Nginx – очень популярный веб-сервер в наши дни.
В этой статье мы расскажем вам о некоторых распространенных ошибках при работе веб-сервера Nginx и возможных решениях.
Это не полный список.
Если вы все еще не можете устранить ошибку, попробовав предложенные решения, пожалуйста, проверьте логи сервера Nginx в каталоге /var/log/nginx/ и поищите в Google, чтобы отладить проблему.
Содержание
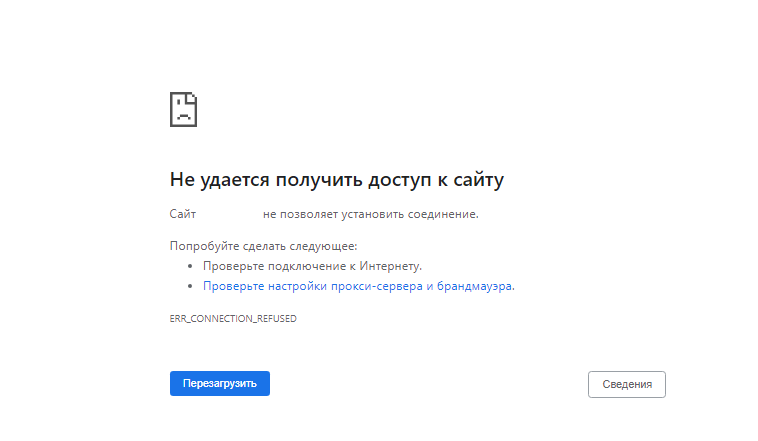
- Unable to connect/Refused to Connect
- The Connection Has Timed Out
- 404 Not Found
- 403 Forbidden
- 500 Internal Server Error
- Nginx показывает страницу по умолчанию
- 504 Gateway time-out
- Размер памяти исчерпан
- PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR
- Resource temporarily unavailable
- Два файла виртуального хоста для одного и того же сайта
- PHP-FPM Connection reset by peer
- Утечки сокетов Nginx
- Заключение
Unable to connect/Refused to Connect
Если при попытке получить доступ к вашему сайту вы видите следующую ошибку:
Firefox can’t establish a connection to the server at www.example.com
или
www.example.com refused to connect
или
The site can't be reached, www.example.com unexpectedly closed the connection.
Это может быть потому, что:
- Nginx не запущен. Вы можете проверить состояние Nginx с помощью sudo systemctl status nginx. Запустите Nginx с помощью sudo systemctl start nginx. Если Nginx не удается запустить, запустите sudo nginx -t, чтобы выяснить, нет ли ошибок в вашем конфигурационном файле. И проверьте логи (sudo journalctl -eu nginx), чтобы выяснить, почему он не запускается.
- Брандмауэр блокирует порты 80 и 443. Если вы используете брандмауэр UFW на Debian/Ubuntu, выполните sudo ufw allow 80,443/tcp, чтобы открыть TCP порты 80 и 443. Если вы используете Firewalld на RHEL/CentOS/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux, выполните sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service={http,https}, затем sudo systemctl reload firewalld, чтобы открыть TCP порты 80 и 443.
- Fail2ban. Если ваш сервер использует fail2ban для блокировки вредоносных запросов, возможно, fail2ban запретил ваш IP-адрес. Выполните команду sudo journalctl -eu fail2ban, чтобы проверить, не заблокирован ли ваш IP-адрес. Вы можете добавить свой IP-адрес в список fail2ban ignoreip, чтобы он больше не был забанен.
- Nginx не прослушивает нужный сетевой интерфейс. Например, Nginx не прослушивает публичный IP-адрес сервера.
The Connection Has Timed Out
Это может означать, что ваш сервер находится в автономном режиме или Nginx работает неправильно.
Однажды у меня возникла проблема нехватки памяти, из-за чего Nginx не смог запустить рабочие процессы.
Если вы увидите следующее сообщение об ошибке в файле /var/log/nginx/error.log, вашему серверу не хватает памяти:
fork() failed while spawning "worker process" (12: Cannot allocate memory)
404 Not Found
404 not found означает, что Nginx не может найти ресурсы, которые запрашивает ваш веб-браузер.
🌐 Как создать пользовательскую страницу ошибки 404 в NGINX
Причина может быть следующей:
- Корневой каталог web не существует на вашем сервере. В Nginx корневой веб-каталог настраивается с помощью директивы root, например, так: root /usr/share/nginx/linuxbabe.com/;. Убедитесь, что файлы вашего сайта (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP) хранятся в правильном каталоге.
- PHP-FPM не запущен. Вы можете проверить статус PHP-FPM с помощью sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm (Debian/Ubuntu) или sudo systemctl status php-fpm.
- Вы забыли включить директиву try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args; в конфигурационный файл сервера Nginx. Эта директива необходима для обработки PHP-кода.
- На вашем сервере нет свободного дискового пространства. Попробуйте освободить немного дискового пространства. Вы можете использовать утилиту ncdu (sudo apt install ncdu или sudo dnf install ncdu), чтобы узнать, какие каталоги занимают огромное количество дискового пространства.
403 Forbidden
Эта ошибка означает, что вам не разрешен доступ к ресурсам запроса.
Возможный сценарий включает:
- Администратор сайта блокирует публичный доступ к запрашиваемым ресурсам с помощью белого списка IP-адресов или других методов.
- На сайте может использоваться брандмауэр веб-приложения, например ModSecurity, который обнаружил атаку вторжения, поэтому заблокировал запрос.
Некоторые веб-приложения могут показывать другое сообщение об ошибке, когда происходит запрет 403. Оно может сказать вам, что “secure connection failed, хотя причина та же.
500 Internal Server Error
Это означает, что в веб-приложении произошла какая-то ошибка.
Это может быть следующее
- Сервер базы данных не работает. Проверьте состояние MySQL/MariaDB с помощью sudo systemctl status mysql. Запустите его с помощью sudo systemctl start mysql. Запустите sudo journalctl -eu mysql, чтобы выяснить, почему он не запускается. Процесс MySQL/MariaDB может быть завершен из-за проблем с нехваткой памяти.
- Вы не настроили Nginx на использование PHP-FPM, поэтому Nginx не знает, как выполнять PHP-код.
- Если ваше веб-приложение имеет встроенный кэш, вы можете попробовать очистить кэш приложения, чтобы исправить эту ошибку.
- Ваше веб-приложение может создавать свой собственный журнал ошибок. Проверьте этот файл журнала, чтобы отладить эту ошибку.
- Возможно, в вашем веб-приложении есть режим отладки. Включите его, и вы увидите более подробные сообщения об ошибках на веб-странице. Например, вы можете включить режим отладки в почтовом сервере хостинг-платформы Modoboa, установив DEBUG = True в файле /srv/modoboa/instance/instance/settings.py.
- PHP-FPM может быть перегружен. Проверьте журнал PHP-FPM (например, /var/log/php7.4-fpm.log). Если вы обнаружили предупреждение [pool www] seems busy (возможно, вам нужно увеличить pm.start_servers, или pm.min/max_spare_servers), вам нужно выделить больше ресурсов для PHP-FPM.
- Иногда перезагрузка PHP-FPM (sudo systemctl reload php7.4-fpm) может исправить ошибку.
Nginx показывает страницу по умолчанию
Если вы пытаетесь настроить виртуальный хост Nginx и при вводе доменного имени в веб-браузере отображается страница Nginx по умолчанию, это может быть следующее
- Вы не использовали реальное доменное имя для директивы server_name в виртуальном хосте Nginx.
- Вы забыли перезагрузить Nginx.
504 Gateway time-out
Это означает, что апстрим, такой как PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB, не может обработать запрос достаточно быстро.
Вы можете попробовать перезапустить PHP-FPM, чтобы временно исправить ошибку, но лучше начать настраивать PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB для более быстрой работы.
Вот конфигурация InnoDB в моем файле /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf.
Это очень простая настройка производительности.
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1024M innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown = ON innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup = ON innodb_log_file_size = 512M innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #Improving disk I/O performance innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_open_files = 400 innodb_io_capacity = 400 innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT innodb_read_io_threads = 64 innodb_write_io_threads = 64 innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 3
Где:
- InnoDB buffer pool size должен быть не менее половины вашей оперативной памяти. (Для VPS с небольшим объемом оперативной памяти я рекомендую установить размер буферного пула на меньшее значение, например 400M, иначе ваш VPS будет работать без оперативной памяти).
- InnoDB log file size должен составлять 25% от размера буферного пула.
- Установите потоки ввода-вывода для чтения и записи на максимум (64).
- Заставьте MariaDB использовать 3 экземпляра буферного пула InnoDB. Количество экземпляров должно соответствовать количеству ядер процессора в вашей системе.
- После сохранения изменений перезапустите MariaDB.
После сохранения изменений перезапустите MariaDB.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Вы также можете установить более длительное значение тайм-аута в Nginx, чтобы уменьшить вероятность тайм-аута шлюза.
Отредактируйте файл виртуального хоста Nginx и добавьте следующие строки в блок server {…}.
proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600;
Если вы используете Nginx с PHP-FPM, то установите для параметра fastcgi_read_timeout большее значение, например 300 секунд.
По умолчанию это 60 секунд.
location ~ .php$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
Затем перезагрузите Nginx.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
PHP-FPM также имеет максимальное время выполнения для каждого скрипта.
Отредактируйте файл php.ini.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
Вы можете увеличить это значение до 300 секунд.
max_execution_time = 300
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Размер памяти исчерпан
Если вы видите следующую строку в журнале ошибок Nginx, это означает, что PHP достиг лимита памяти в 128 МБ.
PHP Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 57134520 bytes)
Вы можете отредактировать файл php.ini (/etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini) и увеличить лимит памяти PHP.
memory_limit = 512M
Затем перезапустите PHP7.4-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Если ошибка все еще существует, скорее всего, в вашем веб-приложении плохой PHP-код, который потребляет много оперативной памяти.
PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR
- Вы настроили Nginx на перенаправление HTTP-запросов на HTTPS, но в Nginx нет блока сервера, обслуживающего HTTPS-запросы.
- Может быть, Nginx не запущен?
- Иногда основной бинарник Nginx запущен, но рабочий процесс может не работать и завершиться по разным причинам. Для отладки проверьте логи ошибок Nginx (/var/log/nginx/error.log).
Resource temporarily unavailable
Некоторые пользователи могут найти следующую ошибку в файле логов ошибок Nginx (в разделе /var/log/nginx/).
connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock failed (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
Обычно это означает, что на вашем сайте много посетителей и PHP-FPM не справляется с обработкой огромного количества запросов.
Вы можете изменить количество дочерних процессов PHP-FPM, чтобы он мог обрабатывать больше запросов.
Отредактируйте файл PHP-FPM www.conf.
(Путь к файлу зависит от дистрибутива Linux).
sudo /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
По умолчанию конфигурация дочернего процесса выглядит следующим образом:
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3
Приведенная выше конфигурация означает.
- PHP-FPM динамически создает дочерние процессы. Нет фиксированного количества дочерних процессов.
- Создается не более 5 дочерних процессов.
- При запуске PHP-FPM запускаются 2 дочерних процесса.
- Есть как минимум 1 незанятый процесс.
- Максимум 3 неработающих процесса.
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 20 pm.start_servers = 8 pm.min_spare_servers = 4 pm.max_spare_servers = 12
Убедитесь, что у вас достаточно оперативной памяти для запуска дополнительных дочерних процессов.
Сохраните и закройте файл.
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM. (Возможно, вам потребуется изменить номер версии).
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Чтобы следить за состоянием PHP-FPM, вы можете включить страницу status .
Найдите следующую строку в файле PHP-FPM www.conf.
Обратите внимание, что
;pm.status_path = /status
Уберите точку с запятой, чтобы включить страницу состояния PHP-FPM.
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Затем отредактируйте файл виртуального хоста Nginx.
Добавьте следующие строки.
Директивы allow и deny используются для ограничения доступа.
Только IP-адреса из “белого списка” могут получить доступ к странице состояния.
location ~ ^/(status|ping)$ {
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow your_other_IP_Address;
deny all;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
Сохраните и закройте файл. Затем протестируйте конфигурацию Nginx.
sudo nginx -t
Если проверка прошла успешно, перезагрузите Nginx, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
В файле PHP-FPM www.conf дается хорошее объяснение того, что означает каждый параметр.
Если PHP-FPM очень занят и не может обслужить запрос немедленно, он поставит его в очередь.
По умолчанию может быть не более 511 ожидающих запросов, определяемых параметром listen.backlog.
listen.backlog = 511
Если вы видите следующее значение на странице состояния PHP-FPM, это означает, что в очереди еще не было ни одного запроса, т.е. ваш PHP-FPM может быстро обрабатывать запросы.
listen queue: 0 max listen queue: 0
Если в очереди 511 ожидающих запросов, это означает, что ваш PHP-FPM очень загружен, поэтому вам следует увеличить количество дочерних процессов.
Вам также может понадобиться изменить параметр ядра Linux net.core.somaxconn, который определяет максимальное количество соединений, разрешенных к файлу сокетов в Linux, например, к файлу сокетов PHP-FPM Unix.
По умолчанию его значение равно 128 до ядра 5.4 и 4096 начиная с ядра 5.4.
$ sysctl net.core.somaxconn net.core.somaxconn = 128
Если у вас сайт с высокой посещаемостью, вы можете использовать большое значение.
Отредактируйте файл /etc/sysctl.conf.
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.cnf
Добавьте следующие две строки.
net.core.somaxconn = 20000 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 65535
Сохраните и закройте файл. Затем примените настройки.
sudo sysctl -p
Примечание: Если ваш сервер имеет достаточно оперативной памяти, вы можете выделить фиксированное количество дочерних процессов для PHP-FPM, как показано ниже.
Два файла виртуального хоста для одного и того же сайта
Если вы запустите sudo nginx -t и увидите следующее предупреждение.
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on [::]:443, ignored nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on 0.0.0.0:443, ignored
Это означает, что есть два файла виртуальных хостов, содержащих одну и ту же конфигурацию server_name.
Не создавайте два файла виртуальных хостов для одного сайта.
PHP-FPM Connection reset by peer
В файле логов ошибок Nginx отображается следующее сообщение.
recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream
Это может быть вызвано перезапуском PHP-FPM.
Если он перезапущен вручную самостоятельно, то вы можете игнорировать эту ошибку.
Утечки сокетов Nginx
Если вы обнаружили следующее сообщение об ошибке в файле /var/log/nginx/error.log, значит, у вашего Nginx проблема с утечкой сокетов.
2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120606 open socket #16 left in connection 163 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120629 open socket #34 left in connection 188 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120622 open socket #9 left in connection 213 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120628 open socket #25 left in connection 217 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120605 open socket #15 left in connection 244 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120614 open socket #41 left in connection 245 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120631 open socket #24 left in connection 255 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120616 open socket #23 left in connection 258 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120615 open socket #42 left in connection 269 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: aborting
Вы можете перезапустить ОС, чтобы решить эту проблему.
Если это не помогает, вам нужно скомпилировать отладочную версию Nginx, которая покажет вам отладочную информацию в логах.
Заключение
Надеюсь, эта статья помогла вам исправить распространенные ошибки веб-сервера Nginx.
см. также:
- 🌐 Как контролировать доступ на основе IP-адреса клиента в NGINX
- 🐉 Настройка http-сервера Kali Linux
- 🌐 Как парсить логи доступа nginx
- 🌐 Ограничение скорости определенных URL-адресов с Nginx
- 🛡️ Как использовать обратный прокси Nginx для ограничения внешних вызовов внутри веб-браузера
- 🔏 Как настроить Nginx с Let’s Encrypt с помощью ACME на Ubuntu
- 🌐 Как собрать NGINX с ModSecurity на Ubuntu сервере
Unable to connect/Refused to Connect
Если при попытке получить доступ к вашему сайту вы видите следующую ошибку:
Firefox can’t establish a connection to the server at www.example.com
или
www.example.com refused to connect
или
The site can’t be reached, www.example.com unexpectedly closed the connection.
Это может быть потому, что:
- Nginx не запущен. Вы можете проверить состояние Nginx с помощью sudo systemctl status nginx. Запустите Nginx с помощью sudo systemctl start nginx. Если Nginx не удается запустить, запустите sudo nginx -t, чтобы выяснить, нет ли ошибок в вашем конфигурационном файле. И проверьте логи (sudo journalctl -eu nginx), чтобы выяснить, почему он не запускается.
- Брандмауэр блокирует порты 80 и 443. Если вы используете брандмауэр UFW на Debian/Ubuntu, выполните sudo ufw allow 80,443/tcp, чтобы открыть TCP порты 80 и 443. Если вы используете Firewalld на RHEL/CentOS/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux, выполните sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service={http,https}, затем sudo systemctl reload firewalld, чтобы открыть TCP порты 80 и 443.
- Fail2ban. Если ваш сервер использует fail2ban для блокировки вредоносных запросов, возможно, fail2ban запретил ваш IP-адрес. Выполните команду sudo journalctl -eu fail2ban, чтобы проверить, не заблокирован ли ваш IP-адрес. Вы можете добавить свой IP-адрес в список fail2ban ignoreip, чтобы он больше не был забанен.
- Nginx не прослушивает нужный сетевой интерфейс. Например, Nginx не прослушивает публичный IP-адрес сервера.
The Connection Has Timed Out
Это может означать, что ваш сервер находится в автономном режиме или Nginx работает неправильно.
Однажды у меня возникла проблема нехватки памяти, из-за чего Nginx не смог запустить рабочие процессы.
Если вы увидите следующее сообщение об ошибке в файле /var/log/nginx/error.log, вашему серверу не хватает памяти:
fork() failed while spawning «worker process» (12: Cannot allocate memory)
404 Not Found
404 not found означает, что Nginx не может найти ресурсы, которые запрашивает ваш веб-браузер.
Причина может быть следующей:
- Корневой каталог web не существует на вашем сервере. В Nginx корневой веб-каталог настраивается с помощью директивы root, например, так: root /usr/share/nginx/linuxbabe.com/;. Убедитесь, что файлы вашего сайта (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP) хранятся в правильном каталоге.
- PHP-FPM не запущен. Вы можете проверить статус PHP-FPM с помощью sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm (Debian/Ubuntu) или sudo systemctl status php-fpm.
- Вы забыли включить директиву try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args; в конфигурационный файл сервера Nginx. Эта директива необходима для обработки PHP-кода.
- На вашем сервере нет свободного дискового пространства. Попробуйте освободить немного дискового пространства. Вы можете использовать утилиту ncdu (sudo apt install ncdu или sudo dnf install ncdu), чтобы узнать, какие каталоги занимают огромное количество дискового пространства.
403 Forbidden
Эта ошибка означает, что вам не разрешен доступ к ресурсам запроса.
Возможный сценарий включает:
- Администратор сайта блокирует публичный доступ к запрашиваемым ресурсам с помощью белого списка IP-адресов или других методов.
- На сайте может использоваться брандмауэр веб-приложения, например ModSecurity, который обнаружил атаку вторжения, поэтому заблокировал запрос.
Некоторые веб-приложения могут показывать другое сообщение об ошибке, когда происходит запрет 403. Оно может сказать вам, что “secure connection failed, хотя причина та же.
500 Internal Server Error
Это означает, что в веб-приложении произошла какая-то ошибка.
Это может быть следующее
- Сервер базы данных не работает. Проверьте состояние MySQL/MariaDB с помощью sudo systemctl status mysql. Запустите его с помощью sudo systemctl start mysql. Запустите sudo journalctl -eu mysql, чтобы выяснить, почему он не запускается. Процесс MySQL/MariaDB может быть завершен из-за проблем с нехваткой памяти.
- Вы не настроили Nginx на использование PHP-FPM, поэтому Nginx не знает, как выполнять PHP-код.
- Если ваше веб-приложение имеет встроенный кэш, вы можете попробовать очистить кэш приложения, чтобы исправить эту ошибку.
- Ваше веб-приложение может создавать свой собственный журнал ошибок. Проверьте этот файл журнала, чтобы отладить эту ошибку.
- Возможно, в вашем веб-приложении есть режим отладки. Включите его, и вы увидите более подробные сообщения об ошибках на веб-странице. Например, вы можете включить режим отладки в почтовом сервере хостинг-платформы Modoboa, установив DEBUG = True в файле /srv/modoboa/instance/instance/settings.py.
- PHP-FPM может быть перегружен. Проверьте журнал PHP-FPM (например, /var/log/php7.4-fpm.log). Если вы обнаружили предупреждение [pool www] seems busy (возможно, вам нужно увеличить pm.start_servers, или pm.min/max_spare_servers), вам нужно выделить больше ресурсов для PHP-FPM.
- Иногда перезагрузка PHP-FPM (sudo systemctl reload php7.4-fpm) может исправить ошибку.
Nginx показывает страницу по умолчанию
Если вы пытаетесь настроить виртуальный хост Nginx и при вводе доменного имени в веб-браузере отображается страница Nginx по умолчанию, это может быть следующее
- Вы не использовали реальное доменное имя для директивы server_name в виртуальном хосте Nginx.
- Вы забыли перезагрузить Nginx.
504 Gateway time-out
Это означает, что апстрим, такой как PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB, не может обработать запрос достаточно быстро.
Вы можете попробовать перезапустить PHP-FPM, чтобы временно исправить ошибку, но лучше начать настраивать PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB для более быстрой работы.
Вот конфигурация InnoDB в моем файле /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf.
Это очень простая настройка производительности.
|
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1024M innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown = ON innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup = ON innodb_log_file_size = 512M innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #Improving disk I/O performance innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_open_files = 400 innodb_io_capacity = 400 innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT innodb_read_io_threads = 64 innodb_write_io_threads = 64 innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 3 |
Где:
- InnoDB buffer pool size должен быть не менее половины вашей оперативной памяти. (Для VPS с небольшим объемом оперативной памяти я рекомендую установить размер буферного пула на меньшее значение, например 400M, иначе ваш VPS будет работать без оперативной памяти).
- InnoDB log file size должен составлять 25% от размера буферного пула.
- Установите потоки ввода-вывода для чтения и записи на максимум (64).
- Заставьте MariaDB использовать 3 экземпляра буферного пула InnoDB. Количество экземпляров должно соответствовать количеству ядер процессора в вашей системе.
- После сохранения изменений перезапустите MariaDB.
После сохранения изменений перезапустите MariaDB.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Вы также можете установить более длительное значение тайм-аута в Nginx, чтобы уменьшить вероятность тайм-аута шлюза.
Отредактируйте файл виртуального хоста Nginx и добавьте следующие строки в блок server {…}.
|
proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600; |
Если вы используете Nginx с PHP-FPM, то установите для параметра fastcgi_read_timeout большее значение, например 300 секунд.
По умолчанию это 60 секунд.
|
location ~ .php$ { try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args; include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.+)$; fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; fastcgi_read_timeout 300; } |
Затем перезагрузите Nginx.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
PHP-FPM также имеет максимальное время выполнения для каждого скрипта.
Отредактируйте файл php.ini.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
Вы можете увеличить это значение до 300 секунд.
max_execution_time = 300
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Размер памяти исчерпан
Если вы видите следующую строку в журнале ошибок Nginx, это означает, что PHP достиг лимита памяти в 128 МБ.
PHP Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 57134520 bytes)
Вы можете отредактировать файл php.ini (/etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini) и увеличить лимит памяти PHP.
memory_limit = 512M
Затем перезапустите PHP7.4-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Если ошибка все еще существует, скорее всего, в вашем веб-приложении плохой PHP-код, который потребляет много оперативной памяти.
PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR
- Вы настроили Nginx на перенаправление HTTP-запросов на HTTPS, но в Nginx нет блока сервера, обслуживающего HTTPS-запросы.
- Может быть, Nginx не запущен?
- Иногда основной бинарник Nginx запущен, но рабочий процесс может не работать и завершиться по разным причинам. Для отладки проверьте логи ошибок Nginx (/var/log/nginx/error.log).
Resource temporarily unavailable
Некоторые пользователи могут найти следующую ошибку в файле логов ошибок Nginx (в разделе /var/log/nginx/).
connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock failed (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
Обычно это означает, что на вашем сайте много посетителей и PHP-FPM не справляется с обработкой огромного количества запросов.
Вы можете изменить количество дочерних процессов PHP-FPM, чтобы он мог обрабатывать больше запросов.
Отредактируйте файл PHP-FPM www.conf.
(Путь к файлу зависит от дистрибутива Linux).
sudo /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
По умолчанию конфигурация дочернего процесса выглядит следующим образом:
|
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3 |
Приведенная выше конфигурация означает.
- PHP-FPM динамически создает дочерние процессы. Нет фиксированного количества дочерних процессов.
- Создается не более 5 дочерних процессов.
- При запуске PHP-FPM запускаются 2 дочерних процесса.
- Есть как минимум 1 незанятый процесс.
- Максимум 3 неработающих процесса.
|
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 20 pm.start_servers = 8 pm.min_spare_servers = 4 pm.max_spare_servers = 12 |
Убедитесь, что у вас достаточно оперативной памяти для запуска дополнительных дочерних процессов.
Сохраните и закройте файл.
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM. (Возможно, вам потребуется изменить номер версии).
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Чтобы следить за состоянием PHP-FPM, вы можете включить страницу status .
Найдите следующую строку в файле PHP-FPM www.conf.
Обратите внимание, что
;pm.status_path = /status
Уберите точку с запятой, чтобы включить страницу состояния PHP-FPM.
Затем перезапустите PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Затем отредактируйте файл виртуального хоста Nginx.
Добавьте следующие строки.
Директивы allow и deny используются для ограничения доступа.
Только IP-адреса из “белого списка” могут получить доступ к странице состояния.
|
location ~ ^/(status|ping)$ { allow 127.0.0.1; allow your_other_IP_Address; deny all; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi_params; #fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock; } |
Сохраните и закройте файл. Затем протестируйте конфигурацию Nginx.
sudo nginx -t
Если проверка прошла успешно, перезагрузите Nginx, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
В файле PHP-FPM www.conf дается хорошее объяснение того, что означает каждый параметр.
Если PHP-FPM очень занят и не может обслужить запрос немедленно, он поставит его в очередь.
По умолчанию может быть не более 511 ожидающих запросов, определяемых параметром listen.backlog.
listen.backlog = 511
Если вы видите следующее значение на странице состояния PHP-FPM, это означает, что в очереди еще не было ни одного запроса, т.е. ваш PHP-FPM может быстро обрабатывать запросы.
listen queue: 0
max listen queue: 0
Если в очереди 511 ожидающих запросов, это означает, что ваш PHP-FPM очень загружен, поэтому вам следует увеличить количество дочерних процессов.
Вам также может понадобиться изменить параметр ядра Linux net.core.somaxconn, который определяет максимальное количество соединений, разрешенных к файлу сокетов в Linux, например, к файлу сокетов PHP-FPM Unix.
По умолчанию его значение равно 128 до ядра 5.4 и 4096 начиная с ядра 5.4.
$ sysctl net.core.somaxconn
net.core.somaxconn = 128
Если у вас сайт с высокой посещаемостью, вы можете использовать большое значение.
Отредактируйте файл /etc/sysctl.conf.
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.cnf
Добавьте следующие две строки.
net.core.somaxconn = 20000
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 65535
Сохраните и закройте файл. Затем примените настройки.
sudo sysctl -p
Примечание: Если ваш сервер имеет достаточно оперативной памяти, вы можете выделить фиксированное количество дочерних процессов для PHP-FPM, как показано ниже.
Два файла виртуального хоста для одного и того же сайта
Если вы запустите sudo nginx -t и увидите следующее предупреждение.
|
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name «example.com» on [::]:443, ignored nginx: [warn] conflicting server name «example.com» on 0.0.0.0:443, ignored |
Это означает, что есть два файла виртуальных хостов, содержащих одну и ту же конфигурацию server_name.
Не создавайте два файла виртуальных хостов для одного сайта.
PHP-FPM Connection reset by peer
В файле логов ошибок Nginx отображается следующее сообщение.
recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream
Это может быть вызвано перезапуском PHP-FPM.
Если он перезапущен вручную самостоятельно, то вы можете игнорировать эту ошибку.
Утечки сокетов Nginx
Если вы обнаружили следующее сообщение об ошибке в файле /var/log/nginx/error.log, значит, у вашего Nginx проблема с утечкой сокетов.
|
2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120606 open socket #16 left in connection 163 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120629 open socket #34 left in connection 188 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120622 open socket #9 left in connection 213 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120628 open socket #25 left in connection 217 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120605 open socket #15 left in connection 244 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120614 open socket #41 left in connection 245 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120631 open socket #24 left in connection 255 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120616 open socket #23 left in connection 258 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120615 open socket #42 left in connection 269 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: aborting |
Вы можете перезапустить ОС, чтобы решить эту проблему.
Если это не помогает, вам нужно скомпилировать отладочную версию Nginx, которая покажет вам отладочную информацию в логах.
Nginx is a very popular web server these days. This article will show you some common errors when running an Nginx web server and possible solutions. This is not a complete list. If you still can’t fix the error after trying the advised solutions, please check your Nginx server logs under /var/log/nginx/ directory and search on Google to debug the problem.
Unable to connect/Refused to Connect
If you see the following error when trying to access your website:
Firefox can’t establish a connection to the server at www.example.com
or
www.example.com refused to connect
or
The site can't be reached, www.example.com unexpectedly closed the connection.
It could be that
- Nginx isn’t running. You can check Nginx status with
sudo systemctl status nginx. Start Nginx withsudo systemctl start nginx. If Nginx fails to start, runsudo nginx -tto find if there is anything wrong with your configuration file. And check the journal (sudo journalctl -eu nginx) to find out why it fails to start. - Firewall blocking ports 80 and 443. If you use the UFW firewall on Debian/Ubuntu, run
sudo ufw allow 80,443/tcpto open TCP ports 80 and 443. If you use Firewalld on RHEL/CentOS/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux, runsudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}, thensudo systemctl reload firewalldto open TCP ports 80 and 443. - Fail2ban. If your server uses fail2ban to block malicious requests, it could be that fail2ban banned your IP address. Run
sudo journalctl -eu fail2banto check if your IP address is banned. You can add your IP address to the fail2banignoreiplist, so it won’t be banned again. - Nginx isn’t listening on the right network interface. For example, Nginx isn’t listening on the server’s public IP address.
If systemctl status nginx shows Nginx is running, but sudo ss -lnpt | grep nginx shows Nginx is not listening on TCP port 80/443, it could be that you deleted the following lines in the /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*;
So Nginx doesn’t use the virtual host files in /etc/nginx/conf.d/ directory. Add this line back.
The Connection Has Timed Out
This could mean that your server is offline, or Nginx isn’t working properly. I once had an out-of-memory problem, which caused Nginx to fail to spawn the worker processes. If you can see the following error message in /var/log/nginx/error.log file, your server is short of memory.
fork() failed while spawning "worker process" (12: Cannot allocate memory)
404 Not Found
404 not found means Nginx can’t find the resources your web browser asks for. The reason could be:
- The web root directory doesn’t exist on your server. In Nginx, the web roor directory is configured using the
rootdirective, like this:root /usr/share/nginx/linuxbabe.com/;. Make sure your website files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP) are stored in the correct directory. - PHP-FPM isn’t running. You can check PHP-FPM status with
sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm(Debian/Ubuntu) orsudo systemctl status php-fpm. - You forgot to include the
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;directive in your Nginx server config file. This directive is needed to process PHP code. - Your server has no free disk space. Try to free up some disk space. You can use the
ncduutility (sudo apt install ncduorsudo dnf install ncdu) to find out which directories are taking up huge amount of disk space.
403 Forbidden
This error means that you are not allowed to access the request resources. Possible scenario includes:
- The website administrator blocks public access to the requested resources with an IP whitelist or other methods.
- The website could be using a web application firewall like ModSecurity, which detected an intrusion attack, so it blocked the request.
Some web applications may show a different error message when 403 forbidden happens. It might tell you that “secure connection failed”, while the cause is the same.
500 Internal Server Error
This means there is some error in the web application. It could be that
- The database server is down. Check MySQL/MariaDB status with
sudo systemctl status mysql. Start it withsudo systemctl start mysql. Runsudo journalctl -eu mysqlto find out why it fails to start. MySQL/MariaDB process could be killed due to out-of-memory issue. - You didn’t configure Nginx to use PHP-FPM, so Nginx doesn’t know how to execute PHP code.
- If your web application has a built-in cache, you can try flushing the app cache to fix this error.
- Your web application may produce its own error log. Check this log file to debug this error.
- Your web application may have a debugging mode. Turn it on and you will see more detailed error messages on the web page. For example, you can turn on debugging mode in the Modoboa mail server hosting platform by setting
DEBUG = Truein the/srv/modoboa/instance/instance/settings.pyfile. - PHP-FPM could be overloaded. Check your PHP-FPM log (such as
/var/log/php7.4-fpm.log). If you can find the[pool www] seems busy (you may need to increase pm.start_servers, or pm.min/max_spare_servers)warning message, you need to allocate more resources to PHP-FPM. - Sometimes reloading PHP-FPM (
sudo systemctl reload php7.4-fpm) can fix the error. - It also might be that you didn’t install the database module for PHP, so PHP can’t connect to the database. For MySQL/MariaDB, install it with
sudo apt install php7.4-mysql. For PostgreSQL, install it withsudo apt install php7.4-pgsql.
Nginx Shows the default page
If you try to set up an Nginx virtual host and when you type the domain name in your web browser, the default Nginx page shows up, it might be
- Your Nginx virtual host file doesn’t have the
server_namedirective. - You didn’t use a real domain name for the
server_namedirective in your Nginx virtual host. - You forgot to reload Nginx.
- You can try deleting the default virtual host file in Nginx (
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default).
The page isn’t redirecting properly
Firefox displays this error as The page isn’t redirecting properly. Google Chrome shows this error as www.example.com redirected you too many times.
This means you have configured Nginx redirection too many times. For example, you may have added an unnecessary return 301 directive in the https server block to redirect HTTP to HTTPS connection.
If you have set up a page cache such as Nginx FastCGI cache, you need to clear your server page cache.
504 Gateway time-out
This means the upstream like PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB isn’t able to process the request fast enough. You can try restarting PHP-FPM to fix the error temporarily, but it’s better to start tuning PHP-FPM/MySQL/MariaDB for faster performance.
Optimize MySQL/MariaDB Performance
Here is the InnoDB configuration in my /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf file. This is a very simple performance tunning.
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1024M innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown = ON innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup = ON innodb_log_file_size = 512M innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #Improving disk I/O performance innodb_file_per_table = 1 innodb_open_files = 400 innodb_io_capacity = 400 innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT innodb_read_io_threads = 64 innodb_write_io_threads = 64 innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 3
Where:
- The InnoDB buffer pool size needs to be at least half of your RAM. ( For VPS with small amount of RAM, I recommend setting the buffer pool size to a smaller value, like 400M, or your VPS would run out of RAM.)
- InnoDB log file size needs to be 25% of the buffer pool size.
- Set the read IO threads and write IO thread to the maximum (64) and
- Make MariaDB use 3 instances of InnoDB buffer pool. The number of instances needs to be the same number of CPU cores on your system.
After saving the changes, restart MariaDB.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Recommended reading: MySQL/MariaDB Database Performance Monitoring with Percona on Ubuntu Server
Find Out Which PHP Script Caused 504 Error
You can check the web server access log to see if there are any bad requests. For example, some folks might find the following lines in the Nextcloud access log file (/var/log/nginx/nextcloud.access).
"GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler" "GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler" "GET /apps/richdocumentscode/proxy.php?req=/hosting/capabilities HTTP/1.1" 499 0 "-" "Nextcloud Server Crawler"
Notice the HTTP status code 499, which means the HTTP client quit the connection before the server gives back an answer. Successful HTTP code should be 2xx or 3xx. If you can find HTTP code 4xx, it means there’s a problem with this HTTP request. In this example, the Nextcloud richdocumentscode app isn’t working.
Increase Timeout Settings
You can also set a longer timeout value in Nginx to reduce the chance of gateway timeout. Edit your Nginx virtual host file and add the following lines in the server {...} block.
proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600;
If you use Nginx with PHP-FPM, then set the fastcgi_read_timeout to a bigger value like 300 seconds. Default is 60 seconds.
location ~ .php$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
Then reload Nginx.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
PHP-FPM also has a max execution time for each script. Edit the php.ini file.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
You can increase the value to 300 seconds.
max_execution_time = 300
Then restart PHP-FPM
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Memory Size Exhausted
If you see the following line in your Nginx error log, it means PHP reached the 128MB memory limit.
PHP Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 57134520 bytes)
You can edit the php.ini file (/etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini) and increase the PHP memory limit.
memory_limit = 512M
Then restart PHP7.4-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
If the error still exists, it’s likely there’s bad PHP code in your web application that eats lots of RAM.
PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR
- You configured Nginx to rediect HTTP request to HTTPS, but there’s no server block in Nginx serving HTTPS request.
- Maybe Nginx isn’t running?
- Sometimes, the main Nginx binary is running, but a worker process can fail and exit due to various reasons. Check the Nginx error log (
/var/log/nginx/error.log) to debug.
PHP-FPM Upstream Time Out
Some folks can find the following error in Nginx error log file ( under /var/log/nginx/).
[error] 7553#7553: *2234677 upstream timed out (110: Connection timed out) while reading response header from upstream
Possible solutions:
- Restart PHP-FPM.
- Upgrade RAM.
- Optimize database performance. Because PHP-FPM needs to fetch data from the database, if the database is slow to process requests, PHP-FPM will time out.
502 Bad Gateway
This error could be caused by:
- PHP-FPM isn’t running. Check its status:
sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm. - PHP-FPM is running, but Nginx isn’t able to connect to PHP-FPM (Resource temporarily unavailable), see how to fix this error below.
- PHP-FPM is running, but Nginx doesn’t have permission to connect to PHP-FPM socket (Permission denied). It might be that Nginx is running as nginx user, but the socket file
/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sockis owned by thewww-datauser. You should configure Nginx to run as thewww-datauser.
Resource temporarily unavailable
Some folks can find the following error in Nginx error log file ( under /var/log/nginx/).
connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock failed (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
This usually means your website has lots of visitors and PHP-FPM is unable to process the huge amounts of requests. You can adjust the number of PHP-FPM child process, so it can process more requests.
Edit your PHP-FPM www.conf file. (The file path varies depending on your Linux distribution.)
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
The default child process config is as follows:
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3
The above configuration means
- PHP-FPM dynamically create child processes. No fixed number of child processes.
- It creates at most 5 child processes.
- Start 2 child processes when PHP-FPM starts.
- There’s at least 1 idle process.
- There’s at most 3 idle processes.
The defaults are based on a server without much resources, like a server with only 1GB RAM. If you have a high traffic website, you probably want to increase the number of child processes, so it can serve more requests. (Make sure you have enough RAM to run more child processes.)
pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 20 pm.start_servers = 8 pm.min_spare_servers = 4 pm.max_spare_servers = 12
Save and close the file. Then we also increase the PHP memory limit.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
Find the following line.
memory_limit = 128M
By default, a script can use at most 128M memory. It’s recommended to set this number to at lest 512M.
memory_limit = 512M
Save and close the file. Restart PHP-FPM. (You might need to change the version number.)
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
To monitor the health of PHP-FPM, you can enable the status page. Find the following line in the PHP-FPM www.conf file.
;pm.status_path = /status
Remove the semicolon to enable PHP-FPM status page. Then restart PHP-FPM.
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Then edit your Nginx virtual host file. Add the following lines. The allow and deny directives are used to restrict access. Only the whitelisted IP addresses can access the status page.
location ~ ^/(status|ping)$ {
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow your_other_IP_Address;
deny all;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
Save and close the file. Then test Nginx configurations.
sudo nginx -t
If the test is successful, reload Nginx for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Sample PHP-FPM status page.
The PHP-FPM www.conf file gives you a good explanation of what each parameter means.
If PHP-FPM is very busy and unable to serve a request immediately, it will queue this request. By default, there can be at most 511 pending requests, determined by the listen.backlog parameter.
listen.backlog = 511
If you see the following value on the PHP-FPM status page, it means there has never been a request put in the queue, i.e. your PHP-FPM can process requests quickly.
listen queue: 0 max listen queue: 0
If there are 511 pending requests in the queue, it means your PHP-FPM is very busy, so you should increase the number of child processes.
You may also need to change the Linux kernel net.core.somaxconn setting, which defines max number of connections allowed to a socket file on Linux, such as the PHP-FPM Unix socket file. By default, its value is 128 before kernel 5.4 and 4096 starting with kernel 5.4.
[email protected]:~$ sysctl net.core.somaxconn net.core.somaxconn = 128
If you run a high traffic website, you can use a big value. Edit /etc/sysctl.conf file.
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
Add the following two lines.
net.core.somaxconn = 20000 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 65535
Save and close the file. Then apply the settings.
sudo sysctl -p
Note: If your server has enough RAM, you can allocate a fixed number of child processes for PHP-FPM like below. In my experience, this fixed the 500 internal error for a Joomla + Virtuemart website.
pm = static pm.max_children = 50
Two Virtual Host files For the Same Website
If you run sudo nginx -t and see the following warning.
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on [::]:443, ignored nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "example.com" on 0.0.0.0:443, ignored
It means there are two virtual host files that contain the same server_name configuration. Don’t create two virtual host files for one website.
PHP-FPM Connection reset by peer
Nginx error log file shows the following message.
recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream
This may be caused by a restart of PHP-FPM. If it’s retarted manually by yourself, then you can ignore this error.
Nginx Socket Leaks
If you find the following error message in the /var/log/nginx/error.log file, your Nginx has a socket leaks problem.
2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120606 open socket #16 left in connection 163 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120629 open socket #34 left in connection 188 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120622 open socket #9 left in connection 213 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120628 open socket #25 left in connection 217 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120605 open socket #15 left in connection 244 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120614 open socket #41 left in connection 245 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120631 open socket #24 left in connection 255 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120616 open socket #23 left in connection 258 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: *120615 open socket #42 left in connection 269 2021/09/28 13:27:41 [alert] 321#321: aborting
You can restart the OS to solve this problem. If it doesn’t work, you need to compile a debug version of Nginx, which will show you debug info in the log.
invalid PID number “” in “/run/nginx.pid”
You need to restart your web server.
sudo pkill nginx sudo systemctl restart nginx
Cloudflare Errors
Here are some common errors and solutions if your website runs behind Cloudflare CDN (Content Delivery Network).
521 Web Server is Down
- Nginx isn’t running.
- You didn’t open TCP ports 80 and 443 in the firewall.
- You changed the server IP address, but forgot to update DNS record in Cloudflare.
The page isn’t redirecting properly
If your SSL setting on the SSL/TLS app is set to Flexible, but your origin server is configured to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS, Your Nginx server sends reponse back to Cloudflare in encrypted connection. Since Cloudflare is expecting HTTP traffic, it keeps resending the same request, resulting in a redirect loop. In this case, you need to use the Full (strict) SSL/TLS option in your Cloudflare settings.
Wrapping Up
I hope this article helped you to fix common Nginx web server errors. As always, if you found this post useful, then subscribe to our free newsletter to get more tips and tricks 🙂
You may want to check out:
- How to Fix Common Let’s Encrypt/Certbot Errors
Ошибки NGINX [alert] 1 open socket left in connection
Основные настройки нжина /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user www-data;
worker_processes auto;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
multi_accept on;
}
http {
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 20;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
gzip on;
gzip_disable «msie6»;
…..
Лог ошибок
2018/04/07 09:27:24 [alert] 22148#22148: *9146 open socket #63 left in connection 33
2018/04/07 09:27:24 [alert] 22148#22148: *9188 open socket #55 left in connection 43
2018/04/07 09:27:24 [alert] 22148#22148: *9149 open socket #69 left in connection 60
2018/04/07 09:27:24 [alert] 22148#22148: *9147 open socket #67 left in connection 62
2018/04/07 09:27:24 [alert] 22148#22148: aborting
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23446#23446: *849 open socket #59 left in connection 18
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23446#23446: aborting
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23445#23445: *950 open socket #53 left in connection 8
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23445#23445: *949 open socket #50 left in connection 19
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23445#23445: *954 open socket #49 left in connection 29
2018/04/07 09:39:40 [alert] 23445#23445: aborting
2018/04/07 09:48:06 [alert] 24112#24112: *498 open socket #52 left in connection 14
2018/04/07 09:48:06 [alert] 24112#24112: aborting
2018/04/07 09:48:14 [alert] 24933#24933: *9 open socket #51 left in connection 9
2018/04/07 09:48:14 [alert] 24933#24933: *10 open socket #52 left in connection 10
2018/04/07 09:48:14 [alert] 24933#24933: aborting
2018/04/07 09:48:29 [alert] 25256#25256: *4 open socket #49 left in connection 7
2018/04/07 09:48:29 [alert] 25256#25256: aborting
2018/04/07 09:53:09 [alert] 25657#25657: *342 open socket #59 left in connection 27
2018/04/07 09:53:09 [alert] 25657#25657: aborting
2018/04/07 19:11:20 [alert] 489#489: *1291 open socket #56 left in connection 16
2018/04/07 19:11:20 [alert] 488#488: *1278 open socket #64 left in connection 7
2018/04/07 19:11:20 [alert] 489#489: aborting
2018/04/07 19:11:20 [alert] 488#488: aborting
Изменение параметров worker_connections и keepalive_timeout особо не влияет на частоту появления ошибок.. причем нжин полностью падает и ни один другой сайт не может в этот момент подключиться и притом Апач не ложиться и нет никаких ошибок в логах
-
#1
nginx stops and starts. seeing this error in /var/log/nginx/error.log:
2017/02/22 04:00:44 [alert] 13939#0: *150 open socket #41 left in connection 13
2017/02/22 04:00:44 [alert] 13939#0: *149 open socket #3 left in connection 14
Plesk Onyx v17.0.17
Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS
-
#2
Did you use Nginx direct from Plesk?
-
#3
Hello Janko1000,
Did you use Nginx direct from Plesk? Yes. Standard Plesk install
Apache MPM mode = prefork
nginx settings:
proxy mode (checked)
smart static files procession (unchecked), this option reduces performance
Serve static files directly by nginx (unchecked), this option reduces performance
PHP settings:
PHP 5.6.30
PHP as (FPM application served by nginx on some sites and FPM application served by Apache on others). I can change this to FPM application served by nginx, FPM application served by Apache or FastCGI application served by Apache and see no difference and see no difference in performance.
-
#4
The error messages are not the cause for an Nginx reload, but a symptom. In some Nginx docs I read that SPDY module is causing the «open socket left in connection» error. SPDY is not needed if you have activated HTTP/2. Maybe you had previously added SPDY?
In the latest Nginx version without third party modules added the warnings should not appear. Refer to https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/debugging/#socket-leaks for more details.
-
#5
Hello Peter,
Maybe you had previously added SPDY? By SPDY I am assuming you are referring to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SPDY. A definite no. No special addons, just the standard plesk install.
I had previously seen the nginx link you are referring to. It doesn’t provide me with a level of detail that I am able to act on which is why I opened a thread here.
Question. Is it possible to remove nginx? Maybe even just for testing. I know that nginx is ‘marketed’ as a making apache better but so far I don’t see it. In fact when I start to use the ‘smart’ nginx options performance drops.
imho adding extra software to a configuration can sometimes just mean more to break. In a case where the extra software does not provide a demonstratable benefit, maybe the simplest solution is to just remove it.
When I see errors that I am not able to track down to a fault or configuration issue, I’m not left with the warmest feeling of confidence. In the back of my mind I am thinking, «OK what am I missing here?»
Thanks. Further suggestions would be appreciated.
-
#6
You can deactivate nginx by this command:
# /usr/local/psa/admin/sbin/nginxmng -d
You can use the same command with parameter -e to enable Nginx again. Either command can take a while to execute, because all web server configuraton files need to be reconfigured.
-
#7
Hello Peter,
«In the latest Nginx version without third party modules added the warnings should not appear.» — So this warning should be considered abnormal?
Re: deactivating nginx. Thanks for the info.
Can you tell me what nginx ‘brings to the table’ for plesk? As I indicated earlier, it seems to drop performance when ‘smart’ options are enabled.
Will deactivating nginx cause other problems?
Thanks
-
#8
I have no idea why your Nginx is slower than an Apache-only configuration. Nginx is the much better, faster system. It can handle more processes with less resources in less time. Nginx-only hosting is proven to be enormously faster than Apache hosting for the same websites, and the combination of both, Nginx and Apache, is great because Nginx is caching files and also deliverying static files directly, circumventing unnecessary Apache overhead.
To my knowledge deactivating Nginx will not cause any problems. It will still be the web server for Plesk GUI, but it will not server subscription or add-on domains.
-
#9
Hello Peter,
Thanks for the feedback. From my experience enabling the nginx options in plesk significantly reduces performance as measured by https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/.
I’m fairly new to plesk (2+ years, versions 12.08, 12.5.30, 17.07) and have seen this performance drop consistently across the last 2 versions (do not recall if this was an issue with 12.0.8).
To put some hard numbers on this I just did some tests on live sites:
Wordpress (w/2017 theme) dropped from 89%/95% to 71%/74%. That’s an 18% and 21% performance drop! (standard wordpress .htaccess file)
Joomla! (custom theme) dropped from 75%/91% to 59%/72% (16% & 19% performance drop) (custom .htaccess file)
Using the standard joomla! .htaccess file the numbers are 71%/87% and drop to 57%70% with nginx smart option. (14% &17% performance drop)
This is with «Smart static files processing» enabled. «Serve static files directly by nginx» did not seem to make any significant difference in any testing.
This is easy to reproduce 100% of the time:
1. Install plesk 17
2. Install latest version of wordpress
3. PageSpeed Test (site is slower)
4. Plesk | Domain to test | Apache & nginx Settings | Uncheck «Smart static files processing», Uncheck «Serve static files directly by nginx» | Apply
5. Retest in PageSpeed (performance improves significantly).
With this test, we can rule out wordpress or joomla! extensions/plugins, .htaccess files, 3rd party plesk addons, etc.
When I first discovered this I thought I was dealing with a simple configuration issue. I changed the PHP handlers, PHP versions, with and without .htaccess files and the only common element was the nginx «Smart static files processing» option.
-
#10
Sorry, but I cannot confirm any of this.
#626
closed
defect
(fixed)
| Reported by: | Owned by: | Valentin Bartenev <vbart@…> | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Priority: | minor | Milestone: | |
| Component: | nginx-core | Version: | 1.6.x |
| Keywords: | spdy, http2 | Cc: | |
| uname -a: | Linux web1 2.6.32-431.23.3.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Jul 31 17:20:51 UTC 2014 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux | ||
| nginx -V: | nginx version: nginx/1.6.1 |
I am using Nginx 1.6.1 from the official Nginx repository and recently (I think starting from 1.6.1) we started getting these errors on reload:
2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *418441897 open socket #786 left in connection 17 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *25679726 open socket #932 left in connection 36 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *250563297 open socket #108 left in connection 64 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *255280874 open socket #467 left in connection 108 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *83647387 open socket #687 left in connection 116 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *172055940 open socket #582 left in connection 158 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *42380963 open socket #370 left in connection 162 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *187857605 open socket #834 left in connection 196 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *96301018 open socket #290 left in connection 226 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *229257100 open socket #520 left in connection 232 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *310210706 open socket #453 left in connection 251 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *273001877 open socket #615 left in connection 307 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *213129612 open socket #329 left in connection 312 2014/09/15 11:00:13 [alert] 15749#0: *60552692 open socket #839 left in connection 347
We got about 650 of these errors last time we reloaded. I don’t remember ever seeing these errors before. Also it doesn’t happen on every reload, only if nginx has been running longer (for now I know that it happens if it’s running for at least 24h).
I don’t know if this is of any help for you, but if I can help you with attaching a configuration file, or anything else feel free to ask.