Table of Contents
Hide
- Python FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
- Example FileNotFoundError
- Misspelled file name
- Invalid file path or directory path
- Using a relative path
- Solution to FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
In Python, when you reference a file, it needs to exist. Otherwise, Python will return a FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory.
In this tutorial, let’s look at what is FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory error means and how to solve this in your code.
Python will raise FileNotFoundError when you use the OS library and try to read a file or write a file that does not exist using an open() statement.
It is, of course, excluding you are creating a new file and writing content to the file. Any error message which states FileNotFoundError means that Python cannot find the path of the file you are referencing.
Example FileNotFoundError
The below code will list all the files in a specified folder. We will be using the OS module and os.listdir() method to get a list of files in the specified folder.
import os
for f in os.listdir("/etc"):
print(f)Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "Main.py", line 2, in <module>
for f in os.listdir("/etc/test"):
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/etc/test'Now you can see that Python is throwing FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory since the folder reference is wrong here.
The possible reasons for this error could be as follows.
Misspelled file name
The error will often occur due to misspelled filenames, so providing the correct file name would solve the issue.
Invalid file path or directory path
Sometimes you might give a wrong file path or directory path which does not exist. It usually happens even with the network path when it’s unreachable. So ensure that the file path is correct and if you are placing the file in the network path, make sure it’s reachable and accessible.
Using a relative path
If you use a relative path, the file would be searched in the current working directory and not in the original path. So ensure you give an absolute path of the file to resolve the error.
Solution to FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
We will correct our above code by referencing the proper directory where the file exists. This time, we will also use an absolute path instead of a relative path to ensure it’s referencing the correct directory.
import os
for f in os.listdir("C:/Projects/Tryouts/etc"):
print(f)Output
python.txt
index.md
Python Data Science Ebook.pdf
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Sign Up for Our Newsletters
Subscribe to get notified of the latest articles. We will never spam you. Be a part of our ever-growing community.
By checking this box, you confirm that you have read and are agreeing to our terms of use regarding the storage of the data submitted through this form.
Like any programming language, an error in python occurs when a given code fails to follow the syntax rules. When a code does not follow the syntax, python cannot recognize that segment of code, so it throws an error. Errors can be of different types, such as runtime error, syntax error, logical error, etc. IOError errno 2 no such file or directory is one such type of error. Let us first understand each individual term of the error.
Note : Starting from Python 3.3, IOError is an aliases of OSError
What is IOError?
An IOError is thrown when an input-output operation fails in the program. The common input-output operations are opening a file or a directory, executing a print statement, etc. IOError is inherited from the EnvironmentError. The syntax of IOError is:
IOError : [Error number] ‘Reason why the error occurred’: ‘name of the file because of which the error occurred’
Examples of IOError are :
- Unable to execute the open() statement because either the filename is incorrect or the file is not present in the specified location.
- Unable to execute the print() statements because either the disk is full or the file cannot be found
- The permission to access the particular file is not given.
What is errno2 no such file or directory?
The ‘errorno 2 no such file or directory‘ is thrown when you are trying to access a file that is not present in the particular file path or its name has been changed.
This error is raised either by ‘FileNotFoundError’ or by ‘IOError’. The ‘FileNotFoundError’ raises ‘errorno 2 no such file or directory‘ when using the os library to read a given file or a directory, and that operation fails.
The ‘IOError’ raises ‘errorno 2 no such file or directory‘ when trying to access a file that does not exist in the given location using the open() function.
Handling ‘IOError [errorno 2] no such file or directory’
‘IOError errorno 2 no such file or directory‘ occurs mainly while we are handling the open() function for opening a file. Therefore, we will look at several solutions to solve the above error.
We will check if a file exists, raise exceptions, solve the error occurring while installing ‘requirements.txt,’ etc.
Checking if the file exists beforehand
If a file or a directory does not exist, it will show ‘IOError [errorno 2] no such file or directory’ while opening it. Let us take an example of opening a file named ‘filename.txt’.
The given file does not exist and we shall see what happens if we try to execute it.
Since the above text file does not exist, it will throw the IOError.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 1, in <module>
f = open('filename.txt')
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'filename.txt'
To avoid the above error from being thrown, we will use several methods which will first check if the file exists or not. It will execute the open() function only if the file exists.
We have two modules containing functions for checking if a file exists.
- OS Module
- Pathlib Module
Using the OS Module
In the os module, there are three functions which can be used:
- os.path.isfile()
- os.path.isdir()
- os.path.exists()
To solve the IOError, we can use either of the above function in a condition statement. We will pass the pathname of the file as an argument to the above functions.
If the file or the directory exists, the function shall return True else False. Bypassing either of the above functions as the conditional statement ensures that python will open a file only if it exists, thus preventing an error from occurring.
We will use os.path.isfile() when we want to check if a file exists or not, os.path.isdir() to check if a directory exists or not and os.path.exists() to check if a path exists or not.
Since we want to check for a file, we can use either the os.path.isfile() function or os.path.exists() function. We shall apply the function to the above example.
import os
path_name = "filename.txt"
if os.path.isfile(path_name):
print("File exists")
f = open(path_name)
#Execute other file operations here
f.close()
else:
print("File does not exist! IOError has occured")
First, we have imported the os module. Then we have a variable named ‘path_name‘ which stores the path for the file.
We passed the path_name as an argument to the os.path.isfile() function. If the os.path.isfile() function returns a true value. Then it will print “File exists” and execute the other file operations.
If the file does not exist, then it will print the second statement in the else condition. Unlike the previous case, here, it will not throw an error and print the message.
File does not exist! IOError has occured
Similarly, we can also use os.path.exists() function.
Using the pathlib module
The pathlib module contains three functions – pathlib.Path.exists(), pathlib.Path.is_dir() and pathlib.Path.is_file().
We will use pathlib.Path.is_file() in this example. Just like the os module, we will use the function in an if conditional statement.
It will execute the open() function only if the file exists. Thus it will not throw an error.
from pathlib import Path
path_name = "filename.txt"
p = Path(path_name)
if p.is_file():
print("File exists")
f = open(path_name)
#Execute other file operations here
f.close()
else:
print("File does not exist! IOError has occured")
Since the file does not exist, the output is :
File does not exist! IOError has occured
Using try – except block
We can also use exception handling for avoiding ‘IOError Errno 2 No Such File Or Directory’. In the try block, we will try to execute the open() function.
If the file is present, it will execute the open() function and all the other file operations mentioned in the try block. But, if the file cannot be found, it will throw an IOError exception and execute the except block.
try:
f = open("filename.txt")
#Execute other operations
f.close()
except IOError as io:
print(io)
Here, it will execute the except block because ‘filename.txt’ does not exist. Instead of throwing an error, it will print the IOError.
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'filename.txt'
We can also print a user defined message in the except block.
try:
f = open("filename.txt")
#Execute other operations
f.close()
except IOError:
print("File does not exist. IOError has occured")
The output will be:
File does not exist. IOError has occured
IOError errno 2 no such file or directory in requirements.txt
Requirements.txt is a file containing all the dependencies in a project and their version details.
Basically, it contains the details of all the packages in python needed to run the project. We use the pip install command to install the requirements.txt file. But it shows the ‘IOError errno 2 no such file or directory’ error.
!pip install -r requirements.txt
The thrown error is:
ERROR: Could not open requirements file: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'requirements.txt'
To solve the above error, we use the pip freeze command. When we use pip freeze, the output will contain the package along with its version.
The output will be in a configuration that we will use with the pip install command.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
Now, we will try to execute the pip install command again. It will no longer throw errors and all the packages will be installed successfully.
Opening file in ‘w+’ mode
While trying to open a text file, the default mode will be read mode. In that case, it will throw the ‘IOError Errno 2 No Such File Or Directory’ error.
f = open("filename.txt")
f.close()
print("Successful")
The output is:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 1, in <module>
f = open("filename.txt")
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'filename.txt'
To solve the error, we can open the file in ‘w+’ mode. This will open the file in both – reading and writing mode. If the file does not exist, it will create a new file, and if the file exists, it will overwrite the contents of the file. This way, it will not throw an error.
f = open("filename.txt", 'w+')
f.close()
print("Successful")
The output is:
Successful
Apart from all the above methods, there are some ways to ensure that the IOError does not occur. You have to ensure that you are giving the absolute path as the path name and not simply the name of the file.
Also, see to that there are no escape sequences in the path name of this file.
For example : In path_name = "C:name.txt ", it will consider the 'n' from 'name.txt' as an escape sequence. So, it will not be able to find the file 'name.txt'.
Also, Read
- How to Solve “unhashable type: list” Error in Python
- How to solve Type error: a byte-like object is required not ‘str’
- Invalid literal for int() with base 10 | Error and Resolution
- How to Solve TypeError: ‘int’ object is not Subscriptable
What is the difference between FileNotFoundError and IOError
Both the errors occur when you are trying to access a file that is not present in the particular file path, or its name has been changed. The difference between the two is that FileNotFoundError is a type of OSError, whereas IOError is a type of Environment Error.
This sums up everything about IOError Errno 2 No Such File Or Directory. If you have any questions, do let us know in the comments below.
Until then, Keep Learning!
Filenotfounderror Errno 2 no such file or directory is a python error always comes when you are not defining proper path for the file or file does not exist in the directory. In this entire tutorial, you will know how to solve Filenotfounderror Errno 2 no such file or directory in an easy way in different scenarios.
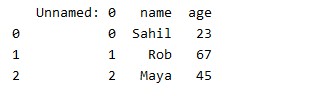
Before going to the various scenarios let’s create a sample CSV file using the panda’s library. The file will contain the name and age of the person. Execute the below line of code to create a person.csv file. It is only for demonstration purposes. You can move to cases if you are already getting the problem.
import pandas as pd
data = {"name":["Sahil","Rob","Maya"],"age":[23,67,45]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_csv("person.csv")It will save the person.csv file to the current working directory of the project.
Case 1: File Name is Incorrect
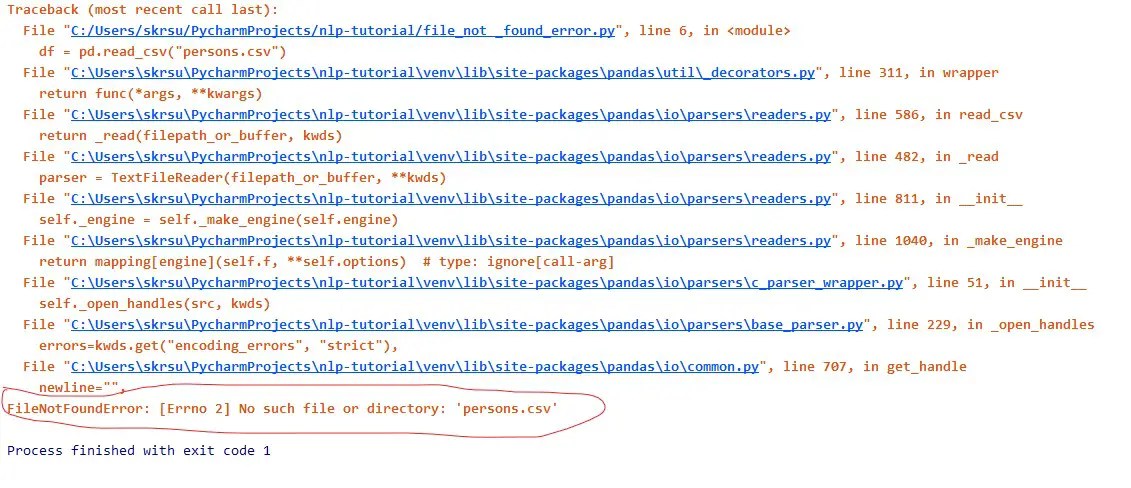
If you are reading the CSV file with the incorrect name then you will get this Filenotfounderror Errno 2 with no such file or directory error. For example, instead of reading the person.csv filename, I am reading persons.csv. Then you will get this filenotfounderror.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("persons.csv")
print(df)Solution
Check the name of the file and write the correct filename with its type.
Case 2: Using the OS Library
Filenotfounderror Errno 2 no such file or directory error also comes when you are using the OS Python library and defining the wrong path. For example, I am passing the wrong path for filename “persons.csv”. It will give me an error.
Solution
Check the path of the working directory and then define the path.
Case 3: Passing the wrong file name or path for the open() method
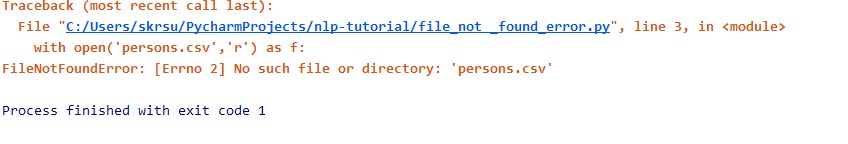
The third case is when this error comes when you are reading the file using the open() method and passing the wrong filename.
import csv
with open('persons.csv','r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
print(row)Solution :
The solution to this problem, in this case, is very simple. Check the filename of the file you want to open and then pass the exact path for the filename for that file. To know the current working directory you have to use the os.getcwd(). The error will be solved.
['', 'name', 'age'] ['0', 'Sahil', '23'] ['1', 'Rob', '67'] ['2', 'Maya', '45']
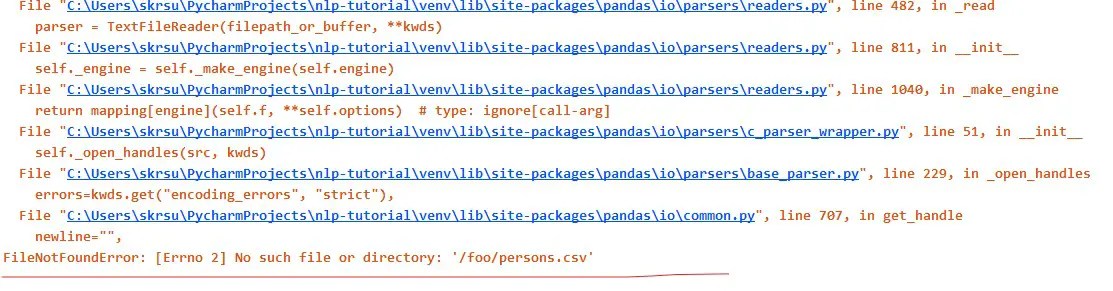
Case 4: Wrong Directory
In most of the cases, Filenotfounderror no such file or directory error comes when you are defining the wrong path for the filename.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("/foo/persons.csv")
print(df)Solution
The solution of this case is that if have forgotten the path for the filename then you have to use the OS library. There is a method for finding the path and it is os.getcwd() and then use it with the filename. Execute the following lines of code.
import pandas as pd
import os
cwd = os.getcwd()
df = pd.read_csv(f'{cwd}/person.csv')
print(df)Now you will get the output.
Conclusion
This type of error is mostly annoying to every programmer. They often get this error. These are the cases for various scenarios where its solution is very simple. I hope you have liked this tutorial. If you have any queries then you can contact us for more help.
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.
When we read data from a file using Python there, we need to specify the file name. And that file needs to exist in the specified directory. If the file we are referencing in our program does not exist in the specified directory or folder, we will receive the
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
Error.
In this Python guide, we will walk through this error in detail and solve it. We will also discuss an example to demonstrate this error in Python. So let’s get started with the error statement.
The error statement
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
can be divided into two parts
- FileNotFoundErrro (Exception Type)
- [Error 2] No such file or directory
1. FileNotFoundError
This
FileNotFoundError
is one of the standard Python exceptions. It comes under the base exception of OSError. It is raised in a Python program when we try to access a file or directory that does not exist.
2. [Errno 2] No such file or directory
The
[[Errno 2] No such file or directory]
statement is the actual error message telling us that the file or directory we want to access in our Python program does not exist.
Common Example Scenario
Let’s discuss this error statement with an example. In Python File Handling, we can read, write and append data between the files. But in the case of reading the data from a file, the file needs to be present in the specified directory. And while mentioning the file for reading, we also need to specify its full name, including the file extension. If we pass a file name that does not exist in the specified directory or even forget to specify the full name, we will receive the FileNotFoundError.
Example (Error)
Let’s say we want to read data from our
data.txt
file, and while opening the file using the context manager
with
we do not mention the
.txt
extension, then see what happens to the program when we run it.
# file name
filename = 'data'
# read the file
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
print(file.read())
Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 5, in
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'data'
Break the code
In this example, we are getting the error in line 5 with »
with open(filename, 'r') as file
» statement. This error was raised because the Python open() function was not able to find any
data
file in the directory.
Solution
To solve the above problem, we need to make sure that the file we want to read mentions its full name. And in the above example, we are supposed to read the
data.txt
file not
data
.
Example Solution
# file name
filename = 'data.txt'
# read the file
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
print(file.read())
Output
Far far away, behind the word mountains, far from the countries Vokalia and Consonantia, there live the blind texts. Separated they live in Bookmarksgrove right at the coast of the Semantics, a large language ocean.
A small river named D.......
Wrapping Up!
The Python
FileNotFoundError: [Error 2] No such file or dirctory
raised in a Python program when we try to access a file that does not exist in the system. You will mostly find this error in your Program when you deal with file handling and operating system file management. When you specify the file or directory name to any method like open(), you need to make sure that you are specifying the correct path and file name.
If you are still getting this error in your python program, please share your code in the comment section. We will try to help you in debugging.
People are also reading:
-
Python NameError name is not defined Solution
-
How To Make a Game With Python
-
Python IndexError: tuple index out of range Solution
-
Enumerate In Python
-
Python indexerror: list index out of range Solution
-
A Guide to Flatten List & List of Lists in Python
-
Python TypeError: list indices must be integers or slices, not tuple Solution
-
How to Convert a List to Dictionary in Python?
-
Python TypeError: ‘int’ object is not callable Solution
-
What can you do with Python?