The error “TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found” happens when you try to join some numbers of type ‘int’ into a new string. The explanation of this guide will help you fix this error and other similar errors you may get in your code.
In Python, join() method joins all items in a collection as a list, a tuple,… to a string. Here is an example using the join() method to join all the strings in a list to a new string with commas separate.
device_list = ["smartphone", "tablet", "laptop", "desktop"] device_str = ','.join(device_list) print(device_str)
Output:
smartphone,tablet,laptop,desktopSometimes, you may want to join a list of integer numbers to a string, and you try to do the same as the example above, but your code does not work as you expected, and you get the error “TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found”.
year_list = [2022, 2023, 2024, 2025] year_str = ','.join(year_list) print(year_str)
Output:
year_str = ','.join(year_list)
TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int foundHow to solve the error?
Method 1: Use Python List Comprehension to create a new list of strings
This error occurs because the join() method requires the list has all of its elements of type ‘str’, not ‘int’. So, to fix this error, you can use the List Comprehension of Python to create a list of strings from the original list as this example.
year_list = [2022, 2023, 2024, 2025] year_str = ','.join([str(year) for year in year_list]) print(year_str)
Output:
2022,2023,2024,2025Method 2: Use map() function
Another way to fix this error is to use the map() function, which applies a function to all elements of the list. In this case, the function you need to use with the map() function is the str() function to convert the element to a string.
year_list = [2022, 2023, 2024, 2025] year_str = ','.join(map(str, year_list)) print(year_str)
Output:
2022,2023,2024,2025Example with a list of multiple datatypes
Both solutions above work not only with a list of integer numbers but also with a list of multiple datatypes.
exam_scores = [8, 8.25, "9.5"]
str1 = ','.join([str(s) for s in exam_scores])
str2 = ','.join(map(str, exam_scores))
print('str1: ' + str1)
print('str2: ' + str2)
Output:
str1: 8,8.25,9.5
str2: 8,8.25,9.5As you can see, the results of both str1 and str2 are the same and work perfectly.
Summary
In this guide, I’ve showed you how to solve the error “TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found” in Python. You can choose to use List Comprehension to create a new list of strings or use the map() function to solve the problem. Both solutions can also work perfectly with a list of multiple datatypes.
Maybe you are interested:
- TypeError: slice indices must be integers or None or have an __index__ method
- typeerror: string indices must be integers in python
- typeerror: takes 1 positional argument but 2 were given
- TypeError: unhashable type: ‘dict’
Hello, I’m Joseph Stanley. My major is IT and I want to share programming languages to you. If you have difficulty with JavaScript, TypeScript, C#, Python, C, C++, Java, let’s follow my articles. They are helpful for you.
Job: Developer
Name of the university: HUST
Major: IT
Programming Languages: JavaScript, TypeScript, C#, Python, C, C++, Java
Python TypeError: sequence item N: expected string, list found
TypeError: sequence item N: expected string, list foundA quick and easy way of fixing this error is by applying the map() function to your join() argument:
nested_list = ['This', 'is', 'a', 'list', 'with', 'a', ['nested', 'list']]
' '.join(map(str, nested_list))Out:
"This is a list with a ['nested', 'list']"In this example, map() is transforming every value in nested_list() to string-type, allowing join() to concatenate all of the list values. This process is explained more in-depth in the map() section of this article.
This error occurs because the list passed as an argument to the join() method contains a nested list. join() can only concatenate string-type objects, so Python throws an error if we use join() with anything that isn’t a string.
As a result, using join() with a list containing integers, floats, or tuples results in a similar error, with list found being replaced by int found, float found, or tuple found.
Today we’ll take a look at an example case of where we might see this error, along with some solutions that demonstrate how we can solve it.
As mentioned in the intro, this error occurs when we apply the join() method while using a list that contains a nested list.
Let’s say you’re analyzing some vehicle data. You’ve got a JSON file that contains data for different vehicles in the following format:
vehicle_details = {
'vehicle_id' : '1',
'make': 'Jaguar',
'model': 'F-Type',
'available_colors': ['yellow', 'red', 'blue'],
'year': '2021'
}We want to view all of the values for a given vehicle. We could try to do this using our Jaguar example with the following:
vehicle_info = vehicle_details.values()
' '.join(vehicle_info)Out:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-3-4d31652d781c> in <module>
----> 1 vehicle_info = vehicle_details.values()
2
3 ' '.join(vehicle_info)
NameError: name 'vehicle_details' is not definedAs the error shows, sequence item 3 (the available_colors row) is a list, which means join() won’t work here. We can get around this by using a for loop, generator, or list comprehension. Here’s an example using a generator:
vehicle_info = vehicle_details.values()
' '.join(str(info) for info in vehicle_info)Out:
"1 Jaguar F-Type ['yellow', 'red', 'blue'] 2021"The generator iterates through each list item and converts the value to a string-type object, allowing join() to work.
We can also troubleshoot this error using the map() function, as shown in the intro. We can apply map() to our vehicle example as follows:
vehicle_info = vehicle_details.values()
' '.join(map(str, vehicle_info))Out:
"1 Jaguar F-Type ['yellow', 'red', 'blue'] 2021"map() works by looping through a list given as the second argument. In our case, this is vehicle_info. It then applies whichever transformation function we provide as the first argument. Using str() as our transformation function converts everything in the list to a string, including our list of colors.
On the surface, a generator essentially goes through the same process as the map() function does, iterating through each item in the list and then applying the str() function. However, Python works its way through the statements very differently, with map() executing much faster than a generator. See below for a speed comparison of our two examples, which shows that our script runs faster while using map():
vehicle_info = vehicle_details.values()
# Create anonymous functions
gen = lambda: ' '.join(str(info) for info in vehicle_info)
mapping = lambda: ' '.join(map(str, vehicle_info))
# Calculate timings
gen_time = %timeit -o -q gen()
map_time = %timeit -o -q mapping()
# Create data table
data = [['map()', map_time.average], ['generator', gen_time.average]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['type', 'microseconds'])
df.microseconds = round(df.microseconds * 1e6, 2)
df.sort_values('microseconds', inplace=True)
dfThe error TypeError: sequence item N: expected string, list found occurs when using the join() method with a list containing a nested list inside it. Similar errors can also be caused by applying join() using a list containing integers, floats, or tuples.
We need to convert list values to string-type objects before join() is applied to avoid this error. We can implement string conversion using the str() function combined with either the map() function or a for loop. Of the two options, we recommend using map(), as it is the faster of the two.
17 авг. 2022 г.
читать 1 мин
Одна ошибка, с которой вы можете столкнуться при использовании Python:
ValueError : setting an array element with a sequence.
Эта ошибка обычно возникает, когда вы пытаетесь втиснуть несколько чисел в одну позицию в массиве NumPy.
В следующем примере показано, как исправить эту ошибку на практике.
Как воспроизвести ошибку
Предположим, у нас есть следующий массив NumPy:
import numpy as np
#create NumPy array
data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
Теперь предположим, что мы пытаемся втиснуть два числа в первую позицию массива:
#attempt to cram values '4' and '5' both into first position of NumPy array
data[0] = np.array([4,5])
ValueError : setting an array element with a sequence.
Ошибка говорит нам, что именно мы сделали неправильно: мы попытались установить один элемент в массиве NumPy с последовательностью значений.
В частности, мы попытались втиснуть значения «4» и «5» в первую позицию массива NumPy.
Это невозможно сделать, поэтому мы получаем ошибку.
Как исправить ошибку
Способ исправить эту ошибку — просто присвоить одно значение первой позиции массива:
#assign the value '4' to the first position of the array
data[0] = np.array([4])
#view updated array
data
array([ 4, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
Обратите внимание, что мы не получаем никаких ошибок.
Если мы действительно хотим присвоить два новых значения элементам массива, нам нужно использовать следующий синтаксис:
#assign the values '4' and '5' to the first two positions of the array
data[0:2] = np.array([4, 5])
#view updated array
data
array([ 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
Обратите внимание, что первые два значения в массиве были изменены, а все остальные значения остались прежними.
Дополнительные ресурсы
В следующих руководствах объясняется, как исправить другие распространенные ошибки в Python:
Как исправить KeyError в Pandas
Как исправить: ValueError: невозможно преобразовать число с плавающей запятой NaN в целое число
Как исправить: ValueError: операнды не могли транслироваться вместе с фигурами
import json
persones = []
def users_persone():
name = input('Введите имя контакта - ')
tel = input('Введите номер - ')
persone = {name: tel}
persones.append(persone)
MyFile = open('C:HPproverka.txt', 'w')
MyFile.writelines(persones)
MyFile.close()
with open('persones.json', 'w') as file:
json.dump(persones, file, ensure_ascii=False)
return persone
def main():
l = True
while l:
users_choise = input("Желаете ввести или получить контактные данные - ")
if users_choise == 'ввести':
users_persone()
elif users_choise == "получить":
print(MyFile)
users_choise_two = input("Желаете остановить програму - ")
if users_choise_two == 'да':
print("Програма закрыта")
l = False
main()хочу что бы код сохранял номер и имя в текстовой файл но выдаёт ошибку
-
Вопрос заданболее года назад
-
462 просмотра
MyFile = open(‘C:HPproverka.txt’, ‘w’)
MyFile.writelines(persones)
MyFile.close()
writelines() ожидает получить на вход массив СТРОК, а ты даёшь массив словарей. Отсюда и ошибка.
Зачем ты вообще этот фрагмент написал, если чуть дальше у тебя нормальное сохранение в json?
Пригласить эксперта
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
10 февр. 2023, в 04:49
50000 руб./за проект
10 февр. 2023, в 02:20
3000 руб./за проект
10 февр. 2023, в 01:33
1500 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
Introduction
In python, we have discussed many concepts and conversions. In this tutorial, we will be discussing the concept of setting an array element with a sequence. When we try to access some value with the right type but not the correct value, we encounter this type of error. In this tutorial, we will be discussing the concept of ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence in Python.
What is Value Error?
A ValueError occurs when a built-in operation or function receives an argument with the right type but an invalid value. A value is a piece of information that is stored within a certain object.
In python, we often encounter the error as ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence is when we are working with the numpy library. This error usually occurs when the Numpy array is not in sequence.
What Causes Valueerror: Setting An Array Element With A Sequence?
Python always throws this error when you are trying to create an array with a not properly multi-dimensional list in shape. The second reason for this error is the type of content in the array. For example, define the integer array and inserting the float value in it.
Examples Causing Valueerror: Setting An Array Element With A Sequence
Here, we will be discussing the different types of causes through which this type of error gets generated:
1. Array Of A Different Dimension
Let us take an example, in which we are creating an array from the list with elements of different dimensions. In the code, you can see that you have created an array of two different dimensions, which will throw an error as ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence.
import numpy as np print(np.array([[1, 2,], [3, 4, 5]],dtype = int))
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have imported the numpy library with an alias name as np.
- Then, we will be making the array of two different dimensions with the data type of integer from the np.array() function.
- The following code will result in the error as Value Error as we cannot access the different dimensions array.
- At last, you can see the output as an error.
Solution Of An Array Of A Different Dimension
If we try to make the length of both the arrays equal, then we will not encounter any error. So the code will work fine.
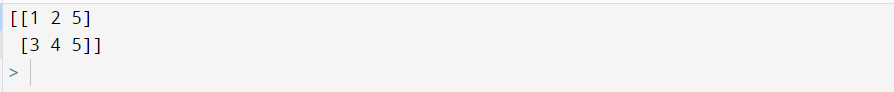
import numpy as np print(np.array([[1, 2, 5], [3, 4, 5]],dtype = int))
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have imported the numpy library with an alias name as np.
- Then, we will make the different dimension array into the same dimension array to remove the error.
- At last, we will try to print the output.
- Hence, you can see the output without any error.
Also, Read | [Solved] IndentationError: Expected An Indented Block Error
2. Different Type Of Elements In An Array
Let us take an example, in which we are creating an array from the list with elements of different data types. In the code, you can see that you have created an array of multiple data types values than the defined data type. If we do this, there will be an error generated as ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence.
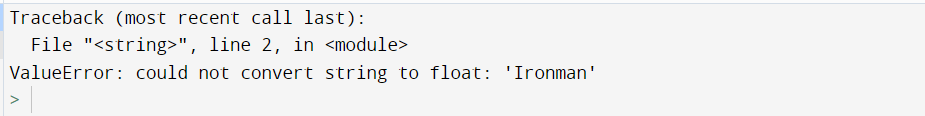
import numpy as np print(np.array([2.1, 2.2, "Ironman"], dtype=float))
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have imported the numpy library with an alias name as np.
- Then, we will be making the array of two different data types with the data type as a float from the np.array() function.
- The array contains two data types, i.e., float and string.
- The following code will result in the error as Value Error as we cannot write the different data types values as the one data type of array.
- Hence, you can see the output as Value Error.
Solution Of Different Type Of Elements In An Array
If we try to make the data type unrestricted, we should use dtype = object, which will help you remove the error.
import numpy as np print(np.array([2.1, 2.2, "Ironman"], dtype=object))
Output:
Explanation:
- Firstly, we have imported the numpy library with an alias name as np.
- Then, if we want to access the different data types values in a single array so, we can set the dtype value as an object which is an unrestricted data type.
- Hence, you can see the correct output, and the code runs correctly without giving any error.
Also, Read | [Solved] TypeError: String Indices Must be Integers
3. Valueerror Setting An Array Element With A Sequence Pandas
In this example, we will be importing the pandas’ library. Then, we will be taking the input from the pandas dataframe function. After that, we will print the input. Then, we will update the value in the list and try to print we get an error.
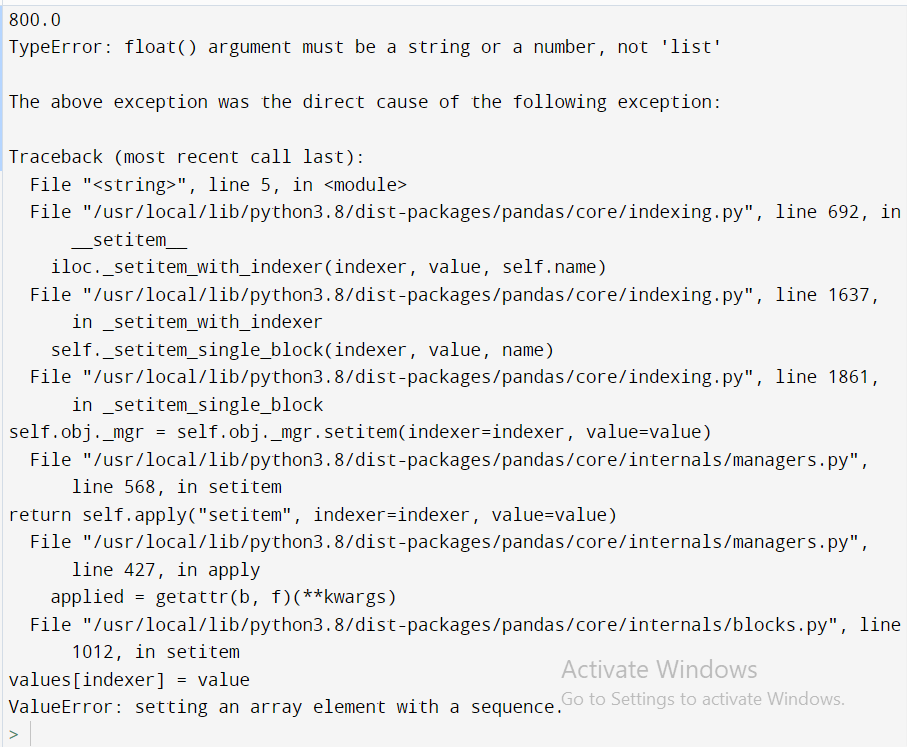
import pandas as pd output = pd.DataFrame(data = [[800.0]], columns=['Sold Count'], index=['Project1']) print (output.loc['Project1', 'Sold Count']) output.loc['Project1', 'Sold Count'] = [400.0] print (output.loc['Project1', 'Sold Count'])
Output:
Solution Of Value Error From Pandas
If we dont want any error in the following code we need to make the data type as object.
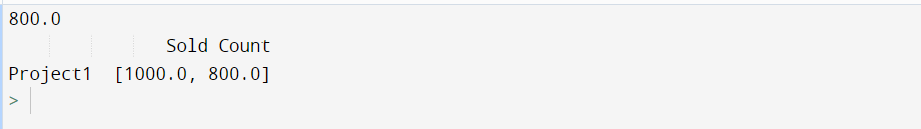
import pandas as pd output = pd.DataFrame(data = [[800.0]], columns=['Sold Count'], index=['Project1']) print (output.loc['Project1', 'Sold Count']) output['Sold Count'] = output['Sold Count'].astype(object) output.loc['Project1','Sold Count'] = [1000.0,800.0] print(output)
Output:
Also, Read | How to Solve TypeError: ‘int’ object is not Subscriptable
4. ValueError Setting An Array Element With A Sequence in Sklearn
Sklearn is a famous python library that is used to execute machine learning methods on a dataset. From regression to clustering, this module has all methods which are needed.
Using these machine learning models over the 2D arrays can sometimes cause a huge ValueError in the code. If your 2D array is not uniform, i.e., if several elements in all the sub-arrays are not the same, it’ll throw an error.
Example Code –
import numpy as np from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.svm import SVC X = np.array([[-1, 1], [2, -1], [1, -1], [2]]) y = np.array([1, 2, 2, 1]) clf = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), SVC(gamma='auto')) clf.fit(X, y)
Here, the last element in the X array is of length 1, whereas all other elements are of length 2. This will cause the SVC() to throw an error ValueError – Setting an element with a sequence.
Solution –
The solution to this ValueError in Sklearn would be to make the length of arrays equal. In the following code, we’ve changed all the lengths to 2.
import numpy as np from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.svm import SVC X = np.array([[-1, 1], [2, -1], [1, -1], [2, 1]]) y = np.array([1, 2, 2, 1]) clf = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), SVC(gamma='auto')) clf.fit(X, y)
Also, Read | Invalid literal for int() with base 10 | Error and Resolution
5. ValueError Setting An Array Element With A Sequence in Tensorflow
In Tensorflow, the input shapes have to be correct to process the data. If the shape of every element in your array is not of equal length, you’ll get a ValueError.
Example Code –
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np # Initialize two arrays x1 = tf.constant([1,2,3,[4,1]]) x2 = tf.constant([5,6,7,8]) # Multiply result = tf.multiply(x1, x2) tf.print(result)
Here the last element of the x1 array has length 2. This causes the tf.multiple() to throw a ValueError.
Solution –
The only solution to fix this is to ensure that all of your array elements are of equal shape. The following example will help you understand it –
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np # Initialize two arrays x1 = tf.constant([1,2,3,1]) x2 = tf.constant([5,6,7,8]) # Multiply result = tf.multiply(x1, x2) tf.print(result)
6. ValueError Setting An Array Element With A Sequence in Keras
Similar error in Keras can be observed when an array with different lengths of elements are passed to regression models. As the input might be a mixture of ints and lists, this error may arise.
Example Code –
model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(12, input_dim=8, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(8, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) # Compile the model model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) # Fit the model model.fit(X, y, epochs=150, batch_size=10) >>> ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence.
Here the array X contains a mixture of integers and lists. Moreover, many elements in this array are not fully filled.
Solution –
The solution to this error would be flattening your array and reshaping it to the desired shape. The following transformation will help you to achieve it. keras.layers.Flatten and pd.Series.tolist() will help you to achieve it.
model = Sequential() model.add(Flatten(input_shape=(2,2))) model.add(Dense(12, input_dim=8, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(8, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) # Compile the model model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) # Fit the model X = X.tolist() model.fit(X, y, epochs=150, batch_size=10)
Also, Read | How to solve Type error: a byte-like object is required not ‘str’
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned about the concept of ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence in Python. We have seen what value Error is? And what is ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence? And what are the causes of Value Error? We have discussed all the ways causing the value Error: setting an array element with a sequence with their solutions. All the examples are explained in detail with the help of examples. You can use any of the functions according to your choice and your requirement in the program.
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
FAQs
1. How Does ValueError Save Us From Incorrect Data Processing?
We will understand this with the help of small code snippet:
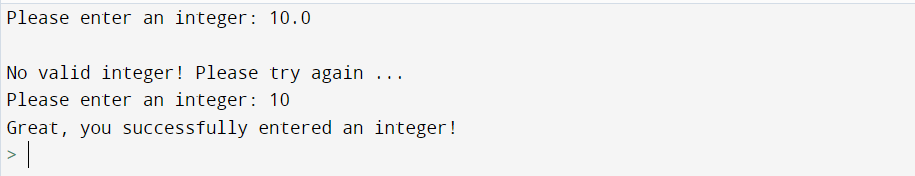
while True:
try:
n = input("Please enter an integer: ")
n = int(n)
break
except ValueError:
print("No valid integer! Please try again ...")
print("Great, you successfully entered an integer!")
Input:
Firstly, we will pass 10.0 as an integer and then 10 as the input. Let us see what the output comes.
Output:
Now you can see in the code. When we try to enter the float value in place of an integer value, it shows me a value error which means you can enter only the integer value in the input. Through this, ValueError saves us from incorrect data processing as we can’t enter the wrong data or input.
2. We don’t declare a data type in python, then why is this error arrises in initializing incorrect datatype?
In python, We don’t have to declare a datatype. But, when the ValueError arises, that means there is an issue with the substance of the article you attempted to allocate the incentive to. This is not to be mistaken for types in Python. Hence, Python ValueError is raised when the capacity gets a contention of the right kind; however, it an unseemly worth it.