Содержание
- Введение в обработку ошибок в Swift 3
- Platform UI Error Handling
- Contents
- Use cases
- Issue to solve
- See the error
- What does it mean to me the user?
- What can I do next?
- Status manager & Status handlers
- Status manager
- Styles
- Status handlers
- StatusAdapter
- The facility and Platform
- WorkbenchStatusHandler and IDEWorkbenchStatusHandler
- Error Messages: User Interface
- Error Messages User Interface Use Cases
- Eclipse mapping
- Use cases
- Main requirements
- New StatusDialog
- Overview
- Use cases
- Usage
Введение в обработку ошибок в Swift 3
Сегодня мы приготовили перевод для тех, кто так же, как автор статьи, при изучении Документации языка программирования Swift избегает главы «Error Handling».
Из статьи вы узнаете:
- что такое оператор if-else и что с ним не так;
- как подружиться с Error Handling;
- когда стоит использовать Try! и Try?
Моя история
Когда я был младше, я начинал изучать документацию языка Swift. Я по несколько раз прочёл все главы, кроме одной: «Error Handling». Отчего-то мне казалось, что нужно быть профессиональным программистом, чтобы понять эту главу.
Я боялся обработки ошибок. Такие слова, как catch, try, throw и throws, казались бессмысленными. Они просто пугали. Неужели они не выглядят устрашающими для человека, который видит их в первый раз? Но не волнуйтесь, друзья мои. Я здесь, чтобы помочь вам.
Как я объяснил своей тринадцатилетней сестре, обработка ошибок – это всего лишь ещё один способ написать блок if-else для отправки сообщения об ошибке.
Сообщение об ошибке от Tesla Motors
Как вы наверняка знаете, у автомобилей Tesla есть функция автопилота. Но, если в работе машины по какой-либо причине происходит сбой, она просит вас взять руль в руки и сообщает об ошибке. В этом уроке мы узнаем, как выводить такое сообщение с помощью Error Handling.
Мы создадим программу, которая будет распознавать такие объекты, как светофоры на улицах. Для этого нужно знать как минимум машинное обучение, векторное исчисление, линейную алгебру, теорию вероятности и дискретную математику. Шутка.
Знакомство с оператором if-else
Чтобы максимально оценить Error Handling в Swift, давайте оглянемся в прошлое. Вот что многие, если не все, начинающие разработчики сделали бы, столкнувшись с сообщением об ошибке:
Самая большая проблема заключается в удобочитаемости кода, когда блок else становится слишком громоздким. Во-первых, вы не поймёте, содержит ли сама функция сообщение об ошибке, до тех пор, пока не прочитаете функцию от начала до конца или если не назовёте ее, например, selfDriveCanCauseError, что тоже сработает.
Смотрите, функция может убить водителя. Необходимо в недвусмысленных выражениях предупредить свою команду о том, что эта функция опасна и даже может быть смертельной, если невнимательно с ней обращаться.
С другой проблемой можно столкнуться при выполнении некоторых сложных функций или действий внутри блока else. Например:
Блок else раздувается, и работать с ним – все равно что пытаться играть в баскетбол в зимней одежде (по правде говоря, я так и делаю, так как в Корее достаточно холодно). Вы понимаете, о чём я? Это некрасиво и нечитабельно.
Поэтому вы просто могли бы добавить функцию в блок else вместо прямых вызовов.
Однако при этом сохраняется первая из выделенных мной проблем, плюс нет какого-то определённого способа обозначить, что функция selfDrive() опасна и что с ней нужно обращаться с осторожностью. Поэтому предлагаю погрузиться в Error Handling, чтобы писать модульные и точные сообщения об ошибках.
Знакомство с Error Handling
К настоящему времени вы уже знаете о проблеме If-else с сообщениями об ошибках. Пример выше был слишком простым. Давайте предположим, что есть два сообщения об ошибке:
- вы заблудились
- аккумулятор автомобиля разряжается.
Я собираюсь создать enum, который соответствует протоколу Error.
Честно говоря, я точно не знаю, что делает Error протокол, но при обработке ошибок без этого не обойдешься. Это как: «Почему ноутбук включается, когда нажимаешь на кнопку? Почему экран телефона можно разблокировать, проведя по нему пальцем?»
Разработчики Swift так решили, и я не хочу задаваться вопросом об их мотивах. Я просто использую то, что они для нас сделали. Конечно, если вы хотите разобраться подробнее, вы можете загрузить программный код Swift и проанализировать его самостоятельно – то есть, по нашей аналогии, разобрать ноутбук или iPhone. Я же просто пропущу этот шаг.
Если вы запутались, потерпите еще несколько абзацев. Вы увидите, как все станет ясно, когда TeslaError превратится в функцию.
Давайте сперва отправим сообщение об ошибке без использования Error Handling.
Итак, если бы я запустил это:
Но давайте используем Error Handling. В первую очередь вы должны явно указать, что функция опасна и может выдавать ошибки. Мы добавим к функции ключевое слово throws.
Теперь функция автоматически говорит вашим товарищам по команде, что autoDriveTesla – особый случай, и им не нужно читать весь блок.
Звучит неплохо? Отлично, теперь пришло время выдавать эти ошибки, когда водитель сталкивается с lostGPA или lowBattery внутри блока Else-If. Помните про enum TeslaError?
Я вас всех поймаю
Если lostGPS равно true, то функция отправит TeslaError.lostGPS. Но что делать потом? Куда мы будем вставлять это сообщение об ошибке и добавлять код для блока else?
Окей, я не хочу заваливать вас информацией, поэтому давайте начнём с того, как выполнить функцию, когда в ней есть ключевое слово throws.
Так как это особый случай, вам необходимо добавлять try внутрь блока do при работе с этой функцией. Вы такие: «Что?». Просто последите за ходом моих мыслей ещё чуть-чуть.
Я знаю, что вы сейчас думаете: «Я очень хочу вывести на экран моё сообщение об ошибке, иначе водитель умрёт».
Итак, куда мы вставим это сообщение об ошибке? Мы знаем, что функция способна отправлять 2 возможных сообщения об ошибке:
- TeslaError.lowBattery
- TeslaError.lostGPS.
Когда функция выдаёт ошибку, вам необходимо её “поймать” и, как только вы это сделаете, вывести на экран соответствующее сообщение. Звучит немного запутанно, поэтому давайте посмотрим.
Теперь всё должно стать понятно. Если понятно не всё, вы всегда можете посмотреть моё видео на YouTube.
Обработка ошибок с Init
Обработка ошибок может применяться не только к функциям, но и тогда, когда вам нужно инициализировать объект. Допустим, если вы не задали имя курса, то нужно выдавать ошибку.
Если вы введёте tryUdemyCourse(name: «»), появится сообщение об ошибке.
Когда использовать Try! и Try?
Хорошо. Try используется только тогда, когда вы выполняете функцию/инициализацию внутри блока do-catch. Однако если у вас нет цели предупредить пользователя о том, что происходит, выводя сообщение об ошибке на экран, или как-то исправить ее, вам не нужен блок catch.
Давайте начнём с try? Хотя это не рекомендуется,
try? всегда возвращает опциональный объект, поэтому необходимо извлечь newCourse
Если метод init выбрасывает ошибку, как, например
то myCourse будет равен nil.
В отличие от try? оно возвращает не опциональное значение, а обычное. Например,
bobCourse не опционально. Однако, если при методе инициализации выдается ошибка вроде,
то приложение упадёт. Так же как и в случае с принудительным извлечением с помощью !, никогда не используйте его, если вы не уверены на 101% в том, что происходит.
Ну вот и всё. Теперь вы вместе со мной поняли концепцию Error Handling. Легко и просто! И не нужно становиться профессиональным программистом.
Источник
Platform UI Error Handling
This proposal is for error messages only. It does not include Log, trace or Application Life Cycle linked to errors in a software application. Yet, this proposal should fit very nicely in above mentioned features.
Contents
Use cases
We will use 4 different customers to ensure the proposal is scalable
- BigCompany is using Eclipse 3.3. They decide to buy different features from different companies. They want an AJAX feature from company AjaxWorldCom and they decide on a database tooling feature from SQLForever Company. All user will have the same desktop feature and all call should be routed to the BigCompany’s help desk. Users do not have access to the web.
- TaxInc develops an Tax Solution software. It has RCP clients and a server. TaxRUS bought the tax solution. They installed a server internally and deployed the RCP client to 250 employees around the world. The employees are not developers. They just use the RCP application to do Tax related tasks. They have an internal help desk.
- BigSoftware develops a set of Eclipse feature for a product named: J2EE development 13.0. User can buy the product off the shelf or order a large amount of products and install them in their enterprise. BigSoftware has a huge support center. BigSoftware also ships 3rd party features it supports in its tooling.
- John is a Java Perl developer. He downloaded Eclipse 3.3 and a Perl feature from the open source web site.
Issue to solve
This is the main issue to solve for the 4 customers
When an error occurs in the tooling (Error message, error dialog, error in the console view, error in the log view, error in the job dialog or any other error), Eclipse needs to provide a way for the users to:
- see what the error is
- understand what it means to the them
- how can they act on the error.
The behavior for each is based on policies.
- The feature who threw the error should have a chance to handle the error and help the customer.
- The feature should have an idea about what the error handler wants it to do.
- i.e. when there is an error opening a view should we show the error view or not
- also do we prompt when the workbench layout cannot be reset?
- The product/branding that is installed can override all feature’s behavior it ships and manage or delegate to them as appropriate.
See the error
It is very important to distinguish between expected and unexpected error.
- Expected Error is when a developer expects the exception to be thrown in particular situation (network not available, resource locked by another person, invalid license etc).
- Unexpected Error is an error that should not happen (internal error, NPE etc).
Generally expected errors should come with idea how to solve the problem, while it should be easy to report unexpected one and/or to get workaround.
When an error occurs, the developer may decide to show the error to the user. The code is opening an error dialog. However handler may ignore developer request and handle the error in different way, f.e. log it. Before opening the error dialog, and based on the policy, the flow can be re-routed and the error dialog may never show up like the developer intended to. There should be a hook in the code, based on policy that will express manage the behavior.
What does it mean to me the user?
Most users are not interested in the ‘stack trace’ of the error. When a user sees an error or actively double clicks on an error we ought to see the information on how to solve the error (without technological background). This presumes the feature or the product or the company provided the data the user can understand and that the associated policy allows such data to be shown.
What can I do next?
Based on the policy, it is the responsibility of the feature provider (component provider), the product provider or the company to decide what the ‘what to do next’ action will do. Eclipse could still provide a ‘show log’ button that policy provider can extend (this is a nice to have…)
Status manager & Status handlers
Status manager
StatusManager is the entry point for all statuses to be reported in the user interface. Handlers are not intended to be used directly. They should be referenced via the StatusManager which selects the handler corresponding to the product to apply. Right now it is impossible to have more than one handler per product because of scalability issues.
The following methods are the API entry points to the StatusManager
The StatusManager singleton is accessed using
The int parameter are for supplying style for handling. See Acceptable styles.
NOTE! the style is a suggestion and may not be honoured by the current handler. For instance a handler may choose to not show the user anything when the SHOW flag is sent. See Status handlers for more details.
The StatusManager gets it’s list of handlers from the extension point org.eclipse.ui.statusHandlers . Should none of those handlers process the status it will fall through to the default handler (the the SDk this is WorkbenchAdvisor#getWorkbenchErrorHandler() ). If a handler is associated with a product, it is used instead of this defined in advisor.
Styles
Below is a list of StatusManager styles which can be combined with logical OR.
- NONE — a style indicating that the status should not be acted on. This is used by objects such as log listeners that do not want to report a status twice
- LOG — a style indicating that the status should be logged only
- SHOW — a style indicating that handlers should show a problem to an user without blocking the calling method while awaiting user response. This is generally done using a non modal dialog
- BLOCK — a style indicating that the handling should block the calling method until the user has responded. This is generally done using a modal window such as a dialog
Status handlers
Status handlers are part of the status handling facility. The handlers are responsible for presenting statuses by logging or showing appropriate feedback to the user (generally dialogs). All status handlers extend org.eclipse.ui.statushandlers.AbstractStatusHandler which requires each handler to implement handle(StatusAdapter status, int style) . This method handles statuses based on a handling style. The style indicates how status handler should handle a status. See Acceptable styles.
There are two ways for adding handlers to the handling flow.
- using extension point org.eclipse.ui.statusHandlers
- by the workbench advisor and its method <@link WorkbenchAdvisor#getWorkbenchErrorHandler()>.
If a handler is associated with a product, it is used instead of this defined in advisor.
A status handler has the id and a set of parameters. The handler can use them during handling. If the handler is added as an extension, both are set during initialization of the handler using elements and attributes of statusHandler element.
WARNING! We have to take the extra action when something has to be logged using the default logging mechanism, because the facility is hooked into it. See Hooking the facility into Platform. For this special case the status manager provides API.
And below is the example of addLoggedStatus(IStatus status) proper usage.
StatusAdapter
The StatusAdapter wraps an instance of IStatus subclass and can hold additional information either by using properties or by adding a new adapter. Used during status handling process.
The facility and Platform
The places where the facility is hooked in
- WorkbenchAdvisor#eventLoopException(Throwable) — it handles all uncaught exceptions from main application loop
- Jobs framework
- Error log file (all logged messages are forwarded to the facility with the LOG style)
- Exceptions from opening a part (the error view and error editor)
Platform is still under refactoring aimed at introducing the status handling facility.
WARNING! The facility isn’t hooked into JFace ErrorDialog or MessageDialog in any way. The code has to be refactored if the facility is to be used.
should be refactored into
WorkbenchStatusHandler and IDEWorkbenchStatusHandler
There are two implementation of status handlers
- org.eclipse.ui.application.WorkbenchErrorHandler which is assigned to WorkbenchAdvisor
- org.eclipse.ui.internal.ide.IDEWorkbenchErrorHandler assigned to IDEWorkbenchAdvisor
The current advisor indicates which handler is the workbench one.
Error Messages: User Interface
Error Messages User Interface Use Cases
There are three types of user interfaces that will present a message, an error or a warning to a user. The three categories are
- Message that requires user’s action now
- Message that requires user’s action that can be done later
- List of messages.
Message that requires action now.
They are typically represented in a modal dialog box. The user has to act on it or he/she will not be able to finish the task. Such a dialog should provide a standard view with an icon and a message. The message can provide an advanced view, in which case a ‘details’ or ‘advanced’ button is present on the standard view. When the user selects the details button, the advanced information about the message are displayed. The provider of the message or the Error handler will provide the user interface that will be embedded in the dialog. The user can pres the details button again, and this will collapse the advanced view. Messages must be persisted in an external file. The message in the modal window is the most relevant to the user and is decided by the ErrorHandler. If the message has offspring, they will be rendered in the advanced user interface.
Message that can have action later.
They are messages that can be error, but do not prevent the user from pursuing his/her task. All message may need to be solved at a certain point, but do not require immediate action. They are usually represented by information and icon in the user interface. The user can finish some other part of the interface before solving the message. Concrete examples are wizard pages and editors. In wizard pages the message is presented at the top of the page, in an editor it is usually embedded in the form editor or on the side of the editor (right or left side) To get more information about the message, the user clicks on it. A modeless window opens with the information. When the user clicks elsewhere, the window closes. Messages do not have to be persistent. The owner of the user interface can decide to save them or decide to recalculate the messages when the user interface is reopened. The owner of the user interface can decide to not allow the task to be saved or finished if the message is not act upon.
The user is presented with a double pane view. One pane represents the list of messages. The user can filter them and reorganized them. Some filter could be based on the resources, the format (tree, table) or the dependency (ex: acting on this message will also resolve the following messages…). The filtering mechanism should be lighter in its usage than the current one. When the user selects a message, the second pane is filled with the details of the message. This will show the exact same information as #1. The messages are persistent. PS: the semantic of this user interface is like an ‘email reader’ where you select the email message to see the content of the email. A provider could replace the first pane of the list of errors. ErrorView and Problem view should be merged in a unique view.
Eclipse mapping
The user must act of them. The best practice is that only error message should appear to the user using this format. Warning and Information messages should not. The error handler can decide if a message is worth showing or not and will also provide the details.
Errors in a background process are of type 2.
We should not open a modal dialog when an issue occurs. The user can ‘glance’ in the result in the bottom right corner, click on it to see the list of errors and click on an error to see a detail.
Wizard messages are of type 1.
The user must act on them to go to the next page but also clicking on them will open a pop up. There is no ‘details’ button in the wizard user interface
Error log is of type 3
The view shows the different errors from the log. The user can click on an error in the list to see more details.
Use cases
The User Interface behavior will depend from the context of the error. If an error occurs during a Job, we will not prompt the user but rather notify the Job View. If the same error occurs in the plug-in itself, we will open a modal window.
The error manager framework must keep track of the context and if the error handler decides to show the error to the user, the Error Manager Framework should use the appropriate User Interface.
Context of the use cases
The plug-in is looking for a file named ‘result.txt’ on a web site. When executing, the plug-in is unable to connect to the web server. The plug-in throws an error using the error handler mechanism. The error is modified to notify the user that the remote site does not answer and that the user should check if there is any proxy of if the site is actually down.
Use Case 1 Modal Dialog
The framework realizes the context and opens an ErrorDialog. The ErrorDialog detail is filled with content from the plug-in error handler.
Use Case 2 Job Error
The framework realizes the context and modifies the user interface for the Job. A red ‘x’ appears in the bottom right hand corner of eclipse. The User double clicks on the red ‘x’ and a window opens, showing the message of the error. When the user clicks on the message; the framework opens a modal window like in use case #1.
Use Case 3 Wizard
The framework realizes the context and updates the top of the wizard with the message. When the user hovers over the message a pop up appears. If the user wants to see more details, a modal window opens.
Use Case 4 Error Log
The error handler decided to not show the user about the error. It decided to only log it. The error appears in the error log view. The user clicks on the entry and a modal dialog (like in #1) opens.
Main requirements
- shows list of the problems
- shows details of the problems
- shows view which helps user to handle or report the problems
Each problem on the list should have error reporting view associated to it. This relation can be set in error handler which handles the problem. This reporting view will be showed in the tray part of the dialog.
For workbench handler it can be simply a basic view with stack trace. For product handler it can be a html view with a form for registering the problem or for checking the state of the problem.
New StatusDialog
Overview
New Status Dialog is integrated with Status Handling facility. Unless no other handler is specified, the default dialog will be used.
- Message — This is the most important piece of information.
- Details — Sometimes there is not enough place to display all necessary info on the dialog, or we do not want to scary the user. Then we can place leading message on the dialog, and all other things make accessible via details area. Currently it is possible to set up one kind of details area provider, but there is no further requirement.
- Support — It is possible to place some contact form on the dialog, so the user will know where to look for help or will be able to easily contact vendor.
Support and Details are terms introduced to distinct the behavior and functionality although they extend common abstract class. One should remember that user expects more information after pressing «Details >>>» button.
Status Dialog uses following messages hierarchy:
- Job name (if available)
- StatusAdapter title
- IStatus message
- MultiStatus information (applies only if MultiStatus is handled).
- message extracted from exception
- exception name
Status Dialog displays always two the most important messages. If first one is not found then the dialog should give information about general error instead. If the second one is not found, dialog should point to the details.
- Only one status is handled
- First message displayed is the most important message.
- Second message displayed is the second most important message.
- Timestamp is displayed in the details (if available)
- More statuses handled — the selection list appears
- There is the most important message used on the selection list.
- The second most important message is displayed right to the severity icon.
- Timestamp (if available) is appended to the message in the selection list.
- Details area can be replaced — it does not display stack trace anymore, rather the error hierarchy (message from Status, Exception, Nested statuses, etc) by default. Product may decide to provide some high level description, or even retrieve description from database.
- Support area can be added — product may hook into the error dialog and place there f.e. browser with url pointing to the helpdesk, or some reporting mechanism.
The basic idea is that even unexperienced user should be able to understand what is going on while looking at details, and should be able to report/get help using support area.
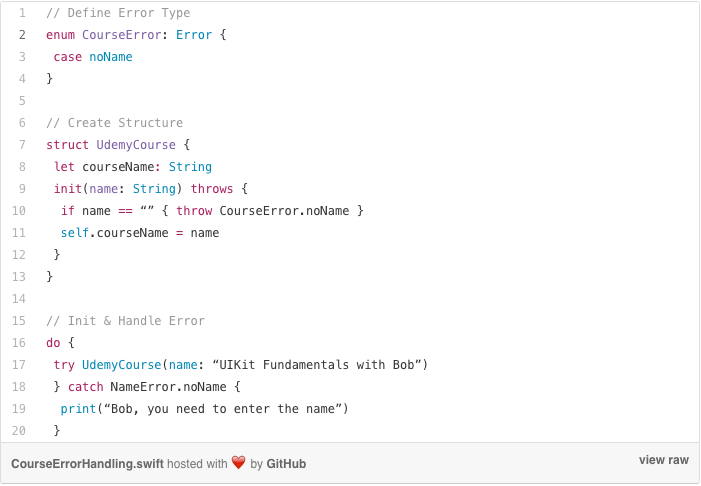
- Only one status is reported. Primary message and secondary message should be displayed. Secondary message should have timestamp if one is available.
- Job reported an error. Display message informing which job, and primary message.

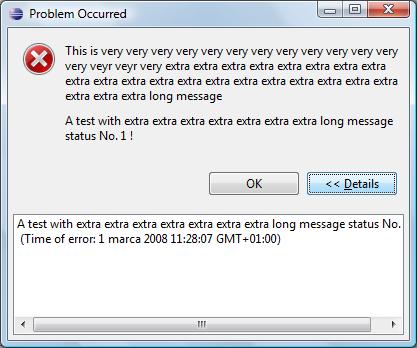
- Multiple errors occured. On the list should be displayed job name or primary message of the status. In the title primary message should appear for jobs and secondary for statuses.
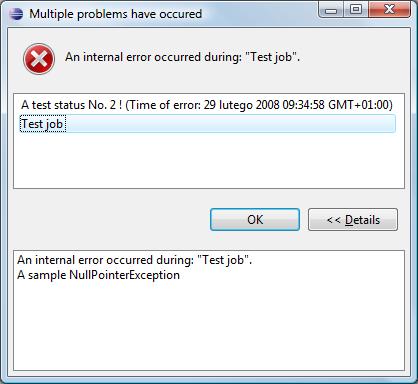
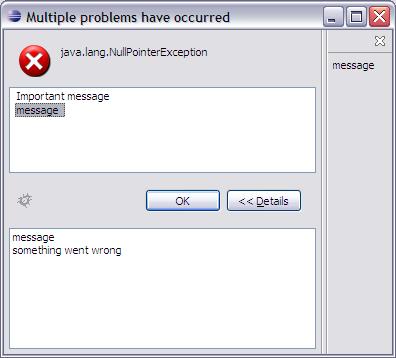
- One stastus has been reported and support is available.

after pressing bug icon:
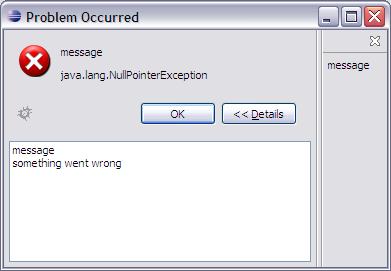
and many statuses. The selected in the list Status is a base for support area.
Use cases
Usage
Note for WorkbenchStatusDialog clients
Please note that WorkbenchStatusDialog#getPrimaryMessage & WorkbenchStatusDialog#getSecondaryMessage begin searching for the message from StatusAdapter title. It means that when we are handling job statuses we display:
- single status
- job name as the first message
- WorkbenchStatusDialog#getPrimaryMessage result as second message
- list
- job name (and eventually timestamp) as the position on the list.
- WorkbenchStatusDialog#getPrimaryMessage result right to the severity icon.
Источник
-
1
error handling
Java used checked exceptions to manage error handling. — Для управления обработкой ошибок Java использует контролируемые исключения bug, error code, error detection, error message, error protection, error stream, error trapping, exception handling, fatal error, hardware error, recoverable error, system error
Англо-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > error handling
-
2
error handling
- обработка ошибок
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > error handling
-
3
error handling
English-Russian base dictionary > error handling
-
4
error handling
English-Russian dictionary of Information technology > error handling
-
5
error handling
English-Russian big medical dictionary > error handling
-
6
error handling
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > error handling
-
7
error handling
Универсальный англо-русский словарь > error handling
-
8
error handling
English-Russian electronics dictionary > error handling
-
9
error handling
The New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > error handling
-
10
error handling
English-Russian dictionary of computer science and programming > error handling
-
11
error handling
Англо-русский словарь по авиации > error handling
-
12
error handling
Англо-русский словарь компьютерных и интернет терминов > error handling
-
13
error handling
English-Russian dictionary of terms that are used in computer games > error handling
-
14
error handling
English-Russian dictionary of technical terms > error handling
-
15
error handling
English-Russian information technology > error handling
-
16
error handling
English-Russian dictionary of computer science > error handling
-
17
error handling
The English-Russian dictionary on reliability and quality control > error handling
-
18
error-handling procedure
- процедура обработки ошибок
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > error-handling procedure
-
19
error-handling procedure
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > error-handling procedure
-
20
error-handling routine
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > error-handling routine
Страницы
- Следующая →
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
См. также в других словарях:
-
Error Handling — [engl.], Fehlerbehandlung … Universal-Lexikon
-
error handling — The way that a program copes with errors or exceptions that occur as the program is running. Good error handling manages unexpected events or wrongly entered data gracefully, usually by opening a dialog box to prompt the user to take the… … Dictionary of networking
-
Error Handling — … Википедия
-
error handling — manner in which a program deals with hardware errors or errors by a user … English contemporary dictionary
-
Error handling routine — Программа обработки ошибок … Краткий толковый словарь по полиграфии
-
Error code — In computer programming, error codes are enumerated messages that correspond to faults in a specific software application. They are typically used to identify faulty hardware, software, or incorrect user input in programming languages that lack… … Wikipedia
-
error — The difference between the expected and the actual. In computing, the way that the operating system reports unexpected, unusual, impossible, or illegal events is by displaying an error number or error message. Errors range from trivial,… … Dictionary of networking
-
Error hiding — is an anti pattern, in computer programming. The programmer hides error messages by overriding them with exception handling. As a result of this the root error message is hidden from the user (hence error hiding ) and so they will not be told… … Wikipedia
-
Handling qualities — Handling qualities, sometimes also referred to as flying qualities is one of the two principle regimes in the science of flight test (the other being performance). Handling qualities involves the study and evaluation of the stability and control… … Wikipedia
-
Error Detection and Handling — In television technology, Error Detection and Handling (EDH) protocol is an optional but commonly used addition to the Standard Definition Serial Digital Interface (SDI) standard. This protocol allows an SD SDI receiver to verify that each field… … Wikipedia
-
Error — The word error has different meanings and usages relative to how it is conceptually applied. The concrete meaning of the Latin word error means wandering or straying . To the contrary of an illusion, an error or a mistake can sometimes be… … Wikipedia
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
обработка ошибок
обработки ошибок
обработку ошибок
обработке ошибок
обработкой ошибок
обрабатывать ошибки
Предложения
For the one case where people needed global control flow transfer (error handling) exceptions were developed.
Для единственного случая, где люди нуждались в глобальном управлении потоком (обработка ошибок), были разработаны исключения.
Improved error handling during driver initialization.
The other rather significant benefit of exceptions is that they clean up error handling code.
Другая, более значимая выгода исключений в том, что они очищают код обработки ошибок.
The change of position of cursor of sequential access with the process of error handling of positioning through bookmarks was detected.
Обнаружилось изменение позиции курсора последовательного доступа в процессе обработки ошибок позиционирования через закладки.
Don’t forget to register error handling — the program should know how to do it in case of a mistake.
Не забывайте прописывать обработку ошибок — программа должна знать, как ей поступить в случае возникновения той или иной ошибки.
So you being little genius, you plan ahead and use exceptions and error handling where appropriate.
Таким образом, вы планируете наперед и используете исключения и обработку ошибок в случае необходимости.
If the address is not found in this routing table the packet will be sent for error handling.
Если адрес не найден в таблице маршрутизации, пакет будет отправлен для обработки ошибок.
The vulnerabilities exist in error handling routines within the minires library and may be exploitable as stack overflows.
Уязвимости присутствуют в процедурах обработки ошибок внутри библиотек minires и могут быть использованы как переполнение стека.
Selected error handling option is not applicable for scripting and will be ignored.
Выбранный параметр обработки ошибок не применим в сценариях и будет пропущен.
Smart error handling so you don’t loose any data
Смарт обработки ошибок, так что вы не потеряете какие-либо данные,
Blockchain technology could also reduce settlement times and eliminate error handling by providing real time tracking of transactions without double spending issues.
Технология блокчейн также может сократить время расчета и устранить обработку ошибок, обеспечивая отслеживание транзакций в реальном времени без двойных затрат.
You’ll also learn how to use and manipulate object references, as well as write simple error handling code.
Они также научаться пользоваться и управлять ссылками на объекты, писать простой код обработки ошибок.
They allow you to define your own error handling rules, as well as modify the way the errors can be logged.
Они дают возможность определять собственные правила обработки ошибок, а также изменять способы их протоколирования.
One of the most important, and often unloved parts of web form design, is error handling.
Одна из самых важных, и часто пропускаемых частей дизайна формы — обработка ошибок.
The primary reason that error handling is absent is memory constraints on mobile devices.
Основная причина того, что обработка ошибок отсутствует, заключается в ограниченной памяти мобильных устройств.
It even has instructions that throw and catch exceptions for error handling.
В нем даже есть команды выбрасывания и перехвата исключений для обработки ошибок.
Investigation of error handling process and exceptional situations.
Исследование процессов обработки ошибок и исключительных ситуаций.
This consistent behaviour in turn simplifies error handling, builds end user confidence, and encourages further interaction.
Согласованное ответ в свою очередь упрощает обработку ошибок, сборку и интерфейс пользователя, поощряет дальнейшее взаимодействие.
I also think that exceptions are necessary for managing the complexity of error handling.
Я думаю также, что исключения совершенно необходимы для управления сложным механизмом обработки ошибок.
Appropriate error handling may be applied in accordance with the invention in the event of a malfunction.
Соответствующая обработка ошибок может быть применена, в соответствии с изобретением, в случае некорректной работы.
Предложения, которые содержат error handling
Результатов: 157. Точных совпадений: 157. Затраченное время: 76 мс
Documents
Корпоративные решения
Спряжение
Синонимы
Корректор
Справка и о нас
Индекс слова: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Индекс выражения: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Индекс фразы: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Error Handling in C++ or: Why You Should Use Eithers in Favor of Exceptions and Error-codes
Consider using an Either type to handle errors as they lift the error into the type-system and have the same performance characteristics as error-codes.
Either Implementations
Introduction
Programming language design is always a matter of trade-offs. In the case of C++, the designers optimized for two things: runtime efficiency and high-level abstraction. This gives the C++ programmer huge flexibility in many areas, one of which is error handling.
Exceptions & Try-Catch
Try-catch is traditionally seen as the most idomatic error-handling method in C++.
Exception Overhead
The try-catch language feature is not zero-cost and the exact price is determined by the compiler implementation. Implementers can choose between increased code-size and increased run-time overhead, both in the success branch and the failure branch.
In most C++ implementations, an interesting choice has been made: code in the try block runs as fast as any other code. However, dispatching to the catch block is orders of magnitude slower. This penalty grows linearly with the depth of the call-stack.
If exceptions make sense for your project will depend on the frequency at which exceptions will be thrown. If the error rate is above 1%, then the overhead will likely be greater than that of alternative approaches. (Source)
Exceptions are not supported by all platforms, and methods that throw cannot be easily understood by C.
Ergonomics
Exceptions are very easy to use and fairly easy to reason about. You can throw and catch exceptions at any point in your code, and the exception can even be an arbitrary type.
The biggest drawback is that handling exceptions is not enforced by the type-system. Unlike, Java, for example, where exceptions must be caught by the caller, catching a C++ exception is optional. This means spotting all the unhandled exceptions during a code review will be challenging, and requires deep knowledge of all of the functions called.
But what about noexcept and throw?
A common misconception is that annotating functions with noexcept or throw can help.
Unfortunately, noexcept and throw simply dictate that a call to std::terminate is made in the case where an unmentioned exception is thrown. This does not enforce any exception-handling at compile-time.
For example, these will compile and throw a run-time error!
Error-codes
Error-codes are ancient and used everywhere. For simplicity, let’s assume error-codes are just integers, but they could be implemented as type-safe enums or even complex objects. For this discussion it won’t really matter.
There are 3 common forms of error-code implementations.
1. Error-codes as Return Values
This pattern is found in many C APIs as it is easy to implement and has no performance overhead, besides the error-handling itself.
This pattern can be followed very dogmatically and it is easy to verify that all cases have been taken care of in a code-review. It is easy to write a C-friendly API using error-codes.
Unfortunately it has some drawbacks:
- Functional composition is hard. The return value is occupied by the error-code, so the result must be an out-variable, which makes the function impure.
- Out-parameters enforce a memory layout which is not optimizer friendly.
- Separating error-handling from the computation is difficult.
- Postponing error-handling requires the programmer to thread the error-code through the call-graph.
2. Error-code as out-parameter
Swapping the semantics of the out-parameter and return value has no significant advantages, except perhaps a slightly cleaner API. In the case where the error-code can be omitted, the API usage is simplified and functional compositionality is made easier.
This approach can be found in boost::asio (in fact boost::asio even makes it optional and falls back to throwing exceptions if no out-parameter is provided).
3. Error Singletons
Error singletons have completely different ergonomics. They are mostly found in low-level libraries that are implementing a system-global state-machine, such as a driver. One prominent example is OpenGL.
Using an error singleton looks like this:
In this paradigm, the status of the driver must be queried at run-time through a separate function. This appears to give you more freedom since you can query for errors when it is most appropriate, enabling you to better separate concerns. This allows the user to write code that resembles exception-based code, but without the cost of automatic stack unwinding.
Benefits for the API consumer:
- Error-handling can be reduced over time to a minimum
- Having fewer error-handling branches yields better performance
- No out-parameters are required, which increases functional compositionality
- Finalization can be performed manually when errors are found
But there are some big caveats:
- Singletons by design have shared state, thus writing thread-safe code is very hard
- No shortcutting of computation pipelines as no stack-unwinding occurs
- It is not clear which errors may be fired on which api-calls. The programmer must check the documentation.
- The severity of errors, and to recover from them, might be unclear
So what about Eithers?
An Either type is a container which takes a single value of one of two different types. A simple implementation might look like this:
To run computations on the wrapped value, an Either can provide some useful methods: leftMap , rightMap and join .
- leftMap transforms the leftValue to a new value if present, leaving a rightValue unchanged.
- rightMap transforms the rightValue to a new value if present, leaving a leftValue unchanged.
- join takes a transformation for both sides of the Either where both transformations result in the same type. This allows an Either to be unified and unwrapped.
This is much easier to understand in code!
Now we are able to lift the exceptions into the type-system:
So what have we gained through this simple change?
We no longer need to pay for the overhead of exceptions and we have also encoded the exception-type into the function signature. This documents the error in the source-code and now the compiler will ensure that we handle the types properly.
This is a big deal, and it illustrates how powerful the C++ language is.
So what are the drawbacks?
First, you will need to add an Either type to you project. It is best not to reinvent the wheel here, and fortunately there are many open-source implementations available.
But what about performance? At first glance, it seems that every call to leftMap and rightMap will add a branch to the executable. In practice, the compiler is smart enough to optimize these away!
Take a look at this Compiler Explorer project; the branches of the various map calls dissappear.
For example, you might have noticed the following identity:
And it turns out that the compiler does too. It combines both lambdas to inline the whole expression. After the optimization step, all abstractions are collapsed. Once complied, there is no significant difference between the error-code implementations and the either-based implementations.
Conclusion
Consider using an Either type to handle errors. They lift the error into the type-system, making them safer than exceptions whilst yielding the same performance characteristics as error-codes.
Источник
Thoughtful Error Handling
Your error handler is one of your most important security defenses
This blog post is part of a series on secure coding principles that may become a future book like my other blog-book Cybersecurity for Executives in the Age of Cloud . If you want to know when the book gets published, follow me on Medium or Twitter — or both!
Do you write error handlers that capture errors when your application executes? All the errors? Do your applications crash miserably with the wrong inputs or fail gracefully? Can your application continue when it needs, even when an error occurs? When a crash occurs do you capture the output and deal with it appropriately or let it spill onto the screen for anyone to read? Does your error handling or logging code have a security vulnerability?
Error handling that gives up secrets
While performing a particular AWS penetration test for a customer I was tasked with testing their APIs. All I had was a Swagger file (a file that defines all the ways you can call the API and the related parameters.) I wrote a custom fuzzer that parsed the Swagger file and inserted attack values into the API calls. Fuzzing is a mechanism for testing code with a lot of attack strings quickly and I wrote more about this fuzzer for IANS Research. I don’t recommend only testing an API because that can provide limited results, but in this case, that’s all I had.
While testing the API I noticed that one of the error messages reflected the data I entered back to the screen. Sure enough, I had a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack. Even worse, I could use that cross-site scripting attack to send me the JSON web token of the user that made the crafted API call. If I could trick a user into going to a page that produced that error I could use obtain their credentials and make additional API calls using them.
If you want to see this in action, I did a demo in my talk at RSA in 2020:
Lack of error handling spills your secrets
Sometimes while performing a penetration test I can obtain helpful information from code that lacks error handling. Improper error handling has provided me with internal server IP addresses, database names, and stack traces that provide information about the libraries and code that produced the error.
A stack trace after an error shows the path the code took that led to the error. It will show that one library called a particular function and then that called a particular function and so on until you get to the function that did not handle the error. Sometimes a stack trace only shows the most recent function. Sometimes it shows all the calls back to the initial one that started the chain.
When you write some code and fail to write error handling your particular programming language or application framework may produce default error output. Sometimes that output is extremely verbose. Some web frameworks produce a custom error page that provides a user-friendly display a lot of data related to an error including IP addresses, code paths, and other useful information. The information helps developers troubleshoot the problem. That same information is useful for attackers who are attempting to reverse-engineer how your system works and break into it or steal data.
I will take a look at the stack trace or error output produced by the code and attempt to find out if the application is using any vulnerable libraries. I can learn more about the system architecture such as versions and potentially file paths to where code exists on a system. If there’s an internal IP address I may try to reach it through an open redirect, SSRF, or DNS rebinding attack. Explaining all those types of attacks is covered in other books I already mentioned and other videos, presentations, and blogs I’ve written. What I’m going to focus on now is writing error handlers that do not expose information to attackers.
Error handling libraries with vulnerabilities
One time while testing a site I was looking for cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities using that same fuzzing mechanism I mentioned before. While testing the site I was able to produce errors such as those I mentioned. The ironic thing is that one of the libraries that produced an error was the cross-site scripting protection library the company used. And … it produced a XSS error, the very thing it was supposed to prevent!
Including tricky code in your error-handling routine could produce errors of their own. If you are going to get fancy with your error handling, make sure you handle the errors in your error handler properly. When you get to an unexpected error sometimes the best thing to do is write the most minimal code possible and log it in a way that won’t create a vulnerability of its own.
When writing to logs you should usually write them to a separate location that can’t affect the running application, is not exposed to the Internet, and properly encode the data to prevent errors when you open the log files. Make the files read-only.
Never allow your error handler to reflect data from a user back to the screen in a web application without properly encoding it to prevent errors in the browser. When an unexpected error occurs, I prefer no reflection ever. That would be the safest approach. But I have tested systems that properly encode data and was not able to produce an error with the values I tried (so far). More on the topic of data inputs and encoding in a later post. For now, we want to write error handlers that properly capture and log errors.
Logging libraries with vulnerabilities
When you write error handlers, you may leverage a library to handle the logging for you. Sometimes these error handlers themselves have security vulnerabilities. An attacker will insert a carefully crafted attack string (or copy and paste one from the Internet) into your program. When that string is parsed by your error logging library, it might have a security vulnerability that allows extraction of memory, data, or access to your system.
You’ve likely heard of the Log4J vulnerability by now if you’re a programmer at the time I’m writing this book. However, future programmers may not know about it and some may not understand exactly what happened so I’ll include some information about it in my book. In the meantime, you can refer to this blog post I wrote previously if you haven’t read it already:
log4j: The Aftermath
Summary of the log4j vulnerability that shook the Internet
In certain applications, such as on a Windows operating system at times, an error will produce a dump file or “crash dump” of system memory. As I already explained in the last post attackers love to produce errors that expose memory, because one of the only places you can’t keep your secrets encrypted at all times is in memory. At some point, the application needs to have access to the value in clear text to process it (with very few exceptions as I explained previously).
Any time your system produces a crash dump you should pay attention to what caused it. Was it a legitimate system error? Or is an attacker is inserting strings to produce that crash dump? Many different types of errors, such as buffer overflows, will dump memory for an attacker. More on buffer overflows later. For now, be aware of any error handling that produces crash dumps or memory output and understand the risk. Be careful where and when it occurs, where that memory output is stored, and who can access it.
Handling errors in your code
If you are like me and every other programmer in the world, you don’t write perfect code. Additionally, sometimes the system gets inputs it doesn’t expect or can’t process. Sometimes you call another library that has a bug that bubbles up to your application. Any time your system can produce an error you should be aware of that possibility and think through what you want to happen when it does.
When you initially write code to define a variable and set a value there’s little chance it will produce a bug.
However, somewhere in the future while your program executes something may change that variable. Any time a value in your application may change is a point where an error can occur. The type of error will depend on your application, programming language, libraries, and many other factors.
To catch an error write error handling code to capture it. The code you use to capture an error will vary by programming language.
In Java, it’s called a try-catch statement and looks like this, courtesy of the web page below.
Java Exceptions (Try. Catch)
When executing Java code, different errors can occur: coding errors made by the programmer, errors due to wrong input…
In JavaScript, C# (.Net), and PHP an error handler would use the same syntax.
Python error handling looks like this:
golang (or go code) uses an error object to track abnormal state. As you write code, you check for errors. This is an interesting approach and I may dive into it a bit deeper in the book, but for now, understand that it exists and use it!
errors
Package errors implements functions to manipulate errors. The New function creates errors whose only content is a text…
Rust is another language that’s becoming more popular. Unlike other languages, it breaks errors into recoverable and unrecoverable errors:
The Rust Programming Language
Rust’s commitment to reliability extends to error handling. Errors are a fact of life in software, so Rust has a number…
Once you determine that an error exists, you may choose to dump the stack trace to show the full execution path that caused the error. You might choose to write some data to the screen if the application has a user interface (UI) that someone is looking at when the error occurred. You may choose to include other useful information in the application logs when the error occurred to help troubleshoot the problem.
Error handling is very important. All those actions will help you fix problems down the line when they occur and you aren’t actively running the code. It’s hard to troubleshoot an application when you don’t know what was happening at the time of the error.
An improperly handled error may be the source of secrets exposure, data exfiltration, or one of the most dangerous types of security vulnerabilities: remote code execution (RCE). That means an attacker can cause your system to do their bidding by finding a way to pass commands to it that it will execute.
Error handling and web applications
When I started programming websites all the technology was brand new. We went from some text on a website that could (which was actually annoying to most people) to full-blown applications in your browser. It’s entertaining now to read what Mozilla has to say about the blink tag:
When we wrote applications using things like Microsoft OLAP and OLE automation. I had to look back at my old software programming resume to remember the names of those technologies. A new technology came out called Java and was followed by JavaScript (and the mantra Java is not JavaScript). Later we moved on to Corba, SOAP, Ajax. Then came REST APIs, microservices, and containers. All of this can now run on cloud platforms which started with AWS
10 years before most competitors became viable solutions. (Though, I do remember working on a system hosted on Joyent for a customer back in the day).
The exciting thing about OLE Automation when it came out was that you could make requests over the Internet. Your requests would get processed and send data back to the browser or some other application! This was crazy new at the time and very cool. However, when errors occurred sometimes you got back no information at all. I remember the person I worked with at the time complaining about how hard it was to troubleshoot. Things just failed. I’ve heard developers recently complaining about Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) errors which may produce similar responses.
JavaScript initially didn’t interact with the server much at all. At some point, I customized a web application to lower costs with brides incessantly trying every pricing option on a quote page. That page was costing me a lot of money in bandwidth (the amount of data flowing over the network related to each request). The cost of wedding invitations and printed items varied by quantity and it was not a simple formula.
Instead of making calls to the server to calculate the price for a quote I wrote some JavaScript to handle the calculations in the browser. My costs went down! The only problem was that some customers reported an error in the browser. I had not included any error handling code to send information back to the server to troubleshoot those problems when they occurred. I didn’t have access to customers’ machines. It was not going to be possible to get the brides-to-be to troubleshoot.
At that point, I had to figure out a way to capture errors and send them back to the server whenever I wrote client-side JavaScript functionality. I wrote some error handling code and used JavaScript to send requests server-side with the information I needed to troubleshoot problems. Of course, I had to also write error handling code server-side where the application received the data since something malicious or at least problematic could have gotten included in the data sent from the client to the server.
Back then almost all application logic got handled by servers. JavaScript was only used to create websites that provide simple user-friendly feedback not to process data (at least not by anyone that understood security). That started to change around that time when I wrote my client-side quote calculator.
Shortly after I used this type of request to process data a new library appeared on the scene called JQuery which made use of something called Ajax. I looked at this library and realized it was doing things similar to what I’d done with my quote page, though it was interacting with the server a bit more.
As I already mentioned, I’m cautious with open-source code so I didn’t end up using JQuery. I didn’t even start with JQuery, in that case. I wrote my own library from scratch so I could better understand AJAX requests and have more control over the requests, responses, and error handling. If you are not going to be very cautious with inputs, outputs, and error handling, that’s likely not something you want to do that was my approach to using Ajax in my e-commerce and content management system.
At the time, I was concerned that there was too much in that library for me to review completely, and was not sure how well the people that wrote it understood web vulnerabilities. There have been a few CVEs as you can see from the lists below. But over time the library has improved as more and more people use it:
Jquery Jquery : CVE security vulnerabilities, versions and detailed reports
CVE is a registred trademark of the MITRE Corporation and the authoritative source of CVE content is MITRE’s CVE web…
CVE — Search Results
The mission of the CVE® Program is to identify, define, and catalog publicly disclosed cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
JQuery was still largely used to process data server-side. It just provided a way to make requests in JavaScript instead of redirecting a browser to a new page. This could allow a web page to load portions of pages and process data without leaving the existing page. Most of the time, the real processing was still handled server-side.
Along came JavaScript-heavy frameworks like Angular and React. Now a lot more data is getting processed client-side. At the point these libraries came into existence, my concern was that developers would not understand the risk of processing data and storing secrets client-side. They also might not log errors back to the server making applications difficult to troubleshoot. I’ve had to answer calls for IANS clients on how to handle security issues in single-page applications, for example, which rely heavily on JavaScript.
No matter what language or framework you use to build your web applications, make sure you understand where errors occur and how they are handled. When you use web technologies that may get errors in the web browser, make sure you have a way to capture that data and send it back to the server. You’ll thank me later.
Error handling for APIs and microservices
A security vendor hired me to re-architect an existing network security product and move it to the cloud. The team I worked with was full of very experienced software engineers but none of them had worked on a cloud platform prior to that project. I had to explain some concepts to the team such as microservices and containers (which sometimes people mistakenly think are the same thing).
Instead of building one monolithic software application, we would build services. These services exposed application programming interfaces (APIs) that would allow one service to call another service to carry out some action in the system. Each team was responsible for a certain aspect of the system functionality (reporting, billing, machine configuration, etc.) and would write a set of APIs that got called by other teams.
Before we started writing any code, I brought the whole team together to decide on certain core principles. From the very beginning, we developed a set of standards for how we would go about writing the APIs the system exposed for teams to integrate the code into one cohesive application.
An important part of that was a definition of the format for errors we would send back and forth so they could be handled in a consistent way. We defined the components of an error message so each team could consume error messages with standardized code.
Even though we had a standard error format, once we started writing the code it became evident that we needed to provide a bit of additional guidance. Some people wrote error messages that lacked enough information to understand the problem and what to do about it. Teams discussed what error messages should include in general. They also worked together to resolve specific problematic error messages that one team wrote and another team could not understand.
When you write a single application and control all the code, it’s easy for you to run your application and insert breakpoints to see the values the system is processing at any given time. I’m presuming here that you know what breakpoints are and how to trigger them in your favorite integrated development environment (IDE).
Consider the case when you are calling an API and an error occurs within that API written by another developer, hosted on another server. You have no way to get into that application directly and see what is going on. You are reliant upon the person who wrote and is hosting that API to provide you with useful information. At the same time, the API should not expose sensitive information or data that might help an attacker use that system to break into the API.
One of the discussions we had in regards to API errors was what the HTTP response code should be. This can be somewhat subjective, but typically you will want to ensure your HTTP response code matches standard error categories. Mozilla lists the following HTTP categories:
You can find these status codes further defined in section 10 of RFC 2616 and the updated RFC 7231. If you are not familiar with standards and RFCs that topic is also covered in Cybersecurity for Executives in the Age of Cloud.
HTTP response status codes — HTTP | MDN
This interim response indicates that the client should continue the request or ignore the response if the request is…
API developers need to balance providing enough, but not too much information. E-commerce gateways have been writing APIs for a long time. They provide a good example of ways to provide useful error messages. Their documentation provides a specific error code — a number or a specific string— and a description for each type of error. In addition, there is generally a catch-all error code for something unidentified. In those cases, you need to reach out to the gateway vendor for more information.
You can catch the error and provide their description or your own to the person that is trying to check out on a website. You know exactly what the error is due to the fact that the system clearly and uniquely identifies it.
When APIs provide error numbers with nonsensical error messages, the results can be painful. One time while working with APIs from a well-known firm that provides clearing and settlement of certain types of transactions we came across an error that took weeks to resolve. Part of the problem was the communication between people working on the project, but a simple adjustment to the error message returned by the API would have saved hours if not weeks on the project.
Financial systems often require the timestamps on systems generating requests and responses. In that case, the timing was off between the two systems. There was nothing wrong with the code. The QA person had simply adjusted the time on her system (apparently). By simply changing the time on the system testing the APIs we no longer had the problem that we spent something like two weeks on the phone trying to resolve. A useful error message would have saved both companies time and money.
Here’s another issue with APIs to consider. That same QA person used the wrong network settings on her computer. She had moved to another team and was making calls to our test environment because she forgot to make a change to her system configuration. That completely skewed our test results. That problem is less error handling code and more about the zero-trust concept I explain in Cybersecurity for Executives in the Age of Cloud. What’s great is that in a cloud environment you can give each team separate networks to test their portion of projects and eliminate such problems. However, logging the IP address that generated the error might have helped us find the problem more quickly.
Error handling in clouds and microservice architectures
Many cloud-native applications are 100% serverless, or in other words, made up of numerous APIs. A serverless function is essentially an API hosted in the cloud. You can leverage many different services that call each other to form a larger system. One of my fellow AWS Heroes and friends, Ben Kehoe, works at iRobot, and at the time of this writing, their systems are almost if not completely run via serverless cloud functions. (By the way, his blog on Medium is currently covering a lot of great security topics and I recommend reading them if you use AWS!)
Applications with many microservices hosted on Kubernetes or something similar will generate errors in different containers. Those different containers may be operated by different teams. Where are those error logs written and how do you retrieve them? Can you pinpoint an error caused by each API or is it buried in calls that don’t provide a complete stack trace that show you where the problem lies?
You may also have systems that leverage third-party APIs. Those APIs may provide error messages or error logs in different formats. How do you access or track errors from these APIs? Can you trace a piece of data derived from a third-party API as it makes its way through your network of microservices and API calls?
When you are writing your code ensure you provide enough information to pinpoint exactly what error occurred in the case of a security incident. Your security team will need to know what system or code triggered the error. You’ll need to ensure you have a copy of the logs and error messages in the event that a container shuts down. Your error messages need to clearly indicate what caused the error.
One time while working on a penetration test, I inserted a value that did something very bad to the system. Let’s just say parts of it were slightly non-functional. My contract states this can happen, which is why I suggest starting in a test environment, then moving to production after that, unless you are sure your developers have handled inputs correctly (something I’ll cover later). If I don’t test it for you, someone else will, like it or not. I wrote about that in The Unrequested Pentest. They had other companies perform pentests in the past which apparently did not uncover the problem.
The developer involved wanted me to pinpoint what I did to cause the system issue. That’s no problem and completely understandable. When I perform a penetration test I have a record of all the requests I make to systems so I could provide that data and work with the team to find the root cause. But I also posed this question back to the team to try to help them think through a potential security incident caused by a similar issue. What if an attacker did this to your system? Would you be able to pinpoint the error and resolve it if I wasn’t here to provide the exact inputs that caused the problem?
Think through your error handling to determine what you might need to troubleshoot a problem in the event of an error. Ensure you can trace an error back to the root cause.
Handle every error — with a few exceptions
I’ve read recommendations that say you should only capture known error types. What do I mean by “known error type?”
Consider the Java Integer class. As you know an integer is a whole number that is not a fraction such as 1, 2, 3…and so on. The Java Integer class has a method called decode() that will allow you to pass a string into it and get back an integer. You can see the definition below from the Java documentation. Notice that if you pass in a string that is not an integer, it throws an exception called “NumberFormatException”.
Источник
Куратор(ы):
1usmus
| Автор | Сообщение | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
В данной теме обсуждаются CPU линейки AMD Ryzen 1X00! (Микроархитектура Zen) Ссылка 1 -> Процессоры AMD Ryzen 2000-й серии (Pinnacle RidgeZen+12nmAM4) Особенности микроархитектуры: По словам AMD, основного внимания достойно увеличение IPC (instructions per clock, операций за такт). В презентации 2016-ого года инженер CERN Ливиу Валсан сообщил, что этот процессор будет использовать технологию SMT (одновременная многопоточность). Переход от микроархитектуры модулей, используемой в Bulldozer, к полноценным ядрам, как ожидается, может увеличить производительность на ядро в операциях с плавающей точкой за счет большего количества блоков FPU. Кэп Zeno о выборе при покупке Самое главное для Ryzen — память, вот вам ссылочка как правильно выбирать память https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6PTzVTk … e=youtu.be Вложение:
Базовая — заявленная минимальная частота при нагрузке
Сравнение размеров крепежных отверстий кулера под AM3 / AM4 #77 Обзоры: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TId-OrXWuOE www.gamersnexus.net >> AMD Ryzen Memory Tweaking & Overclocking Guide (на русском) << >> Фризы, лаги и статтеры : откуда они и как с ними бороться (AMD/Intel) << Статистика разгона Ryzen систем Разгон CPU + DRAM (переключение страниц находится внизу!) Помощь в разгоне ОЗУ >> DRAM Calculator for Ryzen™ 1.5.1 + MEMbench 0.7 +Методическое пособие как разгонять ОЗУ с помощью Ryzen DRAM Calculator Два способа как заполнить калькулятор тут (видео) -> Последнее обновление : 13 мая FAQ , разгон, моддинг биоса, статьи, полезный софт Убедительная просьба, прячьте все (любые) картинки и видео под спойлер — Флуд и оффтоп даже под тэгом /офф или /спойлер — награждается ЖК, как и ответы на сообщения, его содержащие. Краткие правила темы. Увидели сообщение, нарушающее правила — просто жмите СК: отвечать на такие посты не нужно! Последний раз редактировалось 1usmus 06.07.2019 17:22, всего редактировалось 172 раз(а). |
| Реклама | |
|
Партнер |
|
Maddreg |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Maddreg писал(а): а я попробовал поставить заводские 3200 через ХМР, комп стартовал нормально, но начались бсоды со ссылкой на fltmgr.sys Вообще странно, на 3.10 и настроенной вручную 3200 с аналогичными таймингами проблем не было, причем в течение нескольких месяцев короче откатился я на 3.10. На 4.50 конечно берет заводские 3200 по ХМР и даже 3333 с высокими таймингами, но стабильности нет от слова совсем. То БСОДы, то ребуты, то зависоны. А на 3.10 с теми же заводскими таймингами на 3200 все работало как часы несколько месяцев, пусть и нужен небольшой танец с бубном чтоб взять эту частоту |
|
Overan |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Память так и не смог заставить стабильно работать на 3600. При том что на 3466 работает почти с любыми таймингами, правда с первичным ниже 15 не стартует. |
|
Prof |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 писал(а): Но + есть. это самое главное |
|
MONOLIT1986 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Prof на 3.8 он никогда у меня не вис. А вот на 3.9 там да.. Но обсуждение было что врм черезчур высок , а вольтаж на ядрах не тот. Вот на 3.9 вчера проходило все а сегодня нет. Оставил пока 3.8 в батлу поиграл миссию. Температура врм 57 максимум. А в простое 36-37 второй кулер сыграл свою роль Последний раз редактировалось MONOLIT1986 19.01.2018 23:46, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
elesin38 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
1usmus писал(а): C6H 3501 MOD + AFUDOS 4.40 + readme Хм. Не смог почему-то поставить мод, пишет Unknown command. Делал все как по readme, DOS ставил Rufus’ом. |
|
Remarc |
|
|
Advanced member Статус: Не в сети |
Overan писал(а): Есть подозрение что просто проц не может выжать 3600 из памяти. скорее дело в памяти |
|
TepakoT |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Прошил modded 3404. Наконец-то память запустилась на 2933 на полном Auto. И хрен с ней, F4-3600 уже таможню прошла. Вопрос в другом. Решил подпрыгнуть повыше, 3.9 ГГц взял без напряга, тестить и питание подгонять не стал, замахнулся дальше на 4 ГГц. Зависает Linx на 18-20 секунде. Можно что-нибудь подкрутить, чтоб напругу больше не повышать? Я могу конечно, на 3.9 67 градусов, но зачем тогда все эти настройки? Как по английски называется опция «Сделать зашибись»? бивис > CPU Core Ratio [40.00] PS Странно. На 3.8 было 1139 R15, а на 3.95 1127. Какой интересный разгон… Последний раз редактировалось TepakoT 19.01.2018 23:57, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
Prof |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 писал(а): MONOLIT1986 а у тебя ещё троттлинг включён |
|
Overan |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Remarc писал(а): скорее дело в памяти сомнительно, если при 3466 норм работает с напряжением 1.36 и таймингами 15-15-15-15-28-46-260 |
|
Remarc |
|
|
Advanced member Статус: Не в сети |
Overan писал(а): сомнительно, если при 3466 норм работает с напряжением 1.36 и таймингами 15-15-15-15-28-46-260 ну тогда надо полностью написать что ты пробовал на 3600…а так сначала пробуй по 1 планке Последний раз редактировалось Remarc 20.01.2018 0:05, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
MONOLIT1986 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Prof троттлинг есть способ его выключить? http://ipic.su/img/img7/fs/13131313.1516395829.jpg 97 — градусов! Сейчас на 3.9 гоняю все те же у врм 78 градусов Последний раз редактировалось MONOLIT1986 20.01.2018 0:04, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
alexpunga98 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 Последний раз редактировалось alexpunga98 20.01.2018 0:07, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
Prof |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 писал(а): Prof троттлинг есть способ его выключить? ага ,только я не помню как называется а находится в биос там где П-стата (у меня) Добавлено спустя 34 секунды: |
|
MONOLIT1986 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
alexpunga98 Обновил ребят пост выше |
|
Prof |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 писал(а): должна быть включена? Что она дает кстати да включена |
|
Remarc |
|
|
Advanced member Статус: Не в сети |
MONOLIT1986 писал(а): Сейчас на 3.9 гоняю все те же у врм 78 градусов там радиаторы хоть есть? |
|
MONOLIT1986 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
alexpunga98 писал(а): MONOLIT1986 amd cbs->zen common options-> Добавлено спустя 55 секунд: |
|
Overan |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Remarc писал(а): ну тогда надо полностью написать что ты пробовал на 3600 из основного сейф и фаст пресеты по калькулятору с подбором таймингов, процодт и ртт. Напряжение памяти до 1.41, сок до 1.1 |
|
Remarc |
|
|
Advanced member Статус: Не в сети |
Overan писал(а): из основного сейф и фаст пресеты по калькулятору с подбором таймингов, процодт и ртт. Напряжение памяти до 1.41, сок до 1.1 что там за пресеты я без понятия,а напряжение пробуй 1.45v и 1.15v |
|
MONOLIT1986 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Нашел параметр еще Global C-STATE control — отключил. Vcore перестал просаживаться |
—
Кто сейчас на конференции |
|
Сейчас этот форум просматривают: нет зарегистрированных пользователей и гости: 8 |
| Вы не можете начинать темы Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения Вы не можете добавлять вложения |
Лаборатория
Новости
Error handling plays an extremely important role here.
Очень важную роль здесь играет обработка ошибок.
Error handling should be simple and easy to comprehend.
Обработка ошибок должна быть простой и доступной для понимания.
Security, error—handling, and logging, for example, each cut across all of the other features of an application.
Безопасность, обработка ошибок и регистрация, например, пересекаются со всеми другими функциями приложения.
Error handling should be — as far as possible — hierarchical.
Обработку ошибок следует, насколько это возможно, выполнять иерархически.
If you find errors, handle them as described in the Troubleshooting section below.
Обнаружив ошибки, устраните их в соответствии с инструкциями ниже.
The $errlvl variable is combined with the if and goto commands to provide error handling in dip scripts.
Сочетание переменной $errlvi с командами if и goto позволяет реализовать обработку ошибок в сценариях dip.
I said I would do DRM, you would do error handling.
Я же сказал, я сделаю DRM, а ты исправишь ошибки.
When you finish developing your application, you’ll need to tweak the automatically generated error—handling code.
Закончив разрабатывать приложение, измените автоматически генерируемый код обработки ошибок.
This sort of error handling is technically async capable, but it doesn’t compose well at all.
Такой механизм обработки ошибок технически может поддерживать асинхронность, но она плохо работает в композиции.
Error handling has been integrated into the .NET Framework so that it is consistent throughout all languages.
Обработка ошибок интегрирована в .NET Framework, что сделало ее совместимой со всеми языками.
Unfortunately, most developers do not get into the habit of using exceptions for error handling.
К сожалению, большинство разработчиков не привыкло пользоваться исключениями для обработки ошибок.
Using map objects and error handling objects are important steps in the direction of increasing software reliability.
Использование объектов отображения и объектов обработки ошибок — это важнал составляющал повышения надежности ПО.
The most natural form of error handling for most developers is the synchronous try..catch construct.
Самая естественная форма обработки ошибок для большинства разработчиков — синхронная конструкция try..catch.
Tuning Error Handling Problem You want to alter the error-logging sensitivity on a particular page.
Настройка обработки ошибок Задача Требуется изменить «чувствительность» некоторой страницы к ошибкам.
That statement prevents Access from drifting into the error—handling code that follows if an error hasn’t happened.
Этот оператор не дает программе Access попасть в следующий далее код обработки ошибок, если никакой ошибки не произошло.
Here you can do normal debugging and error handling.
В этом случае выполняется нормальная отладка и обработка ошибок.
We’ll leave this kind of error handling to you.
Обработку подобных ошибок мы оставляем вам.
Consequently, the function failed () (§ 19.2.6.1) is available for error handling.
Как следствие, для обработки ошибок доступна функция failed () (§19.2.6.1).
A little bit of error handling’s always a good idea. 4.
Немного обработки ошибок никогда не помешает. 4.
(For brevity, error handling and closing of the process handle, hProcess, is elided.)
(Для краткости я опустил обработку ошибок и закрытие описателя процесса hProcess.)
Is a coherent error—handling strategy provided?
Определена ли согласованная стратегия обработки ошибок?
What if we have multiple families of error handling classes?
А что, если у нас будет несколько семейств классов обработки ошибок?
So for now, use this approach to error handling, but know that it’s not quite ready for primetime.
А сейчас используйте прежний подход к обработке ошибок, но учтите, что для серьезной работы он не годится.
Error handling is a topic worth a separate discussion of its own, later in this chapter.
Обработка ошибок — тема, достойная отдельного обсуждения, и мы еще вернемся к ней далее в этой главе.
And when you can’t, you should make sure to put great care into your error handling.
А когда это невозможно, уделите особое внимание обработке ошибок.
Error handling, in this case, relates to situations where the service fails.
Обработка ошибок в данном контексте относится к случаям отказов в работе услуги.
Enable( TRUE) user error handling or disable( FALSE) user
error handling.
Sensor information Energy metering Error handling User permission level.
Информация датчиков Измерение энергии Обработка ошибок Уровень разреш. пользователей.
or where the output of services contain erroneous cases that require a different treatment;
Обработка ошибок— в случаях нарушения функционирования статистической услуги
или появления в ее результатах
ошибок,
требующих отдельной
обработки;
Julien Grall discovered that incorrect error handling in physical-to-machine memory mappings may result in privilege escalation,
denial of service or an information leak.
Жульен Гралл обнаружил, что неправильная обработка ошибок в отображении физической памяти в машинную может
приводить к повышению привилегий, отказу в обслуживании или утечке информации.
They allow you to define your own error handling rules, as well as modify the way
the
errors
can be logged.
Они дают возможность определять собственные правила обработки ошибок, а также изменять способы их логирования.
It was discovered that incorrect error handling when reading the response from a STUN server
could result in a crash.
Было обнаружено, что некорректная обработка ошибок при чтении ответа от SТUN- сервера может приводить
к аварийному завершению работы.
While examining a number of applications, I came to a conclusion that the error handling code is one of the most unreliable parts
in C/C++ programs’ sources.
Рассматривая множество программ, я пришел к выводу, что код обработки ошибок в Си/ Си++ программах- одно из самых ненадежных мест.
A call to the cmdlet with user controlled error handling, where the user variable is‘myerr’:
Вызов командлета с обработкой ошибок, контролируемой пользователем, где пользовательская переменная- это« myerr»:
We have improved error handling for usage of IBProvider as MSSQL linked server
and have added support for Visual Studio 2015.
Мы улучшили обработку ошибок при использовании IBProvider- а в качестве связанного сервера
MSSQL и добавили поддержку Visual Studio 2015.
Because these are complex devices with multiple points of failure,
effective error handling is arguably more important than with any other transaction.
Потому что это сложные устройства с множественными местами возможных отказов,
эффективная обработка ошибок является, возможно, более важный, чем в случае любых других транзакций.
Not enough funds» in your account
when your balance is zero you must add error handling routine.
Не хватает средств » на вашем аккаунте,
когда ваш баланс равен нулю вы должны добавить процедуру обработки ошибок.
It was discovered that insufficient error handling in the kernel module could lead to denial of service.
Было обнаружено, что неполная обработка ошибок в модуле ядра может привести к отказу в обслуживании.
It is not required that you group task sequence steps; however,
using groups improves the readability of the task sequence and provides better error handling.
Группировка шагов последовательности задач не является обязательной,
однако она улучшает удобочитаемость последовательности задач и обработку ошибок.
In figure 2 and figure 3 the error handling procedures for the VU and the IDE are respectively shown.
На рис. 2 и рис. 3 показаны процедуры обработки ошибок, соответственно, для БУ и для СПА.
block that can
handle
this
error.
который будет ловить эту ошибку.
The change of position of cursor of sequential access with the process of error handling of positioning through bookmarks was detected.
Обнаружилось изменение позиции курсора последовательного доступа в процессе обработки ошибок позиционирования через закладки.
I will try to show you that even in high-quality and popular application things are not very good in the code intended for error handling.
Я постараюсь продемонстрировать, что даже в качественном и известном приложении с кодом для обработки ошибок, все обстоит не самым лучшим образом.
Improving the server-side datatable processing, error handling and robustness agains non-utf8 characters.
Улучшение DataTable
обработки
на стороне сервера, обработка ошибок и надежность Agains не- utf8 символы.
It was discovered that incorrect error handling in the NIO HTTP connector of the Tomcat servlet
and JSP engine could result in information disclosure.
Было обнаружено, что некорректная обработка ошибок в НТТР- соединителе NIO из Tomcat, сервлета и
движка JSP, может приводить к раскрытию информации.
Select an Error Handling option to determine whether the wizard should proceed
or not when it encounters an
error.
Выберите параметр Обработка ошибок, чтобы определить долженли мастер
продолжить работу при возникновении ошибки….
Jan Beulich discovered that improper
x86 shadow mode reference count error handling may result in denial of service or privilege escalation.
Ян Белих обнаружил, что некорректная обработка ошибок при подсчете ссылок в режиме тени для x86
может приводить к отказу в обслуживании или повышению привилегий.
Jan Beulich discovered that incorrect error handling in grant table checks may result
in guest-to-host denial of service and potentially privilege escalation.
Ян Белих обнаружил, что неправильная обработка ошибок в коде проверки таблицы предоставлений может
приводить к отказу в обслуживании по типу гостевая система- главная система и потенциальному повышению привилегий.