Environment
- pip version: 9.0.3
- Python version: 3.6
- OS: Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
Description
My system admin installed Python 3.6 for me in my AWS workspace and i requested him to update the pip version to 18 but while he was trying to upgrade the version, he ran into error. All below-mentioned commands were executed from a Powershell window in Administrative mode:
Output
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip install --upgrade pip
Collecting pip
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5f/25/e52d3f31441505a5f3af41213346e5b6c221c9e086a166f3703d2ddaf940
/pip-18.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (1.3MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 1.3MB 720kB/s
Installing collected packages: pip
Found existing installation: pip 9.0.3
Uninstalling pip-9.0.3:
Exception:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6libshutil.py", line 544, in move
os.rename(src, real_dst)
OSError: [WinError 17] The system cannot move the file to a different disk drive: 'd:\python\3.6\scripts\pip.exe' ->
'C:\Users\sdgadmin\AppData\Local\Temp\pip-o9ithn08-uninstall\python\3.6\scripts\pip.exe'
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespipbasecommand.py", line 215, in main
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespipcommandsinstall.py", line 342, in run
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespipreqreq_set.py", line 778, in install
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespipreqreq_install.py", line 754, in uninstall
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespipreqreq_uninstall.py", line 115, in remove
File "d:python3.6libsite-packagespiputils__init__.py", line 267, in renames
File "d:python3.6libshutil.py", line 559, in move
os.unlink(src)
PermissionError: [WinError 5] Access is denied: 'd:\python\3.6\scripts\pip.exe'
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip list
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "D:Python3.6Scriptspip.exe__main__.py", line 5, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip3 install --upgrade pip
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "D:Python3.6Scriptspip3.exe__main__.py", line 5, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip3 install --upgrade pip3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "D:Python3.6Scriptspip3.exe__main__.py", line 5, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip install --upgrade pip
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "D:Python3.6Scriptspip.exe__main__.py", line 5, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
PS D:python3.6scripts> pip.exe install --upgrade pip
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "d:python3.6librunpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "D:Python3.6Scriptspip.exe__main__.py", line 5, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
Are we doing something wrong here? I also checked few links that suggested using easy_install. I tried that as well but ran into issues.
PS D:python3.6scripts> .easy_install.exe pip
Searching for pip
Reading https://pypi.python.org/simple/pip/
d:python3.6libsite-packagessetuptoolspep425tags.py:89: RuntimeWarning: Config variable 'Py_DEBUG' is unset, Python
ABI tag may be incorrect
warn=(impl == 'cp')):
d:python3.6libsite-packagessetuptoolspep425tags.py:93: RuntimeWarning: Config variable 'WITH_PYMALLOC' is unset, P
ython ABI tag may be incorrect
warn=(impl == 'cp')):
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5f/25/e52d3f31441505a5f3af41213346e5b6c221c9e086a166f3703d2ddaf940/p
ip-18.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl#sha256=070e4bf493c7c2c9f6a08dd797dd3c066d64074c38e9e8a0fb4e6541f266d96c
error: Download error for https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5f/25/e52d3f31441505a5f3af41213346e5b6c221c9e086a166f3
703d2ddaf940/pip-18.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl#sha256=070e4bf493c7c2c9f6a08dd797dd3c066d64074c38e9e8a0fb4e6541f266d96c: [SSL
: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed (_ssl.c:833)
In this article, we will look into how to solve «/usr/bin/python3: No module named pip» error which I believe is a pretty common error in a freshly built Linux System where python3 packages are not installed yet. pip is a very famous python package management tool frequently used by Python Programmers and developers to manage their application packages. If you don’t have pip installed before you are trying to install any of the python modules then you will always end up with "/usr/bin/python3: No module named pip" error just like what I encountered last night. While this may not be the only reason to have this error but this is the common most reason for lot of folks !!
Also Read: How to Check and Log Malicious RPM Installation in 3 Easy Steps
So when I was trying to install a package using pip, I encountered below error in my Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System. You might be getting the same error in different Linux version.
root@cyberithub:~# python3 -m pip install --user pipenv /usr/bin/python3: No module named pip
While this error can come due to multiple reasons but in most of the cases you will see this error because of pip package not installed in your System. So to solve this kind of error, you need to simply install pip package from the default Repo. For example, in my case I have used apt-get install python3-pip command to install this package in my System. More about PIP.
NOTE:
Please note that here I am using root user to run all the below commands. You can use any user with sudo access to run all these commands. For more information Please check Step by Step: How to Add User to Sudoers to provide sudo access to the User.
root@cyberithub:~# apt-get install python3-pip
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
dmeventd libaio1 libdevmapper-event1.02.1 liblvm2cmd2.03 libreadline5 thin-provisioning-tools
Use 'apt autoremove' to remove them.
The following additional packages will be installed:
binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-9 gcc gcc-9 libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl
libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan5 libatomic1 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc6-dev libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libgcc-9-dev
libitm1 liblsan0 libpython3-dev libpython3.8-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-9-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev make manpages-dev python-pip-whl
python3-dev python3-distutils python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.8-dev zlib1g-dev
Suggested packages:
binutils-doc debian-keyring g++-multilib g++-9-multilib gcc-9-doc gcc-multilib autoconf automake libtool flex bison gcc-doc gcc-9-multilib gcc-9-locales
glibc-doc libstdc++-9-doc make-doc python-setuptools-doc
The following NEW packages will be installed:
binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-9 gcc gcc-9 libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl
libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan5 libatomic1 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc6-dev libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libgcc-9-dev
libitm1 liblsan0 libpython3-dev libpython3.8-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-9-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev make manpages-dev python-pip-whl
python3-dev python3-distutils python3-pip python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.8-dev zlib1g-dev
0 upgraded, 43 newly installed, 0 to remove and 171 not upgraded.
Need to get 41.7 MB of archives.
After this operation, 185 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
........................................
If you are using RHEL/CentOS 7 based Systems, then all you need to do in to enable the EPEL Repo and then install the package by using yum install python3-pip command. For RHEL/CentOS 8 based Systems, you can use dnf install python3-pip command.
yum install python3-pip dnf install python3-pip
After successful installation, you can verify the package version by using pip --version command as shown below.
root@cyberithub:~# pip --version pip 20.0.2 from /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pip (python 3.8)
After installing the package I again tried to run the earlier command then this time I noticed that the command worked successfully and now it is not throwing "/usr/bin/python3: No module named pip" error as shown below. Hope this helps !!
root@cyberithub:~# python3 -m pip install --user pipenv
Collecting pipenv
Downloading pipenv-2022.1.8-py2.py3-none-any.whl (3.6 MB)
|████████████████████████████████| 3.6 MB 1.4 MB/s
Requirement already satisfied: pip>=18.0 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from pipenv) (20.0.2)
Collecting virtualenv
Downloading virtualenv-20.13.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (8.7 MB)
|████████████████████████████████| 8.7 MB 11.2 MB/s
Collecting virtualenv-clone>=0.2.5
Downloading virtualenv_clone-0.5.7-py3-none-any.whl (6.6 kB)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from pipenv) (2019.11.28)
Requirement already satisfied: setuptools>=36.2.1 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from pipenv) (45.2.0)
Requirement already satisfied: six<2,>=1.9.0 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from virtualenv->pipenv) (1.14.0)
Collecting distlib<1,>=0.3.1
Downloading distlib-0.3.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (461 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 461 kB 16.4 MB/s
Collecting filelock<4,>=3.2
Downloading filelock-3.6.0-py3-none-any.whl (10.0 kB)
Collecting platformdirs<3,>=2
Downloading platformdirs-2.5.1-py3-none-any.whl (14 kB)
Installing collected packages: distlib, filelock, platformdirs, virtualenv, virtualenv-clone, pipenv
WARNING: The script virtualenv is installed in '/root/.local/bin' which is not on PATH.
Consider adding this directory to PATH or, if you prefer to suppress this warning, use --no-warn-script-location.
WARNING: The script virtualenv-clone is installed in '/root/.local/bin' which is not on PATH.
Consider adding this directory to PATH or, if you prefer to suppress this warning, use --no-warn-script-location.
WARNING: The scripts pipenv and pipenv-resolver are installed in '/root/.local/bin' which is not on PATH.
Consider adding this directory to PATH or, if you prefer to suppress this warning, use --no-warn-script-location.
Successfully installed distlib-0.3.4 filelock-3.6.0 pipenv-2022.1.8 platformdirs-2.5.1 virtualenv-20.13.2 virtualenv-clone-0.5.7
Quick Fix: Python raises the ImportError: No module named 'pip' when it cannot find the library pip. The most frequent source of this error is that you haven’t installed pip explicitly with pip install pip. Alternatively, you may have different Python versions on your computer, and pip is not installed for the particular version you’re using.
Problem Formulation
You’ve just learned about the awesome capabilities of the pip library and you want to try it out, so you start your code with the following statement:
import pip
This is supposed to import the Pandas library into your (virtual) environment. However, it only throws the following ImportError: No module named pip:
>>> import pip
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module>
import pip
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
Solution Idea 1: Install Library pip
The most likely reason is that Python doesn’t provide pip in its standard library. You need to install it first!
Before being able to import the Pandas module, you need to install it using Python’s package manager pip. Make sure pip is installed on your machine.
To fix this error, you can run the following command in your Windows shell:
$ pip install pip
This simple command installs pip in your virtual environment on Windows, Linux, and MacOS. It assumes that your pip version is updated. If it isn’t, use the following two commands in your terminal, command line, or shell (there’s no harm in doing it anyways):
$ python -m pip install --upgrade pip $ pip install pandas
💡 Note: Don’t copy and paste the $ symbol. This is just to illustrate that you run it in your shell/terminal/command line.
Solution Idea 2: Fix the Path
The error might persist even after you have installed the pip library. This likely happens because pip is installed but doesn’t reside in the path you can use. Although pip may be installed on your system the script is unable to locate it. Therefore, it is unable to install the library using pip in the correct path.
To fix the problem with the path in Windows follow the steps given next.
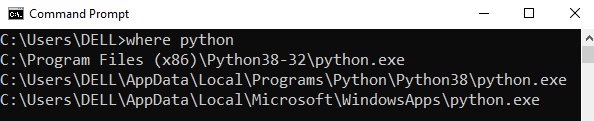
Step 1: Open the folder where you installed Python by opening the command prompt and typing where python
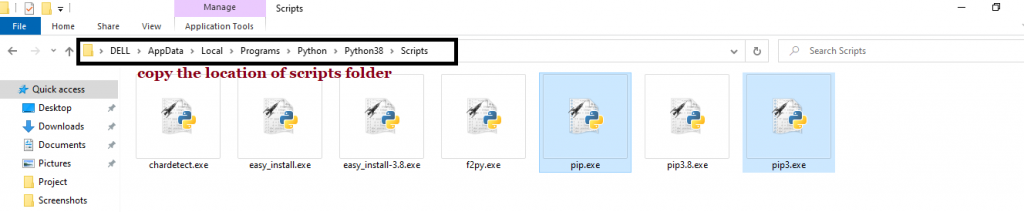
Step 2: Once you have opened the Python folder, browse and open the Scripts folder and copy its location. Also verify that the folder contains the pip file.
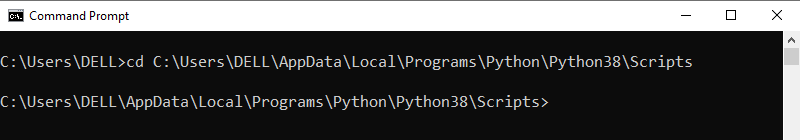
Step 3: Now open the Scripts directory in the command prompt using the cd command and the location that you copied previously.
Step 4: Now install the library using pip install pip command. Here’s an analogous example:
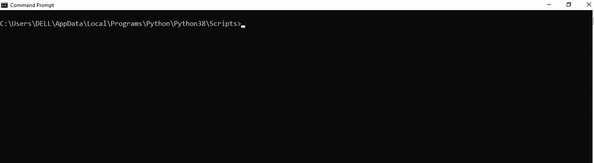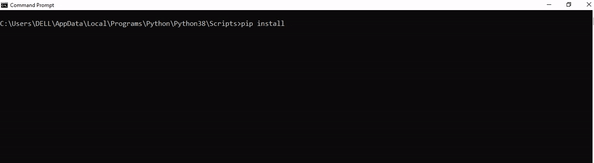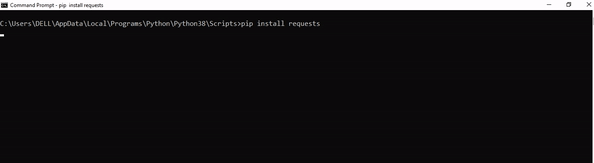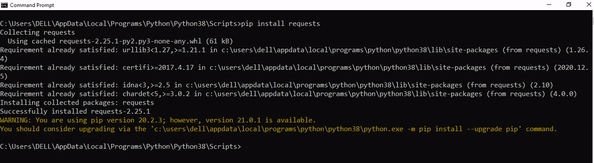
After having followed the above steps, execute our script once again. And you should get the desired output.
Other Solution Ideas
- The
ModuleNotFoundErrormay appear due to relative imports. You can learn everything about relative imports and how to create your own module in this article. - You may have mixed up Python and pip versions on your machine. In this case, to install
pipfor Python 3, you may want to trypython3 -m pip install pipor evenpip3 install pipinstead ofpip install pip - If you face this issue server-side, you may want to try the command
pip install --user pip - If you’re using Ubuntu, you may want to try this command:
sudo apt install pip - You can check out our in-depth guide on installing
piphere. - You can also check out this article to learn more about possible problems that may lead to an error when importing a library.
Understanding the “import” Statement
import pip
In Python, the import statement serves two main purposes:
- Search the module by its name, load it, and initialize it.
- Define a name in the local namespace within the scope of the
importstatement. This local name is then used to reference the accessed module throughout the code.
What’s the Difference Between ImportError and ModuleNotFoundError?
What’s the difference between ImportError and ModuleNotFoundError?
Python defines an error hierarchy, so some error classes inherit from other error classes. In our case, the ModuleNotFoundError is a subclass of the ImportError class.
You can see this in this screenshot from the docs:
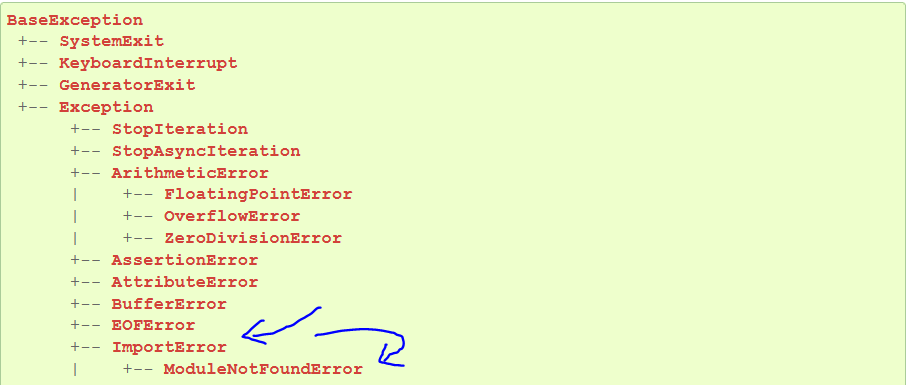
You can also check this relationship using the issubclass() built-in function:
>>> issubclass(ModuleNotFoundError, ImportError) True
Specifically, Python raises the ModuleNotFoundError if the module (e.g., pip) cannot be found. If it can be found, there may be a problem loading the module or some specific files within the module. In those cases, Python would raise an ImportError.
If an import statement cannot import a module, it raises an ImportError. This may occur because of a faulty installation or an invalid path. In Python 3.6 or newer, this will usually raise a ModuleNotFoundError.
Related Videos
The following video shows you how to resolve the ImportError:
How to Fix : “ImportError: Cannot import name X” in Python?
The following video shows you how to import a function from another folder—doing it the wrong way often results in the ModuleNotFoundError:
How to Call a Function from Another File in Python?
How to Fix “ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘pip’” in PyCharm
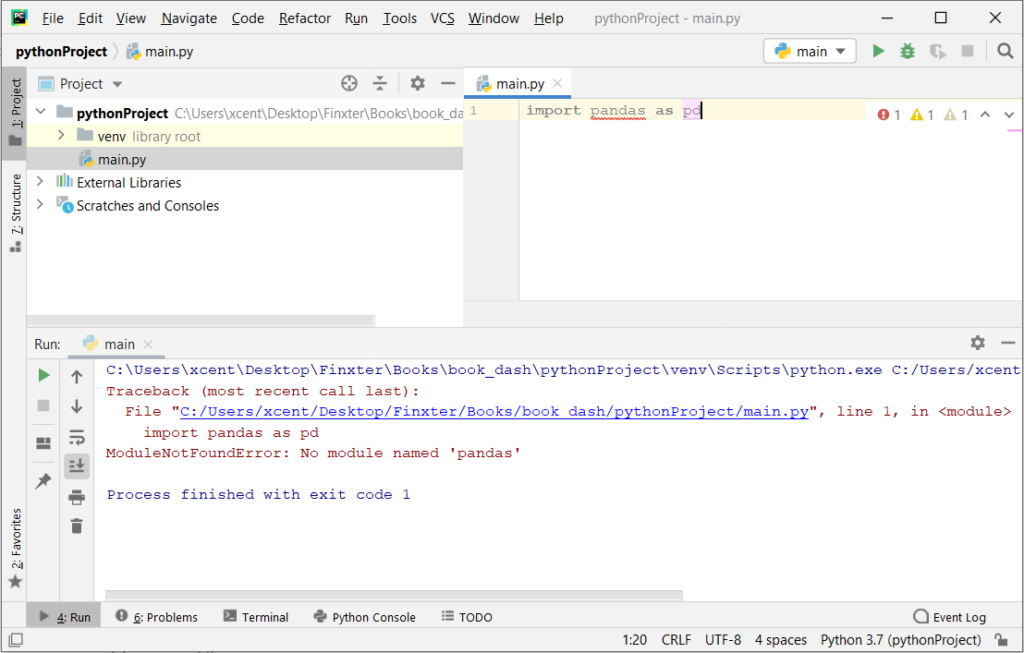
If you create a new Python project in PyCharm and try to import the pip library, it’ll raise the following error message:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/Users/.../main.py", line 1, in <module>
import pip
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
Process finished with exit code 1
The reason is that each PyCharm project, per default, creates a virtual environment in which you can install custom Python modules. But the virtual environment is initially empty—even if you’ve already installed pip on your computer!
Here’s a screenshot exemplifying this for the pandas library. It’ll look similar for pip.
The fix is simple: Use the PyCharm installation tooltips to install Pandas in your virtual environment—two clicks and you’re good to go!
First, right-click on the pandas text in your editor:
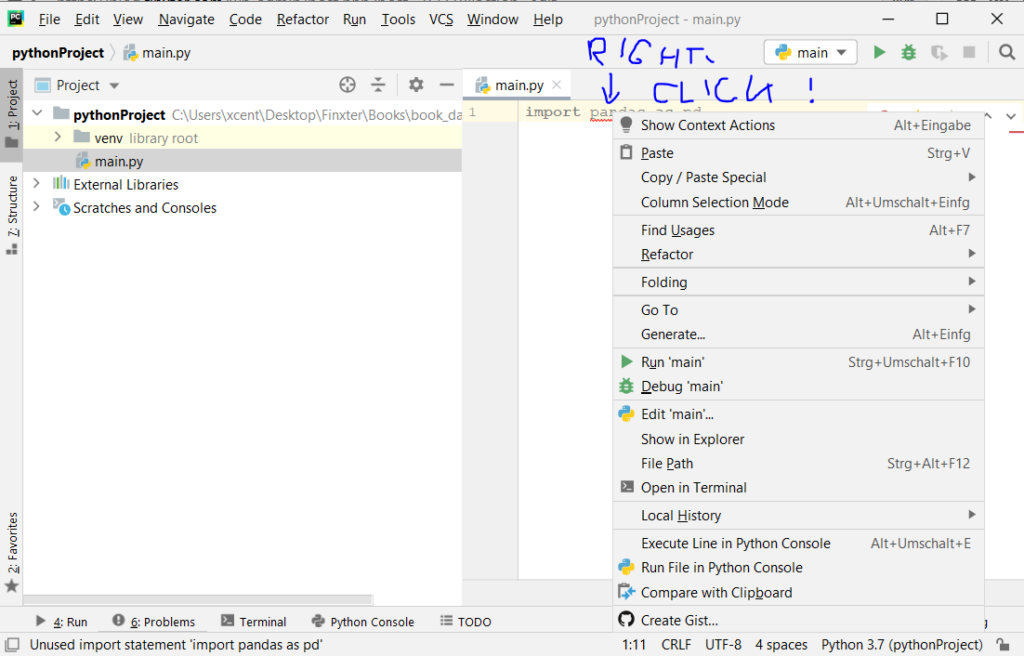
Second, click “Show Context Actions” in your context menu. In the new menu that arises, click “Install Pandas” and wait for PyCharm to finish the installation.
The code will run after your installation completes successfully.
As an alternative, you can also open the Terminal tool at the bottom and type:
$ pip install pip
If this doesn’t work, you may want to set the Python interpreter to another version using the following tutorial: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/2016.1/configuring-python-interpreter-for-a-project.html
You can also manually install a new library such as pip in PyCharm using the following procedure:
- Open
File > Settings > Projectfrom the PyCharm menu. - Select your current project.
- Click the
Python Interpretertab within your project tab. - Click the small
+symbol to add a new library to the project. - Now type in the library to be installed, in your example Pandas, and click
Install Package. - Wait for the installation to terminate and close all popup windows.
Here’s an analogous example:
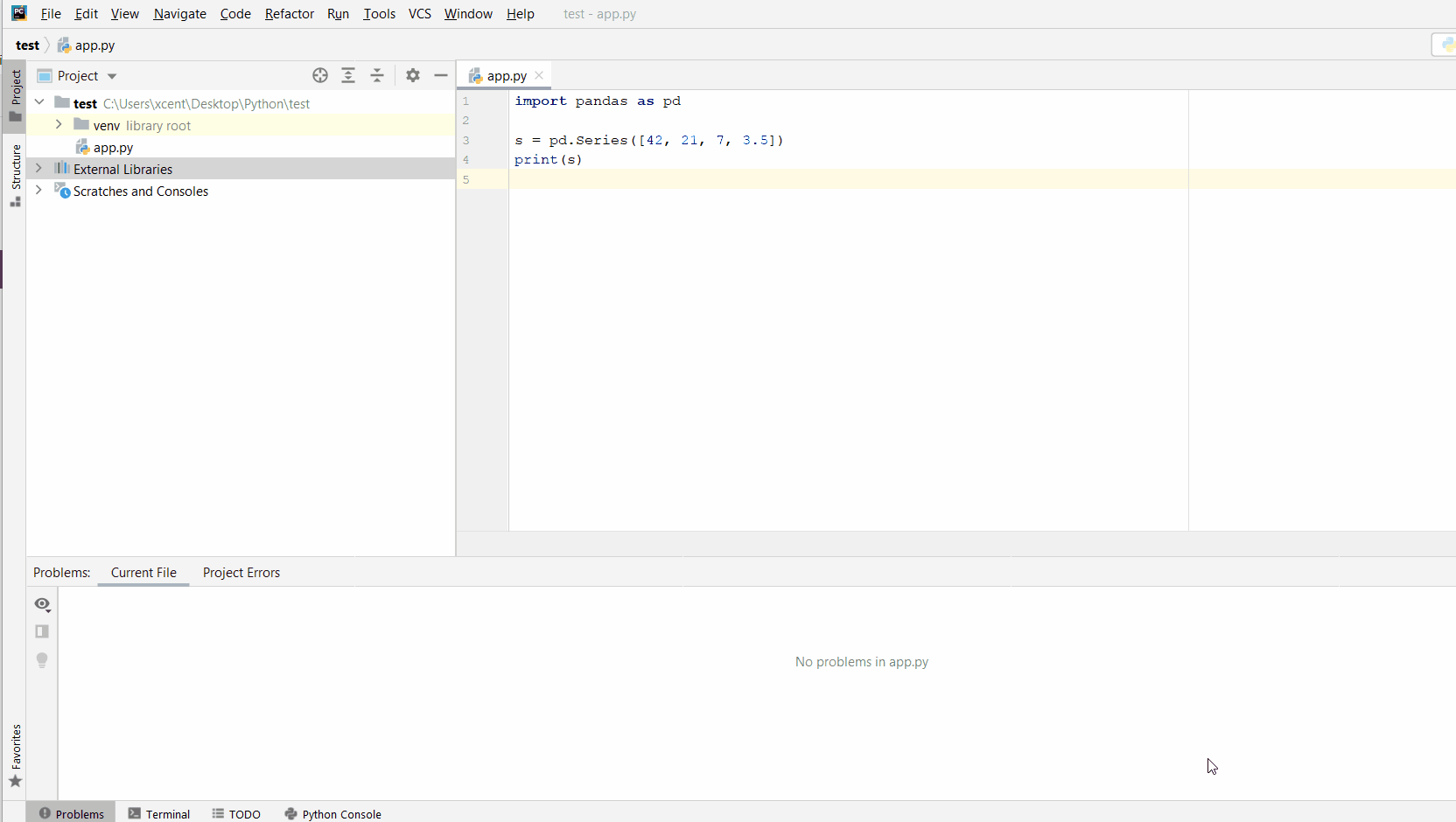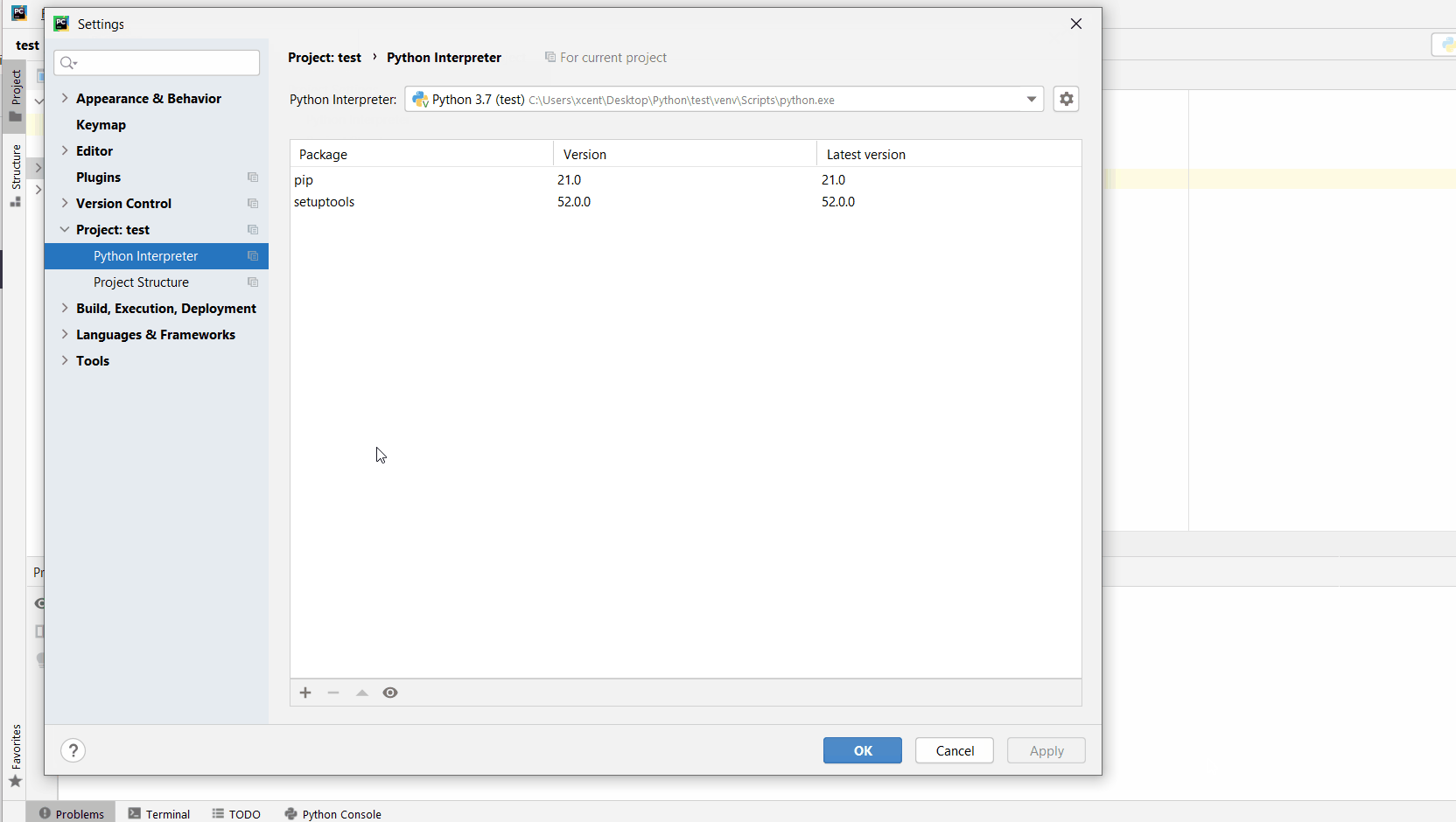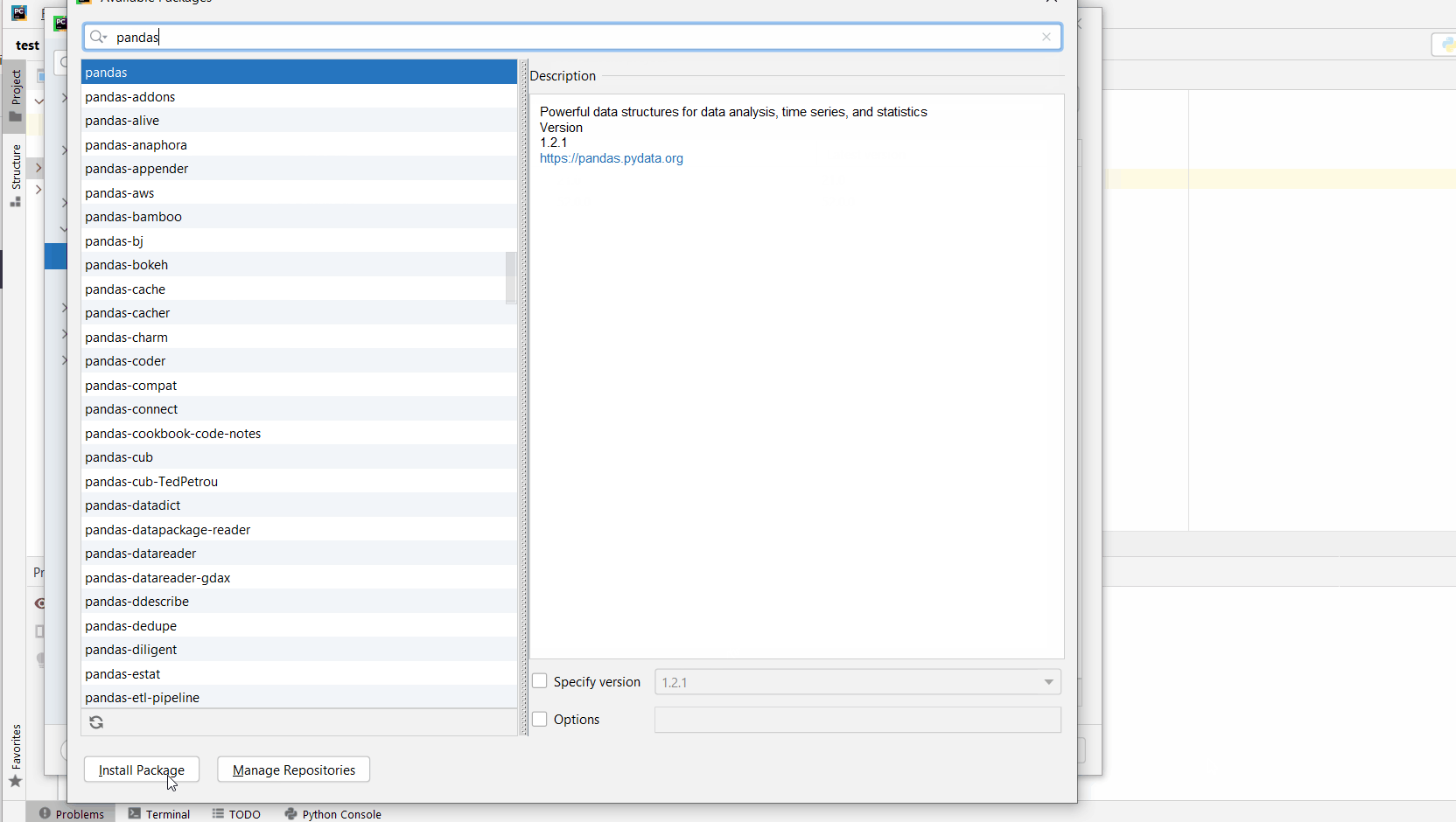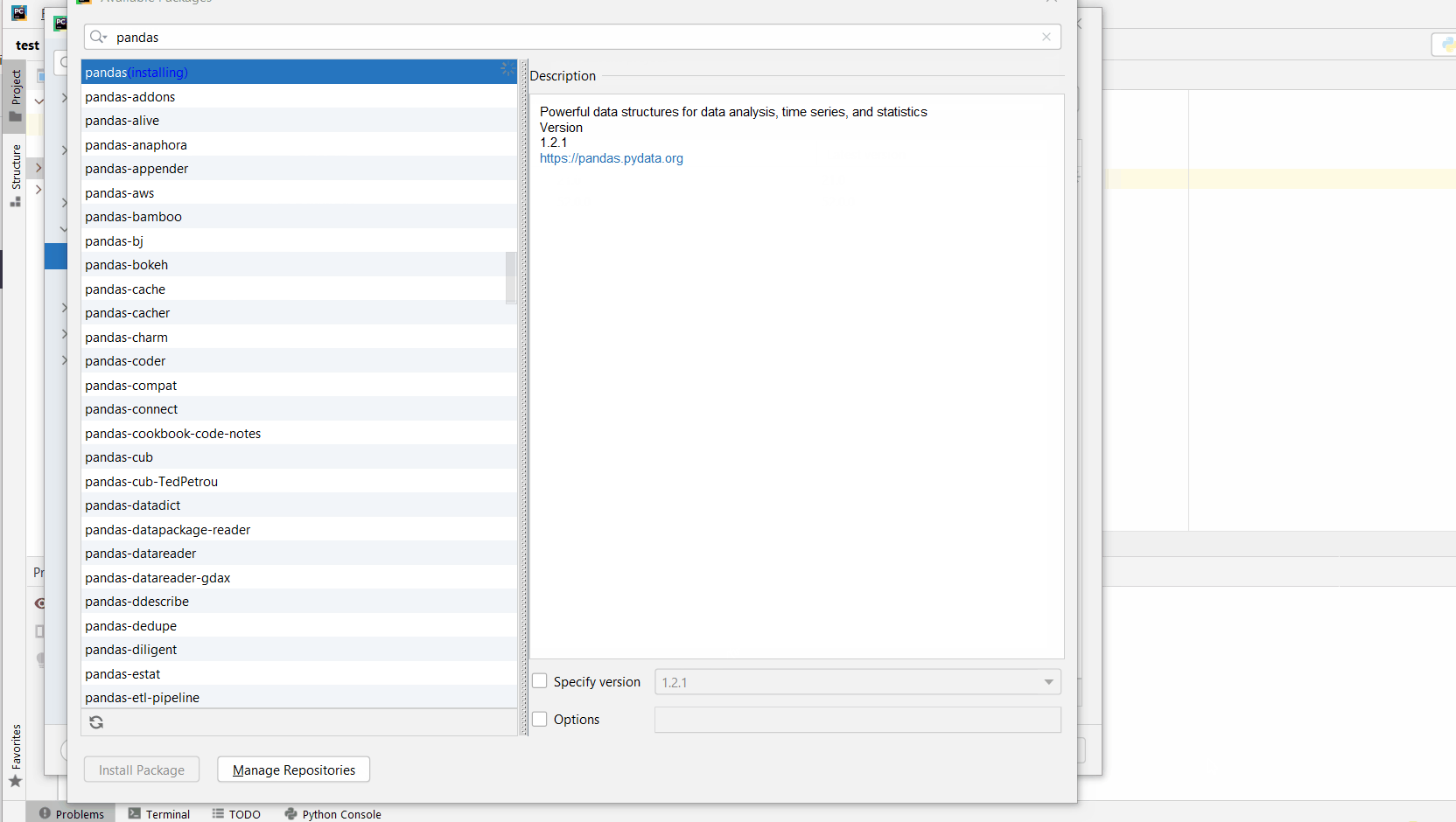
Here’s a full guide on how to install a library on PyCharm.
- How to Install a Library on PyCharm
Nerd Humor
While working as a researcher in distributed systems, Dr. Christian Mayer found his love for teaching computer science students.
To help students reach higher levels of Python success, he founded the programming education website Finxter.com. He’s author of the popular programming book Python One-Liners (NoStarch 2020), coauthor of the Coffee Break Python series of self-published books, computer science enthusiast, freelancer, and owner of one of the top 10 largest Python blogs worldwide.
His passions are writing, reading, and coding. But his greatest passion is to serve aspiring coders through Finxter and help them to boost their skills. You can join his free email academy here.
В Python может быть несколько причин возникновения ошибки ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ...:
- Модуль Python не установлен.
- Есть конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля.
- Есть конфликт зависимости модулей Python.
Рассмотрим варианты их решения.
Модуль не установлен
В первую очередь нужно проверить, установлен ли модуль. Для использования модуля в программе его нужно установить. Например, если попробовать использовать numpy без установки с помощью pip install будет следующая ошибка:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy'Для установки нужного модуля используйте следующую команду:
pip install numpy
# или
pip3 install numpyИли вот эту если используете Anaconda:
conda install numpyУчтите, что может быть несколько экземпляров Python (или виртуальных сред) в системе. Модуль нужно устанавливать в определенный экземпляр.
Конфликт имен библиотеки и модуля
Еще одна причина ошибки No module named — конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля. Предположим, есть следующая структура проекта Python:
demo-project
└───utils
__init__.py
string_utils.py
utils.pyЕсли использовать следующую инструкцию импорта файла utils.py, то Python вернет ошибку ModuleNotFoundError.
>>> import utils.string_utils
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:demo-projectutilsutils.py", line 1, in
import utils.string_utils
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'utils.string_utils';
'utils' is not a package
В сообщении об ошибке сказано, что «utils is not a package». utils — это имя пакета, но это также и имя модуля. Это приводит к конфликту, когда имя модуля перекрывает имя пакета/библиотеки. Для его разрешения нужно переименовать файл utils.py.
Иногда может существовать конфликт модулей Python, который и приводит к ошибке No module named.
Следующее сообщение явно указывает, что _numpy_compat.py в библиотеке scipy пытается импортировать модуль numpy.testing.nosetester.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:demo-projectvenv
Libsite-packages
scipy_lib_numpy_compat.py", line 10, in
from numpy.testing.nosetester import import_nose
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy.testing.nosetester'Ошибка ModuleNotFoundError возникает из-за того, что модуль numpy.testing.nosetester удален из библиотеки в версии 1.18. Для решения этой проблемы нужно обновить numpy и scipy до последних версий.
pip install numpy --upgrade
pip install scipy --upgrade Что означает ошибка ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Ситуация: мы решили заняться бигдатой и обработать большой массив данных на Python. Чтобы было проще, мы используем уже готовые решения и находим нужный нам код в интернете, например такой:
import numpy as np
x = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
nums = np.array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
type(nums)
zeros = np.zeros((5, 4))
lin = np.linspace(1, 10, 20)Копируем, вставляем в редактор кода и запускаем, чтобы разобраться, как что работает. Но вместо обработки данных Python выдаёт ошибку:
❌ModuleNotFoundError: No module named numpy
Странно, но этот код точно правильный: мы его взяли из блога разработчика и, по комментариям, у всех всё работает. Откуда тогда ошибка?
Что это значит: Python пытается подключить библиотеку, которую мы указали, но не может её найти у себя.
Когда встречается: когда библиотеки нет или мы неправильно написали её название.
Что делать с ошибкой ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Самый простой способ исправить эту ошибку — установить библиотеку, которую мы хотим подключить в проект. Для установки Python-библиотек используют штатную команду pip или pip3, которая работает так: pip install <имя_библиотеки>. В нашем случае Python говорит, что он не может подключить библиотеку Numpy, поэтому пишем в командной строке такое:
pip install numpy
Это нужно написать не в командной строке Python, а в командной строке операционной системы. Тогда компьютер скачает эту библиотеку, установит, привяжет к Python и будет ругаться на строчку в коде import numpy.
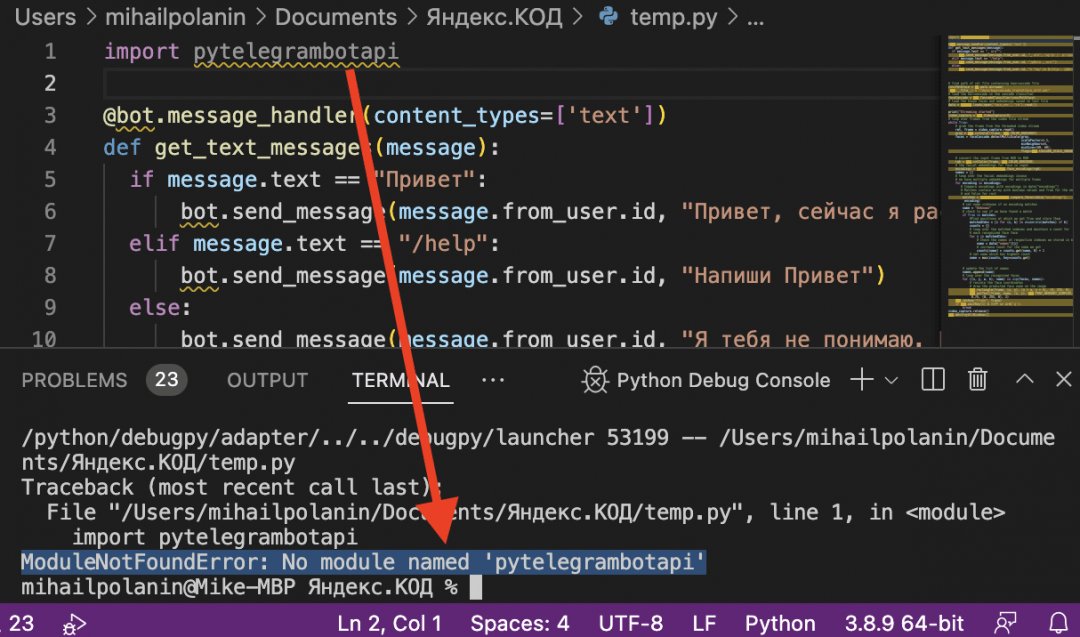
Ещё бывает такое, что библиотека называется иначе, чем указано в команде pip install. Например, для работы с телеграм-ботами нужна библиотека telebot, а для её установки надо написать pip install pytelegrambotapi. Если попробовать подключить библиотеку с этим же названием, то тоже получим ошибку:
А иногда такая ошибка — это просто невнимательность: пропущенная буква в названии библиотеки или опечатка. Исправляем и работаем дальше.
Вёрстка:
Кирилл Климентьев