In Python, you can use the numpy library when working with arrays and certain math concepts like matrices and linear algebra.
But like every other aspect of learning and working with a programming language, errors are unavoidable.
In this article, you’ll learn how to fix the «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error which mostly occurs when using the numpy library.
What Causes the TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars Error in Python?
The «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error is raised when we pass in an array to a method that accepts only one parameter.
Here’s an example:
import numpy as np
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
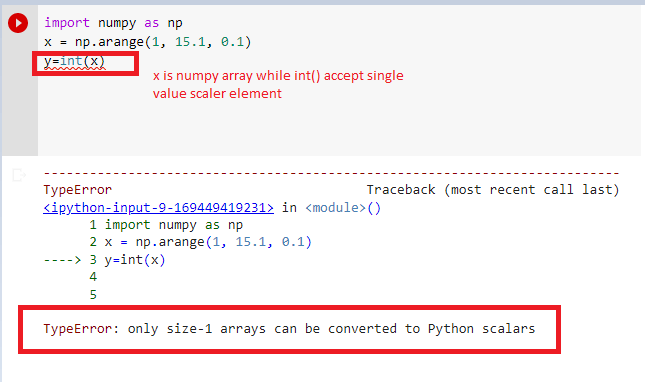
x = np.int(y)
print(x)
# TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
The code above throws the «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error because we passed the y array to the NumPy int() method. The method can only accept one parameter.
In the next section, you’ll see some solutions for this error.
There are two general solutions for fixing the «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error.
Solution #1 – Using the np.vectorize() Function
The np.vectorize() function can accept a sequence/an array as its parameter. When printed out, it returns an array.
Here’s an example:
import numpy as np
vector = np.vectorize(np.int_)
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8])
x = vector(y)
print(x)
# [2, 4, 6, 8]In the example above, we created a vector variable which will «vectorize» any parameter passed to it: np.vectorize(np.int_).
We then created an array and stored it in the y variable: np.array([2, 4, 6, 8]).
Using the vector variable we created initially, we passed the y array as a parameter: x = vector(y).
When printed out, we got the array — [2, 4, 6, 8].
Solution #2 – Using the map() Function
The map() function accepts two parameter in this case — the NumPy method and the array.
import numpy as np
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8])
x = np.array(list(map(np.int_, y)))
print(x)
# [2, 4, 6, 8]In the example above, we nested the map() function in a list() method so that we get the array retuned as a list and not a map object.
Solution #3 – Using the astype() Method
We can use the astype() method to convert a NumPy array to integers. This will prevent the «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error from being raised.
Here’s how:
import numpy as np
vector = np.vectorize(np.int_)
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8])
x = y.astype(int)
print(x)
# [2 4 6 8]Summary
In this article, we talked about the «TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» error in Python.
It is raised when we pass an array as a parameter to a numpy method that accepts only one parameter.
To fix the error, we used different methods like the np.vectorize() function, map() function, and astype() method.
Happy coding!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
17 авг. 2022 г.
читать 1 мин
Одна ошибка, с которой вы можете столкнуться при использовании Python:
TypeError : only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
Эта ошибка возникает чаще всего, когда вы пытаетесь использовать np.int() для преобразования массива значений с плавающей запятой NumPy в массив целочисленных значений.
Однако эта функция принимает только одно значение вместо массива значений.
Вместо этого вы должны использовать x.astype(int) для преобразования массива значений с плавающей запятой NumPy в массив целочисленных значений, поскольку эта функция может принимать массив.
В следующем примере показано, как исправить эту ошибку на практике.
Как воспроизвести ошибку
Предположим, мы создаем следующий массив значений с плавающей запятой NumPy:
import numpy as np
#create NumPy array of float values
x = np.array([3, 4.5, 6, 7.7, 9.2, 10, 12, 14.1, 15])
Теперь предположим, что мы пытаемся преобразовать этот массив значений с плавающей запятой в массив целочисленных значений:
#attempt to convert array to integer values
np.int (x)
TypeError : only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
Мы получаем TypeError , потому что функция np.int() принимает только отдельные значения, а не массив значений.
Как исправить ошибку
Чтобы преобразовать массив значений с плавающей запятой NumPy в целочисленные значения, мы можем вместо этого использовать следующий код:
#convert array of float values to integer values
x.astype (int)
array([ 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15])
Обратите внимание, что массив значений был преобразован в целые числа, и мы не получаем никаких ошибок, поскольку функция astype() может обрабатывать массив значений.
Примечание.Полную документацию по функции astype() можно найти здесь .
Дополнительные ресурсы
В следующих руководствах объясняется, как исправить другие распространенные ошибки в Python:
Как исправить KeyError в Pandas
Как исправить: ValueError: невозможно преобразовать число с плавающей запятой NaN в целое число
Как исправить: ValueError: операнды не могли транслироваться вместе с фигурами
Python has helped thousands of communities to create solutions for their real-life problems. With thousands of useful modules, Python has proved to be one of the top versatile languages in the coding world. In addition, writing in Python is similar to writing in English, and using it is even simpler. With simple single command module installs, you can install almost every dependency to control your problems. Numpy is one of those important modules, and Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error appears while using this module.
Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error is a typical error that appears as a TypeError form in the terminal. This error’s main cause is passing an array to a parameter that accepts a scalar value. In various numpy methods, acceptable parameters are only a scalar value. Hence, if you pass a single dimensional array or multidimensional array in the method, it’ll throw this error. With increasing methods accepting a single parameter, you can expect this error to appear many times.
This post will guide you with the causes of the error and it’s solutions.
Only Size 1 Arrays Error is a TypeError that gets triggered when you enter an array as a parameter in a function or method which accepts a single scalar value. Many functions have inbuilt error handling methods to avoid crashing programs and validate the inputs given for the function. Without the validation, the python program will crash immediately, which can cause issues.
numpy.int() and numpy.float() shows this error due to single-valued parameters. As TypeError originates from an invalid data type, you can get this error by sending an array as a parameter.. There are different ways to avoid this error, which we’ll discuss in the post’s bottom section.
Why do I get Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error?
Errors are an integral part of the programming, and they should be handled properly. With the management of error handling, your program can not only avoid harmful vulnerabilities, but it can also perform in a better way. As a result, you can get the Only Size 1 Arrays error while using numpy. This module’s developers have categorized this error into TypeError, which describes that you supplied the wrong data to the function/method.
Causes of Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error
There are several ways the error can appear while using numpy. All of these errors are solvable by one or the other means. This error is a user sided error and passing appropriate parameters can prevent this error. Following are the causes of this error –
Incorrect Datatype
In Python, every data type has different methods and attributes. Each of these data types has different usage. In many numpy methods, the primary parameter required is a single value. With such methods, if you pass a numpy array as a parameter, Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error can appear.
Example:
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) x = np.int(x)
Output:
TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalarsExplanation:
In the program, x is a simple array with integer elements. If you try to convert this array into int form, it will throw an error because np.int() accept a single value.
Using Single Conversion Function
Single Conversion Functions are the functions that accept a single-valued datatype and convert it to another data type. For example, converting a string to int is a single-valued conversion. In numpy, these functions accept the single numpy element and change its datatype from within. If you pass a numpy array as a parameter, you’ll get an error in such methods.
Example –
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) x = np.float(x)
Output –
TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalarsExplanation –
In the above example, we wanted to convert all the integers from the numpy array to float values. np.float() throws TypeError as it accepts single-valued parameters.
Solutions for Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error
There are multiple ways of solving the TypeError in Python. Most importantly, Numpy modules provide some inbuilt functions which you can use to create a suitable datatype before using it in a method. Following are the solutions to this error –
1. Using Numpy Vectorize Function
In layman’s terms, Vectorize means applying an algorithm to a set of values rather than applying them on a single value. As the TypeError occurs due to its usage on sets of values, you can use numpy.vectorize() in between the algorithm and methods. This method acts like a python map function over a numpy array.
Code –
import numpy as np vector = np.vectorize(np.float) x = np.array([1, 2, 3]) x = vector(x) print(x)
Output –
[1. 2. 3.]Explanation –
Firstly, we started by creating a vector that accepts np.float as a parameter. To apply a method on all the numpy array elements, we’ll use this vector. Nextly, we created a numpy array and then used our vector() to apply np.float over all the values. This method avoids all sorts of TypeError and also converts all the values into the float.
2. Using Map() Function
Surely, the map is the basic inbuilt function in python that applies a function over all array elements. map() function accepts two major parameters. The first one is the function you need to apply over sets of values. The second one is an array that you want to change. Let’s jump on an example –
Code –
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 2, 3]) x = np.array(list(map(np.float, x))) print(x)
Output –
[1. 2. 3.]Explanation –
Firstly, we’ve created a simple integer array and used map(np.float, x) to convert all the elements from numpy array to float. As the map function returns a map object, we need to convert it back to the list and numpy array to restore its datatype. By using this method, you can avoid getting TypeError.
3. Using Loops
Loops are the most brute force methods to apply a function over a set of values. But it provides us control over all parts of the elements and can be used to customize elements if we need.
Code –
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
y = np.array([None]*3)
for i in range(3):
y[i] = np.float(x[i])
print(y)
Output –
[1.0 2.0 3.0]Explanation –
In the above example, we’ve used indexing to fetch the initial integer from the numpy array. Then applied the np.float() method to convert it from float to int. Furthermore, we’ve created a dummy numpy array y, which stores the float values after changing.
4. Using apply_along_axis
Apply_along_axis is a Numpy method that allows the users to apply a function over a numpy array along a specific axis. As numpy is looped according to axis number, you can use it to apply a function over sets of values.
Code –
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 2, 3]) app = lambda y: [np.float(i) for i in y] x = np.apply_along_axis(app, 0, x) print(x)
Output –
[1. 2. 3.]Explanation –
In this example, we’ll use the lambda function to create a function’s vectorized function. Then we’ll use np.apply_along_axis to apply the lambda function over the specific numpy array. You can also specify the axis along which you need to apply the function.
plt.barh TypeError: Only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
plt.barh is a popular function that is used in Matplotlib to plot a horizontal bar graph. This function requires two arrays as input. The first one being the labels on Y-axis and the second one being the numeric values that are extended on the X-axis. In many cases, we try to convert the values of the list to integers by using np.int(). This issue creates a TypeError in the code as the list type of data cannot be converted into an int.
Error Example –
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.barh(np.array(["C", "C++", "Python"]), np.int(np.array(["10", "15", "20"]))) plt.show()
Possible Solution –
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.barh(np.array(["C", "C++", "Python"]), np.array(list(map(np.int, np.array(["10", "15", "20"]))))) plt.show()
Explanation –
Using map() function along with np.int will properly convert each value from str to integer in the array. This method can be used in plt.barh function to avoid TypeError.
Conclusion
Numpy module has provided thousands of useful methods that easily solve hard problems. These methods have their own sets of instructions and parameters that we need to follow properly. Only Size 1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars Error appears when you provide an invalid data type to a function that accepts a scalar value. By following the solutions and alternatives given in the post, you can solve this error in no time!
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
Happy Pythoning!
Welcome to Codingcompiler. In this blog post, we are going to explain why this TypeError: Only Size-1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars occur and how to fix Only Size-1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars in different ways.
Here we’ll explain this Python type error with an example.
Example Python Code:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return np.int(x)
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f(x))
plt.show()
The above Python example gives the “TypeError: only length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars“.
How To Fix TypeError: Only Size-1 Arrays Can Be Converted To Python Scalars
Let’s discuss how to fix this Python TypeError.
Solution – 1
The error “only length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars” is raised when the function expects a single value but you pass an array instead.
If you look at the call signature of np.int, you’ll see that it accepts a single value, not an array. In general, if you want to apply a function that accepts a single element to every element in an array, you can use np.vectorize:
Here is the code example to fix the error:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return np.int(x)
f2 = np.vectorize(f)
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f2(x))
plt.show()
Error explanation:
You can skip the definition of f(x) and just pass np.int to the vectorize function: f2 = np.vectorize(np.int).
Note: That np.vectorize is just a convenience function and basically a for loop. That will be inefficient over large arrays. Whenever you have the possibility, use truly vectorized functions or methods (like astype(int).
Solution – 2
Use: x.astype(int)
Here is the reference.
This error reference: Stackoverflow.
We hope that you got your answer for the error “only length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars“. If anything to discuss, please drop your comment in the below comment box.
Related Python Tutorials:
- All Python Tutorials
- Python Anti Patterns Tutorial
- Secure Shell Connection in Python Tutorial
- Python Security And Cryptography Tutorial
- Performance Optimization In Python Tutorial
- Python Speed Of Program Tutorial
- Profiling in Python Tutorial
- Py.test in Python Tutorial
- Python Common Pitfalls Tutorial
- Python Hidden Features Tutorial
- Python Unit Testing Tutorial
I have such Python code:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return np.int(x)
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f(x))
plt.show()
And such error:
TypeError: only length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
How can I fix it?
asked Apr 17, 2016 at 18:21
The error «only length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» is raised when the function expects a single value but you pass an array instead.
np.int was an alias for the built-in int, which is deprecated in numpy v1.20. The argument for int should be a scalar and it does not accept array-like objects. In general, if you want to apply a function to each element of the array, you can use np.vectorize:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return int(x)
f2 = np.vectorize(f)
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f2(x))
plt.show()
You can skip the definition of f(x) and just pass the function int to the vectorize function: f2 = np.vectorize(int).
Note that np.vectorize is just a convenience function and basically a for loop. That will be inefficient over large arrays. Whenever you have the possibility, use truly vectorized functions or methods (like astype(int) as @FFT suggests).
answered Apr 17, 2016 at 18:32
ayhanayhan
68.1k18 gold badges177 silver badges195 bronze badges
5
Use:
x.astype(int)
Here is the reference.
answered Feb 20, 2017 at 17:26
FFTFFT
8598 silver badges15 bronze badges
1
dataframe['column'].squeeze() should solve this. It basically changes the dataframe column to a list.
Suraj Rao
29.3k11 gold badges96 silver badges103 bronze badges
answered Feb 10, 2021 at 6:21
Take note of what is printed for x. You are trying to convert an array (basically just a list) into an int. length-1 would be an array of a single number, which I assume numpy just treats as a float. You could do this, but it’s not a purely-numpy solution.
EDIT: I was involved in a post a couple of weeks back where numpy was slower an operation than I had expected and I realised I had fallen into a default mindset that numpy was always the way to go for speed. Since my answer was not as clean as ayhan’s, I thought I’d use this space to show that this is another such instance to illustrate that vectorize is around 10% slower than building a list in Python. I don’t know enough about numpy to explain why this is the case but perhaps someone else does?
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
time_start = datetime.datetime.now()
# My original answer
def f(x):
rebuilt_to_plot = []
for num in x:
rebuilt_to_plot.append(np.int(num))
return rebuilt_to_plot
for t in range(10000):
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f(x))
time_end = datetime.datetime.now()
# Answer by ayhan
def f_1(x):
return np.int(x)
for t in range(10000):
f2 = np.vectorize(f_1)
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f2(x))
time_end_2 = datetime.datetime.now()
print time_end - time_start
print time_end_2 - time_end
answered Apr 17, 2016 at 18:30
roganjoshroganjosh
12.3k4 gold badges29 silver badges44 bronze badges
In this case the output has to be a rounded int values.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([2.34, 2.56, 3.12])
output = np.round(arr).astype(int)
print(output)
# array([2, 3, 3])
answered Aug 11, 2021 at 9:32
niek tuytelniek tuytel
8316 silver badges18 bronze badges
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return np.array(list(map(np.int, x)))
x = np.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, f(x))
plt.show()
using np.array(list(map(np.int, x))) will converge numpy array to scaler value and fix the issue for more detail visit this detailed article.
answered Feb 22, 2022 at 13:58
Table of Contents
Hide
- What is TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars?
- How to fix TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars?
- Solution 1 – Vectorize the function using np.vectorize
- Solution 2 – Cast the array using .astype() method
- Conclusion
We get this error generally while working with NumPy and Matplotlib. If you have a function that accepts a single value, but if you pass an array instead, you will encounter TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars.
In this tutorial, we will learn what is TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars and how to resolve this error with examples.
Python generally has a handful of scalar values such as int, float, bool, etc. However, in NumPy, there are 24 new fundamental Python types to describe different types of scalars.
Due to this nature, while working with NumPy, you should ensure to pass a correct type, else Python will raise a TypeError.
Let us take a simple example to reproduce this error.
# import numpy and matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# function which accepts scalar value
def my_function(x):
return int(x)
data = np.arange(1, 22, 0.4)
# passing an array to function
plt.plot(data, my_function(data))
plt.show()
Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "c:PersonalIJSCodemain.py", line 14, in <module>
plt.plot(data, my_function(data))
File "c:PersonalIJSCodemain.py", line 9, in my_function
return int(x)
TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalarsIn the above example, we have an int function that accepts only single values. However, we are passing an array to the np.int() or int() method, which will not work and results in TypeError.
How to fix TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars?
There are two different ways to resolve this error. Let us take a look at both solutions with examples.
Solution 1 – Vectorize the function using np.vectorize
If you are working with a simple array and then vectorizing, this would be the best way to resolve the issue.
The int() accepts a single parameter and not an array according to its signature. We can use np.vectorize() function, which takes a nested sequence of objects or NumPy arrays as inputs and returns a single NumPy array or a tuple of NumPy arrays.
Behind the scenes, it’s a for loop that iterates over each array element and returns a single NumPy array as output.
Let us modify our code to use the np.vectorize() method and run the program.
# import numpy and matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# function which accepts scalar value
def my_function(x):
return int(x)
# vectorize the function
f = np.vectorize(my_function)
data = np.arange(1, 22, 0.4)
# passing an array to function
plt.plot(data, f(data))
plt.show()
Output
We can see that error is gone, the vectorize() function will loop through the array and returns a single array that is accepted by the int() function.
Solution 2 – Cast the array using .astype() method
The np.vectorize() method is inefficient over the larger arrays as it loops through each element.
The better way to resolve this issue is to cast the array into a specific type (int in this case) using astype() method.
# import numpy and matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# function which accepts scalar value
def my_function(x):
# csat the array into integer
return x.astype(int)
data = np.arange(1, 22, 0.4)
# passing an array to function
plt.plot(data, my_function(data))
plt.show()
Output
Conclusion
We get TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to python scalars if we pass an array to the method that accepts only scalar values.
The issue can be resolved by using np.vectorize() function a nested sequence of objects or NumPy arrays as inputs and returns a single NumPy array or a tuple of NumPy arrays.
Another way to resolve the error is to use the astype() method to cast the array into an integer type.
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Sign Up for Our Newsletters
Subscribe to get notified of the latest articles. We will never spam you. Be a part of our ever-growing community.
By checking this box, you confirm that you have read and are agreeing to our terms of use regarding the storage of the data submitted through this form.
In this short tutorial, we look at the typeerror «Only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» in Python. This typeerror is quite common however there are only a handful of tutorials explaining it. In case you are looking for an in-depth explanation of the error I would recommend you follow step by step. If not, feel free to check out the solutions directly.
Table of Contents — Typeerror: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
- What does «Only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» signify?
- Solutions 1: Code & Explanation
- Solutions 2: Code & Explanation
What does «Typeerror: Only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» signify?
You are likely to face the above typeerror while working with NumPy and matplotlib.pyplot. This error arises when you pass an array into a function that is expecting a single value (i.e., scalar value). Python generally works with only a handful of scalar values (Int, float, bool, etc) however while dealing with NumPy we have another 24 new fundamental Python types to describe different types of scalars. You can read more about them here.
Due to the above errors, you ought to be extra cautious while using NumPy. A common error I came across was this:
import numpy as ny
import matplotlib.pyplot as matplot
def ycord(xcord):
return ny.int(xcord)
xcord = ny.arange(1, 5, 2.7)
matplot.plot(xcord, ycord(xcord))
matplot.show()
For the above input, this is the output we receive:
// Output
TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars
This is because the .int function only accepts single values and in our case we are trying to pass x which is an array.
Solution 1: Code and Explanation using the .vectorize function.
In the first method, we use the .vectorize function. The .vectorize function is essentially a for loop that takes in an array and returns a single numpy array. Using this method we iterate over the array x and return a single value. Thus we do not encounter the «only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars» typeerror.
import numpy as ny
import matplotlib.pyplot as matplot
xcord = ny.arange(1, 5, 2.5)
ycord = ny.vectorize(ny.int)
matplot.plot(xcord, ycord(xcord))
matplot.show()
As you can see we no longer need to define a function as we have used the .int function inside the .vectorize function, which loops through the array and returns a single array that is accepted by the .int function.
Solution 2: Code and Explanation using the .astype method
Another method I came across utilizes the .astype method, this method casts the array into a specified type in our case int. Although this method works, I personally recommend the first solution as this method casts a string into an int which is not a desirable method.
import numpy as ny
import matplotlib.pyplot as matplot
def ycord(xcord):
return xcord.astype(int)
xcord = ny.arange(1, 5, 2.5)
matplot.plot(xcord, ycord(xcord))
matplot.show()
These are two solutions that you can be use when faced with the Typeerror: Only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars error.
Only size-1 or length-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalars TypeError occurs when we pass an array in the place of single values like int, float, etc in any function as a parameter. This is a very generic python type error but the majority of developers face this error while working with Matplotlib, Numpy library.
Before I provide you with the solution, Let’s understand the root cause for this error.
Root cause –
The root cause is passing arrays in place of scalers. Now let’s understand what is scaler. It’s really simple as int, float, etc which consists of the magnitude of one element is scaler. For example, 1o is a scalar of type int. The float value 10.2 is a scalar. On the opposite side, the array contains multiple elements of a similar type-together. For example [1,2,3,4] is an array of int type. If you consider this error, you will get the developer to get the same while code in multiple contexts but the root cause will always be the same.
examples –
Hope this small implementation is enough to understand the root cause for this error. Now let’s see some business context where we can get this error.
Solution 1 : Using vectorize() function –
This vectorize() function create single value from NumPy array. Let’s understand with one example.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def custom_function(x):
return np.int(x)
arr1= np.arange(1, 10, 0.5)
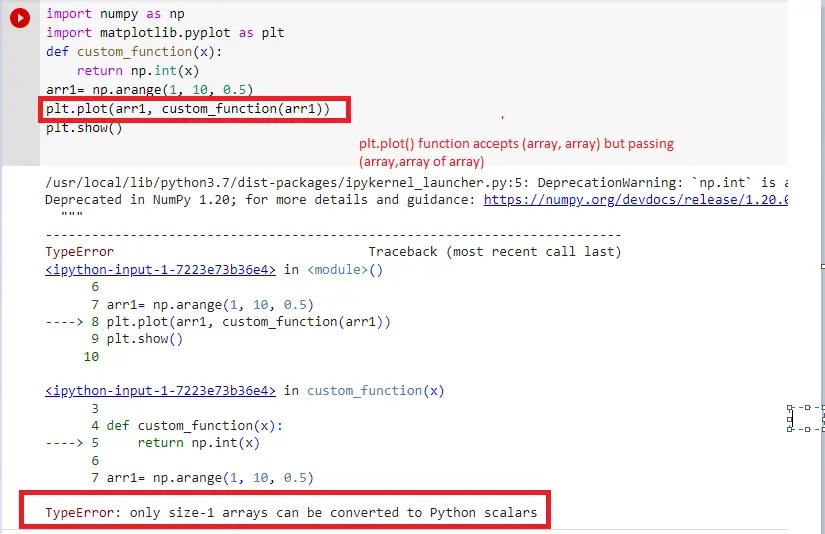
plt.plot(arr1, custom_function(arr1))
plt.show()Now if use vectorize() function we can convert the NumPy array into a singular scaler function. Let’s see with the implementation. Execute the below lines of code.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def custom_function(x):
return np.int(x)
arr1= np.arange(1, 10, 0.5)
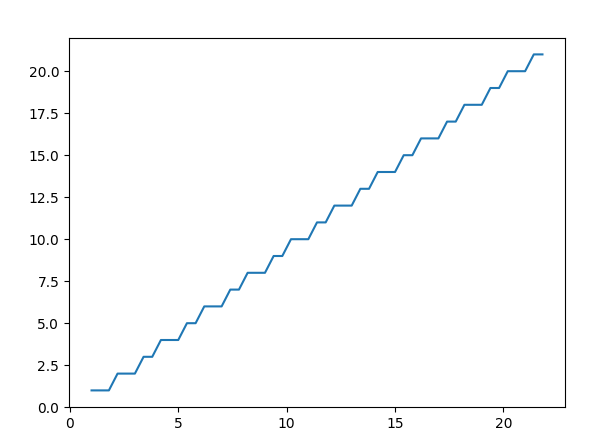
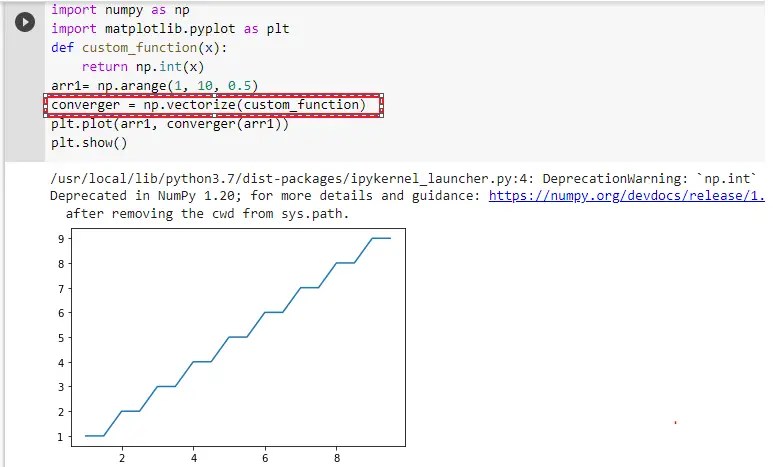
converger = np.vectorize(custom_function)
plt.plot(arr1, converger(arr1))
plt.show()Let’s see the screenshot.
As you can see that we use vectorize() function. And It converged the NumPy array into a singular value and that’s fix the error we were getting.
Solution 2 : Use astype(int) –
The astype() function works on the same principles. It will also converge the numpy array into a singular value and that will fix the issue.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def custom_function(x):
return x.astype(int)
arr1= np.arange(1, 10, 0.5)
plt.plot(arr1, custom_function(arr1))
plt.show()Here is the output for this-
Solution 3 : map() function –
See map function does what, It consumes two parameters. The first parameter is the function that is going to be applied in each data point or sequence. The second parameter is the sequence of data on which this first parameter will apply. In our context, here is the syntax and then the full code.
np.array(list(map(np.int, x)))Solution 4 : apply_along_axis() –
The apply_along_axis() function also converge NumPy error into scaler function. Here is the example for this-
obj = lambda y: [np.int(i) for i in y]
np.apply_along_axis(obj, 0, x)Solution 5: Custom logic using a loop for conversion into scaler value –
One of the easiest ways using loop we can converge multi-value into scaler one.
y = np.array([None]*len(arr1))
for i in range(len(arr1)):
y[i] = np.int(x[i])Firstly we create an empty array with equivalent size and then we will copy the element by operating np.int() function on top of it.
Generally, typerror always comes when you are passing a different datatype of the variable. Here We have covered multiple ways to fix this error but if you need to add more please comment us. You can also contact us for more help.
Thanks
Data Science Learner Team
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.
A popular TypeError in Python is TypeError only length-1 arrays can be converted to python scalar. You might encounter when working with NumPy and Matplotlib libraries. This occurs when the function that you have defined or have created is expecting a single parameter but gets an array instead. You can start fixing this error by passing a single value to the function.
In this article, we will understand more about this error and its solution.
Example:
# Import numpy & matplotlib
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot
# Define your custome function
def myfunction(x):
return numpy.int(x)
x = numpy.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, myfunction(x))
matplotlib.pyplot.show()Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "error-1.py", line 13, in <module>
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, myfunction(x))
File "error-1.py", line 7, in myfunction
return numpy.int(x)
TypeError: only size-1 arrays can be converted to Python scalarsThis error occurs as the function called np.int() takes in a single parameter as per its function definition. But if you are passing an array, it will not work and throw the error.
Solution:
Besides passing in a single element to the function you can also try using the np.vectorize() function. Use the following code to assign the np.int() method to this function:
# import numpy & matplotlib
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot
# define your custom function
def myfunction(x):
return numpy.int(x)
myfunction2 = numpy.vectorize(myfunction)
x = numpy.arange(1, 15.1, 0.1)
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, myfunction2(x))
matplotlib.pyplot.show()Output:
The np.vectorize() function works as a «for loop» that allows the function passed into it to accept a single element from an array. So, a single element is passed onto the np.int() method every time.
Conclusion
You must pass single values to functions that accept a single value. As mentioned earlier, the best way to solve this error is to use numpy.vectorize() method. This will convert the array you pass to the function, into a vector.