A common error you may encounter when using Python is modulenotfounderror: no module named ‘requests’. This error occurs when Python cannot detect the Requests library in your current environment. Requests does not come with the default Python installation. This tutorial goes through the exact steps to troubleshoot this error for the Windows, Mac and Linux operating systems.
ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘requests’
What is ModuleNotFoundError?
The ModuleNotFoundError occurs when the module you want to use is not present in your Python environment. There are several causes of the modulenotfounderror:
The module’s name is incorrect, in which case you have to check the name of the module you tried to import. Let’s try to import the re module with a double e to see what happens:
import ree---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
1 import ree
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'ree'To solve this error, ensure the module name is correct. Let’s look at the revised code:
import re
print(re.__version__)2.2.1You may want to import a local module file, but the module is not in the same directory. Let’s look at an example package with a script and a local module to import. Let’s look at the following steps to perform from your terminal:
mkdir example_package
cd example_package
mkdir folder_1
cd folder_1
vi module.pyNote that we use Vim to create the module.py file in this example. You can use your preferred file editor, such as Emacs or Atom. In module.py, we will import the re module and define a simple function that prints the re version:
import re
def print_re_version():
print(re.__version__)Close the module.py, then complete the following commands from your terminal:
cd ../
vi script.pyInside script.py, we will try to import the module we created.
import module
if __name__ == '__main__':
mod.print_re_version()Let’s run python script.py from the terminal to see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "script.py", line 1, in <module>
import module
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'module'To solve this error, we need to point to the correct path to module.py, which is inside folder_1. Let’s look at the revised code:
import folder_1.module as mod
if __name__ == '__main__':
mod.print_re_version()When we run python script.py, we will get the following result:
2.2.1Lastly, you can encounter the modulenotfounderror when you import a module that is not installed in your Python environment. The simplest way to install requests is to use the package manager for Python called pip. The following instructions are for the major Python version 3.
What is requests?
Requests is an HTTP library for Python. Requests allows you to send HTTP/1.1 requests. Requests does not automatically come installed with Python.
How to install requests on Windows Operating System
You can install pip on Windows by downloading the installation package, opening the command line and launching the installer. You can install pip via the CMD prompt by running the following command.
python get-pip.pyYou may need to run the command prompt as administrator. Check whether the installation has been successful by typing.
pip --versionTo install requests with pip, run the following command from the command prompt.
pip3 install requestsHow to install requests on Mac Operating System
Open a terminal by pressing command (⌘) + Space Bar to open the Spotlight search. Type in terminal and press enter. To get pip, first ensure you have installed Python3:
python3 --versionPython 3.8.8Download pip by running the following curl command:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.pyThe curl command allows you to specify a direct download link. Using the -o option sets the name of the downloaded file.
Install pip by running:
python3 get-pip.pyFrom the terminal, use pip3 to install requests:
pip3 install requestsHow to install requests on Linux Operating System
All major Linux distributions have Python installed by default. However, you will need to install pip. You can install pip from the terminal, but the installation instructions depend on the Linux distribution you are using. You will need root privileges to install pip. Open a terminal and use the commands relevant to your Linux distribution to install pip.
Installing pip for Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint
sudo apt install python-pip3Installing pip for CentOS 8 (and newer), Fedora, and Red Hat
sudo dnf install python-pip3Installing pip for CentOS 6 and 7, and older versions of Red Hat
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install python-pip3Installing pip for Arch Linux and Manjaro
sudo pacman -S python-pipInstalling pip for OpenSUSE
sudo zypper python3-pipOnce you have installed pip, you can install requests using:
pip3 install requestsCheck requests Version
Once you have successfully installed requests, you can use two methods to check the version of requests. First, you can use pip show from your terminal.
pip show requestsName: requests
Version: 2.25.1
Summary: Python HTTP for Humans.
Home-page: https://requests.readthedocs.io
Author: Kenneth Reitz
Author-email: [email protected]
License: Apache 2.0
Location: /Users/Yusufu.Shehu/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages
Requires: urllib3, chardet, idna, certifi
Required-by: tensorboard, Sphinx, requests-oauthlib, jupyterlab-server, conda, conda-repo-cli, conda-build, anaconda-project, anaconda-clientSecond, within your python program, you can import requests and then reference the __version__ attribute:
import requests
print(requests.__version__)2.25.1Installing requests Using Anaconda
Anaconda is a distribution of Python and R for scientific computing and data science. You can install Anaconda by going to the installation instructions. Once you have installed Anaconda, you can install requests using the following command:
conda install -c anaconda requestsSummary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial. The modulenotfounderror occurs if you misspell the module name, incorrectly point to the module path or do not have the module installed in your Python environment. If you do not have the module installed in your Python environment, you can use pip to install the package. However, you must ensure you have pip installed on your system. You can also install Anaconda on your system and use the conda install command to install the requests library.
For further reading on ModuleNotFoundErrors, go to the article: How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘ConfigParser’.
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!
In Python, if you try to import Requests without installing the module using pip, you will get ImportError: no module named requests error.
In this tutorial, let’s look at installing the Requests module correctly in different operating systems and solve no module named requests error.
Requests are not a built-in module (it doesn’t come with the default python installation) in Python, you need to install it explicitly using the pip installer and then use it.
If you are getting an error installing pip checkout pip: command not found to resolve the issue.
Install Requests in OSX/Linux
The recommended way to install the requests module is using pip or pip3 for Python3 if you have pip installed already.
Using Python 2
$ sudo pip install requests
Using Python 3
$ sudo pip3 install requests
Alternatively, if you have easy_install in your system, you can install requests using the below command.
Using easy install
$ sudo easy_install -U requests
For CentOs
$ yum install python-requests
For Ubuntu
To install requests module on Debian/Ubuntu for Python2:
$ sudo apt-get install python-requests
And for Python3, the command is:
$ sudo apt-get install python3-requests
Install Requests in Windows
In the case of windows, you can use pip or pip3 based on the Python version you have to install the requests module.
$ pip3 install requests
If you have not added the pip to the environment variable path, you can run the below command in Python 3, which will install the requests module.
$ py -m pip install requests
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Sign Up for Our Newsletters
Subscribe to get notified of the latest articles. We will never spam you. Be a part of our ever-growing community.
By checking this box, you confirm that you have read and are agreeing to our terms of use regarding the storage of the data submitted through this form.
Today I am trying to use the requests package in my python app But I am facing the following error: ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ in Python. In this Exerror article, We are going to learn about How to reproduce this error and we will discuss All Possible Solutions Let’s Get Start With This Article.
Contents
- How ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error Occurs?
- How To Solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error?
- Solution 1: Install the Request package
- Solution 2: Package is Installed for different Version
- Solution 3: Install For Virtual Env
- Solution 4: Select Python interpreter
- Solution 5: Check requests is Installed or Not
- Solution 6: Reinstall Package
- Conclusion
How ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error Occurs?
I am trying to use the requests package in my python app But I am facing the following error.
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'requests'So here I am writing all the possible solutions that I have tried to resolve this error.
How To Solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error?
- How To Solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error?
To Solve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error Sometimes You have installed python for different versions Just like You are using Python3 and You have installed a request for Python2 then you will face a module not found error. So First of all check which version of python are you using. Just run this command: python –version. Now, You know You are using Python 3.10 then you can install the request package for Python 3.10 By just running this command: pip3.10 install requests And now, You can use requests without any error. Thank You.
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error Occurs whenever you don’t have the Request package installed so You just need to install the request package and then your error will be solved. First of all open your terminal and just run the following. If You are using Python 2 then run this command: pip install requests And then you can import it and you can use it without facing any error. Thank you.
Solution 1: Install the Request package
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’ Error Occurs whenever you don’t have the Request package installed so You just need to install the request package and then your error will be solved.
First of all open your terminal and just run the following. If You are using Python 2 then run this command.
pip install requests
And If you are using python3 then run the following command.
pip3 install requestsYou don’t have pip in the Path variable then you can run this command.
python -m pip install requestsAnd if you are using python3 and your Pip is not settled into the path variable then run this command.
python3 -m pip install requestsAnd then you can import it and you can use it without facing any error. Just like this.
import requests
res = requests.get('your_url_here')
print(res)Thanks.
Solution 2: Package is Installed for different Version
Sometimes You have installed python for different versions Just like You are using Python3 and You have installed a request for Python2 then you will face a module not found error. So First of all check which version of python are you using. Just run this command.
python --version
And Your Output will be something like this.
C:Usersssc>python --version
Python 3.10.4Now, You know You are using Python 3.10 then you can install the request package for Python 3.10 By just running this command.
pip3.10 install requestsAnd now, You can use requests without any error. Thank You.
Solution 3: Install For Virtual Env
If you are using a virtual environment then You need to install the request package for your particular virtual env. First of all You can create new virtual env if you don’t have.
python3 -m venv venvThen activate it by running this command.
source venv/bin/activate # macOS
venvScriptsactivate.bat # Windowsand then You can install requests in this environment.
pip install requestsNow, Your error must be solved. Thanks.
Solution 4: Select Python interpreter
Make Sure You are using the Right Python interpreter If You are using VS Code then Press CTRL + Shift + P OR Command + Shift + P to Open the command palette. And then type Python select interpreter and then select Desire version of Python and your error will be solved. Thank you.
Solution 5: Check requests is Installed or Not
If You are still facing an error then First of all check request module is actually installed or not. Just run this command in your terminal.
pip3 show requests
OR
python3 -m pip show requests
By running pip3 show requests command it will show you package is installed or not. If you don’t have requests installed then run this command.
pip3 install requests
OR
python3 -m pip install requests
Now, Your error will be solved. Thank You.
Solution 6: Reinstall Package
First of all Just uninstall requests by running this command.
pip3 uninstall requests
OR
python3 -m pip uninstall requestsand then run this command to install the package.
pip3 install requests
OR
python3 -m pip install requestsand Now, Your error must be solved. Thanks.
Conclusion
It’s all About this error. I hope We Have solved Your error. Comment below Your thoughts and your queries. Also, Comment below which solution worked for you?
Also, Read
- ValueError: I/O operation on closed file in Python
- An unhandled exception occurred: catch clause variable is not an Error instance
- fatal: detected dubious ownership in repository
- Composer detected issues in your platform: Your Composer dependencies require a PHP version
- Unable to locate file in Vite manifest: resources/css/app.css
Importerror: no module named requests error comes into the picture when the requests module not available or uninstalled. In this article, We will see various ways to install the requests python package.
Let’s see the various ways to install the requests module for fixing the bug no module named requests.
1.Use pip for requests module-
The easiest and popular way to install the requests package is a pip. Let’s directly jump into the command section. Use the below command.
pip install requestsIf you are specifically using a python 3 interpreter and you want to install the requests package. You may use the alternative command.
pip3 install requestsIn case you have already installed the pip manager but the path is not proper. You may use the below command.
python -m pip install requestsOf course like we have specifically done python3 in the place of python. The same rules apply here.
python3 -m pip install requests2. Use easy install for requests module-
Like pip package manager, we may use an easy install package. Here is the command for this.
sudo easy_install -U requests3. Use System package manager ( Linux family OS only) –
This will only work with linux family OS like centos and Ubuntu. You may use yum or apt-get package manager. Here is the command for them.
apt-get install python-requestsLets try the yum also.
yum install python-requestsRequest package is useful in invoking the rest of APIs and sending HTTP/1.1 requests. It has so many configurations which make the Sessions with Cookie Persistence extremely easy. It also supports Browser-style TLS/SSL Verification seamless. You may also parameterize the Connection Timeouts with the requests package.
Conclusion –
The python module requests are one of the most common and useful modules for every python developer. I hope this article must help you in resolving the bug ( importerror: no module named requests ).
Thanks
Data Science Learner Team
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.
Are you trying to run python program and getting "ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'requests" error ? Do you want to Know how to solve "ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'requests'" error ? Do you want to know how to install a Python module on RHEL/CentOS Based Servers ? If you are looking answer for all these queries then you have reached the correct place. In this article, I will show you how to install Python requests module if it is currently missing in your server. You can install this or any other python modules by using 2 different ways. Both ways are explained below with examples.
Also Read: How to Properly Search PHP Modules using YUM tool in Linux(RHEL/CentOS 7/8)
If you are getting «ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests'» error then it means either requests module is not installed or if it is installed then python is not able to find it. If it is not installed then you can easily install by using python3 -m pip install requests command as shown below. Here you can notice that for this command to work you need to have python3 installed in your Server. If you don’t have python3 installed in your Server then you can install it by using yum install python3 -y command. Now if you run the python program again you won’t see «ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests'» error.
[root@localhost ~]# python3 -m pip install requests WARNING: Running pip install with root privileges is generally not a good idea. Try `__main__.py install --user` instead. Collecting requests Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/45/1e/0c169c6a5381e241ba7404532c16a21d86ab872c9bed8bdcd4c423954103/requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 71kB 1.8MB/s Collecting certifi>=2017.4.17 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5e/c4/6c4fe722df5343c33226f0b4e0bb042e4dc13483228b4718baf286f86d87/certifi-2020.6.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (156kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 163kB 1.8MB/s Collecting idna<3,>=2.5 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a2/38/928ddce2273eaa564f6f50de919327bf3a00f091b5baba8dfa9460f3a8a8/idna-2.10-py2.py3-none-any.whl (58kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 4.7MB/s Collecting chardet<4,>=3.0.2 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/a9/01ffebfb562e4274b6487b4bb1ddec7ca55ec7510b22e4c51f14098443b8/chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 143kB 4.1MB/s Collecting urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/56/aa/4ef5aa67a9a62505db124a5cb5262332d1d4153462eb8fd89c9fa41e5d92/urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 133kB 4.7MB/s Installing collected packages: certifi, idna, chardet, urllib3, requests Successfully installed certifi-2020.6.20 chardet-3.0.4 idna-2.10 requests-2.24.0 urllib3-1.25.11
Other way that you can use to install requests module is through pip3.6 tool. You can use simply use pip3.6 install requests command to install requests module in your Server. You don’t require yum tool here. Here you only need to make sure that you have pip3.6 tool available as per the python version that you are going to use. Since here we are using python3 so we need to use pip3.6 to install modules for this version. If you don’t have this pip version installed then you can install it by using yum install python3-pip -y command.
[root@localhost ~]# pip3.6 install requests WARNING: Running pip install with root privileges is generally not a good idea. Try `pip3.6 install --user` instead. Collecting requests Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/45/1e/0c169c6a5381e241ba7404532c16a21d86ab872c9bed8bdcd4c423954103/requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 71kB 2.0MB/s Collecting certifi>=2017.4.17 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5e/c4/6c4fe722df5343c33226f0b4e0bb042e4dc13483228b4718baf286f86d87/certifi-2020.6.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (156kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 163kB 1.9MB/s Collecting urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/56/aa/4ef5aa67a9a62505db124a5cb5262332d1d4153462eb8fd89c9fa41e5d92/urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 133kB 4.3MB/s Collecting chardet<4,>=3.0.2 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/a9/01ffebfb562e4274b6487b4bb1ddec7ca55ec7510b22e4c51f14098443b8/chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 143kB 4.2MB/s Collecting idna<3,>=2.5 (from requests) Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a2/38/928ddce2273eaa564f6f50de919327bf3a00f091b5baba8dfa9460f3a8a8/idna-2.10-py2.py3-none-any.whl (58kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 5.7MB/s Installing collected packages: certifi, urllib3, chardet, idna, requests Successfully installed certifi-2020.6.20 chardet-3.0.4 idna-2.10 requests-2.24.0 urllib3-1.25.11
Similarly, you can install other python modules as well by using pip3.6 install <python_module> command. If you want to uninstall requests module then you can do it by using pip3.6 uninstall requests command as shown below. So you can use pip3.6 tool for installation as well as for uninstallation of python modules. More can be checked on pip Official Documentation.
[root@localhost ~]# pip3.6 uninstall requests Uninstalling requests-2.24.0: /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/DESCRIPTION.rst /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/INSTALLER /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/LICENSE.txt /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/METADATA /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/RECORD /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/WHEEL /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/metadata.json /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests-2.24.0.dist-info/top_level.txt /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__init__.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/__init__.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/__version__.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/_internal_utils.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/adapters.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/api.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/auth.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/certs.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/compat.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/cookies.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/exceptions.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/help.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/hooks.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/models.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/packages.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/sessions.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/status_codes.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/structures.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__pycache__/utils.cpython-36.pyc /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/__version__.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/_internal_utils.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/adapters.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/api.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/auth.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/certs.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/compat.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/cookies.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/exceptions.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/help.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/hooks.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/models.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/packages.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/sessions.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/status_codes.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/structures.py /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/requests/utils.py Proceed (y/n)? y Successfully uninstalled requests-2.24.0
Popular Recommendations:-
Solved: FATAL: Authentication Helper Program /usr/lib/squid/basic_ncsa_auth: (2) No Such File or Directory
How to Install and Configure Squid Proxy Server on RHEL/CentOS 7/8
Primitive Data Types in Java — int, char, byte, short, long, float, double and boolean
5 Best Ways to Become root user or Superuser in Linux (RHEL/CentOS/Ubuntu)
11 Best Python OS Module Examples on Linux
How to Install MariaDB 5.5 Server on RHEL/CentOS 7 Linux with Easy Steps
6 Simple Steps to Change/Reset MariaDB root password on RHEL/CentOS 7/8
Best Steps to Install Java on RHEL 8/CentOS 8
Quick Fix: Python raises the ImportError: No module named 'requests' when it cannot find the library requests. The most frequent source of this error is that you haven’t installed requests explicitly with pip install requests. Alternatively, you may have different Python versions on your computer, and requests is not installed for the particular version you’re using.
Problem Formulation
You’ve just learned about the awesome capabilities of the requests library and you want to try it out, so you start your code with the following statement:
import requests
This is supposed to import the Pandas library into your (virtual) environment. However, it only throws the following ImportError: No module named requests:
>>> import requests
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module>
import requests
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'requests'
Solution Idea 1: Install Library requests
The most likely reason is that Python doesn’t provide requests in its standard library. You need to install it first!
Before being able to import the Pandas module, you need to install it using Python’s package manager pip. Make sure pip is installed on your machine.
To fix this error, you can run the following command in your Windows shell:
$ pip install requests
This simple command installs requests in your virtual environment on Windows, Linux, and MacOS. It assumes that your pip version is updated. If it isn’t, use the following two commands in your terminal, command line, or shell (there’s no harm in doing it anyways):
$ python -m pip install --upgrade pip $ pip install pandas
💡 Note: Don’t copy and paste the $ symbol. This is just to illustrate that you run it in your shell/terminal/command line.
Solution Idea 2: Fix the Path
The error might persist even after you have installed the requests library. This likely happens because pip is installed but doesn’t reside in the path you can use. Although pip may be installed on your system the script is unable to locate it. Therefore, it is unable to install the library using pip in the correct path.
To fix the problem with the path in Windows follow the steps given next.
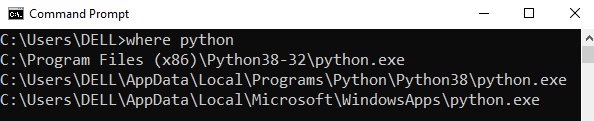
Step 1: Open the folder where you installed Python by opening the command prompt and typing where python
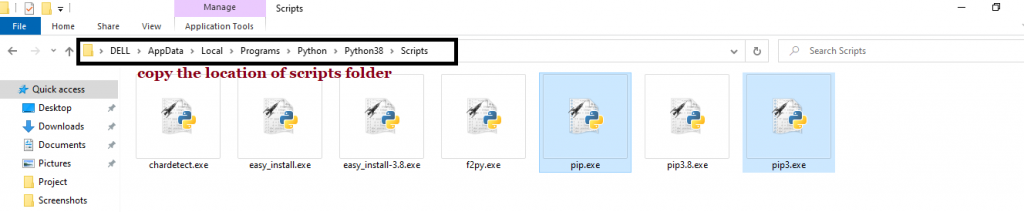
Step 2: Once you have opened the Python folder, browse and open the Scripts folder and copy its location. Also verify that the folder contains the pip file.
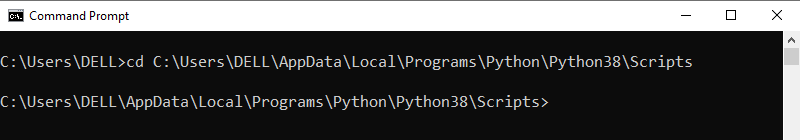
Step 3: Now open the Scripts directory in the command prompt using the cd command and the location that you copied previously.
Step 4: Now install the library using pip install requests command. Here’s an analogous example:
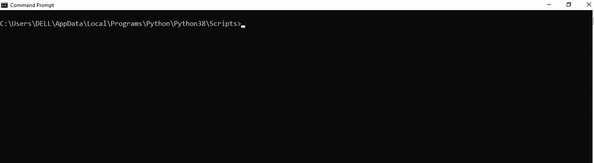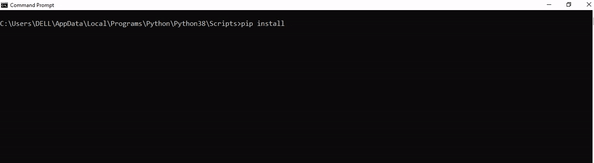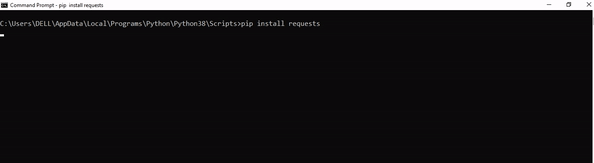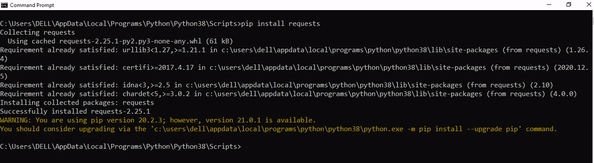
After having followed the above steps, execute our script once again. And you should get the desired output.
Other Solution Ideas
- The
ModuleNotFoundErrormay appear due to relative imports. You can learn everything about relative imports and how to create your own module in this article. - You may have mixed up Python and pip versions on your machine. In this case, to install
requestsfor Python 3, you may want to trypython3 -m pip install requestsor evenpip3 install requestsinstead ofpip install requests - If you face this issue server-side, you may want to try the command
pip install --user requests - If you’re using Ubuntu, you may want to try this command:
sudo apt install requests - You can check out our in-depth guide on installing
requestshere. - You can also check out this article to learn more about possible problems that may lead to an error when importing a library.
Understanding the “import” Statement
import requests
In Python, the import statement serves two main purposes:
- Search the module by its name, load it, and initialize it.
- Define a name in the local namespace within the scope of the
importstatement. This local name is then used to reference the accessed module throughout the code.
What’s the Difference Between ImportError and ModuleNotFoundError?
What’s the difference between ImportError and ModuleNotFoundError?
Python defines an error hierarchy, so some error classes inherit from other error classes. In our case, the ModuleNotFoundError is a subclass of the ImportError class.
You can see this in this screenshot from the docs:
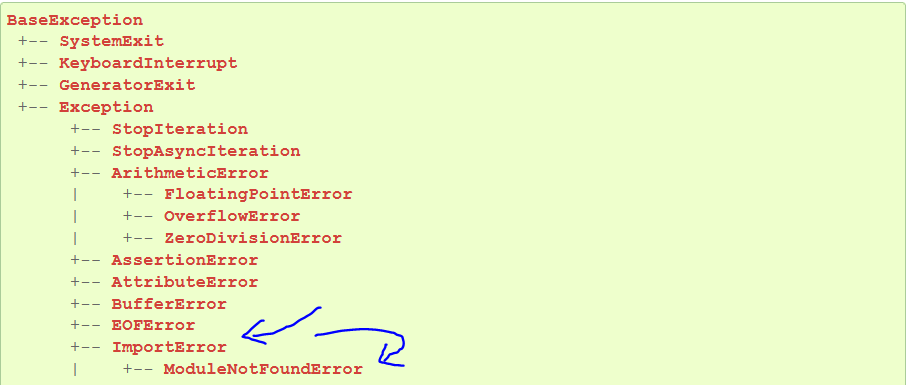
You can also check this relationship using the issubclass() built-in function:
>>> issubclass(ModuleNotFoundError, ImportError) True
Specifically, Python raises the ModuleNotFoundError if the module (e.g., requests) cannot be found. If it can be found, there may be a problem loading the module or some specific files within the module. In those cases, Python would raise an ImportError.
If an import statement cannot import a module, it raises an ImportError. This may occur because of a faulty installation or an invalid path. In Python 3.6 or newer, this will usually raise a ModuleNotFoundError.
Related Videos
The following video shows you how to resolve the ImportError:
How to Fix : “ImportError: Cannot import name X” in Python?
The following video shows you how to import a function from another folder—doing it the wrong way often results in the ModuleNotFoundError:
How to Call a Function from Another File in Python?
How to Fix “ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘requests’” in PyCharm
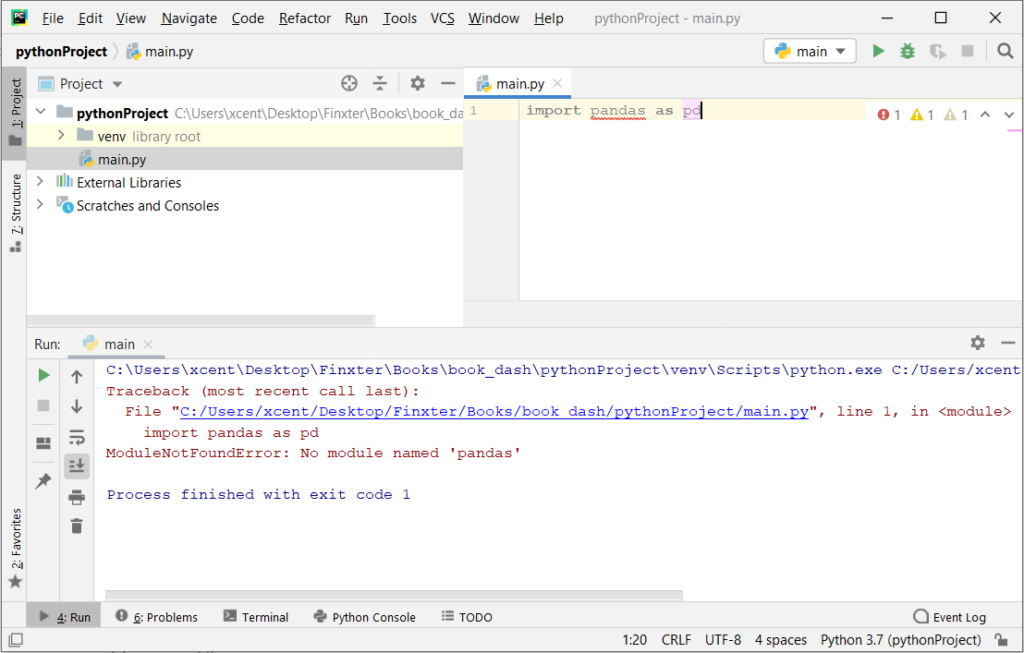
If you create a new Python project in PyCharm and try to import the requests library, it’ll raise the following error message:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/Users/.../main.py", line 1, in <module>
import requests
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'requests'
Process finished with exit code 1
The reason is that each PyCharm project, per default, creates a virtual environment in which you can install custom Python modules. But the virtual environment is initially empty—even if you’ve already installed requests on your computer!
Here’s a screenshot exemplifying this for the pandas library. It’ll look similar for requests.
The fix is simple: Use the PyCharm installation tooltips to install Pandas in your virtual environment—two clicks and you’re good to go!
First, right-click on the pandas text in your editor:
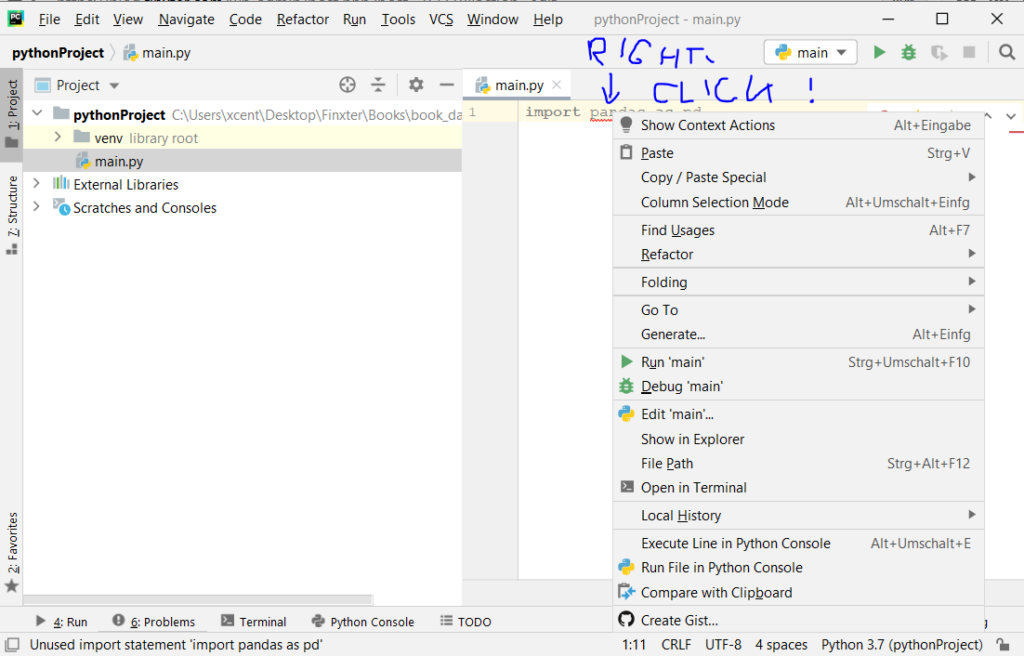
Second, click “Show Context Actions” in your context menu. In the new menu that arises, click “Install Pandas” and wait for PyCharm to finish the installation.
The code will run after your installation completes successfully.
As an alternative, you can also open the Terminal tool at the bottom and type:
$ pip install requests
If this doesn’t work, you may want to set the Python interpreter to another version using the following tutorial: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/2016.1/configuring-python-interpreter-for-a-project.html
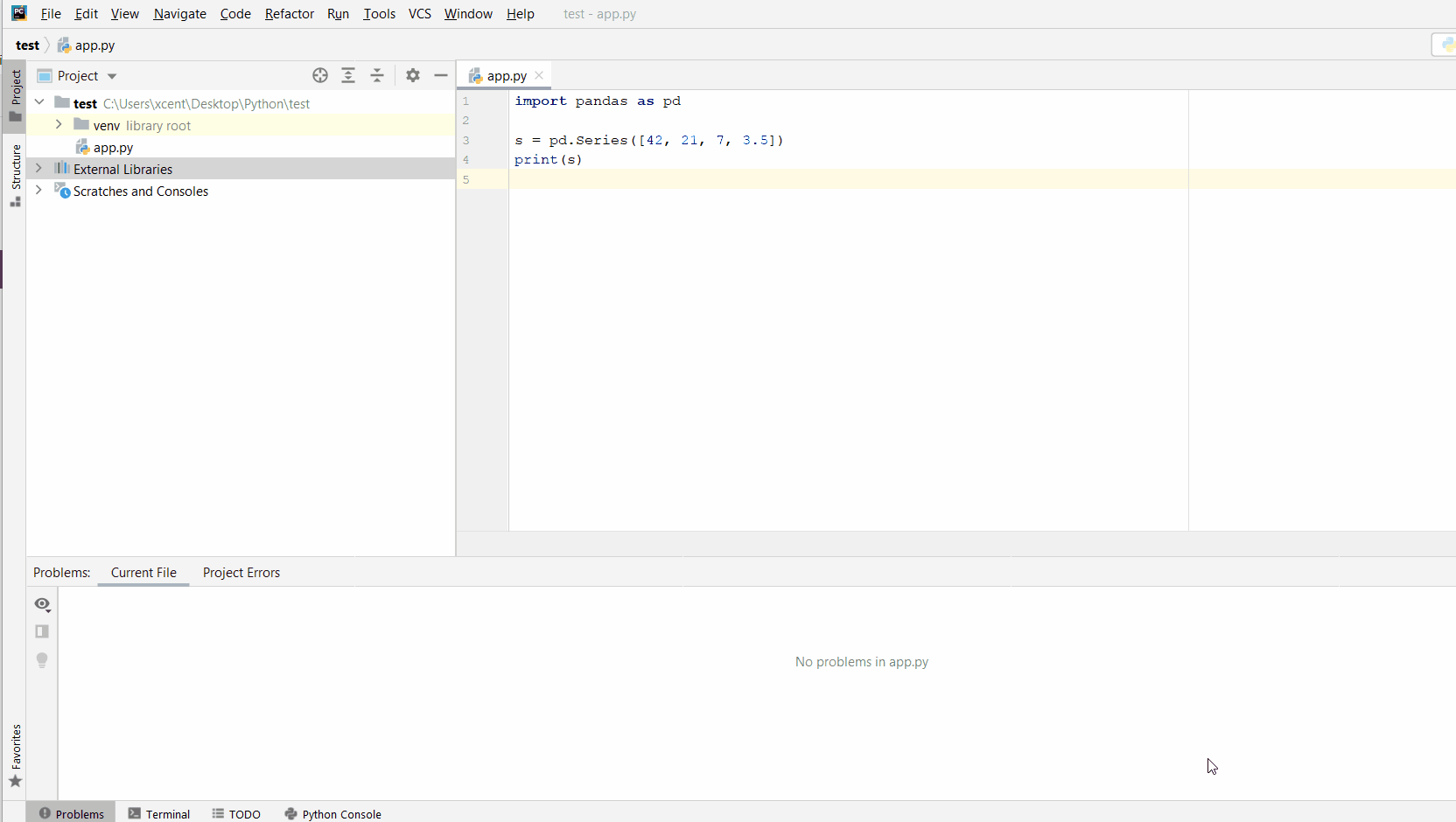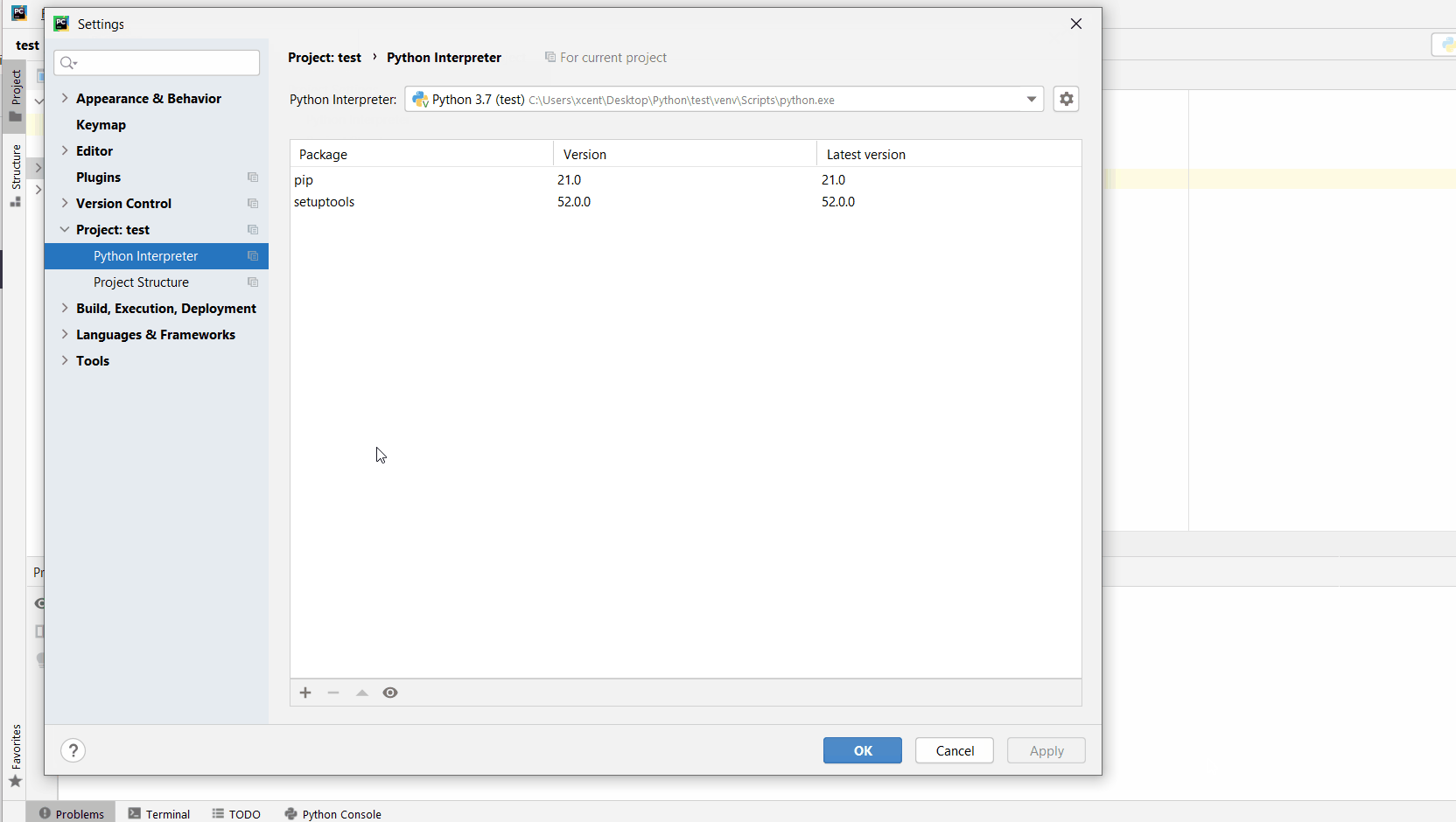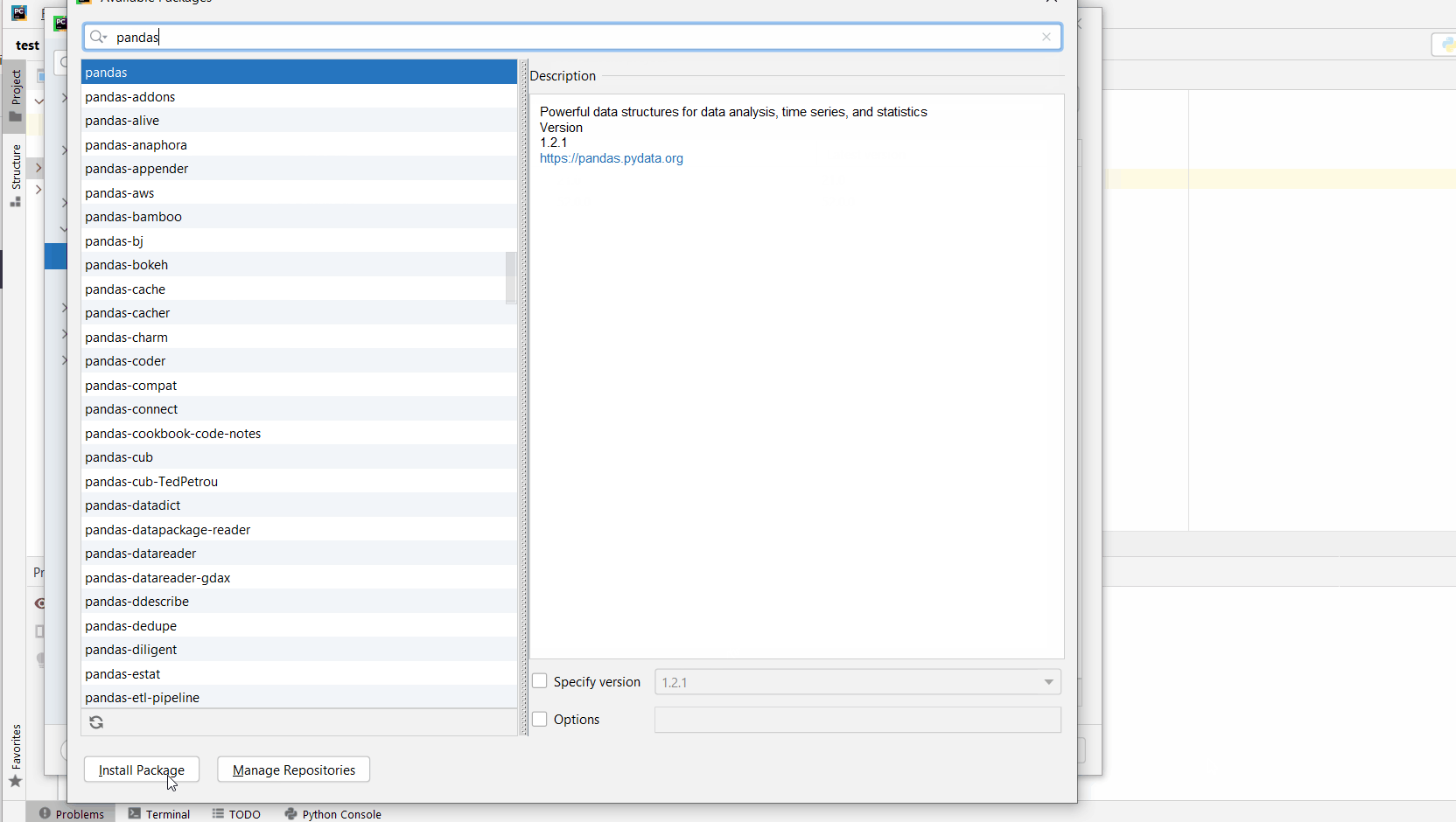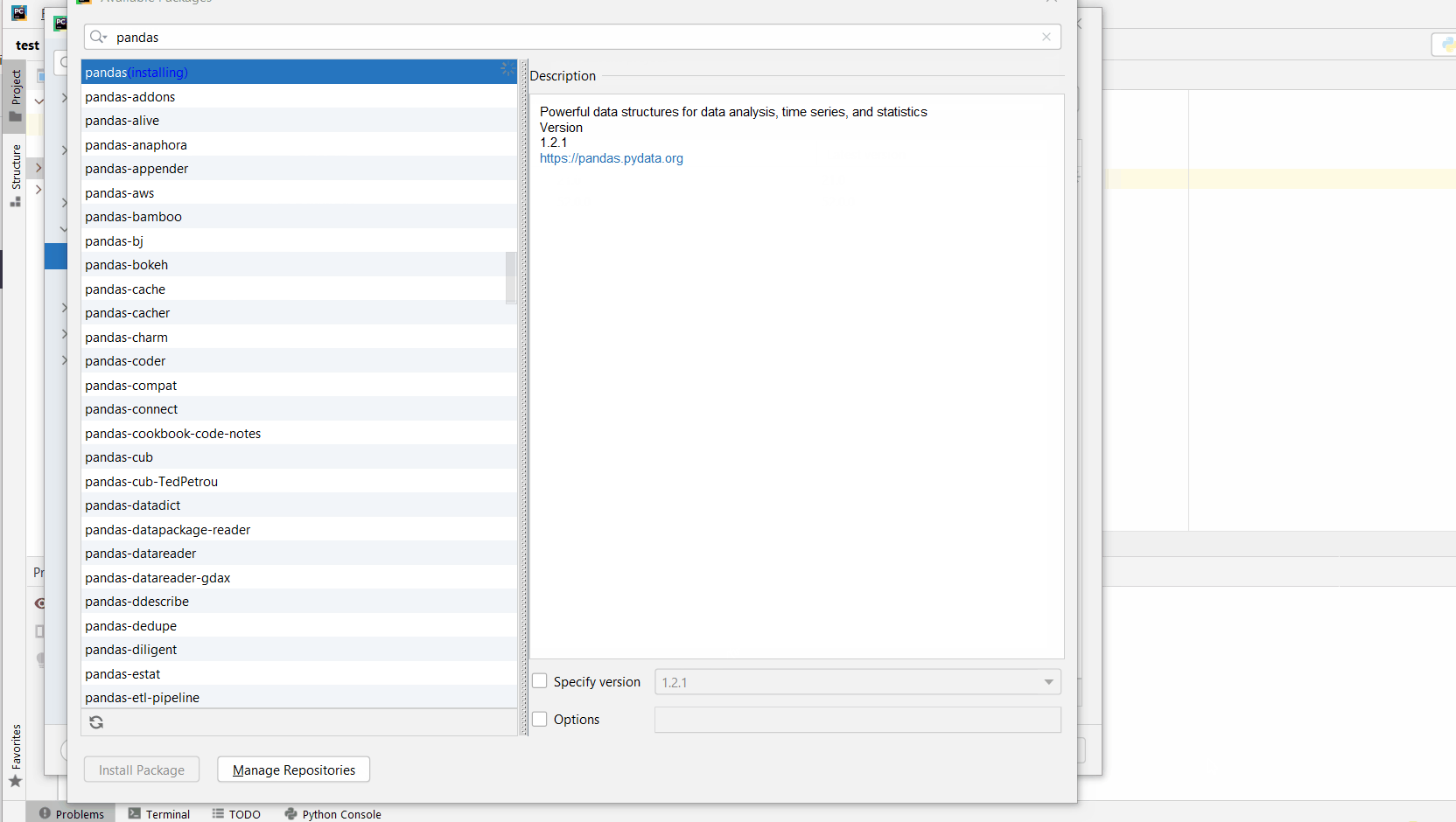
You can also manually install a new library such as requests in PyCharm using the following procedure:
- Open
File > Settings > Projectfrom the PyCharm menu. - Select your current project.
- Click the
Python Interpretertab within your project tab. - Click the small
+symbol to add a new library to the project. - Now type in the library to be installed, in your example Pandas, and click
Install Package. - Wait for the installation to terminate and close all popup windows.
Here’s an analogous example:
Here’s a full guide on how to install a library on PyCharm.
- How to Install a Library on PyCharm
While working as a researcher in distributed systems, Dr. Christian Mayer found his love for teaching computer science students.
To help students reach higher levels of Python success, he founded the programming education website Finxter.com. He’s author of the popular programming book Python One-Liners (NoStarch 2020), coauthor of the Coffee Break Python series of self-published books, computer science enthusiast, freelancer, and owner of one of the top 10 largest Python blogs worldwide.
His passions are writing, reading, and coding. But his greatest passion is to serve aspiring coders through Finxter and help them to boost their skills. You can join his free email academy here.