В период работы с астериском рано или поздно задумываешься о том, почему не получается прозвониться и обычное чтение лога не помогает. На помощь приходит снятый дамп. В этой статье рассмотрим разные дампы SIP сообщений и постараемся разобрать на примерах причины неисправностей, а также найти виновника найденной неполадки. Структура SIP SIP – это структурированный многоуровневый протокол […]

В период работы с астериском рано или поздно
задумываешься о том, почему не получается прозвониться и обычное чтение лога не
помогает. На помощь приходит снятый дамп. В этой статье рассмотрим разные дампы
SIP сообщений
и постараемся разобрать на примерах причины неисправностей, а также найти
виновника найденной неполадки.
Работы проводились на CentOS release 6.9 (Final) Asterisk 13.21.0
Структура SIP
SIP – это структурированный многоуровневый протокол связи, который описывает тип установки и завершения сеанса связи, также включает обмен мультимедиа.
Категории запросов:
- Одинарные методы — методы на которые
требуется единичный ответ, без дополнительных запросов. - Диалоговые методы — методы,
которые сопровождаются многочисленными ответными сообщениями и поддерживают
диалоговые соединения.
В одинарные запросы входят пакеты со следующими
методами:
- OPTIONS – метод
позволяющий определить доступность того или иного VOIP устройства подключенного в АТС. Запрос о
функциональных возможностях АТС. - SUBSCRIBE – метод
позволяющий получать информацию о статусах в пределах всего сеанса подключения - PUBLISH — публикация события на сервере.
- INFO – передача
какой либо информации, которая не меняет состояние сессии - NOTIFY – уведомление
о событии для пользователя, отправившего PUBLISH - ACK – подтверждение
ответа на запрос INVITE
К диалоговым методам можно отнести:
- INVITE – приглашение
пользователя на сеанс связи - REGISTER – передает
серверу информацию для регистрации пользователя
Детально рассмотреть можно здесь .
Далее все дампы сохранялись командой tcpdump -nnvy any -s0 port 5060 — w /tmp/sipdump.pcap
Пакет INVITE
Структура
сообщений в SIP
одинакова.
Стартовая строка → Заголовки → Пустая строка → Тело сообщения. Для примера
рассмотрим Пакет INVITE:
Анализ дампа можно проводить в программе sngrep. Для того, чтобы открыть снятый вами дамп ткройте его командой sngrep -I /<путь>/<к>/<дампу>.pcap
|
Стартовая строка |
INVITE sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 |
| Заголовки |
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 192.168.170.105:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPjR1lZ8c09xesG.6AE497.qhlZlf2nwJxa Max-Forwards: 70 From: «102» <sip:[email protected]>;tag=5EH8QhIiuvpzL62cHe9uhXXbQbsSg8-s To: <sip:[email protected]> Contact: «102» <sip:[email protected]:5060;ob> Call-ID: ks2EUm46cCnW9jlRCYfkIuXT0AdEaZzt CSeq: 31529 INVITE Allow: PRACK, INVITE, ACK, BYE, CANCEL, UPDATE, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, REFER, MESSAGE, OPTIONS Supported: replaces, 100rel, timer, norefersub Session-Expires: 1800 Min-SE: 90 User-Agent: Digium D40 1_3_0_1_53901 Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 442 |
| Пустая строка | |
| SDP данные |
v=0 o=- 240683915 240683915 IN IP4 192.168.170.105 s=digphn c=IN IP4 192.168.170.105 t=0 0 a=X-nat:0 m=audio 4062 RTP/AVP 9 8 0 18 58 118 58 111 96 a=rtcp:4063 IN IP4 192.168.170.105 a=rtpmap:9 G722/8000 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:18 G729/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16/16000 a=rtpmap:118 L16/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16-256/16000 a=rtpmap:111 G726-32/8000 a=sendrecv a=rtpmap:96 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:96 0-15 |
Для определения действия и направления пакета в SIP используется первая строка:
Далее следует основное тело пакета с полями
заголовков. В основной своей части используются заголовки:
- Via
- Max-Forwards
- From
- To
- Contact
- Call-ID
- Cseq
В заголовоке Via записывается адрес устройства, отправившего
сообщение, Транспортный протокол, номер порта на который нужно отправить
обратно и идентификатор транзакции.
Поле Max-Forwards указывает максимальное количество полей Via может быть в пакете.
Стандартно — в Max-Forwards указано число 70.
Заголовок From предназначен для обозначения инициатора запроса с
указанием адреса uri
и
отображаемого имени.
Параметр tag формирует отправляющая сторона<br>
В заголовок To подставляется информация о получателе сообщения. Зачастую формируется из значения Ruri. Т.к. в дальнейшем на клиентской стороне может быть изменена.
Изменения также можно проводить для поля From
Заголовок Call—ID – это
уникальный идентификатор, сохраняющийся на протяжении всего диалога.
При инициализации нового диалога снова генерируется Call-ID.
В рамках одного вызова может быть инициализировано несколько диалогов.
В Cseq
записывается
порядковый номер запроса и имя метода, которое передается,
В ответных пакетах в поле Cseq записывается имя метода, на который происходит ответ.
В поле Contact записывается URI адрес того устройства, на которое должен прийти
ответ. Т.е. в приведенном выше примере, ответ прийдет из всех
зарегистрированных устройств пользователя 102 на устройство
<sip:[email protected]:5060;ob>
Т.е. сравните поля From и Contact
в
нашем примере:
В поле From
указан
адрес сервера астериска, а в поле Contact
указан
адрес устройства.
Причины
отбоя INVITE
- В дампе вы видите только один или несколько
инвайтов.

Причиной данной неполадки может быть:
- Не правильно
настроенный iptables - Попали в бан. (Проверять fail2ban)
Если в дампе видите только запросы к оператору связи из этого вывод, что с их стороны работают указанные выше пункты. Или к вам не приходят ответные пакеты оператора. Проверяйте описанные выше пункты.
Если в дампе видите только запросы к оператору связи из этого вывод, что с их стороны работают указанные выше пункты. Или к вам не приходят ответные пакеты оператора. Проверяйте описанные выше пункты
- Вызов от неавторизованного пользователя.
Схема вызова в данном случае читается следующим образом:
- Отправляется инициирующий INVITE
- Получаем ответ от астериска 401 Unauthorized, что
говорит нам о том, что пользователь не зарегистрированный - Клиент подтверждает что не авторизован пакетом ACK
- Снова отправляется INVITE с авторизационными данными. Смотрим заголовок Authorization

- Получаем ответ от сервера 403 Forbidden, что
указывает на то, что пользователя с такими авторизационными данными не
существует на АТС - Клиент подтверждает полученный ответ пакетом ACK
Примеры вызовов
Рассмотрим корректный вызов:

- Отправляется инициирующий INVITE
- Получаем ответ от астериска 401 Unauthorized, что
говорит нам о том, что пользователь не зарегистрированный - Клиент подтверждает что не авторизован пакетом ACK
- Снова отправляется INVITE с авторизационными данными.
- АТС видит что пользователь авторизован и посылает
ответ 100 Trying - Следом посылаются к инициатору пакеты 180 Ringing с
различным интервалом. Пока не поднимут трубку. - Пакет 200 OK (SDP) от
вызываемой стороны означает что трубка была снята, сейчас будут ходить RTP пакеты. - Инициатор вызова отправляет пакет ACK с подтверждением. Что увидел сигнал о снятии
трубки - По завершению вызова будет отправлен пакет BYE со стороны инициатора разрыва линии.
- Вторая
сторона разговора отправляет пакет 200 OK без SDP
для
подтверждения завершения вызова
Вызов на не зарегистрированного пользователя.

- Отправляется инициирующий INVITE
- Получаем ответ от астериска 401 Unauthorized,
что говорит нам о том, что пользователь не зарегистрированный - Клиент подтверждает что не авторизован пакетом ACK
- Снова отправляется INVITE с авторизационными данными.
- АТС видит что пользователь авторизован и посылает
ответ 100 Trying - От сервера видим пакет 503 Service Unavailable
В пакете мы видим причину разъединения в полях X-Asterisk-HangupCause и X-Asterisk-HangupCauseCode (в данном примере это пользователь не найден).
7. Инициатор, подтверждает завершение вызова.
Пакет
REGISTER
Рассмотрим пример пакета REGISTER и опишем его работу
| Первая строка | REGISTER sip:192.168.170.220:5060 SIP/2.0 |
| Заголовки |
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 192.168.170.105:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPj.J5KVeS0GGU4BV3DE1Wk0YLCSGSGQzjq Max-Forwards: 70 From: «102» <sip:[email protected]>;tag=J6Kk9pzb8UEm9uUgGMIZrwzdkuxw48f- To: «102» <sip:[email protected]> Call-ID: ARjJonSDAVAJADPRCdFlWj6Ww5jw3JU1 CSeq: 48583 REGISTER User-Agent: Digium D40 1_3_0_1_53901 Contact: «102» <sip:[email protected]:5060;ob> Expires: 0 Content-Length: 0 |
Для определения действия и направления пакета в SIP используется первая строка:

Заголовки
пакета и их назначение
Основные заголовки пакета:
Поле Via содержит
адреса устройств, через которые маршрутизировался этот пакет, это могут быть
различные АТС, proxy сервера и т. д.
Max-Forwards – указывается максимальное
колличество хопов (прыжков/переадресаций) которые может пройти пакет до пункта
назначения
Стандартно — в Max-Forwards указано число 70.
Заголовок From предназначен для обозначения инициатора запроса с
указанием адреса uri
и
отображаемого имени.
В заголовок To подставляется информация о получателе сообщения.
Зачастую формируется из значения Ruri.
В дальнейшем на клиентской стороне поле To может быть изменено.
Заголовок Call—ID – это
уникальный идентификатор, сохраняющийся на протяжении всего диалога.
В рамках диалога REGISTER заголовок Call-ID не меняется
В Cseq
записывается
порядковый номер запроса и имя метода, которое передается.
В ответных сообщениях в это поле вписывается метод на который производится ответ.

Заголовок Expires содержит информацию о времени , через которое
истекает регистрация. Значение указывается целочисленно в секундах от 0 до (2 ** 32) -1.
Измеряется с момента получения запроса.
Возможные причины отбоя
регистрации
В этом блоке будем рассматривать
самые распространенные причины сбоев в регистрации
Будем рассматривать регистрации только относительно астериска.
- Вы не видите ответа на пакет REGISTER

Причинами этой ситуации может быть:
- Firewall не пропускает, нужно проверить
правила.

- IP инициатора запроса попал в бан

- Сетевое оборудование не пропускает.
В данном случае, вы вообще не увидите запросов на АТС. - Ответ на REGISTER есть, но регистрация не проходит.

- Не верный логин или пароль от extension (см. рис6)
Решение
Смотреть
лог или консоль астериска
- Не верный permit (см. рис6)
Решение
Смотреть лог или консоль астериска.

- Указан не верный транспорт (UDP, TCP, TLS) (см. рис6)
Решение
Смотреть лог или консоль астериска.

Примеры
регистрации
Рассмотрим корректную регистрацию:
- Digium
посылает
регистрацию на астериск. - REGISTER
с
заголовком Authorization
| Authorization: |
Digest username=»102″, realm=»pbx574″, nonce=»50117049″, uri=»sip:192.168.170.220:5060″, response=»026616e569998328028072d869333f72″, algorithm=MD5 |
- Получаем ответ отастериска пакет 200 OK
Рассмотрим не верную авторизацию:
- Телефон Digium посылает регистрацию на астериск.
- АТС отвечает сообщением 401 Unauthorized. Это означает что АТС не увидела авторизационные данные.
- Телефон заново посылает пакет REGISTER с заголовком Authorization
- В ответ PBX отвечает 403 Forbidden. Что означает что какие то данные не верны. Нужно смотреть консоль астериска.
Icon
This page is currently under construction. Please refrain from commenting until this warning is removed.
Overview
Are you having problems getting your PJSIP setup working properly? If you are encountering a common problem then hopefully your answer can be found on this page.
Before looking any further here, you should make sure that you have gathered enough information from Asterisk to know what your issue is. It is suggested that you perform the following actions at the Asterisk CLI:
core set verbose 4core set debug 4pjsip set logger on
With these options enabled, this will allow you to more easily see what is going on behind the scenes in your failing scenario. It also can help you to cross-reference entries on this page since several debug, warning, and error messages will be quoted here.
Inbound Calls
Unrecognized Endpoint
All inbound SIP traffic to Asterisk must be matched to a configured endpoint. If Asterisk is unable to determine which endpoint the SIP request is coming from, then the incoming request will be rejected. If you are seeing messages like:
- Overview
- Inbound Calls
- Unrecognized Endpoint
- Authentication is failing
- Authentication Not Attempted
- Asterisk cannot find the specified extension
- ARGH! NAT!
- Outbound Calls
- Asterisk says my endpoint does not exist
- Asterisk cannot route my call
- ARGH! NAT! (Part 2)
- Bridged Calls
- Direct media is not being used
- Inbound Registrations
- Outbound Registrations
- Inbound Subscriptions
- Presence/Dialog Info
- MWI
- Configuration Issues
- Can’t create an IPv6 transport
[2014-10-13 16:12:17.349] DEBUG[27284]: res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_user.c:106 username_identify: Could not identify endpoint by username 'eggowaffles'
or
[2014-10-13 16:13:07.201] DEBUG[27507]: res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ip.c:113 ip_identify_match_check: Source address 127.0.0.1:5061 does not match identify 'david-ident'
then this is a good indication that the request is being rejected because Asterisk cannot determine which endpoint the incoming request is coming from.
How does Asterisk determine which endpoint a request is coming from? Asterisk uses something called «endpoint identifiers» to determine this. There are three endpoint identifiers bundled with Asterisk: user, ip, and anonymous.
Identify by User
The user endpoint identifier is provided by the res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_user.so module. If nothing has been explicitly configured with regards to endpoint identification, this endpoint identifier is the one being used. The way it works is to use the user portion of the From header from the incoming SIP request to determine which endpoint the request comes from. Here is an example INVITE:
<--- Received SIP request (541 bytes) from UDP:127.0.0.1:5061 ---> INVITE sip:[email protected]:5060 SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 127.0.0.1:5061;branch=z9hG4bK-27600-1-0 From: breakfast <sip:[email protected]:5061>;tag=27600SIPpTag001 To: sut <sip:[email protected]> Call-ID: [email protected] CSeq: 1 INVITE Contact: sip:[email protected]:5061 Max-Forwards: 70 Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 163 v=0 o=user1 53655765 2353687637 IN IP4 127.0.0.1 s=- c=IN IP4 127.0.0.1 t=0 0 m=audio 6000 RTP/AVP 0 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=ptime:20
In this example, the URI in the From header is «sip:[email protected]:5061». The user portion is «eggowaffles», so Asterisk attempts to look up an endpoint called «eggowaffles» in its configuration. If such an endpoint is not configured, then the INVITE is rejected by Asterisk. The most common cause of the problem is that the user name referenced in the From header is not the name of a configured endpoint in Asterisk.
But what if you have configured an endpoint called «eggowaffles»? It is possible that there was an error in your configuration, such as an option name that Asterisk does not recognize. If this is the case, then the endpoint may not have been loaded at all. Here are some troubleshooting steps to see if this might be the case:
- From the CLI, issue the «pjsip show endpoints» command. If the endpoint in question does not show up, then there likely was a problem attempting to load the endpoint on startup.
-
Go through the logs from Asterisk startup. You may find that there was an error reported that got lost in the rest of the startup messages. For instance, be on the lookout for messages like:
[2014-10-13 16:25:01.674] ERROR[27771]: config_options.c:710 aco_process_var: Could not find option suitable for category 'eggowaffles' named 'setvar' at line 390 of [2014-10-13 16:25:01.674] ERROR[27771]: res_sorcery_config.c:275 sorcery_config_internal_load: Could not create an object of type 'endpoint' with id 'eggowaffles' from configuration file 'pjsip.conf'
In this case, I set an endpoint option called «setvar» instead of the appropriate «set_var». The result was that the endpoint was not loaded.
- If you do not see such error messages in the logs, but you do not see the endpoint listed in «pjsip show endpoints», it may be that you forgot to put
type = endpointin your endpoint section. In this case, the entire section would be ignored since Asterisk did not know that this was an endpoint section.
Identify by IP address
Asterisk can also recognize endpoints based on the source IP address of the SIP request. This requires setting up a type = identify section in your configuration to match IP addresses or networks to a specific endpoint. Here are some troubleshooting steps:
-
Ensure that
res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ip.sois loaded and running. From the CLI, runmodule show like res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ip.so. The output should look like the following:Module Description Use Count Status Support Level res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ip.so PJSIP IP endpoint identifier 0 Running core
- Run the troubleshooting steps from the Identify by User section to ensure that the endpoint you have configured has actually been properly loaded.
-
From the Asterisk CLI, run the command
pjsip show endpoint <endpoint name>. Below the headers at the top of the output, you should see something like the following:Endpoint: david/6001 Unavailable 0 of inf InAuth: david-auth/david Aor: david 10 Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060 Identify: 10.24.16.36/32Notice the bottom line. This states that the endpoint is matched based on the IP address 10.24.16.36. If you do not see such a line for the endpoint that you expect to be matched, then there is likely a configuration error. If the line does appear, then ensure that the IP address listed matches what you expect for the endpoint.
-
If you are noticing that Asterisk is matching the incorrect endpoint by IP address, ensure that there are no conflicts in your configuration. Run the
pjsip show endpointscommand and look for issues such as the following:Endpoint: carol/6000 Unavailable 0 of inf InAuth: carol-auth/carol Aor: carol 10 Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060 Identify: 10.0.0.0/8 Endpoint: david/6001 Unavailable 0 of inf InAuth: david-auth/david Aor: david 10 Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060 Identify: 10.24.16.36/32Notice that if a SIP request arrives from 10.24.16.36, it is ambiguous if the request should be matched to carol or david.
If you run pjsip show endpoint <endpoint name> and do not see an «Identify» line listed, then there is likely a configuration issue somewhere. Here are some common pitfalls
- Ensure that your identify section has
type = identifyin it. Without this, Asterisk will completely ignore the configuration section. - Ensure that your identify section has an
endpointoption set in it and that the endpoint is spelled correctly. - Double-check your
matchlines for common errors:- You cannot use FQDNs or hostnames. You must use IP addresses.
- Ensure that you do not have an invalid netmask (e.g. 10.9.3.4/255.255.255.300, 127.0.0.1/33).
- Ensure that you have not mixed up /0 and /32 when using CIDR notation.
-
If you are using a configuration method other than a config file, ensure that
sorcery.confis configured correctly. Since identify sections are not provided by the baseres_pjsip.somodule, you must ensure that the configuration resides in theres_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ipsection ofsorcery.conf. For example, if you are using dynamic realtime, you might have the following configuration:[res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_ip] identify = realtime,ps_endpoint_id_ips
And then you would need the corresponding config in
extconfig.conf:[settings] ps_endpoint_id_ips => odbc
Anonymous Identification
Anonymous endpoint identification allows for a specially-named endpoint called «anonymous» to be matched if other endpoint identifiers are not able to determine which endpoint a request originates from. The res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_anonymous.so module is responsible for matching the incoming request to the anonymous endpoint. If SIP traffic that you expect to be matched to the anonymous endpoint is being rejected, try the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Ensure that
res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_anonymous.sois loaded and running. From the Asterisk CLI, runmodule show like res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_anonymous.so. The output should look like the following:Module Description Use Count Status Support Level res_pjsip_endpoint_identifier_anonymous.so PJSIP Anonymous endpoint identifier 0 Running core
- Ensure that the «anonymous» endpoint has been properly loaded. See the troubleshooting steps in the Identify by User section for more details about how to determine if an endpoint has been loaded.
Authentication is failing
The first thing you should check if you believe that authentication is failing is to ensure that this is the actual problem. Consider the following SIP call from endpoint 200 to Asterisk:
<--- Received SIP request (1053 bytes) from UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> INVITE sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPjQevrxvXqk9Lk5xSW.pzQQb8SAWnJ5Lll Max-Forwards: 70 From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]> Contact: "200" <sip:[email protected]:5060;ob> Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR CSeq: 9775 INVITE Allow: PRACK, INVITE, ACK, BYE, CANCEL, UPDATE, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, REFER, MESSAGE, OPTIONS Supported: replaces, 100rel, timer, norefersub Session-Expires: 1800 Min-SE: 90 User-Agent: Digium D40 1_4_0_0_57389 Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 430 v=0 o=- 108683760 108683760 IN IP4 10.24.16.37 s=digphn c=IN IP4 10.24.16.37 t=0 0 a=X-nat:0 m=audio 4046 RTP/AVP 0 8 9 111 18 58 118 58 96 a=rtcp:4047 IN IP4 10.24.16.37 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:9 G722/8000 a=rtpmap:111 G726-32/8000 a=rtpmap:18 G729/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16/16000 a=rtpmap:118 L16/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16-256/16000 a=sendrecv a=rtpmap:96 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:96 0-15 <--- Transmitting SIP response (543 bytes) to UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> SIP/2.0 401 Unauthorized Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;received=10.24.16.37;branch=z9hG4bKPjQevrxvXqk9Lk5xSW.pzQQb8SAWnJ5Lll Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]>;tag=z9hG4bKPjQevrxvXqk9Lk5xSW.pzQQb8SAWnJ5Lll CSeq: 9775 INVITE WWW-Authenticate: Digest realm="asterisk",nonce="1413305427/8dd1b7f56aba97da45754f7052d8a688",opaque="3b9c806b61adf911",algorithm=md5,qop="auth" Content-Length: 0 <--- Received SIP request (370 bytes) from UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> ACK sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPjQevrxvXqk9Lk5xSW.pzQQb8SAWnJ5Lll Max-Forwards: 70 From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]>;tag=z9hG4bKPjQevrxvXqk9Lk5xSW.pzQQb8SAWnJ5Lll Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR CSeq: 9775 ACK Content-Length: 0 <--- Received SIP request (1343 bytes) from UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> INVITE sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPjCrZnx79augJPtGcTbYlXEs2slZNtwYeC Max-Forwards: 70 From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]> Contact: "200" <sip:[email protected]:5060;ob> Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR CSeq: 9776 INVITE Allow: PRACK, INVITE, ACK, BYE, CANCEL, UPDATE, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, REFER, MESSAGE, OPTIONS Supported: replaces, 100rel, timer, norefersub Session-Expires: 1800 Min-SE: 90 User-Agent: Digium D40 1_4_0_0_57389 Authorization: Digest username="200", realm="asterisk", nonce="1413305427/8dd1b7f56aba97da45754f7052d8a688", uri="sip:[email protected]", response="2da759314909af8507a59cd1b6bc0baa", algorithm=md5, cnonce="-me-qsYc.rGU-I5A6n-Dy8IhCBg9wKe8", opaque="3b9c806b61adf911", qop=auth, nc=00000001 Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 430 v=0 o=- 108683760 108683760 IN IP4 10.24.16.37 s=digphn c=IN IP4 10.24.16.37 t=0 0 a=X-nat:0 m=audio 4046 RTP/AVP 0 8 9 111 18 58 118 58 96 a=rtcp:4047 IN IP4 10.24.16.37 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:9 G722/8000 a=rtpmap:111 G726-32/8000 a=rtpmap:18 G729/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16/16000 a=rtpmap:118 L16/8000 a=rtpmap:58 L16-256/16000 a=sendrecv a=rtpmap:96 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:96 0-15 <--- Transmitting SIP response (543 bytes) to UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> SIP/2.0 401 Unauthorized Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;received=10.24.16.37;branch=z9hG4bKPjCrZnx79augJPtGcTbYlXEs2slZNtwYeC Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]>;tag=z9hG4bKPjCrZnx79augJPtGcTbYlXEs2slZNtwYeC CSeq: 9776 INVITE WWW-Authenticate: Digest realm="asterisk",nonce="1413305427/8dd1b7f56aba97da45754f7052d8a688",opaque="0b5a53ab6484480a",algorithm=md5,qop="auth" Content-Length: 0 <--- Received SIP request (370 bytes) from UDP:10.24.16.37:5060 ---> ACK sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPjCrZnx79augJPtGcTbYlXEs2slZNtwYeC Max-Forwards: 70 From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=DTD-tYEwFMmbPyu0YWalLQdbEUGSLGN5 To: <sip:[email protected]>;tag=z9hG4bKPjCrZnx79augJPtGcTbYlXEs2slZNtwYeC Call-ID: q.TF2SAaX3jn8dtaLTOCuIO8FRyDCsSR CSeq: 9776 ACK Content-Length: 0
At first glance, it would appear that the incoming call was challenged for authentication, and that 200 then failed to authenticate on the second INVITE sent. The actual problem here is that the endpoint 200 does not exist within Asterisk. Whenever a SIP request arrives and Asterisk cannot match the request to a configured endpoint, Asterisk will respond to the request with a 401 Unauthorized response. The response will contain a WWW-Authenticate header to make it look as though Asterisk is requesting authentication. Since no endpoint was actually matched, the authentication challenge created by Asterisk is just dummy information and is actually impossible to authenticate against.
The reason this is done is to prevent an information leak. Consider an attacker that sends SIP INVITEs to an Asterisk box, each from a different user. If the attacker happens to send a SIP INVITE from a user name that matches an actual endpoint on the system, then Asterisk will respond to that INVITE with an authentication challenge using that endpoint’s authentication credentials. But what happens if the attacker sends a SIP INVITE from a user name that does not match an endpoint on the system? If Asterisk responds differently, then Asterisk has leaked information by responding differently. If Asterisk sends a response that looks the same, though, then the attacker is unable to easily determine what user names are valid for the Asterisk system.
So if you are seeing what appears to be authentication problems, the first thing you should do is to read the Unrecognized Endpoint section above and ensure that the endpoint you think the SIP request is coming from is actually configured properly. If it turns out that the endpoint is configured properly, here are some trouble-shooting steps to ensure that authentication is working as intended:
- Ensure that username and password in the
type = authsection are spelled correctly and that they are using the correct case. If you have «Alice» as the username on your phone and «alice» as the username in Asterisk, things will go poorly. - If you are using the
md5_credoption in an auth section, ensure the following:- Ensure that you have set
auth_type = md5. - Ensure that the calculated MD5 sum is composed of username:realm:password
- Ensure that the calculated MD5 sum did not contain any extraneous whitespace, such as a newline character at the end.
- Ensure there were no copy-paste errors. An MD5 sum is exactly 32 hexadecimal characters. If the option in your config file contains fewer or greater than 32 characters, or if any of the characters are not hexadecimal characters, then the MD5 sum is invalid.
- Ensure that you have set
- Ensure that you have specified a
username. Asterisk does not imply a username based on the name of the auth section. - Ensure that the configured
realmis acceptable. In most cases, simple SIP devices like phones will authenticate to whatever realm is presented to them, so you do not need to configure one explicitly. However, if a specific realm is required, be sure it is configured. Be sure that if you are using themd5_credoption that this realm name is used in the calculation of the MD5 sum. - Ensure that the endpoint that is communicating with Asterisk uses the «Digest» method of authentication and the «md5» algorithm. If they use something else, then Asterisk will not understand and reject the authentication attempt.
Authentication Not Attempted
The opposite problem of authentication failures is that incoming calls are not being challenged for authentication where it would be expected. Asterisk chooses to challenge for authentication if the endpoint from which the request arrives has a configured auth option on it. From the CLI, run the pjsip show endpoint <endpoint name> command. Below the initial headers should be something like the following:
Endpoint: david/6001 Unavailable 0 of inf
InAuth: david-auth/david
Aor: david 10
Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060
Identify: 10.24.16.36/32
Notice the «InAuth» on the second line of output. This shows that the endpoint’s auth is pointing to a configuration section called «david-auth» and that the auth section has a username of «david». If you do not see an «InAuth» specified for the endpoint, then this means that Asterisk does not see that the endpoint is configured for authentication. Check the following:
- Ensure that there is an
authline in your endpoint’s configuration. - Ensure that the auth that your endpoint is pointing to actually exists. Spelling is important.
- Ensure that the auth that your endpoint is pointing to has
type = authspecified in it.
Asterisk cannot find the specified extension
If you are seeing a message like the following on your CLI when you place an incoming call:
[2014-10-14 13:22:45.886] NOTICE[1583]: res_pjsip_session.c:1538 new_invite: Call from '201' (UDP:10.24.18.87:5060) to extension '456789' rejected because extension not found in context 'default'.
then it means that Asterisk was not able to direct the incoming call to an appropriate extension in the dialplan. In the case above, I dialled «456789» on the phone that corresponds with endpoint 201. Endpoint 201 is configured with context = default and the «default» context in my dialplan does not have an extension «456789».
The NOTICE message can be helpful in this case, since it tells what endpoint the call is from, what extension it is looking for, and in what context it is searching. Here are some helpful tips to be sure that calls are being directed where you expect:
- Be sure that the endpoint has the expected context configured. Be sure to check spelling.
- Be sure that the extension being dialled exists in the dialplan. From the Asterisk CLI, run
dialplan show <context name>to see the extensions for a particular context. If the extension you are dialing is not listed, then Asterisk does not know about the extension.- Ensure that if you have modified
extensions.confrecently that you have saved your changes and issued adialplan reloadfrom the Asterisk CLI. - Ensure that the extension being dialled has a 1 priority.
- Ensure the the extension being dialled is in the expected dialplan context.
- Ensure that if you have modified
ARGH! NAT!
NAT is objectively terrible. Before having a look at this section, have a look at this page to be sure that you understand the options available to help combat the problems NAT can cause.
NAT can adversely affect all areas of SIP calls, but we’ll focus for now on how they can negatively affect the ability to allow for incoming calls to be set up. The most common issues are the following:
- Asterisk routes responses to incoming SIP requests to the wrong location.
- Asterisk gives the far end an unroutable private address to send SIP traffic to during the call.
Asterisk sends traffic to unroutable address
The endpoint option that controls how Asterisk routes responses is force_rport. By default, this option is enabled and causes Asterisk to send responses to the address and port from which the request was received. This default behavior works well when Asterisk is on a different side of a NAT from the device that is calling in. Since Asterisk presumably cannot route responses to the device itself, Asterisk instead routes the response back to where it received the request from.
Asterisk gives unroutable address to device
By default, Asterisk will place its own IP address into Contact headers when responding to SIP requests. This can be a problem if the Asterisk server is not routable from the remote device. The local_net, external_signaling_address, and external_signaling_port transport options can assist in preventing this. By setting these options, Asterisk can detect an address as being a «local» address and replace them with «external» addresses instead.
Outbound Calls
Asterisk says my endpoint does not exist
If you see a message like the following:
[2014-10-14 15:50:50.407] ERROR[2004]: chan_pjsip.c:1767 request: Unable to create PJSIP channel - endpoint 'hammerhead' was not found
then this means that Asterisk thinks the endpoint you are trying to dial does not exist. For troubleshooting tips about how to ensure that endpoints are loaded as expected, check the Identify by User subsection in the Incoming Calls section.
Alternatively, if you see a message like the following:
[2014-10-14 15:55:06.292] ERROR[2578][C-00000000]: netsock2.c:303 ast_sockaddr_resolve: getaddrinfo("hammerhead", "(null)", ...): Name or service not known
[2014-10-14 15:55:06.292] WARNING[2578][C-00000000]: chan_sip.c:6116 create_addr: No such host: hammerhead
[2014-10-14 15:55:06.292] DEBUG[2578][C-00000000]: chan_sip.c:29587 sip_request_call: Cant create SIP call - target device not registered
or
[2014-10-14 15:55:58.440] WARNING[2700][C-00000000]: channel.c:5946 ast_request: No channel type registered for 'SIP' [2014-10-14 15:55:58.440] WARNING[2700][C-00000000]: app_dial.c:2431 dial_exec_full: Unable to create channel of type 'SIP' (cause 66 - Channel not implemented)
then it means that your dialplan is referencing «SIP/hammerhead» instead of «PJSIP/hammerhead». Change your dialplan to refer to the correct channel driver, and don’t forget to dialplan reload when you are finished.
Asterisk cannot route my call
If Asterisk is finding your endpoint successfully, it may be that Asterisk has no address information when trying to dial the endpoint. You may see a message like the following:
[2014-10-14 15:58:06.690] WARNING[2743]: res_pjsip/location.c:155 ast_sip_location_retrieve_contact_from_aor_list: Unable to determine contacts from empty aor list [2014-10-14 15:58:06.690] WARNING[2834][C-00000000]: app_dial.c:2431 dial_exec_full: Unable to create channel of type 'PJSIP' (cause 3 - No route to destination)
If you see this, then the endpoint you are dialling either has no associated address of record (AoR) or the associated AoR does not have any contact URIs bound to it. AoRs are necessary in order to determine the appropriate destination of the call. To see if your endpoint has an associated AoR, run pjsip show endpoint <endpoint name> from the Asterisk CLI. The following is sample output of an endpoint that does have an AoR configured on it:
Endpoint: david/6001 Unavailable 0 of inf
InAuth: david-auth/david
Aor: david 10
Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060
Identify: 10.24.16.36/32
Notice the third line. The endpoint points to the AoR section called «david». If your endpoint does not have an AoR associated with it, this third line will be absent.
If you think you have associated your endpoint with an AoR, but one does not appear in the CLI, then here are some troubleshooting steps:
- Ensure that you have set the
aorsoption on the endpoint. Notice that the option is notaor(there is an ‘s’ at the end). - Ensure that the AoR pointed to by the
aorsoption exists. Check your spelling!
If those appear to be okay, it may be that there was an error when attempting to load the AoR from configuration. From the Asterisk CLI, run the command pjsip show aor <aor name>. If you see a message like
Unable to find object heman.
Then it means the AoR did not get loaded properly. Here are some troubleshooting steps to ensure your AoR is configured correctly:
- Ensure that your AoR has
type = aorset on it. -
Ensure that there were no nonexistent configuration options set. You can check the logs at Asterisk startup to see if there were any options Asterisk did not understand. For instance, you may see something like:
[2014-10-14 16:16:20.658] ERROR[2939]: config_options.c:710 aco_process_var: Could not find option suitable for category '1000' named 'awesomeness' at line 219 of [2014-10-14 16:16:20.659] ERROR[2939]: res_sorcery_config.c:275 sorcery_config_internal_load: Could not create an object of type 'aor' with id '1000' from configuration file 'pjsip.conf'
In this case, I tried to set an option called «awesomeness» on the AoR 1000. Since Asterisk did not recognize this option, AoR 1000 was unable to be loaded.
- The
contactoption can be a pitfall. There is an object type called «contact» that is documented on the wiki, which may make you think that the AoR option should point to the name of a contact object that you have configured. On the contrary, thecontactoption for an AoR is meant to be a SIP URI. The resulting contact object will be created by Asterisk based on the provided URI. Make sure when setting thecontactthat you use a full SIP URI and not just an IP address.
Another issue you may encounter is that you have properly configured an AoR on the endpoint but that this particular AoR has no contact URIs bound to it. From the CLI, run the pjsip show aor <aor name> command to see details about the AoR. Here is an example of an AoR that has a contact URI bound to it.
The «Contact:» line shows the URI «sip:[email protected]:5060;ob» is bound to the AoR 201. If the AoR does not have any contacts bound to it, then no Contact lines would appear. The absence of Contact lines can be explained by any of the following:
- If the device is expected to register, then it may be that the device is either not properly configured or that there was a registration failure. See the Inbound Registrations section for details on how to resolve that problem.
- If the device is not intended to register, then the AoR needs to have a
contactoption set on it. See the previous bulleted list for possiblecontact-related pitfalls.
ARGH! NAT! (Part 2)
NAT makes babies cry.
For outbound calls, the main NAT issue you are likely to come across is Asterisk publishing an unroutable private address in its Contact header. If this is an issue you are facing, this can be corrected by setting the local_net, external_signaling_address, and external_signaling_port options for the transport you are using when communicating with the endpoint. For more information on how this can be set up, please see this page.
Bridged Calls
Direct media is a feature that allows for media to bypass Asterisk and flow directly between two endpoints. This can save resources on the Asterisk system and allow for more simultaneous calls. The following conditions are required for direct media. If any are not met, then direct media is not possible:
- There must only be two endpoints involved in the call.
- Both endpoints involved in the call must have the
direct_mediaoption enabled. - The call must be a regular person-to-person call. Calls through ConfBridge() and Meetme() cannot use direct media.
- The sets of codecs in use by each endpoint during the call must have a non-empty intersection. In other words, each endpoint must be using at least one codec that the other endpoint is using.
- Any features in Asterisk that manipulate, record, or inject media may not be used. This includes:
- The Monitor() and Mixmonitor() applications
- The Chanspy() application
- The JACK() application
- The VOLUME() function
- The TALK_DETECT() function
- The SPEEX() function
- The PERIODIC_HOOK() function
- The ‘L’ option to the Dial() application
- An ARI snoop
- A jitter buffer
- A FAX gateway
- No features that require that Asterisk intercept DTMF may be used. This includes the T, t, K, k, W, w, X, and x options to the Dial() application.
- If either endpoint has the
disable_direct_media_on_natoption set, and a possible media NAT is detected, then direct media will not be used. This option is disabled by default, so you would have to explicitly set this option for this to be a problem. - The two endpoints must be in the same bridge with each other. If the two endpoints are in separate bridges, and those two bridges are connected with one or more local channels, then direct media is not possible.
Double-check that all requirements are met. Unfortunately, Asterisk does not provide much in the way of debug for determining why it has chosen not to use direct media.
Inbound Registrations
For inbound registrations, a lot of the same problems that can happen on inbound calls may occur. Asterisk goes through the same endpoint identification and authentication process as for incoming calls, so if your registrations are failing for those reasons, consult the troubleshooting guide for incoming calls to determine what the problem may be.
If your problem is not solved by looking in those sections, then you may have a problem that relates directly to the act of registering. Before continuing, here is a sample REGISTER request sent to an Asterisk server:
REGISTER sip:10.24.20.249:5060 SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 10.24.16.37:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bKPj.rPtUH-P33vMFd68cLZjQj0QQxdu6mNx Max-Forwards: 70 From: "200" <sip:[email protected]>;tag=BXs-nct8-XOe7Q7tspK3Vl3iqUa0cmzc To: "200" <sip:[email protected]> Call-ID: C0yYQJ8h776wbheBiUEqCin.ZhcBB.tZ CSeq: 5200 REGISTER User-Agent: Digium D40 1_4_0_0_57389 Contact: "200" <sip:[email protected]:5060;ob> Expires: 300 Allow: PRACK, INVITE, ACK, BYE, CANCEL, UPDATE, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, REFER, MESSAGE, OPTIONS Content-Length: 0
This REGISTER was sent by the endpoint 200. The URI in the To header is «sip:[email protected]». Asterisk extracts the username portion of this URI to determine the address of record (AoR) that the REGISTER pertains to. In this case, the AoR has the same name as the endpoint, 200. The URI in the Contact header is «sip:[email protected]:5060;ob». The REGISTER request is attempting to bind this contact URI to the AoR. Ultimately, what this means is that when someone requests to reach endpoint 200, Asterisk will check the AoRs associated with the endpoint, and send requests to all contact URIs that have been bound to the AoR. In other words, the REGISTER gives Asterisk the means to locate the endpoint.
You can ensure that your configuration is sane by running the the pjsip show endpoint <endpoint name> CLI command. Part of the output is to show all AoRs associated with a particular endpoint, as well as contact URIs that have been bound to those AoRs. Here is sample output from running pjsip show endpoint 200 on a system where registration has succeeded:
Endpoint: 200/200 Not in use 0 of inf
Aor: 200 1
Contact: 200/sip:[email protected]:5060;ob Unknown nan
Transport: main-transport udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5060
This shows that endpoint 200 has AoR 200 associated with it. And you can also see that the contact «sip:[email protected]:5060;ob» has been bound to the AoR.
If running this command shows no AoR, then ensure that the endpoint has the aors option set. Note that the name is aors, not aor.
More likely, the issue will be that an AoR will be listed, but there will be no associated contact. If this is the case, here are some possible troubleshooting steps:
- Ensure that the AoR has actually been loaded. Run the CLI command
pjsip show aor <aor name>. If no AoR is displayed, then that means the AoR was not loaded.- Ensure that the configuration section has
type = aorspecified. - Ensure that all configuration options specified on the AoR are options that Asterisk recognizes.
- Ensure that the configuration section has
-
Ensure that the
res_pjsip_registrar.somodule is loaded and running. Runningmodule show like res_pjsip_registrar.soshould show the following:Module Description Use Count Status Support Level res_pjsip_registrar.so PJSIP Registrar Support 0 Running core
-
Ensure that the AoR has a
max_contactsvalue configured on it. If this option is not set, then registration cannot succeed. You will see this message on the CLI:[2014-10-16 11:34:07.887] WARNING[2940]: res_pjsip_registrar.c:685 registrar_on_rx_request: AOR '200' has no configured max_contacts. Endpoint '200' unable to register
Asterisk will transmit a 403 Forbidden in response to the registration attempt.
If you initially have successful registrations but they later start failing, then here are some further troubleshooting steps for you to try:
- If you intend for new registrations to replace old ones, then enable the
remove_existingoption for the AoR. -
Ensure that if you are attempting to bind multiple contacts to an AoR that the
max_contactsfor the AoR is large enough. If themax_contactsvalue is not high enough, you will see the following CLI message:[2014-10-16 11:34:07.887] WARNING[2940]: res_pjsip_registrar.c:411 rx_task: Registration attempt from endpoint '200' to AOR '200' will exceed max contacts of 1
Asterisk will respond to the registration attempt with a 403 Forbidden.
Outbound Registrations
If you are having troubles with outbound registrations and unfamiliar with the mechanics involved, please see this page. It will explain quite a few of the concepts that Asterisk uses and may give you some clues for solving your issue.
If you are still having trouble, here are some troubleshooting steps:
- If Asterisk is not sending an outbound REGISTER at all, then it is likely that there was an error when trying to load the outbound registration.
- Ensure that the outbound registration has
type = registrationin it. - Ensure that there are no configuration options that Asterisk does not recognize.
- Ensure that the outbound registration has
-
Another reason Asterisk may not be sending an outbound REGISTER is that you do not have a valid SIP URI for your
server_uriorclient_uri. You may see a message like this on the CLI if this is the case:[2014-10-16 12:05:16.064] ERROR[3187]: res_pjsip_outbound_registration.c:724 sip_outbound_registration_regc_alloc: Invalid server URI '[email protected]' specified on outbound registration 'outreg'
In this case, I left off the initial «sip:» from the URI.
- If your outbound REGISTER receives no response, then you may have misconfigured the
server_urito point somewhere the REGISTER is not meant to be sent. - If Asterisk has stopped sending REGISTER requests, then either the maximum number of retries has been attempted or the response that Asterisk received from the registrar was considered to be a permanent failure. If you want to get Asterisk to start sending REGISTER requests again after making configuration adjustments, you can do so by running the
module reload res_pjsip_registrar.soCLI command.
Inbound Subscriptions
The first thing to acknowledge with inbound subscriptions is that the handling of the inbound SUBSCRIBE messages starts the same as for inbound calls. This means that if you are having troubles where Asterisk does not recognize the endpoint sending the SUBSCRIBE or if authentication is failing, you should check the troubleshooting guide for incoming calls for details on how to solve these issues.
It is also important to ensure that res_pjsip_pubsub.so is loaded and running. This module is the core of all of Asterisk’s handling of subscriptions, and if it is not loaded, then Asterisk will not be able to set up subscriptions properly.
Presence/Dialog Info
A tutorial about subscribing to presence and dialog-info can be found on this page. Reading that page may point you towards how to resolve the issue you are facing.
If you are attempting to subscribe to the presence or dialog event packages, then here are some troubleshooting steps for determining what is going wrong.
- Ensure that the
res_pjsip_exten_state.somodule is loaded. - Ensure that the Event header in inbound subscribe messages are one of «presence» or «dialog».
- Ensure all necessary modules are loaded, depending on what values are in the Accept header of inbound SUBSCRIBE requests.
- Subscriptions that use Accept: application/pidf+xml will need to have
res_pjsip_pidf_body_generator.soloaded. - Subscriptions that use Accept: application/xpidf+xml will need to have
res_pjsip_xpidf_body_generator.soloaded. - Subscriptions that use Accept: application/dialog-info+xml will need to have
res_pjsip_dialog_info_body_generator.soloaded.
- Subscriptions that use Accept: application/pidf+xml will need to have
-
When subscribing, you may see a message like the following on the CLI:
[2014-10-16 12:56:58.605] WARNING[3780]: res_pjsip_exten_state.c:337 new_subscribe: Extension blah does not exist or has no associated hint
The warning message is self-explanatory. If you think you have placed extension «blah» in your
extensions.conffile and it contains a hint, then be sure that it exists in the same context as thecontextoption on the endpoint that is attempting to subscribe. Also be sure that if you have recently changed yourextensions.conffile that you have saved the changes and run thedialplan reloadCLI command.
MWI
If you are attempting to subscribe to the message-summary package, then here are some troubleshooting steps for determining what is going wrong.
- Ensure that the
res_pjsip_mwi.soand theres_pjsip_mwi_body_generator.somodules are loaded. - Ensure that the AoR that the MWI SUBSCRIBE is being sent to has
mailboxesconfigured on it. Note that the option name ismailboxesand notmailbox. -
When subscribing to MWI, you may see a message like the following:
[2014-10-16 13:06:51.323] NOTICE[3963]: res_pjsip_mwi.c:566 mwi_validate_for_aor: Endpoint '200' already configured for unsolicited MWI for mailbox '200'. Denying MWI subscription to 200
The most likely cause of something like this is that you have an endpoint and an AoR that both have
mailboxes = 200in your configuration. The endpoint withmailboxes = 200attempts to subscribe to the AoR that hasmailboxes = 200. In this case, since Asterisk is already sending MWI notifications about mailbox 200 to the endpoint, the subscription to the AoR is denied. To fix this, remove themailboxesoption from your endpoint, or configure your device not to attempt to subscribe to MWI. - Asterisk has multiple ways of having MWI state set, but the most common way is to use
app_voicemailthat comes with Asterisk.app_voicemailhas a requirement that mailbox names must follow the format «[email protected]». If you are usingapp_voicemailand you configure MWI inpjsip.confand only provide the mailbox name without a context, then you will not receive MWI updates when the state of the mailbox changes.
Configuration Issues
Can’t create an IPv6 transport
You’ve configured a transport in pjsip.conf to bind to an IPv6 address or block. However, Asterisk fails to create the transport when loading!
If you look into your logs you might messages similar to the following:
[Dec 12 00:58:31] ERROR[10157] config_options.c: Error parsing bind=:: at line 8 of [Dec 12 00:58:31] ERROR[10157] res_sorcery_config.c: Could not create an object of type 'transport' with id 'my-ipv6-transport' from configuration file 'pjsip.conf'
The most likely issue is that you have not compiled pjproject with support for IPv6. You can find instructions at PJSIP-pjproject.
1. Список команд для диагностики Asterisk
|
Назначение |
Команда |
|
Диагностика |
|
|---|---|
|
Посмотреть лог Asterisk |
cat /var/log/asterisk/messages либо /var/log/asterisk/full |
|
Следить за логом |
tail -f /var/log/asterisk/messages |
|
Проверить подключение/отключение телефонов клиента |
cat /var/log/asterisk/messages |grep -I reach |
|
Вывести информацию о зарегистрированных IP-телефонах |
asterisk -rx «sip show peers» |
|
Вывести информацию о SIP-транках |
asterisk -rx «sip show registry» |
2. Статусы IP-телефонов
Команда: asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
|
Статус IP-телефона |
Значение |
|
OK |
Сервер регистрации доступен и отвечает на SIP ping (запросы OPTIONS) |
|
UNREACHABLE |
Сервер регистрации недоступен и отвечает на SIP ping (запросы OPTIONS) |
3. Статусы SIP-транков
Команда: asterisk -rx «sip show registry» и asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
|
Состояние транка |
Значение |
|
Registered |
Зарегистрирован |
|
Auth. sent |
Сервер регистрации не отвечает на запрос |
|
OK |
Сервер регистрации доступен и отвечает на SIP ping (запросы OPTIONS) |
|
UNREACHABLE |
Сервер регистрации недоступен и отвечает на SIP ping (запросы OPTIONS) |
4. Диагностика
4.1 Не работает исходящая и входящая связь
4.1.1 Проблема: у одного сотрудника
Входящие: не работает у одного сотрудника
Исходящие: не работает у одного сотрудника
Внутренние: не работает у одного сотрудника
Возможные причины
-
Нет регистрации IP-телефона
-
Не указан номер в профиле сотрудника в личном кабинете ВАТС
-
Ошибки при исходящем вызове от коммутатора оператора, предоставляющего номер
Диагностика
-
Проверить регистрацию IP-телефона
asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Пример: root@MSCelecom1:~# sipteco_vm_peers virt21
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
101/101 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (40 ms) Cached RT
102/102 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (40 ms) Cached RT
103/103 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (38 ms) Cached RT
104/104 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (39 ms) Cached RT
74956639622/74956639622 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (2 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
6 sip peers [Monitored: 6 online, 0 offline Unmonitored: 0 online, 0 offline]
root@MSCelecom1:~#
Вывод команды показал
|
Телефон зарегистрирован (ОК) |
Телефон не зарегистрирован (UNREACHABLE) |
|
переходим в п. 2) диагностики |
Проверка настроек телефонного аппарата |
4.1.2 Проблема: внешние вызовы не работают, внутренние работают у всех сотрудников
Входящие: не работает у всех сотрудников
Исходящие: не работает у всех сотрудников
Внутренние: работают у всех сотрудников
Возможные причины
-
Недоступен SIP-сервер оператора связи
-
Указан неверный пароль для регистрации на SIP-сервере оператора связи
Диагностика
Шаг №1 Проверить состояние SIP-транков
Команда проверки: asterisk -rx «sip show registry»
Пример:
root@MSCelecom1:~# asterisk -rx «sip show registry»
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
101/101 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (56 ms) Cached RT
102/102 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (40 ms) Cached RT
103/103 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (39 ms) Cached RT
104/104 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (40 ms) Cached RT
74956639622/74956639622 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (2 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
6 sip peers [Monitored: 6 online, 0 offline Unmonitored: 0 online, 0 offline]
Host dnsmgr Username Refresh State Reg.Time
91.218.111.145:5060 N 74956639622@ 105 Auth. sent Thu, 07 May 2015 19:01:41
1 SIP registrations.
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
SIP-транк зарегистрирован (состояние Registered, Reachable) |
SIP-транк не зарегистрирован (состояние Auth sent, unreachable) |
|
Предварительный вывод |
ошибки на стороне коммутатора оператора, предоставляющего исходящую связь |
Проблема с регистрацией SIP-транка |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
|
|
4.1.3 Проблема: не работают ни внешние ни внутренние вызовы.
Входящие: не работает у всех сотрудников
Исходящие: не работает у всех сотрудников
Внутренние: не работает у всех сотрудников
Возможные причины
-
Проблемы с регистрацией IP-телефонов клиента, возможны проблемы во внутренней сети клиента.
-
Проблемы с сетью датацентра
Диагностика
Шаг №1 Проверка регистрации IP-телефонов клиента
Команда: sipteco_vm_peers VMname
root@MSCelecom1:~# asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
101/101 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (69 ms) Cached RT
102/102 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (43 ms) Cached RT
103/103 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (78 ms) Cached RT
104/104 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (37 ms) Cached RT
74956639622/74956639622 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (2 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
6 sip peers [Monitored: 6 online, 0 offline Unmonitored: 0 online, 0 offline]
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
SIP-транк зарегистрирован (состояние Registered, Reachable) |
SIP-транк не зарегистрирован (состояние Auth sent, unreachable) |
|
Предварительный вывод |
ошибки на стороне коммутатора оператора, предоставляющего исходящую связь |
Проблема с регистрацией SIP-транка |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
|
|
|
Решение |
Передать проблему оператору связи, предоставляющему SIP-транк |
Передать проблему оператору связи, предоставляющему SIP-транк |
Шаг №2 Проверить регистрации телефонов в других доменах.
Если проблема в сети датацентра, в котором установлен сервер ВАТС, то проблема с регистрацией телефонов будет наблюдаться у всех доменов
4.2 Не работает SIP-транк
Возможные причины
-
Не работает SIP-транк оператора, предоставляющего номер
Диагностика
Шаг №1 Проверить регистрацию SIP-транка
Команда: asterisk -rx «sip show registry»
Пример:
root@MSCelecom1:~# asterisk -rx «sip show registry»
asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Host dnsmgr Username Refresh State Reg.Time
91.218.111.145:5060 N 74996414100@ 105 Registered Thu, 23 Apr 2015 15:00:46
1 SIP registrations.
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
101/101 (Unspecified) D N 0 UNREACHABLE Cached RT
102/102 (Unspecified) D N 0 UNKNOWN Cached RT
103/103 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (489 ms) Cached RT
105/105 (Unspecified) D N 0 UNREACHABLE Cached RT
106/106 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (101 ms) Cached RT
74996414100/74996414100 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (2 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
7 sip peers [Monitored: 4 online, 3 offline Unmonitored: 0 online, 0 offline]
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
SIP-транк зарегистрирован (состояние Registered, Reachable) |
SIP-транк не зарегистрирован (состояние Auth sent, unreachable) |
|
Предварительный вывод |
ошибки на стороне коммутатора оператора, предоставляющего исходящую связь |
Проблема с регистрацией SIP-транка |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
|
|
|
Решение |
Передать проблему оператору связи, предоставляющему SIP-транк |
Передать проблему оператору связи, предоставляющему SIP-транк |
4.4 Проблемы в сети клиента
Возможные причины
-
Проблемы в локальной сети клиента
-
Проблемы провайдера, предоставляющего интернет
Диагностика
Шаг №1 Проверить отключались ли телефоны клиента от ВАТС
Команда: sipteco_vm_log_reach <название домена>
Пример:
root@MSCelecom1:~# sipteco_vm_log_reach virt57
[2015-04-23 00:26:04] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (70ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 00:26:05] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (65ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 01:00:08] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (48ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 01:29:09] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (40ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 03:43:59] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (30ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 08:31:47] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 41
[2015-04-23 09:13:51] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (148ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 09:13:51] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (39ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 09:23:56] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 46
[2015-04-23 09:24:11] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (149ms / 2000ms)
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
Есть подключения и отключения IP-телефонов (записи is now Reachable и is now UNREACHABLE! ) |
Нет подключений и отключений IP-телефонов (записи is now Reachable и is now UNREACHABLE! ) |
|
Предварительный вывод |
Проблема в сети клиента либо у оператора, который предоставляет клиенту доступ в интернет |
Проблем с сетью клиента нет |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
Проверить другие домены сервера, чтобы исключить проблему в датацентре |
|
|
Решение |
4.5 Нет регистрации телефона клиента
Возможные причины
-
Неправильные настройки телефона: не указан Outbound proxy, неверный пароль
-
Были произведены изменения в личном кабинете, после которых пропала регистрация телефона
Диагностика и устранение
-
Проверяем регистрацию телефона клиента
Команда: asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Пример:
root@MSCelecom1:~# asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
801/801 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (68 ms) Cached RT
802/802 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (66 ms) Cached RT
803/803 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (102 ms) Cached RT
804/804 (Unspecified) D N 0 UNREACHABLE Cached RT
805/805 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (33 ms) Cached RT
celecom-74995196338/74995 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (1 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
7 sip peers [Monitored: 6 online, 1 offline Unmonitored: 0 online, 0 offline]
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
Телефон зарегистрирован (ОК) |
Телефон не зарегистрирован (UNREACHABLE) |
|
Предварительный вывод |
Телефон зарегистировался и проблема должна быть решена |
Проверка настроек телефонного аппарата |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
|
|
|
Решение |
Проверка настроек телефонного аппарата |
2. Проверить правильный ли пароль введен в телефон
-
Включаем слежение за логом ВАТС
-
Просим клиента перезагрузить телефон
Слежение за логом
Команда: tail -f /var/log/asterisk/messages
Если пароль неверный, то в логе появится запись:
[2015-04-23 15:42:24] NOTICE[3120] chan_sip.c: Registration from ‘110 <sip:110@ajuraudit.quickfon.ru>’ failed for ‘194.135.75.14’ — Wrong password
Если пароль верный, то в логе появится запись:
root@MSCelecom1:~# sipteco_vm_log_tail virt57
[2015-04-23 15:30:21] VERBOSE[16674] chan_sip.c: > Saved useragent «Zoiper r30645» for peer 102
[2015-04-23 15:30:21] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (105ms / 2000ms)
3. Если в логе записей нет, то необходимо проверить настройки телефона — поля адрес сервера и Outbound proxy
Для телефонов Grandstream поле SIP-server заполняется полным именем домена virt57.s1.celecom.ru, а Outbound proxy указывается IP адрес
4.6 Клиент вбил неправильный пароль в телефон и не понимает почему не работает
Повторяем действия п. 3.5
4.7 Клиент жалуется на недозвон по направлению
Возможные причины
-
Проблемы у оператора, предоставляющего исходящую связь
Диагностика и устранение
-
Запускаем команду следить за логом tail -f /var/log/asterisk/messages
-
Делаем тестовый вызов
-
В логах смотрим ошибки при исходящем вызове
Нормальный вызов:
-
[2015-03-25 14:37:55] VERBOSE[6970] app_dial.c: — Called 79852927460@74992905059
-
[2015-03-25 14:37:55] VERBOSE[6968] app_dial.c: — Local/79852927460@local-c580;1 is ringing
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:00] VERBOSE[6970] app_dial.c: — SIP/74992905059-00000015 is making progress passing it to Local/79852927460@local-c580;2
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:00] VERBOSE[6970] app_dial.c: — SIP/74992905059-00000015 is ringing
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:00] VERBOSE[6968] app_dial.c: — Local/79852927460@local-c580;1 is ringing
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:04] VERBOSE[6970] app_dial.c: — SIP/74992905059-00000015 answered Local/79852927460@local-c580;2
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:04] VERBOSE[6968] app_dial.c: — Local/79852927460@local-c580;1 stopped sounds
-
[2015-03-25 14:38:04] VERBOSE[6968] app_dial.c: — Local/79852927460@local-c580;1 answered SIP/74992905059-00000014
Строка №1 — звоним по номеру 79852927460 через канал SIP транк 74992905059
Строка №8 — ответ вызываемой стороны
Проблемный вызов
Закончится ошибкой SIP
4.8 Клиент жалуется на отсутствие связи конкретных внутренних номеров
Возможные причины
-
Как правило это связано с тем, что IP-телефоны клиента не зарегистрированы
Диагностика и устранение
asterisk -rx «sip show peers»
Name/username Host Dyn Nat ACL Port Status Realtime
100/100 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (35 ms) Cached RT
101/101 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (34 ms) Cached RT
102/102 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (35 ms) Cached RT
103/103 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (35 ms) Cached RT
106/106 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (17 ms) Cached RT
107/107 95.213.157.34 D N 5060 OK (16 ms) Cached RT
74995196141/74995196141 91.218.111.145 N 5060 OK (2 ms)
siptest/siptest 127.0.0.1 D A 5060 OK (1 ms)
Вывод: сейчас все телефоны зарегистрированы
cat /var/log/asterisk/messages|grep -i reach
[2015-03-25 08:58:10] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 17
[2015-03-25 08:58:12] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘107’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 16
[2015-03-25 13:21:58] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (65ms / 2000ms)
[2015-03-25 13:21:59] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘107’ is now Reachable. (104ms / 2000ms)
[2015-03-25 13:46:03] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 17
[2015-03-25 13:46:05] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘107’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 18
[2015-03-25 13:47:23] NOTICE[1988] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (154ms / 2000ms)
Вывод: в 08:58, 13:21, 13:46, 13:47 телефоны 106 и 107 отключались от АТС и не могли принимать входящие вызовы
4.9 Не работает перевод вызовов на внутренние номера
Возможные причины
-
IP-телефоны настроены на передачу DTMF в формате отличном от RFC2833
Решение:
-
Настроить формат передачи DTMF в RFC2833
4.10 Не работает переадресация
Возможные причины:
-
Проблемы с исходящей связью
Решение:
-
Диагностика проблемы аналогично разделу 6.1
4.11 Не работает последовательность отработки входящих вызовов
Возможные причины
-
Неверно настроена входящая маршрутизация
Решение
-
Запустить слежение за логом tail -f /var/log/asterisk/messages
-
Сделать тестовый входящий вызов и посмотреть последовательность отработки входящих вызовов
-
Отредактировать маршруты в личном кабинете
4.13 Клиент жалуется на плохую связь, пропадение голоса
Возможные причины
-
Проблемы в локальной сети клиента
-
Проблемы провайдера, предоставляющего интернет
Диагностика
Шаг №1 Послушать запись разговора в которой проблема
Если на записи слышны потери:
-
Вы слышите потери голоса нашего клиента — проблема в локальной сети клиента. Идем на шаг №2
-
Клиента вы слышите хорошо, но того с кем он разговаривает слышно плохо — проблемы на стороне оператора связи, который предоставляет городской номер. Сдаем заявку этому оператору
Если на записи потери не слышны потери в локальной сети клиента. Идем на шаг №2
Шаг №2 Проверить отключались ли телефоны клиента
Команда: cat /var/log/asterisk/messages |grep -I reach
Пример:
root@MSCelecom1:~# cat /var/log/asterisk/messages |grep -I reach
[2015-04-23 00:26:04] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (70ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 00:26:05] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (65ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 01:00:08] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (48ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 01:29:09] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (40ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 03:43:59] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (30ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 08:31:47] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 41
[2015-04-23 09:13:51] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (148ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 09:13:51] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘106’ is now Reachable. (39ms / 2000ms)
[2015-04-23 09:23:56] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now UNREACHABLE! Last qualify: 46
[2015-04-23 09:24:11] NOTICE[16674] chan_sip.c: Peer ‘102’ is now Reachable. (149ms / 2000ms)
Вывод команды показал
|
Вывод команды показал, что |
Есть подключения и отключения IP-телефонов (записи is now Reachable и is now UNREACHABLE! ) |
Нет подключений и отключений IP-телефонов (записи is now Reachable и is now UNREACHABLE! ) |
|---|---|---|
|
Предварительный вывод |
Проблема в сети клиента либо у оператора, который предоставляет клиенту доступ в интернет |
Проблем с сетью клиента нет |
|
Второй шаг диагностики |
Проверить сеть на АТС сервера, чтобы исключить проблему . Запустить ping, mtr |
Аналоговая связь уходит в прошлое, и большинство компаний выбирают SIP-телефонию. Это возможность быстро обеспечить офис связью и звонить в любой конец света. Но при некорректных настройках пользователи сталкиваются и с минусами. Эхо, задержка звука, низкое качество связи — мы составили гайд по самым частым проблемам цифровой телефонии и даем пошаговую инструкцию по их исправлению.
О том, как работает связь по интернету, читайте в статье «Простыми словами: что такое SIP-телефония».
А эта статья предназначена для всех, кто пользуется SIP-аккаунтами, программами или сервисами для связи. Решения, которые мы предлагаем, основаны на нашем собственном опыте. В каждом разделе «Что делать» описано пошаговое решение проблемы. Сначала выполните пункт, который описан первым. Если не помогло — переходите ко второму. Если же и это не сработало, то обратитесь к системному администратору или другому профильному специалисту.
Если же не хотите столкнуться с подобными проблемами — используйте Виртуальную АТС 2.0 от Ringostat. Это телефон прямо в браузере и аналитический ассистент менеджера по продажам.
Подробней его возможности описаны в статье «Виртуальная АТС Ringostat: омниканальное решение для отделов продаж».
1. Задержка звука
Чаще всего происходит по двум причинам — из-за проблем с сетью или задержки при обработке данных. Рассмотрим их особенности.
Сетевая
Возникает в таких случаях:
- если вы подключаетесь к интернету не напрямую через кабель, а с помощью wi-fi;
- маршрутизатор/роутер загружен, из-за чего данные IP-телефонии не могут «пробиться» и задерживаются.
В первом случае мощности wi-fi не хватает, чтобы обеспечить бесперебойную передачу данных. На втором остановимся немного подробней.
Представим, что в офисе один сотрудник что-то скачивает, а другой разговаривает по телефону. Канал, по которому передаются данные, целиком «забит» качающейся информацией, и для пакетов SIP-телефонии места не остается. Для нее не нужен большой канал, но он должен быть отдельно выделен под связь.
Сложность в том, что эту проблему непросто диагностировать — ведь сайты при загруженности маршрутизатора или плохом качестве wi-fi подключения все равно будут загружаться быстро. Но телефония при этом будет страдать, т. к. она использует потоковую загрузку, и звук должен транслироваться непрерывно. А, например, при серфинге страниц данные могут загружаться «рывками», что недопустимо в случае с телефонией.
Задержка обработки
Когда вы разговариваете с собеседником с помощью SIP-телефонии, ваш голос сначала кодируется и после передачи по сети раскодируется «на выходе». Обычно это происходит почти мгновенно и незаметно для разговаривающих. Но если звонить на компьютере, процессор которого загружен, то появляется такая проблема — ведь устройство не успевает вовремя обрабатывать задачи.
Что делать
- Убедитесь, что вы подключены к сети не по wi-fi, а с помощью кабеля. Чаще всего проблема задержки решается так.
- Исключите проблему с устройством. Например, настройте связь на другом компьютере и попробуйте позвонить с него. Для обеспечения наилучшего качества рекомендуем использовать SIP-телефоны.
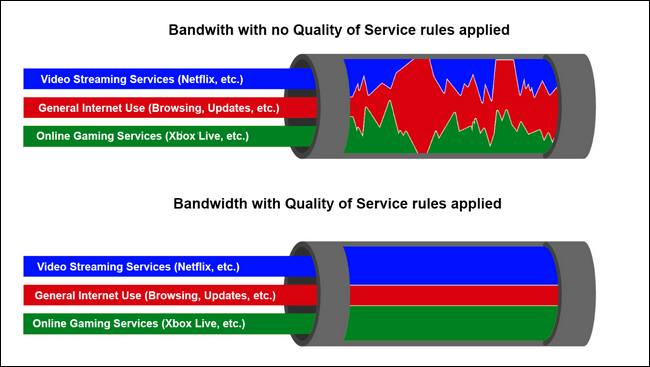
- Настройте приоритезацию трафика на вашем маршрутизаторе — подробней об этом описано в статье «Настройка QoS для повышения качества IP-телефонии». На схеме с сайта VAS Experts показано, как работает устройство без настроенной функции приоритизации и с ней:
- Если первые три пункта не помогли, проверьте, как работает связь, подключившись через другого провайдера. Например, возьмите ноутбук домой или в другой офис и настройте связь там. При подтверждении проблемы обратитесь к провайдеру для её решения.
2. Односторонняя слышимость
Если собеседник вас не слышит или вы его, то проблема связана с настройками вашей сети. Причина может быть в NAT — технологии трансляции сетевых адресов, которая используется большинством провайдеров и в домашних или офисных сетях. Она предназначена решать проблему нехватки IP-адресов и обеспечивать безопасность локальных сетей, подключенных к интернету.
Например, у компании есть несколько реальных IP-адресов, но гораздо больше компьютеров с локальными адресами, которым нужен выход в сеть. NAT подменяет локальный адрес на наружный общедоступный адрес. На скрине ниже показан пример подмены адресов для нескольких компьютеров.
Но при этом может возникнуть проблема с передачей голосовых данных. Например, Абонент 1 звонит Абоненту 2 с локального адреса, используя NAT. Абонент 2 отвечает, но не может отправить голосовые данные по назначению. Это происходит из-за того, указанный адрес Абонента 1 не маршрутизируется в интернете. В результате возникает односторонняя слышимость или звук вообще отсутствует.
Что делать
- Настройте на SIP-устройстве STUN-сервер — специальную технологию для VoIP-устройств, которые используют NAT. Ее суть в том, что устройство сначала отправляет запрос на STUN-сервер. Он сообщает текущий внешний адрес и порт, который потом используется для приема. Если вы используете Ringostat, то можете использовать наш адрес STUN-сервера — stun.ringostat.com:3479. На примере ниже его настройка в приложении Phonerlite:
- Включите на маршрутизаторе поддержку SIP-телефонии. Эта функция присутствует на большинстве современных устройств, достаточно найти инструкцию в сети.
- Если это не помогло, то понадобится проброс портов, которые используются SIP-телефонией. Для этого лучше обратиться к сисадмину или специалисту по настройке сетей.
3. Эхо и низкое качество звука при разговоре
Иногда случается, что человек при разговоре слышит сам себя или собеседник слышит его плохо. Либо наоборот — слишком громкие звуки окружения. Причин этому может быть несколько:
- плохая гарнитура;
- вы или ваш собеседник держит трубку слишком далеко или включил громкую связь;
- происходит задержка данных.
Что делать
- Большинство проблем с качеством звука происходит из-за некачественной или дешевой гарнитуры. Она отражает в микрофон звуки, которые слышны из наушников. Чтобы этого не происходило, не экономьте на оборудовании. При выборе читайте отзывы и используйте профессиональные марки. Например, наша техподдержка рекомендует USB-гарнитуру Jabra или Sennheiser. Если выберете именно USB-гарнитуру, то исключите проблемы с аудиокартами и драйверами — см. пункт 3.
- Если звоните с ноутбука, убедитесь, что не используете его внешний микрофон вместо микрофона на гарнитуре. Это довольно частая ситуация, которая отражается на качестве звука. Для этого откройте программу, с которой обычно звоните, и переключите в ней внешний микрофон на внутренний.
- Если звоните с компьютера и используете не USB, а обычную гарнитуру, то проверьте, установлены ли последние драйвера на аудиокарту от производителя.
- Использование нестандартных кодеков. Например, есть кодек GSM, который сохраняет связь, но голос при этом очень плохо звучит. А есть один из последних — G729, где голос звучит отлично. Мы же рекомендуем использовать стандартные кодеки, которые хорошо поддерживают большинство операторов связи. Выберите в настройках устройства только кодеки 711-A и 711-U, отключив остальные.
- Попробуйте настроить программу для связи и устройство на другом компьютере. После этого проверьте качество связи.
4. Не поступают звонки, потому что аккаунт в офлайне
Случается, что при использовании SIP-телефонии на устройство перестают поступать входящие звонки. Это может быть временной ситуацией, и потом можно дозвониться вновь. При этом у вас на устройстве, скорей всего, будет писаться, что аккаунт в сети — но сервер считает, что он в офлайне. Причина этого кроется в настройках сети.
Многие провайдеры SIP-телефонии постоянно «пингуют», т. е. отправляют пакеты раз в какое-то время. Это нужно, чтобы проверить, находится ли устройство в сети, и знать его актуальный статус. Даже если устройство проходит регистрацию на один час, провайдер все равно в это время будет отправлять пакеты для проверки на случай внезапного отключения устройства.
Еще одна причина — маршрутизатор спустя какое-то время закрывает у себя порт, и SIP-сервер не может проверить статус. Это продиктовано требованиями безопасности некоторых устройств.
Что делать
- Уменьшите тайм-аут регистрации SIP-аккаунта со стандартных 3600 секунд, как у большинства программ и телефонов, до 60. Это позволит чаще проходить регистрацию, и порт на маршрутизаторе будет чаще открываться.
- Включите на маршрутизаторе поддержку SIP-телефонии либо настройте проброс портов с помощью специалиста.
5. Пропадает звук
Эта проблема очень похожа по своим предпосылкам на пункт 1 — задержка звука. Причина может быть в интернете или в вашем устройстве: SIP-телефоне, компьютере.
Что делать
Компьютер
- Если использовать гарнитуру и компьютер, может возникнуть сетевая проблема. Убедитесь, что вы подключены по кабелю, и нет потери пакетов. Для этого используйте команду PING к серверу sip.ringostat.com, если вы используете наш сервис.
- Процессор компьютера слишком загружен, поэтому при кодировании и декодировании звука происходит прерывание. Чтобы этого избежать, отключите лишние программы.
- Используются нестандартные кодеки, которые плохо поддерживаются — решение этой проблемы описано в пункте об эхо и низком качестве звука.
- Проблема с SIP-клиентом — попробуйте установить другой.
Воспользуйтесь инструкциями по настройке различных SIP-клиентов из нашей базы знаний.
SIP-трубка, SIP-телефон, SIP-шлюз
- Может быть проблема с интернетом или повреждением сетевого кабеля. Временно подключите другой и проверьте, не решится ли проблема.
- Используются нестандартные кодеки — об этом мы уже писали выше.
- Если устройство новое и проблема появилась сразу, обновите прошивку, скачав ее с сайта производителя по инструкции к вашему устройству. Часто бывает, что производитель делает много устройств с проблемами в ПО и затем их исправляет, обновив прошивку. Так как большинство подобных устройств не поддерживают автообновление, прошивку нужно обновлять вручную.
Мы постарались максимально просто описать причины проблем SIP-телефонии и их решения. Если вас более детально интересует их техническая подоплека, рекомендуем статью «Почему возникают проблемы с качеством IP-телефонии». Также можете оставить комментарии с вопросами к этой статье или написать нам в чат.
show
sip
service
Use this command to display the status of SIP call service on a SIP gateway.
The following sample output shows that SIP call service is enabled:
Example:
Router# show sip service
SIP Service is up
The following sample output shows that SIP call service was shut down with the shutdown command:
Example:
Router# show sip service
SIP service is shut globally
under 'voice service voip'
The following sample output shows that SIP call service was shut down with the call service stop command:
Example:
Router# show sip service
SIP service is shut
under 'voice service voip', 'sip' submode
The following sample output shows that SIP call service was shut down with the shutdown forced command:
Example:
Router# show sip service
SIP service is forced shut globally
under 'voice service voip'
The following sample output shows that SIP call service was shut down with the call service stop forced command:
Example:
Router# show sip service
SIP service is forced shut
under 'voice service voip', 'sip' submode
show
sip-ua
register
status
Use this command to display the status of E.164 numbers that a SIP gateway has registered with an external primary SIP registrar.
Example:
Router# show sip-ua register status
Line peer expires(sec) registered
4001 20001 596 no
4002 20002 596 no
5100 1 596 no
9998 2 596 no
show
sip-ua
statistics
Use this command to display response, traffic, and retry SIP statistics, including whether call redirection is disabled.
The following sample shows that four registers were sent:
Example:
Router# show sip-ua statistics
SIP Response Statistics (Inbound/Outbound)
Informational:
Trying 0/0, Ringing 0/0,
Forwarded 0/0, Queued 0/0,
SessionProgress 0/0
Success:
OkInvite 0/0, OkBye 0/0,
OkCancel 0/0, OkOptions 0/0,
OkPrack 0/0, OkPreconditionMet 0/0,
OkSubscribe 0/0, OkNOTIFY 0/0,
OkInfo 0/0, 202Accepted 0/0
OkRegister 12/49
Redirection (Inbound only except for MovedTemp(Inbound/Outbound)) :
MultipleChoice 0, MovedPermanently 0,
MovedTemporarily 0/0, UseProxy 0,
AlternateService 0
Client Error:
BadRequest 0/0, Unauthorized 0/0,
PaymentRequired 0/0, Forbidden 0/0,
NotFound 0/0, MethodNotAllowed 0/0,
NotAcceptable 0/0, ProxyAuthReqd 0/0,
ReqTimeout 0/0, Conflict 0/0, Gone 0/0,
ReqEntityTooLarge 0/0, ReqURITooLarge 0/0,
UnsupportedMediaType 0/0, BadExtension 0/0,
TempNotAvailable 0/0, CallLegNonExistent 0/0,
LoopDetected 0/0, TooManyHops 0/0,
AddrIncomplete 0/0, Ambiguous 0/0,
BusyHere 0/0, RequestCancel 0/0,
NotAcceptableMedia 0/0, BadEvent 0/0,
SETooSmall 0/0
Server Error:
InternalError 0/0, NotImplemented 0/0,
BadGateway 0/0, ServiceUnavail 0/0,
GatewayTimeout 0/0, BadSipVer 0/0,
PreCondFailure 0/0
Global Failure:
BusyEverywhere 0/0, Decline 0/0,
NotExistAnywhere 0/0, NotAcceptable 0/0
Miscellaneous counters:
RedirectRspMappedToClientErr 0
SIP Total Traffic Statistics (Inbound/Outbound)
Invite 0/0, Ack 0/0, Bye 0/0,
Cancel 0/0, Options 0/0,
Prack 0/0, Comet 0/0,
Subscribe 0/0, NOTIFY 0/0,
Refer 0/0, Info 0/0
Register 49/16
Retry Statistics
Invite 0, Bye 0, Cancel 0, Response 0,
Prack 0, Comet 0, Reliable1xx 0, NOTIFY 0
Register 4
SDP application statistics:
Parses: 0, Builds 0
Invalid token order: 0, Invalid param: 0
Not SDP desc: 0, No resource: 0
Last time SIP Statistics were cleared: <never>
The following sample output shows the RedirectResponseMappedToClientError status message. An incremented number indicates
that 3xx
responses are to be treated as 4xx
responses. When call redirection is enabled (default), the RedirectResponseMappedToClientError status message is not incremented.
Example:
Router# show sip-ua statistics
SIP Response Statistics (Inbound/Outbound)
Informational:
Trying 0/0, Ringing 0/0,
Forwarded 0/0, Queued 0/0,
SessionProgress 0/0
Success:
OkInvite 0/0, OkBye 0/0,
OkCancel 0/0, OkOptions 0/0,
OkPrack 0/0, OkPreconditionMet 0/0,
OKSubscribe 0/0, OkNotify 0/0,
202Accepted 0/0
Redirection (Inbound only):
MultipleChoice 0, MovedPermanently 0,
MovedTemporarily 0, UseProxy 0,
AlternateService 0
Client Error:
BadRequest 0/0, Unauthorized 0/0,
PaymentRequired 0/0, Forbidden 0/0,
NotFound 0/0, MethodNotAllowed 0/0,
NotAcceptable 0/0, ProxyAuthReqd 0/0,
ReqTimeout 0/0, Conflict 0/0, Gone 0/0,
ReqEntityTooLarge 0/0, ReqURITooLarge 0/0,
UnsupportedMediaType 0/0, BadExtension 0/0,
TempNotAvailable 0/0, CallLegNonExistent 0/0,
LoopDetected 0/0, TooManyHops 0/0,
AddrIncomplete 0/0, Ambiguous 0/0,
BusyHere 0/0, RequestCancel 0/0
NotAcceptableMedia 0/0, BadEvent 0/0
Server Error:
InternalError 0/0, NotImplemented 0/0,
BadGateway 0/0, ServiceUnavail 0/0,
GatewayTimeout 0/0, BadSipVer 0/0,
PreCondFailure 0/0
Global Failure:
BusyEverywhere 0/0, Decline 0/0,
NotExistAnywhere 0/0, NotAcceptable 0/0
Miscellaneous counters:
RedirectResponseMappedToClientError 1,
SIP Total Traffic Statistics (Inbound/Outbound)
Invite 0/0, Ack 0/0, Bye 0/0,
Cancel 0/0, Options 0/0,
Prack 0/0, Comet 0/0,
Subscribe 0/0, Notify 0/0,
Refer 0/0
Retry Statistics
Invite 0, Bye 0, Cancel 0, Response 0,
Prack 0, Comet 0, Reliable1xx 0, Notify 0
SDP application statistics:
Parses: 0, Builds 0
Invalid token order: 0, Invalid param: 0
Not SDP desc: 0, No resource: 0
show
sip-ua
status
Use this command to display status for the SIP user agent (UA), including whether call redirection is enabled or disabled.
Example:
Router# show sip-ua status
SIP User Agent Status
SIP User Agent for UDP : ENABLED
SIP User Agent for TCP : ENABLED
SIP User Agent bind status(signaling): DISABLED
SIP User Agent bind status(media): DISABLED
SIP max-forwards : 6
SIP DNS SRV version: 1 (rfc 2052)
Redirection (3xx) message handling: ENABLED
show
sip-ua
timers
Use this command to display the current settings for the SIP user-agent (UA) timers.
The following sample output shows the waiting time before a register request is sent—that is, the value that is set with
the timers register command:
Example:
Router# show sip-ua timers
SIP UA Timer Values (millisecs)
trying 500, expires 180000, connect 500, disconnect 500
comet 500, prack 500, rel1xx 500, notify 500
refer 500, register 500
SIP ошибки и их значение
SIP/2.0 400 Bad Request — ошибка в сигнализации, скорее всего что-то с настройками оборудования
SIP/2.0 401 Unauthorized — нормальный ответ сервера о том, что пользователь еще неавторизировался, обычно после этого на абонентское оборудование отправляет на сервер логин и пароль
SIP/2.0 401 Expired Authorization — время регистрации истекло
SIP/2.0 403 No Such User — нет такого пользователя, ошибка в номере, логине или пароле
SIP/2.0 403 User Disabled — пользователь отключен
SIP/2.0 403 Wrong Guess — ошибка в пароле
SIP/2.0 403 Forbidden — абонент не зарегистрирован
SIP/2.0 403 Empty Route Set — нет ни одного шлюза в роутинге
SIP/2.0 403 Caller Not Registered — нет такого пользователя
SIP/2.0 403 Out of Look-Ahead Retries — перебор узлов закончен
SIP/2.0 403 Invalid Phone Number — нет такого направления
SIP/2.0 404 Not found — вызываемый абонент не найден, нет такого SIP-номера
SIP/2.0 404 Undefined Reason — неопределенное направление
SIP/2.0 404 Unknown user account — логин и пароль не найдены
SIP/2.0 405 Method Not Allowed — метод не поддерживается, может возникать если пользователь пытается отправлять голосовую почту и т.п.
SIP/2.0 406 No codecs match — неправильная конфигурация кодеков
SIP/2.0 406 Not Acceptable
SIP/2.0 407 Proxy Authentication Required — что-то с регистрацией
SIP/2.0 408 Request Timeout — превышение ожижание ответа на запрос
SIP/2.0 408 Login timed out — за отведенное время не получен ответ от сервера на запрос авторизации
SIP/2.0 410 No Route — вариант SIP/2.0 403 Empty Route Set
SIP/2.0 415 No Media — несоответствие кодеков
SIP/2.0 480 Invalid Phone Number — неправильный номер телефона
SIP/2.0 480 Destination Not Found In Client Plan — направления не существует
SIP/2.0 480 Codec Mismatch — несоответствие кодеков
SIP/2.0 480 Empty Route Set — что-то с маршрутизацией
SIP/2.0 480 No money left — недостаточно денег на счете
SIP/2.0 480 Temporarily Unavailable — временно недоступное направление — попробуйте позвонить позже
SIP/2.0 481 Call Leg/Transaction Does Not Exist — действие не выполнено, нормальный ответ при поступлении дублирующего пакета
SIP/2.0 487 Request Terminated — запрос отменен, обычно приходит при отмене вызова
SIP/2.0 486 Busy Here — абонент занят
SIP/2.0 488 Codec Mismatch — нет шлюзов с поддержкой заказанного кодека
SIP/2.0 488 Private IP Address — адрес RTP media из сетей RFC1918
SIP/2.0 499 Codec Mismatch — отсутствует кодек
SIP/2.0 500 Internal Server Error — внутренняя ошибка сервера
SIP/2.0 500 DB Timeout — нет ответа от базы данных
SIP/2.0 500 Database Error — то же самое, но в другой момент
SIP/2.0 500 Wrong DB Response — неправильный ответ базы данных
SIP/2.0 500 Undefined Reason — неопределенная причина
SIP/2.0 500 account has been moved to a remote system — аккаунт перенесен в удаленную систему (дословно)
SIP/2.0 5хх — проблемы с SoftSwitch-ом
SIP/2.0 603 Decline — отказ в обслуживании звонка
Читайте другие страницы сайта.
Introduction[]
This article displays SIP error codes and a definition of such codes
Categories of SIP messages[]
- 1xx is ‘Informational’
- 2xx is ‘Success’
- 3xx is a ‘Redirection’
- 4xx is a ‘Client Error’
- 5xx is a ‘Server Error’
- 6xx is a ‘Global Failure’
1xx—Provisional Responses[]
- As mentioned earlier, a 1xx SIP response code can be sent at anytime while a connection is being established. Some of the regularly received codes are
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 Trying | This response indicates that the request has been received by the next-hop server and that some unspecified action is being taken on behalf of this call (for example, a database is being consulted). This response, like all other provisional responses, stops retransmissions of an INVITE by a UAC. The 100 (Trying) response is different from other provisional responses, in that it is never forwarded upstream by a stateful proxy. | ||
| 180 Ringing | Destination user agent received INVITE, and is alerting user of call. | ||
| 181 Call is being forwarded | Servers can optionally send this response to indicate a call is being forwarded. | ||
| 182 QUeued | The called party is temporarily unavailable, but the server has decided to queue the call rather than reject it. When the callee becomes available, it will return the appropriate final status response. The reason phrase MAY give further details about the status of the call, for example, «5 calls queued; expected waiting time is 15 minutes». The server MAY issue several 182 (Queued) responses to update the caller about the status of the queued call. | ||
| 183 Session Progress | The 183 (Session Progress) response is used to convey information about the progress of the call that is not otherwise classified. The Reason-Phrase, header fields, or message body MAY be used to convey more details about the call progress. | ||
| 199 Early Dialog Terminated | Can be used by User Agent Server to indicate to upstream SIP entities (including the User Agent Client (UAC)) that an early dialog has been terminated. |
2xx—Successful Responses[]
The 2xx response codes are used to indicate that a SIP request has been successfully processed. You’ll typically see the following versions:
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 OK | Indicates the request was successful. | ||
| 202 Accepted | Indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. | ||
| 204 No Notification | Indicates the request was successful, but the corresponding response will not be received. |
3xx—Redirection Responses[]
3xx responses give information about the user’s new location, or about alternative services that might be able to satisfy the call.
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 Multiple Choices | The address in the request resolved to several choices, each with its own specific location, and the user (or UA) can select a preferred communication end point and redirect its request to that location.
The response MAY include a message body containing a list of resource characteristics and location(s) from which the user or UA can choose the one most appropriate, if allowed by the Accept request header field. However, no MIME types have been defined for this message body. |
||
| 301 Moved Permanently | The user can no longer be found at the address in the Request-URI, and the requesting client SHOULD retry at the new address given by the Contact header field. The requester SHOULD update any local directories, address books, and user location caches with this new value and redirect future requests to the address(es) listed. | ||
| 302 Moved Temporarily | The requesting client SHOULD retry the request at the new address(es) given by the Contact header field. The Request-URI of the new request uses the value of the Contact header field in the response.
The duration of the validity of the Contact URI can be indicated through an Expires header field or an expires parameter in the Contact header field. Both proxies and UAs MAY cache this URI for the duration of the expiration time. If there is no explicit expiration time, the address is only valid once for recursing, and MUST NOT be cached for future transactions. |
||
| 305 Use Proxy | The requested resource MUST be accessed through the proxy given by the Contact field. The Contact field gives the URI of the proxy. The recipient is expected to repeat this single request via the proxy. 305 (Use Proxy) responses MUST only be generated by UASs. | ||
| 380 Alternative Service | The call was not successful, but alternative services are possible.
The alternative services are described in the message body of the response. Formats for such bodies are not defined here, and may be the subject of future standardization. |
4xx—Client Failure Responses[]
4xx responses are definite failure responses from a particular server. The client SHOULD NOT retry the same request without modification (for example, adding appropriate authorization). However, the same request to a different server might be successful.
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | The request could not be understood due to malformed syntax. The Reason-Phrase SHOULD identify the syntax problem in more detail, for example, «Missing Call-ID header field». | ||
| 401 Unauthorized | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by UASs and registrars. | ||
| 402 Payment Required | Reserved for future use. | ||
| 403 Forbidden | The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Sometimes (but not always) this means the call has been rejected by the receiver. | ||
| 404 Not Found | The server has definitive information that the user does not exist at the domain specified in the Request-URI. This status is also returned if the domain in the Request-URI does not match any of the domains handled by the recipient of the request. | ||
| 405 Method Not Allowed | The method specified in the Request-Line is understood, but not allowed for the address identified by the Request-URI. | ||
| 406 Not Acceptable | The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities that have content characteristics but not acceptable according to the Accept header field sent in the request. | ||
| 407 Proxy Authentication Required | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by proxys. | ||
| 408 Request Timeout | Couldn’t find the user in time. The server could not produce a response within a suitable amount of time, for example, if it could not determine the location of the user in time. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time. | ||
| 409 Conflict | User already registered. | ||
| 410 Gone | The user existed once, but is not available here any more. | ||
| 411 Length Required | The server will not accept the request without a valid Content-Length. | ||
| 412 Conditional Request Failed | The given precondition has not been met. | ||
| 413 Request Entity Too Large | The server is refusing to process a request because the request entity-body is larger than the server is willing or able to process. The server MAY close the connection to prevent the client from continuing the request.
If the condition is temporary, the server SHOULD include a Retry-After header field to indicate that it is temporary and after what time the client MAY try again. |
||
| 414 Request-URI Too Long | The server is refusing to service the request because the Request-URI is longer than the server is willing to interpret. | ||
| 415 Unsupported Media Type | The server is refusing to service the request because the message body of the request is in a format not supported by the server for the requested method. The server MUST return a list of acceptable formats using the Accept, Accept-Encoding, or Accept-Language header field, depending on the specific problem with the content. | ||
| 416 Unsupported URI Scheme | The server cannot process the request because the scheme of the URI in the Request-URI is unknown to the server. | ||
| 417 Unknown Resource-Priority | There was a resource-priority option tag, but no Resource-Priority header. | ||
| 420 Bad Extension | The server did not understand the protocol extension specified in a Proxy-Require or Require header field. The server MUST include a list of the unsupported extensions in an Unsupported header field in the response. | ||
| 421 Extension Required | The UAS needs a particular extension to process the request, but this extension is not listed in a Supported header field in the request. Responses with this status code MUST contain a Require header field listing the required extensions.
A UAS SHOULD NOT use this response unless it truly cannot provide any useful service to the client. Instead, if a desirable extension is not listed in the Supported header field, servers SHOULD process the request using baseline SIP capabilities and any extensions supported by the client. |
||
| 422 Session Interval Too Small | The received request contains a Session-Expires header field with a duration below the minimum timer. | ||
| 423 Interval Too Brief | The server is rejecting the request because the expiration time of the resource refreshed by the request is too short. This response can be used by a registrar to reject a registration whose Contact header field expiration time was too small. | ||
| 424 Bad Location Information | The request’s location content was malformed or otherwise unsatisfactory. | ||
| 428 Use Identity Header | The server policy requires an Identity header, and one has not been provided. | ||
| 429 Provide Referrer Identity | The server did not receive a valid Referred-By token on the request.
A specific flow to a user agent has failed, although other flows may succeed. This response is intended for use between proxy devices, and should not be seen by an endpoint (and if it is seen by one, should be treated as a 400 Bad Request response). |
||
| 433 Anonymity Disallowed | The request has been rejected because it was anonymous. | ||
| 436 Bad Identity-Info | The request has an Identity-Info header, and the URI scheme in that header cannot be dereferenced. | ||
| 437 Unsupported Certificate | The server was unable to validate a certificate for the domain that signed the request. | ||
| 438 Invalid Identity Header | The server obtained a valid certificate that the request claimed was used to sign the request, but was unable to verify that signature. | ||
| 439 First Hop Lacks Outbound Support | The first outbound proxy the user is attempting to register through does not support the «outbound» feature of RFC 5626, although the registrar does. | ||
| 440 Max-Breadth Exceeded | If a SIP proxy determines a response context has insufficient Incoming Max-Breadth to carry out a desired parallel fork, and the proxy is unwilling/unable to compensate by forking serially or sending a redirect, that proxy MUST return a 440 response. A client receiving a 440 response can infer that its request did not reach all possible destinations. | ||
| 469 Bad Info Package | If a SIP UA receives an INFO request associated with an Info Package that the UA has not indicated willingness to receive, the UA MUST send a 469 response, which contains a Recv-Info header field with Info Packages for which the UA is willing to receive INFO requests. | ||
| 470 Consent Needed | The source of the request did not have the permission of the recipient to make such a request. | ||
| 480 Temporarily Unavailable | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully but the callee is currently unavailable (for example, is not logged in, logged in but in a state that precludes communication with the callee, or has activated the «do not disturb» feature). The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. The user could also be available elsewhere (unbeknownst to this server). The reason phrase SHOULD indicate a more precise cause as to why the callee is unavailable. This value SHOULD be settable by the UA. Status 486 (Busy Here) MAY be used to more precisely indicate a particular reason for the call failure.
This status is also returned by a redirect or proxy server that recognizes the user identified by the Request-URI, but does not currently have a valid forwarding location for that user. |
||
| 481 Call/Transaction Does Not Exist | Server received a request that does not match any dialog or transaction. | ||
| 482 Loop Detected | Server has detected a loop. | ||
| 483 Too Many Hops | Max-Forwards header has reached the value ‘0’. | ||
| 484 Address Incomplete | The server received a request with a Request-URI that was incomplete. Additional information SHOULD be provided in the reason phrase.
This status code allows overlapped dialing. With overlapped dialing, the client does not know the length of the dialing string. It sends strings of increasing lengths, prompting the user for more input, until it no longer receives a 484 (Address Incomplete) status response. |
||
| 485 Ambiguous | The Request-URI was ambiguous. The response MAY contain a listing of possible unambiguous addresses in Contact header fields. Revealing alternatives can infringe on privacy of the user or the organization. It MUST be possible to configure a server to respond with status 404 (Not Found) or to suppress the listing of possible choices for ambiguous Request-URIs.
Some email and voice mail systems provide this functionality. A status code separate from 3xx is used since the semantics are different: for 300, it is assumed that the same person or service will be reached by the choices provided. While an automated choice or sequential search makes sense for a 3xx response, user intervention is required for a 485 (Ambiguous) response. |
||
| 486 Busy Here | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully, but the callee is currently not willing or able to take additional calls at this end system. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. The user could also be available elsewhere, such as through a voice mail service. Status 600 (Busy Everywhere) SHOULD be used if the client knows that no other end system will be able to accept this call. | ||
| 487 Request Terminated | The request was terminated by a BYE or CANCEL request. This response is never returned for a CANCEL request itself. | ||
| 488 Not Acceptable Here | The response has the same meaning as 606 (Not Acceptable), but only applies to the specific resource addressed by the Request-URI and the request may succeed elsewhere.
A message body containing a description of media capabilities MAY be present in the response, which is formatted according to the Accept header field in the INVITE (or application/sdp if not present), the same as a message body in a 200 (OK) response to an OPTIONS request. |
||
| 489 Bad Event | The server did not understand an event package specified in an Event header field. | ||
| 491 Request Pending | Server has some pending request from the same dialog. | ||
| 493 Undecipherable | The request was received by a UAS that contained an encrypted MIME body for which the recipient does not possess or will not provide an appropriate decryption key. This response MAY have a single body containing an appropriate public key that should be used to encrypt MIME bodies sent to this UA. | ||
| 494 Security Agreement Required | The server has received a request that requires a negotiated security mechanism, and the response contains a list of suitable security mechanisms for the requester to choose between, or a digest authentication challenge. |
5xx—Server Failure Responses[]
5xx responses relate to server error issues and are mostly generated by the likes of proxy servers, location servers, and redirect servers. You’ll be familiar with some of these: — 500 Server Internal Error — 501 Not Implemented — 502 Bad Gateway — 503 Service Unavailable — 504 Server Time-Out
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Server Internal Error | The server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. The client MAY display the specific error condition and MAY retry the request after several seconds.
If the condition is temporary, the server MAY indicate when the client may retry the request using the Retry-After header field. |
||
| 501 Not Implemented | The server does not support the functionality required to fulfill the request. This is the appropriate response when a UAS does not recognize the request method and is not capable of supporting it for any user. (Proxies forward all requests regardless of method.)
Note that a 405 (Method Not Allowed) is sent when the server recognizes the request method, but that method is not allowed or supported. |
||
| 502 Bad Gateway | The server is acting as a gateway or proxy, and received an invalid response from a downstream server while attempting to fulfill the request. | ||
| 503 Service Unavailable | The server is temporarily unable to process the request due to a temporary overloading or maintenance of the server. The server MAY indicate when the client should retry the request in a Retry-After header field. If no Retry-After is given, the client MUST act as if it had received a 500 (Server Internal Error) response.
A client (proxy or UAC) receiving a 503 (Service Unavailable) SHOULD attempt to forward the request to an alternate server. It SHOULD NOT forward any other requests to that server for the duration specified in the Retry-After header field, if present. |
||
| 504 Server Time-out | The server did not receive a timely response from an external server it accessed in attempting to process the request. 408 (Request Timeout) should be used instead if there was no response within the period specified in the Expires header field from the upstream server. | ||
| 505 Version Not Supported | The server does not support, or refuses to support, the SIP protocol version that was used in the request. The server is indicating that it is unable or unwilling to complete the request using the same major version as the client, other than with this error message. | ||
| 513 Message Too Large | The server was unable to process the request since the message length exceeded its capabilities. | ||
| 580 Precondition Failure | The server is unable or unwilling to meet some constraints specified in the offer. |
6xx—Global Failure Responses[]
Finally, the 6xx response codes relate to Global Error issues. They include: — 600 Busy Everywhere — 603 Decline — 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere — 606 Not Acceptable
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 Busy Everywhere | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully but the callee is busy and does not wish to take the call at this time. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field.
If the callee does not wish to reveal the reason for declining the call, the callee uses status code 603 (Decline) instead. This status response is returned only if the client knows that no other end point (such as a voice mail system) will answer the request. Otherwise, 486 (Busy Here) should be returned. |
||
| 603 Decline | The callee’s machine was successfully contacted but the user explicitly does not wish to or cannot participate. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. This status response is returned only if the client knows that no other end point will answer the request. | ||
| 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere | The server has authoritative information that the requested user does not exist anywhere. | ||
| 606 Not Acceptable | The user’s agent was contacted successfully but some aspects of the session description such as the requested media, bandwidth, or addressing style were not acceptable.
A 606 (Not Acceptable) response means that the user wishes to communicate, but cannot adequately support the session described. The 606 (Not Acceptable) response MAY contain a list of reasons in a Warning header field describing why the session described cannot be supported. |
||
| 607 Unwanted | The called party did not want this call from the calling party. Future attempts from the calling party are likely to be similarly rejected. |
Introduction[]
This article displays SIP error codes and a definition of such codes
Categories of SIP messages[]
- 1xx is ‘Informational’
- 2xx is ‘Success’
- 3xx is a ‘Redirection’
- 4xx is a ‘Client Error’
- 5xx is a ‘Server Error’
- 6xx is a ‘Global Failure’
1xx—Provisional Responses[]
- As mentioned earlier, a 1xx SIP response code can be sent at anytime while a connection is being established. Some of the regularly received codes are
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 Trying | This response indicates that the request has been received by the next-hop server and that some unspecified action is being taken on behalf of this call (for example, a database is being consulted). This response, like all other provisional responses, stops retransmissions of an INVITE by a UAC. The 100 (Trying) response is different from other provisional responses, in that it is never forwarded upstream by a stateful proxy. | ||
| 180 Ringing | Destination user agent received INVITE, and is alerting user of call. | ||
| 181 Call is being forwarded | Servers can optionally send this response to indicate a call is being forwarded. | ||
| 182 QUeued | The called party is temporarily unavailable, but the server has decided to queue the call rather than reject it. When the callee becomes available, it will return the appropriate final status response. The reason phrase MAY give further details about the status of the call, for example, «5 calls queued; expected waiting time is 15 minutes». The server MAY issue several 182 (Queued) responses to update the caller about the status of the queued call. | ||
| 183 Session Progress | The 183 (Session Progress) response is used to convey information about the progress of the call that is not otherwise classified. The Reason-Phrase, header fields, or message body MAY be used to convey more details about the call progress. | ||
| 199 Early Dialog Terminated | Can be used by User Agent Server to indicate to upstream SIP entities (including the User Agent Client (UAC)) that an early dialog has been terminated. |
2xx—Successful Responses[]
The 2xx response codes are used to indicate that a SIP request has been successfully processed. You’ll typically see the following versions:
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 OK | Indicates the request was successful. | ||
| 202 Accepted | Indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. | ||
| 204 No Notification | Indicates the request was successful, but the corresponding response will not be received. |
3xx—Redirection Responses[]
3xx responses give information about the user’s new location, or about alternative services that might be able to satisfy the call.
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 Multiple Choices | The address in the request resolved to several choices, each with its own specific location, and the user (or UA) can select a preferred communication end point and redirect its request to that location.
The response MAY include a message body containing a list of resource characteristics and location(s) from which the user or UA can choose the one most appropriate, if allowed by the Accept request header field. However, no MIME types have been defined for this message body. |
||
| 301 Moved Permanently | The user can no longer be found at the address in the Request-URI, and the requesting client SHOULD retry at the new address given by the Contact header field. The requester SHOULD update any local directories, address books, and user location caches with this new value and redirect future requests to the address(es) listed. | ||
| 302 Moved Temporarily | The requesting client SHOULD retry the request at the new address(es) given by the Contact header field. The Request-URI of the new request uses the value of the Contact header field in the response.
The duration of the validity of the Contact URI can be indicated through an Expires header field or an expires parameter in the Contact header field. Both proxies and UAs MAY cache this URI for the duration of the expiration time. If there is no explicit expiration time, the address is only valid once for recursing, and MUST NOT be cached for future transactions. |
||
| 305 Use Proxy | The requested resource MUST be accessed through the proxy given by the Contact field. The Contact field gives the URI of the proxy. The recipient is expected to repeat this single request via the proxy. 305 (Use Proxy) responses MUST only be generated by UASs. | ||
| 380 Alternative Service | The call was not successful, but alternative services are possible.
The alternative services are described in the message body of the response. Formats for such bodies are not defined here, and may be the subject of future standardization. |
4xx—Client Failure Responses[]
4xx responses are definite failure responses from a particular server. The client SHOULD NOT retry the same request without modification (for example, adding appropriate authorization). However, the same request to a different server might be successful.
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | The request could not be understood due to malformed syntax. The Reason-Phrase SHOULD identify the syntax problem in more detail, for example, «Missing Call-ID header field». | ||
| 401 Unauthorized | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by UASs and registrars. | ||
| 402 Payment Required | Reserved for future use. | ||
| 403 Forbidden | The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Sometimes (but not always) this means the call has been rejected by the receiver. | ||
| 404 Not Found | The server has definitive information that the user does not exist at the domain specified in the Request-URI. This status is also returned if the domain in the Request-URI does not match any of the domains handled by the recipient of the request. | ||
| 405 Method Not Allowed | The method specified in the Request-Line is understood, but not allowed for the address identified by the Request-URI. | ||
| 406 Not Acceptable | The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities that have content characteristics but not acceptable according to the Accept header field sent in the request. | ||
| 407 Proxy Authentication Required | The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by proxys. | ||
| 408 Request Timeout | Couldn’t find the user in time. The server could not produce a response within a suitable amount of time, for example, if it could not determine the location of the user in time. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time. | ||
| 409 Conflict | User already registered. | ||
| 410 Gone | The user existed once, but is not available here any more. | ||
| 411 Length Required | The server will not accept the request without a valid Content-Length. | ||
| 412 Conditional Request Failed | The given precondition has not been met. | ||
| 413 Request Entity Too Large | The server is refusing to process a request because the request entity-body is larger than the server is willing or able to process. The server MAY close the connection to prevent the client from continuing the request.
If the condition is temporary, the server SHOULD include a Retry-After header field to indicate that it is temporary and after what time the client MAY try again. |
||
| 414 Request-URI Too Long | The server is refusing to service the request because the Request-URI is longer than the server is willing to interpret. | ||
| 415 Unsupported Media Type | The server is refusing to service the request because the message body of the request is in a format not supported by the server for the requested method. The server MUST return a list of acceptable formats using the Accept, Accept-Encoding, or Accept-Language header field, depending on the specific problem with the content. | ||
| 416 Unsupported URI Scheme | The server cannot process the request because the scheme of the URI in the Request-URI is unknown to the server. | ||
| 417 Unknown Resource-Priority | There was a resource-priority option tag, but no Resource-Priority header. | ||
| 420 Bad Extension | The server did not understand the protocol extension specified in a Proxy-Require or Require header field. The server MUST include a list of the unsupported extensions in an Unsupported header field in the response. | ||
| 421 Extension Required | The UAS needs a particular extension to process the request, but this extension is not listed in a Supported header field in the request. Responses with this status code MUST contain a Require header field listing the required extensions.
A UAS SHOULD NOT use this response unless it truly cannot provide any useful service to the client. Instead, if a desirable extension is not listed in the Supported header field, servers SHOULD process the request using baseline SIP capabilities and any extensions supported by the client. |
||
| 422 Session Interval Too Small | The received request contains a Session-Expires header field with a duration below the minimum timer. | ||
| 423 Interval Too Brief | The server is rejecting the request because the expiration time of the resource refreshed by the request is too short. This response can be used by a registrar to reject a registration whose Contact header field expiration time was too small. | ||
| 424 Bad Location Information | The request’s location content was malformed or otherwise unsatisfactory. | ||
| 428 Use Identity Header | The server policy requires an Identity header, and one has not been provided. | ||
| 429 Provide Referrer Identity | The server did not receive a valid Referred-By token on the request.
A specific flow to a user agent has failed, although other flows may succeed. This response is intended for use between proxy devices, and should not be seen by an endpoint (and if it is seen by one, should be treated as a 400 Bad Request response). |
||
| 433 Anonymity Disallowed | The request has been rejected because it was anonymous. | ||
| 436 Bad Identity-Info | The request has an Identity-Info header, and the URI scheme in that header cannot be dereferenced. | ||
| 437 Unsupported Certificate | The server was unable to validate a certificate for the domain that signed the request. | ||
| 438 Invalid Identity Header | The server obtained a valid certificate that the request claimed was used to sign the request, but was unable to verify that signature. | ||
| 439 First Hop Lacks Outbound Support | The first outbound proxy the user is attempting to register through does not support the «outbound» feature of RFC 5626, although the registrar does. | ||
| 440 Max-Breadth Exceeded | If a SIP proxy determines a response context has insufficient Incoming Max-Breadth to carry out a desired parallel fork, and the proxy is unwilling/unable to compensate by forking serially or sending a redirect, that proxy MUST return a 440 response. A client receiving a 440 response can infer that its request did not reach all possible destinations. | ||
| 469 Bad Info Package | If a SIP UA receives an INFO request associated with an Info Package that the UA has not indicated willingness to receive, the UA MUST send a 469 response, which contains a Recv-Info header field with Info Packages for which the UA is willing to receive INFO requests. | ||
| 470 Consent Needed | The source of the request did not have the permission of the recipient to make such a request. | ||
| 480 Temporarily Unavailable | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully but the callee is currently unavailable (for example, is not logged in, logged in but in a state that precludes communication with the callee, or has activated the «do not disturb» feature). The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. The user could also be available elsewhere (unbeknownst to this server). The reason phrase SHOULD indicate a more precise cause as to why the callee is unavailable. This value SHOULD be settable by the UA. Status 486 (Busy Here) MAY be used to more precisely indicate a particular reason for the call failure.
This status is also returned by a redirect or proxy server that recognizes the user identified by the Request-URI, but does not currently have a valid forwarding location for that user. |
||
| 481 Call/Transaction Does Not Exist | Server received a request that does not match any dialog or transaction. | ||
| 482 Loop Detected | Server has detected a loop. | ||
| 483 Too Many Hops | Max-Forwards header has reached the value ‘0’. | ||
| 484 Address Incomplete | The server received a request with a Request-URI that was incomplete. Additional information SHOULD be provided in the reason phrase.
This status code allows overlapped dialing. With overlapped dialing, the client does not know the length of the dialing string. It sends strings of increasing lengths, prompting the user for more input, until it no longer receives a 484 (Address Incomplete) status response. |
||
| 485 Ambiguous | The Request-URI was ambiguous. The response MAY contain a listing of possible unambiguous addresses in Contact header fields. Revealing alternatives can infringe on privacy of the user or the organization. It MUST be possible to configure a server to respond with status 404 (Not Found) or to suppress the listing of possible choices for ambiguous Request-URIs.
Some email and voice mail systems provide this functionality. A status code separate from 3xx is used since the semantics are different: for 300, it is assumed that the same person or service will be reached by the choices provided. While an automated choice or sequential search makes sense for a 3xx response, user intervention is required for a 485 (Ambiguous) response. |
||
| 486 Busy Here | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully, but the callee is currently not willing or able to take additional calls at this end system. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. The user could also be available elsewhere, such as through a voice mail service. Status 600 (Busy Everywhere) SHOULD be used if the client knows that no other end system will be able to accept this call. | ||
| 487 Request Terminated | The request was terminated by a BYE or CANCEL request. This response is never returned for a CANCEL request itself. | ||
| 488 Not Acceptable Here | The response has the same meaning as 606 (Not Acceptable), but only applies to the specific resource addressed by the Request-URI and the request may succeed elsewhere.
A message body containing a description of media capabilities MAY be present in the response, which is formatted according to the Accept header field in the INVITE (or application/sdp if not present), the same as a message body in a 200 (OK) response to an OPTIONS request. |
||
| 489 Bad Event | The server did not understand an event package specified in an Event header field. | ||
| 491 Request Pending | Server has some pending request from the same dialog. | ||
| 493 Undecipherable | The request was received by a UAS that contained an encrypted MIME body for which the recipient does not possess or will not provide an appropriate decryption key. This response MAY have a single body containing an appropriate public key that should be used to encrypt MIME bodies sent to this UA. | ||
| 494 Security Agreement Required | The server has received a request that requires a negotiated security mechanism, and the response contains a list of suitable security mechanisms for the requester to choose between, or a digest authentication challenge. |
5xx—Server Failure Responses[]
5xx responses relate to server error issues and are mostly generated by the likes of proxy servers, location servers, and redirect servers. You’ll be familiar with some of these: — 500 Server Internal Error — 501 Not Implemented — 502 Bad Gateway — 503 Service Unavailable — 504 Server Time-Out
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Server Internal Error | The server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. The client MAY display the specific error condition and MAY retry the request after several seconds.
If the condition is temporary, the server MAY indicate when the client may retry the request using the Retry-After header field. |
||
| 501 Not Implemented | The server does not support the functionality required to fulfill the request. This is the appropriate response when a UAS does not recognize the request method and is not capable of supporting it for any user. (Proxies forward all requests regardless of method.)
Note that a 405 (Method Not Allowed) is sent when the server recognizes the request method, but that method is not allowed or supported. |
||
| 502 Bad Gateway | The server is acting as a gateway or proxy, and received an invalid response from a downstream server while attempting to fulfill the request. | ||
| 503 Service Unavailable | The server is temporarily unable to process the request due to a temporary overloading or maintenance of the server. The server MAY indicate when the client should retry the request in a Retry-After header field. If no Retry-After is given, the client MUST act as if it had received a 500 (Server Internal Error) response.
A client (proxy or UAC) receiving a 503 (Service Unavailable) SHOULD attempt to forward the request to an alternate server. It SHOULD NOT forward any other requests to that server for the duration specified in the Retry-After header field, if present. |
||
| 504 Server Time-out | The server did not receive a timely response from an external server it accessed in attempting to process the request. 408 (Request Timeout) should be used instead if there was no response within the period specified in the Expires header field from the upstream server. | ||
| 505 Version Not Supported | The server does not support, or refuses to support, the SIP protocol version that was used in the request. The server is indicating that it is unable or unwilling to complete the request using the same major version as the client, other than with this error message. | ||
| 513 Message Too Large | The server was unable to process the request since the message length exceeded its capabilities. | ||
| 580 Precondition Failure | The server is unable or unwilling to meet some constraints specified in the offer. |
6xx—Global Failure Responses[]
Finally, the 6xx response codes relate to Global Error issues. They include: — 600 Busy Everywhere — 603 Decline — 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere — 606 Not Acceptable
| Message Id | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 Busy Everywhere | The callee’s end system was contacted successfully but the callee is busy and does not wish to take the call at this time. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field.
If the callee does not wish to reveal the reason for declining the call, the callee uses status code 603 (Decline) instead. This status response is returned only if the client knows that no other end point (such as a voice mail system) will answer the request. Otherwise, 486 (Busy Here) should be returned. |
||
| 603 Decline | The callee’s machine was successfully contacted but the user explicitly does not wish to or cannot participate. The response MAY indicate a better time to call in the Retry-After header field. This status response is returned only if the client knows that no other end point will answer the request. | ||
| 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere | The server has authoritative information that the requested user does not exist anywhere. | ||
| 606 Not Acceptable | The user’s agent was contacted successfully but some aspects of the session description such as the requested media, bandwidth, or addressing style were not acceptable.
A 606 (Not Acceptable) response means that the user wishes to communicate, but cannot adequately support the session described. The 606 (Not Acceptable) response MAY contain a list of reasons in a Warning header field describing why the session described cannot be supported. |
||
| 607 Unwanted | The called party did not want this call from the calling party. Future attempts from the calling party are likely to be similarly rejected. |