Party tool
- MSSQLSERVER_3414
- Сведения
- Объяснение
- Причина
- Рекомендуемые действия
- Исправляемые ошибки и отложенные транзакции
- MSSQLSERVER_3414
- Details
- Explanation
- Cause
- User action
- Correctable errors and deferred transactions
How to Resolve Error Code 3414 MS SQL Server 2008-r2?
SQL Server goes into whole recovery phase on each time login and sometimes there are complaints by the users stating crash down of the server with an error like this.
It can occur even while applying any functions or manipulations and when the SQL Server service is not started with the login on the SQL Server. Here, as we can see in the error message, the recovery failure occurred due to the service-specific error code 3414. In the Event Log, the reason behind this failure can be detected as it depends on the preceding error logs with log files having similar SPID value.
When user tries to roll forward a transaction log with read page operation on the database, the checksum error appears like this:
With the failure of database recovery and onset of this error, the database goes into SUSPECT mode which is visible against the server database name in the SQL Server Management Studio.
If any user tries to use the database in this SUSPECT mode, he has to encounter the progressive error stating –
So, there is a need to fix this error code 3414 issue to get back the normal database functioning once again. As we know handling the SQL Server, its features and functions is a bit complex task. So, there is a need of technical knowledge for performing manual solutions which might include running SQL Server queries to repair or restore the SUSPECT database in SQL Server; you can also restore SQL Database with a different name.
How to Fix SQL Server 2008-R2 Error with Code 3414?
As recommended by Microsoft itself, we are explaining some of the workable manual methods for fixing or resolving this SQL Server error. Keep following carefully these methods and use them accordingly.
1st Method: Go for Restoring SQL Data through Recent Database Backup
If SQL Server user is in good practice of taking regular backups of their SQL database file and need to access it urgently. Then, restoring data from backup is a nice and easy choice. Perform these easy steps in order to restore your database from backup file.
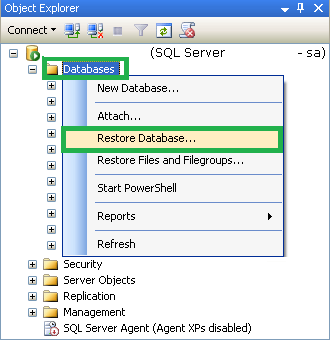
- Launch the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio as an administrator.
- Go to Object Explorer panel on the left, make connection to SQL Server Database Engine, select it and expand.
- Now select Databases option and right-click on it. Select Restore Database option from the list.
- Next, on the General page, under Source section, choose the Database option and add the recent database backup file from the list.
- The restore process will get started and complete based on the database size.
- Restart the SQL Server and check for the error code oncoming again.
For users who don’t have any backup file for the SQL database, we have other manual solutions as well.
2nd Method: Perform Emergency Repair Solution via DBCC CHECKDB
SQL Server provides its users certain SQL Query and commands to check upon the integrity of the SQL Database. DBCC CHECKDB command is helpful in checking the database in terms of accessibility and fixing related issues. Databases should be put in emergency mode as transaction consistency (no tracking of transaction roll back and forward) is not possible with DBCC command alone.
To put the databases in emergency mode, execute this command in New Query in SQL Server Management Studio run as administrator on your SQL system.
Provide SQL Server database name at the required locations in the commands.
Perform integrity check on the SQL Server database using the following command.
After checking the consistency of the database, the minimal repair recommendation would display. For that, to allow repair, set the database to single user executing this command.
Run the DBCC repair command as follows with introduction of “Repair Allow Data Loss” feature.
Exit the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio. Now, restart the server and check if the issue is resolved.
What to do if this method did not work?
It is possible that simply executing DBCC CHECKDB command in emergency mode does not fix the error. You can use COPY OUT command to copy the whole database to a new database but needs to put the databases in the emergency mode using this command as used earlier.
Note: SQL administrators can follow the online troubleshooting solutions provided in the Event Error Log itself.
How manual solutions are not completely reliable?
Restoring database manually from backup file does not ensure the complete backup of SQL database objects. It might include data loss or modification during the whole process. Also DBCC CHECKDB command is not helpful due to issues of transaction log files tracking as some or other manual errors can be expected even in the Emergency mode. All these tricks require good amount of time and efforts with some technical knowledge. So, limitations might hold back users and lead them to look for a better alternative.
Alternative Option – Third Party tool
If you lack trust in manual solutions or already tried the above tricks but not succeeded, we offer you the best SQL Server recovery tool in the market which includes the most advanced programming and algorithms to tackle all kinds of SQL Server errors including SQL database corruptions and resolve it within few minutes. It only requires the database file for the repair process and supports all SQL Server versions widely. Go on this utility website and checkout all the features in detail. You can download the trial version for free and get the experience of efficient Recovery anytime.
Conclusion
We have concluded that SQL Server errors can be tackled manually (as some methods like restore from backup, DBCC CHECKDB repair in emergency mode are explained) but from these tricks, complete reliability cannot be assured. Third-party utility which could be your savior in dealing with complex SQL Server error codes.
Источник
MSSQLSERVER_3414
Применимо к: SQL Server (все поддерживаемые версии)
Сведения
| attribute | Значение |
|---|---|
| Название продукта | SQL Server |
| Идентификатор события | 3414 |
| Источник события | MSSQLSERVER |
| Компонент | SQLEngine |
| Символическое имя | REC_GIVEUP |
| Текст сообщения | Во время восстановления произошла ошибка, препятствующая перезапуску базы данных «%.*ls» (идентификатор базы данных %d). Проведите диагностику ошибок восстановления и исправьте их, или проведите восстановление из проверенной рабочей резервной копии. Если ошибки не устранены или ожидаются в будущем, свяжитесь со службой технической поддержки. |
Объяснение
Заданная база данных была восстановлена, но не была запущена, так как при восстановлении возникли ошибки. В результате этой ошибки состояние базы данных изменилось на SUSPECT. Первичная файловая группа и, возможно, другие файловые группы могут быть повреждены. Эта база данных не может быть восстановлена во время загрузки SQL Server и поэтому недоступна. Для разрешения этой проблемы требуется вмешательство пользователя. Состояние SUSPECT отображается как в SQL Server Management Studio (рядом со значком базы данных), так и при просмотре столбца sys.databases.state_desc. Любая попытка использовать базу данных в этом состоянии приведет к следующей ошибке.
Следует отметить, что, если эта ошибка возникает для базы данных tempdb, экземпляр SQL Server завершает работу.
Причина
Эта ошибка может вызываться временным состоянием, существовавшим в системе во время данной попытки запуска экземпляра сервера или восстановления базы данных. Эта ошибка может быть также вызвана неустранимым сбоем, который возникает при каждой попытке запуска базы данных. Причина сбоя восстановления обычно находится в ошибках, которые предшествуют ошибке 3414 в журнале ошибок или журнале событий. Предыдущая ошибка в файле журнала содержит то же значение spid . Например, следующая ошибка восстановления возникает из-за ошибки контрольной суммы при попытке чтения блока журнала. Обратите внимание, что spid15s есть во всех строках.
Существует широкий диапазон ошибок, которые могут привести к сбою восстановления базы данных. Хотя каждую ошибку необходимо оценивать отдельно, проблема сбоя восстановления базы данных обычно решается так, как описано в разделе «Действия пользователя» ниже.
Рекомендуемые действия
Для получения сведений о причине возникновения ошибки 3414 проверьте журнал событий Windows или журнал ошибок на наличие предыдущего сообщения об ошибке, в котором указан конкретный сбой. Соответствующее действие пользователя зависит от того, что указывают сведения в журнале событий Windows: ошибка SQL Server была вызвана временным состоянием или неустранимым сбоем. В сообщении об ошибке указано: «Проведите диагностику ошибок восстановления и исправьте их или проведите восстановление из проверенной рабочей резервной копии». Таким образом, можно попытаться исправить возникшую ошибку, чтобы завершить восстановление (см. Исправляемые ошибки и отложенные транзакции).
Если ошибки не удается исправить, рекомендуется восстановить базу данных из работоспособной резервной копии. Если восстановление из резервной копии невозможно, у вас есть еще два варианта, которые не гарантируют полного восстановления данных: используйте аварийное восстановление с помощью DBCC CHECKDB или попытайтесь скопировать как можно больше данных в другую базу данных.
- Восстановление из последней известной работоспособной резервной копии базы данных.
- Использование метода аварийного восстановления с помощью DBCC CHECKDB.
- Попытка скопировать как можно больше данных в другую базу данных.
Первый способ — восстановление работоспособной резервной копии базы данных — это лучший вариант для перевода базы данных в гарантированно согласованное состояние.
Второй оптимальный вариант, если резервная копия недоступна, — восстановить доступность базы данных. Но вы должны понимать, что согласованность транзакций не может быть гарантирована после сбоя восстановления. Нет способа узнать, для каких транзакций должен быть выполнен откат или накат, который не состоялся из-за сбоя восстановления. Инструкции по аварийному восстановлению приводятся в разделе Устранение ошибок базы данных в аварийном режиме в документации по DBCC CHECKDB.
Если аварийное восстановление не работает и вы хотите попытаться спасти некоторые данные в другую базу данных, способ получения доступа к базе данных — установить базу данных в режиме экстренного реагирования с помощью команды ALTER DATABASE SET EMERGENCY. Затем можно попытаться скопировать данные из таблиц.
Исправляемые ошибки и отложенные транзакции
Не все ошибки, обнаруженные во время восстановления базы данных, приводят к сбою восстановления и подозрительной базе данных.
Ошибки при первом открытии базы данных и/или файлов журнала транзакций возникают перед восстановлением. Примерами таких ошибок являются 17204 и 17207. После исправления этих ошибок выполнение операции восстановления может быть продолжено (но не обязательно завершится успешно, если возникнут другие ошибки восстановления). Такие ошибки, как 17204 и 17207, не приводят к состоянию базы данных SUSPECT. При возникновении этих проблем база данных имеет состояние RECOVERY_PENDING.
SQL Server позволяет выполнять восстановление даже при возникновении ошибки на уровне страницы и поддерживает согласованность транзакций. Этот процесс сократил количество ситуаций, когда возникает состояние SUSPECT. Эта концепция называется отложенными транзакциями.
Если ошибка, возникшая во время восстановления, указывает на проблему со страницей базы данных, например ошибку контрольной суммы или сообщение 824, завершение восстановления может быть разрешено с ошибками в состоянии ожидания. В случае, когда транзакция не зафиксирована, ошибка на странице может привести к отложенной транзакции, позволяя выполнить восстановление.
В следующих записях журнала ошибок показан пример сообщения об ошибке 824, возникшей во время восстановления, но завершение восстановления было разрешено с отложенной транзакцией. Обратите внимание на отсутствие ошибки 3414 в этой ситуации и на сообщение о завершении восстановления базы данных.
Если необходимо выполнить накат зафиксированной транзакции, эта страница может быть помечена как недоступная (любые дальнейшие попытки получить доступ к странице приведут к сообщению об ошибке 829) и восстановление может завершиться. В этом случае ошибку необходимо исправить, восстановив страницу из резервной копии или отменив выделение страницы с помощью инструкции DBCC CHECKDB во время восстановления.
Источник
MSSQLSERVER_3414
Applies to: SQL Server (all supported versions)
Details
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | SQL Server |
| Event ID | 3414 |
| Event Source | MSSQLSERVER |
| Component | SQLEngine |
| Symbolic Name | REC_GIVEUP |
| Message Text | An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘%.*ls’ (database ID %d) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support. |
Explanation
The specified database was recovered, but failed to start, because errors occurred during recovery. This error has put the database in the SUSPECT state. The primary filegroup, and possibly other filegroups, are suspect and may be damaged. The database cannot be recovered during startup of SQL Server and is therefore unavailable. User action is required to resolve the problem. You will see the SUSPECT status in both SQL Server Management Studio (next to the database icon) and when you look at the sys.databases.state_desc column. Any attempt to use a database in this state will result in the following error:
Note that when this error occurs in tempdb, the SQL Server instance shuts down.
Cause
This error can be caused by a transient condition that existed on the system during a given attempt to start up the server instance or to recover a database. This error can also be caused by a permanent failure that occurs every time that you attempt to start the database. The cause of the recovery failure is typically found in error(s) that precedes Error 3414 in the ERRORLOG or Event Log. The preceding error in the log file contains the same spid value. For example, the following recovery failure is due to a checksum error when trying to read a log block. Note spid15s is present in all lines:
There are a wide range of errors that could cause database recovery to fail. While you must evaluate each error on a case by case basis, the resolution to a database recovery failure is typically the same as described in the User Action section below.
User action
For information about the cause of this occurrence of error 3414, examine the Windows Event Log or ERRORLOG for a previous error that indicates the specific failure. The appropriate user action depends on whether the information in the Windows Event Log indicates that the SQL Server error was caused by a transient condition or a permanent failure. The error message states to «diagnose recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup». Therefore, you can attempt to correct the error that you encounter to allow recovery to complete (see Correctable errors and deferred transactions).
If the errors cannot be corrected, the first and best option to resolve this problem is to restore from a good backup. However, if you cannot recover from a backup, you have two additional options, which do not guarantee full data recovery: use emergency repair with DBCC CHECKDB or attempt to copy out as much data as possible to another database.
- Restore from the last known good database backup
- Use the emergency repair method provided by DBCC CHECKDB
- Attempt to copy out as much data as possible to another database.
The first method of restoring a good database backup is the best choice to bring a database to a known consistent state.
The second best choice, if no backup is available, is to get the database online and accessible. However, you must realize that transactional consistency cannot be guaranteed since recovery failed. There is no way to know what transactions should have been rolled back or rolled forward but were not allowed because of the recovery failure. The steps to proceed with emergency repair are described in the section titled Resolving Database Errors in Emergency Mode in the DBCC CHECKDB documentation.
If emergency repair does not work and you want to try to salvage some data to another database, the way to get access to the database is by setting the database in emergency mode via the ALTER DATABASE SET EMERGENCY command. Then you can attempt to copy data out from tables.
Correctable errors and deferred transactions
Not all errors encountered during database recovery will result in a recovery failure and a suspect database:
Errors when opening the database and/or transaction log files for the first time, occur before recovery. Examples of such errors are 17204 and 17207. Once these errors are corrected, recovery may be allowed to proceed (but not guaranteed to complete if other recovery errors occur). Errors such as 17204 and 17207 do not result in a SUSPECT database. In fact, the status of the database is RECOVERY_PENDING when these problems occur.
SQL Server allows recovery to complete even when a page-level error occurs and will still maintain transactional consistency. This process has reduced the number of scenarios resulting in a SUSPECT database. This concept is referred to as deferred transactions.
If the error encountered during recovery indicates a problem with a database page, for example as a checksum error or Msg 824, recovery may be allowed to complete with errors pending. In the case where a transaction is uncommitted, an error on a page can result in a deferred transaction allowing recovery to complete.
The following ERRORLOG entries show an example of a Msg 824 error encountered during recovery but recovery was allowed to complete with a deferred transaction. Note the absence of Error 3414 in this situation and the message that recovery has completed for the database:
If a committed transaction is to be rolled forward, the page can be marked inaccessible (any future attempts to access the page result in Msg 829) and recovery can complete. In this situation, the error must be corrected by restoring the page from a backup or by deallocating the page using DBCC CHECKDB with repair.
Источник
SQL Server
Know How to Fix SQL Server Error Code 3414 Issue
Sherry James ~
Published: May 27, 2019 ~ 4 Minutes Reading
Microsoft SQL server is a relational database management system that is used to store and extract data from the connected application. It is a secure and safe database server. But this application is also prone to unexpected errors. One of the common error faced by the users is SQL server Error Code 3414. So due to this problem the user has to face immense inconveniences in accessing their data. Until the error is resolved the SQL user will be restricted to working with the database.
This post shed some light on the topic of SQL server error code 3414. We will discuss the main possible causes of this problem. We will also discuss the solution of this problem by using the manual as a well automated solution. So keep reading here…
SQL Server Error Code 3414: Everything You Need To Know
This type of error can occur when the SQL server does not start during the login or startup of database recovery. Also, the status of the database is set to suspect mode. The suspect status can be seen in SSMS and in sys.databases.state_desc. In case if the user tried to operate the database then the user might encounter “SQL server database suspect error 926”. The basic reason for this error SQL server error code 3414 is the same SPID value (SQL Server Process ID) in the server log file. So if you want to resolve this problem then the user can try to restore from the backup. But many times the user will not be able to recover the database from the backup. So, in that case, the user can take the help of an automated solution to resolve this issue.
Resolve SQL server Error Code 3414 By Using Manual Workarounds
The user can try to resolve this problem manually. This manual technique helps the user to retrieve the database in an online and accessible state. But this method does not guarantee the consistency of the transactions. Follow the commands to repair the database.
- This set of commands will put the SQL database in emergency mode.
EXEC sp_resetstatus ‘database name’;
ALTER DATABASE database name SET Emergency
2. Now perform the integrity and the consistency check on the database.
DBCC CHECKDB (‘database name’)
3. This check will recommend the minimum repair level. Now set the database to a single user to allow repair.
ALTER DATABASE database name SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
4. Now the user has to run the repair command as shown below
DBCC CHECKDB ( ‘database name’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS)
5. After the completion of the repair, set the database to the multi-user to allow connections.
ALTER DATABASE database name SET MULTI_USER
Note: In some cases, DBCC CHECKDB fails to repair recover database from the suspect mode. So, in that case, the user can copy out as much as data from the suspect mode. So in order to do this, the user simply needs to put the database in Emergency mode. This helps the user to access the database. So the user has to copy the database into a new database. Try to use the following command to put the database in the EMERGENCY mode.
EXEC sp_resetstatus ‘database name’
ALTER DATABASE database name SET EMERGENCY
Automated Solution to Solve SQL Server Error Code 3414
In case if by using the above method failed to fix this error then, in that case, the user can try SQL Database Recovery. This software can easily recover the corrupt SQL database items. Also the user by using this software the user can easily recover table, views, stored procedure, functions, triggers, etc. This application has a simple and intuitive user interface so that everyone can easily use this software with ease.
Download Purchase Now
Final Words
In this article, we have discussed the SQL server error code 3414 problem faced by most of the users. We have given the reasons for this problem and to resolve this issue we have given the manual as well as an automated solution. If the user won’t be able to repair the corrupted database of SQL server then, in that case, the user can try to take the help of automated solution to resolve this issue.
SQL Server goes into whole recovery phase on each time login and sometimes there are complaints by the users stating crash down of the server with an error like this.
It can occur even while applying any functions or manipulations and when the SQL Server service is not started with the login on the SQL Server. Here, as we can see in the error message, the recovery failure occurred due to the service-specific error code 3414. In the Event Log, the reason behind this failure can be detected as it depends on the preceding error logs with log files having similar SPID value.
When user tries to roll forward a transaction log with read page operation on the database, the checksum error appears like this:
“2010-03-31 17:33:13.00 spid15s Error: 824, Severity: 24, State: 4.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.00 spid15s SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error: (bad checksum). It occurred during a read of page (0:-1) in database ID 13 at offset 0x0000000000b800 in file ‘C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQL2008MSSQLDATAmydb_log.LDF’. Additional messages in the SQL Server error log or system event log may provide more detail. This is a severe error condition that threatens database integrity and must be corrected immediately. Complete a full database consistency check (DBCC CHECKDB). This error can be caused by many factors; for more information, see SQL Server Books Online.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.16 spid15s Error: 3414, Severity: 21, State: 1.
2010-03-31 17:33:13.16 spid15s An error occurred during recovery, preventing the database ‘mydb’ (database ID 13) from restarting. Diagnose the recovery errors and fix them, or restore from a known good backup. If errors are not corrected or expected, contact Technical Support”
With the failure of database recovery and onset of this error, the database goes into SUSPECT mode which is visible against the server database name in the SQL Server Management Studio.
If any user tries to use the database in this SUSPECT mode, he has to encounter the progressive error stating –
“Msg 926, Level 14, State 1, Line 1
Database ‘mydb’ cannot be opened. It has been marked SUSPECT by recovery. See the SQL Server errorlog for more information”
So, there is a need to fix this error code 3414 issue to get back the normal database functioning once again. As we know handling the SQL Server, its features and functions is a bit complex task. So, there is a need of technical knowledge for performing manual solutions which might include running SQL Server queries to repair or restore the SUSPECT database in SQL Server; you can also restore SQL Database with a different name.
As recommended by Microsoft itself, we are explaining some of the workable manual methods for fixing or resolving this SQL Server error. Keep following carefully these methods and use them accordingly.
1st Method: Go for Restoring SQL Data through Recent Database Backup
If SQL Server user is in good practice of taking regular backups of their SQL database file and need to access it urgently. Then, restoring data from backup is a nice and easy choice. Perform these easy steps in order to restore your database from backup file.
- Launch the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio as an administrator.
- Go to Object Explorer panel on the left, make connection to SQL Server Database Engine, select it and expand.
- Now select Databases option and right-click on it. Select Restore Database option from the list.
- Next, on the General page, under Source section, choose the Database option and add the recent database backup file from the list.
- The restore process will get started and complete based on the database size.
- Restart the SQL Server and check for the error code oncoming again.
For users who don’t have any backup file for the SQL database, we have other manual solutions as well.
2nd Method: Perform Emergency Repair Solution via DBCC CHECKDB
SQL Server provides its users certain SQL Query and commands to check upon the integrity of the SQL Database. DBCC CHECKDB command is helpful in checking the database in terms of accessibility and fixing related issues. Databases should be put in emergency mode as transaction consistency (no tracking of transaction roll back and forward) is not possible with DBCC command alone.
To put the databases in emergency mode, execute this command in New Query in SQL Server Management Studio run as administrator on your SQL system.
EXEC sp_resetstatus ‘db_name’;
ALTER DATABASE db_name SET EMERGENCY
Provide SQL Server database name at the required locations in the commands.
Perform integrity check on the SQL Server database using the following command.
DBCC CHECKDB (‘database_name’)
After checking the consistency of the database, the minimal repair recommendation would display. For that, to allow repair, set the database to single user executing this command.
ALTER DATABASE database_name SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
Run the DBCC repair command as follows with introduction of “Repair Allow Data Loss” feature.
DBCC CHECKDB (‘database_name’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS)
After this repair, users can set the database to multi-user for connections using this command.
ALTER DATABASE database_name SET MULTI_USER
And if the steps failed to repair the SUSPECT database, try copying out data from the database to a new database after putting it back in emergency mode. It will let you access the database content.
EXEC sp_resetstatus ‘db_name’;
ALTER DATABASE db_name SET EMERGENCY
Exit the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio. Now, restart the server and check if the issue is resolved.
What to do if this method did not work?
It is possible that simply executing DBCC CHECKDB command in emergency mode does not fix the error. You can use COPY OUT command to copy the whole database to a new database but needs to put the databases in the emergency mode using this command as used earlier.
EXEC sp_resetstatus ‘db_name’;
ALTER DATABASE db_name SET EMERGENCY
Note: SQL administrators can follow the online troubleshooting solutions provided in the Event Error Log itself.
How manual solutions are not completely reliable?
Restoring database manually from backup file does not ensure the complete backup of SQL database objects. It might include data loss or modification during the whole process. Also DBCC CHECKDB command is not helpful due to issues of transaction log files tracking as some or other manual errors can be expected even in the Emergency mode. All these tricks require good amount of time and efforts with some technical knowledge. So, limitations might hold back users and lead them to look for a better alternative.
Alternative Option – Third Party tool
If you lack trust in manual solutions or already tried the above tricks but not succeeded, we offer you the best SQL Server recovery tool in the market which includes the most advanced programming and algorithms to tackle all kinds of SQL Server errors including SQL database corruptions and resolve it within few minutes. It only requires the database file for the repair process and supports all SQL Server versions widely. Go on this utility website and checkout all the features in detail. You can download the trial version for free and get the experience of efficient Recovery anytime.
Download Now
Conclusion
We have concluded that SQL Server errors can be tackled manually (as some methods like restore from backup, DBCC CHECKDB repair in emergency mode are explained) but from these tricks, complete reliability cannot be assured. Third-party utility which could be your savior in dealing with complex SQL Server error codes.
Read Related Blog
- Fix SQL database consistency errors
- Fix SQL Server Error Code 823
- Recover Data from Corrupted SQL Transaction Log File
- SQL Database Restoration With NORECOVERY
- Recover SQL Database From Suspect Mode