Skip to content
Some people stumbled upon a problem when installing LogAnalyzer v3.0.0. They got the following error message:
No syslog records found (code 8 ) – Error Details:
Unknown or unhandeled error occured.
Additionally, when “MiscShowDebugMsg” is enabled they would see the following:
LogStreamPDO|PrintDebugError: Invalid SQL: SELECT id, devicereportedtime, fromhost, infounitid, facility, priority, syslogtag, eventid, eventlogtype, eventsource, eventcategory, eventuser, systemid, checksum, message FROM systemevents WHERE id <= 45 ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT 100
Errorcode: 42703
Detail error: 42703;7;ERROR: column “checksum” does not exist
Error Code: 42703
These error messages result from a missing column in the database. More specifically, this is resulting in the need of LogAnalyzer’s report module for the checksum column in the database (usually this is the table SystemEvents), which is already present when creating the database with some of the MonitorWare Products, but which will not be created when using LogAnalyzer 3.0.0 to set up the tables for storing Events. This is indeed a bug. Usually, the checksum column is not part of the regular MonitorWare database scheme, because it is not needed. Currently only LogAnalyzer and MonitorWare Console need it.
There are two possibilities to resolve this issue. The first is to insert the column manually into the database. You can use the following SQL script to do this. Please note, that you might need to alter the tablename if you don’t use the default name SystemEvents.
ALTER TABLE `systemevents` ADD `Checksum` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’ AFTER `SystemID`;
The second option is to update to LogAnalyzer 3.0.1. You can download it here: http://loganalyzer.adiscon.com/downloads/loganalyzer-3-0-1-v3-beta
When updating to the newest version, the database can be upgraded automatically for MySQL and PostgreSQL databases. If you use a different database, you have to insert the column manually into the SystemEvents table.
Содержание
- How to Install LogAnalyzer On Centos 8
- Install and Setup Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8
- Step 1./ Install Prerequisites
- Step 2./ Create LogAnalyzer Database
- Step 3./ Configure Rsyslog Server
- Step 4./ Install LogAnalyzer
- Step 5./ start LogAnalyzer web installer
- Conclusion
- Logonalayser with rsyslog and mysql not working.
How to Install LogAnalyzer On Centos 8
Adiscon LogAnalyzer is a web interface to syslog/Rsyslog and other network event data. Although, it provides easy browsing, analysis of real time network events and reporting services. In this guide, we are going to learn how to install and Setup Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8.
Install and Setup Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8
Step 1./ Install Prerequisites
In order for LogAnalyzer to function correctly, there are a number few required packages that need to be installed on our system.
01- Install Httpd, rsyslog-mysql packages:
02- Make sure the Httpd is up and running if not run the below command:
03- If the firewalld is installed, you have to allow the http protocol :
Step 2./ Create LogAnalyzer Database
01- First, import the default database scheme offered by RSYSLOG using the below command:
02- Second, let’s verify if the Syslog database was imported correctly and create a new user:
Step 3./ Configure Rsyslog Server
01- To start, we need to configure Rsyslog server to accept syslog from remote servers. First, make sure to backup your rsyslog configuration File:
02- Now, find and uncomment the following lines to make your the Rsyslog server to listen on the udp and tcp ports.
03- To forward logs into MySQL/MariaDB database. So, add the following lines to enable ommysql module and to create a new forwarding rule:
04- After, you finished editing the file. Save and restart the rsyslog service
05- If the firewalld is installed, you have to allow the following ports to enable to receive logs from remote servers:
Step 4./ Install LogAnalyzer
01- First go to the official Adiscon Loganlayzer website and download the most recent version of the software to your server.
02- Create the LogAnalyzer directory under the apache web directory:
03- Copy the installation files into loganalyzer directory using the following commands:
04- Create a blank configuration file named config.php in loganalyzer directory and configure the correct Apache Selinux context using the following commands:
Step 5./ start LogAnalyzer web installer
01- After completing above steps open following url in your favorite web browser to start LogAnalyzer web installer.
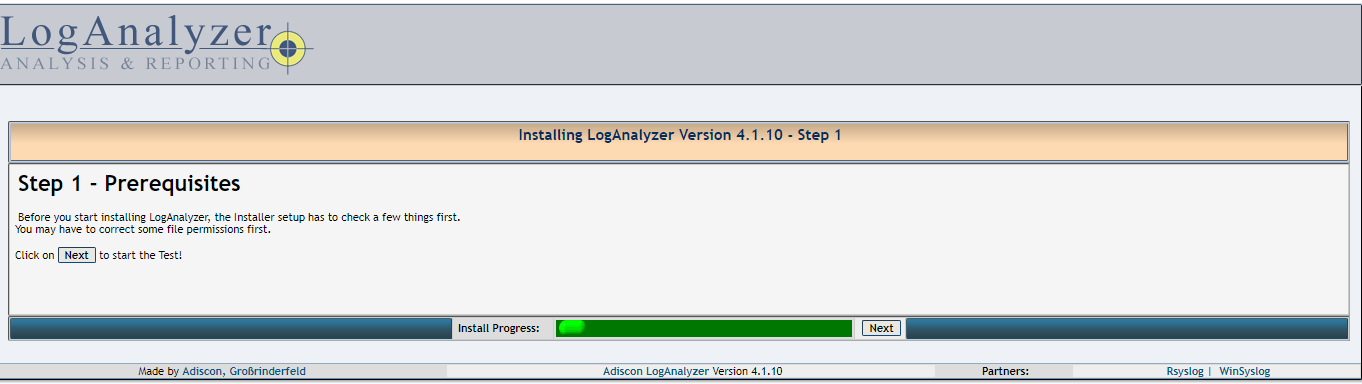
02- Just click Next
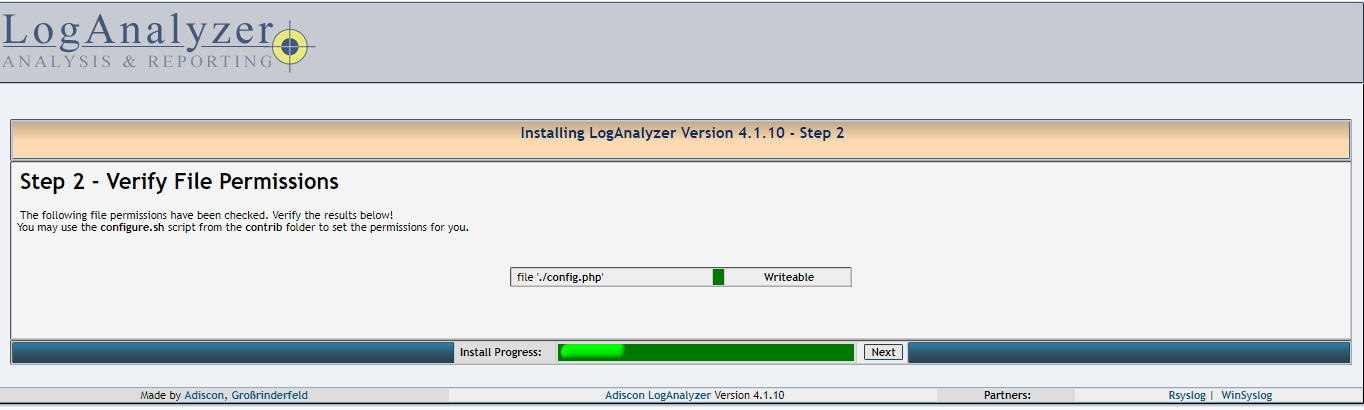
03- Make sure config.php is writable and click Next
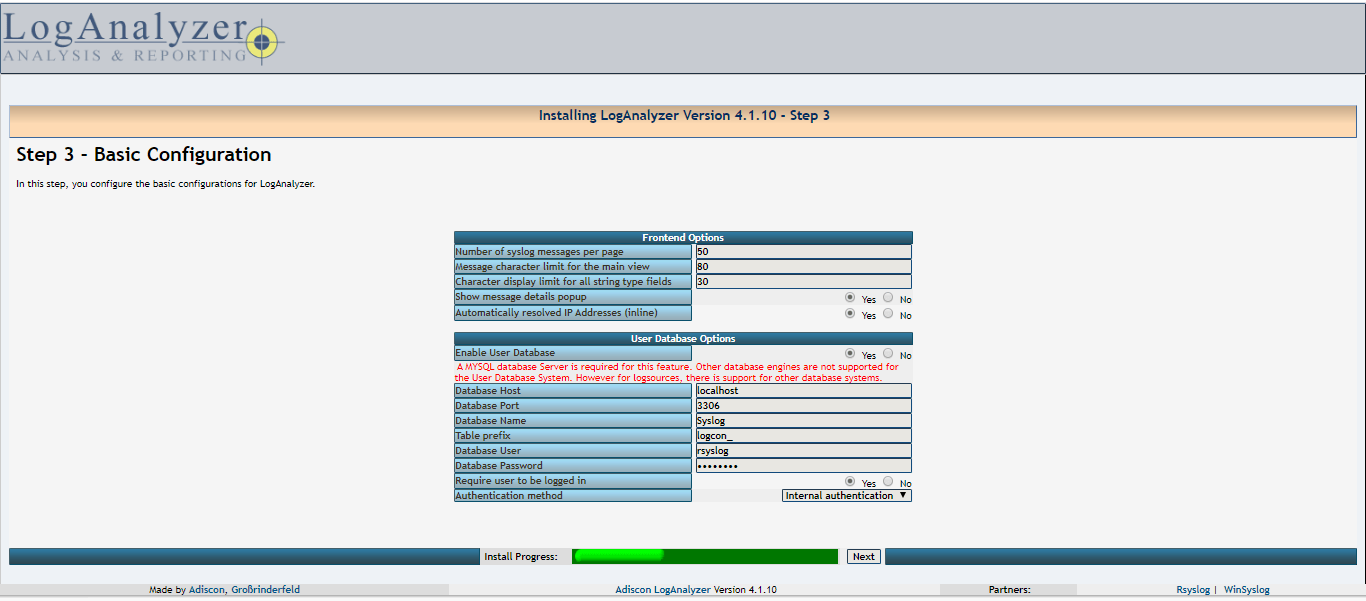
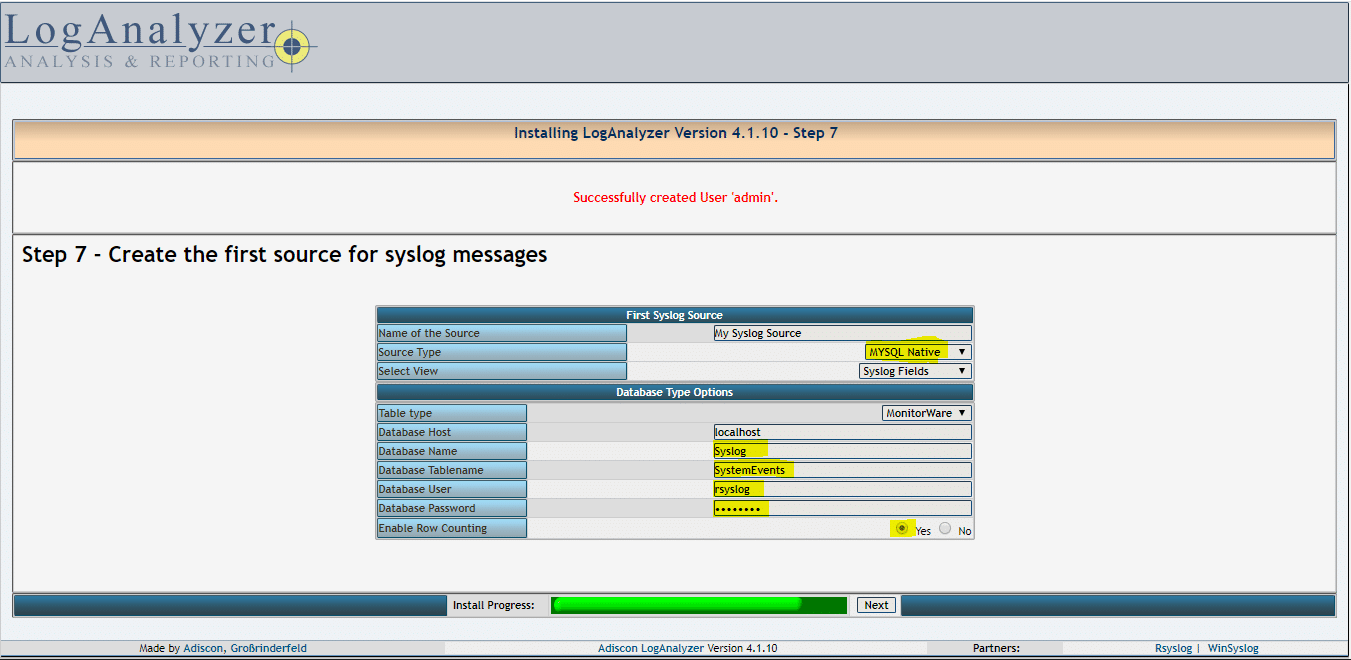
04- Fill the database details for loganalyzer, with the rsyslog database name, user and password created in latest steps and click Next.
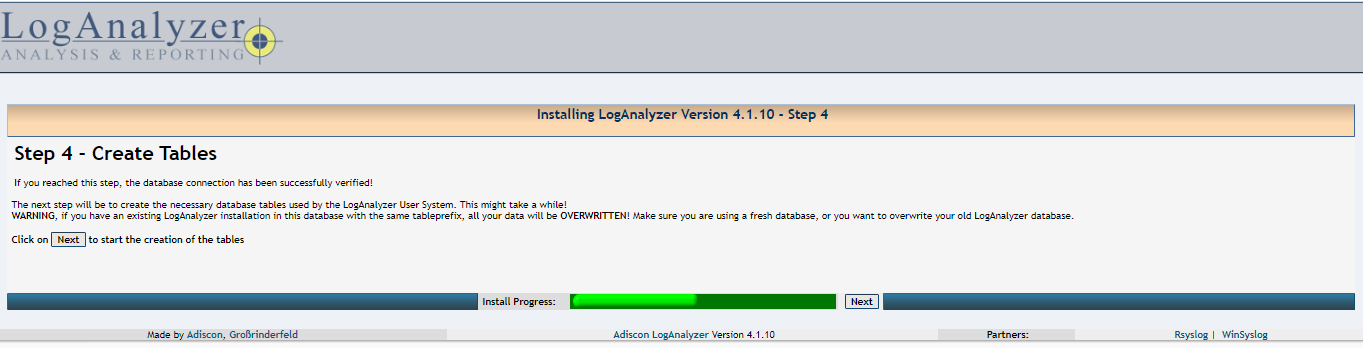
05- Just click Next
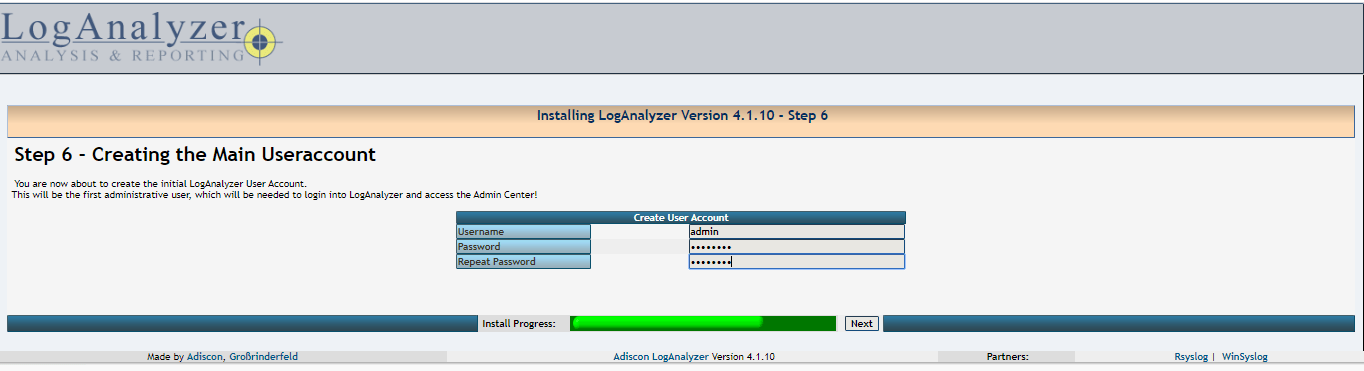
06- Create an Administrator account and click Next.
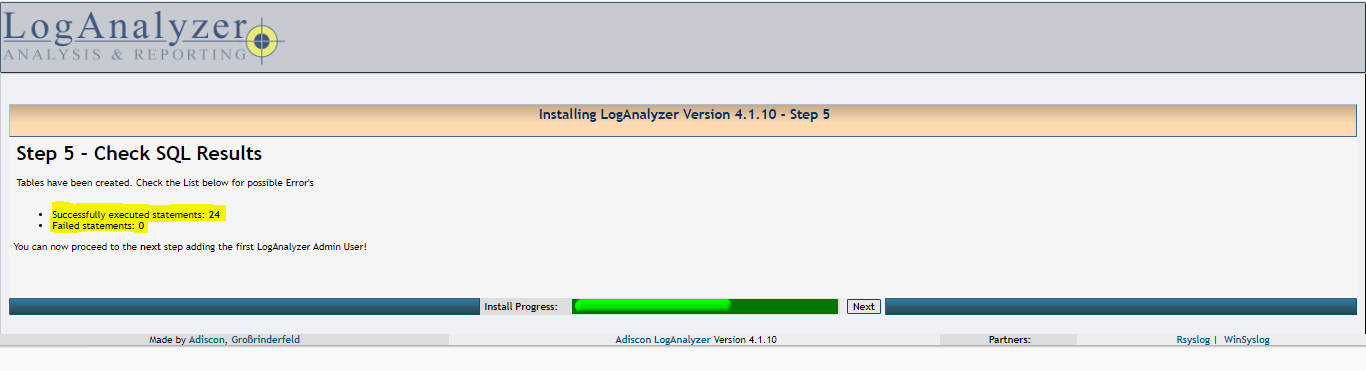
07- Fill the Rsyslog database details, the tablename should be SystemEvents and click Next
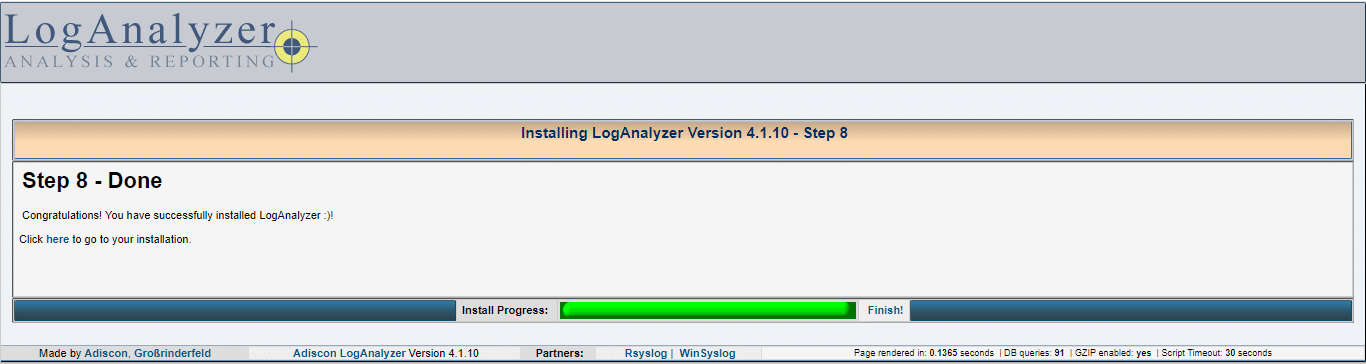
08- click Finish
09- Login to LogAnalyzer using Administrator credentials
Conclusion
You have successfully installed Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8. You might want to check the following guides:
If you like our content, please consider buying us a coffee. Thank you for your support!
Источник
Logonalayser with rsyslog and mysql not working.
I have perviously (october 2013 actually with this guide http://www.unixmen.com/install-and-configure-rsyslog-in-centos-6-4-rhel-6-4/) set up Loganalyser with mysql and rsyslog to receive log information from vmware vsphere hosts and store them. This has been running for some months. When I enter the webpage at http;//hostname/loganalyse r I get the information below;
>>
No syslog records found — Error Details:
No syslog records found
Logstream Warning
While reading the logstream, the php script timeout forced me to abort at this point.
If you want to avoid this, please increase the LogAnalyzer script timeout in your config.php. If the user system is installed, you can do that in Admin center.
config.php
(pasting relevvant information)
$CFG[‘UserDBEnabled’] = true;
$CFG[‘UserDBServer’] = ‘localhost’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPort’] = 3306;
$CFG[‘UserDBName’] = ‘rsysdb’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPref’] = ‘logcon_’;
$CFG[‘UserDBUser’] = ‘rsyslog’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPass’] = ‘password!’;
$CFG[‘UserDBLoginRequired’ ] = true;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘ID’] = ‘Source1’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘Name’] = ‘My Syslog Source’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘ViewID’] = ‘SYSLOG’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘SourceTy pe’] = SOURCE_DB;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBTableT ype’] = ‘monitorware’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBType’] = DB_MYSQL;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBServer ‘] = ‘localhost’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBName’] = ‘rsysdb’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBUser’] = ‘rsyslog’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBPasswo rd’] = ‘password’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBTableN ame’] = ‘SystemEvents’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’] [‘DBEnable RowCountin g’] = true;
# mysql -u rsyslog -p
Enter password:
(Connection was sussessful)
mysql> use rsysdb;
Database changed
mysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents;
Killed
# du -h /mnt/syslogs
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql/rsysdb
1000K /mnt/syslogs/mysql/mysql
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql
16K /mnt/syslogs/lost+found
28G /mnt/syslogs
# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
(Connection was sussessful)
mysql> use rsysdb;
mysql> delete from SystemEvents where ReceivedAt exit
# du -h /mnt/syslogs
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql/rsysdb
1000K /mnt/syslogs/mysql/mysql
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql
16K /mnt/syslogs/lost+found
28G /mnt/syslogs
mysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents where ReceivedAt > DATE_SUB(CONCAT(CURDATE(), ’13:29:00′), INTERVAL 1 WEEK);
Empty set, 65535 warnings (17 min 21.13 sec)
mysql> SELECT CONCAT(table_schema, ‘.’, table_name),
-> CONCAT(ROUND(table_rows / 1000000, 2), ‘M’) rows,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(data_length / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) DATA,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(index_length / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) idx,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(( data_length + index_length ) / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) total_size,
-> ROUND(index_length / data_length, 2) idxfrac
-> FROM information_schema.TABLES
-> ORDER BY data_length + index_length DESC
-> LIMIT 10;
+————————- ———- —-+—— —-+—— —+—— -+——— —-+—— —-+
| CONCAT(table_schema, ‘.’, table_name) | rows | DATA | idx | total_size | idxfrac |
+————————- ———- —-+—— —-+—— —+—— -+——— —-+—— —-+
| rsysdb.SystemEvents | 133.78M | 25.82G | 1.28G | 27.11G | 0.05 |
| mysql.help_topic | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.04 |
| mysql.help_keyword | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.18 |
| mysql.help_relation | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 1.92 |
| mysql.help_category | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.13 |
| mysql.db | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 1.94 |
| mysql.tables_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| mysql.procs_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| mysql.columns_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| rsysdb.logcon_searches | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 3.79 |
+————————- ———- —-+—— —-+—— —+—— -+——— —-+—— —-+
10 rows in set (0.32 sec)
mysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents;
Killed
# tail /var/log/messages
Apr 2 13:52:37 NOC-SYSLOG01 kernel: Out of memory: Kill process 7140 (mysql) score 932 or sacrifice child
Apr 2 13:52:37 NOC-SYSLOG01 kernel: Killed process 7140, UID 0, (mysql) total-vm:7960704kB, anon-rss:3681596kB, file-rss:104kB
>> MySQLTuner 1.3.0 — Major Hayden
>> Bug reports, feature requests, and downloads at http://mysqltuner.com/
>> Run with ‘—help’ for additional options and output filtering
Please enter your MySQL administrative login: root
Please enter your MySQL administrative password:
[OK] Currently running supported MySQL version 5.1.69
[OK] Operating on 64-bit architecture
——— Storage Engine Statistics ————————— ———- ——-
[—] Status: +CSV +InnoDB +MRG_MYISAM
[—] Data in MyISAM tables: 25G (Tables: 13)
[!!] InnoDB is enabled but isn’t being used
[!!] Total fragmented tables: 1
——— Security Recommendations ————————— ———- ——-
[!!] User ‘mysql@localhost’ has no password set.
[!!] User ‘root@127.0.0.1’ has no password set.
[!!] User ‘root@hostname’ has no password set.
——— Performance Metrics ————————— ———- ———- —
[—] Up for: 8d 22h 16m 54s (12M q [16.532 qps], 77 conn, TX: 288B, RX: 4B)
[—] Reads / Writes: 0% / 100%
[—] Total buffers: 34.0M global + 2.7M per thread (151 max threads)
[OK] Maximum possible memory usage: 449.2M (11% of installed RAM)
[OK] Slow queries: 0% (34/12M)
[OK] Highest usage of available connections: 7% (11/151)
[OK] Key buffer size / total MyISAM indexes: 8.0M/1.3G
[OK] Key buffer hit rate: 99.9% (118M cached / 170K reads)
[!!] Query cache is disabled
[!!] Sorts requiring temporary tables: 1360% (952 temp sorts / 70 sorts)
[!!] Temporary tables created on disk: 37% (674 on disk / 1K total)
[!!] Thread cache is disabled
[!!] Table cache hit rate: 19% (64 open / 332 opened)
[OK] Open file limit used: 9% (100/1K)
[OK] Table locks acquired immediately: 99% (12M immediate / 12M locks)
[!!] Connections aborted: 7%
——— Recommendations ————————— ———- ———- ——-
General recommendations:
Add skip-innodb to MySQL configuration to disable InnoDB
Run OPTIMIZE TABLE to defragment tables for better performance
Enable the slow query log to troubleshoot bad queries
When making adjustments, make tmp_table_size/max_heap_ta ble_size equal
Reduce your SELECT DISTINCT queries without LIMIT clauses
Set thread_cache_size to 4 as a starting value
Increase table_cache gradually to avoid file descriptor limits
Read this before increasing table_cache over 64: http://bit.ly/1mi7c4C
Your applications are not closing MySQL connections properly
Variables to adjust:
query_cache_size (>= 8M)
sort_buffer_size (> 1M)
read_rnd_buffer_size (> 256K)
tmp_table_size (> 16M)
max_heap_table_size (> 16M)
thread_cache_size (start at 4)
table_cache (> 64)
To sum things up:
* Every day I delete every record from rsysdb.SystemEvents older then 93 days with a cron job. rsysdb.SystemEvents is the main contributor to the size of rsysdb with 27.11GB.
* I have tried to manually delete from the database, the command executes, but the size of the database is still the same.
* I have tried selecting from rsysdb.SystemEvents data that has been entered within a month, and a week, but receive no result.
* I have tried selecting from rsysdb.SystemEvents data without select limiting at all, and my who mysql connection gets killed.
* I tried running a mysqltuner script, but could’nt see it offered me any information I needed.
When checking /var/log/messages I can see log entries from the ESXi hosts(from the start of it):
Mar 30 14:20:03 hostname.vmware.host hostprofiletrace: ^^^hostProfiles-15811-2014 0330-14200 3-cli-comm ands.trc^^ ^168^^^ Command: esxcli [‘system’, ‘coredump’, ‘network’, ‘get’], status: (0), output: » <‘Network Server IP’
: », ‘Host VNic’: », ‘Enabled’: False, ‘Network Server Port’: 0>»#012#000
But this information is not available to my any longer from the database as I can see.
I check /etc/rsyslog.conf:
$ModLoad imuxsock # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
$ModLoad imklog # provides kernel logging support (previously done by rklogd)
$ModLoad immark # provides —MARK— message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerAddress >hostIpAddressIsHere rsyslog,>p asswordIsH ere Linux MySQL Server Linux Networking
Источник
Adiscon LogAnalyzer is a web interface to syslog/Rsyslog and other network event data. Although, it provides easy browsing, analysis of real time network events and reporting services. In this guide, we are going to learn how to install and Setup Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8.
Install and Setup Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8
Step 1./ Install Prerequisites
In order for LogAnalyzer to function correctly, there are a number few required packages that need to be installed on our system.
01- Install Httpd, rsyslog-mysql packages:
$ yum install httpd php-mysqlnd wget rsyslog-mysql
02- Make sure the Httpd is up and running if not run the below command:
$ systemctl enable --now httpd
03- If the firewalld is installed, you have to allow the http protocol :
$ firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http $ firewall-cmd --reload
Step 2./ Create LogAnalyzer Database
01- First, import the default database scheme offered by RSYSLOG using the below command:
$ mysql -u root -p < /usr/share/doc/rsyslog/mysql-createDB.sql Enter password:
02- Second, let’s verify if the Syslog database was imported correctly and create a new user:
$ mysql -u root -p Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MariaDB connection id is 20 Server version: 10.3.17-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | Syslog | | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON Syslog.* TO 'rsyslog'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Password'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.002 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.002 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> exit Bye
Step 3./ Configure Rsyslog Server
01- To start, we need to configure Rsyslog server to accept syslog from remote servers. First, make sure to backup your rsyslog configuration File:
$ cp /etc/rsyslog.conf /etc/rsyslog.conf.org
02- Now, find and uncomment the following lines to make your the Rsyslog server to listen on the udp and tcp ports.
[...] # Provides UDP syslog reception # for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imudp.html module(load="imudp") # needs to be done just once input(type="imudp" port="514") # Provides TCP syslog reception # for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imtcp.html module(load="imtcp") # needs to be done just once input(type="imtcp" port="514")
03- To forward logs into MySQL/MariaDB database. So, add the following lines to enable ommysql module and to create a new forwarding rule:
[...] # Load the MySQL Module module(load="ommysql") [...] #*.* :ommysql:127.0.0.1,Syslog_Database,syslog_user,password *.* :ommysql:127.0.0.1,Syslog,rsyslog,Password
04- After, you finished editing the file. Save and restart the rsyslog service
$ systemctl restart rsyslog
05- If the firewalld is installed, you have to allow the following ports to enable to receive logs from remote servers:
$ firewall-cmd --add-port=514/{tcp,udp} --permanent
$ firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4./ Install LogAnalyzer
01- First go to the official Adiscon Loganlayzer website and download the most recent version of the software to your server.
$ VERSION=4.1.10
$ wget http://download.adiscon.com/loganalyzer/loganalyzer-4.1.10.tar.gz -P /tmp
$ tar -xzvf /tmp/loganalyzer-${VERSION}.tar.gz -C /tmp/
02- Create the LogAnalyzer directory under the apache web directory:
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir /var/www/html/loganalyzer
03- Copy the installation files into loganalyzer directory using the following commands:
$ cp -r /tmp/loganalyzer-${VERSION}/src/* /var/www/html/loganalyzer
$ cp /tmp/loganalyzer-${VERSION}/contrib/configure.sh /var/www/html/loganalyzer
04- Create a blank configuration file named config.php in loganalyzer directory and configure the correct Apache Selinux context using the following commands:
$ cd /var/www/html/loganalyzer $ bash configure.sh $ chcon -h -t httpd_sys_script_rw_t config.php
Step 5./ start LogAnalyzer web installer
01- After completing above steps open following url in your favorite web browser to start LogAnalyzer web installer.
http://localhost/loganalyzer
02- Just click Next
03- Make sure config.php is writable and click Next
04- Fill the database details for loganalyzer, with the rsyslog database name, user and password created in latest steps and click Next.
05- Just click Next
06- Create an Administrator account and click Next.
07- Fill the Rsyslog database details, the tablename should be SystemEvents and click Next
08- click Finish
09- Login to LogAnalyzer using Administrator credentials
Conclusion
You have successfully installed Adiscon LogAnalyzer on CentOS 8. You might want to check the following guides:
- How To Setup A Centralized Log Server Using Rsyslog
- How to Setup A Centralized Log Server Using Rsyslog on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
If you like our content, please consider buying us a coffee. Thank you for your support!
Lotfi Waderni
I’m a technical writer with a background in Linux and windows server administration.
I have perviously (october 2013 actually with this guide http://www.unixmen.com/install-and-configure-rsyslog-in-centos-6-4-rhel-6-4/) set up Loganalyser with mysql and rsyslog to receive log information from vmware vsphere hosts and store them. This has been running for some months. When I enter the webpage at http;//hostname/loganalyser I get the information below;
>>
No syslog records found — Error Details:
No syslog records foundLogstream Warning
While reading the logstream, the php script timeout forced me to abort at this point.If you want to avoid this, please increase the LogAnalyzer script timeout in your config.php. If the user system is installed, you can do that in Admin center.
<<
I then start by checking the configuration and various outher troubleshooting steps shown below:
# more /var/www/html/loganalyser/config.php
(pasting relevvant information)
$CFG[‘UserDBEnabled’] = true;
$CFG[‘UserDBServer’] = ‘localhost’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPort’] = 3306;
$CFG[‘UserDBName’] = ‘rsysdb’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPref’] = ‘logcon_’;
$CFG[‘UserDBUser’] = ‘rsyslog’;
$CFG[‘UserDBPass’] = ‘password!’;
$CFG[‘UserDBLoginRequired’] = true;$CFG[‘DefaultSourceID’] = ‘Source1’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘ID’] = ‘Source1’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘Name’] = ‘My Syslog Source’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘ViewID’] = ‘SYSLOG’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘SourceType’] = SOURCE_DB;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBTableType’] = ‘monitorware’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBType’] = DB_MYSQL;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBServer’] = ‘localhost’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBName’] = ‘rsysdb’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBUser’] = ‘rsyslog’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBPassword’] = ‘password’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBTableName’] = ‘SystemEvents’;
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBEnableRowCounting’] = true;# mysql -u rsyslog -p
Enter password:
(Connection was sussessful)
mysql> use rsysdb;Database changed
mysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents;
Killed# du -h /mnt/syslogs
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql/rsysdb
1000K /mnt/syslogs/mysql/mysql
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql
16K /mnt/syslogs/lost+found
28G /mnt/syslogs# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
(Connection was sussessful)mysql> use rsysdb;
mysql> delete from SystemEvents where ReceivedAt < subdate(curdate(), 93); #Also, this command runs via cron every day
Query OK, 0 rows affected (12 min 27.65 sec)mysql> exit
# du -h /mnt/syslogs
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql/rsysdb
1000K /mnt/syslogs/mysql/mysql
28G /mnt/syslogs/mysql
16K /mnt/syslogs/lost+found
28G /mnt/syslogsmysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents where ReceivedAt > DATE_SUB(CONCAT(CURDATE(), ’13:29:00′), INTERVAL 1 WEEK);
Empty set, 65535 warnings (17 min 21.13 sec)mysql> SELECT CONCAT(table_schema, ‘.’, table_name),
-> CONCAT(ROUND(table_rows / 1000000, 2), ‘M’) rows,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(data_length / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) DATA,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(index_length / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) idx,
-> CONCAT(ROUND(( data_length + index_length ) / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ), 2), ‘G’) total_size,
-> ROUND(index_length / data_length, 2) idxfrac
-> FROM information_schema.TABLES
-> ORDER BY data_length + index_length DESC
-> LIMIT 10;
+—————————————+———+———+——-+————+———+
| CONCAT(table_schema, ‘.’, table_name) | rows | DATA | idx | total_size | idxfrac |
+—————————————+———+———+——-+————+———+
| rsysdb.SystemEvents | 133.78M | 25.82G | 1.28G | 27.11G | 0.05 |
| mysql.help_topic | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.04 |
| mysql.help_keyword | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.18 |
| mysql.help_relation | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 1.92 |
| mysql.help_category | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.13 |
| mysql.db | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 1.94 |
| mysql.tables_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| mysql.procs_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| mysql.columns_priv | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | NULL |
| rsysdb.logcon_searches | 0.00M | 0.00G | 0.00G | 0.00G | 3.79 |
+—————————————+———+———+——-+————+———+
10 rows in set (0.32 sec)mysql> select CustomerID, ReceivedAt, DeviceReportedTime, Facility, FromHost from SystemEvents;
Killed# tail /var/log/messages
Apr 2 13:52:37 NOC-SYSLOG01 kernel: Out of memory: Kill process 7140 (mysql) score 932 or sacrifice child
Apr 2 13:52:37 NOC-SYSLOG01 kernel: Killed process 7140, UID 0, (mysql) total-vm:7960704kB, anon-rss:3681596kB, file-rss:104kB# ./mysqltuner.pl
>> MySQLTuner 1.3.0 — Major Hayden <major@mhtx.net>
>> Bug reports, feature requests, and downloads at http://mysqltuner.com/
>> Run with ‘—help’ for additional options and output filtering
Please enter your MySQL administrative login: root
Please enter your MySQL administrative password:
[OK] Currently running supported MySQL version 5.1.69
[OK] Operating on 64-bit architecture——— Storage Engine Statistics ——————————————-
[—] Status: +CSV +InnoDB +MRG_MYISAM
[—] Data in MyISAM tables: 25G (Tables: 13)
[!!] InnoDB is enabled but isn’t being used
[!!] Total fragmented tables: 1——— Security Recommendations ——————————————-
[!!] User ‘mysql@localhost’ has no password set.
[!!] User ‘root@127.0.0.1’ has no password set.
[!!] User ‘root@hostname’ has no password set.——— Performance Metrics ————————————————-
[—] Up for: 8d 22h 16m 54s (12M q [16.532 qps], 77 conn, TX: 288B, RX: 4B)
[—] Reads / Writes: 0% / 100%
[—] Total buffers: 34.0M global + 2.7M per thread (151 max threads)
[OK] Maximum possible memory usage: 449.2M (11% of installed RAM)
[OK] Slow queries: 0% (34/12M)
[OK] Highest usage of available connections: 7% (11/151)
[OK] Key buffer size / total MyISAM indexes: 8.0M/1.3G
[OK] Key buffer hit rate: 99.9% (118M cached / 170K reads)
[!!] Query cache is disabled
[!!] Sorts requiring temporary tables: 1360% (952 temp sorts / 70 sorts)
[!!] Temporary tables created on disk: 37% (674 on disk / 1K total)
[!!] Thread cache is disabled
[!!] Table cache hit rate: 19% (64 open / 332 opened)
[OK] Open file limit used: 9% (100/1K)
[OK] Table locks acquired immediately: 99% (12M immediate / 12M locks)
[!!] Connections aborted: 7%——— Recommendations ——————————————————
General recommendations:
Add skip-innodb to MySQL configuration to disable InnoDB
Run OPTIMIZE TABLE to defragment tables for better performance
Enable the slow query log to troubleshoot bad queries
When making adjustments, make tmp_table_size/max_heap_table_size equal
Reduce your SELECT DISTINCT queries without LIMIT clauses
Set thread_cache_size to 4 as a starting value
Increase table_cache gradually to avoid file descriptor limits
Read this before increasing table_cache over 64: http://bit.ly/1mi7c4C
Your applications are not closing MySQL connections properly
Variables to adjust:
query_cache_size (>= 8M)
sort_buffer_size (> 1M)
read_rnd_buffer_size (> 256K)
tmp_table_size (> 16M)
max_heap_table_size (> 16M)
thread_cache_size (start at 4)
table_cache (> 64)
To sum things up:
* Every day I delete every record from rsysdb.SystemEvents older then 93 days with a cron job. rsysdb.SystemEvents is the main contributor to the size of rsysdb with 27.11GB.
* I have tried to manually delete from the database, the command executes, but the size of the database is still the same.
* I have tried selecting from rsysdb.SystemEvents data that has been entered within a month, and a week, but receive no result.
* I have tried selecting from rsysdb.SystemEvents data without select limiting at all, and my who mysql connection gets killed.
* I tried running a mysqltuner script, but could’nt see it offered me any information I needed.
When checking /var/log/messages I can see log entries from the ESXi hosts(from the start of it):
Mar 30 14:20:03 hostname.vmware.host hostprofiletrace: ^^^hostProfiles-15811-20140330-142003-cli-commands.trc^^^168^^^ Command: esxcli [‘system’, ‘coredump’, ‘network’, ‘get’], status: (0), output: «{‘Network Server IP’
: », ‘Host VNic’: », ‘Enabled’: False, ‘Network Server Port’: 0}»#012#000
But this information is not available to my any longer from the database as I can see.
I check /etc/rsyslog.conf:
#### MODULES ####$ModLoad imuxsock # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
$ModLoad imklog # provides kernel logging support (previously done by rklogd)
$ModLoad immark # provides —MARK— message capability# Provides UDP syslog reception
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerAddress >hostIpAddressIsHere<
$UDPServerRun 514# Provides TCP syslog reception
$ModLoad imtcp
$InputTCPServerRun 514$ModLoad ommysql
*.* :ommysql:127.0.0.1,rsysdb,rsyslog,>passwordIsHere<
$AllowedSender UDP, 127.0.0.1, x.x.x.0/24
$AllowedSender TCP, 127.0.0.1, x.x.x.0/24
This looks good to me, and it has worked before.
Trying a restart:
# service rsyslog restart
Shutting down system logger: [ OK ]
Starting system logger: [ OK ]
What is the best way to handle this? I would like loganalyser to be up and running and data to be accessible, and also handeled correctly.

Настраиваем хранение логов в базе данных MySQL
Не всегда есть возможность зайти на удалённый сервер для просмотра журналов системы или приложений. Иногда возникает необходимость делегировать другому сотруднику задачи мониторинга. А может, под рукой не оказалось средств для удалённого доступа? Этих проблем можно избежать при помощи средств, настройка которых будет описана в данной статье.
Для решения поставленных целей нам понадобится следующее ПО – rsyslog (http://www.rsyslog.com) и phpLogcon (http://www.phplogcon.com). Первое будет записывать различные события журналов в базу данных MySQL, второе – предоставлять веб-интерфейс для их просмотра.
Необходимые требования:
- Сервер MySQL (http://www.mysql.com).
- Веб-сервер Apache (http://apache.org).
- PHP5 (http://php.net).
- Перед запуском rsyslogd системный демон syslogd должен быть остановлен и деактивирован в автозагрузке системы.
Примечание: все действия по установке ПО на *nix-сервере выполняем под пользователем root.
Установка rsyslog
Авторизуемся под учётной записью root на сервере с помощью консоли или используя ssh-клиент, удалённо (к примеру, putty – http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty). Для работы с файлами на удалённом *nix-сервере можно использовать WinSCP (будет рассмотрена далее).
Загружаем последнюю стабильную версию (для порядка лучше создать директорию, в которой будут лежать все дистрибутивы, к примеру, это может быть /usr/Distr), после чего распаковываем полученный архив:
#mkdir /usr/Distr
# cd /usr/Distr/
#wget http://www.rsyslog.com/Downloads-req-viewsdownload-sid-1.phtml
# tar -zxf rsyslog-3.20.5
#cd rsyslog-3.20.5
Конфигурируем rsyslog (с поддержкой MySQL):
./configure CFLAGS=»-I/usr/local/include/» LDFLAGS=»-L/usr/local/lib» —enable-mysql
После чего выполняем:
#make
#make install
Создаём базу MySQL для rsyslog, используя файл createDB.sql. В нашем случае он находится в директории /usr/Distr/rsyslog-3.20.5/plugins/ommysql/. Также нам необходим пользователь баз данных samaglog с паролем samagpassword, который имеет все права на созданную базу данных с именем Syslog:
# /usr/local/bin/mysql —user=root —password=password < /usr/Distr/rsyslog-3.20.5/plugins/ommysql/createDB.sql
# /usr/local/bin/mysql —user=root —password=password
mysql>create user ‘samaglog’@’localhost’ identified by ‘samagpassword’;
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON Syslog.* TO ‘samaglog’@’localhost’;
mysql>quit;
Модифицируем rsyslog.conf. По умолчанию он находится в директории /etc. Включаем поддержку MySQL:
$ModLoad ommysql.so
Синтаксис записи событий в определённый файл схож с системным. Для базы MySQL он будет следующим:
*.* >servername,dbname,user,password
Рассмотрим пример записи событий системы, связанных с безопасностью:
security.* >127.0.0.1,syslog,samaglog,samagpassword
Запускаем демон rsyslogd со следующими параметрами:
rsyslogd -c3 -4 -f /etc/rsyslog.conf
где:
- c – обязательный параметр для определения совместимости со старыми версиями rsyslog,
- 4 – использование ipv4,
- f – путь к файлу конфигурации.
Дополнительную информацию о ключах запуска смотрите в документации по адресу http://wiki.rsyslog.com/index.php/Main_Page.
На этом установка rsyslog закончена, и мы переходим к phpLogcon.
Установка phpLogcon
Скачиваем последнюю стабильную версию phpLogcon и распаковываем её в новую директорию нашего веб-сервера:
# mkdir /var/www/samaglogs/ && cd /var/www/samaglogs/
# wget http://www.phplogcon.org/Downloads-req-getit-lid-54.phtml
# tar -zxf phplogcon-2.6.2.tar.gz
# cp -R phplogcon-2.6.2/src/* .
# rm -r phplogcon*
Создаём пустой файл конфигурации и устанавливаем необходимые разрешения:
# touch /var/www/samaglogs/config.php
# chmod 666 /var/www/samaglogs/config.php
Для запуска скрипта установки phpLogcon необходимо открыть в браузере следующий адрес: http://samag.local/samaglogs/install.php, где samag.local – это имя или IP-адрес вашего веб-сервера.
Следуя указаниям мастера, доходим до 7-го шага и в поле Source Type выбираем MySQL Native, как показано на рис. 1. Обращаю ваше внимание на то, что данные в поле Database Tablename чувствительны к регистру.
Рисунок 1. Настройка базы MySQL для phpLogcon
Если после установки возникнет ошибка:
No syslog records found — Error Details:
Could not find the configured table, maybe misspelled or the tablenames are case sensitive
Значит, вы неверно указали имя таблицы (вместо SystemEvents написали systemevents). В случае возникновения данной ошибки нужно исправить следующую строчку в файле /var/www/samaglogs/config.php:
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBTableName’] = ‘SystemEvents’;
Практика
Рассмотрим пример использования нескольких экземпляров rsyslogd и phplogcon. Нам необходим мониторинг событий mail.* (почтового сервера).
Модифицируем в файле createDB.sql в /usr/Distr/rsyslog-3.20.5/plugins/ommysql две первые строчки:
CREATE DATABASE Maillog;
USE Maillog;
Остальное оставляем без изменений.
Аналогично установке rsyslog создаём базу и даём на неё все права пользователю samaglog:
# /usr/local/bin/mysql —user=root —password=password < /usr/Distr/rsyslog-3.20.5/plugins/ommysql/createDB.sql
# /usr/local/bin/mysql —user=root —password=password
mysql>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON Maillog.* TO ‘samaglog’@’localhost’;
mysql>quit;
Копируем файл /etc/rsyslog.conf в /etc/rsyslogmail.conf. После перечисления модулей в файле /etc/rsyslogmail.conf оставляем лишь:
mail.* >127.0.0.1,maillog,samaglog,samagpassword
Запускаем rsyslogd со следующими ключами:
rsyslogd -c3 -4 -f /etc/ rsyslogmail.conf -i /var/run/samag.pid
где i – путь к pid-файлу, для второго экземпляра rsyslogd.
Копируем директорию /var/www/samaglogs/ в другую (к примеру, /var/www/samagmaillogs/).
Переходим в новую директорию и изменяем следующую строчку в конце файла config.php:
$CFG[‘Sources’][‘Source1’][‘DBName’] = ‘maillog’;
Получаем отдельный мониторинг по адресу http://samag.local/samagmaillogs, как показано на рис. 2.
Рисунок 2. Пример работы phpLogcon
Как видно из примера, просматривать журналы намного удобнее через веб-интерфейс. Можно задавать различные фильтры, выбирать тип отображаемых данных и просматривать графики. Также rsyslog можно использовать для консолидации журналов нескольких серверов или сетевых устройств. Один интерфейс просмотра всегда удобнее, чем несколько.
WinSCP
В заключение рассмотрим упомянутый выше инструмент – WinSCP (http://winscp.net/eng/docs/lang:ru). Это файл-менеджер, который работает по протоколу SFTP (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SFTP).
При помощи WinSCP вы можете работать с удалённым сервером *nix посредством демона SSH. WinSCP имеет следующие возможности:
- графический интерфейс;
- интеграция с ОС Windows (drag&drop, поддержка схем URL, ярлыки);
- все основные файловые операции.
Остальное вы найдёте на официальном сайте проекта по адресу http://winscp.net/eng/docs/lang:ru#возможности_программы.
Для работы с WinSCP необходимо настроить сервис SSH. Раскомментируйте в файле /etc/ssh/sshd_config следующую строчку:
Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/sftp-server
После чего перезапустите демон sshd, используя следующую команду:
kill -HUP $(cat /var/run/sshd.pid)
где /var/run/sshd.pid – путь к pid-файлу демона sshd.
Пример работы WinSCP показан на рис. 3.
Рисунок 3. Пример работы WinSCP
Заключение
Оптимизация повседневных задач упрощает вашу работу. Единая система мониторинга позволит избежать многих проблем. Грамотное использование средств администрирования, будь то скрипты или сторонне ПО, в большинстве своём принесут только пользу.
Большой каталог свободно распространяемого ПО вы найдёте по адресу http://sf.net.