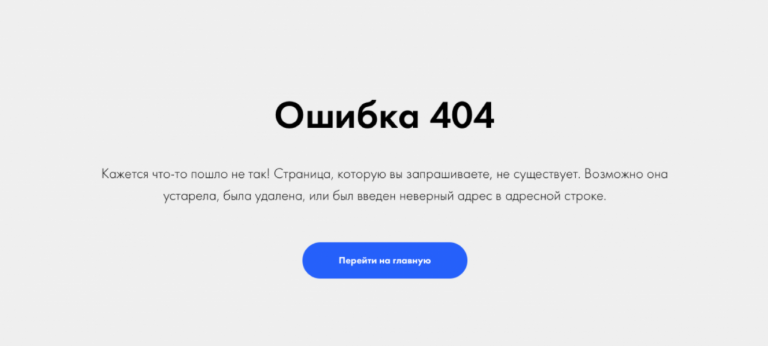
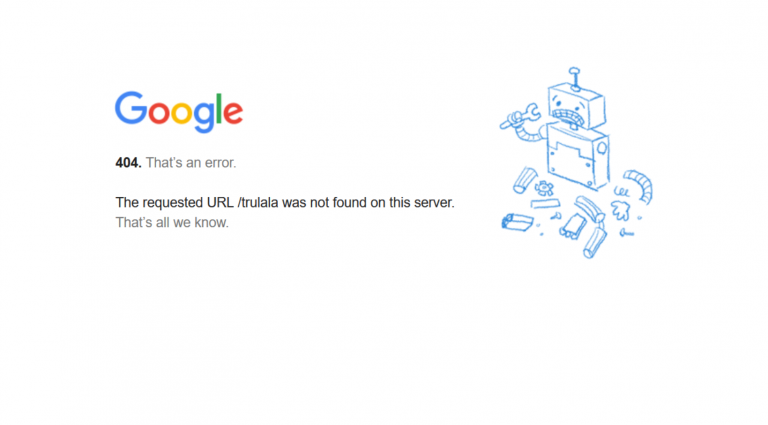
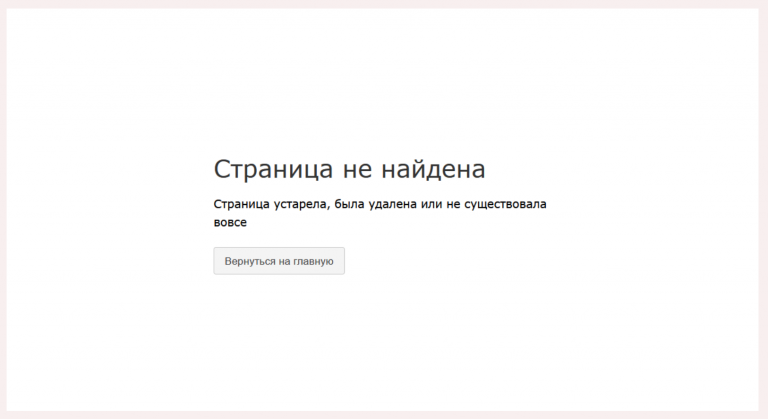
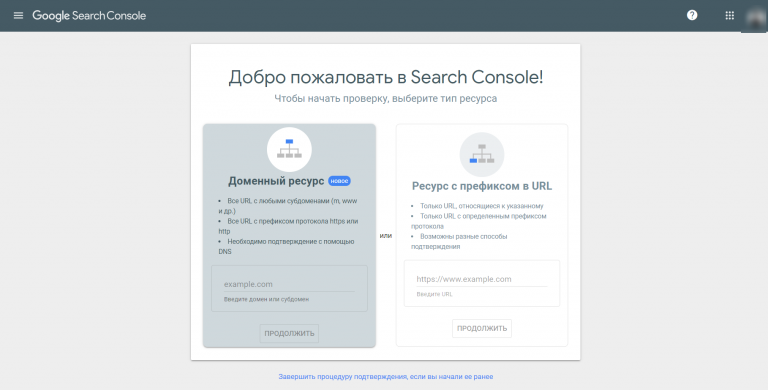
Ошибка 404, либо Error 404 Not Found — ошибка, которая появляется, если браузеру не удалось обнаружить на сервере указанный URL.
Сообщение об ошибке 404
Что означает ответ 404
Error 404 Not Found отображается по-разному: «HTTP 404 не найден», «Ошибка 404 Not Found», «404 Страница не найдена». Смысл надписи всегда остаётся тем же: страница отсутствует либо просто не работает. Not Found в переводе означает «не найдено».
Ошибка 404 — классический код ответа по протоколу HTTP. Он свидетельствует, что связь с сервером установлена, но данных по заданному запросу на сервере нет.
Однако если просто ввести в поисковую строку произвольный набор символов, то браузер не покажет ошибку 404 Not Found — появится сообщение, что установить соединение с конкретным сервером невозможно.
Разберёмся в техническом формировании ответа Error 404 Not Found.
Техническая сторона вопроса. При связи по HTTP браузер запрашивает указанный URL и ждёт цифрового ответа. То есть любой запрос пользователя направляется на сервер размещения искомого сайта. Когда браузеру удаётся связаться с сервером, он получает кодированный ответ. Если запрос корректный и страница найдена, отправляется ответ с кодом 200 OK, что соответствует благополучной загрузке. При отсутствии страницы отправляется ответ об ошибке.
Что значит код «404». В ответе 404 первая четвёрка указывает на то, что запрос был чрезмерно длительным или в самом адресе была ошибка. Ноль предполагает синтаксическую неточность. Завершающая цифра кода отображает конкретную причину ошибки — «4» означает отсутствие данной ссылки.
Какие ещё ошибки бывают. Ошибку 404 не нужно путать с другими ответами, которые указывают на невозможность связи с сервером. Например, ошибка 403 сообщает, что доступ к URL ограничен, а ответ «Сервер не найден» свидетельствует, что браузер не смог обнаружить место размещения сайта.
Google на 404 странице сообщает о возможных причинах ошибки
Причины ошибки
Причины, по которым HTTP возвращает ответ 404 Not Found:
- Неверный адрес. К примеру, при ручном наборе пользователь допустил опечатку в адресе либо ссылка ведёт на несуществующую страницу. При этом домен должен быть написан верно. Если пользователь ошибется в названии домена, страница вообще не загрузится (без показа ошибки).
- Битая ссылка. Это нерабочий URL, который никуда не ведёт. Данный вариант иногда возникает при внутренней перелинковке. К примеру, раньше страница существовала, а потом её удалили и забыли убрать ссылку.
- Удалённая страница. Когда пользователь попытается перейти на удалённую с сервера страницу, он также увидит ошибку 404. Ссылка для перехода может сохраниться в браузерных закладках или на сторонних ресурсах.
- Неправильный редирект на страницу с изменённым адресом. Допустим, в процессе редизайна URL изменили, но оставили без внимания связанные ссылки.
- Неполадки на сервере. Это самый редкий вариант.
В большинстве ситуаций ошибка 404 отображается, когда не удаётся обнаружить нужную страницу на доступном сервере.
Причины отсутствия страницы на сайте бывают разными
Возможные последствия для сайта
Нужно ли считать 404 ошибку опасной для сайтов? Кажется, что нет ничего плохого в том, что пользователь не смог открыть одну веб-страницу. Однако если такая ситуация будет повторяться регулярно, это чревато оттоком аудитории. Одни пользователи решат, что сайт вовсе не существует. Другие подумают, что лучше не заходить на сайт, который работает с ошибками. Третьи будут игнорировать ресурс, на котором не смогли получить обещанную информацию.
Поисковые системы относятся к Not Found более лояльно. Например, Google отмечает, что 404 страницы не влияют на рейтинг. Но если при индексации роботы будут находить все больше ошибочных страниц, вряд ли это приведёт к более высокому ранжированию.
Если вы хотите улучшить взаимодействие с посетителями, важно найти и исправить все ошибки 404 на сайте.
Как выявить ошибку
На небольшом ресурсе легко проверить работоспособность ссылок вручную. Но если на сайте сотни и тысячи страниц, без дополнительного софта не обойтись. Есть немало сервисов и программ, позволяющих находить битые ссылки. Рассмотрим некоторые из них.
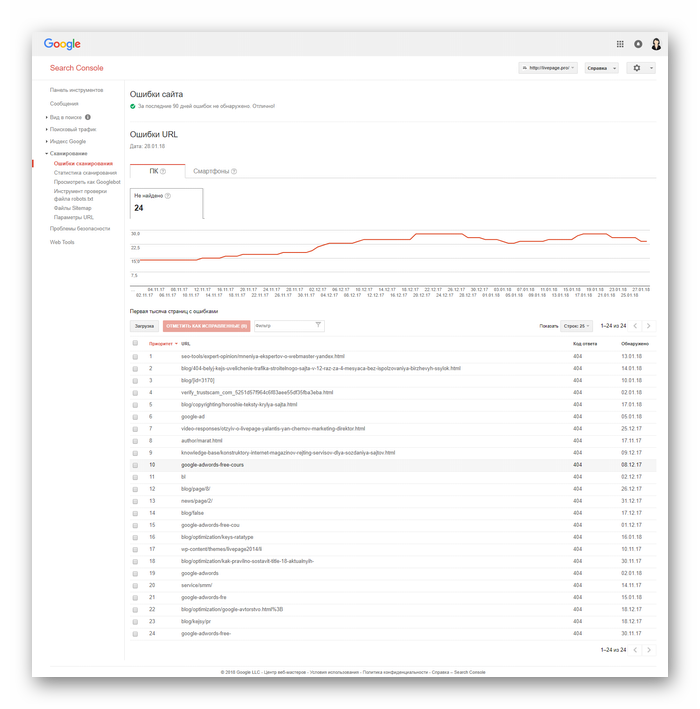
Search Console Google
Консоль поиска Google позволяет находить страницы с ошибкой 404 за несколько кликов:
- Войдите в учётную запись Google и перейдите в Search Console.
- Откройте раздел «Ошибки сканирования» → «Диагностика».
- Кликните на «Not Found».
Чтобы получить список страниц с ошибками, подтвердите права на ресурс — добавьте проверочную запись TXT в записи DNS регистратора домена. Такая запись не повлияет на работу сайта. Подробнее о процедуре подтверждения, читайте в справке Google.
Для использования Search Console Google нужно подтвердить свои права на сайт
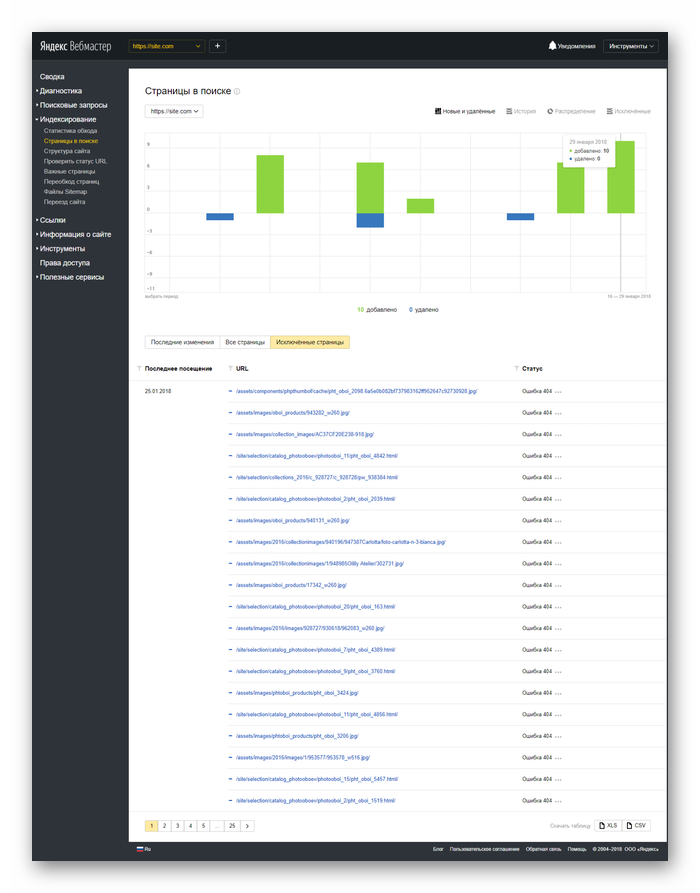
Яндекс Вебмастер
Сервис для вебмастеров от Яндекса поможет быстро найти все ошибки 404:
- Откройте Вебмастер после авторизации в Яндекс-аккаунте.
- Выберите «Индексирование» → «Доступные для поиска страницы» → «Исключённые страницы».
- В выданном списке выберите фильтр «Ошибка HTTP: 404».
Чтобы использовать Яндекс.Вебмастер, также нужно подтвердить право владения сайтом — добавить метатег в HTML-код главной страницы.
Для входа в Вебмастер авторизуйтесь в Яндексе
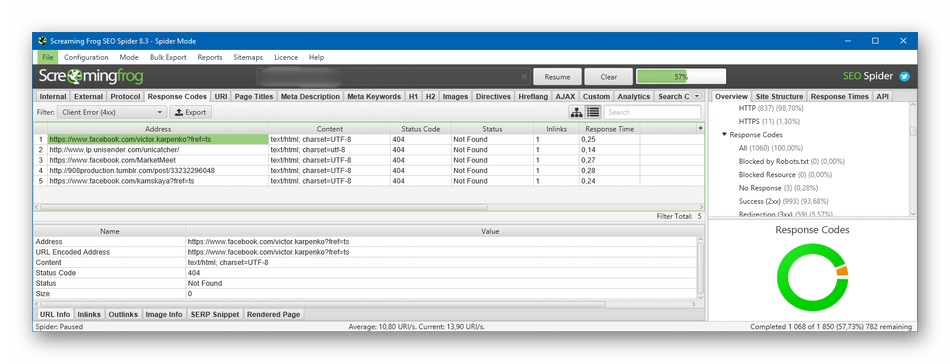
Screaming Frog
Для начала загрузите и установите программу на компьютер. После запуска добавьте URL проверяемого сайта и начните поиск проблем. Неработающие ссылки можно искать даже в бесплатной версии.
Инструмент SEO-паук в Screaming Frog помогает найти технические неисправности сайта
SiteAnalyzer
Эта бесплатная десктопная программа позволяет обнаружить технические погрешности на сайте. SiteAnalyzer быстро отыщет нерабочие и несуществующие ссылки.
SiteAnalyzer бесплатно найдёт неработающие URL
Как исправить ошибку Not Found
Выбор конкретного решения зависит от причины ошибки:
- Ссылка ведёт в никуда из-за неверного URL. Для решения проблемы замените ошибочную ссылку на правильный адрес, чтобы сервер отдавал код 200 OK.
- Битая ссылка. Подобная ситуация не редкость при внутренней перелинковке страниц. К примеру, ссылка есть, а саму страницу давно удалили. Решений два: удалить ссылку или заменить её на другую.
Удалять и менять ссылки вручную удобно только на небольших сайтах. Исправление ошибок на крупных порталах лучше автоматизировать. Например, с помощью специальных плагинов для внутренней перелинковки (Terms Description, Dagon Design Sitemap Generator) и для автоматического формирования адресов страниц (Cyr-To-Lat).
Чтобы ошибки 404 появлялись как можно реже, достаточно соблюдать простые рекомендации:
- Не присваивайте сложные адреса основным разделам сайта. Это снизит число ошибок, связанных с опечатками в URL.
- Не меняйте адреса страниц слишком часто. Это неудобно для пользователей и вводит в заблуждение поисковых роботов.
- Размещайте сайт на надёжном сервере. Это предотвратит ошибки, возникающие из-за неработоспособности сервера.
Мы разобрались, как найти и исправить ошибки Not Found внутри сайта. Но неработающая ссылка может быть расположена и на стороннем ресурсе. Допустим, когда-то на другом сайте разместили рекламную публикацию со ссылкой на определённую страницу. Спустя какое-то время страницу удалили. В этом случае появится ошибка 404. Устранить её можно, связавшись с администрацией ссылающегося сайта. Если же удалить/исправить ссылку нельзя, постарайтесь использовать ошибку с выгодой.
Как сделать страницу 404 полезной
Грамотно оформленная страница с ошибкой Error 404 Not Found — действенный инструмент конвертации посетителей. Ограничений по использованию страницы с ошибкой 404 нет. При этом практически все CMS позволяют настраивать дизайн этой страницы.
Что публиковать на странице 404:
- меню с кликабельными ссылками;
- ссылку на главную страницу;
- анонс последних публикаций;
- контакты для обратной связи.
При оформлении страницы-ошибки желательно опираться на рекомендации поисковиков:
- Яндекс настоятельно рекомендует, чтобы страница контрастировала с основным содержанием сайта — иные цвета, другие графические приёмы либо их отсутствие. Необходимо чётко и понятно объяснить пользователю, что запрошенной страницы не существует и предложить другое решение.
- Google советует придерживаться единого стиля оформления. Но также рекомендует понятно рассказать об ошибке и предложить полезные материалы.
Главное — по возможности отказаться от стандартной страницы 404. Подумайте, как привлечь внимание пользователя. Расскажите ему об отсутствии искомой страницы и предложите взамен что-то полезное или интересное.
Примеры оформления страниц 404
Designzillas
Мультяшная страница креативной студии привлекает внимание и её хочется досмотреть до конца. Если прокрутить страницу, можно увидеть, как из яйца вылупится дракон. При этом на странице есть ссылки на все основные разделы сайта.
Меню на сайте Designzillas есть и на 404 странице
Domenart Studio
Веб-студия «Домен АРТ» использует красочную страницу 404, оформленную в единой стилистике ресурса. Заблудившимся пользователям предлагают попробовать ещё раз ввести адрес или перейти в нужный раздел.
Контакты, поиск, меню — и всё это на 404 странице Domenart Studio
E-co
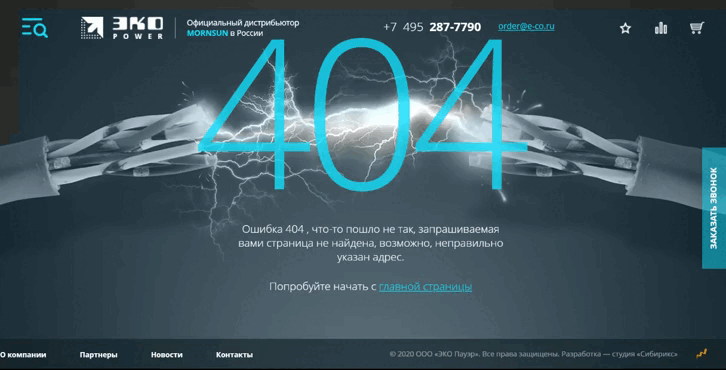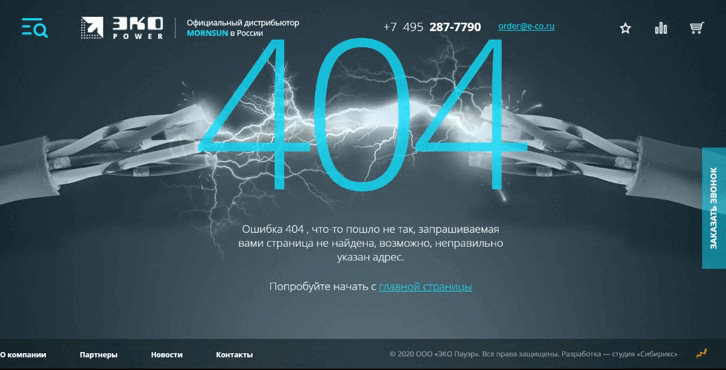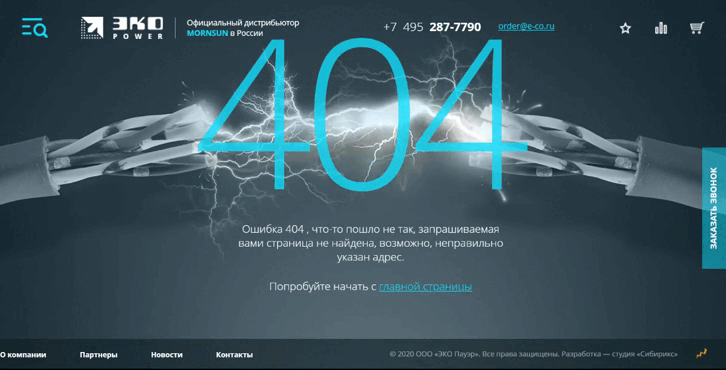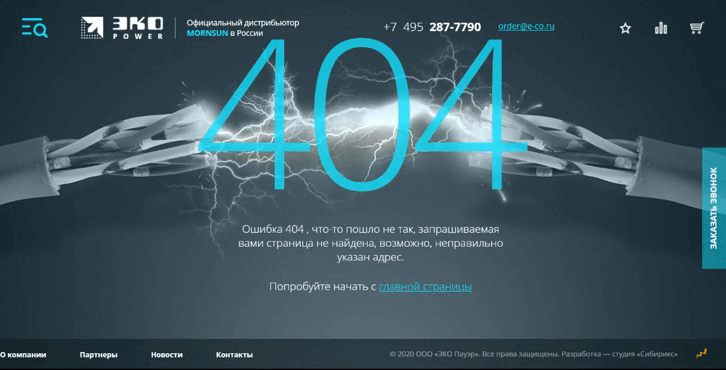
«Эко Пауэр», дистрибьютор производителя источников питания, демонстрирует короткое замыкание как символ ошибки. Посетителям предлагают перейти на главную.
Ошибка 404 «Эко Пауэр» выглядит как страница входа
Дом со всем
Компания «Дом со всем», занимающаяся бурением скважин, разместила на странице 404 свои контакты и перечень услуг. Со страницы можно перейти в любой раздел сайта или заказать обратный звонок. С таким наполнением посетителю не нужно искать дополнительную информацию где-то ещё.
Компания «Дом со всем» предлагает заказать обратный звонок
Kualo
Страница 404 на веб-хостинге Kualo может заставить пользователя забыть, зачем он сюда пришёл. Увлекательная игра притягивает внимание. В конце игры посетителю предлагают посмотреть сайт хостинга.
На странице Kualo можно просто поиграть и заработать скидки
Рано или поздно с ошибкой 404 сталкивается большинство сайтов. При регулярной проверке можно своевременно исправить неработающие ссылки, чтобы в ответ пользователи получали код 200 OK. Но для крупного ресурса лучше настроить оригинальную страницу, которая будет отображаться при появлении ошибки Not Found и подскажет посетителям, что делать дальше.
Главные мысли
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.[1]
The website hosting server will typically generate a «404 Not Found» web page when a user attempts to follow a broken or dead link; hence the 404 error is one of the most recognizable errors encountered on the World Wide Web.
English Wikipedia’s 404 Page
Overview
When communicating via HTTP, a server is required to respond to a request, such as a web browser request for a web page, with a numeric response code and an optional, mandatory, or disallowed (based upon the status code) message. In code 404, the first digit indicates a client error, such as a mistyped Uniform Resource Locator (URL). The following two digits indicate the specific error encountered. HTTP’s use of three-digit codes is similar to the use of such codes in earlier protocols such as FTP and NNTP. At the HTTP level, a 404 response code is followed by a human-readable «reason phrase». The HTTP specification suggests the phrase «Not Found»[1] and many web servers by default issue an HTML page that includes both the 404 code and the «Not Found» phrase.
A 404 error is often returned when pages have been moved or deleted. In the first case, it is better to employ URL mapping or URL redirection by returning a 301 Moved Permanently response, which can be configured in most server configuration files, or through URL rewriting; in the second case, a 410 Gone should be returned. Because these two options require special server configuration, most websites do not make use of them.
404 errors should not be confused with DNS errors, which appear when the given URL refers to a server name that does not exist. A 404 error indicates that the server itself was found, but that the server was not able to retrieve the requested page.
Soft 404 errors
Some websites report a «not found» error by returning a standard web page with a «200 OK» response code, falsely reporting that the page loaded properly; this is known as a soft 404. The term «soft 404» was introduced in 2004 by Ziv Bar-Yossef et al.[2]
Soft 404s are problematic for automated methods of discovering whether a link is broken. Some search engines, like Yahoo and Google, use automated processes to detect soft 404s.[3] Soft 404s can occur as a result of configuration errors when using certain HTTP server software, for example with the Apache software, when an Error Document 404 (specified in a .htaccess file) is specified as an absolute path (e.g. http://example.com/error.html) rather than a relative path (/error.html).[4] This can also be done on purpose to force some browsers (like Internet Explorer) to display a customized 404 error message rather than replacing what is served with a browser-specific «friendly» error message (in Internet Explorer, this behavior is triggered when a 404 is served and the received HTML is shorter than a certain length, and can be manually disabled by the user).
There are also «soft 3XX» errors where content is returned with a status 200 but comes from a redirected page, such as when missing pages are redirected to the domain root/home page.
Proxy servers
Some proxy servers generate a 404 error when a 500-range error code would be more correct. If the proxy server is unable to satisfy a request for a page because of a problem with the remote host (such as hostname resolution failures or refused TCP connections), this should be described as a 5xx Internal Server Error, but might deliver a 404 instead. This can confuse programs that expect and act on specific responses, as they can no longer easily distinguish between an absent web server and a missing web page on a web server that is present.
Intentional 404s
In July 2004, the UK telecom provider BT Group deployed the Cleanfeed content blocking system, which returns a 404 error to any request for content identified as potentially illegal by the Internet Watch Foundation.[5] Other ISPs return a HTTP 403 «forbidden» error in the same circumstances.[6] The practice of employing fake 404 errors as a means to conceal censorship has also been reported in Thailand[7] and Tunisia.[8] In Tunisia, where censorship was severe before the 2011 revolution, people became aware of the nature of the fake 404 errors and created an imaginary character named «Ammar 404» who represents «the invisible censor».[9]
Microsoft Internet Server 404 substatus error codes
The webserver software developed by Microsoft, Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS), returns a set of substatus codes with its 404 responses. The substatus codes take the form of decimal numbers appended to the 404 status code. The substatus codes are not officially recognized by IANA and are not returned by non-Microsoft servers.
Substatus codes
Microsoft’s IIS 7.0, IIS 7.5, and IIS 8.0 servers define the following HTTP substatus codes to indicate a more specific cause of a 404 error:
- 404.0 – Not found.
- 404.1 – Site Not Found.
- 404.2 – ISAPI or CGI restriction.
- 404.3 – MIME type restriction.
- 404.4 – No handler configured.
- 404.5 – Denied by request filtering configuration.
- 404.6 – Verb denied.
- 404.7 – File extension denied.
- 404.8 – Hidden namespace.
- 404.9 – File attribute hidden.
- 404.10 – Request header too long.
- 404.11 – Request contains double escape sequence.
- 404.12 – Request contains high-bit characters.
- 404.13 – Content length too large.
- 404.14 – Request URL too long.
- 404.15 – Query string too long.
- 404.16 – DAV request sent to the static file handler.
- 404.17 – Dynamic content mapped to the static file handler via a wildcard MIME mapping.
- 404.18 – Query string sequence denied.
- 404.19 – Denied by filtering rule.
- 404.20 – Too Many URL Segments.
Custom error pages
The Wikimedia 404 message
Web servers can typically be configured to display a customised 404 error page, including a more natural description, the parent site’s branding, and sometimes a site map, a search form or 404-page widget. The protocol level phrase, which is hidden from the user, is rarely customized. Internet Explorer, however, will not display custom pages unless they are larger than 512 bytes, opting instead to display a «friendly» error page.[10] Google Chrome included similar functionality, where the 404 is replaced with alternative suggestions generated by Google algorithms, if the page is under 512 bytes in size.[11] Another problem is that if the page does not provide a favicon, and a separate custom 404-page exists, extra traffic and longer loading times will be generated on every page view.[12][13]
Many organizations use 404 error pages as an opportunity to inject humor into what may otherwise be a serious website. For example, Metro UK shows a polar bear on a skateboard, and the web development agency Left Logic has a simple drawing program.[14] During the 2015 UK general election campaign the main political parties all used their 404 pages to either take aim at political opponents or show relevant policies to potential supporters.[15] In Europe, the NotFound project, created by multiple European organizations including Missing Children Europe and Child Focus, encourages site operators to add a snippet of code to serve customized 404 error pages[16] which provide data about missing children.[17]
While many websites send additional information in a 404 error message—such as a link to the homepage of a website or a search box—some also endeavor to find the correct web page the user wanted. Extensions are available for some content management systems (CMSs) to do this.[18]
Tracking 404 errors
A number of tools exist that crawl through a website to find pages that return 404 status codes. These tools can be helpful in finding links that exist within a particular website. The limitation of these tools is that they only find links within one particular website, and ignore 404s resulting from links on other websites. As a result, these tools miss out on 83% of the 404s on websites.[19] One way around this is to find 404 errors by analyzing external links.[20]
One of the most effective ways to discover 404 errors is by using Google Search Console, Google Analytics or crawling software.
Another common method is tracking traffic to 404 pages using log file analysis.[21] This can be useful to understand more about what 404s users reached on the site. Another method of tracking traffic to 404 pages is using JavaScript-based traffic tracking tools.[22]
See also
- Blue screen of death
- Funky caching
- Link rot
- List of HTTP status codes
References
- ^ a b Fielding, R.; Reschke, J. (June 2014). Fielding, R; Reschke, J (eds.). «RFC 7231, HTTP/1.1 Semantics and Content, Section 6.5.4 404 Not Found». ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. S2CID 14399078. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ Ziv Bar-Yossef; Andrei Z. Broder; Ravi Kumar; Andrew Tompkins (2004). Sic Transit Gloria Telae: Towards an Understanding of the Web’s Decay. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW). pp. 328–337. doi:10.1145/988672.988716. ISBN 978-1581138443. S2CID 587547.
- ^ «Why is your crawler asking for strange URLs that have never existed on my site?». Yahoo Ysearch Help page. Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
- ^ «Farewell to soft 404s». Google Official Blog. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «LINX Public Affairs » Cleanfeed: the facts». Publicaffairs.linx.net. 10 September 2004. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ «DEMON – Error 403». Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Sambandaraksa, Don (18 February 2009). «The old fake ‘404 Not Found’ routine — Dead link». Bangkok Post. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ^ Noman, Helmi (12 September 2008). «Tunisian journalist sues government agency for blocking Facebook, claims damage for the use of 404 error message instead of 403». Open Net Initiative. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ «Anti-censorship movement in Tunisia: creativity, courage and hope!». Global Voices Advocacy. 27 May 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Friendly HTTP Error Pages». msdn.com. 18 August 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ «Issue 1695: Chrome needs option to turn off «Friendly 404″ displays». bugs.chromium.org. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Heng, Christopher (7 September 2008). «What is Favicon.ico and How to Create a Favicon Icon for Your Website». The Site Wizard. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ «The Dastardly «favicon.ico not found» Error». Internet Folks. 3 August 1999.
- ^ «From skateboarding bears to missing children: The power of the 404 Not Found error page». Metro. 6 June 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ «The political Page 404 war». BBC Newsbeat. 27 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- ^ «Notfound.org». notfound. notfound. Archived from the original on 2 September 2014.
- ^ «Missing children messages go on 404 error pages». BBC News. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ Swenson, Sahala (19 August 2008). «Make your 404 pages more useful». Official Google Webmaster Central Blog. Google, Inc. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ «Sources Leading To 404s». SpringTrax. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Cushing, Anne (2 April 2013). «A Data-Centric Approach To Identifying 404 Pages Worth Saving». Search Engine Land. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Tracking and Preventing 404 Errors». 404errorpages.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ^ «Understand 404 Errors». SpringTrax.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
External links
- A More Useful 404
- 404 Not Found of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content specification, at the Internet Engineering Task Force
- ErrorDocument Directive – instructions on custom error pages for the Apache 2.0 web server
- 404: Not Found – an award-winning song about the error code
Ошибка с кодом 404 появляется у пользователя при попытке открыть страницу, которой не существует на сайте. Виной тому может быть битая ссылка или просто неверно введенный адрес, однако сама проблема появляется довольно часто, так что вопрос, как исправить ошибку 404, возникает как у владельцев сайтов, так и у обычных пользователей.
Причины появления ошибки с кодом 404
Из описания выше вы узнали, что значит рассматриваемая ошибка, однако не совсем понятна картина того, как она может появиться. Существуют четыре основные причины, из-за которых вместо стандартной загрузки страницы и появляется соответствующее уведомление. Выглядят они следующим образом:
- Неверный адрес. Чаще всего появляется, когда юзер вручную вводит адрес страницы или пытается перейти в несуществующий раздел сайта.
- Удаленная страница. Иногда страницы удаляются с сайта его владельцем, однако из поисковика они не пропадают еще некоторое время. Кроме того, прямые ссылки могут храниться в закладках у некоторых пользователей. Соответственно, при переходе и появится соответствующее уведомление об ошибке сервера.
- Битая ссылка. Такая страница когда-то действительно существовала, однако сбой произошел при перелинковке, и теперь ссылка ведет в никуда, что и влияет на возникновение проблемы.
- Проблемы функционирования сервера. Последняя причина появляется крайне редко и связана со сбоями на сервере, где размещен сайт.
Казалось бы, все перечисленные выше причины схожи между собой, однако владельцу сайта придется подойти по-разному к их решению, а от обычного юзера требуется только проверить правильность введения адреса страницы.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Поиск битых ссылок на сайте
Если вы являетесь владельцем сайта, можно проверить наличие битых ссылок и удаленных страниц при помощи специальных онлайн-сервисов или программ. Существует несколько популярных инструментов, о которых и пойдет речь далее.
Яндекс.Вебмастер
Проще всего использовать сайт Яндекс.Вебмастер. Потребуется авторизоваться в сервисе и добавить собственный сайт, выполнив простые инструкции, которые будут отображаться на экране. После этого выполните такую последовательность действий:
- Через левое меню откройте раздел «Индексирование».
- Там вас интересует категория «Страницы в поиске».
- Снизу перейдите на вкладку «Исключительные страницы».
- Задайте фильтрацию, чтобы сначала отображались результаты, где присутствует «ошибка 404: страница не найдена».
Google Search Console
Онлайн-сервис от известной компании Google Search Console функционирует примерно по такому же принципу, а для поиска проблемных страниц пользователю потребуется выполнить следующие действия:
- Выполните вход и добавьте свой сайт.
- Откройте раздел «Сканирование».
- Перейдите к категории «Ошибки сканирования».
- Используйте фильтр или самостоятельно ознакомьтесь с присутствующими ошибками.
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog – специализированное программное обеспечение, подходящее для сканирования сайтов. Если приведенные выше онлайн-сервисы вам не подошли, скачайте это решение с официального сайта, подключите к нему ваш сайт и произведите сканирование.
Благодаря данному инструменту у вас получится легко обнаружить все проблемные страницы, в том числе и страницы с другими ошибками сервера.
Исправление ошибки 404
С принципом обнаружения проблемных страниц все понятно, однако как исправить ошибку 404 Page Not Found? Здесь все зависит непосредственно от возникшей ситуации, а также того, используется ли на сайте CMS. Давайте по очереди разберем каждую ситуацию.
При использовании CMS
Сейчас многие сайты создаются при помощи CMS. Это может быть WordPress, Joomla, 1С-Битрикс или какие-либо другие системы управления содержимым. Если проблема возникает на таком сайте, а на экране при переходе к сайту вы видите следующее изображение, значит, потребуется выполнить ряд действий для исправления неполадки.
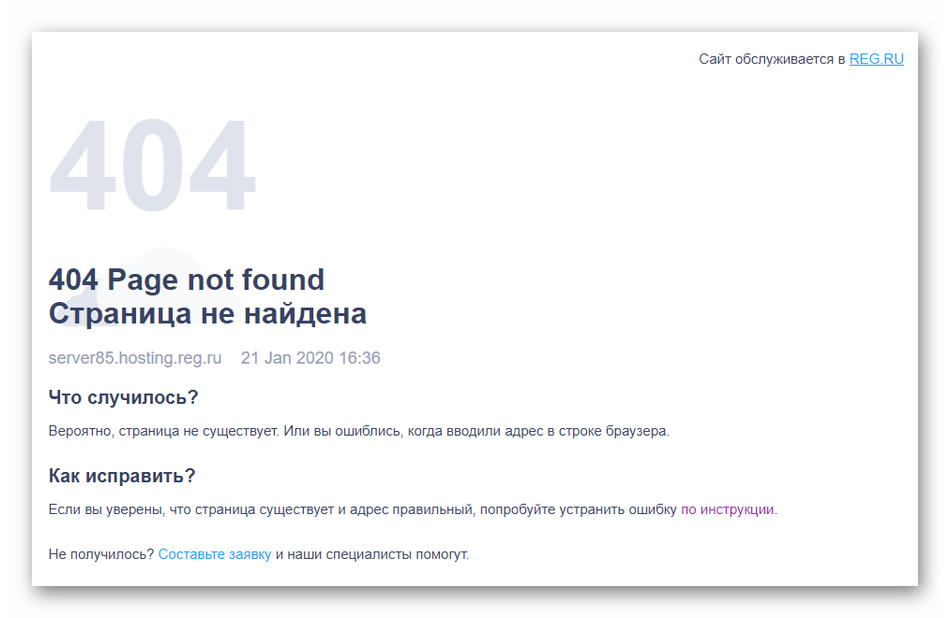
Однако иногда неполадка может сохраняться даже при условии, что файл был создан или существовал изначально. Тогда не остается другого варианта, кроме как обратиться напрямую в техническую поддержку хостинга.
Описанная выше ситуация подразумевает, что ошибку 404 выдает сам хостинг, однако бывает, что она отображается от самой CMS, а в браузере это выглядит примерно следующим образом:
В таких ситуациях вам необходимо проверить каждое название ссылки на правильность ввода, а также убедиться в том, что установленные SEO-плагины функционируют нормально и не влияют на проблемную генерацию ссылок. После проверки каждой ссылки ошибка http 404 должна исчезнуть.
Без использования CMS
Иногда сайты функционируют и без использования CMS. В таких ситуациях метод решения будет другим, поскольку, скорее всего, причина возникновения неполадки связана с отсутствием файлов в папке сайта или их неправильном расположении.
Только что мы разобрались с тем, что значит ошибка 404 Not Found, а также рассмотрели методы ее решения для разных ситуаций. Владельцу сайта нужно внимательно подойти к этому вопросу и всегда быть аккуратным при составлении адресов ссылок. От обычного же юзера требуется только соблюдать правильность ввода URL, если речь идет о ручном наборе в адресной строке браузера.
В статье мы расскажем, что означает ошибка 404 на сайте. Также она может называться:
- 404 page not found,
- http error 404,
- error 404.
Ниже мы опишем, почему возникает ошибка 404, а также как её отследить и исправить.
404 ошибка (http error 404) — что это значит?
Ошибка 404 page not found — это код ответа сервера. Что это значит?
Когда вы вводите адрес сайта, браузер запрашивает его стартовую страницу у сервера. Если сервер не может найти страницу, он сообщает об этом браузеру с помощью кода 404. Это сообщение отображается на экране пользователя в браузере.
Почему такое может произойти? Есть несколько возможных причин:
- Вы допустили ошибку при вводе адреса страницы или при открытии файла в браузере. Или браузеру не удалось найти IP-адрес сервера. Сервер не может найти и выдать данные потому, что вы дали ему неправильные «координаты». В таком случае вам достаточно просто исправить ошибку в URL-адресе, и вместо страницы с ошибкой 404 появятся искомые страница/файл.
- Данные (страница или файл) не размещены на сервере, или CMS неверно отвечает на запрос пользователя. В этом случае дело обстоит сложнее и быстро справиться с проблемой не получится. Чтобы устранить ошибку 404, определите, как создавался сайт, на котором обнаружена ошибка (на CMS или без использования CMS). От этого будет зависеть способ решения проблемы.
Мы рассмотрим, что делать с ошибкой 404 и как исправить.
Как убрать ошибку 404 на сайте, созданном на CMS (WordPress, Joomla, 1С-Битрикс и т.д.)
На сайтах, созданных с использованием CMS, встречаются различные страницы с ошибкой 404 (http status 404). В зависимости от типа страницы с ошибкой различаются причины возникновения и пути решения проблемы:
- Если вы видите на своём сайте стандартную ошибку 404 REG.RU:
В большинстве случаев проблема связана с отсутствием конфигурационного файла .htaccess. Как избавиться от ошибки 404? Создайте в корневой папке сайта пустой текстовый файл с расширением .htaccess и добавьте в него стандартные директивы для используемой CMS. Стандартные директивы приведены в статье: Файлы .htaccess для популярных CMS.
Важно: в панели управления cPanel файл .htaccess по умолчанию скрыт (т.е. он существует, но не виден). Следуйте инструкции, чтобы включить отображение файла. Затем сверьте его содержимое со стандартным.
Если файл .htaccess существует и его содержимое корректно, а ошибка 404 not found сохраняется, обратитесь в техническую поддержку.
- Если вы видите иную страницу ошибки, которую отдает CMS сайта. Например:
Ошибка на WordPress
Пользовательская ошибка 404 not found
Возможно, страница не создана или не опубликована на этапе размещения сайта в админке CMS. Также ошибка может быть связана с формированием «человекопонятных» ЧПУ-ссылок с помощью SEO-плагинов. Чтобы избавиться от проблемы, необходимо обратиться к веб-разработчикам сайта или на тематические форумы, на которых представлена необходимая техническая информация (ошибка http 404).
Как быстро устранить ошибку 404 на сайте, созданном без использования CMS
На сайтах, созданных без использования CMS, код ошибки 404 отображается следующим образом:
Что означает это сообщение? Запрашиваемые страница/файл отсутствуют или размещены в неправильной папке (не в корневой папке сайта).
Что делать? Откройте корневую папку сайта в панели управления хостингом и проверьте, находятся ли в ней файлы вашего сайта.
- Если искомые файлы отсутствуют, следуйте инструкции: Как загрузить файл в корневой каталог сайта? После размещения файлов в корневой папке ошибка 404 должна исчезнуть.
- Если файлы существуют и находятся в корневой папке, обратитесь в техническую поддержку.
Как находить и мониторить код ошибки 404?
Если вы владелец сайта, вы можете найти страницы с ошибкой с помощью специальных сервисов. Самые популярные сервисы:
- Яндекс.Вебмастер,
- Google Search Console,
- Screaming Frog.
Ниже мы описали, как работать с каждым из них.
Яндекс.Вебмастер
-
Авторизуйтесь в Яндекс.Вебмастер.
-
Перейдите в раздел Индексирование — Страницы в поиске:
HTTP status 404 — что это
- Выберите Исключенные страницы:
- Добавьте фильтр, при котором отобразятся результаты с ошибкой «404 page not found»:
Google Search Console
-
Авторизуйтесь в Google Search Console.
-
Разверните блок Индекс и выберите Покрытие:
404 ошибка: что это
- Используйте фильтр, который покажет код ошибки 404. Для этого перейдите в раздел Сведения и кликните Отправленный URL не найден (ошибка 404):
Ошибка 404: что значит и как исправить
Screaming Frog
-
Загрузите программу с официального сайта.
-
Установите её на компьютер.
-
Откройте программу, введите ссылку на сайт и нажмите Start:
- Перейдите во вкладку Response Code. Из выпадающего списка выберите фильтр Client Error (4xx):
Открывается только главная страница сайта, на внутренних страницах ошибка 404 или 500
Рассмотрим, что значит и как исправить ошибку отображения внутренних страниц сайта (error 404 или 500). Причиной проблемы является отсутствие файла .htaccess (либо он пустой, либо в нем не хватает необходимых директив для работы CMS). Решить проблему может замена текущего файла .htaccess стандартным для данной CMS.
На хостинге Linux
Если у вас ISPmanager, проверьте, не включены ли Автоподдомены. Если они включены, отключите их, проверьте актуальность проблемы.
В остальных случаях для устранения внутренней ошибки 404 или 500, перейдите в корневую папку сайта: Как узнать корневую папку сайта
Создайте файл .htaccess (или замените его) со следующим содержимым:
Файл .htaccess для Joomla
##
# @version $Id: htaccess.txt 14401 2010-01-26 14:10:00Z louis $
# @package Joomla
# @copyright Copyright (C) 2005 - 2010 Open Source Matters. All rights reserved.
# @license http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html GNU/GPL
# Joomla! is Free Software
##
#####################################################
# READ THIS COMPLETELY IF YOU CHOOSE TO USE THIS FILE
#
# The line just below this section: 'Options +FollowSymLinks' may cause problems
# with some server configurations. It is required for use of mod_rewrite, but may already
# be set by your server administrator in a way that dissallows changing it in
# your .htaccess file. If using it causes your server to error out, comment it out (add # to
# beginning of line), reload your site in your browser and test your sef url's. If they work,
# it has been set by your server administrator and you do not need it set here.
#
#####################################################
## Can be commented out if causes errors, see notes above.
Options +FollowSymLinks
#
# mod_rewrite in use
RewriteEngine On
########## Begin - Rewrite rules to block out some common exploits
## If you experience problems on your site block out the operations listed below
## This attempts to block the most common type of exploit `attempts` to Joomla!
#
## Deny access to extension xml files (uncomment out to activate)
#<Files ~ ".xml$">
#Order allow,deny
#Deny from all
#Satisfy all
#</Files>
## End of deny access to extension xml files
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} mosConfig_[a-zA-Z_]{1,21}(=|%3D) [OR]
# Block out any script trying to base64_encode crap to send via URL
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} base64_encode.*(.*) [OR]
# Block out any script that includes a <script> tag in URL
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} (<|%3C).*script.*(>|%3E) [NC,OR]
# Block out any script trying to set a PHP GLOBALS variable via URL
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} GLOBALS(=|[|%[0-9A-Z]{0,2}) [OR]
# Block out any script trying to modify a _REQUEST variable via URL
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} _REQUEST(=|[|%[0-9A-Z]{0,2})
# Send all blocked request to homepage with 403 Forbidden error!
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php [F,L]
#
########## End - Rewrite rules to block out some common exploits
# Uncomment following line if your webserver's URL
# is not directly related to physical file paths.
# Update Your Joomla! Directory (just / for root)
# RewriteBase /
########## Begin - Joomla! core SEF Section
#
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !^/index.php
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} (/|.php|.html|.htm|.feed|.pdf|.raw|/[^.]*)$ [NC]
RewriteRule (.*) index.php
RewriteRule .* - [E=HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:%{HTTP:Authorization},L]
#
########## End - Joomla! core SEF Section
Файл .htaccess для WordPress
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
Файл .htaccess для HostCMS
Options +FollowSymlinks
AddDefaultCharset Off
<IfModule mod_php4.c>
php_flag magic_quotes_gpc off
php_flag magic_quotes_runtime off
php_flag register_globals off
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_php5.c>
php_flag magic_quotes_gpc off
php_flag magic_quotes_runtime off
php_flag register_globals off
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
DirectoryIndex index.php index.htm index.html
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /index.php
</IfModule>
Файл .htaccess для Bitrix
Options -Indexes
ErrorDocument 404 /404.php
<IfModule mod_php5.c>
php_flag allow_call_time_pass_reference 1
php_flag session.use_trans_sid off
#php_value display_errors 1
#php_value mbstring.func_overload 2
#php_value mbstring.internal_encoding UTF-8
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
Options +FollowSymLinks
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-l
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !/bitrix/urlrewrite.php$
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /bitrix/urlrewrite.php [L]
RewriteRule .* - [E=REMOTE_USER:%{HTTP:Authorization}]
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive on
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 3 day"
ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 3 day"
</IfModule>
Файл .htaccess для ModX
# MODx supports Friendly URLs via this .htaccess file. You must serve web
# pages via Apache with mod_rewrite to use this functionality, and you must
# change the file name from ht.access to .htaccess.
#
# Make sure RewriteBase points to the directory where you installed MODx.
# E.g., "/modx" if your installation is in a "modx" subdirectory.
#
# You may choose to make your URLs non-case-sensitive by adding a NC directive
# to your rule: RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?q=$1 [L,QSA,NC]
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
# Rewrite www.domain.com -> domain.com -- used with SEO Strict URLs plugin
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} .
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^example-domain-please-change.com [NC]
#RewriteRule (.*) http://example-domain-please-change.com/$1 [R=301,L]
#
# or for the opposite domain.com -> www.domain.com use the following
# DO NOT USE BOTH
#
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} .
#RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www.example-domain-please-change.com [NC]
#RewriteRule (.*) http://www.example-domain-please-change.com/$1 [R=301,L]
#
# Rewrite secure requests properly to prevent SSL cert warnings, e.g. prevent
# https://www.domain.com when your cert only allows https://secure.domain.com
#RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} !^443
#RewriteRule (.*) https://example-domain-please-change.com.com/$1 [R=301,L]
#
# The Friendly URLs part
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?q=$1 [L,QSA]
#
# Make sure .htc files are served with the proper MIME type, which is critical # for XP SP2. Un-comment if your host allows htaccess MIME type overrides.
#AddType text/x-component .htc
#
# If your server is not already configured as such, the following directive
# should be uncommented in order to set PHP's register_globals option to OFF.
# This closes a major security hole that is abused by most XSS (cross-site
# scripting) attacks. For more information: http://php.net/register_globals
#
# To verify that this option has been set to OFF, open the Manager and choose
# Reports -> System Info and then click the phpinfo() link. Do a Find on Page
# for "register_globals". The Local Value should be OFF. If the Master Value
# is OFF then you do not need this directive here.
#
# IF REGISTER_GLOBALS DIRECTIVE CAUSES 500 INTERNAL SERVER ERRORS :
#
# Your server does not allow PHP directives to be set via .htaccess. In that
# case you must make this change in your php.ini file instead. If you are
# using a commercial web host, contact the administrators for assistance in
# doing this. Not all servers allow local php.ini files, and they should
# include all PHP configurations (not just this one), or you will effectively
# reset everything to PHP defaults. Consult www.php.net for more detailed
# information about setting PHP directives.
#
#php_flag register_globals Off
#
# For servers that support output compression, you should pick up a bit of
# speed by un-commenting the following lines.
#
#php_flag zlib.output_compression On
#php_value zlib.output_compression_level 5
#
# The following directives stop screen flicker in IE on CSS rollovers. If
# needed, un-comment the following rules. When they're in place, you may have
# to do a force-refresh in order to see changes in your designs.
#
#ExpiresActive On
#ExpiresByType image/gif A2592000
#ExpiresByType image/jpeg A2592000
#ExpiresByType image/png A2592000
#BrowserMatch "MSIE" brokenvary=1
#BrowserMatch "Mozilla/4.[0-9]{2}" brokenvary=1
#BrowserMatch "Opera" !brokenvary
#SetEnvIf brokenvary 1 force-no-vary
Файл .htaccess для Drupal
#
# Apache/PHP/Drupal settings:
#
# Protect files and directories from prying eyes.
<FilesMatch ".(engine|inc|info|install|make|module|profile|test|po|sh|.*sql|theme|tpl(.php)?|xtmpl)$|^(..*|Entries.*|Repository|Root|Tag|Template)$">
Order allow,deny
</FilesMatch>
# Don't show directory listings for URLs which map to a directory.
Options -Indexes
# Follow symbolic links in this directory.
Options +FollowSymLinks
# Make Drupal handle any 404 errors.
ErrorDocument 404 /index.php
# Force simple error message for requests for non-existent favicon.ico.
<Files favicon.ico>
# There is no end quote below, for compatibility with Apache 1.3.
ErrorDocument 404 "The requested file favicon.ico was not found.
</Files>
# Set the default handler.
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html index.htm
# Override PHP settings that cannot be changed at runtime. See
# sites/default/default.settings.php and drupal_initialize_variables() in
# includes/bootstrap.inc for settings that can be changed at runtime.
# PHP 5, Apache 1 and 2.
<IfModule mod_php5.c>
php_flag magic_quotes_gpc off
php_flag magic_quotes_sybase off
php_flag register_globals off
php_flag session.auto_start off
php_value mbstring.http_input pass
php_value mbstring.http_output pass
php_flag mbstring.encoding_translation off
</IfModule>
# Requires mod_expires to be enabled.
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
# Enable expirations.
ExpiresActive On
# Cache all files for 2 weeks after access (A).
ExpiresDefault A1209600
<FilesMatch .php$>
# Do not allow PHP scripts to be cached unless they explicitly send cache
# headers themselves. Otherwise all scripts would have to overwrite the
# headers set by mod_expires if they want another caching behavior. This may
# fail if an error occurs early in the bootstrap process, and it may cause
# problems if a non-Drupal PHP file is installed in a subdirectory.
ExpiresActive Off
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule>
# Various rewrite rules.
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine on
# Block access to "hidden" directories whose names begin with a period. This
# includes directories used by version control systems such as Subversion or
# Git to store control files. Files whose names begin with a period, as well
# as the control files used by CVS, are protected by the FilesMatch directive
# above.
#
# NOTE: This only works when mod_rewrite is loaded. Without mod_rewrite, it is
# not possible to block access to entire directories from .htaccess, because
# <DirectoryMatch> is not allowed here.
#
# If you do not have mod_rewrite installed, you should remove these
# directories from your webroot or otherwise protect them from being
# downloaded.
RewriteRule "(^|/)." - [F]
# If your site can be accessed both with and without the 'www.' prefix, you
# can use one of the following settings to redirect users to your preferred
# URL, either WITH or WITHOUT the 'www.' prefix. Choose ONLY one option:
#
# To redirect all users to access the site WITH the 'www.' prefix,
# (http://example.com/... will be redirected to http://www.example.com/...)
# uncomment the following:
# RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www. [NC]
# RewriteRule ^ http://www.%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
#
# To redirect all users to access the site WITHOUT the 'www.' prefix,
# (http://www.example.com/... will be redirected to http://example.com/...)
# uncomment the following:
# RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.(.+)$ [NC]
# RewriteRule ^ http://%1%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
# Modify the RewriteBase if you are using Drupal in a subdirectory or in a
# VirtualDocumentRoot and the rewrite rules are not working properly.
# For example if your site is at http://example.com/drupal uncomment and
# modify the following line:
# RewriteBase /drupal
#
# If your site is running in a VirtualDocumentRoot at http://example.com/,
# uncomment the following line:
# RewriteBase /
# Pass all requests not referring directly to files in the filesystem to
# index.php. Clean URLs are handled in drupal_environment_initialize().
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !=/favicon.ico
RewriteRule ^ index.php [L]
# Rules to correctly serve gzip compressed CSS and JS files.
# Requires both mod_rewrite and mod_headers to be enabled.
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
# Serve gzip compressed CSS files if they exist and the client accepts gzip.
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Accept-encoding} gzip
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME}.gz -s
RewriteRule ^(.*).css $1.css.gz [QSA]
# Serve gzip compressed JS files if they exist and the client accepts gzip.
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Accept-encoding} gzip
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME}.gz -s
RewriteRule ^(.*).js $1.js.gz [QSA]
# Serve correct content types, and prevent mod_deflate double gzip.
RewriteRule .css.gz$ - [T=text/css,E=no-gzip:1]
RewriteRule .js.gz$ - [T=text/javascript,E=no-gzip:1]
<FilesMatch "(.js.gz|.css.gz)$">
# Serve correct encoding type.
Header append Content-Encoding gzip
# Force proxies to cache gzipped & non-gzipped css/js files separately.
Header append Vary Accept-Encoding
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule>
</IfModule>
Файл .htaccess для NetCat
AddDefaultCharset windows-1251
ErrorDocument 404 /netcat/require/e404.php
<ifModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-l
RewriteRule ^(.+)$ /netcat/require/e404.php?REQUEST_URI=$1 [L,QSA]
</ifModule>
Файл .htaccess для DLE
DirectoryIndex index.php
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
# Редиректы
RewriteRule ^page/(.*)$ index.php?cstart=$1 [L]
# Сам пост
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+),(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=showfull&year=$1&month=$2&day=$3&news_page=$4&cstart=$5&news_name=$6 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/page,([0-9]+),(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=showfull&year=$1&month=$2&day=$3&news_page=$4&news_name=$5 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/print:page,([0-9]+),(.*).html(/?)+$ engine/print.php?subaction=showfull&year=$1&month=$2&day=$3&news_page=$4&news_name=$5 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=showfull&year=$1&month=$2&day=$3&news_name=$4 [L]
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$4&news_page=$2&cstart=$3&seourl=$5&seocat=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$3&news_page=$2&seourl=$4&seocat=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/print:page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ engine/print.php?news_page=$2&newsid=$3&seourl=$4&seocat=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$2&seourl=$3&seocat=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$3&news_page=$1&cstart=$2&seourl=$4 [L]
RewriteRule ^page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$2&news_page=$1&seourl=$3 [L]
RewriteRule ^print:page,([0-9]+),([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ engine/print.php?news_page=$1&newsid=$2&seourl=$3 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]+)-(.*).html(/?)+$ index.php?newsid=$1&seourl=$2 [L]
# За день
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1&month=$2&day=$3 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1&month=$2&day=$3&cstart=$4 [L]
# За весь месяц
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1&month=$2 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1&month=$2&cstart=$3 [L]
# Вывод за весь год
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^([0-9]{4})/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?year=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
# вывод отдельному тегу
RewriteRule ^tags/([^/]*)(/?)+$ index.php?do=tags&tag=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^tags/([^/]*)/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?do=tags&tag=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
# вывод для отдельного юзера
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)/rss.xml$ engine/rss.php?subaction=allnews&user=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)/news(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=allnews&user=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)/news/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=allnews&user=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
RewriteRule ^user/([^/]*)/news/rss.xml(/?)+$ engine/rss.php?subaction=allnews&user=$1 [L]
# вывод всех последних новостей
RewriteRule ^lastnews/(/?)+$ index.php?do=lastnews [L]
RewriteRule ^lastnews/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?do=lastnews&cstart=$1 [L]
# вывод в виде каталога
RewriteRule ^catalog/([^/]*)/rss.xml$ engine/rss.php?catalog=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^catalog/([^/]*)(/?)+$ index.php?catalog=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^catalog/([^/]*)/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?catalog=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
# вывод непрочитанных статей
RewriteRule ^newposts(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=newposts [L]
RewriteRule ^newposts/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?subaction=newposts&cstart=$1 [L]
# вывод избранных статей
RewriteRule ^favorites(/?)+$ index.php?do=favorites [L]
RewriteRule ^favorites/page/([0-9]+)(/?)+$ index.php?do=favorites&cstart=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^rules.html$ index.php?do=rules [L]
RewriteRule ^statistics.html$ index.php?do=stats [L]
RewriteRule ^addnews.html$ index.php?do=addnews [L]
RewriteRule ^rss.xml$ engine/rss.php [L]
RewriteRule ^sitemap.xml$ uploads/sitemap.xml [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/page/([0-9]+)/$ index.php?do=cat&category=$1&cstart=$2 [L]
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/$ index.php?do=cat&category=$1 [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^([^.]+)/rss.xml$ engine/rss.php?do=cat&category=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^page,([0-9]+),([^/]+).html$ index.php?do=static&page=$2&news_page=$1 [L]
RewriteRule ^print:([^/]+).html$ engine/print.php?do=static&page=$1 [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^([^/]+).html$ index.php?do=static&page=$1 [L]
Файл .htaccess для Opencart
Options +FollowSymlinks
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^([^?]*) index.php?_route_=$1 [L,QSA]
Файл .htaccess для Webasyst
<FilesMatch ".md5$">
Deny from all
</FilesMatch>
DirectoryIndex index.php
Options -Indexes
# Comment the following line, if option Multiviews not allowed here
Options -MultiViews
AddDefaultCharset utf-8
<ifModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
# Uncomment the following line, if you are having trouble
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !.(js|css|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|svg|ttf|eot|otf|woff|woff2)$ [or]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} apple-touch-icon.png$ [or]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_METHOD} ^(POST|PUT|COPY|MOVE|DELETE|PROPFIND|OPTIONS|MKCOL)$ [or]
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Translate} ^.+$ [or]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} ^(DavClnt|litmus|gvfs|davfs|wdfs|WebDAV|cadaver|Cyberduck)
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php [L,QSA]
</ifModule>
<ifModule mod_headers.c>
<FilesMatch ".(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|js|css|svg|ttf|eot|otf|woff|woff2)$">
Header set Cache-Control "max-age=3153600, public"
</FilesMatch>
</ifModule>Если у вас хостинг Windows
На хостинге Windows файл .htaccess не поддерживается. Его функцию выполняет файл web.config. Если вы наблюдаете внутреннюю ошибку 404 или 500 на хостинге Windows, рекомендуем обратиться к разработчикам сайта или на тематические форумы с вопросом, как убрать 404, заменив файл web.config.
Что будет, если не исправлять ошибку 404
Во-первых, есть риск потерять потенциальных клиентов. Когда пользователь не получает информацию, которую искал, он уходит на другой сайт, который ему предложил браузер. Если ошибка встречается на веб-ресурсе часто, можно потерять и уже имеющихся пользователей, так как они решат, что использование такого сайта небезопасно.
Во-вторых, есть риск потерять хорошую позицию в поисковой выдаче. Сама по себе страница с ошибкой 404 не вызывает у поисковой системы недоверия. Она просто удаляется из индексации. Однако там могли находиться ключевые слова, которые могли повлиять положительно на поисковую выдачу. Если на сайте много страниц с ошибкой, тогда поисковые роботы действительно могут отнестись с недоверием ко всему веб-ресурсу и сайт может потерять высокий рейтинг.
Сделайте страницу 404 полезной
Ошибка 404 (страница не найдена) может появиться в любое время. Важно, чтобы пользователь при входе на эту страницу не потерял доверия к сайту. Страницы с ошибкой 404 можно создавать самостоятельно. Например, если у вас сайт на WordPress или вы пользуетесь услугой REG.Site, страницу с ошибкой можно легко создать с помощью плагина 404page.
Вот несколько советов по созданию страницы:
- дизайн этой страницы должен соответствовать всему ресурсу (цвет, шрифт, иллюстрации),
- поместите ссылку на главную страницу,
- добавьте дайджесты последних публикаций на сайте,
- поместите контакты организации (номер телефона, адрес) и службы поддержки,
- можно предложить действия для решения проблемы доступа к странице.
После посещения такой страницы посетитель хоть и не получит нужную информацию, однако у него останется положительное впечатление от посещения сайта, и в следующий раз он не откажется зайти на него снова.
Если перечисленные способы не помогли исправить ошибку, обратитесь в службу поддержки REG.RU.
Видеосправка. Об ошибке 404 и как создать страницу для неё
Of the many potential errors you might see on your WordPress site, Error 404 Not Found is one of the tamer ones. But that doesn’t mean it isn’t frustrating when you or your visitors try to browse your site and keep running into the Error 404 Not Found message. 😒 That’s the last thing you want first-time potential customers seeing from your brand. A 404 error can also be an indicator to you that something has changed or moved and a 301 redirect probably needs to be added for SEO.
In this post, we’re going to try to help you get your site working again by explaining a few things:
Prefer to watch the video version?
What is the Error 404 Not Found?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the error 404 Not Found as:
The 404 (Not Found) status code indicates that the origin server did not find a current representation for the target resource or is not willing to disclose that one exists. A 404 status code does not indicate whether this lack of representation is temporary or permanent; the 410 (Gone) status code is preferred over 404 if the origin server knows, presumably through some configurable means, that the condition is likely to be permanent.
Whenever you, or one of your visitors, visit your website, your browser sends a request to the web server and receives back data including something called an HTTP header. The HTTP header includes HTTP status codes to explain “what happened” with the request.
Most of the time, the request works perfectly and you never actually see the HTTP status code (unless you go looking). But if something goes wrong, your web browser will usually display a message with the HTTP status code to indicate the exact problem.
Just like other error messages (500 error, 502 error, 503 error, 504 error, etc.), the Error 404 Not Found message is the result of that process.
What Does Error 404 Not Found Actually Mean?
Basically, it means that the client (your, or your visitor’s, web browser) was able to successfully connect to the host (your website’s server), but it was unable to find the actual resource that was requested (e.g. a specific URL or filename).
For example, if someone tries to access yoursite.com/post-name but you don’t have any content with the slug post-name. The visitor will then see a 404 error because, even though your web server is functioning normally, the resource that was requested doesn’t exist.
It’s not just posts or pages either, any asset missing can generate a 404 error on the server, such as a missing image file, missing JavaScript, missing CSS, etc.
What Causes Error 404 Not Found on WordPress?
If you see this error on all of your site’s content, it’s typically due to an issue with your WordPress site’s permalinks. If you only see it on individual pieces of content, though, it’s most likely because you changed a piece of content’s slug without setting up a redirect.
Additionally, the 404 error isn’t always a bad thing – it’s only bad when it’s interfering with usability. And sometimes things are just out of your control!
For example, sometimes a person might just type the wrong URL in their address bar. In that case, they’ll still see a 404 error, but there’s no actual problem with how your site is configured. This is actually the desired response, and you can create your own custom 404 page to help get visitors to the right spot (we’ll show you how later on).
Error 404 Not Found Variations
Because different browsers display error messages differently, you might see a different message for this error. Other common variations include:
- “Error 404”
- “404 Not Found”
- “HTTP Error 404”
- “Not Found”
- “Page Not Found”
- “The requested URL was not found on this server.”
- “The page cannot be found”
- “We can’t find the page you’re looking for.”
- “The requested URL /~ was not found on this server. That’s all we know.
The Error 404 Not Found message is also unique in that many sites will actually create a custom page to address the error, rather showing one of the messages above. Some WordPress themes also include custom 404 pages by default. For that reason, you might not actually see the error message at all because many sites will use funny or creative 404 pages instead.
Below is an example of our own 404 page at Kinsta. We include a search box and some of our recent blog posts to help visitors find what they might have been looking for. Always include search functionality on your 404 page.
Error 404 Not Found Impact on SEO
Error 404 Not Found doesn’t have any inherent negative impact on SEO. But it might have a negative impact depending on the reason for why the error is happening.
For example, if a visitor just mistypes a URL and sees a 404 error – there won’t be a negative impact on SEO. But if you have individual errors because of broken URLs, that will inhibit Google’s ability to properly crawl your site and have a negative SEO effect in that way.
Additionally, if a permalink issue is causing sitewide 404 errors, Google won’t be able to crawl any of your site’s content. In other words, always fix your 404 errors as soon as possible.
Error 404 Not Found Impact on Site Performance
Many don’t realize it, but sites that generate a lot of 404 errors can easily run into performance issues, as these responses aren’t typically cached. We saw this a lot on larger sites and it can be a big problem if you accidentally promote or get a surge of viral traffic to a 404 page. To minimize the impact of 404 requests on site performance, we automatically cache 404 pages for 15 minutes. If you create a new page with the same URL as the cached 404 page, we’ll automatically purge the cache so your visitors will be able to see the new page immediately. This means your site will be protected from PHP and CPU spikes caused by traffic to dynamic 404 pages.
You are probably generating more 404 errors than you think! Our MyKinsta analytics tool can help you determine the exact amount (as seen below).
You can also quickly see what the top 404 errors are. In this example below, you can see the site is missing some mobile icons, such as /apple-touch-icon.png. These are most likely in a theme or plugin’s code that is getting queried, but the actual icons were never added. Therefore, the server generates a 404 error as it can’t find the resources.
You can also check 404 errors in Google Search Console or install a third-party plugin such as Redirection which logs 404 errors. However, remember that plugins like these also have an impact on performance. It’s much better to rely on a server-level tool. That’s why we provide these tools for all Kinsta clients.
The reason these errors are bad is that many 404 pages are very resource intensive. For large sites, you’ll want to avoid a heavy 404 page. Create a simple 404 template that avoids querying the database any further if possible.
How to Fix Error 404 Not Found on WordPress
Below, we’ll cover a couple different methods for how to fix the Error 404 Not Found message, depending on whether it’s happening sitewide or to specific content.
Update Your WordPress Site’s Permalinks
If you’re experiencing sitewide 404 errors when trying to access content, the most likely cause is an issue with your permalinks (or your .htaccess file, if your host uses Apache). If you’re a Kinsta client, we utilize Nginx, so you can rule out the .htaccess file as a possible cause.
The easiest way to fix this is to update your permalink settings through the WordPress dashboard. All you need to do is go to Settings → Permalinks and click Save Changes (you don’t need to make any changes – clicking Save Changes is enough).
Set Up 301 Redirects For Moved or Renamed Content
If you’re experiencing 404 errors on a specific piece of content, the issue is likely that you:
- Changed the URL slug for that content.
- Moved that piece of content manually, e.g. by deleting the existing post and pasting it into a new post.
Users then try to access the content at the old location and see a 404 page instead of the resource they were expecting. The best way to fix this is to automatically redirect anyone who tries to access the old location to the new location. That way, they’ll make it to the right spot without any 404 errors. It’s also good for SEO. If you move or rename a post without adding a redirect, you lose all the domain authority attached to the backlinks pointed at that post.
WordPress by default will attempt to redirect changed/moved content. But it doesn’t always work and you should never rely on WordPress for this functionality. But don’t worry, there are several easy ways to set up redirects in WordPress:
First, you can use the free Redirection plugin to manage redirects from your WordPress dashboard. Once you’ve installed and activated the plugin, go to Tools → Redirection and enter the 404 page URL in the Source URL box and the new location of the content in the Target URL box:
If you’re hosting with Kinsta, you can also manage redirects from the MyKinsta dashboard. Using Kinsta’s tool is actually a better way to go about it as the rules are implemented at the server level, which is a much more optimal way in terms of performance. It also means one less third-party plugin you have to worry about.
Go to the site you want to manage. Then, click on the “Redirects” tab. To add a new redirect, click the large “Add Redirect Rule” button:
Finally, if your host uses the Apache server, you can use .htaccess to set up redirects. The .htaccess Generator site can help you generate the proper code to add to your site’s .htaccess file.
How to Create Your Own Error 404 Not Found Page
While you can do your best to prevent 404 errors by following the tips above, it’s impossible to entirely eliminate 404 errors because some things are just plain outside your control. It’s not uncommon for small WordPress sites to have thousands of 404 errors every month.
For example, if a visitor mistypes the URL, or if another website links to a page that doesn’t exist, people are going to get 404 errors no matter what.
To provide a more user-friendly error page, you can use one of the many 404 page plugins. For example, the free 404page plugin lets you set up a custom 404 error page with:
- A search box
- Important links
- Contact information
Another important feature of the 404page plugin is that it doesn’t create redirects. A 404 page should never be redirected to a physical page such as yoursite.com/404. The 404 error should always be generated dynamically on the page in question.
By including these elements, you give visitors the tools they need to find their way to the right page. But remember, keep your 404 page light for better performance. Only include what is absolutely needed.
How to Monitor 404 Errors Going Forward
Going forward, it can be beneficial to pay attention to which requests are causing 404 errors at your site. This can help you:
- Find broken links that are sending people to a non-existent resource (these could be internal links or external links from other sites). You’d then want to do your best to fix those links if at all possible.
- See which pages Google is having trouble crawling. You’d then want to figure out why Google is trying to crawl a non-existent page and set up a redirect if needed.
- Troubleshoot performance related issues with 404 errors.
Option 1 – Google Analytics
If you use Google Analytics, you can set up a custom report to track 404 errors from external links. Rebelytics has a good tutorial on the topic.
Option 2 – WordPress Plugin
If you want to use a WordPress plugin, the aforementioned Redirection plugin can help you monitor for 404 errors from your WordPress dashboard.
Option 3 – Third-Party Audit Tool
You can also use a third-party audit tool like Ahrefs to monitor for 404 errors on your WordPress site. You can even set this up to run on a schedule.
Option 4 – Google Search Console
Lastly, you can track 404 errors that Google’s crawlers encounter in Google Search Console. Once you’ve verified your site with Google Search Console, go to Crawl → Crawl Errors → Not found to view a list of 404 errors that Google has encountered. This is by far one of the easiest ways. It’s also the best in terms of performance because it requires no third-party plugins or additional scanning against your site. Google’s bots are already crawling your site on a regular basis, so why not simply take advantage of the data they already provide? 😉
Summary
Unfortunately, 404 errors will happen on your site whether you like it or not. The larger your WordPress site is, the more you’ll start seeing. We recommend getting a good workflow together for how you monitor these types of errors and go about fixing them. 404 errors are never good for visitors, your brand, and Google doesn’t like to see them either.
Have any other tips or questions regarding the Error 404 Not Found message or how it impacts your WordPress site? Let us know below in the comments.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Apart from the 404 error, how many other HTML error pages do you know about? Have you ever thought about what happens in the background when you see any of these HTML error pages on your screen?
Those codes are meant to convey important information to the user. It can be useful to know them better, especially if you are a website owner. Using them properly reduces your bounce rate, improves your search engine ranking and gives you knowledge on the performance of your site.
Read also:
- Creative Error 404 Pages – Part I
- Creative Error 404 Pages – Part II
Understanding Status Codes
Behind every error page you see on the web there is an HTTP status code sent by the web server. Status codes come in the format of 3 digit numbers. The first digit marks the class of the status code:
- 1XX status codes have informational purposes
- 2XX indicates success
- 3XX is for redirection
None of these three classes result in an HTML error page as in this cases the client knows what to do and goes on with the task without hesitation. What we usually see are the 4XX and 5XX kind:
- 4XX represent client-side errors
- 5XXs indicate problems on the server side
HTML error pages are displayed in these cases because the client has no idea about what how to move on. Let’s see what happens in the background when something goes south and what you can do about it.
Client-Side Errors (4XX)
1. 400 – Bad Request
Whenever the client sends a request the server is unable to understand, the 400 Bad Request error page shows up. It usually happens when the data sent by the browser doesn’t respect the rules of the HTTP protocol, so the web server is clueless about how to process a request containing a malformed syntax.
When you see a 400 error page the reason is most likely that there’s something unstable on the client side: a not sufficiently protected operating system, an instable internet connection, a defective browser or a caching problem. So it’s always a good idea to test a bit your own PC before you contact the owner of the website.
Open the same webpage in a different browser, clear the cache, and check if you are due with security updates. If you regularly meet the 400 error on different sites, your PC or Mac is awaiting a thorough security checkup.
2. 401 – Authorization Required
When there’s a password-protected web page behind the client’s request, the server responds with a 401 Authorization Required code. 401 doesn’t return a classical error message at once, but a popup that asks the user to provide a login-password combination.
If you have the credentials, everything is all right, and you can go on without any problem and get access to the protected site. Otherwise you are redirected to the Authorization Required error page.
If you are a website owner, you can add the same password-protection to your site or a part of it through your cPanel account.
Click on the “Password Protect Directories” submenu inside the “Security” menu box and choose the web folder you want to protect. It can be a good security layer to restrict access to your admin area like the wp-admin folder in a WordPress site.
3. 403 – Forbidden
You can encounter the 403 Forbidden error page when the server understands the client’s request clearly, but for some reasons refuses to fulfil it. This is neither a malformation nor an authorization problem. By returning the 403 status code the server basically rejects the client with a big loud “No” without any explanation
The most common reason is that the website owner doesn’t permit visitors to browse the file directory structure of the site. When this kind of protection is enabled you can’t access folders directly on the website. The other frequent reason is that the specific file the client requested doesn’t have the permission to be viewed from the web.
You can set 403 protection for security reasons on your own site. It can be useful to harden your site against being hacked by hiding the directory structure or files that contain vulnerable information.
Luckily many web hosts provide this service to their clients by default, but if you want to add an extra security layer, open your cPanel account, navigate to the Advanced menu box, and click on Index Manager.
Here you can customize how your visitors view a specific directory on your site. If you choose No Indexing the client will receive an 403 error page if it tries to access the given directory.
4. 404 – Not Found
404 is the most well-known HTTP status code out there, and you have surely read many great posts about how to customize 404 pages. The browser returns a 404 HTML page when the server doesn’t find anything on the requested location.
There are two main scenarios that can result in a 404 Not Found page. Either the visitor mistyped the URL, or the permalink structure of the site has been changed and the incoming links point to pages that were moved to different locations. 404 error pages sometimes can appear on top level URLs too. It usually happens when a site has recently moved to another web server and the DNS still points to the old location. This kind of problem usually disappears after a short time.
You can find SEO experts on the web who claim too many 404s have a negative effect on your site’s search engine ranking, but Google claims that “404 errors don’t impact your site’s ranking in Google, and you can safely ignore them” as 404s are seen as a normal part of the web by the search engine.
You may want to reduce the number of your 404s because they increase the bounce rate (people who leave immediately) of your site. The most common solution for this is using 301 redirects for permanently removed pages, and 302s for those that are temporarily unavailable.
5. 408 – Request Time-Out
When the request of the client takes too long, the server times out, closes the connection, and the browser displays a 408 Request Time-Out error message. The time-out happens because the server didn’t receive a complete request from the client within the timeframe it was prepared to wait. Persistent 408 errors can occur because of the heavy workload on either the server or on the client’s system.
In some cases both ends of the connection work properly but a temporary internet surge slows down the delivery of the message. Bigger websites tend to customize 408 error pages just like most of you do, in case of 404s. 408 errors can usually be fixed by reloading the page with the help of the F5 button.
6. 410 – Gone
The 410 Gone error page is very close to the well-known 404. Both mean that the server doesn’t find the requested file, but while 404 suggests that the target file may be available somewhere on the server, 410 indicates a permanent condition.
410 shows the client that the resource was made intentionally unavailable, and the website owner wants incoming links to be removed from the Web. 404 is used when the server is unsure if the unavailability of the file is permanent, but 410 always indicates a complete certainty.
If you are in charge of your own server, it’s important to understand how 404s and 410s are treated differently by Google crawlers. In this video Matt Cutts, Google’s head of search spam explains the gist of this distinction. It’s a good idea to distinguish between 404 and 410 to enhance your Google-friendliness.
Server Errors (5XX)
7. 500 – Internal Server Error
Internal Server Error is the most well-known server error, as it’s used whenever the server encounters an unexpected condition that prevents it from fulfilling the client’s request. The 500 error code is a generic one, it’s returned when no other server-side 5XX error codes make any sense.
Although in this case the problem is not on your end, you can do some things to resolve it such as reload the page (as the error may be temporary), clear your browser’s cache (as the issue may occur with the cached version of the site), and delete your browser’s cookies and restart the browser.
You can also contact the webmaster (like in case of any other server-side problems) – they may be grateful for your contribution but there’s also a chance that they are aware of the problem and already working on it.
If you encounter the 500 error page on your own site, it will be wise to contact your hosting provider. The reason is most likely a permission error, a corrupt .htaccess file or a too low memory limit. If you have a WordPress site, the 500 error can also caused by a third party plugin; you can test this by deactivating your plugins, one by one, until the culprit is found.
8. 502 – Bad Gateway
The 502 error message represents a communication problem between two servers. It occurs when the client connects to a server acting as a gateway or a proxy that needs to access an upstream server that provides additional service to it. The other server is located higher in the server hierarchy. It can be for example an Apache web server that’s accessed by a proxy server, or the name server of a large internet service provider that’s accessed by a local name server.
When you encounter the Bad Gateway error page the server receives an invalid response from an upstream server.
In most cases it doesn’t mean that the upstream server is down but that the two communicating servers don’t agree on the protocol about how to exchange data. This usually happens when one of the machines is incorrectly configured or programmed. Contact your hosting provider if you see 502 on your own site.
9. 503 – Service Temporarily Unavailable
You see the Service Temporarily Unavailable (sometimes Out of Resources) message any time there’s a temporary overload on the server, or when it’s going through a scheduled maintenance. The 503 error code means that the web server is currently not available. This is usually a temporary condition that will be resolved after some delay.
If you are a website owner it’s important to have appropriate knowledge about the 503 status code to properly handle scheduled maintenance. If you don’t handle scheduled maintenance in the correct way, you may hurt the search engine ranking of your site.
Learn how to do this via this tutorial on Yoast’s SEO blog or this one on moz.com.
10. 504 – Gateway Time-Out
There is a server-server communication problem behind the Gateway Time-Out error message, just like behind the 502 Bad Gateway error code. When the 504 status code is returned there’s also a higher-level server in the background that is supposed to send data to the server that is connected to our client. In this case the lower-level server doesn’t receive a timely response from the upstream server it accessed.
This is the same time-out problem that occurs in case of the 408 Request Time-Out status code, but here it doesn’t happen between the client and the server but between two servers in the back end. The Gateway Time-Out error page usually indicates slow communication between the two servers, and it can also happen that the higher-level server is completely down.
As 504 is a network problem in the background only people who have access to that network can solve it. As with other server-side HTTP errors, sometimes it’s enough to refresh the page a few minutes later to tackle the issue – of course only if the service providers work on the problem meanwhil.