На чтение 2 мин Опубликовано 06.04.2020
крипты работали очень хорошо, когда я выполнял их напрямую, например «./script.sh» и «sh script.sh».
Но они не работали, когда я запускал их командой run-parts.
Для тех, кто интересуется, команда run-parts запускает все скрипты в каталоге.
Если вы получили такую ошибку при запуске скрипта, этот быстрый совет поможет вам исправить ошибку «Exec format error» при запуске скриптов с командой run-parts на Linux.
Решение ошибки «Exec format» при запуске скриптов командой run-parts
Чтобы запустить все скрипты в папке «Documents», я запустил:
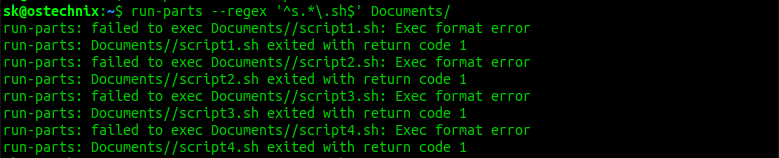
$ run-parts --regex '^s.*.sh$' Documents
Я получил следующее сообщение об ошибке:
run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script1.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script1.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script2.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script2.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script3.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script3.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script4.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script4.sh exited with return code 1
Чтобы исправить «ошибку формата Exec», вам нужно добавить шебанг в начале ваших скриптов, чтобы ядро знало, как их запускать.
Для тех, кому интересно, шебанг – это последовательность символов, состоящая из знака числа символов и восклицательного знака (#!) в начале скрипта.
Когда вы добавляете shebang в начале текстового файла, он интерпретируется как исполняемый файл.
Большинство скриптов начинается с шебанга.
Вот несколько типичных примеров Шебанга:
Bourne shell, или совместимый шеллl:
#!/bin/sh
Bash:
Perl:
Python 2.x:
Python 3.x:
#!/usr/bin/python3
Это то, что мы называем шебанг.
Теперь вернемся к теме.
Отредактируйте ваши скрипты, используя ваш любимый редактор:
$ nano Documents/itsecforu.sh
Добавьте шебанг в начале скрипта:
#!/bin/sh
Теперь вы можете без проблем запускать скрипты с помощью команды run-parts, используя команду run-parts.
Вы также можете использовать утилиту ShellCheck для поиска проблем в своих скриптах оболочки.
Пожалуйста, не спамьте и никого не оскорбляйте.
Это поле для комментариев, а не спамбокс.
Рекламные ссылки не индексируются!
When I was trying to run all scripts in a directory using run-parts command, I encountered with an error — «run-parts: failed to exec script.sh: Exec format error». The scripts worked just fine when I directly execute them like «./script.sh» and «sh script.sh». But they didn’t work when I ran them with run-parts command. For those wondering, the run-parts command will run all scripts in a directory. If you got an error like this while running a script, this quick tip will help you to fix «Exec format error» when running scripts with run-parts command in Linux.
Fix «Exec format error» When Running Scripts With run-parts Command
To run all scripts in the Documents folder, I ran:
$ run-parts --regex '^s.*.sh$' Documents/
I got the following error message:
run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script1.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script1.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script2.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script2.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script3.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script3.sh exited with return code 1 run-parts: failed to exec Documents/script4.sh: Exec format error run-parts: Documents/script4.sh exited with return code 1
run-parts: failed to exec script.sh: Exec format error
To fix «Exec format error», you need to add a shebang at the start of your scripts so the kernel will know how to run them. For those wondering, a shebang is the character sequence consisting of the characters number sign and exclamation mark (#!) at the beginning of a script. When you add the shebang at the start of a text file, it is interpreted as an executable file.
Most scripts starts with a shebang. Here are some typical shebang examples.
Bourne shell, or a compatible shell:
#!/bin/sh
Bash:
Perl:
Python 2.x:
Python 3.x:
This is what we call a shebang.
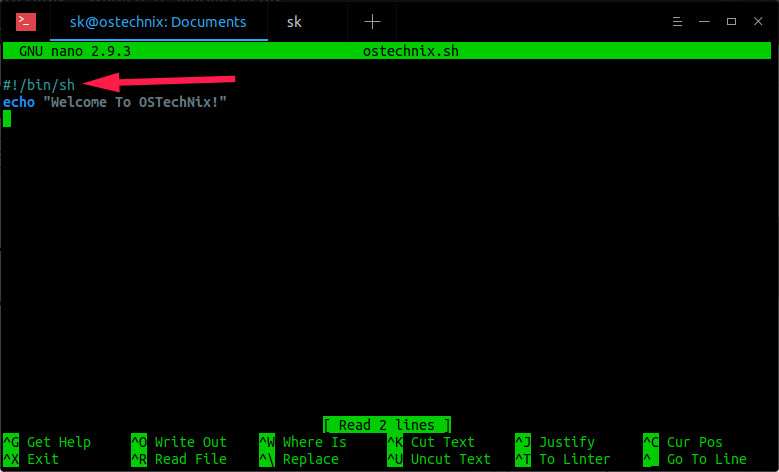
Now, let us get back to the topic. Edit your scripts using your favorite editor:
$ nano Documents/ostechnix.sh
Add the following shebang at the beginning of the script:
#!/bin/sh
Fix «Exec format error» When Running Scripts With run-parts
Now you can be able to run the scripts with run-parts command without any issues using run-parts command.
Update:
As one of our reader Mr.Danesh mentioned in the comment section below, Instead of hard-coding the path of the interpreter, e.g.
#!/usr/bin/python3
We can use:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
This is more portable in case the interpreter is installed in some other (non-default) directory. env is a shell command for Linux and Unix-like operating systems. It is often used by shell scripts to launch the correct interpreter.
You can also use ShellCheck utility to find problems in your shell scripts.
- ShellCheck – A Free Utility To Find Bugs In Your Shell Scripts
Hope this helps.
Содержание
- Fix “Exec format error” When Running Scripts With run-parts Command
- Fix «Exec format error» When Running Scripts With run-parts Command
- Fixing exec format errors with Docker ENTRYPOINT Scripts on Windows
- You may have gotten cryptic errors when trying to use ENTRYPOINT scripts in your images while running Windows. Here’s how to fix them.
- Does This Error Look Familiar?
- My ENTRYPOINT Script Was Super Basic
- Time to Investigate the Dockerfile
- Thought Process on Debugging This Further
- Resolving the Error on IRC
- Configuring VSCode and WSL for LF Line Endings
- Installing and Using dos2unix
- BONUS: Applying This Process to Other Problems
- Free Intro to Docker Email Course
- Handle Exec Format Error In 8 Simple Points
- What is Exec Format Error?
- Exec Format Error Linux
- Exec format error macOS
- Exec format error java
- Exec format error python
- Exec format error docker
- Exec format error raspberry pi
- How to execute arm binary files on Linux
Fix “Exec format error” When Running Scripts With run-parts Command
When I was trying to run all scripts in a directory using run-parts command, I encountered with an error — «run-parts: failed to exec script.sh: Exec format error». The scripts worked just fine when I directly execute them like «./script.sh» and «sh script.sh». But they didn’t work when I ran them with run-parts command. For those wondering, the run-parts command will run all scripts in a directory. If you got an error like this while running a script, this quick tip will help you to fix «Exec format error» when running scripts with run-parts command in Linux.
Fix «Exec format error» When Running Scripts With run-parts Command
To run all scripts in the Documents folder, I ran:
I got the following error message:
run-parts: failed to exec script.sh: Exec format error
To fix «Exec format error», you need to add a shebang at the start of your scripts so the kernel will know how to run them. For those wondering, a shebang is the character sequence consisting of the characters number sign and exclamation mark (#!) at the beginning of a script. When you add the shebang at the start of a text file, it is interpreted as an executable file.
Most scripts starts with a shebang. Here are some typical shebang examples.
Bourne shell, or a compatible shell:
Bash:
Perl:
Python 2.x:
Python 3.x:
This is what we call a shebang.
Now, let us get back to the topic. Edit your scripts using your favorite editor:
Add the following shebang at the beginning of the script:
Fix «Exec format error» When Running Scripts With run-parts
Now you can be able to run the scripts with run-parts command without any issues using run-parts command.
Update:
As one of our reader Mr.Danesh mentioned in the comment section below, Instead of hard-coding the path of the interpreter, e.g.
This is more portable in case the interpreter is installed in some other (non-default) directory. env is a shell command for Linux and Unix-like operating systems. It is often used by shell scripts to launch the correct interpreter.
You can also use ShellCheck utility to find problems in your shell scripts.
Источник
Fixing exec format errors with Docker ENTRYPOINT Scripts on Windows
You may have gotten cryptic errors when trying to use ENTRYPOINT scripts in your images while running Windows. Here’s how to fix them.
Docker ENTRYPOINT scripts are a wonderful thing, but it’s not so wonderful when they start failing in unexpected ways, especially when you’re very confident that “identical” ENTRYPOINT scripts worked on other Docker hosts.
Does This Error Look Familiar?
standard_init_linux.go:195: exec user process caused «exec format error»
I’m not someone who hacks on the Docker code base itself but when I encountered this error, the exec caught my eye. I thought “hmm, well I’m using exec «$@» in my entrypoint, maybe something is wrong with that?”.
But I knew there wasn’t much that could go wrong because the script did nothing especial.
My ENTRYPOINT Script Was Super Basic
It does nothing except pass control back to whatever process is ran in your CMD instruction in your Dockerfile . That’s what exec «$@» does.
Setting #!/bin/sh is standard for setting up a shell environment. This is exactly what the official PostgreSQL image uses in its ENTRYPOINT script. It also uses set -e which tells your shell to halt on any error, and finally it also ends its script off with exec «$@» .
Using that logic, we can conclude without a doubt that there is nothing wrong with the above script in terms of syntax, yet it continues to throw that exec error.
Time to Investigate the Dockerfile
If the script isn’t the issue then it must be the ENTRYPOINT instruction or something to do with permissions on the script itself. Here’s the important bits of the Dockerfile :
If I’ve learned anything from working as a web developer for the last
20 years, it’s that you should never trust anything from the client.
In this context, that means I shouldn’t trust that the script is already executable when building the Docker image, so even though it adds an extra layer to the image, it’s important to chmod +x the script in the Dockerfile .
I was already doing that because I’ve been bit by that issue in the past.
The entrypoint location is also normal. That’s the absolute path to where it exists inside of the Docker image (it was COPY вЂd in a previous step not listed above).
Thought Process on Debugging This Further
At this point the Docker image builds but it fails to run due to the script. The next step is simple then, just comment out the ENTRYPOINT instruction and re-build it. Sure enough, the image builds and runs correctly.
With this new information we now have 5 facts:
- The script itself has no syntax errors
- The script is most definitely executable
- The Docker image builds, so the ENTRYPOINT has the correct file location
- A very popular Docker image (PostgreSQL) is using a nearly identical entrypoint
- The script is causing the error because it works without the ENTRYPOINT instruction
It’s unlikely there’s something wrong with the Docker daemon since the PostgreSQL image confirms it works, so I’m happy to rule that out considering I’ve ran the PostgreSQL image using the same Docker daemon version as I did with my entrypoint script.
Resolving the Error on IRC
At this point my eye was starting to twitch, and when that happens, that means it’s time to ask for external help, so I hopped on IRC.
I explained the situation and within a few minutes we uncovered the issue. I’m including the conversation here because I think the process is what’s important, not the solution:
Looking back, I like ada’s comment here about questioning me on what I meant by “works”. When it comes to real time communication, sometimes you don’t pick your words wisely. What I should have said was the Docker image builds successfully.
Anyways, let’s continue with the conversation:
Yep, I used the word “literally” wrong here because it had set -e and empty lines too! I just wanted to keep the script short on IRC (terrible idea btw).
Oh, now that’s a good idea. I didn’t even think about executing the script manually inside of the container. Thinking back, that was such an obvious thing to do, but guess what, this is how you learn.
If an entrypoint script ever goes wrong in the future for me, or if one of the people taking my Docker course has a problem with an entrypoint script, you can be sure running it in the container directly will be near the top of my list of things to do / ask.
Ok, so, what’s line 3 of the script? Ah, it’s an empty new line. Side note, I didn’t include my exact script when asking for help which was a mistake because from their POV, line 3 was something different. Never try to be tricky when asking for help, but that’s a lesson for another day!
I have to admit, seeing foundypoint.sh there threw me off. What the heck does that have to do with anything. Looking at it now, the entire error is : not foundypoint.sh: 3: docker-entrypoint.sh:
That really says “not found” and point.sh is part of the docker-entrypoint.sh file name. Why it came out like that is above my pay grade, but at least it could in theory make some sense now.
Well, now it’s starting to add up. Guess who moved their code editor to be running in Windows the other month? Also, guess who recently moved to using VSCode? This guy!
Prior to that, I was running Sublime Text in a Linux driven VM for the last
5 years. CRLF vs LF line endings isn’t something I dealt with in over 5+ years.
Let’s continue with the story because it shows how to detect the issue and resolve it.
Things are starting to drift a little off topic, but ada guides us back to the main problem.
Bingo, that confirms the issue. Pesky CRLF line endings ( rn ) are in the file. The PostgreSQL entrypoint script has Unix style LF line endings ( n ), but most code editors and GitHub don’t visibly show this, so it was invisible to the naked eye.
Special thanks to ada, programmerq and mgolisch for helping solve this mystery.
Now we know what we need to do, so let’s do it.
Configuring VSCode and WSL for LF Line Endings
Forcing Unix line endings in VSCode was very straight forward. Just drop this into your user settings: «files.eol»: «n» . You could alternatively place that into a workspace setting for specific projects, in case you have projects that run on both Linux and Windows.
New files that you create should have a LF in the bottom right of the VSCode window instead of CRLF, but existing files that have CRLF line endings will continue to be CRLF.
Installing and Using dos2unix
From within WSL run sudo apt-get install dos2unix to install a utility that will automatically convert CRLF to LF.
Then just use it on a file by running dos2unix docker-entrypoint.sh or whatever file you’re converting. Done deal!
Now if you ran file docker-entrypoint.sh it would look like this instead: docker-entrypoint.sh: POSIX shell script, ASCII text executable . It no longer has with CRLF line terminators as we saw in the IRC chat log.
Of course, if you’ve been setting CRLF line endings for a project, you probably have a ton of files to convert and doing it 1 by 1 would be really tedious.
For that you can use the power of Unix pipes to recursively run dos2unix against a directory path of your choosing.
Recursively run dos2unix against all files in a path:
All you have to do is run find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 dos2unix .
That will run it against the current directory. Replace . with a different path if you want.
If you’ve made it this far, now you know why the problem happened and how to fix it.
BONUS: Applying This Process to Other Problems
This is why I stand by the statement that breaking down problems is the #1 skill to have as a software developer. The solution was simple once the problem was understood and we got there by breaking things down and using a process of elimination.
And in case you’re wondering, I most definitely used the Rubber Duck debugging technique before I asked for help on IRC.
Have you ever been bit by CRLF vs LF line endings? Let me know below!
Free Intro to Docker Email Course
Over 5 days you’ll get 1 email per day that includes video and text from the premium Dive Into Docker course. By the end of the 5 days you’ll have hands on experience using Docker to serve a website.
Источник
Handle Exec Format Error In 8 Simple Points
The exec format error is a class of errors in the Unix-based operating systems that occurs when a user tries to run a binary file on its system originally intended to run on a different architecture. For example, when the user tries to execute a binary file originally compiled for the ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) on the x86 platform, an ‘exec format error’ is encountered. It is not in this particular case of arm and x86, but it could happen in any permutation of mismatched system architecture. In this article, we will look at this error in some detail and discuss some points that would help resolve this error.
What is Exec Format Error?
Different types of computer systems have different kinds of underlying architectures. Here, the term architecture means the circuitry and design of the CPU on how it handles and processes instructions and other computational tasks. System software and applications are compiled differently for a different architecture. Even the operating systems are designed specifically with a particular architecture in mind. There are two mainstream system architectures, The x86_64 and ARM. The x86_64 is mainly used in desktop computers and workstations, and ARM is used in mobile devices such as phones or tablets.
The x86_64 architecture can also be subdivided into 32bit and 64bits types. It represents the CPU’s memory handling capacity. Programs designed for ARM architecture can’t work on x86_64 systems and vice versa. But, the applications built for a 32bit machine can run on a 64bit. All combinations such as CPU architecture, Operating System build, and application design must come in to make everything work properly. And, If anything mismatches, an exec format error can show up.
Exec Format Error Linux
If you are trying to run incompatible programs or scripts in the Linux environment that doesn’t support the intended architecture, you are more likely to receive an exec format error. Linux itself comes in various forms and flavors in different distros. It is available on both x86_64 and ARM architecture. The most common cause of users receiving exec format errors is when 64bit programs are made to run on 32bit systems. If you are facing this error for a particular program due to an architectural issue, here are a few things that you could do.
- Open the terminal emulator, enter the command uname -m, the m stands for machine. This command would output your system architecture. x86 -> 32 bit x86, x86_64 -> 64bit, arm64 -> ARM.
- After knowing the correct architecture of your system, try to find the your program for that type of compatibility. The 32bit versions of the 64bit programs are ususally available on the internet.
- If you are on a ARM system, then try to download the program through your default package manager as they usually have arm version of most of the programs availbale to install through official repositories.
Exec format error macOS
macOS also throws an exec format error when you execute a program or script intended for a different architecture. This is usually the case with older binary programs that do not work well on modern operating systems. There are ways to execute older OS programs using the zsh shell, but you will have to build the executable yourself.
Download the program’s source code (if available ) you wish to run. Compile the program for your system using macOS’s make compiler. You would have to download make first, part of apple developer tools. It can be downloaded from http://developer.apple.com/.
Exec format error java
Java is a multipurpose, multiplatform object-oriented programming language that is a part of the whole JDK (java development kit). If you are trying to compile a java file on your system but receiving an exec format error instead, then chances are you have installed an incompatible version of the Java JDK on your system. Follow the given step to install the compatible version of JDK on your Linux machine as per the system architecture.
- First check your system architecture using the uname -m command.
- Now Open your Web browser.
- Head to https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#jdk17-linux.
- Now download the compatible version from the download options available.
You could also install the compatible version of JDK on your Linux installation using the default package manager of your distribution. Use the dpkg package manager on Debian-based and Pacman package manager on Arch-based Linux to install the correct implementation of java on your system.
Exec format error python
Python throws an exception in the form of exec format error. The python subprocess library provides the ability to run shell commands through the python interpreter. If any incompatible command or program is encountered during the python script, the python interpreter throws an OS exception. If you are running bash shell scripts through the subprocess library, keep the following points in mind to avoid exec format errors in python.
- Add !/bin/sh in the top first line of your shell script file.
- Use os library’s path method to open your .sh file, instead of opening it directly.
- Make sure the script file has executable permission.
Exec format error docker
Docker is a software platform that provides operating system-level isolation environments called containers. The containers provide different separate development environments for specific projects or purposes. Users are reported to have been facing exec format errors while running the docker test command on their environment. This happens due to a missing statement in the script file. Run the following command to run the docker test without format error.
Exec format error raspberry pi
Raspberry pi is a small form-factor mini computer. It is a small computer that runs on low voltage power and has an ARM processor installed on it. The exec format error is frequently encountered in the raspberry pi as people often try to execute x86_64 on raspberry pi’s arm processor.
To avoid this error on the raspberry pi you have two potential options. You could either download the pi-compatible arm binary executables from their official repositories or download the program’s source code and compile it yourself for your intended system architecture. Luckily, Rasberry pi comes with its package manager apt (advance packaging tool) that can be used to install arm binaries on your raspberry pi.
How to execute arm binary files on Linux
Arm binary files are not directly executable on x86_64 Linux. The file command is used in Linux to check the file type in Linux. You can check the type and architecture of your file using it. If you want to run the arm files natively on Linux, you could download a package such as qemu, which could run the native arm files on the x86_64 machine. Follow the given steps to download and install the qemu to execute arm binaries on Arch.
- Open the terminal. (ctrl + alt + t )
- type sudo pacman -S qemu.
- Enter the root password.
- Enter Y when prompted and let the download finish.
- After installation use the syntex qemu to execute the binary.
Источник
Using Ubuntu 16. I have the following script in cron.daily folder. However I am getting an error via email notification:
/etc/cron.daily/clamscan_daily:
run-parts: failed to exec /etc/cron.daily/clamscan_daily: Exec format error
run-parts: /etc/cron.daily/clamscan_daily exited with return code 1
Script
#!/bin/bash
LOGFILE="/var/log/clamav/clamav-$(date +'%Y-%m-%d').log";
EMAIL_MSG="Please see the log file attached.";
EMAIL_FROM="no-reply@domain.com";
EMAIL_TO="admin@domain.com";
DIRTOSCAN="/var/www";
for S in ${DIRTOSCAN}; do
DIRSIZE=$(du -sh "$S" 2>/dev/null | cut -f1);
echo "Starting a daily scan of "$S" directory.
Amount of data to be scanned is "$DIRSIZE".";
clamscan -ri "$S" >> "$LOGFILE";
# get the value of "Infected lines"
MALWARE=$(tail "$LOGFILE"|grep Infected|cut -d" " -f3);
# if the value is not equal to zero, send an email with the log file attached
if [ "$MALWARE" -ne "0" ];then
# using heirloom-mailx below
echo "$EMAIL_MSG"|mail -a "$LOGFILE" -s "Malware Found" -r "$EMAIL_FROM" "$EMAIL_TO";
fi
done
exit 0
I can’t figure out the problem here. Any ideas?
I tried runnig this on the terminal and got:
./clamscan_daily
Starting a daily scan of /var/www directory.
Amount of data to be scanned is 427M.
./clamscan_daily: line 15: /var/log/clamav/clamav-2017-10-25.log: Permission denied
tail: cannot open '/var/log/clamav/clamav-2017-10-25.log' for reading: No such file or directory
./clamscan_daily: line 21: [: : integer expression expected
UPDATE 2:
When I run ls -l — I can see the number 2 for this script only. Could that be the problem?
ls -l
total 56
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 376 Mar 31 2016 apport
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1474 Oct 31 2016 apt-compat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 355 May 22 2012 bsdmainutils
-rwxr-xr-x 2 root root 751 Oct 4 2016 clamscan_daily
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1597 Nov 26 2015 dpkg
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 372 May 6 2015 logrotate
UPDATE #3
ls -l /var/log/clamav
total 388
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 15 2016 clamav-2016-09-15.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Sep 16 2016 clamav-2016-09-16.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Sep 17 2016 clamav-2016-09-17.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Sep 18 2016 clamav-2016-09-18.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 19 2016 clamav-2016-09-19.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Sep 20 2016 clamav-2016-09-20.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 21 2016 clamav-2016-09-21.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 22 2016 clamav-2016-09-22.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 23 2016 clamav-2016-09-23.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232 Sep 24 2016 clamav-2016-09-24.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232 Sep 25 2016 clamav-2016-09-25.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232 Sep 26 2016 clamav-2016-09-26.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 27 2016 clamav-2016-09-27.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233 Sep 28 2016 clamav-2016-09-28.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232 Sep 29 2016 clamav-2016-09-29.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Sep 30 2016 clamav-2016-09-30.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Oct 1 2016 clamav-2016-10-01.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Oct 2 2016 clamav-2016-10-02.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Oct 3 2016 clamav-2016-10-03.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 Oct 4 2016 clamav-2016-10-04.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 238 Oct 25 15:06 clamav-2017-10-25.log
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 5688 Oct 25 15:27 clamav.log
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 13196 Oct 22 06:25 clamav.log.1
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 2001 Aug 21 06:25 clamav.log.10.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 896 Aug 13 06:25 clamav.log.11.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1894 Aug 7 06:25 clamav.log.12.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1359 Oct 16 06:25 clamav.log.2.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1153 Oct 8 06:25 clamav.log.3.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1869 Oct 2 06:25 clamav.log.4.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 898 Sep 24 06:25 clamav.log.5.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1336 Sep 18 06:25 clamav.log.6.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1710 Sep 10 06:25 clamav.log.7.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1373 Sep 4 06:25 clamav.log.8.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 1794 Aug 27 06:25 clamav.log.9.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 46135 Oct 25 15:26 freshclam.log
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 83017 Oct 22 06:25 freshclam.log.1
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6219 Aug 21 06:25 freshclam.log.10.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 4737 Aug 13 06:25 freshclam.log.11.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6389 Aug 7 06:25 freshclam.log.12.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6382 Oct 16 06:25 freshclam.log.2.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 5228 Oct 8 06:25 freshclam.log.3.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6415 Oct 2 06:25 freshclam.log.4.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 4580 Sep 24 06:25 freshclam.log.5.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6596 Sep 18 06:25 freshclam.log.6.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 5320 Sep 10 06:25 freshclam.log.7.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 6921 Sep 4 06:25 freshclam.log.8.gz
-rw-r----- 1 clamav adm 15812 Aug 27 06:25 freshclam.log.9.gz
- Forum
- The Ubuntu Forum Community
- Ubuntu Specialised Support
- Ubuntu Servers, Cloud and Juju
- Server Platforms
- CRON job stopped working — SOLVED
-
CRON job stopped working — SOLVED
Hi everyone
We have a server that runs U14.04.3 LTS.
We had a cron script working until a recent batch of updates. The contents are:
csv.csv {
su vrs vrs
daily
dateext
compress
postrotate
pkill -HUP python3.4
endscript
rotate 30
}This worked well but now returns:
/etc/cron.daily/mlat-server:
run-parts: failed to exec /etc/cron.daily/mlat-server: Exec format error
run-parts: /etc/cron.daily/mlat-server exited with return code 1We have not been able to work out why this has stopped working.
Can anyone throw some light on this?
Thanks
Jon
MLAT Radar Admin Support
www.mlat-radar.netLast edited by Jon_Fear; September 2nd, 2015 at 08:34 AM.
Reason: Add SOLVED label
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
Thread moved to the «Server Platforms» forum.
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
That looks like a definition file for the logrotate program. It certainly isn’t executable by itself. We need to see the contents of the mlat-server file.
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
Originally Posted by Jon_Fear
run-parts: failed to exec /etc/cron.daily/mlat-server: Exec format error
An ‘exec format error’ usually means that the system cannot figure which interpreter to use on a file (shell, python, perl, whatever)
Add a shebang line (#!/bin/sh) to the top of /etc/cron.daily/mlat-server.
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
Hi
Well there’s the thing. That is the complete contents of the mlat-server file which is currently residing in /etc/cron.daily. In addition we have tried adding the shebang to the top of the file and that screws the file completely. The output starts complaining of all sorts. This file listed above is the same as the file in /etc/logrotate.d.
Hence the reason for asking here, google is meant to be our friend, in this case not…!
Thanks for the quick replies.
Jon
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
By default, logrotate runs out of /etc/cron.daily so you shouldn’t need any special task. It should just read the file in /etc/logrotate.d/ when logrotate runs each day. Try deleting mlat-server from cron.daily and see what happens tomorrow.
-
Re: CRON job stopped working
Thanks for the tip, I have removed the offending file, let’s see what happens tonight!
Jon
-
Re: CRON job stopped working — SOLVED
Originally Posted by SeijiSensei
By default, logrotate runs out of /etc/cron.daily so you shouldn’t need any special task. It should just read the file in /etc/logrotate.d/ when logrotate runs each day. Try deleting mlat-server from cron.daily and see what happens tomorrow.
Thank you for the advice. That worked a treat, now working correctly.
Jon
Bookmarks
Bookmarks

Posting Permissions
Содержание
- Решение проблемы с ошибкой «bash: не удаётся запустить бинарный файл: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла»
- О разрядности дистрибутивов Linux и о программ
- Запуск ARM файлов в Linux
- Заключение
- execvp: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла
- 🛠️ Исправление ошибки «Exec format» при запуске скриптов командой run-parts
- Решение ошибки «Exec format» при запуске скриптов командой run-parts
- Решение проблемы с ошибкой «bash: не удаётся запустить бинарный файл: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла»
- О разрядности дистрибутивов Linux и о программ
- Запуск ARM файлов в Linux
- Заключение
Решение проблемы с ошибкой «bash: не удаётся запустить бинарный файл: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла»
В операционной системе Linux при запуске скаченного файла, либо при запуске самостоятельно скомпилированного файла вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой:
Если у вас англоязычная локаль, то ошибка будет примерно такой:
Причинами данной ошибки могут быть:
Чтобы получить информацию о файле, который вы пытаетесь запустить, можно использовать утилиту file, после которой укажите путь до файла:
Здесь мы видим, что файл предназначен для 64-битной системы, об этом говорит запись 64-bit, для процессора с архитектурой x86-64.
Этот файл для 32-битных систем, для процессора с архитектурой ARM EABI4.
Если вы не знаете, какой битности ваша система, то выполните команду:
Для 64-битных систем будет выведено x86_64, а для 32-битных – x86.
О разрядности дистрибутивов Linux и о программ
На компьютер с 32-битным процессором вы можете установить только 32-битную операционную систему и в ней запускать только 32-битные программы.
На компьютер с 64-битным процессором вы можете установить как 64-битную ОС, так и 32-битный Linux. В случае, если вы установили 64-битный дистрибутив Linux, то в нём вы можете запускать и 64-битные программы и 32-битные. А если вы установили 32-битный дистрибутив, то в нём возможно запускать только 32-битные программы.
Итак, если у вас 32-битная система, а файл для 64-битной системы или даже для ARM архитектуры, то у вас следующие варианты:
Запуск ARM файлов в Linux
Часто можно запустить исполнимые образы ARM на amd64 системах если установить пакеты binfmt-support, qemu, и qemu-user-static:
Заключение
Итак, ошибка формата выполняемого файла с невозможностью запустить бинарный файл возникает из-за несоответствия программы операционной системе или архитектуре процессора. Эта проблема не должна возникать, если вы установили программу из исходных репозиториев (кроме случаев неправильной настройки источников репозитория). При возникновении этой проблемы поищите файл, подходящий для вашей архитектуры или скомпилируйте файл из исходных кодов под архитектуру вашей операционной системы.
Источник
execvp: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла
3) (Запускается только до перезагрузки ПК и только через root)
QStandardPaths: XDG_RUNTIME_DIR not set, defaulting to ‘/tmp/runtime-root’
void Autorization::listen() *2 62000
bool Setting::connectDatabase() QThread(0x5617d599a3a0)
void SqlWorker::connectToDatabase(QString) «/root/.joxi/setting»
После каждой перезагрузки ПК, Joxi перестаёт запускаться и заново надо его переустанавливать.
Скрипт joxi.sh выдаёт ошибку «execvp: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла«.
[sudo] пароль для alexandr:
Creating directory joxi
Verifying archive integrity. 100% MD5 checksums are OK. All good.
-rwx—— 1 alexandr alexandr 351 июн 5 22:32 install.sh
-rwx—— 1 alexandr alexandr 4305176 июн 5 22:32 joxi
-rwx—— 1 alexandr alexandr 86 июн 5 22:32 joxi.desktop
-rwx—— 1 alexandr alexandr 50 июн 5 22:32 joxi.sh
Available platform plugins are: eglfs, linuxfb, minimal, minimalegl, offscreen, vnc, wayland-egl, wayland, wayland-xcomposite-egl, wayland-xcomposite-glx, webgl, xcb.
Available platform plugins are: eglfs, linuxfb, minimal, minimalegl, offscreen, vnc, wayland-egl, wayland, wayland-xcomposite-egl, wayland-xcomposite-glx, webgl, xcb.
Operating System: KDE neon 5.18
KDE Plasma Version: 5.18.5
KDE Frameworks Version: 5.70.0
Qt Version: 5.14.2
Kernel Version: 5.3.0-53-generic
OS Type: 64-bit
Источник
🛠️ Исправление ошибки «Exec format» при запуске скриптов командой run-parts
Решение ошибки «Exec format» при запуске скриптов командой run-parts
Чтобы запустить все скрипты в папке «Documents», я запустил:
Я получил следующее сообщение об ошибке:
Bourne shell, или совместимый шеллl:
Bash:
Perl:
Python 2.x:
Python 3.x:
Это то, что мы называем шебанг.
Теперь вернемся к теме.
Отредактируйте ваши скрипты, используя ваш любимый редактор:
Добавьте шебанг в начале скрипта:
Теперь вы можете без проблем запускать скрипты с помощью команды run-parts, используя команду run-parts.
Вы также можете использовать утилиту ShellCheck для поиска проблем в своих скриптах оболочки.
Anything in here will be replaced on browsers that support the canvas element
Источник
Я пытаюсь запустить программу, но ошибка происходит так:
Результатом file program было:
Как я могу исправить эту ошибку?
Я использую Ubuntu 14.04.2 (amd64) с VMware. Я тоже пробовал с Ubuntu i386, но результат был таким же.
Вы пытаетесь запустить исполняемый файл, скомпилированный для архитектуры ARM на архитектуре x86-64, что очень похоже на запрос вашего процессора, который говорит только по-английски, указывать направление на китайском.
Если вам нужно запустить этот исполняемый файл, у вас есть два варианта:
Получить версию исполняемого файла x86-64 (любым способом; если вам не удается получить версию исполняемого файла x86-64, но вы можете получить его исходный код, вы можете попытаться перекомпилировать его на виртуальной машине );
Установите Ubuntu Server for ARM вместо Ubuntu 14.04.2 (amd64). Для этого требуется либо физическая машина, работающая на архитектуре ARM, либо программное обеспечение для виртуализации, которое может эмулировать ее.
Это также может произойти, если вы попытаетесь запустить исполняемый файл x86-64 на 32-разрядной платформе.
В одном конкретном случае я скачал код Visual Studio и попытался запустить его на своей установке Ubuntu, но я не понял, что я установил 32-битную Ubuntu в эту виртуальную машину. Я получил эту ошибку, но после загрузки 32-разрядной версии, он работал без проблем.
qemu затем выполнит эмуляцию syscall при запуске исполняемого файла. Это работает для большинства двоичных файлов ARM, но есть некоторые, которые могут работать неправильно.
Такая ошибка может возникнуть, если выполняются все следующие условия:
Если java в системе установлено более одного, это может произойти и не будет установлено по умолчанию. На Ubuntu14.04 LTS я мог решить ее, выполнив следующее и выбрав java нужное.
Это также может произойти, если двоичный файл использует реализацию libc, которая не является libc, например, musl. В эти дни эта конкретная проблема, скорее всего, встречается при попытке запуска двоичного файла с libc в контейнере Docker с изображением, основанным на alpine. Ничто не может быть сделано с самим двоичным файлом для поддержки обеих сред, потому что реализация libc всегда должна быть статически связана, то есть встроена непосредственно в двоичный файл, по причинам.
Источник
Решение проблемы с ошибкой «bash: не удаётся запустить бинарный файл: Ошибка формата выполняемого файла»
В операционной системе Linux при запуске скаченного файла, либо при запуске самостоятельно скомпилированного файла вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой:
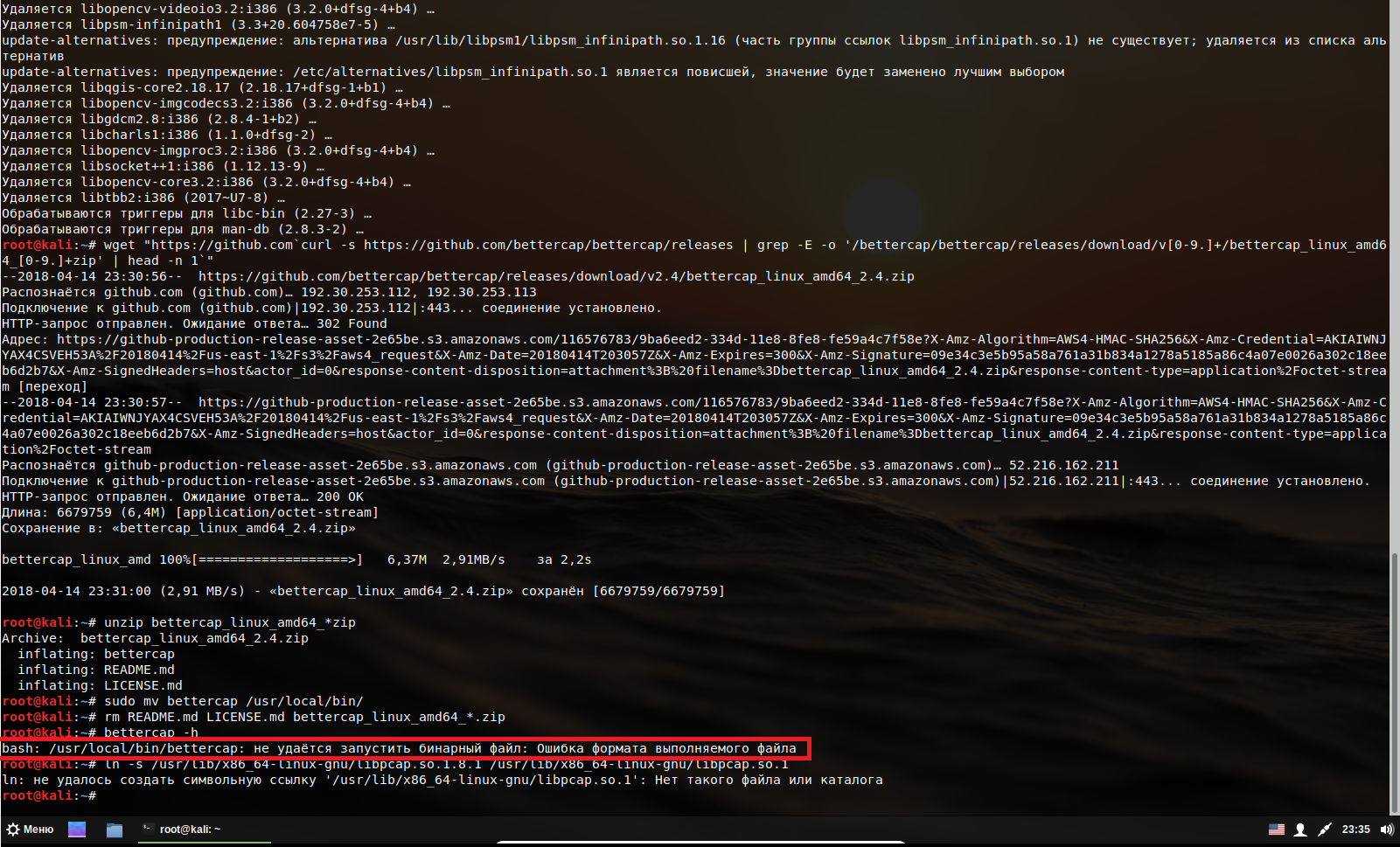
Если у вас англоязычная локаль, то ошибка будет примерно такой:
Причинами данной ошибки могут быть:
Чтобы получить информацию о файле, который вы пытаетесь запустить, можно использовать утилиту file, после которой укажите путь до файла:
Здесь мы видим, что файл предназначен для 64-битной системы, об этом говорит запись 64-bit, для процессора с архитектурой x86-64.
Этот файл для 32-битных систем, для процессора с архитектурой ARM EABI4.
Если вы не знаете, какой битности ваша система, то выполните команду:
Для 64-битных систем будет выведено x86_64, а для 32-битных – x86.
О разрядности дистрибутивов Linux и о программ
На компьютер с 32-битным процессором вы можете установить только 32-битную операционную систему и в ней запускать только 32-битные программы.
На компьютер с 64-битным процессором вы можете установить как 64-битную ОС, так и 32-битный Linux. В случае, если вы установили 64-битный дистрибутив Linux, то в нём вы можете запускать и 64-битные программы и 32-битные. А если вы установили 32-битный дистрибутив, то в нём возможно запускать только 32-битные программы.
Итак, если у вас 32-битная система, а файл для 64-битной системы или даже для ARM архитектуры, то у вас следующие варианты:
Запуск ARM файлов в Linux
Часто можно запустить исполнимые образы ARM на amd64 системах если установить пакеты binfmt-support, qemu, и qemu-user-static:
Заключение
Итак, ошибка формата выполняемого файла с невозможностью запустить бинарный файл возникает из-за несоответствия программы операционной системе или архитектуре процессора. Эта проблема не должна возникать, если вы установили программу из исходных репозиториев (кроме случаев неправильной настройки источников репозитория). При возникновении этой проблемы поищите файл, подходящий для вашей архитектуры или скомпилируйте файл из исходных кодов под архитектуру вашей операционной системы.
Источник