What is Memory Error?
Python Memory Error or in layman language is exactly what it means, you have run out of memory in your RAM for your code to execute.
When this error occurs it is likely because you have loaded the entire data into memory. For large datasets, you will want to use batch processing. Instead of loading your entire dataset into memory you should keep your data in your hard drive and access it in batches.
A memory error means that your program has run out of memory. This means that your program somehow creates too many objects. In your example, you have to look for parts of your algorithm that could be consuming a lot of memory.
If an operation runs out of memory it is known as memory error.
Types of Python Memory Error
Unexpected Memory Error in Python
If you get an unexpected Python Memory Error and you think you should have plenty of rams available, it might be because you are using a 32-bit python installation.
The easy solution for Unexpected Python Memory Error
Your program is running out of virtual address space. Most probably because you’re using a 32-bit version of Python. As Windows (and most other OSes as well) limits 32-bit applications to 2 GB of user-mode address space.
We Python Pooler’s recommend you to install a 64-bit version of Python (if you can, I’d recommend upgrading to Python 3 for other reasons); it will use more memory, but then, it will have access to a lot more memory space (and more physical RAM as well).
The issue is that 32-bit python only has access to ~4GB of RAM. This can shrink even further if your operating system is 32-bit, because of the operating system overhead.
For example, in Python 2 zip function takes in multiple iterables and returns a single iterator of tuples. Anyhow, we need each item from the iterator once for looping. So we don’t need to store all items in memory throughout looping. So it’d be better to use izip which retrieves each item only on next iterations. Python 3’s zip functions as izip by default.
Must Read: Python Print Without Newline
Python Memory Error Due to Dataset
Like the point, about 32 bit and 64-bit versions have already been covered, another possibility could be dataset size, if you’re working with a large dataset. Loading a large dataset directly into memory and performing computations on it and saving intermediate results of those computations can quickly fill up your memory. Generator functions come in very handy if this is your problem. Many popular python libraries like Keras and TensorFlow have specific functions and classes for generators.
Python Memory Error Due to Improper Installation of Python
Improper installation of Python packages may also lead to Memory Error. As a matter of fact, before solving the problem, We had installed on windows manually python 2.7 and the packages that I needed, after messing almost two days trying to figure out what was the problem, We reinstalled everything with Conda and the problem was solved.
We guess Conda is installing better memory management packages and that was the main reason. So you can try installing Python Packages using Conda, it may solve the Memory Error issue.
Most platforms return an “Out of Memory error” if an attempt to allocate a block of memory fails, but the root cause of that problem very rarely has anything to do with truly being “out of memory.” That’s because, on almost every modern operating system, the memory manager will happily use your available hard disk space as place to store pages of memory that don’t fit in RAM; your computer can usually allocate memory until the disk fills up and it may lead to Python Out of Memory Error(or a swap limit is hit; in Windows, see System Properties > Performance Options > Advanced > Virtual memory).
Making matters much worse, every active allocation in the program’s address space can cause “fragmentation” that can prevent future allocations by splitting available memory into chunks that are individually too small to satisfy a new allocation with one contiguous block.
1 If a 32bit application has the LARGEADDRESSAWARE flag set, it has access to s full 4gb of address space when running on a 64bit version of Windows.
2 So far, four readers have written to explain that the gcAllowVeryLargeObjects flag removes this .NET limitation. It does not. This flag allows objects which occupy more than 2gb of memory, but it does not permit a single-dimensional array to contain more than 2^31 entries.
How can I explicitly free memory in Python?
If you wrote a Python program that acts on a large input file to create a few million objects representing and it’s taking tons of memory and you need the best way to tell Python that you no longer need some of the data, and it can be freed?
The Simple answer to this problem is:
Force the garbage collector for releasing an unreferenced memory with gc.collect().
Like shown below:
import gc
gc.collect()

Memory error in Python when 50+GB is free and using 64bit python?
On some operating systems, there are limits to how much RAM a single CPU can handle. So even if there is enough RAM free, your single thread (=running on one core) cannot take more. But I don’t know if this is valid for your Windows version, though.
How do you set the memory usage for python programs?
Python uses garbage collection and built-in memory management to ensure the program only uses as much RAM as required. So unless you expressly write your program in such a way to bloat the memory usage, e.g. making a database in RAM, Python only uses what it needs.
Which begs the question, why would you want to use more RAM? The idea for most programmers is to minimize resource usage.
if you wanna limit the python vm memory usage, you can try this:
1、Linux, ulimit command to limit the memory usage on python
2、you can use resource module to limit the program memory usage;
if u wanna speed up ur program though giving more memory to ur application, you could try this:
1threading, multiprocessing
2pypy
3pysco on only python 2.5
How to put limits on Memory and CPU Usage
To put limits on the memory or CPU use of a program running. So that we will not face any memory error. Well to do so, Resource module can be used and thus both the task can be performed very well as shown in the code given below:
Code #1: Restrict CPU time
# importing libraries
import signal
import resource
import os
# checking time limit exceed
def time_exceeded(signo, frame):
print("Time's up !")
raise SystemExit(1)
def set_max_runtime(seconds):
# setting up the resource limit
soft, hard = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_CPU)
resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_CPU, (seconds, hard))
signal.signal(signal.SIGXCPU, time_exceeded)
# max run time of 15 millisecond
if __name__ == '__main__':
set_max_runtime(15)
while True:
pass
Code #2: In order to restrict memory use, the code puts a limit on the total address space
# using resource import resource def limit_memory(maxsize): soft, hard = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS) resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS, (maxsize, hard))
Ways to Handle Python Memory Error and Large Data Files
1. Allocate More Memory
Some Python tools or libraries may be limited by a default memory configuration.
Check if you can re-configure your tool or library to allocate more memory.
That is, a platform designed for handling very large datasets, that allows you to use data transforms and machine learning algorithms on top of it.
A good example is Weka, where you can increase the memory as a parameter when starting the application.
2. Work with a Smaller Sample
Are you sure you need to work with all of the data?
Take a random sample of your data, such as the first 1,000 or 100,000 rows. Use this smaller sample to work through your problem before fitting a final model on all of your data (using progressive data loading techniques).
I think this is a good practice in general for machine learning to give you quick spot-checks of algorithms and turnaround of results.
You may also consider performing a sensitivity analysis of the amount of data used to fit one algorithm compared to the model skill. Perhaps there is a natural point of diminishing returns that you can use as a heuristic size of your smaller sample.
3. Use a Computer with More Memory
Do you have to work on your computer?
Perhaps you can get access to a much larger computer with an order of magnitude more memory.
For example, a good option is to rent compute time on a cloud service like Amazon Web Services that offers machines with tens of gigabytes of RAM for less than a US dollar per hour.
4. Use a Relational Database
Relational databases provide a standard way of storing and accessing very large datasets.
Internally, the data is stored on disk can be progressively loaded in batches and can be queried using a standard query language (SQL).
Free open-source database tools like MySQL or Postgres can be used and most (all?) programming languages and many machine learning tools can connect directly to relational databases. You can also use a lightweight approach, such as SQLite.
5. Use a Big Data Platform
In some cases, you may need to resort to a big data platform.
Summary
In this post, you discovered a number of tactics and ways that you can use when dealing with Python Memory Error.
Are there other methods that you know about or have tried?
Share them in the comments below.
Have you tried any of these methods?
Let me know in the comments.
If your problem is still not solved and you need help regarding Python Memory Error. Comment Down below, We will try to solve your issue asap.
A segfaulting program might be the symptom of a bug in C code–or it might be that your process is running out of memory.
Crashing is just one symptom of running out of memory.
Your process might instead just run very slowly, your computer or VM might freeze, or your process might get silently killed.
Sometimes if you’re lucky you might even get a nice traceback, but then again, you might not.
So how do you identify out-of-memory problems?
With some understanding of how memory works in your operating system and in Python, you can learn to identify all the different ways out-of-memory problems can manifest:
- A slow death.
- An obvious death.
- A corrupted death.
- Death by assassination.
A slow death: Swapping
When your computer’s RAM fills up, the operating system will start moving chunks of memory out of RAM and on to your disk, aka “swapping”.
Specifically, it will try to move chunks of memory that aren’t being used.
When some code tries to read or write to these chunks they will get loaded back into RAM.
Now, your disk is much slower than RAM, so this can lead to slowness if you’re doing a lot of swapping.
At the extreme, your computer will technically still be running but for practical purposes will be completely locked up as the amount of data the operating is system is trying to read and write to disk exceeds the disk’s bandwidth.
This is more common on personal computers, where you’re running many different programs that might use and touch a lot of memory: a browser, an IDE, the program you’re testing, and so on.
Even with swapping, if you allocate enough memory you’ll eventually run out of the combined RAM and swap space.
At this point allocating more memory is impossible.
An obvious death: MemoryError tracebacks and other error messages
What happens when you can’t allocate any more memory?
When using Python, this will often result in the interpreter’s memory allocation APIs failing to allocate.
At this point, Python will try to raise a MemoryError exception.
>>> import numpy
>>> numpy.ones((1_000_000_000_000,))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib64/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/core/numeric.py", line 192, in ones
a = empty(shape, dtype, order)
MemoryError: Unable to allocate 7.28 TiB for an array with shape (1000000000000,) and data type float64
This will get handled by whatever mechanisms your program uses for unexpected exceptions; with any luck, it’ll end up in the logs or terminal for you to read.
Of course, handling and printing that traceback also uses memory.
So this sort of useful, clear traceback is much more likely when you did a large allocation that didn’t fit in memory.
The big allocation fails, which means available memory doesn’t change, and hopefully there’s enough available to handle the exception.
If there’s not enough memory to handle the error reporting my expectation is that you will eventually get some sort of crash, e.g. due to a stack overlow as you get an infinite recursion of creating a new MemoryError failing due to lack of memory.
A disguised death: Segfaults in C code
Under the hood, Python eventually delegates memory allocation to the standard C library APIs malloc(), free(), and related functions.
When you call malloc(), you get back the address of a newly allocated chunk of memory.
And if allocation fails you’ll get back NULL, the address 0.
For example, here we see the first allocation returns the address of the newly allocated memory:
>>> import ctypes
>>> libc = ctypes.CDLL("libc.so.6")
>>> libc.malloc(100)
439108304
The second allocation fails because I asked for far too much memory:
>>> libc.malloc(1_000_000_000_000)
0
Now, well-behaved code will check for a NULL returned from malloc(), and handle the error as best it can.
It might exit with an error, or as we saw the Python interpreter raises a MemoryError exception.
Buggy code will assume malloc() always return successfully, and treat the 0 returned by malloc() as a valid memory address.
Trying to write to address 0 will then result in a crash.
Consider the following C program:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *p;
size_t allocation_size = strtoll(argv[1], &p, 10);
char* data = malloc(allocation_size);
/* Uh oh, didn't check for NULL return result. */
data[0] = 'O';
data[1] = 'K';
data[2] = 'n';
data[3] = 0;
printf("%s", data);
}
It allocates some memory based on the first argument, and then writes to it—but it doesn’t check for a failed allocation.
If I run it with a small, successful allocation, everything works fine:
But if the allocation is too big, the program crashes because it doesn’t have any error handling code.
$ ./naive-malloc 10000000000000000
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
Of course, segfaults happen for other reasons as well, so to figure out the cause you’ll need to inspect the core file with a debugger like gdb, or run the program under the Fil memory profiler.
Death by assassination: The out-of-memory killer
On Linux and macOS, there is another way your process might die: the operating system can decide your process is using too much memory, and kill it preemptively.
The symptom will be your program getting killed with SIGKILL (kill -9), with a corresponding exit code.
- On Linux, you can see OOM killer logs in
dmesg, and either/var/log/messagesor/var/log/kern.log, depending on your distribution.
Notifications are available via cgroups v1 or v2 (most distributions still use the former). - I am not sure where to find logs on macOS, but you can learn more about macOS out-of-memory handling and notifications here.
Debugging and preventing out-of-memory issues
Out-of-memory conditions can result in a variety of failure modes, from slowness to crashes, and the relevant information might end up in stderr, the application-level logging, system-level logging, or implicit in a core dump file.
This makes debugging the cause of the problem rather tricky.
There are some ways to improve the situation, however.
- For production server workloads, setting memory limits and limiting swap will at least keep memory leaks from freezing things up—eventually the leaky process will get killed and restarted.
- For production batch data processing, you can model expected memory usage based on input size and then ensure you’re running with enough memory upfront.
- If you’re running processes manually, you can use the open source Fil memory profiler to automatically catch and debug Python out-of-memory problems.
A MemoryError means that the interpreter has run out of memory to allocate to your Python program. This may be due to an issue in the setup of the Python environment or it may be a concern with the code itself loading too much data at the same time.
An Example of MemoryError
To have a look at this error in action, let’s start with a particularly greedy piece of code. In the code below, we start with an empty array and use nested arrays to add strings to it. In this case, we use three levels of nested arrays, each with a thousand iterations. This means at the end of the program, the array s has 1,000,000,000 copies of the string «More.«
s = []
for i in range(1000):
for j in range(1000):
for k in range(1000):
s.append("More")Output
As you might expect, these million strings are a bit much for, let’s say, a laptop to handle. The following error is printed out:
C:codePythonMemErrvenv3KScriptspython.exe C:/code/python/MemErr/main.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/code/python/MemErr/main.py", line 6, in <module>
s.append("More")
MemoryErrorIn this case, the traceback is relatively simple as there are no libraries involved in this short program. After the traceback showing the exact function call which caused the issue, we see the simple but direct MemoryError.
Two Ways to Handle A MemoryError in Python
Appropriate Python Set-up
This simplest but possibly least intuitive solution to a MemoryError actually has to do with a potential issue with your Python setup. In the event that you have installed the 32-bit version of Python on a 64-bit system, you will have extremely limited access to the system’s memory. This restricted access may cause MemoryErrors on programs that your computer would normally be able to handle.
Attention to Large Nested Loops
If your installation of Python is correct and these issues still persist, it may be time to revisit your code. Unfortunately, there is no cut and dry way to entirely remove this error outside of evaluating and optimizing your code. Like in the example above, pay special attention to any large or nested loops, along with any time you are loading large datasets into your program in one fell swoop.
In these cases, the best practice is often to break the work into batches, allowing the memory to be freed in between calls. As an example, in the code below, we have broken out earlier nested loops into 3 separate loops, each running for 333,333,333 iterations. This program still goes through one million iterations but, as the memory can be cleared through the process using a garbage collection library, it no longer causes a MemoryError.
An Example of Batching Nested Loops
import gc
s = []
t = []
u = []
for i in range(333333333):
s.append("More")
gc.collect()
for j in range(333333333):
t.append("More")
gc.collect()
for k in range(333333334):
u.append("More")
gc.collect()How to Avoid a MemoryError in Python
Python’s garbage collection makes it so that you should never encounter issues in which your RAM is full. As such, MemoryErrors are often indicators of a deeper issue with your code base. If this is happening, it may be an indication that more code optimization or batch processing techniques are required. Thankfully, these steps will often show immediate results and, in addition to avoiding this error, will also vastly shorten the programs’ runtime and resource requirements.
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Python errors easier than ever. Sign Up Today!
What exactly is a Memory Error?
Python Memory Error or, in layman’s terms, you’ve run out of Random access memory (RAM) to sustain the running of your code. This error indicates that you have loaded all of the data into memory. For large datasets, batch processing is advised. Instead of packing your complete dataset into memory, please save it to your hard disk and access it in batches.
Your software has run out of memory, resulting in a memory error. It indicates that your program generates an excessive number of items. You’ll need to check for parts of your algorithm that consume a lot of memory in your case.
A memory error occurs when an operation runs out of memory.
Python has a fallback exception, as do all programming languages, for when the interpreter runs out of memory and must abandon the current execution. Python issues a MemoryError in these (hopefully infrequent) cases, giving the script a chance to catch up and break free from the present memory dearth. However, because Python’s memory management architecture is based on the C language’s malloc() function, It is unlikely that all processes will recover – in some situations, a MemoryError will result in an unrecoverable crash.
A MemoryError usually signals a severe fault in the present application. A program that takes files or user data input, for example, may encounter MemoryErrors if it lacks proper sanity checks. Memory restrictions might cause problems in various situations, but we’ll stick with a simple allocation in local memory utilizing strings and arrays for our code example.
The computer architecture on which the executing system runs is the most crucial element in whether your applications are likely to incur MemoryErrors. Or, to be more particular, the architecture of the Python version you’re using. The maximum memory allocation granted to the Python process is meager if you’re running a 32-bit Python. The maximum memory allocation limit fluctuates and is dependent on your system. However, it is generally around 2 GB and never exceeds 4 GB.
64-bit Python versions, on the other hand, are essentially restricted only by the amount of memory available on your system. Thus, in practice, a 64-bit Python interpreter is unlikely to have memory problems, and if it does, the pain is much more severe because it would most likely affect the rest of the system.
To verify this, we’ll use psutil to get information about the running process, specifically the psutil.virtual memory() method, which returns current memory consumption statistics when called. The print() memory usage method prints the latter information:
Python Memory Errors There are Several Types of Python Memory Errors
In Python, an unexpected memory error occurs
Even if you have enough RAM, you could get an unexpected Python Memory Error, and you may be using a 32-bit Python installation.
Unexpected Python Memory Error: A Simple Solution
Your software has used up all of the virtual address space available to it. It’s most likely because you’re using a 32-bit Python version. Because 32-bit applications are limited to 2 GB of user-mode address space in Windows (and most other operating systems),
We Python Poolers recommend installing a 64-bit version of Python (if possible, update to Python 3 for various reasons); it will use more memory, but it will also have much more memory space available (and more physical RAM as well).
The problem is Python 32-bit only has 4GB of RAM. So it can be reduced due to operating system overhead even more if your operating system is 32-bit.
For example, the zip function in Python 2 accepts many iterables and produces a single tuple iterator. In any case, for looping, we only require each item from the iterator once. As a result, we don’t need to keep all of the things in memory while looping. As a result, it’s preferable to utilize izip, which retrieves each item only on subsequent cycles. Thus, by default, Python 3’s zip routines are called izip.
Memory Error in Python Because of the Dataset
Another choice, if you’re working with a huge dataset, is dataset size. The latter has already been mentioned concerning 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Loading a vast dataset into memory and running computations on it, and preserving intermediate results of such calculations can quickly consume memory. If this is the case, generator functions can be pretty helpful. Many major Python libraries, such as Keras and TensorFlow, include dedicated generator methods and classes.
Memory Error in Python Python was installed incorrectly
Improper Python package installation can also result in a Memory Error. In fact, before resolving the issue, we had manually installed python 2.7 and the programs that I need on Windows. We replaced everything using Conda after spending nearly two days attempting to figure out what was wrong, and the issue was resolved.
Conda is probably installing improved memory management packages, which is the main reason. So you might try installing Python Packages with Conda to see if that fixes the Memory Error.
Conda is a free and open-source package management and environment management system for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Conda is a package manager that installs, runs, and updates packages and their dependencies in a matter of seconds.
Python Out of Memory Error
When an attempt to allocate a block of memory fails, most systems return an “Out of Memory” error, but the core cause of the problem rarely has anything to do with being “out of memory.” That’s because the memory manager on almost every modern operating system will gladly use your available hard disk space for storing memory pages that don’t fit in RAM. In addition, your computer can usually allocate memory until the disk fills up, which may result in a Python Out of Memory Error (or a swap limit is reached; in Windows, see System Properties > Performance Options > Advanced > Virtual memory).
To make matters worse, every current allocation in the program’s address space can result in “fragmentation,” which prevents further allocations by dividing available memory into chunks that are individually too small to satisfy a new allocation with a single contiguous block.
- When operating on a 64bit version of Windows, a 32bit application with the LARGEADDRESSAWARE flag set has access to the entire 4GB of address space.
- Four readers have contacted in to say that the gcAllowVeryLargeObjects setting removes the.NET restriction. No, it doesn’t. This setting permits objects to take up more than 2GB of memory, limiting the number of elements in a single-dimensional array to 231 entries.
In Python, how do I manually free memory?
If you’ve written a Python program that uses a large input file to generate a few million objects, and it’s eating up a lot of memory, what’s the best approach to tell Python that some of the data is no longer needed and may be freed?
This problem has a simple solution:
You can cause the garbage collector to release an unreferenced memory() by using gc.collect.
As illustrated in the example below:
Do you get a memory error when there are more than 50GB of free space in Python, and you’re using 64-bit Python?
On some operating systems, the amount of RAM that a single CPU can handle is limited. So, even if there is adequate RAM available, your single thread (=one core) will not be able to take it anymore. However, we are not certain that this applies to your Windows version.
How can you make python scripts use less memory?
Python uses garbage collection and built-in memory management to ensure that the application consumes as much memory as needed. So, unless you explicitly construct your program to balloon memory utilization, such as creating a RAM database, Python only utilizes what it requires.
Which begs the question of why you’d want to do it in the first place – consume more RAM in the first place. For most programmers, the goal is to use as few resources as possible.
If you wish to keep Python’s memory use low, virtual machine to a minimum, try this:
- On Linux, use the ulimit command to set a memory limit for Python.
- You can use the resource module to limit how much memory the program uses
Consider the following if you wish to speed up your software by giving it more memory: Multiprocessing, threading.
On only python 2.5, use pysco
How can I set memory and CPU usage limits?
To limit the amount of memory or CPU used by an application while it is running. So that we don’t have any memory problems. To accomplish so, the Resource module can be used, and both tasks can be completed successfully, as demonstrated in the code below:
Code 1: Limit CPU usage
# libraries being imported
import signal
import resource
import os
# confirm_exceed_in_time.py
# confirm if there is an exceed in time limit
def exceeded_time(sig_number, frame):
print("Time is finally up !")
raise SystemExit(1)
def maximum_runtime(count_seconds):
# resource limit setup
if_soft, if_hard = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_CPU)
resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_CPU, (count_seconds, if_hard))
signal.signal(signal.SIGXCPU, exceeded_time)
# set a maximum running time of about 25 millisecond
if __name__ == '__main__':
maximum_runtime(25)
while True:
pass
Code #2: To minimize memory usage, the code restricts the total address space available.
# using resource
import resource
def limit_memory(maxsize):
if_soft, if_hard = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS)
resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS, (maxsize, if_hard))
How to Deal with Python Memory Errors and Big Data Files
Increase the amount of memory available
A default memory setup may limit some Python tools or modules.
Check to see if your tool or library may be re-configured to allocate more RAM.
That is a platform built to handle massive datasets and allow data transformations. On top of that and machine learning algorithms will be applied.
Weka is a fantastic example of this, as you may increase memory as a parameter when running the app.
Use a Smaller Sample Size
Are you sure you require all of the data?
Take a random sample of your data, such as the first 5,000 or 100,000 rows, before fitting a final model to Use this smaller sample to work through your problem instead of all of your data (using progressive data loading techniques).
It is an excellent practice for machine learning in general, as it allows for quick spot-checks of algorithms and results turnaround.
You may also compare the amount of data utilized to fit one algorithm to the model skill in a sensitivity analysis. Perhaps you can use a natural point of declining returns as a guideline for the size of your smaller sample.
Make use of a computer that has more memory
Is it necessary for you to use your computer? Of course, – it is possible to lay your hand’s on a considerably larger PC with significantly more memory. A good example is renting computing time from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services, which offers workstations with tens of gigabytes of RAM for less than a dollar per hour.
Make use of a database that is relational
Relational databases are a standard method of storing and retrieving massive datasets.
Internally, data is saved on a disk, loaded in batches, and searched using a standard query language (SQL).
Most (all?) programming languages and many machine learning tools can connect directly to relational databases, as can free open-source database solutions like MySQL or Postgres. You can also use SQLite, which is a lightweight database.
Use a big data platform to your advantage
In some cases, you may need to use a big data platform.
Error Monitoring Software
Airbrake’s powerful error monitoring software delivers real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all of your development projects. Airbrake’s cutting-edge web dashboard keeps you up to current on your application’s health and error rates at all times. Airbrake effortlessly interacts with all of the most common languages and frameworks, no matter what you’re working on. Furthermore, Airbrake makes it simple to adjust exception parameters while providing you complete control over the active error filter system, ensuring that only the most critical errors are collected.
Check out Airbrake’s error monitoring software for yourself and see why so many of the world’s greatest engineering teams rely on it to transform their exception handling techniques!
Summary
In this article, you learned about various strategies and methods for coping with Python Memory Error.
Would you mind letting us know in the comments section if you have used any of these methods?
Впервые я столкнулся с Memory Error, когда работал с огромным массивом ключевых слов. Там было около 40 млн. строк, воодушевленный своим гениальным скриптом я нажал Shift + F10 и спустя 20 секунд получил Memory Error.
Memory Error — исключение вызываемое в случае переполнения выделенной ОС памяти, при условии, что ситуация может быть исправлена путем удаления объектов. Оставим ссылку на доку, кому интересно подробнее разобраться с этим исключением и с формулировкой. Ссылка на документацию по Memory Error.
Если вам интересно как вызывать это исключение, то попробуйте исполнить приведенный ниже код.
print('a' * 1000000000000)
Почему возникает MemoryError?
В целом существует всего лишь несколько основных причин, среди которых:
- 32-битная версия Python, так как для 32-битных приложений Windows выделяет лишь 4 гб, то серьезные операции приводят к MemoryError
- Неоптимизированный код
- Чрезмерно большие датасеты и иные инпут файлы
- Ошибки в установке пакетов
Как исправить MemoryError?
Ошибка связана с 32-битной версией
Тут все просто, следуйте данному гайдлайну и уже через 10 минут вы запустите свой код.
Как посмотреть версию Python?
Идем в cmd (Кнопка Windows + R -> cmd) и пишем python. В итоге получим что-то похожее на
Python 3.8.8 (tags/v3.8.8:024d805, Feb 19 2021, 13:18:16) [MSC v.1928 64 bit (AMD64)]
Нас интересует эта часть [MSC v.1928 64 bit (AMD64)], так как вы ловите MemoryError, то скорее всего у вас будет 32 bit.
Как установить 64-битную версию Python?
Идем на официальный сайт Python и качаем установщик 64-битной версии. Ссылка на сайт с официальными релизами. В скобках нужной нам версии видим 64-bit. Удалять или не удалять 32-битную версию — это ваш выбор, я обычно удаляю, чтобы не путаться в IDE. Все что останется сделать, просто поменять интерпретатор.
Идем в PyCharm в File -> Settings -> Project -> Python Interpreter -> Шестеренка -> Add -> New environment -> Base Interpreter и выбираем python.exe из только что установленной директории. У меня это
C:/Users/Core/AppData/LocalPrograms/Python/Python38
Все, запускаем скрипт и видим, что все выполняется как следует.
Оптимизация кода
Пару раз я встречался с ситуацией когда мои костыли приводили к MemoryError. К этому приводили избыточные условия, циклы и буферные переменные, которые не удаляются после потери необходимости в них. Если вы понимаете, что проблема может быть в этом, вероятно стоит закостылить пару del, мануально удаляя ссылки на объекты. Но помните о том, что проблема в архитектуре вашего проекта, и по настоящему решить эту проблему можно лишь правильно проработав структуру проекта.
Явно освобождаем память с помощью сборщика мусора
В целом в 90% случаев проблема решается переустановкой питона, однако, я просто обязан рассказать вам про библиотеку gc. В целом почитать про Garbage Collector стоит отдельно на авторитетных ресурсах в статьях профессиональных программистов. Вы просто обязаны знать, что происходит под капотом управления памятью. GC — это не только про Python, управление памятью в Java и других языках базируется на технологии сборки мусора. Ну а вот так мы можем мануально освободить память в Python:
Introduction to Python Memory Error
Memory Error is a kind of error in python that occurs when where the memory of the RAM we are using could not support the execution of our code since the memory of the RAM is smaller and the code we are executing requires more than the memory of our existing RAM, this often occurs when a large volume of data is fed to the memory and when the program has run out of memory in processing the data.
Syntax of Python Memory Error
When performing an operation that generates or using a big volume of data, it will lead to a Memory Error.
Code:
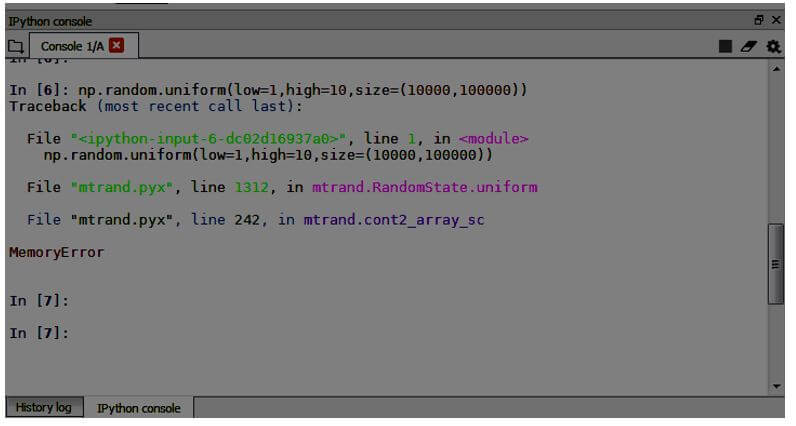
## Numpy operation which return random unique values
import numpy as np
np.random.uniform(low=1,high=10,size=(10000,100000))Output:
For the same function, let us see the Name Error.
Code:
## Functions which return values
def calc_sum(x,y):
op = x + y
return(op)The numpy operation of generating random numbers with a range from a low value of 1 and highest of 10 and a size of 10000 to 100000 will throw us a Memory Error since the RAM could not support the generation of that large volume of data.
How does Memory Error Works?
Most often, Memory Error occurs when the program creates any number of objects, and the memory of the RAM runs out. When working on Machine Learning algorithms most of the large datasets seems to create Memory Error. Different types of Memory Error occur during python programming. Sometimes even if your RAM size is large enough to handle the datasets, you will get a Memory Error. This is due to the Python version you might be using some times; 32-bit will not work if your system is adopted to a 64-bit version. In such cases, you can go uninstall 32-bit python from your system and install the 64-bit from the Anaconda website. When you are installing different python packages using the pip command or other commands may lead to improper installation and throws a Memory Error.
In such cases, we can use the conda install command in python prompt and install those packages to fix the Memory Error.
Example:
Another type of Memory Error occurs when the memory manager has used the Hard disk space of our system to store the data that exceeds the RAM capacity. Upon working, the computer stores all the data and uses up the memory throws a Memory Error.
Avoiding Memory Errors in Python
The most important case for Memory Error in python is one that occurs during the use of large datasets. Upon working on Machine Learning problems, we often come across large datasets which, upon executing an ML algorithm for classification or clustering, the computer memory will instantly run out of memory. We can overcome such problems by executing Generator functions. It can be used as a user-defined function that can be used when working with big datasets.
Generators allow us to efficiently use the large datasets into many segments without loading the complete dataset. Generators are very useful in working on big projects where we have to work with a large volume of data. Generators are functions that are used to return an iterator. Iterators can be used to loop the data over. Writing a normal iterator function in python loops the entire dataset and iters over it. This is where the generator comes in handy it does not allow the complete dataset to loop over since it causes a Memory Error and terminates the program.
The generator function has a special characteristic from other functions where a statement called yield is used in place of the traditional return statement that returns the output of the function.
A sample Generator function is given as an example:
Code:
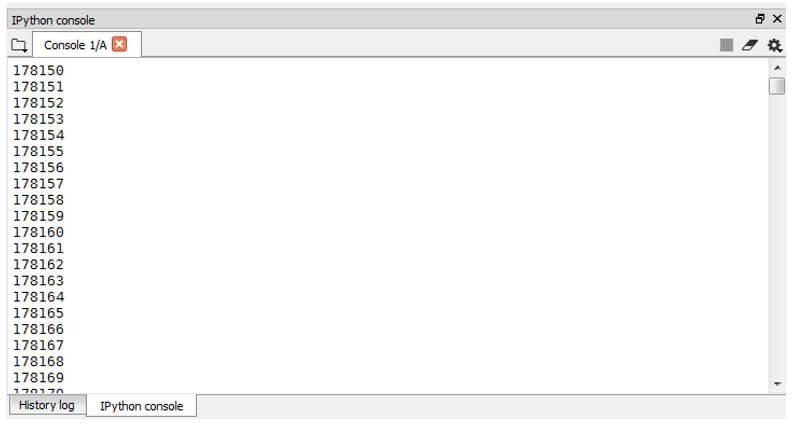
def sample_generator():
for i in range(10000000):
yield i
gen_integ= sample_generator()
for i in gen_integ:
print(i)Output:
In this sample generator function, we have generated integers using the function sample generator, which is assigned to the variable gen_integ, and then the variable is iterated. This allows us to iter over one single value at a time instead of passing the entire set of integers.
In the sample code given below, we have tried to read a large dataset into small bits using the generator function. This kind of reading would allow us to process large data in a limited size without using up the system memory completely.
Code:
def readbits(filename, mode="r", chunk_size=20):
with open(filename, mode) as f:
while True:
data = f.read(chunk_size)
if not data:
break
yield data
def main():
filename = "C://Users//Balaji//Desktop//Test"
for bits in readbits(filename):
print(bits) Output:
There is another useful technique that can be used to free memory while we are working on a large number of objects. A simple way to erase the objects that are not referenced is by using a garbage collector or gc statement.
Code:
import gc
gc.collect()The import garbage collector and gc.collect() statement allows us to free the memory by removing the objects which the user does not reference.
There are additional ways in which we can manage the memory of our system CPU where we can write code to limit the CPU usage of memory.
Code:
import resource
def limit_memory(Datasize):
min_, max_ = resource.getrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS)
resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_AS, (Datasize, max_)) This allows us to manage CPU usage to prevent Memory Error.
Some of the other techniques that can be used to overcome the Memory Error are to limit our sample size of we are working on, especially while performing complex machine learning algorithms. Or we could update our system with more memory, or we can use the cloud services like Azure, AWS, etc. that provides the user with strong computing capabilities.
Another way is to use the Relational Database Management technique where open-source databases like MySQL are available free of cost. It can be used to store large volumes of data; also, we can adapt to big data storage services to effectively work with large volumes.
Conclusion
In detail, we have seen the Memory Error that occurs in the Python programming language and the techniques to overcome the Name Error. The main take away to remember in python Memory Error is the memory usage of our RAM where the operations are taking place, and efficiently using the above-mentioned techniques will allow us to overcome the Memory Error.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python Memory Error. Here we discuss the introduction, working and avoiding memory errors in python, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Python IOError
- Custom Exception in Python
- Python AssertionError
- Python Object to String

This Python tutorial will assist you in resolving a memory error. We’ll look at all of the possible solutions to memory errors. There are some common issues that arise when memory is depleted.
What is Memory Error?
The python memory error occurs when your python script consumes a large amount of memory that the system does not have.
The python error occurs it is likely because you have loaded the entire data into memory.
The python operation runs out of memory it is known as memory error, due to the python script creates too many objects, or loaded a lot of data into the memory.
You can also checkout other python File tutorials:
- How To Read Write Yaml File in Python3
- Read and Write CSV Data Using Python
- How To Convert Python String To Array
- How to Trim Python string
Unexpected Memory Error Due to 32-bit Python
If you encounter an unexpected Python Memory Error while running a Python script. You may have plenty of memory but still receive a Memory Error. You should check if you are using 32-bit Python libraries, and if so, you should update to 64-bit.
Because 32-bit applications consume more memory than 64-bit applications. Windows allocates 2 GB of user-mode address space to 32-bit applications.
Python Memory Error Due to Dataset
This is yet another possibility for a python memory error to occur when working with a large dataset. Your Python scripts are loading a large dataset into memory and performing operations on it, which can rapidly fill up your memory. You must scan your script and correct any errors in the code, or use third-party Python libraries if they are available.
Python Memory Error Due to inappropriate package
Improper python package installation is also causing memory error, We can use Conda for package installation and management. The Conda is installing better memory management packages. The Conda is an open-source package management system and environment management system that runs on Windows, macOS and Linux. The Conda quickly installs, runs and updates packages and their dependencies.
How To Free memory in Python Using Script
Python uses garbage collection and built-in memory management to ensure the program only uses as much RAM as required.
Force the garbage collector for releasing an unreferenced memory with gc.collect().
Содержание
- Ошибка памяти Python | Как решить ошибку памяти в Python
- Ошибка памяти Python | Как решить ошибку памяти в Python
- Что такое Ошибка памяти?
- Типы ошибок памяти Python
- Неожиданная ошибка памяти в Python
- Простое решение для неожиданной ошибки памяти Python
- Ошибка памяти Python Из-за набора данных
- Ошибка памяти Python Из – за неправильной установки Python
- Ошибка нехватки памяти в Python
- Как я могу явно освободить память в Python?
- Ошибка памяти в Python, когда 50+ГБ свободны и используют 64-битный python?
- Как вы устанавливаете использование памяти для программ python?
- Как установить ограничения на использование памяти и процессора
- Способы обработки ошибок памяти Python и больших файлов данных
- 1. Выделите Больше Памяти
- 2. Работа с меньшим образцом
- 3. Используйте компьютер с большим объемом памяти
- 4. Используйте реляционную базу данных
- 5. Используйте платформу больших данных
- Резюме
- Ошибка Out of memory — как исправить
- Причины появления дисфункции
- Как исправить ошибку «Out of memory»
- Заключение
Ошибка памяти Python | Как решить ошибку памяти в Python
Ошибка памяти Python или на непрофессиональном языке-это именно то, что означает, что у вас закончилась память в оперативной памяти для выполнения кода Python.
Автор: Team Python Pool
Дата записи
Ошибка памяти Python | Как решить ошибку памяти в Python
Что такое Ошибка памяти?
Ошибка памяти Python или на языке непрофессионалов-это именно то, что означает, что у вас закончилась память в вашей оперативной памяти для выполнения вашего кода.
Когда эта ошибка возникает, это, скорее всего, потому, что вы загрузили все данные в память. Для больших наборов данных вы захотите использовать пакетную обработку . Вместо того чтобы загружать весь набор данных в память, вы должны хранить свои данные на жестком диске и получать к ним доступ пакетами.
Ошибка памяти означает, что ваша программа исчерпала память. Это означает, что ваша программа каким-то образом создает слишком много объектов. В вашем примере вы должны искать части вашего алгоритма, которые могут потреблять много памяти.
Если у операции заканчивается память, это называется ошибкой памяти .
Типы ошибок памяти Python
Неожиданная ошибка памяти в Python
Если вы получаете неожиданную ошибку памяти Python и думаете, что у вас должно быть много доступных ОЗУ, это может быть связано с тем, что вы используете 32-битную установку python .
Простое решение для неожиданной ошибки памяти Python
У вашей программы заканчивается виртуальное адресное пространство. Скорее всего, потому, что вы используете 32-битную версию Python. Поскольку Windows (как и большинство других ОС) ограничивает 32-разрядные приложения до 2 ГБ адресного пространства пользовательского режима.
Мы рекомендуем вам установить 64-битную версию Python (если вы можете, я бы рекомендовал обновить ее до Python 3 по другим причинам); она будет использовать больше памяти, но тогда у нее будет доступ к большему объему памяти (и больше физической оперативной памяти).
Проблема в том, что 32-битный python имеет доступ только к
4 ГБ оперативной памяти. Это может уменьшиться еще больше, если ваша операционная система 32-разрядная, из-за накладных расходов операционной системы.
Например, в Python 2 функция zip принимает несколько итераций и возвращает один итератор кортежей. Во всяком случае, каждый элемент итератора нужен нам один раз для циклирования. Таким образом, нам не нужно хранить все элементы в памяти на протяжении всего цикла. Поэтому было бы лучше использовать izip, который извлекает каждый элемент только на следующих итерациях. Python 3 zip по умолчанию функционирует как izip.
Должен Читать: Python Print Без Новой Строки
Ошибка памяти Python Из-за набора данных
Как и в случае с 32-битной и 64-битной версиями, другой возможностью может быть размер набора данных, если вы работаете с большим набором данных.Загрузка большого набора данных непосредственно в память и выполнение над ним вычислений и сохранение промежуточных результатов этих вычислений могут быстро заполнить вашу память. Функции генератора очень пригодятся, если это ваша проблема. Многие популярные библиотеки python, такие как Keras и TensorFlow, имеют специальные функции и классы для генераторов.
Ошибка памяти Python Из – за неправильной установки Python
Неправильная установка пакетов Python также может привести к ошибке памяти . На самом деле, прежде чем решить проблему, Мы установили на windows вручную python 2.7 и пакеты, которые мне были нужны, после того, как возились почти два дня, пытаясь выяснить, в чем проблема, Мы переустановили все с помощью Conda , и проблема была решена.
Мы предполагаем, что Honda устанавливает лучшие пакеты управления памятью, и это было главной причиной. Таким образом, вы можете попробовать установить пакеты Python с помощью Conda, это может решить проблему ошибки памяти.
Ошибка нехватки памяти в Python
Большинство платформ возвращают “Out of Memory error”, если попытка выделить блок памяти завершается неудачей, но первопричина этой проблемы очень редко имеет какое-либо отношение к тому, что действительно “out of memory”.” Это происходит потому, что почти в каждой современной операционной системе диспетчер памяти с радостью использует доступное место на жестком диске в качестве места для хранения страниц памяти, которые не помещаются в оперативную память; ваш компьютер обычно может выделять память до тех пор, пока диск не заполнится, и это может привести к ошибке Python Out of Memory(или к превышению лимита подкачки; в Windows см. раздел Свойства системы > Параметры производительности > Дополнительно > Виртуальная память).
Что еще хуже, каждое активное выделение в адресном пространстве программы может вызвать “фрагментацию”, которая может предотвратить будущие выделения, разбивая доступную память на куски, которые по отдельности слишком малы, чтобы удовлетворить новое выделение одним непрерывным блоком.
1 Если 32-битное приложение имеет установленный флаг LARGEADDRESSAWARE, оно имеет доступ к полным 4 гб адресного пространства при работе на 64-битной версии Windows.
2 До сих пор четыре читателя написали, чтобы объяснить, что флаг gcAllowVeryLargeObjects устраняет это ограничение .NET. Это не так. Этот флаг позволяет объектам, которые занимают более 2 Гб памяти, но он не позволяет одномерному массиву содержать более 2^31 записей.
Как я могу явно освободить память в Python?
Если вы написали программу Python, которая действует на большой входной файл, чтобы создать несколько миллионов объектов, представляющих собой, и это занимает тонны памяти, и вам нужен лучший способ сказать Python, что вам больше не нужны некоторые данные, и они могут быть освобождены?
Простой ответ на эту проблему:
Принудительно вызовите сборщик мусора для освобождения несвязанной памяти с помощью gc.collect().
Как показано ниже:
Ошибка памяти в Python, когда 50+ГБ свободны и используют 64-битный python?
В некоторых операционных системах существуют ограничения на объем оперативной памяти, который может обрабатывать один процессор. Таким образом, даже если есть достаточно свободной оперативной памяти, ваш единственный поток на одном ядре) не может взять больше. Но я не знаю, действительно ли это для вашей версии Windows.
Как вы устанавливаете использование памяти для программ python?
Python использует сборку мусора и встроенное управление памятью, чтобы гарантировать, что программа использует только столько оперативной памяти, сколько требуется. Поэтому, если вы специально не пишете свою программу таким образом, чтобы увеличить использование памяти, например, создавая базу данных в оперативной памяти, Python использует только то, что ему нужно.
В связи с этим возникает вопрос: почему вы хотите использовать больше оперативной памяти? Идея большинства программистов сводится к минимизации использования ресурсов.
если вы хотите ограничить использование памяти виртуальной машины python, вы можете попробовать следующее:1、Linux, команда ulimit для ограничения использования памяти на python2、вы можете использовать модуль ресурсов для ограничения использования памяти программы; если вы хотите ускорить программу ur, хотя и дать больше памяти приложению ur, вы можете попробовать следующее:1threading, multiprocessing2pypy3pysco только на python 2.5
Как установить ограничения на использование памяти и процессора
Чтобы ограничить использование памяти или процессора запущенной программой. Так что мы не столкнемся с какой-либо ошибкой памяти. Для этого можно использовать модуль ресурсов , и таким образом обе задачи могут быть выполнены очень хорошо, как показано в приведенном ниже коде:
Код #1: Ограничение процессорного времени
Код #2: Чтобы ограничить использование памяти, код устанавливает ограничение на общее адресное пространство
Способы обработки ошибок памяти Python и больших файлов данных
1. Выделите Больше Памяти
Некоторые инструменты или библиотеки Python могут быть ограничены конфигурацией памяти по умолчанию.
Проверьте, можете ли вы перенастроить свой инструмент или библиотеку, чтобы выделить больше памяти.
То есть платформа, предназначенная для обработки очень больших наборов данных, которая позволяет использовать преобразования данных и алгоритмы машинного обучения поверх нее.
Хорошим примером является Weka, где вы можете увеличить объем памяти в качестве параметра при запуске приложения.
2. Работа с меньшим образцом
Вы уверены, что вам нужно работать со всеми данными?
Возьмите случайную выборку данных, например первые 1000 или 100 000 строк. Используйте эту меньшую выборку для проработки вашей проблемы, прежде чем подгонять окончательную модель ко всем вашим данным (используя прогрессивные методы загрузки данных).
Я думаю, что это хорошая практика в целом для машинного обучения, чтобы дать вам быструю выборочную проверку алгоритмов и поворот результатов.
Вы также можете рассмотреть возможность проведения анализа чувствительности объема данных, используемых для подгонки одного алгоритма, по сравнению с навыком модели. Возможно, существует естественная точка уменьшения отдачи, которую вы можете использовать в качестве эвристического размера вашей меньшей выборки.
3. Используйте компьютер с большим объемом памяти
Вам обязательно работать на компьютере?
Возможно, вы сможете получить доступ к гораздо большему компьютеру с на порядок большим объемом памяти.
Например, хорошим вариантом является аренда вычислительного времени на облачном сервисе, таком как Amazon Web Services, который предлагает машины с десятками гигабайт оперативной памяти менее чем за доллар США в час.
4. Используйте реляционную базу данных
Реляционные базы данных обеспечивают стандартный способ хранения и доступа к очень большим наборам данных.
Внутренне данные, хранящиеся на диске, могут быть постепенно загружены пакетами и могут быть запрошены с помощью стандартного языка запросов (SQL).
Бесплатные инструменты базы данных с открытым исходным кодом, такие как href=”https://www.mysql.com/”>MySQL или href=”https://www.postgresql.org/”>Postgres можно использовать, и большинство (все?) языков программирования и многие инструменты машинного обучения могут подключаться непосредственно к реляционным базам данных. Вы также можете использовать легкий подход, например href=”https://www.sqlite.org/”>SQLite. href=”https://www.mysql.com/”>MySQL или href=”https://www.postgresql.org/”>Postgres можно использовать, и большинство (все?) языков программирования и многие инструменты машинного обучения могут подключаться непосредственно к реляционным базам данных. Вы также можете использовать легкий подход, например href=”https://www.sqlite.org/”>SQLite. href=”https://www.postgresql.org/”>Postgres можно использовать, и большинство (все?) языков программирования и многие инструменты машинного обучения могут подключаться непосредственно к реляционным базам данных. Вы также можете использовать легкий подход, например href=”https://www.sqlite.org/”>SQLite. href=”https://www.sqlite.org/”>SQLite.
5. Используйте платформу больших данных
В некоторых случаях вам может потребоваться прибегнуть к платформе больших данных.
Резюме
В этом посте вы обнаружили ряд тактик и способов, которые можно использовать при работе с ошибкой памяти Python.
Есть ли другие методы, о которых вы знаете или пробовали?Поделитесь ими в комментариях ниже.
Вы пробовали какой-нибудь из этих методов?Дайте мне знать в комментариях.
Если ваша проблема все еще не решена и вам нужна помощь относительно Python Memory Error. Прокомментируйте ниже, мы постараемся решить вашу проблему как можно скорее.
Источник
Ошибка Out of memory — как исправить
Многие пользователи ПК во время работы с какой-либо программой могут столкнуться с «вылетом» указанной программы, и появившимся сообщением «Out of memory». Возникшая проблема может иметь множество причин, начиная от банального недостатка памяти на пользовательском ПК, и заканчивая некорректной работой с памятью какой-либо программы.
Причины появления дисфункции
Сообщение «Out of memory» (в переводе дословно «вне памяти», или «недостаточно памяти») обычно возникает при недостатке памяти на пользовательском компьютере. В частности же, в появлении данной ошибки «виновен» следующий набор факторов:
- Недостаток памяти RAM на вашем ПК (рабочей памяти, планки которой установлены на материнской плате вашего компьютера). Если на вашем компьютере установлен всего 1 гигабайт памяти, вы будете встречаться с описываемой ошибкой довольно часто. Нормальным же ныне считается наличие на компьютере 4 гигабайт памяти и выше;
- Недостаток места на жёстком диске.
Когда вашему компьютеру не хватает физической R.A.M. памяти, он заимствует часть места на жёстком диске, и создаёт так называемую «виртуальную память». Система временно хранит в такой виртуальной памяти ту часть данных, которая не помещается в памяти обычной. Такие данные обычно хранятся в файле «pagefile.sys», размер которого может увеличиваться или уменьшаться в зависимости от специфики работы вашей ОС. Если на диске будет недостаточно места, файл «pagefile.sys» не сможет расти, и пользователь получит рассматриваемую ошибку.
- При одновременном запуске на ПК большого количества программ, каждая из которых бронирует часть памяти ПК под свои задачи;
- При запуск большого количества вкладок браузера. Веб-навигаторы уровня «Firefox» или «Google Chrome» способны занимать от 500 мегабайт до 1 гигабайта памяти под свой функционал, при этом число открытых вкладок и соответствующей обслуживающей памяти может быть ограничено системой. Специалисты Майрософт называют такую проблему «the desktop heap limitation» — «ограничение кучи рабочего стола»);
- Некорректная работа с памятью ряда программ (наиболее часто это игровые программы);
- Не оптимальный размер файла подкачки, с которым работает система.
Как исправить ошибку «Out of memory»
Для решения указанной проблемы рекомендую сделать следующее:
- Перезагрузите ваш ПК, и запустите требуемую программу вновь. Возможно, что проблема имеет случайный характер, и более повторяться не будет;
- Перед запуском нужной программы закройте другие ненужные программы (браузер, музыкальный или видео плеер, текстовый или графический редактор, мессенджер и так далее);
- Если проблема возникает во время серфинга в сети, закройте всё множество вкладок вашего браузера (при наличии), оставив лишь одну или две.
Альтернативным вариантом решения проблемы является установка соответствующего фикса от Майкрософт. Или использование расширений или дополнений для браузера уровня «The Great Suspender» для «Google Chrome», хорошо работающего с ненужными вкладками браузера.
- Добавьте оперативной памяти на ваш ПК. Если у вас на компьютере установлено 1-2 гигабайта памяти, будет оптимальным довести её объём до 4 гигабайт (а для 64-битных Виндовс 7, 8 и 10 версии рекомендую 8 и более гигабайт);
- Убедитесь, что на вашем жёстком диске (или SSD) достаточно свободного места. При необходимости, освободите диск от ненужных файлов;
- Используйте инструмент командной строки BCDEdit для изменения параметров загрузки системы. Если у вас на ПК установлена Виндовс 7 и более, запустите командную строку от имени администратора на Виндовс 7 и Виндовс 10, и в ней наберите:
bcdedit/set IncreaseUserVa 3072
И нажмите на ввод, и перезагрузите ваш ПК. Функционал данной команды позволяет выделить пользовательским приложениям 3 гигабайта оперативной памяти для работы. В некоторых системах этого может быть слишком много, потому если после ввода данной команды система начала чаще сбоить, то введите в командной строке от имени администратора:
bcdedit /set IncreaseUserVa 2560 — что позволит задействовать 2,5 гигабайта вместо ранее забронированных 3.
Если ситуацию этим исправить не удалось, верните настройки на состояние по умолчанию:
bcdedit /deletevalue IncreaseUserVa
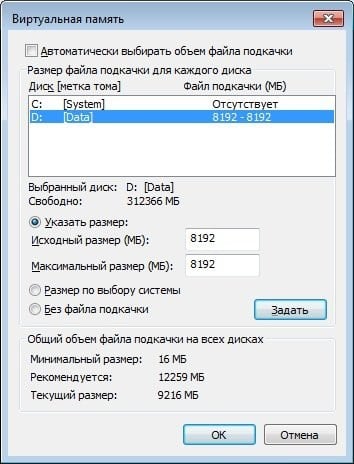
- Увеличьте объём файла подкачки. Нажмите кнопку «Пуск», в строке поиска введите sysdm.cpl и нажмите ввод. В открывшемся окне настроек системы выберите «Дополнительно» — «Быстродействие» — «Параметры» — «Дополнительно» — «Виртуальная память» — «Изменить». Снимите галочку с опции автоматического размера, поставьте галочку на «Указать размер», и поставьте исходный размер в 8192, и максимальный в 8192. Затем выберите «Задать»;
Установите нужный размер файла подкачки
Заключение
Ошибка «Out of memory» может иметь множество причин, связанных как с физическим недостатком памяти на ПК, так и другими детерминантами, изложенными мной выше. Для решения проблемы советую закрыть ненужные программы (вкладки браузера) на вашем компьютере (тем самым разгрузив его память), а самым эффективным инструментом является установка дополнительной планки памяти на ПК, что в большинстве случаев поможет избавиться от ошибки на вашем компьютере.
Источник