I am running this on a Travis CI instance. I get the following result:
if [[ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "docker" ]]; then docker pull cdrx/pyinstaller-linux; fi
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from cdrx/pyinstaller-linux
Status: Downloaded newer image for cdrx/pyinstaller-linux:latest
if [[ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "docker" ]]; then docker run -v "$(pwd)/src:/src/" cdrx/pyinstaller-linux pyinstaller stacoan.py; fi
Collecting yattag (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading yattag-1.10.0.tar.gz
Building wheels for collected packages: yattag
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for yattag: started
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for yattag: finished with status 'done'
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/a2/23/18/c17e8653e0af1b67d72c02f2d48451d031b9ed889c210272de
Successfully built yattag
Installing collected packages: yattag
Successfully installed yattag-1.10.0
You are using pip version 8.1.1, however version 9.0.1 is available.
You should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command.
pyinstaller stacoan.py
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME]
[--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>]
[--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR]
[--hidden-import MODULENAME]
[--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH]
[--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES]
[--key KEY] [-d] [-s] [--noupx] [-c] [-w]
[-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns>]
[--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>] [-r RESOURCE]
[--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies]
[--win-no-prefer-redirects]
[--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER]
[--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--distpath DIR]
[--workpath WORKPATH] [-y] [--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a]
[--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]
scriptname [scriptname ...]
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptname
I’m really happy that I found your project because I am wasting the past days on finding a way to compile my application for windows on a Linux environment. Pywin32 broke my previous build construction 😢
(mhammond/pywin32#1172 (comment))
Содержание
- Build A Stand-Alone Executable Elasticsearch Application Using Python
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Building an executable Python script with PyInstaller
- Installing PyInstaller and building a Python application on Windows
- Install the PyInstaller package for Python 3 on Windows
- PyInstaller command-not-found error in Windows
- Windows doesn’t know the path to the PyInstaller executable file
- Add the path for the ‘pyinstaller.exe’ to your Windows environment variables
- Verify that the PyInstaller command for Python 3 is now working
- Build a Windows executable using the Pyinstaller package for Python
- Installing the PyInstaller Package on Ubuntu distros of Linux
- Change into the PyInstaller’s ‘dist’ directory
- Execute the ‘elastic_query’ file created by PyInstaller with a query
- Elasticsearch cluster response returned from the PyInstaller application’s API request
- Conclusion
- Just the Code
- Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
- Pyinstaller error the following arguments are required scriptname
- How to Create Python Executable File .exe from .py file in Windows 10, 8 and 7
- 1. How to install Python PYINSTALLER batteries-included Package or Module
- 2. How to Create Python Executable File .exe from .py file
- Pyinstaller не распознается как внутренняя или внешняя команда
Build A Stand-Alone Executable Elasticsearch Application Using Python
- Elasticsearch
- PyInstaller
- Python
Introduction
This article will explain how to build a stand-alone Elasticsearch query application using Python.
The original Python code used for the app can be found in this ObjectRocket article explaining how to query Elasticsearch documents in a terminal window.
Prerequisites
Building an executable Python script with PyInstaller
Installing PyInstaller and building a Python application on Windows
It’s recommended that you use or switch to Python 3 instead of Python 2.7 since Python 2 is now deprecated and scheduled to lose support by 2020.
Type cmd in the Windows Search bar, or type run and then type cmd in the modal window to open a new instance of Command Prompt to get started.
Install the PyInstaller package for Python 3 on Windows
Depending on your installations of Python you’ll need to use the pip3 or pip command to install PyInstaller for Python 3. Type python —version into a Command Prompt terminal. You should see a response that tells says Python 3.x.
If the response says you have version 2.7 installed, or if it raises an error, then try the following command instead:
If Python 3 used the python alias (without the 3 ), then use the pip command to install PyInstaller:
NOTE: Use the —user option if Windows raises a permissions error.
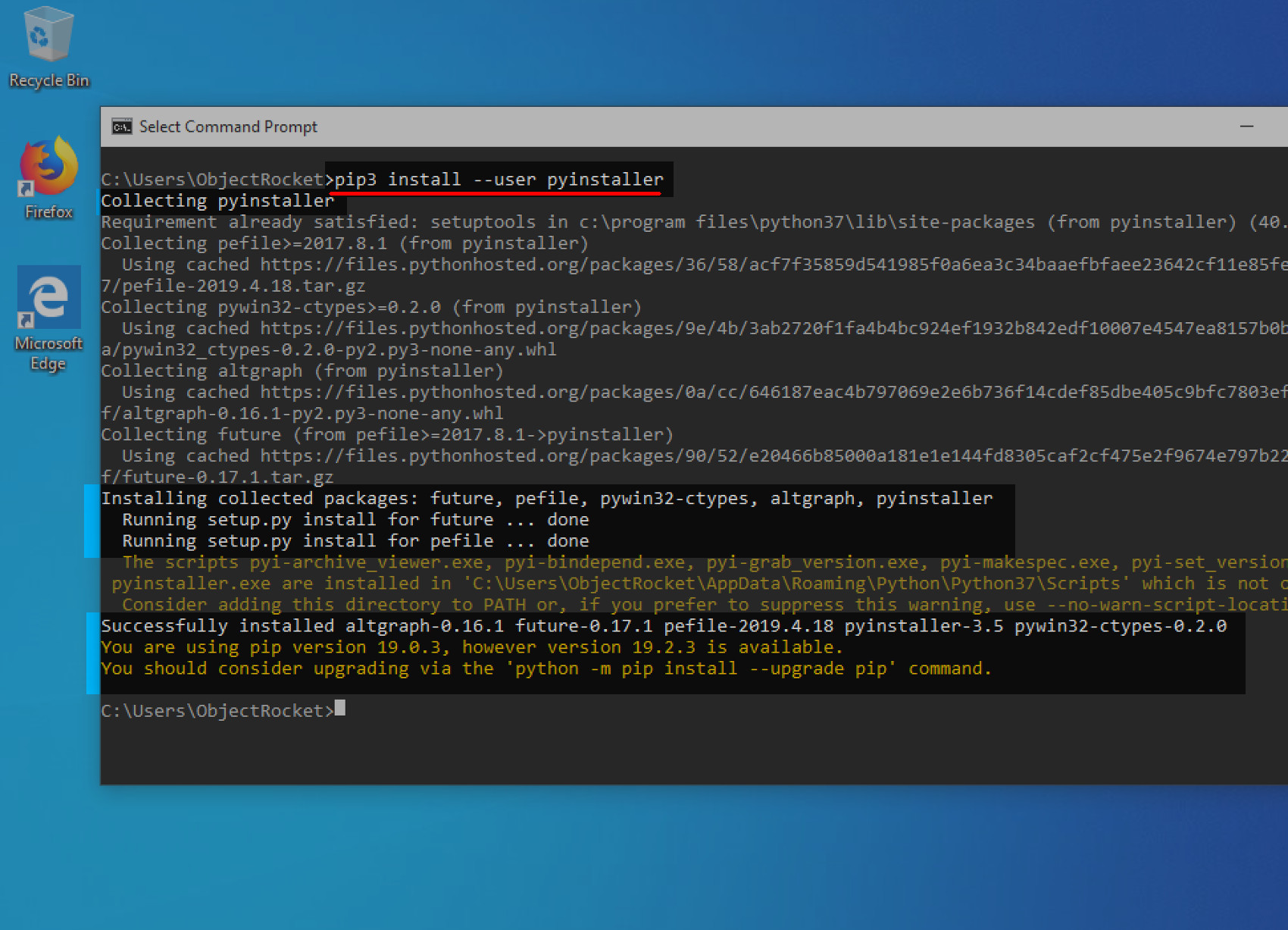
Otherwise use pip3 to installed the package:
Here’s the command to upgrade your current version of PyInstaller:
PyInstaller command-not-found error in Windows
Type python -m PyInstaller , pyinstaller , or PyInstaller into your Command Prompt window and press return. If none of these commands work, then it probably means that the pyinstaller.exe executable file is not set in your system’s environmental variables path.
Windows doesn’t know the path to the PyInstaller executable file
Use the echo %PATH in your command line to have it return a list of all the paths for your environmental variables.
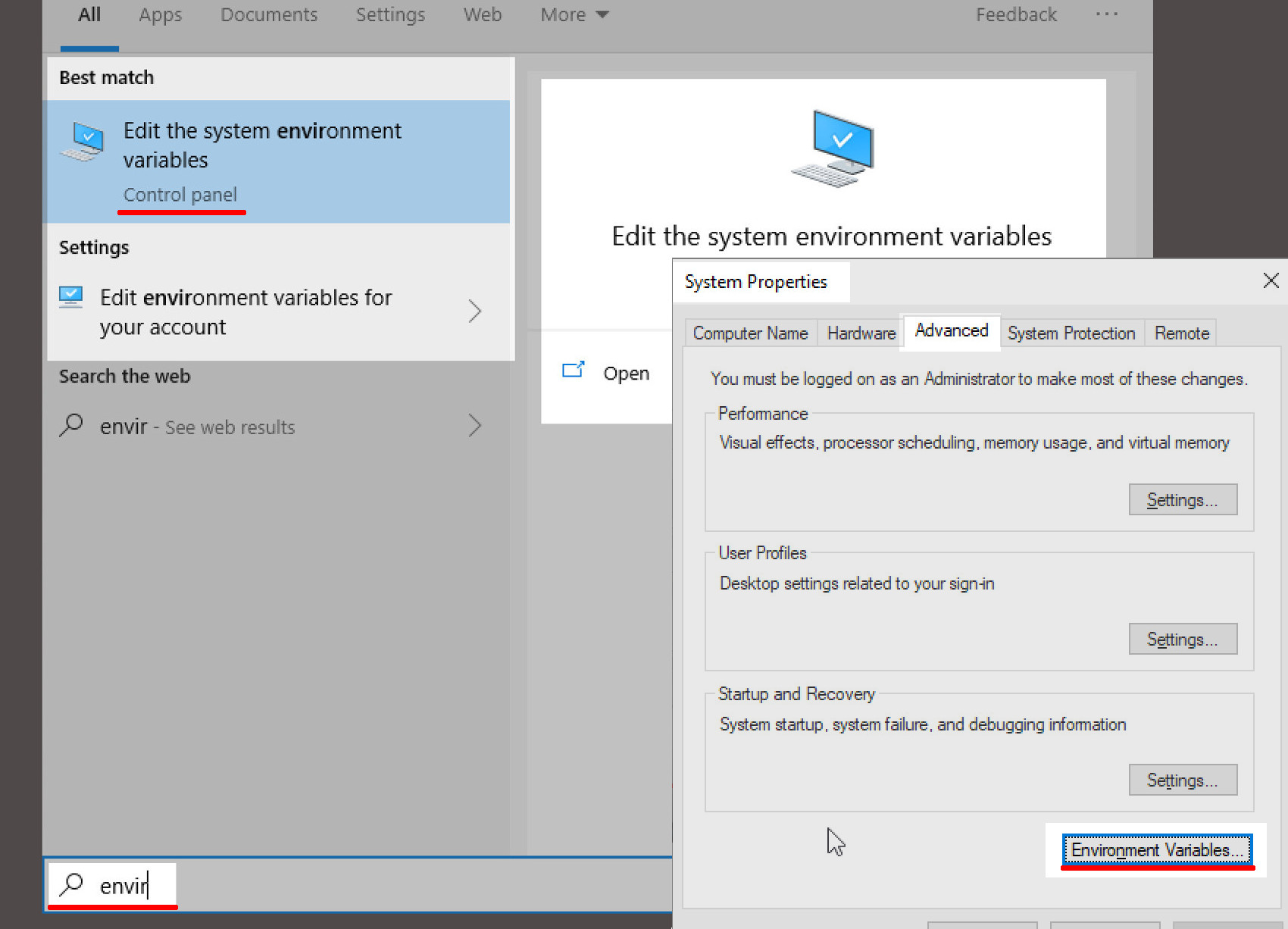
Type environment into the Windows Search bar, or just open the System Properties window in your Control Panel. Make sure to click on the Advanced tab in System Properties, and then click the Environment Variables button:
Add the path for the ‘pyinstaller.exe’ to your Windows environment variables
Open a instance of File Explorer and navigate to C:Program FilesPython37Scripts or C:UsersUSER_NAMEAppDataRoamingPythonPython37Scripts and look for the executable. Once you find the file make sure to get its full path.
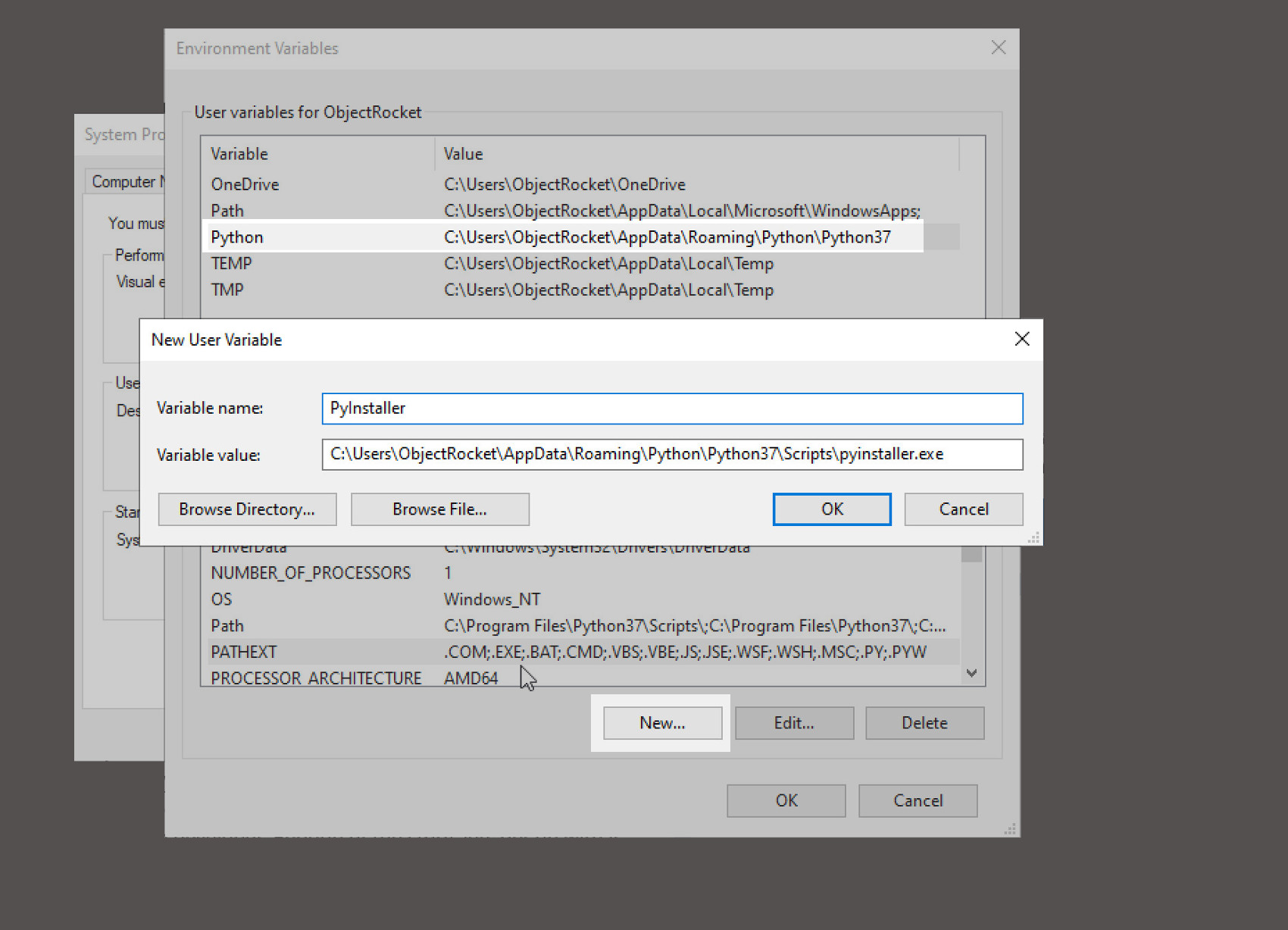
Click the New.. button in your Environmental Variables to add the system path for the pyinstaller.exe file. Make sure to type PyInstaller in the Variable name input field, and the path to the .exe file in the Variable value field.
Verify that the PyInstaller command for Python 3 is now working
Close all your instances of Command Prompt, and re-open it. Type PyInstaller or python PyInstaller into the window’s prompt, and it should now return a response from the executable.
Build a Windows executable using the Pyinstaller package for Python
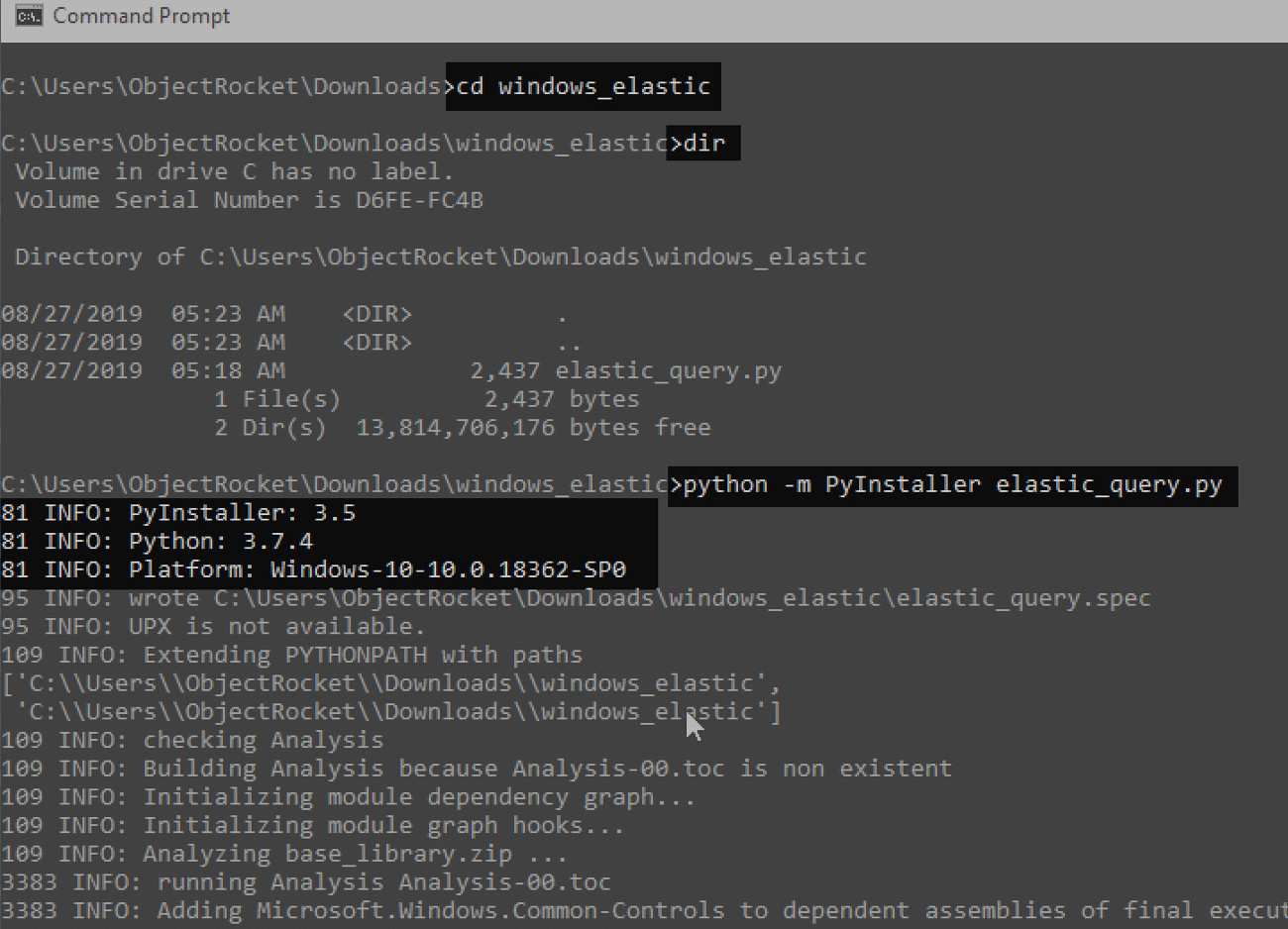
You should now be able to build an executable from a Python script using PyInstaller using the following command:
NOTE: Make sure to first change ( cd ) into the directory containing the Python script before running the PyInstaller command.
python -m pip install –upgrade –user pip python -m pip install –upgrade –user pyinstaller
pip -v install –user elasticsearch
python -m PyInstaller
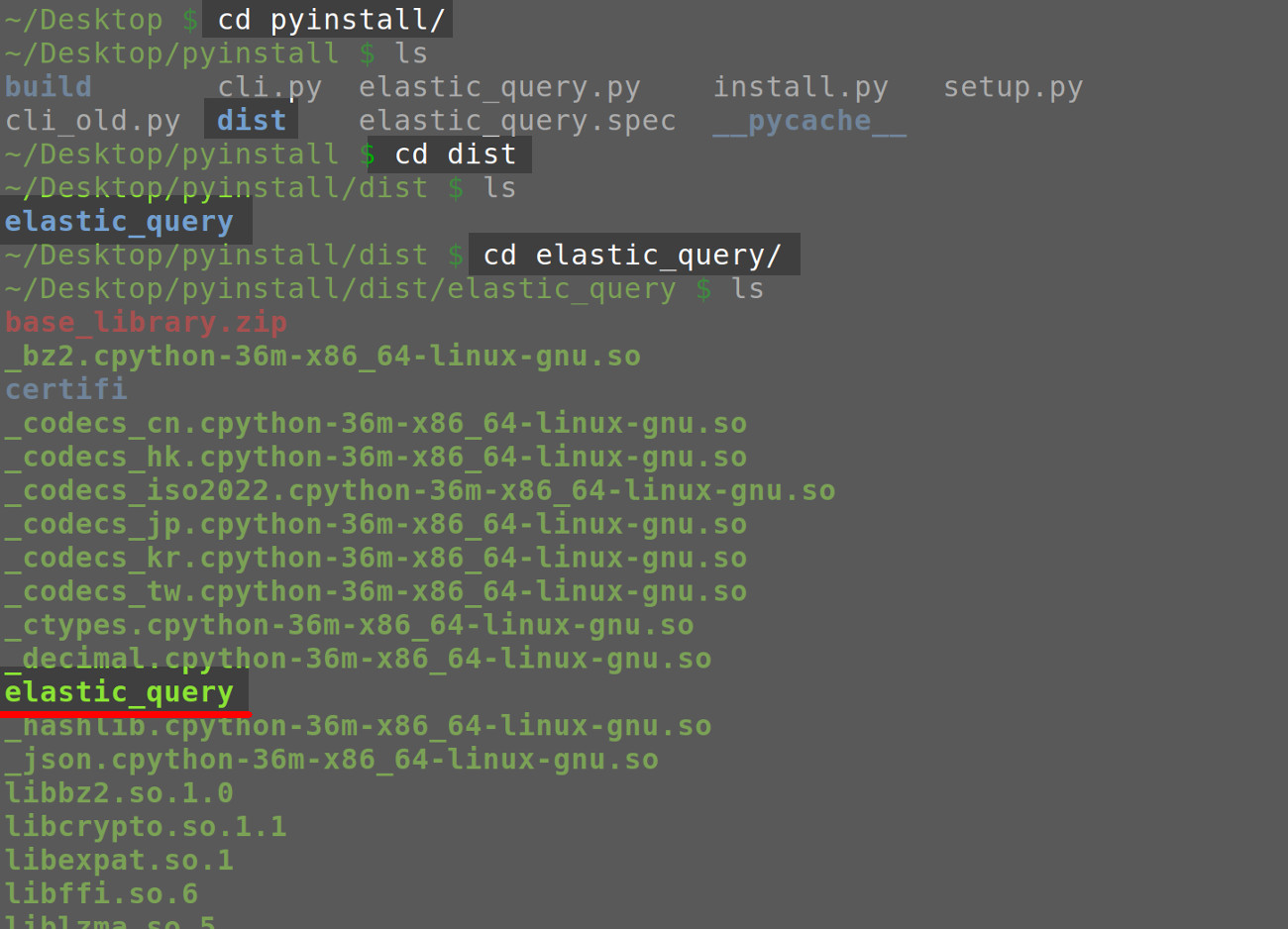
Installing the PyInstaller Package on Ubuntu distros of Linux
pip3 install pyinstaller
sudo apt-get install libc-bin sudo apt-get install binutils
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptname
pyinstaller cli.py python3 -O -m PyInstaller elastic_query.py
sudo rm -rf build/; sudo rm -rf dist/; sudo rm -rf pycache/; sudo rm elastic_query.spec
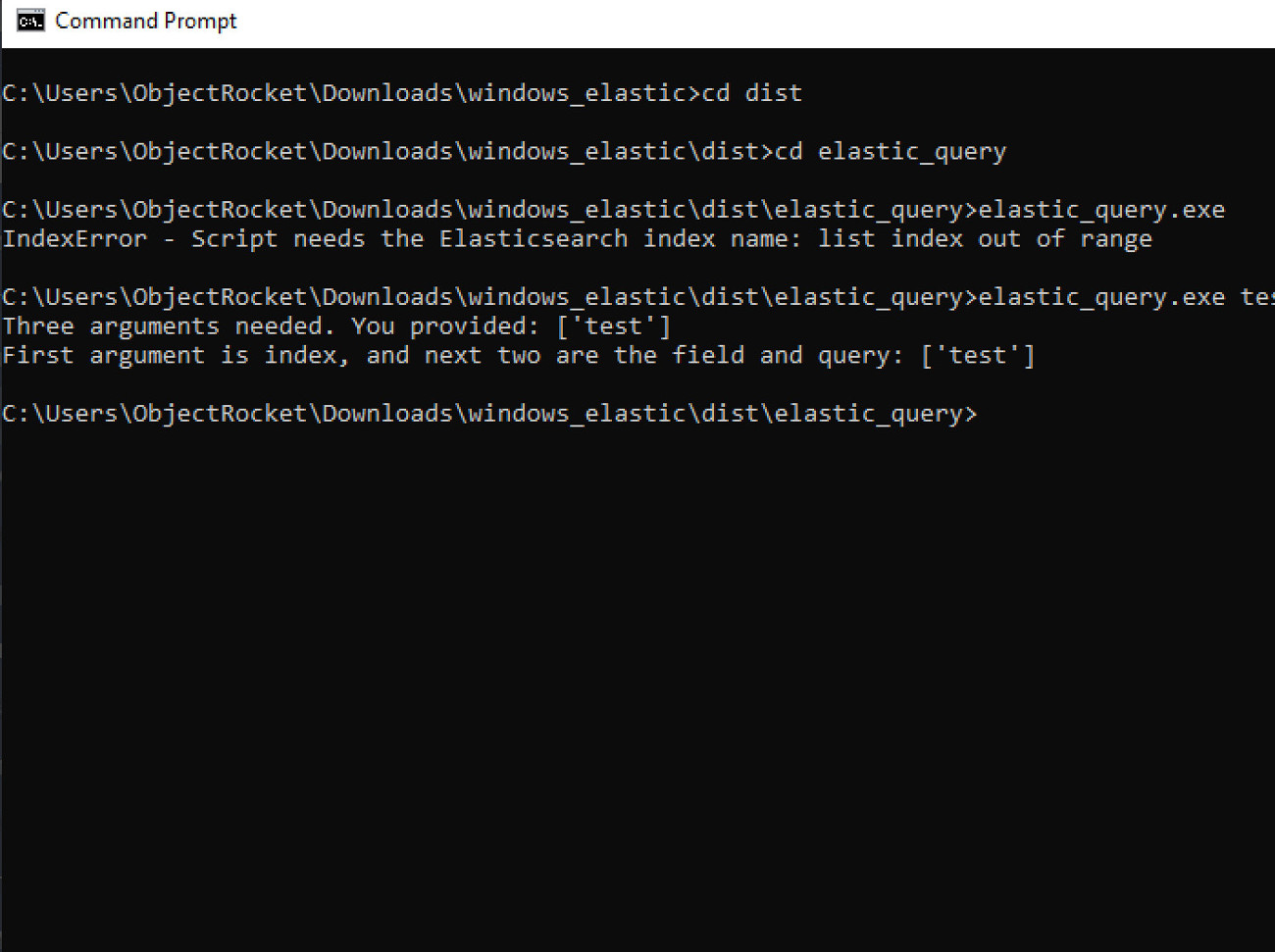
Change into the PyInstaller’s ‘dist’ directory
Execute the ‘elastic_query’ file created by PyInstaller with a query
pass a query to its parameters
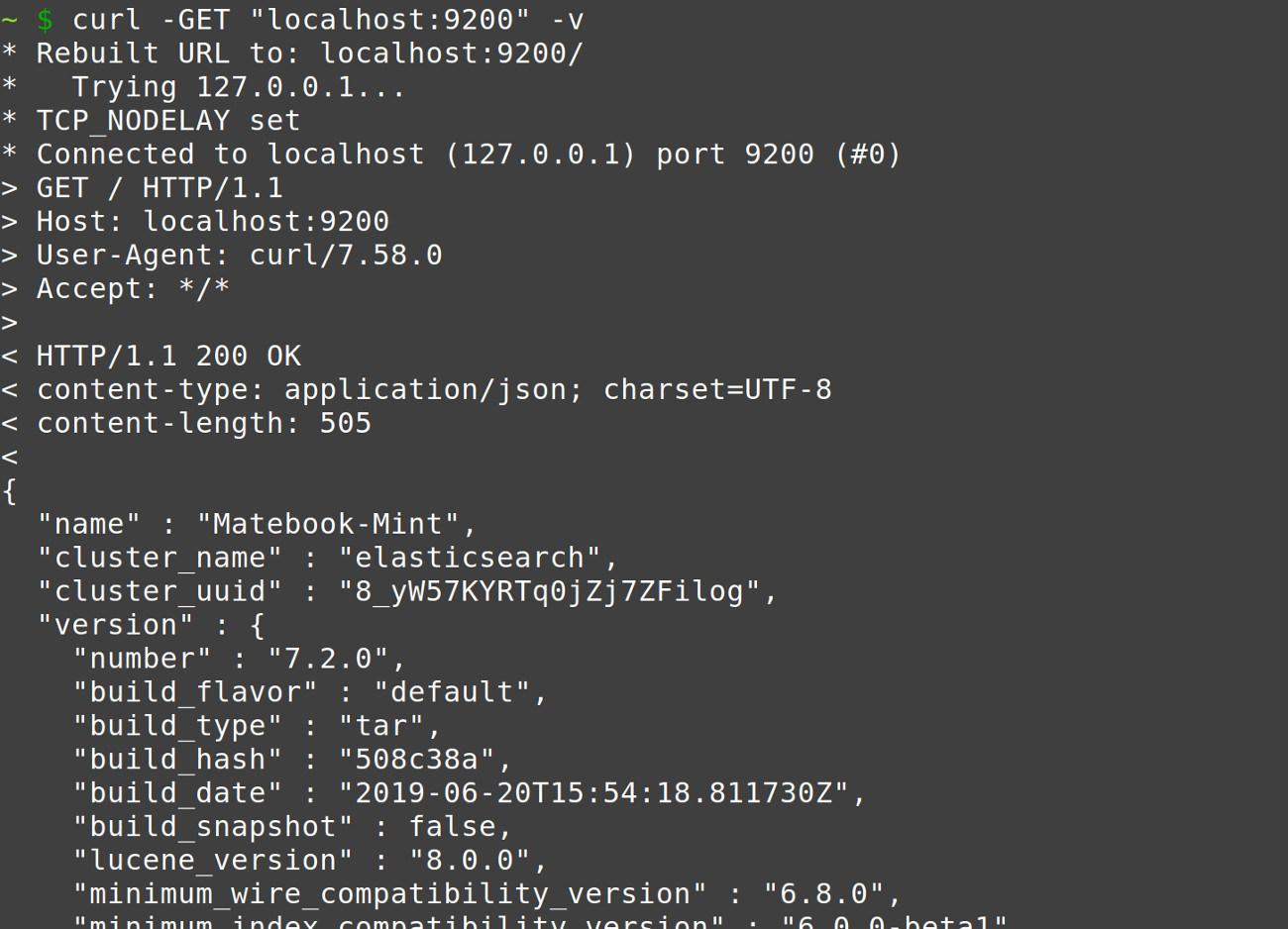
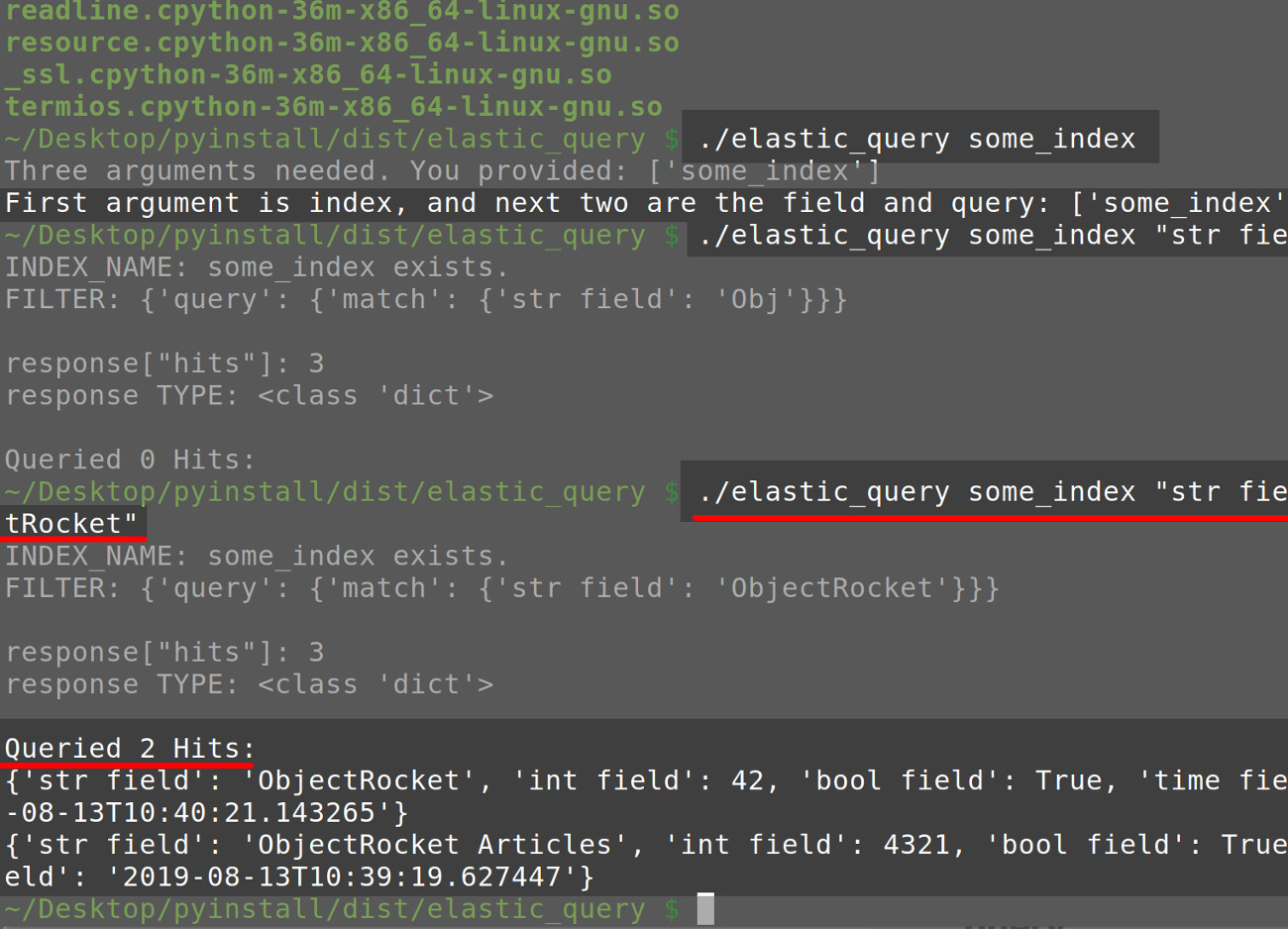
Elasticsearch cluster response returned from the PyInstaller application’s API request
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed this tutorial on how to build a stand-alone Elasticsearch query application with Python. You can grab any or all of the code we used below.
Just the Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# use sys for system arguments passed to script
import sys
# import the Elasticsearch client library
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# create a client instance of Elasticsearch
client = Elasticsearch ( «http://localhost:9200» )
# The script name is the first arg [0], but the second arg [1]
# can be used for the Elasticsearch index’s name
try :
INDEX_NAME = sys . argv [ 1 ]
except IndexError as err:
print ( «IndexError — Script needs the Elasticsearch index name:» , err )
sys . exit ( )
def make_query ( filter ) :
index_exists = client. indices . exists ( index = INDEX_NAME )
# check if the index exists
if index_exists == True :
print ( «INDEX_NAME:» , INDEX_NAME , «exists.» )
print ( «FILTER:» , filter , » n » )
# pass filter query to the client’s search() method
response = client. search ( index = INDEX_NAME , body = filter )
# print the query response`
print ( ‘response[«hits»]:’ , len ( response [ «hits» ] ) )
print ( ‘response TYPE:’ , type ( response ) )
# iterate the response hits
print ( » n Queried %d Hits:» % response [ ‘hits’ ] [ ‘total’ ] [ ‘value’ ] )
for hit in response [ ‘hits’ ] [ ‘hits’ ] :
print ( hit [ «_source» ] )
except Exception as err:
print ( «search(index) ERROR» , err )
response = < «error» : err >
# return an empty dict if index doesn’t exist
else :
response =
# declare variable for system arguments list
sys_args = sys . argv
# remove Python script name from args list
sys_args. pop ( 0 )
# quit the script if there are not exactly 3 arguments
if len ( sys_args ) != 3 :
print ( «Three arguments needed. You provided:» , sys_args )
print ( «First argument is index, and next two are the field and query:» , sys_args )
sys . exit ( )
else :
# get the field name and query value from sys args
field_name = sys_args [ 1 ]
value = sys_args [ 2 ]
# pass the field name and value args to filter dict
filter = <
‘query’ : <
‘match’ : <
field_name: value
>
>
>
# pass the filter dict to the make_query() function
resp = make_query ( filter )
# have interpreter call the main() func
if __name__ == «__main__» :
main ( )
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Источник
Pyinstaller error the following arguments are required scriptname
This question might have gotten lost in the other thread so here it is again.
I was able to get PyInstaller to work from the command line (thanks for the replies!), but that’s only for Python 2.7.
So now, I’m trying to get it working inside PyCharm, but so far, not quite.
I’ve imported both PyIntaller and PyInstaller Hooks.
My setup.py code looks like this:
setup.py», line 4
pyinstaller SearchBinaryFile.py
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Any suggestions on what I need to do I can build a standalone file using PyInstaller within PyCharm (so I can use 3.6 with f-strings, etc.)?
Command line seems like the way to go. Just making sure.
So, I have python3 installed, and I installed Pyinstaller within the IDE for Python3, but how would I run pyinstaller under python3 at the command line when the default python at the command line is 2.7?
Adding Pyinstaller to PyCharm can be done by adding it as an external tool:
- In Pycharm — File->Settings->Tools->External Tools
- Click on the ‘+’ sign to add a new tool (if it is the first tool you add, just fill the form, no need for the ‘+’)
- Fill the fields:
Name: Pyinstaller
Description: Generate a single executable
Program: pyinstaller.exe $FileName$ (Make sure that Pyinstaller is recognized in PyCharm Project. )
Arguments: —onefile
Working directory: $FileDir$dist
In PyCharm: Tools->External Tools->Pyinstaller
The exe file will appear on a dist subfolder of the .py file folder
(Jan-13-2019, 12:11 PM) DarkLight Wrote: —some errors reported — so I update:
Adding Pyinstaller to PyCharm can be done by adding it as an external tool:
- In Pycharm — File->Settings->Tools->External Tools
- Click on the ‘+’ sign to add a new tool (if it is the first tool you add, just fill the form, no need for the ‘+’)
- Fill the fields:
Name: Pyinstaller
Description: Generate a single executable
Program: C:Users[your_user_here]AppDataRoamingPythonScriptspyinstaller.exe (Make sure that Pyinstaller is recognized in PyCharm Project. )
Arguments: —onefile $FilePath$
Working directory: $FileDir$
In PyCharm: Tools->External Tools->Pyinstaller
The exe file will appear on a dist subfolder of the .py file folder
Источник
How to Create Python Executable File .exe from .py file in Windows 10, 8 and 7
End users like Executable files in Windows. So, a developer should be able to create a Python Executable File (.exe) from the source file (.py). Let us create an exe file from a python file using a predefined module » pyinstaller » using this last minute tutorial in Windows 10, 8 an 7.
1. In the first step, you should install a PYINSTALLER.
2. In the second step, you should use the PYINSTALLER to generate a .exe file from the .py file.
1. How to install Python PYINSTALLER batteries-included Package or Module
Batteries-Included is the phrase used to indicate that it is a Python Package or Module that can be imported into our project and use right away. To install the Python PYINSTALLER, you should use the command » pip install pyinstaller » in the DOS command prompt in administrator mode like below.
The above installation trace shows a warning message «Defaulting to user installation because normal site-packages is not writeable». It is because of not using the DOS prompt in admin mode. So, do not forget to open DOS prompt in administrator mode when installing any module. If the usage is limited to only compiling and running python programs, admin mode is not required.
To test the successful installation of PYINSTALLER, just type pyinstaller in the command prompt like below.
If the pyinstaller command does not work, it means that it has been installed in a directory outside «C:Program FilesPython39Scripts». The scripts should contain a file pyinstaller.exe.
This script path is added to the Windows Environment Variables at the time of installing Python software. This is the reason for the availability of python and pyinstaller commands globally from any directory.
Alternatively (the second way), you can install the PYINSTALLER package from the Python Shell window.
Let us move to using pyinstaller to generate an exe file from .py file.
2. How to Create Python Executable File .exe from .py file
Now, you know that it is the PYINSTALLER that converts the python source file in .py format to the .exe format. Let us use the pyinstaller command to create an executable file.
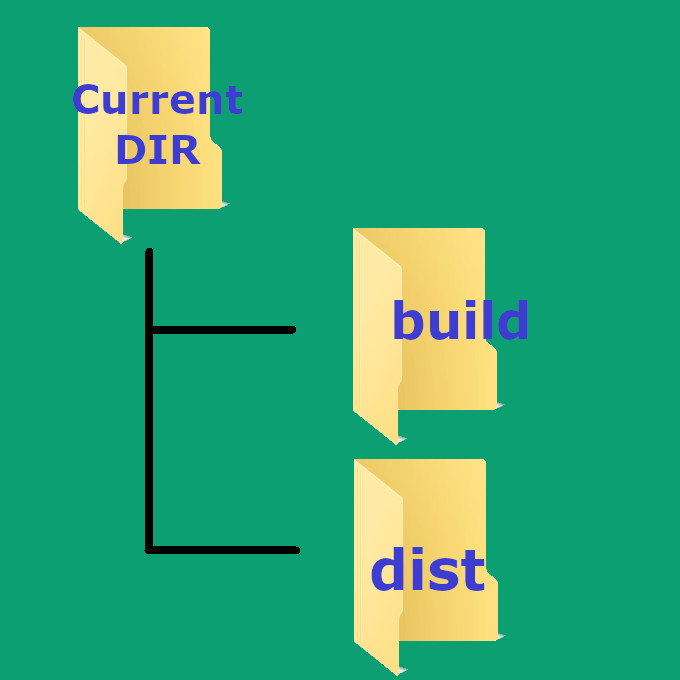
You can observe that «pyinstaller» command created two directories namely » dist » and » build » in the current path. In each folder, it creates a new folder with the same name as that of the Python-Program-Name. So, you should distribute folder with the name » dist/Python-Program-Name «. It contains an executable file with the same name as «Python-Program-Name«. This is the file to be opened by the end-user.
The end-user can either double click the exe file or type the name of the exe file in the command prompt to run the distributed python program.
The size of the python distributable folder will be in MegaBytes as it contains DLL, PYD, H, TCL and other files.
The PYINSTALLER is intelligent enough to pack all third-party libraries used by your Python program to create an executable file. This is how to convert python py files to .exe in Windows 10, 8 and 7.
Share this Last Minute Python tutorial with your friends and colleagues to encourage authors.
Источник
Pyinstaller не распознается как внутренняя или внешняя команда
Я пытаюсь использовать pyinstaller в cmd, но получаю сообщение об ошибке:
Когда я использую эту команду в папке Scripts в python, она работает:
Вы должны изменить переменную среды User PATH, чтобы включить файлы C:Users[USERNAME]AppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36-32Scripts .
Чтобы узнать, как добавить/изменить переменные среды PATH, см .
Для Python 3.7 вам нужно будет добавить папку Scripts из AppData/Roaming (%appdata%) в переменную PATH.
Я правильно настроил свой путь к скрипту, мне пришлось запустить python -m PyInstaller script.py , чтобы он заработал
Для каждого сценария я должен следовать этому шаблону, python -m [script name] [args]
версия питона 3.10.0
Скопируйте «pyinstaller.exe» в папку, в которой находится файл .py, который вы хотите преобразовать. Когда вы закончите, просто удалите «pyinstaller.exe». Удачи.
Это решение работает для Python 3.9
Прежде всего найдите местоположение pyinstaller.exe . Для этого вы можете попробовать этот трюк: (не нажимайте «y», просто посмотрите на приведенную выше копию пути, который вы ищете)
Прежде чем что-либо вводить, он покажет вам путь, где находится pyinstaller.exe. После этого скопируйте местоположение и запустите эту команду на терминале: (это пример)
Во-первых, вам нужно знать, где находится pyinstaller. В моем случае я побежал
Прежде чем он будет удален, он попросит вас подтвердить, хотите ли вы удалить следующий файл.
Большой! Теперь, сделав это, вы знаете свой путь к pyinstaller. Просто введите «Нет» и выйдите из процесса удаления, так как наша цель — просто получить путь. Теперь просто добавьте этот путь в переменную PATH.
Как изменить переменную PATH. Проверьте здесь
Скопируйте путь к папке со скриптом, C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36-32Scripts вставьте его в: environment varibales> system varibales> path и сохраните. Затем перезагрузите компьютер и попробуйте запустить pyinsatller откуда угодно.
Была точно такая же проблема:
- Найдите папку Python и перейдите к PythonPython38Libsite-packages
- Оттуда удалите модуль Pyinstaller и папку Pyinstaller dis.info.
- Переустановите Pyinstaller, используя pip install pyinstaller
Перейдите к пути «C:UsersUsernameanaconda3Scripts», скопируйте «pyinstaller.exe» и вставьте его в каталог, где вы хотите использовать pyinstaller, у меня это сработало.
- Откройте команду cmd по этому пути: ctrl+r, напишите «cmd» в поле
- Удалите pyinstaller: pip uninstall pyinstaller
- Установите его снова: pip install pyinstaller
- Используйте pyinstaller, написав pyinstaller
Я нашел, как мы должны исправить эту ошибку:
Мы должны ввести этот код в cmd pip install pyinstaller, если он снова не работает, вы должны пойти C:/user/pc name/Appdata (папка Appdata скрыта) / python, теперь вы должны скопировать папку скрипта C:/program files/python39 и скопировать пакет сайта в C:/program files/python39/lib
затем, если вы наберете pyinstaller в cmd, вы увидите, что он работает
Как ни странно, для меня изменение заглавных букв решило проблему. я набрал python -m [scriptname] [args] . Я [scriptname] набрал PyInstaller вместо, pyinstaller и это действительно сработало. Я пробовал оба способа несколько раз.
если вы ничего не можете сделать или у вас меньше времени, вы можете сделать виртуальную среду и установить туда pyinstaller, затем сгенерировать исполняемый файл
Введите в административной консоли: pip install pyinstaller
Если установка pyinstaller и создание переменных «путь» по-прежнему не работают, вы можете использовать этот обходной путь:
Найдите pyinstaller.exe в возможном каталоге python, таком как C:Users «UserName» AppDataLocalPackagesPythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.10_qbz5n2kfra8p0LocalCachelocal-packagesPython310Scripts
Скопируйте его в каталог, в котором у вас есть файл .py, который вы хотите скомпилировать как .exe.
Источник
Introduction
This article will explain how to build a stand-alone Elasticsearch query application using Python.
The original Python code used for the app can be found in this ObjectRocket article explaining how to query Elasticsearch documents in a terminal window.
Prerequisites
|
1 |
curl -GET «localhost:9200» -v |
Building an executable Python script with PyInstaller
Installing PyInstaller and building a Python application on Windows
It’s recommended that you use or switch to Python 3 instead of Python 2.7 since Python 2 is now deprecated and scheduled to lose support by 2020.
Type cmd in the Windows Search bar, or type run and then type cmd in the modal window to open a new instance of Command Prompt to get started.
Install the PyInstaller package for Python 3 on Windows
Depending on your installations of Python you’ll need to use the pip3 or pip command to install PyInstaller for Python 3. Type python --version into a Command Prompt terminal. You should see a response that tells says Python 3.x.
If the response says you have version 2.7 installed, or if it raises an error, then try the following command instead:
If Python 3 used the python alias (without the 3), then use the pip command to install PyInstaller:
|
1 |
python -m pip install —user pyinstaller |
NOTE: Use the --user option if Windows raises a permissions error.
Otherwise use pip3 to installed the package:
|
1 |
pip3 install —user pyinstaller |
Here’s the command to upgrade your current version of PyInstaller:
|
1 |
python -m pip install —upgrade —user pyinstaller |
PyInstaller command-not-found error in Windows
Type python -m PyInstaller, pyinstaller, or PyInstaller into your Command Prompt window and press return. If none of these commands work, then it probably means that the pyinstaller.exe executable file is not set in your system’s environmental variables path.
Windows doesn’t know the path to the PyInstaller executable file
Use the echo %PATH in your command line to have it return a list of all the paths for your environmental variables.
Type environment into the Windows Search bar, or just open the System Properties window in your Control Panel. Make sure to click on the Advanced tab in System Properties, and then click the Environment Variables button:
Add the path for the ‘pyinstaller.exe’ to your Windows environment variables
Open a instance of File Explorer and navigate to C:Program FilesPython37Scripts or C:UsersUSER_NAMEAppDataRoamingPythonPython37Scripts and look for the executable. Once you find the file make sure to get its full path.
Click the New.. button in your Environmental Variables to add the system path for the pyinstaller.exe file. Make sure to type PyInstaller in the Variable name input field, and the path to the .exe file in the Variable value field.
Verify that the PyInstaller command for Python 3 is now working
Close all your instances of Command Prompt, and re-open it. Type PyInstaller or python PyInstaller into the window’s prompt, and it should now return a response from the executable.
Build a Windows executable using the Pyinstaller package for Python
You should now be able to build an executable from a Python script using PyInstaller using the following command:
|
1 |
python -m PyInstaller script_name.py |
NOTE: Make sure to first change (cd) into the directory containing the Python script before running the PyInstaller command.
python -m pip install –upgrade –user pip
python -m pip install –upgrade –user pyinstaller
pip -v install –user elasticsearch
PyInstaller
C:UsersObjectRocketAppDataRoamingPythonPython37Scriptspyinstaller.exe
Python
echo %PATH%
C:UsersObjectRocketAppDataRoamingPythonPython37Scripts
python -m PyInstaller
pyinstaller –version
Installing the PyInstaller Package on Ubuntu distros of Linux
pip3 install pyinstaller
sudo apt-get install libc-bin
sudo apt-get install binutils
pyinstaller
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptname
pyinstaller cli.py
python3 -O -m PyInstaller elastic_query.py
cd dist/elastic_query/
./elastic_query test
sudo rm -rf build/; sudo rm -rf dist/; sudo rm -rf pycache/; sudo rm elastic_query.spec
Change into the PyInstaller’s ‘dist’ directory
Execute the ‘elastic_query’ file created by PyInstaller with a query
pass a query to its parameters
Elasticsearch cluster response returned from the PyInstaller application’s API request
|
1 |
./elastic_query some_index «str field» «ObjectRocket» |
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed this tutorial on how to build a stand-alone Elasticsearch query application with Python. You can grab any or all of the code we used below.
Just the Code
|
1 |
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # use sys for system arguments passed to script # import the Elasticsearch client library # create a client instance of Elasticsearch # The script name is the first arg [0], but the second arg [1] def make_query(filter): # check if the index exists try: # pass filter query to the client’s search() method # print the query response` # iterate the response hits except Exception as err: return response def main(): # declare variable for system arguments list # remove Python script name from args list # quit the script if there are not exactly 3 arguments else: # pass the field name and value args to filter dict # pass the filter dict to the make_query() function # have interpreter call the main() func |
Apr-19-2018, 07:11 AM
(This post was last modified: Apr-19-2018, 09:08 AM by snippsat.)
Hi All,
I am facing the below issue when using PyInstaller
Error:
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME]
[--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>]
[--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR]
[--hidden-import MODULENAME]
[--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH]
[--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES]
[--key KEY] [-d] [-s] [--noupx] [-c] [-w]
[-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns>]
[--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>] [-r RESOURCE]
[--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies]
[--win-no-prefer-redirects]
[--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER]
[--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--distpath DIR]
[--workpath WORKPATH] [-y] [--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a]
[--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]
scriptname [scriptname ...]
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptnameI have created a json file to provide the required arguments and a small program to take the data from the json file.
{
"name": "PythonApp",
"paths": "",
"script": "app.py",
"src_dir": "C:...\PythonApp",
"dest_dir": "C:...\PythonApp\installation",
"files": [["core_content/settings.json", "core_content"],
["appConfig.json", "installation"],
["resources.qrc", "installation"]
],
"dirs": [["core_content", "core_content"], ["images", "images"], ["log", "log"], ["resources", "resources"], ["ui", "ui"]],
"cmd": "pyinstaller --onedir --onefile --debug --name={} --paths="{}" "{}""
}
import shutil, errno
import configparser
import json
import os
import sys
import subprocess
with open("compile.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
config = json.load(f)
des_dir = config.get("dest_dir")
app_name = config.get("name")
script = config.get("script")
src_dir = config.get("src_dir")
cmd = config.get("cmd")
dirs = config.get("dirs")
files = config.get("files")
if not all([app_name, script, src_dir, des_dir]):
print("Not all mandatory arguments were given")
sys.exit(0)
if os.path.isdir(des_dir):
shutil.rmtree(des_dir)
os.mkdir(des_dir)
os.chdir(des_dir)
script = os.path.join(src_dir, script)
print("Current directory:", os.getcwd())
installer_cmd = cmd.format(app_name, src_dir, script)
print("cmd", installer_cmd)
p = subprocess.Popen(installer_cmd)
p.communicate()
def copy(src, dst):
try:
shutil.copytree(src, dst)
except NotADirectoryError:
if not os.path.exists(dst):
os.makedirs(dst)
shutil.copy(src, dst)
def copy_dirs():
if not dirs:
print("No dirs to copy")
for src, dest in dirs:
src, dest = os.path.join(src_dir, src), os.path.join(des_dir, "dist", dest)
copy(src, dest)
def copy_files():
if not files:
print("No files to copy")
for src, dest in files:
src, dest = os.path.join(src_dir, src), os.path.join(des_dir, "dist", dest)
copy(src, dest)
copy_dirs()
copy_files()
shutil.make_archive(app_name, "zip", os.path.join(des_dir, "dist"))
for f in os.listdir("."):
if f not in (app_name + ".zip"):
if os.path.isdir(f):
shutil.rmtree(f)
elif os.path.isfile(f):
os.remove(f)
Posts: 7,843
Threads: 148
Joined: Sep 2016
Reputation:
572
Apr-19-2018, 10:44 AM
(This post was last modified: Apr-19-2018, 10:45 AM by buran.)
could you post the exact command you use to make it exe?
it looks like you don’t supply the name of your script that you want to convert to exe.
In simplest case (with no options whatsoever) you will go to the folder of your script and run
pyintstaller yourscript.py
see at the bottom of https://www.pyinstaller.org/
Posts: 127
Threads: 3
Joined: Mar 2018
Reputation:
9
I suggest you make your first executable from helloworld.py to verify that you can get PyInstaller to work properly. After that try on your file.
There are two basic ways to run PyInstaller:
a. The Kitchen sink method which is probably not what you want (includes a lot of files):
[b]PyInstaller helloworld.py[/b]
This creates a subfolder named ‘helloworld’ in the ‘dist’ subfolder. You must create a zip file of the ‘helloworld’ subfolder. The zip file is what you distribute.
b. The one file method:
[b]PyInstaller -F helloworld.py[/b]
This creates file ‘helloworld.exe’ in the ‘dist’ subfolder. The only file you have to distribute is ‘helloworld.exe’.
For more information see the ‘Bundling to One Folder’ section and the ‘Bundling to One File’ section in https://pyinstaller.readthedocs.io/en/st…-mode.html
NOTE: I get a Fatal Python error: Py_Initialize: can't initialize sys standard streams when there is a file named abc.py in the same folder as the file being compiled. Either I am doing something wrong or this is a PyInstaller Feature.
Lewis
Posts: 6,575
Threads: 116
Joined: Sep 2016
Reputation:
487
Apr-19-2018, 01:17 PM
(This post was last modified: Apr-19-2018, 01:17 PM by snippsat.)
As mention test that all work with Pyinstaller before doing that stuff with reading json an use subprocess.
installer_cmd = cmd.format(app_name, src_dir, script)
print("cmd", installer_cmd)
p = subprocess.Popen(installer_cmd)
p.communicate()
Will not work without shell=True(unsecure) as you pass in string installer_cmd.
p = subprocess.Popen(installer_cmd, shell=True)
If Pynstaller is in Windows Path,which it will be if Python are in(environment variables Path).
You can call pyinstaller direct no cmd.
This is a test that work,here i use a list so no shell=True.
# sub_run.py from subprocess import run out = run(['pyinstaller', '--onefile', 'hello.py'])
# hello.py
print('hello world')
input('press enter to exit')
Test run:
C:1sub_run λ python sub.py 550 INFO: PyInstaller: 3.3.1 550 INFO: Python: 3.6.4 553 INFO: Platform: Windows-10-10.0.16299-SP0 554 INFO: wrote C:1sub_runhello.spec ....... ect
Posts: 127
Threads: 3
Joined: Mar 2018
Reputation:
9
Apr-21-2018, 08:42 PM
(This post was last modified: Apr-21-2018, 11:33 PM by ljmetzger.)
Message deleted by poster — incorrect posting.
Posts: 6,575
Threads: 116
Joined: Sep 2016
Reputation:
487
(Apr-21-2018, 08:42 PM)ljmetzger Wrote: when there is a file named abc.py in the same folder as the file being compiled
There can be problems if name a file abc.py,because of Abstract Base Classes.
So python has a file named abc.py that use this module.
>>> import abc >>> >>> abc.__file__ 'C:\Python36\lib\abc.py
Answer by Josue Nielsen
Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers.,and this error also occured,but I don’t understand which file or folder I have to copy and where I have to paste it,
and also find it,
Unpinning the accepted answer from the top of the list of answers
I’m trying to create an exe file to distribute among users in my company.
the exe file open a simple GUI (made with Tkinter), which allows the user to select a txt file from their pc and inserts the data from the txt into a Google sheet.
I tested my python script before attempting to turn it into an exe and it worked great.
but now, when I’m trying to use Pyinstaller it shows the following error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "pygsheetssheet.py", line 39, in __init__
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'C:\Users\<Awais Bin Riaz>\AppData\Local\Temp\_MEI104322\pygsheets\data\sheets_discovery.json'
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cli.py", line 4, in <module>
main()
File "rps_nba__main__.py", line 272, in main
client = pygsheets.authorize(service_file = key_file)
File "pygsheetsauthorization.py", line 131, in authorize
File "pygsheetsclient.py", line 61, in __init__
File "pygsheetssheet.py", line 42, in __init__
File "googleapiclient_helpers.py", line 134, in positional_wrapper
File "googleapiclientdiscovery.py", line 291, in build
File "googleapiclientdiscovery.py", line 405, in _retrieve_discovery_doc
googleapiclient.errors.UnknownApiNameOrVersion: name: sheets version: v4
[28348] Failed to execute script cli
but don’t know what is src-file and dst-file, I tried many time but error occured of this
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME] [--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>]
[--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR] [--hidden-import MODULENAME]
[--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH] [--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES]
[--key KEY] [-d {all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}] [-s] [--noupx] [--upx-exclude FILE] [-c] [-w]
[-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns or "NONE">] [--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>]
[-r RESOURCE] [--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies] [--win-no-prefer-redirects]
[--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER] [--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--bootloader-ignore-signals]
[--distpath DIR] [--workpath WORKPATH] [-y] [--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a] [--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]
scriptname [scriptname ...]
pyinstaller: error: argument --add-data: invalid add_data_or_binary value: "'C:\Users\AWAIS BIN RIAZ\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\Lib\site-packages\pygsheets\sheet.py';"
and this error also occured
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME] [--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>]
[--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR] [--hidden-import MODULENAME]
[--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH] [--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES]
[--key KEY] [-d {all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}] [-s] [--noupx] [--upx-exclude FILE] [-c] [-w]
[-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns or "NONE">] [--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>]
[-r RESOURCE] [--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies] [--win-no-prefer-redirects]
[--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER] [--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--bootloader-ignore-signals]
[--distpath DIR] [--workpath WORKPATH] [-y] [--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a] [--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]
scriptname [scriptname ...]
pyinstaller: error: the following arguments are required: scriptname
Answer by Marley Randall
then I tried clicking the exe file, which was when it returned the above error.,I tried everything!! any help / tips would be amazing! Thanks in advance!,I am receiving the same error converting my script to an EXE via pyinstaller. This is only when I run the .exe file. The python file runs with no issues.,this is the cmd command I used to create the exe file:
C:UsersAsusPycharmProjectsdmtrialvenv>pyinstaller —onefile DMPulse2GS.py
C:UsersAsusPycharmProjectsdmtrialvenvdist>DMPulse2GS.exe
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "pygsheetssheet.py", line 39, in __init__
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'C:\Users\Asus\AppData\Local\Temp\_MEI102362\pygsheets\data\sheets_discovery.json'
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "DMPulse2GS.py", line 39, in <module>
File "pygsheetsauthorization.py", line 131, in authorize
File "pygsheetsclient.py", line 61, in __init__
File "pygsheetssheet.py", line 42, in __init__
File "googleapiclient_helpers.py", line 134, in positional_wrapper
File "googleapiclientdiscovery.py", line 291, in build
File "googleapiclientdiscovery.py", line 405, in _retrieve_discovery_doc
googleapiclient.errors.UnknownApiNameOrVersion: name: sheets version: v4
[11284] Failed to execute script DMPulse2GS
Answer by Edward Rose
When you run the bundled app and it terminates with an ImportError,
that is the time to examine the warning file.
Then see Helping PyInstaller Find Modules below for how to proceed.,If Analysis thinks it has found all the imports,
but the app fails with an import error,
the problem is a hidden import; that is, an import that is not
visible to the analysis phase.,Understanding PyInstaller Hooks,Changelog for PyInstaller
./hello: error while loading shared libraries: libz.so.1:
failed to map segment from shared object: Operation not permitted
Answer by Gabriela Glass
pygsheets installed from (github or pypi): pip,pygsheets installed from (github or pypi): pypi,Cause:
numericise() is structured to only receive strings as input. However, when using ValueRenderOption.UNFORMATTED_VALUE, numericise() receives ints or floats.
Doing int(value) on a float value gives no error, hence an int is returned.,Merge branch ‘staging’ of github.com:nithinmurali/pygsheets into staging
Describe the solution you’d like
I would like to rename by writing as follows.
client = pygsheets.authorize(user_auth_credentials)
sp = client.create_spreadsheet(book_name)
sp.sheet1.rename(sheet_name='new_name') # rename is a feature method.
Answer by Mya Stewart
Creating a PyInstaller package,Testing a PyInstaller package,Refining a PyInstaller package,There’s a fair chance your first attempt to use PyInstaller to package an app won’t be completely successful.
Creating a PyInstaller package
PyInstaller is a Python package, installed with pip (pip install pyinstaller). PyInstaller can be installed in your default Python installation, but it’s best to create a virtual environment for the project you want to package and install PyInstaller there.
pipCreating a PyInstaller package
PyInstaller is a Python package, installed with pip (pip install pyinstaller). PyInstaller can be installed in your default Python installation, but it’s best to create a virtual environment for the project you want to package and install PyInstaller there.
pip install pyinstallerAnswer by Rory Moody
Conversion— Use the following command to convert the Python file into a Windows executable:,Let’s go step by step to convert the Python file to a Windows executable:,Change folder location — Use the following command and direct the command prompt to the location of your Python code:,To convert the Python code into an executable file, we will be using Pyinstaller package. Use the standard ‘pip install’ command to install this package.
For this tutorial, we have written a small Python code that reads a ‘.csv’ file from the Windows folder location. This file has 2 columns, each containing a set of random numbers. The code creates a new column that contains the sum of numbers from the 2 input columns. The modified file is saved at the same folder location as the old one.
#### Importing the required libraryimport pandas as pd#### Reading csv filedf = pd.read_csv("C:\Ujjwal\New_File_V1.csv")#### Adding 2 columnsdf["Third_Column"] = df["Randome Numbers 1"] + df["Random Numbers 2"]#### Exporting the data to same locationdf.to_csv("C:\Ujjwal\New_File_V2.csv",index = False)To convert the Python code into an executable file, we will be using Pyinstaller package. Use the standard ‘pip install’ command to install this package.
#### Install Commandpip install pyinstaller- Open the command prompt— The conversion of the Python script to Windows executable is done using the command line. For this purpose, we have to go to the command prompt. Type “cmd” in your Windows search box and open the command prompt
- Change folder location — Use the following command and direct the command prompt to the location of your Python code:
#### Change Folder Locationcd folder_location- Conversion— Use the following command to convert the Python file into a Windows executable:
#### Command for conversionpyinstaller --onefile filenameThe most common error which one can face when executing the executable file is “ModuleNotFoundError: No module named module name”. A sample screenshot of this error and the actual error prompt is as follows:
#### Error Prompt MessageModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas._libs.tslibs.nattypes' - Go to the Windows location where the pyinstaller package is installed. Since I am using Anaconda distribution, the following is the location on my system:
#### Package LocationC:UsersUjjwalAnaconda3Libsite-packages- The reason behind the error is the malfunctioning of the command where ‘hiddenimports’ is getting initialized. Comment this statement and add a new one in which the ‘hiddenimports’ is initialized with the same module name which has raised the error. For our case, it was ‘pandas._libs.tslibs.nattype’. The code line to be added is as follows:
#### Code line for hook filehiddenimports = 'pandas._libs.tslibs.nattype'- Once the hook file is modified, save it and re-create the new executable. Before recreating, please ensure that the old executable file and associated folders are deleted. If the error persists, continue to add the other missing modules in your hook file. Please note that multiple modules should be added as a list structure.
#### Code line after adding multiple moduleshiddenimports = ['pandas._libs.tslibs.np_datetime','pandas._libs.tslibs.nattype','pandas._libs.skiplist']