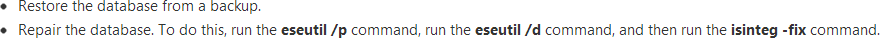- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
client has a exchange database in a Dirty Shutdown state, there is no backup
There is a corupt log file e00.log
I deleted the corrupted log file and named the last log file e00.log
I run a soft recovery with the /A switch and got the following result.
Can someone please help me!
F:ExchangeMailbox»Logfile location»>eseutil /r e00 /A /d «F:exchang
emailboxdatabase location«Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server
Version 14.01
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved.Initiating RECOVERY mode…
Logfile base name: e00
Log files: <current directory>
System files: <current directory>
Database Directory: F:exchangemailboxmailbox databsePerforming soft recovery…
Restore Status (% complete)0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|—-|
………………………………………….XOperation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outst
anding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, bu
t database is missing or does not match attachment info) after 41738.629 seconds
.F:ExchangeMailboxMailbox DatabaseCatalogData>
IT consultant
Answers
-
So a couple of options but NO MATTER what you do MAKER A COPY OF THAT DB FIRST so that you are not in a bigger pickle if things go south
1. Perhaps this article can assist
http://blogs.technet.com/b/mspfe/archive/2012/09/06/why-exchange-databases-might-remain-dirty-after-eseutil-r-recovery.aspx2. you may have to do an eseutil /P to correct the issue as the article above mentions
3. If you want to validate the database is intact check out our DigiScope product
http://www.lucid8.com/product/digiscope.asp and use the forensic mount process. If that work you can do a dial tone restore to get email flowing again and then use DigiScope to restore the email
from the offline EDB into the production
Search, Recover, & Extract Mailboxes, Folders, & Email Items from Offline Exchange Mailbox and Public Folder EDB’s and Live Exchange Servers or Import/Migrate direct from Offline EDB to Any Production Exchange Server, even cross version i.e. 2003 —>
2007 —> 2010 —> 2013 with Lucid8’s
DigiScope-
Proposed as answer by
Friday, September 18, 2015 9:24 AM
-
Marked as answer by
Lynn-Li
Monday, September 28, 2015 1:57 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
You know how when you are nervous about something and so try to do a perfect job and hope for the best, things will inevitably go wrong! Yeah, they don’t lie about that. 
I had to do an Exchange 2013 restore. My first time, to be honest, if you don’t count the one time I restored a folder in my home lab. And things didn’t go as smoothly as one would have hoped for. But hey it’s not a bad thing coz I get to learn a lot in the process. So no complaints, but it has been a nervous experience.
Initially I had a lot of DPM troubles restoring. These were solved by attaching my Azure recovery vault to a different server and doing a restore from there. In the process though I didn’t get DPM to clean up and mount the database directly on Exchange; rather I asked it to restore as files to a location and I decided to do the restore from there.
It is pretty straightforward according to the docs.
- Restore the database files.
- Bring the files of the restored database to a clean shutdown state
- Create a new recovery database, pointing to the previously cleaned up database files.
- Mount database.
- Do a restore request.
That’s all!
Here’s some more useful details I picked up along the way, including an error that caused some delays for me.
1 Restore all files to a location
Now, this is important. After restoring *do not* rename the database file. I did that and it an “Operation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch)” error. You don’t want that! Keep the database name as is. Keep the folder names too as is, it doesn’t really matter.
2.1 Check the database state
You run the eseutil /mh “pathtoedbfile” command for this.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
[C:] eseutil /mh f:Recovery2RecoveryDBRecoveryDB.edb Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server Version 15.00 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Initiating FILE DUMP mode... Database: RecoveryDB.edb DATABASE HEADER: Checksum Information: Expected Checksum: 0xdd62a2ca Actual Checksum: 0xdd62a2ca Fields: File Type: Database Checksum: 0xdd62a2ca Format ulMagic: 0x89abcdef Engine ulMagic: 0x89abcdef Format ulVersion: 0x620,20 Engine ulVersion: 0x620,20 Created ulVersion: 0x620,20 DB Signature: Create time:04/17/2018 20:18:47.835 Rand:697063639 Computer: cbDbPage: 32768 dbtime: 4400444 (0x43253c) State: Dirty Shutdown <——————— note the state Log Required: 785885—785891 (0xbfddd—0xbfde3) <——————— I have these Log Committed: 0—785892 (0x0—0xbfde4) Log Recovering: 0 (0x0) |
Two things to note. First, the state – “Dirty Shutdown” – so I need to clean up the database. And second, the logs required. If I check the restored folder I should see files of this name there. In my case I did have files along these lines:
|
f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDDD.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDDE.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDDF.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDE0.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDE1.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDE2.log f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFDE3.log |
2.2 Confirm that the logs are in a good state
You run the eseutil /mh “pathtolog filesEXX” command for this (where XX is the log prefix).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
[C:] eseutil /ml f:Recovery2RecoveryDBe02 Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server Version 15.00 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Initiating FILE DUMP mode... Verifying log files... Base name: e02 Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD93.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD94.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD95.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD96.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD97.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD98.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD99.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD9A.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD9B.log — OK Log file: f:Recovery2RecoveryDBE02000BFD9C.log — OK |
All looks good.
2.3 Bring the database files to a clean shutdown state
For this you run eseutil /R EXX /l “pathtologfiles” /s “pathtoedbfile” /d “pathtoedbfile” (where XX is the log prefix). I remember the /lsd switches coz they look like LSD. 
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
[C:] eseutil /r e02 /l “f:Recovery2RecoveryDB» /s «f:Recovery2RecoveryDB» /d »f:Recovery2RecoveryDB« Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server Version 15.00 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Initiating RECOVERY mode... Logfile base name: e02 Log files: RecoveryDB System files: RecoveryDB Database Directory: RecoveryDB Performing soft recovery... Restore Status (% complete) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 |——|——|——|——|——|——|——|——|——|——| ................................................... Operation completed successfully in 0.797 seconds. |
Looks good!
The first few times I ran this command I got the following error –
|
Operation terminated with error —1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outstanding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, but database is missing or does not match attachment info) after 0.344 seconds. |
I went on a tangent due to this. 
eseutil command without this switch didn’t make any difference. I had to start from scratch (luckily I was working on a copy of the restored files, so didn’t have to do a fresh restore!).
Later I had the smart idea of checking the event logs to see why this was happening. And there I saw entries like this:
|
eseutil (4132) Database recovery failed with error —1216 because it encountered references to a database, ‘f:Recovery2RecoveryDBMailbox Database 10.edb’, which is no longer present. The database was not brought to a Clean Shutdown state before it was removed (or possibly moved or renamed). The database engine will not permit recovery to complete for this instance until the missing database is re—instated. If the database is truly no longer available and no longer required, procedures for recovering from this error are available in the Microsoft Knowledge Base or by following the «more information» link at the bottom of this message. |
You see I had the “smart” idea of renaming my database file to something else. It was a stupid idea because the database still had references to the old name and that’s why this was failing. None of the blog posts or articles I read did a database rename, but none of them said don’t do it either … so how was I to know? 
Anyways, if you haven’t renamed your database you should be fine. You could still get this or any other error … but again, don’t be an idiot like me and go Googling. Check your event logs. That’s what I usually do when I am sensible, just that being nervous and all here I skipped my first principles.
2.4 Confirm the database state is clean
Run the eseutil /mh command of step 2.1 and now it should say “Clean Shutdown”.
At this point your recovered database files are in a clean state. Now to the next step!
3 Create a new recovery database, pointing to the restored database files.
Do this in the Exchange Management Shell.
|
New—MailboxDatabase —Recovery —Name «Recovery DB» —EdbFilePath ‘F:Recovery2RecoveryDBRecoveryDB.edb’ —LogFolderPath ‘F:Recovery2RecoveryDB’ —Server rak1exch01 |
You will get a warning about restarting the Information Store service. Don’t do it! Restarting the Information Store will cause all Outlook connections to that server to disconnect and reconnect – you definitely don’t want that in a production environment! 
Also, remember that Recovery databases don’t appear in EAC so don’t worry if you don’t see it there.
If you want to read more on Recovery databases this is a good article.
4 Mount the recovery database
Again in EMS:
|
Mount—Database “Recovery DB« |
5 Do a restore request
Still in EMS:
|
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceDatabase «Recovery DB» -SourceStoreMailbox «User Mailbox» -TargetRootFolder «RecoveredContacts» -TargetMailbox “User Mailbox« -SourceRootFolder Contacts -AllowLegacyDNMismatch |
I am restoring a folder called “Contacts” from “User Mailbox” back to “User Mailbox” under a folder called “RecoveredContacts”.
You can keep an eye on the restore request thus:
|
Get—MailboxRestoreRequest | Get—MailboxRestoreRequestStatistics | fl percentcomplete,itemstransferred,*count* |
5+ Cleanup tasks
And once done you can remove all completed requests:
|
Get—MailboxRestoreRequest —Status Completed | Remove—MailboxRestoreRequest |
That’s it!
You can also remove the Recovery database now. Dismount it first.
|
Dismount—Database «RecoveryDB» |
|
Remove—MailboxDatabase «Recovery DB» |
This doesn’t remove the EDB files or logs, so remove them manually.
Some links that I came across while reading up on this:
- https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/mspfe/2012/09/06/why-exchange-databases-might-remain-dirty-after-eseutil-r-recovery/ – a very good blog post.
- https://practical365.com/exchange-server/restoring-exchange-server-2016-mailboxes-and-items-using-a-recovery-database/ – another very good blog post; covers more scenarios than I did above. One difference is the author of this post creates the Recovery Database first and then restores the files to it, followed by bringing it up to a clean shutdown state. Same difference I guess, I dunno.
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/move-a-mailbox-database-using-database-portability-exchange-2013-help – database portability. This is for when you want to recover the whole database to a different server. (I too was recovering to a different server, but my servers were part of the same DAG and so it doesn’t matter I guess. Or maybe I was only restoring the contents of a single folder from the database and so it didn’t matter. I am not a 100% sure).
- You find a lot of articles saying you can try
eseutil /pto recover a database that stays in a “dirty shutdown” state even after running recovery. This blog post tells you what this switch does. Also as a reminder to myself, copy-pasting this definition of eseutil for my own reference: “ESEUTIL.exe or the Exchange Storage Engine Utility is an executable file residing in the bin directory which is used to perform various operations like recovery, repair, integrity check on an Exchange database while it is offline.“
My first baby step production Exchange 2013 restore. Finally! 
Содержание
- /AlexxHost/
- четверг, 7 октября 2010 г.
- Восстановление баз данных при помощи ESEUTIL
- Принцип работы базы данных почтовых ящиков
- Реанимация базы данных
- Оценив ситуацию, давайте перейдем непосредственно к реанимации базы
- Заключение
- Operation terminated with error 1216
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
- Operation terminated with error 1216
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
- Microsoft Exchange Server Made Easy
- Label overview
- Total Pageviews
- Blog Archive
- Wednesday, December 9, 2020
- Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch [RESOLVED]
- Know How to Resolve Exchange Error 1216
- Cause Behind the Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch
- Solution to Remove Exchange Error 1216
- Output You Get After Implementing the command to Fix Exchange Error 1216
/AlexxHost/
Вы попали на блог, целиком и полностью посвященный продуктам компании Microsoft. В основном речь будет идти про системы корпоративных коммуникаций на базе Exchange Server.
четверг, 7 октября 2010 г.
Восстановление баз данных при помощи ESEUTIL

Так вот, прежде чем приступить к вопросу восстановления нужно понять принцип работы базы данных на сервере Exchange.
Принцип работы базы данных почтовых ящиков
Дело в том, что актуальная информация о состоянии почтовых ящиков пользователей хранится в двух местах:
- в файле с расширением *.EDB – файл самой базы;
- в лог-файлах.
При этом лог-файлов есть несколько видов
- E00.log — это лог файл, используемый в настоящее время механизмом базы данных;
- E00tmp.log — новый лог файл, который создается в текущий момент;
- E00000003A.log, E00000003B.log, E00000003C.log — это лог файлы, хранящиеся на диске, которые можно использовать для восстановления;
- E00res00001.jrs и E00res00002.jrs — это предварительно созданные лог файлы, используемые, когда диск, содержащий лог файлы, заполнен.
Ещё в папке с логами есть файл E00.chk — это файл контрольной точки, используемой для отслеживания отношений между лог-файлами и файлом базы данных.
В результате процесс работы базы данных можно проиллюстрировать следующим образом:
Рис.1: Работа базы данных
- Почтовые данные сначала обрабатываются в памяти, разделяются на страницы (32 Kb – Exchange 2010, 8 Kb – Exchange 2007).
- Обновленные страницы, образующие транзакцию, записываются в лог файл — E00.log.
- Если страницы больше не требуются, они записываются в базу данных.
- Файл контрольной точки (E00.chk) обновляется и отображает новое место контрольной точки, файл E00.log переименовывается в следующий E0000000. log, а на место него приходит E00tmp.log.
Примечание: В пределах сервера у каждой базы должен быть индивидуальные префикс, в данном примере это E00, для следующей созданной на сервере базы данных будет сгенерирован префикс E01 и т.д..
В процессе создания и получения новых писем, может возникнуть ситуация когда новая информация находится только в транзакционном логе и еще не была записана в файл базы данных. Следовательно, если некорректно выключить сервер, то часть данных останется в файле E00.log. При этом база останется в состоянии «Неправильного отключения» (Dirty Shutdown).
Если отключить базу корректно при помощи командлета Unmount-Database, то вся информация будет перемещена в основной файл базы данных (*.EDB) и логи можно будет удалять. При этом база будет в состоянии «Правильного отключения» (Clean Shutdown). Для того, чтобы смонтировать базу на сервер Exchange, её нужно перевести в состояние Clean Shutdown.
Справедливости ради, нужно отметить, что если у вас просто внезапно пропало питание на сервере и после перезагрузки все нормально запустилось, то в подавляющем большинстве случаев, несмотря на то, что после загрузки база будет в состоянии Dirty Shutdown, сервер сам проведет проверку базы и смонтирует её. В этом случае вам больше беспокоиться ни о чем не стоит. Также, если вы восстанавливаете базу данных из архивной копии в её исходное расположение, то вероятнее всего она будет смонтирована сервером без проблем.
Далее давайте рассмотрим ситуацию, когда сама база не монтируется, либо она повреждена и вам нужно её восстановить.
Реанимация базы данных
Все манипуляции с файлами базы данных придется производить из командной строки при помощи утилиты ESEUTIL.
Первое что нам нужно сделать – это оценить обстановку, для этого используем ключи /MH и /ML для получения информации из заголовков файла базы данных и лог-файлов.
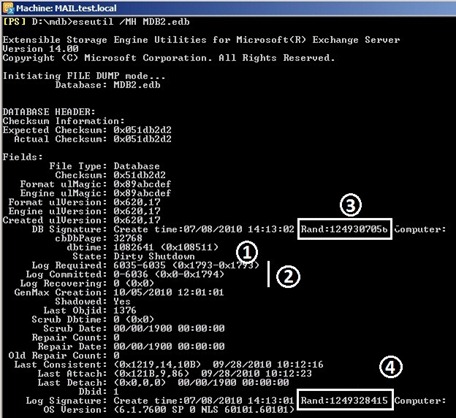
Eseutil /MH MDB.edb
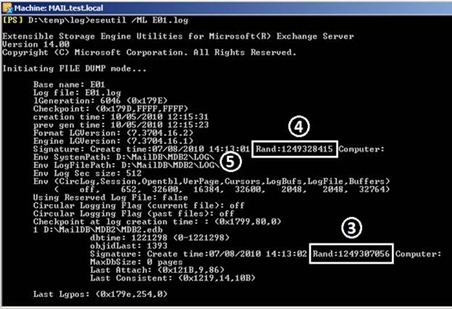
Eseutil /ML E00.log
Для проверки целостности всех лог-файлов нужно использовать команду:
Рис.2: Заголовок edb-фала.
Рис.3: Заголовок лог-файла
В результате мы получаем достаточно много информации о самой базе и о её состоянии. Особенное внимание нужно уделить следующим строчкам:
1. State – Dirty Shutdown – говорит нам о том, что база была отключена не корректно;
2. Информация о связанных лог-файлах;
3. Сигнатура базы;
4. Сигнатура лог-файлов;
5. Системные директории.
Также можно обратить внимание на строку lGeneration – это номер, под которым будет сохранен текущий лог-файл. А по сигнатурам лог-файлов и базы можно оценить принадлежность этих файлов конкретной базе.
Оценив ситуацию, давайте перейдем непосредственно к реанимации базы
Начать стоит с мягкого восстановления, для этого используется ключ /R – Recovery, следующим образом:
При этом нужно обратить внимание на такую вещь, как расположение файла базы данных и лог-файлов. Если мы вернемся к рис.3, то под цифрой 5 на нем указано, где должны лежать системные файлы, лог-файлы и файл базы данных. Следовательно, если мы восстанавливаем базу из архива в альтернативное место, то нам нужно перезаписать эту информацию новыми значениями. Здесь проще всего положить лог-файлы в каталог с самой базой данных и использовать ключик /D для перезаписи путей.
Примечание: Нужно знать, что совместно с ключом /R ключик /D не дефрагментирует базу, а выполняет перезапись путей. Если переключатель /D указан без пути, в качестве пути к файлам базы данных будет использован текущий каталог. Если сразу за переключателем /D следует путь к файлу (без пробелов), этот путь будет использован для поиска файлов базы данных.
Если все же вы хотите использовать альтернативные системные директории, то вам понадобятся ключи /S – для системных файлов, /L – для лог-файлов, /D – для файла базы данных. При этом в данном контексте писать путь нужно НЕ отделяя его пробелом от ключа.
В результате, перейдя в каталог с файлом базы данных (edb), для мягкого восстановления можно использовать следующую команду:
Eseutil /R E00 /D /Ld:templogs /Sd:templogs
Рис.4: Мягкое восстановление базы данных и проверка состояния файла EDB.
Примечание: Из собственного опыта — если какое-либо действие по восстановлению базы закончилось ошибкой, то лучше заново скопировать файлы базы из архива и попробовать выполнить другую команду, в противном случае результат трудно прогнозируется.
Если в ходе восстановления вы получаете ошибку:
Operation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outstanding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, but database is missing or does not match attachment info)
то к команде следует добавить ключ /i.
Заключение
Если мягкое восстановление прошло удачно и база перешла в состояние Clear Shutdown, значит у вас все получилось и теперь можно монтировать EDB-файл к базе данных восстановления, либо к любой другой базе в этом лесе.
В случае, если такого не произошло, и мягкое восстановление окончилось неудачей, то стоит прибегнуть к другим методам, о которых мы поговорим в следующей части данной статьи.
Источник
Operation terminated with error 1216
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
client has a exchange database in a Dirty Shutdown state, there is no backup
There is a corupt log file e00.log
I deleted the corrupted log file and named the last log file e00.log
I run a soft recovery with the /A switch and got the following result.
Can someone please help me!
F:ExchangeMailbox»Logfile location»>eseutil /r e00 /A /d «F:exchang
emailboxdatabase location«
Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server
Version 14.01
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Initiating RECOVERY mode.
Logfile base name: e00
Log files:
System files:
Database Directory: F:exchangemailboxmailbox databse
Performing soft recovery.
Restore Status (% complete)
Operation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outst
anding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, bu
t database is missing or does not match attachment info) after 41738.629 seconds
.
Answers
So a couple of options but NO MATTER what you do MAKER A COPY OF THAT DB FIRST so that you are not in a bigger pickle if things go south
2. you may have to do an eseutil /P to correct the issue as the article above mentions
Источник
Operation terminated with error 1216
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
client has a exchange database in a Dirty Shutdown state, there is no backup
There is a corupt log file e00.log
I deleted the corrupted log file and named the last log file e00.log
I run a soft recovery with the /A switch and got the following result.
Can someone please help me!
F:ExchangeMailbox»Logfile location»>eseutil /r e00 /A /d «F:exchang
emailboxdatabase location«
Extensible Storage Engine Utilities for Microsoft(R) Exchange Server
Version 14.01
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Initiating RECOVERY mode.
Logfile base name: e00
Log files:
System files:
Database Directory: F:exchangemailboxmailbox databse
Performing soft recovery.
Restore Status (% complete)
Operation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outst
anding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, bu
t database is missing or does not match attachment info) after 41738.629 seconds
.
Answers
So a couple of options but NO MATTER what you do MAKER A COPY OF THAT DB FIRST so that you are not in a bigger pickle if things go south
2. you may have to do an eseutil /P to correct the issue as the article above mentions
Источник
Microsoft Exchange Server Made Easy
Exchange Guide is the complete encyclopedia for all the possible queries related to MS Exchange Server . Contains expert solutions , tips , tricks and explanations to frequently asked terms/questions.


Label overview
Total Pageviews
Blog Archive
Wednesday, December 9, 2020
Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch [RESOLVED]
Know How to Resolve Exchange Error 1216
The worst situation for the Exchange administrator is when Exchange EDB file gets corrupted or damaged. We all know that Exchange stores all its data in EDB format that can only be used via MS Outlook email applications without any issue. However, just like other file extensions, there are the conditions when EDB data files get corrupted and displays errors. One such error is Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch. Users facing this error have to face so many problems. So, in this blog, we are going to discuss the solutions to remove the specified error.
Usually, when the one gets Jet Error then, it is not manageable practically to utilize Exchange database files. However, these instances give out the result in data loss situation. In order, to get back the access of crucial data then, first figure out the main reason behind the issue. Out of which, one such error is:
Rapid Solution: SysTools Exchange Server Recovery software is a complete solution that makes easy to recover Exchange mailbox and EDB file from all the corrupted or inaccessible data. The utility retrieves all the data in exact form without losing a bit of data information. This application is capable enough to export the recoverd Exchange mailboxes to Live Exchange Server, Office 365 and PDF, EML, MBOX, PST, MSG, HTML file format.
Cause Behind the Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch
1. Network related issue ad any major corrupted Exchange Database File leads to 1216 Jet error
2. This error is due to assessment of header information in log files. Moreover, databases displays that there has been the removal of files. If soft recovery is run for this error then, it may begin the storage group or it will left the storage group running with various missing of data files.
3. If you execute soft recovery, it may be hard to include lost information into storage group. When the storage group starts, whether the earlier shutdown was unusual, information of header is inspected by machine; if the assessment of system files headers disclosures inconsistencies, 1216 Jet error is returned.
Solution to Remove Exchange Error 1216
If the storage group simply stops all of sudden then, there are the chances that almost all database files become inconsistent. If issue leads to stoppage of storage group then, it leaves more than one database files unreachable. In that case, an error message is logged in event log of application.
One can simply identify the inconsistence of files by using ESEUTIL command against the files.
If you are utilizing higher edition of MS Exchange Server then, you can get the state of database file by simply executing the command as discussed below:
Output You Get After Implementing the command to Fix Exchange Error 1216
All the logs must be present for successful database recover but in case, any logs are missing. Then, you will not be able to do recovery of database. It will be left with no other option than doing the following:
Migrate all database files, which are missing in the last Consistent logs to safe location. After that, restore the residual files by simply mounting them.
Reinstate the database from backup repair database. To execute this, you require executing eseutil /p command, eseutil /d command. After that, isinteg -fixing command.
Источник
How to Resolve Exchange Jet Error 1216 in MS Exchange 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, 2003 ?
In this post, we have covered all about Exchange Jet error 1216 in Microsoft Exchange 2010. What all are reasons behind it and how it can be resolved in an efficient way.
Microsoft Exchange is one of the popularly used emailing platforms, but like any other application MS Exchange also encountered many errors. Most of the times errors are easily resolved through simple fixes. But, when it comes to the major errors like Jet Exchange Error 1216, it requires more attention and deeper knowledge to resolve it completely.
All these Jet Engine errors of Exchange 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, 2003 are not easy to resolve and have the ability to corrupt or damaged the EDB or Exchange Database File. Therefore, to fix Exchange error 1216, a user first needs to understand the main cause of this error.
Jet Exchange Error 1216 : jet_errattacheddatabasemismatch
One of the common errors that are associated with the Jet engine is Exchange error 1216. Whenever an administrator tries to mount database in Microsoft Exchange Server, then they may encounter an error message:
‘Error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch)’
This message determines that Exchange Database Recovery failed with Jet Engine error 1216. It mainly occurs when the header information assessment in database and log files indicates that some of the important data or files have been erased or removed. It is because sometimes running storage group stops suddenly in between, which leads inconsistencies in almost all files of the database.
There can be many possible reasons due to which error encountered and all of them are discussed below:
1. If running storage group stops suddenly in between due to which there may be some of the loss of data. So, if the storage group starts running again but with missing files. This will result in Exchange error 1216.
2. Another possible reason behind this error is any network related issue.
3. If there is any badly corrupted Exchange Database file or EDB file, then also it leads to Jet error 1216.
4. Someone has made changes to the important files, which are necessary to work with Exchange Server database 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, 2003.
Solutions to Resolve Exchange Jet Error 1216
Considering the requirement of the users both manual and automatic solutions to resolve Exchange error 1216 are discussed. A user can choose between them based on their convenience.
Manual to Fix Jet Error 1216 Exchange 2010
To fix database file using ESUETIL command manually, one needs to follow the step-wise instruction given below:
Step 1: First of all, you need to find the files that have inconsistencies. For this, run the command given below:
ESEUTIL /mh | find /i "consistent"
A user can use this command in Microsoft Exchange Server versions 2003 and for above versions use:
ESEUTIL /mh | find /i "Shutdown"
As the above commands complete its execution to resolve Jet Exchange Error 1216 : jet_errattacheddatabasemismatch, you need to check the sample of the output. Make sure that all process logs are available to repair database successfully. However, if any of the logs is missing in then it is not possible to perform recovery. In that case, a user needs to follow the steps given below:
Step 2: Now, you need to transfer all files, which are missing (from the last Consistent logs) to some safe location and after that restore all other files simply by mounting them.
Step 3: After that, you have to restore the database from last created backup
Step 4: In last, repair the database.
To complete this task successfully, a user needs to execute the ESEUTIL /p command, ESEUTIL /d command. After running this, a user is advised to run the ISINTEG -fix command.
Professional Solution to Resolve Exchange Jet Error 1216
It might be possible that the above-discussed manual may not work in every situation. Therefore, in order to have a guaranteed solution, a user is recommended to use this one-stop solution by SysTools i.e. EDB Reapir Tool to repair corrupted EDB file. It recovers all Exchange mailboxes and data items: emails, contacts, calendars, etc., without any file size limitation.

The dual scanning mode of this utility i.e. Quick and Advance scan mode recovers and repair EDB file from corruption with no data loss. Depending on the level of corrupted Exchange database file users can select the scan mode option. After recovery, users can easily export the recovered Exchange mailboxes directly to the Live Exchange Server, Office 365 and EML, MBOX, MSG, PST, PDF, HTML file formats.
The advance scan option also recovers hard deleted Exchange mailboxes and data items from loaded offline / dismounted .edb file. Now users can easily recover deleted mailbox after retention period and extract mailbox from EDB file Exchange 2016, 2013, 2010 & below versions in a hassle freeway.
Conclusion
Any type of error in Exchange Database file can create a trouble for the users. Among all, one such error is Exchange Jet Error 1216 : jet_errattacheddatabasemismatch. In order to resolve this in a single without any loss of data, a user is directly suggested to take help of professional software to complete task in few clicks only. Therefore, if a user finds any issue in EDB file of Exchange Server, then can use this professional without any doubt.

Так вот, прежде чем приступить к вопросу восстановления нужно понять принцип работы базы данных на сервере Exchange.
Принцип работы базы данных почтовых ящиков
Дело в том, что актуальная информация о состоянии почтовых ящиков пользователей хранится в двух местах:
- в файле с расширением *.EDB – файл самой базы;
- в лог-файлах.
При этом лог-файлов есть несколько видов
- E00.log — это лог файл, используемый в настоящее время механизмом базы данных;
- E00tmp.log — новый лог файл, который создается в текущий момент;
- E00000003A.log, E00000003B.log, E00000003C.log — это лог файлы, хранящиеся на диске, которые можно использовать для восстановления;
- E00res00001.jrs и E00res00002.jrs — это предварительно созданные лог файлы, используемые, когда диск, содержащий лог файлы, заполнен.
Ещё в папке с логами есть файл E00.chk — это файл контрольной точки, используемой для отслеживания отношений между лог-файлами и файлом базы данных.
В результате процесс работы базы данных можно проиллюстрировать следующим образом:
Рис.1: Работа базы данных
- Почтовые данные сначала обрабатываются в памяти, разделяются на страницы (32 Kb – Exchange 2010, 8 Kb – Exchange 2007).
- Обновленные страницы, образующие транзакцию, записываются в лог файл — E00.log.
- Если страницы больше не требуются, они записываются в базу данных.
- Файл контрольной точки (E00.chk) обновляется и отображает новое место контрольной точки, файл E00.log переименовывается в следующий E0000000…log, а на место него приходит E00tmp.log.
Примечание: В пределах сервера у каждой базы должен быть индивидуальные префикс, в данном примере это E00, для следующей созданной на сервере базы данных будет сгенерирован префикс E01 и т.д..
В процессе создания и получения новых писем, может возникнуть ситуация когда новая информация находится только в транзакционном логе и еще не была записана в файл базы данных. Следовательно, если некорректно выключить сервер, то часть данных останется в файле E00.log. При этом база останется в состоянии «Неправильного отключения» (Dirty Shutdown).
Если отключить базу корректно при помощи командлета Unmount-Database, то вся информация будет перемещена в основной файл базы данных (*.EDB) и логи можно будет удалять. При этом база будет в состоянии «Правильного отключения» (Clean Shutdown). Для того, чтобы смонтировать базу на сервер Exchange, её нужно перевести в состояние Clean Shutdown.
Справедливости ради, нужно отметить, что если у вас просто внезапно пропало питание на сервере и после перезагрузки все нормально запустилось, то в подавляющем большинстве случаев, несмотря на то, что после загрузки база будет в состоянии Dirty Shutdown, сервер сам проведет проверку базы и смонтирует её. В этом случае вам больше беспокоиться ни о чем не стоит. Также, если вы восстанавливаете базу данных из архивной копии в её исходное расположение, то вероятнее всего она будет смонтирована сервером без проблем.
Далее давайте рассмотрим ситуацию, когда сама база не монтируется, либо она повреждена и вам нужно её восстановить.
Реанимация базы данных
Все манипуляции с файлами базы данных придется производить из командной строки при помощи утилиты ESEUTIL.
Первое что нам нужно сделать – это оценить обстановку, для этого используем ключи /MH и /ML для получения информации из заголовков файла базы данных и лог-файлов.
Eseutil /MH MDB.edb
Eseutil /ML E00.log
Для проверки целостности всех лог-файлов нужно использовать команду:
Eseutil /ML E00
Рис.2: Заголовок edb-фала.
Рис.3: Заголовок лог-файла
В результате мы получаем достаточно много информации о самой базе и о её состоянии. Особенное внимание нужно уделить следующим строчкам:
1. State – Dirty Shutdown – говорит нам о том, что база была отключена не корректно;
2. Информация о связанных лог-файлах;
3. Сигнатура базы;
4. Сигнатура лог-файлов;
5. Системные директории.
Также можно обратить внимание на строку lGeneration – это номер, под которым будет сохранен текущий лог-файл. А по сигнатурам лог-файлов и базы можно оценить принадлежность этих файлов конкретной базе.
Оценив ситуацию, давайте перейдем непосредственно к реанимации базы
Начать стоит с мягкого восстановления, для этого используется ключ /R – Recovery, следующим образом:
Eseutil /R E00
При этом нужно обратить внимание на такую вещь, как расположение файла базы данных и лог-файлов. Если мы вернемся к рис.3, то под цифрой 5 на нем указано, где должны лежать системные файлы, лог-файлы и файл базы данных. Следовательно, если мы восстанавливаем базу из архива в альтернативное место, то нам нужно перезаписать эту информацию новыми значениями. Здесь проще всего положить лог-файлы в каталог с самой базой данных и использовать ключик /D для перезаписи путей.
Примечание: Нужно знать, что совместно с ключом /R ключик /D не дефрагментирует базу, а выполняет перезапись путей. Если переключатель /D указан без пути, в качестве пути к файлам базы данных будет использован текущий каталог. Если сразу за переключателем /D следует путь к файлу (без пробелов), этот путь будет использован для поиска файлов базы данных.
Если все же вы хотите использовать альтернативные системные директории, то вам понадобятся ключи /S – для системных файлов, /L – для лог-файлов, /D – для файла базы данных. При этом в данном контексте писать путь нужно НЕ отделяя его пробелом от ключа.
В результате, перейдя в каталог с файлом базы данных (edb), для мягкого восстановления можно использовать следующую команду:
Eseutil /R E00 /D /Ld:templogs /Sd:templogs
Рис.4: Мягкое восстановление базы данных и проверка состояния файла EDB.
Примечание: Из собственного опыта — если какое-либо действие по восстановлению базы закончилось ошибкой, то лучше заново скопировать файлы базы из архива и попробовать выполнить другую команду, в противном случае результат трудно прогнозируется.
Если в ходе восстановления вы получаете ошибку:
Operation terminated with error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch, An outstanding database attachment has been detected at the start or end of recovery, but database is missing or does not match attachment info)
то к команде следует добавить ключ /i.
Заключение
Если мягкое восстановление прошло удачно и база перешла в состояние Clear Shutdown, значит у вас все получилось и теперь можно монтировать EDB-файл к базе данных восстановления, либо к любой другой базе в этом лесе.
В случае, если такого не произошло, и мягкое восстановление окончилось неудачей, то стоит прибегнуть к другим методам, о которых мы поговорим в следующей части данной статьи.
A crashing Exchange can be a server administrator’s worst nightmare. With thousands of mailboxes hosted on each Exchange server, even a minor issue that triggers a crash could lead to work interruption for hundreds of users. That’s the reason strategies like regular backups and extensive OST file usage are emphasized and are gaining momentum.
In this article, however, we’ll be focusing in detail on Exchange Jet Error 1216 and Exchange Jet Error 1018 which are directly related to the Exchange database. Let’s see what causes these errors and how they can be resolved easily.
Exchange Jet Error 1018
Whenever a transaction is performed with the Exchange database, it is written to a transaction log file. Thereafter, the transaction is committed to the database. During this process, the Jet engine and the hardware device driver do a lot of work to write the 4KB page of data to the database on the disk. If everything goes through successfully, Jet continues. Sometimes however, hardware or device drivers may perform successfully but errors may occur during the process of actually writing the data.
For instance in the case of error -1018, a mismatch of checksum values while writing data to the disk causes a JET_errReadVerifyFailure (-1018) to be thrown. More often than not, this happens due to page-level database corruption during online backup creation.
Why it occurs?
Though we’ve outlined the main reasons behind the occurrence of Exchange Jet Error 1018, here they are listed down in an easy to grasp manner:
- The checksum values stored in the database header and those calculated while writing database to the disk don’t match
- The Exchange server itself is acting wary and generating this error due to incorrect checksum value generation for the page
- There is an error with the NTFS file system
- Data is being written to an incorrect location on the hard disk
Resolving error 1018
There are many ways in which the error can be resolved.
- Full database restore from backup
Often the best, most straightforward and most reliable way to deal with a problem as grave as the 1018 error is to restore from the last known good backup. Doing a full backup restore is however time taking and it may not provide a permanent solution to the 1018 error. To get rid of it for good you will need to eradicate its root cause that might in most cases is a hardware problem. You may try Stellar Phoenix Exchange Server Backup for free to restore database from Exchange Backup from here:
- Using Eseutil.exe
Another way to repair error 1018 is by using Eseutil.exe for Exchange server 2010, 2013 and other earlier versions. Eseutil is low-level Jet database utility that defragment and check the consistency of the database. To repair bad pages and remove them if repair is unsuccessful, these utilities can be used as follows:
Eseutil /p <dbname>
However, you should take care to take a full database backup before as well as after using this utility.
- Other troubleshooting tips
If both the above steps fail to yield satisfactory results, you could try some of the below mentioned fixes. After each of these fixes check to verify if the problem has resolved.
- Run Chkdsk.exe to check hard disk integrity
- Run Performance Optimizer (Perfwiz.exe) on the server
- Verify all hard disk drivers and utilities from the OEM are of the latest versions. If not, update them
- Restart the information store and directory services from the Control Panel
- Use the Performance Monitor counters associated with Cache, PhysicalDisk, Memory, Server, Thread, System etc. to detect potential problems
If none of the above-mentioned steps seem to solve the problem, rope in a trustworthy third-party Exchange Repair Tool like Stellar Repair for Exchange. We’ve mentioned one at the end to make the selection process easy for you.
Moving on to our next error in focus.
Exchange Jet Error 1216
Another common error associated with the Jet engine is 1216. Many administrators while trying to mount database in the Exchange Server out of nowhere face the error message:
‘Error -1216 (JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch)’
Which indicates that exchange database recovery failed with error 1216.
Alternatively, the storage groups might stop working suddenly with strange looking errors and a description saying:
‘Information Store (4312) Database recovery failed with error -1216 because it encountered references to a database‘
This is an alarming situation that needs to be tackled at the earliest in order to bring the server back to a working state. But to find a solution, the administrator must identify the real problem behind the error first.
Why it occurs?
The main reason behind the occurrence of this error is missing crucial files. If the header information in the log file shows that some important files required to work Exchange Server have been deleted or altered, then error -1216 is generated.
The error implies that the administrator can run soft recovery to start the storage group however that will mean that it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to recover and incorporate the lost information into the storage group. The admin might also choose to let the storage group run but with a number of files missing as a temporary turnaround.
Resolving error 1216
If a storage group stops suddenly, almost all database files will become inconsistent. To identify which files have become inconsistent, execute the following eseutil command:
eseutil /mh name_of_database | find /i “consistent”
If you are using Exchange Server 2010/ 2007/ 2003, then the same can be done by running the command:
eseutil /mh database_name | find /i “Shutdown”
If this technique doesn’t work, try out the following:
- Transfer all missing Consistent logs files to a safe location and then restore the remaining files by mounting them.
- Perform a full backup restore
- Repair the database. To perform this, you need to run the eseutil /p command, eseutil /d command, and after that run the isinteg -fix command.
Hope our helpful pointer will assist you in fixing errors 1216 and 1018 of Exchange Jet. If however, you’re unable to get satisfactory results from these techniques, try Exchange Server Recovery software to fix all EDB files and recover every piece of data within them. This software will definitely help you to start afresh.
About The Author
Admin
Blog admin is a certified Exchange Server Administrator who handles the critical issues in Exchange Server environment. Having 10+ years of experience in Microsoft technologies, you can ask him any query related Exchange Server & Outlook issues in the comment box.
In Exchange 2000 server, this error appear when set of files are missing or have been replaced in the database. When this kind of error occurs, Exchange 2000 terminates soft recovery because if the soft recovery task starts, it starts the storage group but with some missing data. Also, the recovery task makes the re-integration process of missing files impossible with the storage group.
Thus, to overcome through this problem you need to restore the missing files but if the files are not available then you need to go first with Eseutil option to override the error and then proceeds the soft recovery task despite of missing or mismatched files.
If you go for soft recovery task using Eseutil then you must have the following things:
Above three things is located in the General Tab of the storage group in ESM (Exchange Server Manager) and after having the complete set type, put the command exactly in the command line:
Solution:
ESEUTIL /R Enn /I /L[log_path] /S[system_path]
Resolve 1216 Errors When More Than One Database File Is Inconsistent
If the storage group is created problem or stopped unexpectedly, also, it display the following error message, it mean that multiple database files are unavailable and database’s leads into an inconsistent state.
You can find either the database is in inconsistent place or not. To check, run this command in the command line:
eseutil /mh database_name | find /i «consistent»
If you have higher edition from Exchange Server 2000 then you need to run this command to know the inconsistency of the database:
eseutil /mh database_name | find /i «Shutdown»
Now, when you find the database inconsistent in the storage group then you have to prefer extreme caution with all transaction log files. You need to define which log file of each database is required for recovery by using Eseutil tool, so to identify the log put the command in the command line:
eseutil /mh database_name | find /i «log required
Also, you need to specify the range of the log file which is listed from decimal to hexadecimal.
In most cases, you unable to find the highest log, to find the highest log run this command:
eseutil /ml E0n.log | find /i «lgeneration»
Solution:
Now, if you are missing any of the log file then recovery task of the database doesn’t work anymore and it leads you with the two alternative ways:
Or
There are several other methods from where you can restore databases:
Finally, you can recover all databases along with their information in the available log set by running the ESEUTIL /R /I /L /S command.
Note: If you still get the error message of 1216 even after applying all the above method like; backup restoring or by using eseutil and isinteg repair tool then it is recommended to use third party tool in order to recover database from 1216 error.
Know How to Recover Database, If All The Above Methods Are Failed
The only way left for recovery of the database is Exchange Recovery Software. It can recover all mailboxes from exchange database file .edb even if the exchange database is corrupt or offline. By using this software you can recover data from priv, pub or stm files even if you get error 1216.
Resolving Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch

Experts in data recovery from corrupt Exchange mailboxes, SQL database, and Outlook emails.
Published: 2017-12-20
Browse All Articles > Resolving Exchange Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch
Among the most obnoxious of Exchange errors is error 1216 – Attached Database Mismatch error of the Jet Database Engine. When faced with this error, users may have to suffer from mailbox inaccessibility and in worst situations, permanent data loss.
Stellar Phoenix Mailbox Exchange Recovery emerges as the sure-shot solution to this and many other Exchange Jet errors.
Microsoft Jet Database Engine is a critical internal component of the Exchange database whose proper functioning is vital to keep the server running smoothly. Problems like dirty shutdown state of the database or EDB file corruption can cause the Jet engine to fault leading to bigger issues like mailbox inaccessibility and even data loss. Thus, if Exchange users face Jet errors, they should assume that the Exchange database is either in dirty shutdown state or corrupted and should take immediate remedial actions to restore the database to avoid worsening the damage.
Jet engine errors are mostly recognized through numerical error codes which usually depict what has caused that particular error. Depending upon the cause of the error, the right solution is devised. Herein, we’re focusing on the Jet error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch.
Jet Error 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch
In some cases of EDB file corruption or Exchange dirty shutdown, methods like soft recovery can fail to fix the damage and instead, fail with the error code 1216 JET_errAttachedDatabaseMismatch. The following list includes all possible reasons that may trigger this occurrence:
- Wrong assessment of header information in log files
- Deleted Exchange system files
- EDB file corruption
- Network problems
In addition to halting your work, the above mentioned error might eventually cause the database to fail to mount. Thus, the only way to prevent complete inaccessibility of mailbox data is to resolve this error at the earliest.
How to resolve the error?
To resolve this error first ensure compliance to the following:
- Take a proper backup of all database and log files in their current state
- Ensure that all log files associated with the database are present
Following the below mentioned tricks should help you resolve the error without any trouble. But please remember to proceed to the next fix only when you’ve tried the previous one and failed.
- Move all consistent logs to another folder and then try to mount the database
- Restore the database from a recent relevant backup
- Perform a hard recovery on the database using the following steps:
- 1. Execute the command eseutil /p (Note: Using this command can result in major data loss. The eseutil repair mode (/p) finds errors within Exchange database pages and tries to fix them. The pages which cannot be fixed are discarded. Please use this method only as a last resort.)
- 2. One the database has been repaired with eseutil /p, defragment it using the command eseutil /d.
- 3. Finally, execute the isinteg –fix command to repair database consistency.
- If you’ve tried all of the above tricks but failed to get rid of the error, the only option left is to use reliable third-party software to repair EDB files. Discover the best EDB file repair software in the next section.
The recommended solution
When everything else fails, resorting to trustworthy and risk-free third-party automated software is suggested. Our top pick for the most competent EDB file repair tool is Stellar Phoenix Mailbox Exchange Recovery. This software is powered by advanced scanning and repair algorithms that can detect and fix the severest of corruption within Exchange database files. The product can efficiently repair offline as well as dismounted EDB files and that too, multiple files simultaneously. What’s more, it comes with a fully interactive GUI which makes it easy for all kinds of home users to operate it too. Compatible with many Exchange versions and easy to install, this product is your best bet to recover EDB file data when errors strike.