in cmd, ‘Query Session’ command is returning,
Error 5 getting sessionnames
Error [5]:Access is denied
on Windows 10 Remote desktop — Administrator user.
we have set, AllowRemoteRPC ‘s value to 1
under this HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server
But still problem persists.
Questions:
- what does
AllowRemoteRPCactually do and how it’s value is being used. - what to do to make Query Session command work.
asked Jan 2, 2019 at 9:03
9
I think the problem is in the UAC remote restrictions.
Do this on the target computer:
- Run
regedit -
Navigate to the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystem -
If an entry named
LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicyregistry entry does not exist,
create it as DWORD -
Double-click
LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicyand set its value to1.
Reference:
Microsoft’s
Description of User Account Control and remote restrictions in Windows Vista.
answered Jan 9, 2019 at 16:57
harrymcharrymc
431k30 gold badges495 silver badges876 bronze badges
1
Rather than changing registry values, you could always use PSEXEC from a command prompt or Invoke-Command from a PowerShell prompt to execute QWINSTA locally. Both of these will require you have administrative rights on the remote machine (which means opening the command prompt under other credentials, including the credentials as PSEXEC switches or, in the case of PowerShell, including -Credential (Get-Credential) in the command.
Command prompt example:
PSEXEC \MYPC cmd /c "qwinsta /server:localhost"
PowerShell example:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName MyPC -ScriptBlock { qwinsta /server:localhost }
zx485
2,17011 gold badges16 silver badges23 bronze badges
answered Sep 25, 2019 at 21:35
Содержание
- Как узнать имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере?
- Утилиты PSLoggedOn и Qwinsta
- Получаем имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере через PowerShell
- PowerShell скрипт для проверки пользователей на удаленных компьютерах
- Qwinsta server error 5
- Fork Bomb for Flutter
- Discovering Domains via a Time-Correlation Attack on Certificate Transparency
- Researching Open Source apps for XSS to RCE flaws
- Exploiting Arbitrary Object Instantiations in PHP without Custom Classes
- A Kernel Hacker Meets Fuchsia OS
- Catching bugs in VMware: Carbon Black Cloud Workload Appliance and vRealize Operations Manager
- Hunting for bugs in VMware: View Planner and vRealize Business for Cloud
- Fuzzing for XSS via nested parsers condition
- WinRAR’s vulnerable trialware: when free software isn’t free
- qwinsta — «Ошибка [5] — Отказано в доступе»
- Qwinsta server error 5
- Answered by:
- Question
- Answers
- All replies
Как узнать имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере?
Довольно часто администратору нужно быстро узнать имя пользователя, который выполнил вход на удаленном компьютере Windows. В это статье мы рассмотрим несколько утилит и PowerShell скриптов, которые помогут вам узнать имена пользователей, залогиненых на удаленных компьютерах в сети.
Утилиты PSLoggedOn и Qwinsta
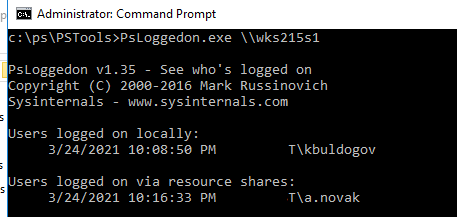
В комплекте утилит SysInternals PSTools от Microsoft есть консольная утилита PSLoggedOn.exe, которую можно использовать для получения имени пользователя, который вошел на удаленный компьютер, а также список подключенных к нему SMB сеансов.
Скачайте утилиту и запустите ее в формате:
Как вы видите, утилита вернула имя залогиненного пользователя (Users logged on locally), а также список пользователей, которые по сети используют ресурсы с этого компьютера (Users logged on via resource shares).
Если нужно получить только имя пользователя, вошедшего локально, используйте опцию –l:
Psloggedon.exe \wks215s1 –l
Утилита Psloggedon подключается к реестру и проверяет в нем имя пользователя, вошедшего локально. Для этого должна быть включена служба RemoteRegistry. Вы можете запустить ее и настроить автозапуск службы с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service RemoteRegistry –startuptype automatic –passthru
Start-Service RemoteRegistry
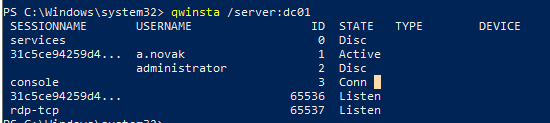
Также можно получить список сессий на удаленном компьютере с помощью встроенной утилиты qwinsta . Эта утилита должна быть знакома любому администратору, управляющему терминальными серверами с Remote Desktop Services. Чтобы получить список сессий с удаленного компьютера, выполнит команду:
Утилита возвращает список всех сессий (активных и отключенных по таймауту) на RDS сервере или десктопной редакции Windows 10 (даже если вы разрешили к ней множественные RDP подключения).
reg add «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server» /v «AllowRemoteRPC» /t «REG_DWORD» /d «1» /f
Получаем имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере через PowerShell
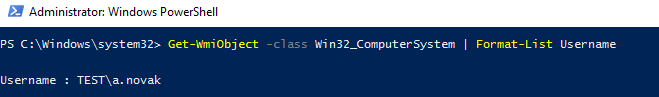
Вы можете получить имя пользователя, который залогинен на компьютере через WMI класс Win32_ComputerSystem. Откройте консоль PowerShell и выполните команду:
Get-WmiObject -class Win32_ComputerSystem | Format-List Username
Команда вернула имя пользователя, который выполнил вход на компьютер.
У командлета Get-WmiObject есть параметр –ComputerName, который можно использовать для получения доступа к WMI объектам на удаленном компьютере. Следующая команда вернет имя пользователя с удаленного компьютера:
(Get-WmiObject -class Win32_ComputerSystem –ComputerName wks215s1).Username
Данная команда показывает только пользователя, вошедшего на консоль (не через RDP).
Если нужно получить только имя пользователя на компьютере (без домена), воспользуетесь следующими командами:
$userinfo = Get-WmiObject -ComputerName ‘wks215s1’ -Class Win32_ComputerSystem
$user = $userinfo.UserName -split ‘\’
$user[1]
Get-CimInstance –ComputerName wks215s1 –ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem | Select-Object UserName
(Get-CimInstance -ComputerName wks215s1 -ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem).CimInstanceProperties | where<$_.Name -like «UserName»>| select value
GetCiminstance использует WinRM для подключения к удаленным компьютерам, поэтому на них нужно включить и настроить WinRM через GPO или командой:
PowerShell скрипт для проверки пользователей на удаленных компьютерах
Если вам нужно собрать информацию о пользователях сразу с нескольких компьютерах, можете использовать следующую PowerShell функцию получить имена пользователей.
На вход функции Get-LoggedUser нужно передать имена компьютеров, на которых нужно проверить имена пользователей:
Если для какого-то компьютера функция вернула пустое имя пользователя, значит на компьютер никто не залогинен.
Можно получить имена пользователей, которые работают на компьютерах в домене Active Directory. Для получения списка компьютеров нужно использовать командлет Get-ADComputer. В следующем примере мы получим имена пользователей, которые работают за активными компьютерами в определенном OU домена. Чтобы скрипт работал быстрее перед тем, как обратится к обратится к удаленному компьютеру, я добавил проверку его доступности по сети через ICMP пинг с помощью командлета Test-NetConnection:
Также обратите внимание, что вы можете хранить в свойствах компьютеров в AD имя пользователя, который выполнил вход. Для этого можно использовать логон скрипт, описанный в статье “Set-ADComputer: добавляем информацию о пользователе в свойства компьютеров AD”
После этого вам не нужно сканировать все компьютеры, чтобы найти где залогинен определенный пользователь. Можно найти компьютер пользователя простым запросом к Active Directory:
$user=’dvpetrov’
$user_cn=(get-aduser $user -properties *).DistinguishedName
Get-ADComputer -Filter «ManagedBy -eq ‘$user_cn’» -properties *|select name,description,managedBy|ft
Источник
Qwinsta server error 5
To properly assess the security of a web application, it’s important to analyze it with regard to the server it will run on. Many things depend on the server, from processing user requests to the easiest way of achieving RCE. Armed with knowledge about the server, we can identify vulnerabilities in an application and make it more secure.
In this article we’ll look at Jetty, a well-known web server and Java web container that is typically deployed behind an Apache or NGINX proxy server. Here’s what we’ll cover:
- How to find paths to all web applications on the server.
- How to achieve RCE using an XML file.
- How to bypass a web application firewall and remain unnoticed.
Continue reading
Fork Bomb for Flutter
Flutter applications can be found in security analysis projects or bugbounty programs. Most often, such assets are simply overlooked due to the lack of methodologies and ways to reverse engineer them. I decided not to skip this anymore and developed the reFlutter tool. This article describes the results of my research.
Discovering Domains via a Time-Correlation Attack on Certificate Transparency
Many modern websites employ an automatic issuance and renewal of TLS certificates. For enterprises, there are DigiCert services. For everyone else, there are free services such as Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL.
There is a flaw in a way that deployment of TLS certificates might be set up. It allows anyone to discover all domain names used by the same server. Sometimes, even when there is no HTTPS there!
In this article, I describe a new technique for discovering domain names. Afterward, I show how to use it in threat intelligence, penetration testing, and bug bounty.
Researching Open Source apps for XSS to RCE flaws
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is one of the most commonly encountered attacks in web applications. If an attacker can inject a JavaScript code into the application output, this can lead not only to cookie theft, redirection or phishing, but also in some cases to a complete compromise of the system.
In this article I’ll show how to achieve a Remote Code Execution via XSS on the examples of Evolution CMS, FUDForum, and GitBucket.
Exploiting Arbitrary Object Instantiations in PHP without Custom Classes
During an internal penetration test, I discovered an unauthenticated Arbitrary Object Instantiation vulnerability in LAM (LDAP Account Manager), a PHP application.
PHP’s Arbitrary Object Instantiation is a flaw in which an attacker can create arbitrary objects. This flaw can come in all shapes and sizes. In my case, the vulnerable code could have been shortened to one simple construction:
That’s it. There was nothing else there, and I had zero custom classes to give me a code execution or a file upload. In this article, I explain how I was able to get a Remote Code Execution via this construction.
A Kernel Hacker Meets Fuchsia OS
Fuchsia is a general-purpose open-source operating system created by Google. It is based on the Zircon microkernel written in C++ and is currently under active development. The developers say that Fuchsia is designed with a focus on security, updatability, and performance. As a Linux kernel hacker, I decided to take a look at Fuchsia OS and assess it from the attacker’s point of view. This article describes my experiments.
Catching bugs in VMware: Carbon Black Cloud Workload Appliance and vRealize Operations Manager
Last year we found a lot of exciting vulnerabilities in VMware products. The vendor was notified and they have since been patched. This is the second part of our research. This article covers an Authentication Bypass in VMware Carbon Black Cloud Workload Appliance (CVE-2021-21978) and an exploit chain in VMware vRealize Operations (CVE-2021-21975, CVE-2021-22023, CVE-2021-21983) which led to Remote Code Execution.
Hunting for bugs in VMware: View Planner and vRealize Business for Cloud
Last year we found a lot of exciting vulnerabilities in VMware products. They were disclosed to the vendor, responsibly and have been patched. It’ll be a couple of articles, that disclose the details of the most critical flaws. This article covers unauthenticated RCEs in VMware View Planner (CVE-2021-21978) and in VMware vRealize Business for Cloud (CVE-2021-21984).
We want to thank VMware and their security response center for responsible cooperation. During the collaboration and communication, we figured out, that the main goal of their approach to take care of their customers and users.
Fuzzing for XSS via nested parsers condition
When communicating online, we constantly use emoticons and put text in bold. Some of us encounter markdown on Telegram or GitHub, while forum-dwellers might be more familiar with BBCode.
All this is made possible by parsers, which find a special string (code/tag/character) in messages and convert it into beautiful text using HTML. And as we know, wherever there is HTML, there can be XSS.
This article reveals our novel technique for finding sanitization issues that could lead to XSS attacks. We show how to fuzz and detect issues in the HTML parsers with nested conditions. This technique allowed us to find a bunch of vulnerabilities in the popular products that no one had noticed before.
The technique was presented at Power Of Community 2021.
WinRAR’s vulnerable trialware: when free software isn’t free
In this article we discuss a vulnerability in the trial version of WinRAR which has significant consequences for the management of third-party software. This vulnerability allows an attacker to intercept and modify requests sent to the user of the application. This can be used to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) on a victim’s computer. It has been assigned the CVE ID – CVE-2021-35052.
Источник
qwinsta — «Ошибка [5] — Отказано в доступе»
Я получаю сообщение об ошибке «Доступ запрещен», хотя у меня нет проблем с подключением к удаленному рабочему столу. Мой компьютер — Win7, цели — WinXP или Server 2003.
Возможно, я неправильно указываю имя СЕРВЕРА:
qwinsta /SERVER:XXYYZZ02
я пробовал
qwinsta /SERVER:\XXYYZZ02
qwinsta /SERVER:domainXXYYZZ02
qwinsta /SERVER:domain/XXYYZZ02
qwinsta /SERVER:1.2.3.4
Я делаю что-то неправильно? TIA .
(Проблема, которую я пытаюсь решить, состоит в том, что нескольким сотрудникам службы поддержки необходимо подключиться к одним и тем же серверам и отключить друг друга в середине сеанса.)
Найдено на веб-сайте Dell, это сработало для меня с той же проблемой. «Это означает, что удаленному компоненту RPC не удалось выполнить запрошенную операцию. Это связано с тем, что по умолчанию ему не разрешено работать со службой терминала (удаленный рабочий стол) через RPC. Чтобы изменить этот параметр, чтобы включить API удаленного рабочего стола через RPC, вам необходимо найдите следующий раздел реестра:
HKLM SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Control Терминальный сервер
Затем добавьте значение DWORD с именем «AllowRemoteRPC» и измените его значение на 1. «
В моем случае он был установлен на «0». Я поменял его на 1, и все было хорошо.
Обратитесь к этой ссылке для получения правильных имен команд и альтернатив: http://makezine.com/2007/08/15/howto-kill-terminal-services-s/
Возможно, вы захотите попробовать выполнить из окна cmd, запущенного в режиме администратора.
Можете ли вы войти в систему любым другим способом? например: mstsc / console или через виртуальную консоль? Я спрашиваю, потому что тогда вы можете проверить настройки аутентификации сервера на серверах.
Источник
Qwinsta server error 5
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Answered by:
Question
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Answers
OK, it is fine to issue that inside that machine. Let us name this machine as PC A. Is it possible to get the same information, from one other machine (not PC A), which resides on the same domain of PC A?
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Yes you can see remote machine’s running tasks using «tasklist /s « command. Here, in our case we need to get info about RDP sessions of PC A from non PC A system and command will be.
C:>tasklist /s «PC A» /v /fi «IMAGENAME eq mstsc.exe»
Regards, Ravikumar P
Could you please elaborate more and what are you trying to accomplish?
Regards, Ravikumar P
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Supposing I am now acting as Network administrator, and I want to see whether one specific user is using Terminal service and is right now accessing any other machine remotely.
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Probably this thread will explain you, how we can accomplish it.
Regards, Ravikumar P
A similar discussion
List open sessions multiple servers
I do not represent the organisation I work for, all the opinions expressed here are my own.
This posting is provided «AS IS» with no warranties or guarantees and confers no rights.
If you found this post helpful, please give it a «Helpful» vote.
If it answered your question, remember to mark it as an «Answer».
This posting is provided «AS IS» with no warranties and confers no rights! Always test ANY suggestion in a test environment before implementing!
Thanks all. If I get this in the client machine,
C:Usershuamin>qwinsta /server. 5.44
Error 5 getting sessionnames
Error [5]:Access is denied.
does it mean I must have logged in as administrator of the network?
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Thanks all. If I get this in the client machine,
C:Usershuamin>qwinsta /server. 5.44
Error 5 getting sessionnames
Error [5]:Access is denied.
does it mean I must have logged in as administrator of the network?
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Yes you must be a administrator to perform this command.This sort of error you get when you does not have admin right to particular machine/server.
As I suggested you above check this thread http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/is/winserverDS/thread/8dffac95-2b58-4ede-8868-b7d1e7cf4fbb to know information about the workstation and corresponding logged on users.
Regards, Ravikumar P
Many thanks. On one other machine, in which I am using administrator login and am having one terminal session to one other machine, but I do not see the details of that, by this?
C:UsersHP>qwinsta /server. 241.33
SESSIONNAME USERNAME ID STATE TYPE DEVICE
services 0 Disc
rdp-tcp#0 HP 1 Active rdpwd
console 3 Conn
rdp-tcp 65536 Listen
For instance, I can’t see machine name of that remote session. why?
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Many thanks. On one other machine, in which I am using administrator login and am having one terminal session to one other machine, but I do not see the details of that, by this?
C:UsersHP>qwinsta /server. 241.33
SESSIONNAME USERNAME ID STATE TYPE DEVICE
services 0 Disc
rdp-tcp#0 HP 1 Active rdpwd
console 3 Conn
rdp-tcp 65536 Listen
For instance, I can’t see machine name of that remote session. why?
Many Thanks & Best Regards, Hua Min
Command qwinsta is used to display the sessions of particular server/workstation, which you want to query. Seems you are using IP address of the host to find active sessions.If you want to know host name use nbtstat command and the syntax can be nbtstat -A IP address
qwinsta command syntax is:qwinsta /server:
Источник
Довольно часто администратору нужно быстро узнать имя пользователя, который выполнил вход на удаленном компьютере Windows. В это статье мы рассмотрим несколько утилит и PowerShell скриптов, которые помогут вам узнать имена пользователей, залогиненых на удаленных компьютерах в сети.
Содержание:
- Утилиты PSLoggedOn и Qwinsta
- Получаем имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере через PowerShell
- PowerShell скрипт для проверки пользователей на удаленных компьютерах
Утилиты PSLoggedOn и Qwinsta
В комплекте утилит SysInternals PSTools от Microsoft есть консольная утилита PSLoggedOn.exe, которую можно использовать для получения имени пользователя, который вошел на удаленный компьютер, а также список подключенных к нему SMB сеансов.
Скачайте утилиту и запустите ее в формате:
psloggedon \RemoteCompName
Как вы видите, утилита вернула имя залогиненного пользователя (Users logged on locally), а также список пользователей, которые по сети используют ресурсы с этого компьютера (Users logged on via resource shares).
Если нужно получить только имя пользователя, вошедшего локально, используйте опцию –l:
Psloggedon.exe \wks215s1 –l
Утилита Psloggedon подключается к реестру и проверяет в нем имя пользователя, вошедшего локально. Для этого должна быть включена служба RemoteRegistry. Вы можете запустить ее и настроить автозапуск службы с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service RemoteRegistry –startuptype automatic –passthru
Start-Service RemoteRegistry
Также можно получить список сессий на удаленном компьютере с помощью встроенной утилиты
qwinsta
. Эта утилита должна быть знакома любому администратору, управляющему терминальными серверами с Remote Desktop Services. Чтобы получить список сессий с удаленного компьютера, выполнит команду:
qwinsta /server:dc01
Утилита возвращает список всех сессий (активных и отключенных по таймауту) на RDS сервере или десктопной редакции Windows 10 (даже если вы разрешили к ней множественные RDP подключения).
Если при подключении к удаленному серверу через qwinsta вы получаете ошибку Error 5 Access Denied, проверьте что на удаленном компьютере разрешено удаленное управление пользователями через RPC. Включите, если нужно через реестр следующей командой или через GPO:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server" /v "AllowRemoteRPC" /t "REG_DWORD" /d "1" /f
Получаем имя пользователя на удаленном компьютере через PowerShell
Вы можете получить имя пользователя, который залогинен на компьютере через WMI класс Win32_ComputerSystem. Откройте консоль PowerShell и выполните команду:
Get-WmiObject -class Win32_ComputerSystem | Format-List Username
Команда вернула имя пользователя, который выполнил вход на компьютер.
У командлета Get-WmiObject есть параметр –ComputerName, который можно использовать для получения доступа к WMI объектам на удаленном компьютере. Следующая команда вернет имя пользователя с удаленного компьютера:
(Get-WmiObject -class Win32_ComputerSystem –ComputerName wks215s1).Username
Данная команда показывает только пользователя, вошедшего на консоль (не через RDP).
Также для получения информации с удаленных компьютеров можно использовать PSRemoting с помощью командлета Invoke-Command.
Если нужно получить только имя пользователя на компьютере (без домена), воспользуетесь следующими командами:
$userinfo = Get-WmiObject -ComputerName 'wks215s1' -Class Win32_ComputerSystem
$user = $userinfo.UserName -split '\'
$user[1]
В современных версиях PowerShell Core (pwsh.exe) вместо Get-WmiObject нужно использовать CIM командлет Get-CimInstance:
Get-CimInstance –ComputerName wks215s1 –ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem | Select-Object UserName
Или
(Get-CimInstance -ComputerName wks215s1 -ClassName Win32_ComputerSystem).CimInstanceProperties | where{$_.Name -like "UserName"}| select value
GetCiminstance использует WinRM для подключения к удаленным компьютерам, поэтому на них нужно включить и настроить WinRM через GPO или командой:
WinRM quickconfig
PowerShell скрипт для проверки пользователей на удаленных компьютерах
Если вам нужно собрать информацию о пользователях сразу с нескольких компьютерах, можете использовать следующую PowerShell функцию получить имена пользователей.
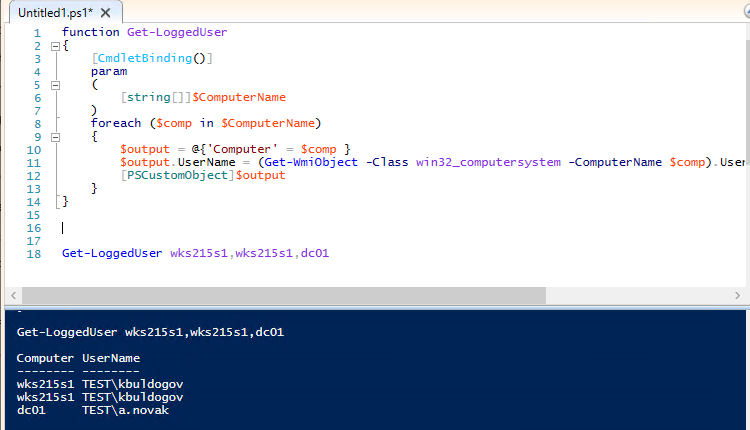
function Get-LoggedUser
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param
(
[string[]]$ComputerName
)
foreach ($comp in $ComputerName)
{
$output = @{'Computer' = $comp }
$output.UserName = (Get-WmiObject -Class win32_computersystem -ComputerName $comp).UserName
[PSCustomObject]$output
}
}
На вход функции Get-LoggedUser нужно передать имена компьютеров, на которых нужно проверить имена пользователей:
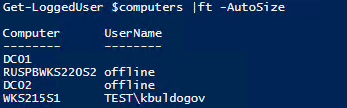
Get-LoggedUser wks215s1,wks215s2,dc01
Если для какого-то компьютера функция вернула пустое имя пользователя, значит на компьютер никто не залогинен.
Можно получить имена пользователей, которые работают на компьютерах в домене Active Directory. Для получения списка компьютеров нужно использовать командлет Get-ADComputer. В следующем примере мы получим имена пользователей, которые работают за активными компьютерами в определенном OU домена. Чтобы скрипт работал быстрее перед тем, как обратится к обратится к удаленному компьютеру, я добавил проверку его доступности по сети через ICMP пинг с помощью командлета Test-NetConnection:
function Get-LoggedUser
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param
(
[string[]]$ComputerName
)
foreach ($comp in $ComputerName)
{
if ((Test-NetConnection $comp -WarningAction SilentlyContinue).PingSucceeded -eq $true)
{
$output = @{'Computer' = $comp }
$output.UserName = (Get-WmiObject -Class win32_computersystem -ComputerName $comp).UserName
}
else
{
$output = @{'Computer' = $comp }
$output.UserName = "offline"
}
[PSCustomObject]$output
}
}
$computers = (Get-AdComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true"} -SearchBase 'OU=Kazan,DC=winitpro,DC=loc').Name
Get-LoggedUser $computers |ft -AutoSize
Также обратите внимание, что вы можете хранить в свойствах компьютеров в AD имя пользователя, который выполнил вход. Для этого можно использовать логон скрипт, описанный в статье “Set-ADComputer: добавляем информацию о пользователе в свойства компьютеров AD”
После этого вам не нужно сканировать все компьютеры, чтобы найти где залогинен определенный пользователь. Можно найти компьютер пользователя простым запросом к Active Directory:
$user='dvpetrov'
$user_cn=(get-aduser $user -properties *).DistinguishedName
Get-ADComputer -Filter "ManagedBy -eq '$user_cn'" -properties *|select name,description,managedBy|ft
Содержание
- Ошибка 5 при получении имен сеанса msg windows 10
- Вопрос
- Все ответы
- Как исправить ошибку 5 при получении имен сеансов в Windows 10
- Ошибка 5 Получение имен сеансов в решении Windows 10
- Registry Tweak
- How to Fix Error 5 Getting Session Names in Windows 10
- Error 5 Getting Session Names in Windows 10 Solution
- Registry Tweak
- Ошибка 5 при получении имен сеанса msg windows 10
- Вопрос
- Команда MSG – отправить сообщение пользователю.
Ошибка 5 при получении имен сеанса msg windows 10
Вопрос
Ok after 2 days of research and messing with policys i still have yet to resolve this issue. Due to vista not having netsend anymore I tried using the msg.exe command. So far I have got it to work just on my local computer. But sending it to other vista computers It gives me an error:
Error 5 getting session names
I am computer Atlantis
Destination: computer designated as «Challenger»
Both running Vista Business SP1
msg /server:atlantis admin «Test Message»
(local to local pc works)
msg /server:challenger admin «Test Message»
—> Response: «Error 5 Getting Session Names»
We are in the same work group, we are not part of a domain
Any help would be appreciated. From reading it seems to be a policy edit that needs to be changed, but I do not know what to change, so any detailed instructions would be greatly appreciated.
Alternative i tried: Also i downloaded netsend by czero.com and I can only send the message to XP computers. I cannot send a message to even myself.
Все ответы
Msg.exe can only send message to a terminal server role, based on my test.
Both Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 with terminal service correctly configured can receive the message sent by Msg.exe from Windows Vista-based PC.
So if this only works as a terminal service role then what is the alternative to netsend because the program from cezeo as the netsend replacement doesn’t seem to work either.
Based on some discussions about this topic, some community members provide the following tool as the replacement of net send that is not included in Windows Vista:
It’s said to support Windows Vista. Please give it a try.
Important Note: This response contains a reference to a third party World Wide Web site. Microsoft is providing this information as a convenience to you. Microsoft does not control these sites and has not tested any software or information found on these sites; therefore, Microsoft cannot make any representations regarding the quality, safety, or suitability of any software or information found there. There are inherent dangers in the use of any software found on the Internet, and Microsoft cautions you to make sure that you completely understand the risk before retrieving any software from the Internet.
Actually based on my research and use of this tool, this seems to only work for machines doing Vista->XP machines
Just an update on this issue that I forgot to post on this thread.
The cezero netsend allows you to send netsend messages but it doesn’t actually allow receiving because there is no winpopup installed on vista. As an alternative, msg.exe does work only in a domain environment.
For those of you on a workgroup environment such as me, I have found a solution that actually works.
Program called WinSent 1.1, install that czero netsend and just run this program, it is a freeware basic messaging window that is the closest thing I can find on the web to resemble netsend. It pops up and can be closed down.
Issue I ran into working at a library environment, patrons tend to turn the program off, work around I found.
I’m sorry I can’t find the tiny program, but there is a program that can be found on google, its about 50k big, what it does is search for a particular instance of a program of your choice and if its closed it reopens it to your system tray, the little program runs as a hidden process and you can set it to whatever time you want it to check. ex: 1 second, 5 seconds etc.
Other issue that I have yet to fix nor will I be able to fix, once the pop up message window actualyl opens, it can be dragged out of the viewable range and that is the end of that. Only work around I found is that when you log off using steadystate and log back into the profile it is reset.
Источник
Как исправить ошибку 5 при получении имен сеансов в Windows 10
Сервер Windows 10 позволяет отправлять сообщения, применяя команду MSG (msg.exe) в той же локальной сети. Эта функция была доступна со времен стартовой версии Windows, но тогда использовалась команда «time net send». Команда MSG заменила команду time net send в Windows Vista. Немногие пользователи жалуются, что при выполнении команды возникает ошибка 5 при получении имен сеансов.
Вы можете отправить SMS в командной строке (admin), используя синтаксис msg. msg.exe предназначен для обмена сообщениями с пользователями терминалов, поэтому причиной этой проблемы является неправильная конфигурация или отсутствие правильных настроек на сервере. Таким образом, простая настройка реестра устраняет проблему и позволяет снова отправлять сообщения.
Команда msg.exe не требует сторонних или встроенных средств. service и работает на Windows 10 pro и business. К сожалению, процесс заканчивается ошибкой 5 при получении имен сеансов или отказом в доступе на некоторых машинах.
Ошибка 5 Получение имен сеансов в решении Windows 10
Прежде чем переходить к следующему решению, убедитесь, что вы используете правильный синтаксис в командной строке с повышенными привилегиями. Например, определите сервер, пользователя и поместите сообщение в строковом формате. Предположим, что пользователь — Джей Роберт, который запускает jrobert-PC, тогда синтаксис msg.exe будет
C: msg/server: jrobert-pc jrobert «Пожалуйста, помогите мне», где Пожалуйста, помогите мне — это текст отправляемого сообщения.
Когда вы используете IP-адрес вместо имени ПК, вы можете столкнуться с проблемой, например, отказано в доступе или Ошибка 5 при получении имен сеансов.
Убедитесь, что вы вошли в Windows 10 как администратор и используете разрешение для сеанса, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять сообщения с помощью команды msg.
Registry Tweak
Манипуляции с ключами реестра — рискованная работа, поэтому мы рекомендуем сделать резервную копию перед запуском процесса.
Шаг 1. Нажмите клавишу с логотипом Windows, введите regedit.exe и затем нажмите Enter. Выберите Да в запросе управления учетной записью пользователя, блокируя экран.
Шаг 2: Скопируйте путь
Computer HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Control Terminal Server
вставьте в адресную строку редактора реестра и нажмите Enter.
Шаг 3. Перейдите на правую панель и найдите ключ AllowRemoteRPC. Найдя его, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите в меню «Изменить».
Закройте редактор реестра, перезагрузите систему Windows 10 и пользуйтесь командой MSG.
Источник
How to Fix Error 5 Getting Session Names in Windows 10
Windows 10 server lets you send a message applying MSG command (msg.exe) on the same Local network. This feature has been available since the starting version of Windows, but that time “time net send” command was used. MSG command replaced the time net send in Windows Vista. Few users complain that the get Error 5 Getting Session Names issue while running the command.
You can send SMS at command prompt (admin) using msg syntax. msg.exe is designed for messaging to terminal users so the cause of this issue is a misconfiguration or lack of proper settings on the server. So a simple registry tweak repairs the issue and makes you able to send messages again.
msg.exe command doesn’t need a 3rd party or built-in service and works on Windows 10 pro and business. Unfortunately, the process ends up with Error 5 getting session names or Access denied on some machines.
Error 5 Getting Session Names in Windows 10 Solution
Before going for the following solution, make sure that you are using correct syntax in the elevated Command prompt. For example, define the server, user, and put the message in string format. Suppose the user is J Robert who is running jrobert-PC then the syntax for msg.exe would be
C: msg /server:jrobert-pc jrobert “Please help me” where Please help me is the text of the message you are sending.
When you use IP Address instead of the PC name you might find the issue like Access denied or Error 5 getting session names.
Ensure that you have logged into Windows 10 as an administrator and avail the permission for the session to be able to send the messages employing msg command.
Registry Tweak
Registry key manipulation is a risky work so we recommend taking a backup of the prior to starting the process.
Step-1: Press Windows logo key, type regedit.exe and then hit Enter. Select Yes on the User account control prompt locking the screen.
Step-2: Copy the path
paste into the address bar of the Registry Editor and press Enter.
Step-3: Go to the right pane and locate the key AllowRemoteRPC. Once found, make a right click and select Modify from the menu.
Step-4: On the Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value pop up, enter 1 in the value data field and select OK.
Close the registry editor, reboot the Windows 10 system and enjoy using MSG command.
Источник
Ошибка 5 при получении имен сеанса msg windows 10
Вопрос
I’m trying to send a message to another computer over network by using msg command. Both computers are using Win 7 Ultimate and are in same workgroup. I can send messages to myself just fine, but I get «Error 1825 getting session names» when I try to send a message to that (or any other) computer.
-known solution to Error 5 (setting AllowRemoteRPC to 1 in registry)
-turning off firewall
-starting any service that has something to do with remote connection
-fixing WMI ports and port-forwarding them. Don’t know if I succeeded and if it’s even relevant, but I came across this when searching for solution to error 1825
I have a feeling it has something to do with router. I replaced original firmware with Tomato (v1.27) because of «quality of service». Router model is Linksys WRT54G/GS/GL. Any settings I should look for?
UPDATE: I created a homegroup, and while both computers are joined, msg command gives me error 5 instead of 1825. As I said, I already applied known fix for error 5, so it must be something else. Also, homegroup doesn’t work as it should, computers don’t detect each other and I do share libraries.
Another thing, when I joined the homegroup, cmd font became smaller on both computers. It should be 8×12 size by default, but 8×12 option disappeared. I fixed that now, but it’s still weird that joining a homegroup removed default font size in command prompt. It makes me wondering what else did homegroup mess up.
Источник
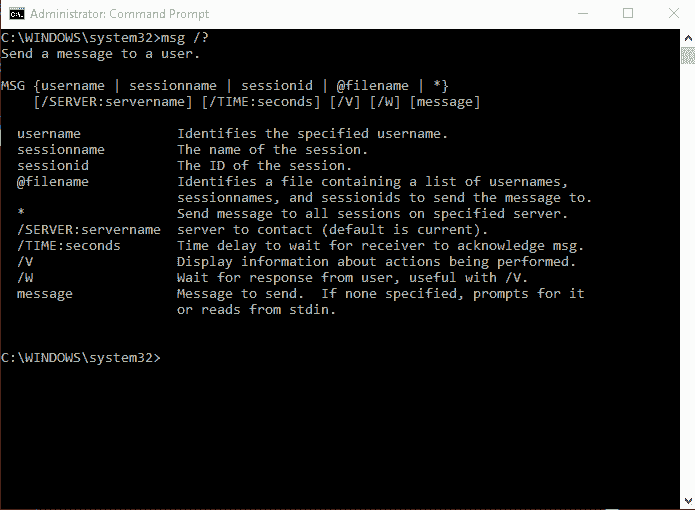
Команда MSG – отправить сообщение пользователю.
Формат командной строки:
Описание параметров командной строки :
Нынешняя реализация msg.exe прекрасно подходит для обмена сообщениями между сеансами локальных и терминальных пользователей в пределах одной системы, однако, в случаях обмена между разными компьютерами локальной сети, потребуется изменить некоторые настройки безопасности, принятые по умолчанию в операционных системах Windows Vista, 7 и более поздних.
При стандартных настройках, отправка сообщения пользователям удаленных компьютеров не выполняется и сопровождается сообщением:
Ошибка 1722 при получении имен сеанса
Это означает, что на компьютере, где должно приниматься посылаемое сообщение, невозможно получить информацию о вошедших в систему пользователях. Причиной может быть то, что брандмауэр блокирует входящие соединения, недостаточны права пользователя по отношению к удаленной системе, запрет удаленного вызова процедур в параметрах службы сервера терминалов. Как минимум, для обмена сообщениями с использованием команды msg между компьютерами, необходимо иметь учетную запись пользователя, действительную по отношению к удаленной системе и выполнить следующие настройки:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server]
«AllowRemoteRPC»=dword:00000001
Примеры использования MSG :
Для выполнения команды msg от имени другого пользователя можно воспользоваться утилитой PSExec из пакета PSTools или штатным средством runas.exe
runas /user:otheruser «msg * /server:win10 Test message»
Сообщения, отправляемые командой msg локальному пользователю компьютера с операционной системой Windows XP, который отсутствует ( еще не вошел в Windows ) отображаются в окне с приглашением к регистрации в системе и могут быть доступны посторонним.
Источник