socket.error: [Errno 10061] indicates that the port you are trying to connect to is not open. You need to make sure that the port is open and something is listening for your connection to be made.
It appears that you are trying to test a chat server. In order for the chat server to work properly you will want to make sure that it is currently listening on the specified port.
Twisted provides a good framework if you haven’t checked it out previously.
from twisted.internet.protocol import Factory
from twisted.protocols.basic import LineReceiver
from twisted.internet import reactor
class Chat(LineReceiver):
def __init__(self, users):
self.users = users
self.name = None
self.state = "GETNAME"
def connectionMade(self):
self.sendLine("What's your name?")
def connectionLost(self, reason):
if self.users.has_key(self.name):
del self.users[self.name]
def lineReceived(self, line):
if self.state == "GETNAME":
self.handle_GETNAME(line)
else:
self.handle_CHAT(line)
def handle_GETNAME(self, name):
if self.users.has_key(name):
self.sendLine("Name taken, please choose another.")
return
self.sendLine("Welcome, %s!" % (name,))
self.name = name
self.users[name] = self
self.state = "CHAT"
def handle_CHAT(self, message):
message = "<%s> %s" % (self.name, message)
for name, protocol in self.users.iteritems():
if ':' in message:
self.exc(message.split(':')[0])
if protocol != self:
protocol.sendLine(message)
def exc(self, cmd):
print cmd
if cmd == 'who':
for i in self.users:
print i
class ChatFactory(Factory):
def __init__(self):
self.users = {} # maps user names to Chat instances
def buildProtocol(self, addr):
return Chat(self.users)
reactor.listenTCP(8123, ChatFactory())
reactor.run()
hi i have this working on local machine when im on accounts/register and try create a new user i get this error
^***************************+
error at /accounts/register/
[Errno 10061] No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it
Request Method: POST
Request URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/register/
Django Version: 1.5
Exception Type: error
Exception Value:
[Errno 10061] No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it
Exception Location: C:Python27libsocket.py in create_connection, line 571
Python Executable: C:Python27python.exe
Python Version: 2.7.3
Python Path:
[‘C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusic’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdistribute-0.6.35-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdjango_audiotracks-0.2.1-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesmutagen-1.20-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdjango_registration_email-0.5-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Windowssystem32python27.zip’,
‘C:Python27DLLs’,
‘C:Python27lib’,
‘C:Python27libplat-win’,
‘C:Python27liblib-tk’,
‘C:Python27’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packages’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesPIL’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagessetuptools-0.6c11-py2.7.egg-info’]
Server time: Tue, 26 Mar 2013 03:55:14 +0100
Traceback Switch to copy-and-paste view
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocorehandlersbase.py in get_response
response = callback(request, *callback_args, **callback_kwargs)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesregistrationviews.py in register
new_user = backend.register(request, **form.cleaned_data)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesregistrationbackendsdefault__init__.py in register
password, site)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangodbtransaction.py in inner
return func(*args, **kwargs)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusicimpromusicappsregistrationmodels.py in create_inactive_user
registration_profile.send_activation_email(site)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusicimpromusicappsregistrationmodels.py in send_activation_email
self.user.email_user(subject, message, settings.DEFAULT_FROM_EMAIL)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocontribauthmodels.py in email_user
send_mail(subject, message, from_email, [self.email])
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocoremail__init__.py in send_mail
connection=connection).send()
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocoremailmessage.py in send
return self.get_connection(fail_silently).send_messages([self])
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocoremailbackendssmtp.py in send_messages
new_conn_created = self.open()
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocoremailbackendssmtp.py in open
local_hostname=DNS_NAME.get_fqdn())
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsmtplib.py in __init__
(code, msg) = self.connect(host, port)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsmtplib.py in connect
self.sock = self._get_socket(host, port, self.timeout)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsmtplib.py in _get_socket
return socket.create_connection((port, host), timeout)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsocket.py in create_connection
raise err
...
▶ Local vars
Do i have to configure the email server on settings.py for use your app?
Yes but the easier way is to put this into your local settings:
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend'
Then all emails will be printed in your console.
If you really want to test your emails, it gets more complicated, an easy way would be to put this into your local settings:
ADMINS = (
('Yourname', 'yourname@gmail.com'),
)
MANAGERS = ADMINS
# When you are playing around with the app and you expect that an email should
# have been sent, just run `./manage.py send_mail` and you will get the mail
# to the ADMINS account, no matter who the real recipient was.
MAILER_EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django_libs.test_email_backend.EmailBackend'
TEST_EMAIL_BACKEND_RECIPIENTS = ADMINS
FROM_EMAIL = ADMINS[0][1]
EMAIL_SUBJECT_PREFIX = '[dev yourprojectname] '
EMAIL_HOST = 'smtp.gmail.com'
EMAIL_HOST_USER = FROM_EMAIL
# Enter your gmail PW from the ADMINS email entered above.
EMAIL_HOST_PASSWORD = 'yourgmailpw'
EMAIL_PORT = 587
Note that you need to install django-libs for this to work. The test email backend in django-libs makes sure that ALL emails are ALWAYS sent to yourself, no matter who the recipient is. This is super helpful if you downloaded the life database and you are debugging things — without such a test email backend you might accidentally send emails to your users and cause a lot of confusion.
EDIT: The above assumes that you use django-mailer for dispatching your emails (if you don’t, you should consider using it, it is awesome)
ehy ty for your answer it worked and now i can see the activation code on the console, now im having 2 differents error, i have the deprecationgwarning, the md5 module is deprecated, use hashlib instead, i have seen somebody feedbacks it to you, how did he solve it?
The second and maybe is related, when i go to the activation page, something like http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/activate/cddfd602398ed8f7801ad46d1634c45d45250c41/ , im having the next error:
************************+
TypeError at /accounts/activate/cddfd602398ed8f7801ad46d1634c45d45250c41/
can’t compare offset-naive and offset-aware datetimes
Request Method: GET
Request URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/activate/cddfd602398ed8f7801ad46d1634c45d45250c41/
Django Version: 1.5
Exception Type: TypeError
Exception Value:
can’t compare offset-naive and offset-aware datetimes
Exception Location: C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusicimpromusicappsregistrationmodels.py in activation_key_expired, line 201
Python Executable: C:Python27python.exe
Python Version: 2.7.3
Python Path:
[‘C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusic’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdistribute-0.6.35-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdjango_audiotracks-0.2.1-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesmutagen-1.20-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesdjango_registration_email-0.5-py2.7.egg’,
‘C:Windowssystem32python27.zip’,
‘C:Python27DLLs’,
‘C:Python27lib’,
‘C:Python27libplat-win’,
‘C:Python27liblib-tk’,
‘C:Python27’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packages’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagesPIL’,
‘C:Python27libsite-packagessetuptools-0.6c11-py2.7.egg-info’]
Server time: Tue, 26 Mar 2013 13:03:58 +0100
Traceback Switch to copy-and-paste view
C:Python27libsite-packagesdjangocorehandlersbase.py in get_response
response = callback(request, *callback_args, **callback_kwargs)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesregistrationviews.py in activate
account = backend.activate(request, **kwargs)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Python27libsite-packagesregistrationbackendsdefault__init__.py in activate
activated = RegistrationProfile.objects.activate_user(activation_key)
...
▶ Local vars
C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusicimpromusicappsregistrationmodels.py in activate_user
if not profile.activation_key_expired():
...
▶ Local vars
C:Usersujakeimpromusicimpromusicimpromusicappsregistrationmodels.py in activation_key_expired
(self.user.date_joined + expiration_date <= datetime.datetime.now())
...
▶ Local vars
Ty so much
EDIT: ty for the tip im installing it now.
Hi uyak,
seems you have set the PASSWORD_HASHERS setting, right? Please take a look::
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/ref/settings/#std:setting-PASSWORD_HASHERS
Just remove it or add e.g. 'django.contrib.auth.hashers.PBKDF2PasswordHasher'. MD5 is deprecated in newer Django versions.
Second issue:
In Django 1.5 you need to use timezone. Please take a look::
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/topics/i18n/timezones/
Maybe it’s sufficient to set the USE_TZ setting to True.
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/ref/settings/#use-tz
Hope this helps.
Hy Tyrdalla, ty for your help, i didnt have PASSWORD_HASHERS on settings, i did what you said me and add it on settings.py of my project. Now the error on the shield is
C:/Python27/lib/site-pakages/django/utils/hashcompat.py:9:a DeprecationWarning:Django.utils.hashcompat is deprecated; use hashlib instead
and now if i change the password_hashers i continue having the same new error.
I had USE_TZ = True
Mbrochh i will be waiting ty.
that’s just a deprecation warning, not an error, you can ignore that. I’ll
try to fix it tomorrow…
On Mar 27, 2013 12:15 AM, «uyak» notifications@github.com wrote:
Hy Tyrdalla, ty for your help, i didnt have PASSWORD_HASHERS on settings,
i did what you said me and add it on settings.py of my project. Now theerror on the shield is
C:/Python27/lib/site-pakages/django/utils/hashcompat.py:9:a
DeprecationWarning:Django.utils.hashcompat is deprecated; use hashlibinstead
and now if i change the password_hashers i continue having the same new
error.I had USE_TZ = True
Mbrochh i will be waiting ty.
—
Reply to this email directly or view it on GitHubhttps://github.com//issues/8#issuecomment-15468251
.
@uyak I have released version 0.5.1 — the deprecation warning should be gone now. Are you still having the timezone error?
A socket error 10061 is a connection that is refused or forcefully denied. While this error can technically be seen with any type of server connection, it is most often seen when a user attempts to connect to an email server. There are many reasons for a socket error 10061. A firewall could be blocking the connection, the service may be unavailable, the server program making the server work may be disabled or shut off, the servers may be overloaded, or the ports may be blocked. Each cause has a different fix that should allow the user to connect to the server.
The socket error 10061 code can appear whenever a user connects to a server. This is most often seen with email servers, because the most common server connection users encounter is one used with an email service. Computers that link to other servers, such as for business uses, may also see this problem. Regardless of how the error is caused, it still has the same common causes and fixes.
A firewall blocking the connection and causing a socket error 10061 is the easiest to fix. Firewalls keep malicious codes or connections from occurring, but a firewall sometimes gets confused and also blocks good connections. This most often happens if the user is connecting to a server for the first time or if the firewall was recently reset. In this instance, the user either has to list the server as friendly or shut down the firewall. If the firewall needs to be shut down, the user should put it back up after the server connection is finished.
Another cause for a socket error 10061 is a blocked port or ports. Ports need to be open for sockets to connect. Each server will require a different port, and each program will have a different way of opening ports. To fix this error, the user should contact the server’s customer service to see what ports are needed, and read the user manual or talk to customer service about how to open the specified port or ports.
The other causes, which cannot be controlled by the user, include a server being unavailable, the server program not running, and the server being overloaded. In these cases, the server must be repaired or turned on, or the user must wait until the busy surge has stopped and bandwidth has been freed up. In this instance, the user may wait from a few minutes to a few hours; in catastrophic instances days, may be needed to connect with the server.
This blog post was originally posted on JetBrains .NET blog.
Rider consists of several processes that send messages to each other via sockets. To ensure the reliability of the whole application, it’s important to properly handle all the socket errors. In our codebase, we had the following code which was adopted from Mono Debugger Libs and helps us communicate with debugger processes:
protected virtual bool ShouldRetryConnection (Exception ex, int attemptNumber)
{
var sx = ex as SocketException;
if (sx != null) {
if (sx.ErrorCode == 10061) //connection refused
return true;
}
return false;
}
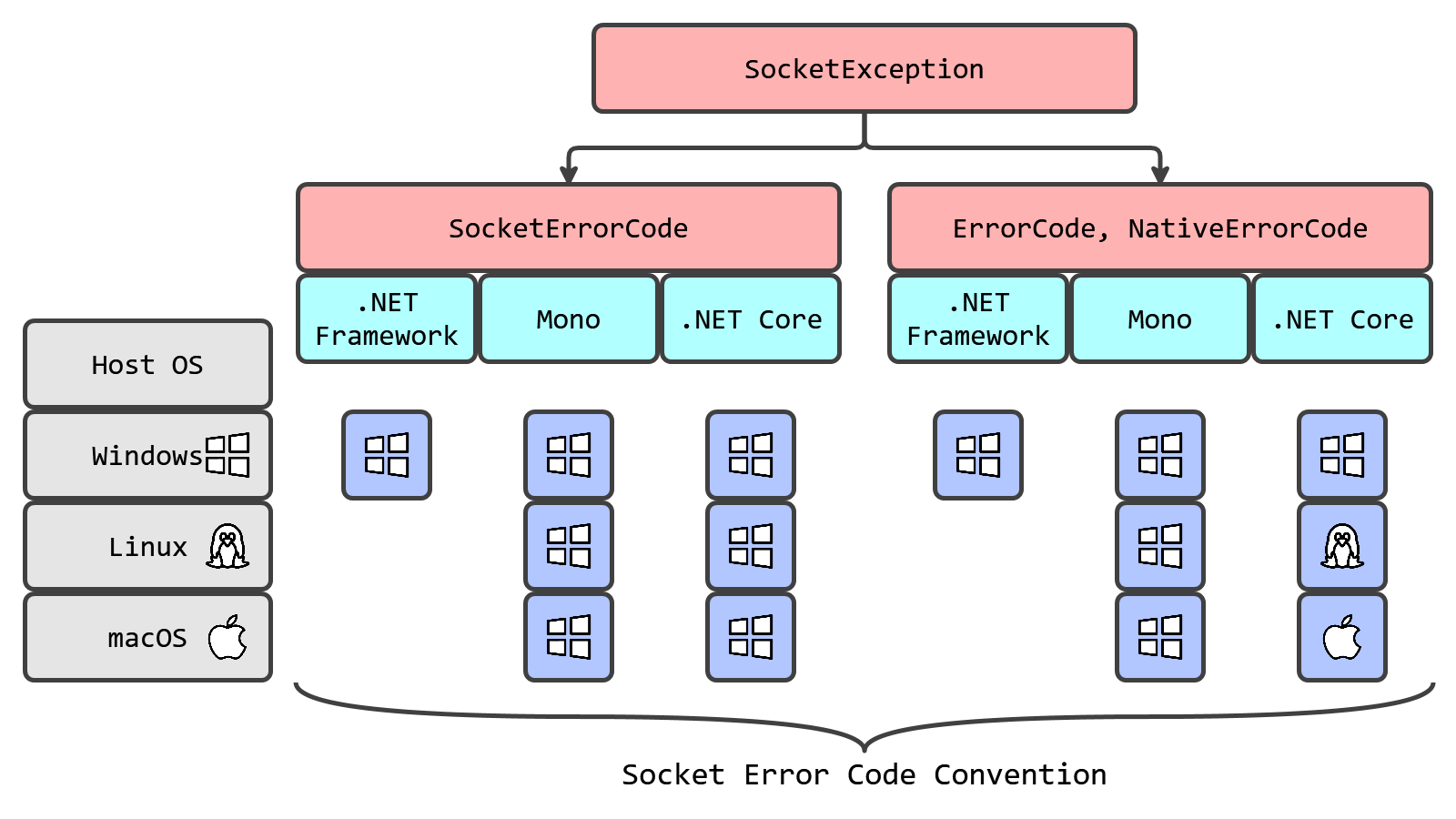
In the case of a failed connection because of a “ConnectionRefused” error, we are retrying the connection attempt. It works fine with .NET Framework and Mono. However, once we migrated to .NET Core, this method no longer correctly detects the “connection refused” situation on Linux and macOS. If we open the SocketException documentation, we will learn that this class has three different properties with error codes:
SocketError SocketErrorCode: Gets the error code that is associated with this exception.int ErrorCode: Gets the error code that is associated with this exception.int NativeErrorCode: Gets the Win32 error code associated with this exception.
What’s the difference between these properties? Should we expect different values on different runtimes or different operating systems? Which one should we use in production? Why do we have problems with ShouldRetryConnection on .NET Core? Let’s figure it all out!
Digging into the problem
Let’s start with the following program, which prints error code property values for SocketError.ConnectionRefused:
var se = new SocketException((int) SocketError.ConnectionRefused);
Console.WriteLine((int)se.SocketErrorCode);
Console.WriteLine(se.ErrorCode);
Console.WriteLine(se.NativeErrorCode);
If we run it on Windows, we will get the same value on .NET Framework, Mono, and .NET Core:
| SocketErrorCode | ErrorCode | NativeErrorCode | |
| .NET Framework | 10061 | 10061 | 10061 |
| Mono | 10061 | 10061 | 10061 |
| .NET Core | 10061 | 10061 | 10061 |
10061 corresponds to the code of the connection refused socket error code in Windows (also known as WSAECONNREFUSED).
Now let’s run the same program on Linux:
| SocketErrorCode | ErrorCode | NativeErrorCode | |
| Mono | 10061 | 10061 | 10061 |
| .NET Core | 10061 | 111 | 111 |
As you can see, Mono returns Windows-compatible error codes. The situation with .NET Core is different: it returns a Windows-compatible value for SocketErrorCode (10061) and a Linux-like value for ErrorCode and NativeErrorCode (111).
Finally, let’s check macOS:
| SocketErrorCode | ErrorCode | NativeErrorCode | |
| Mono | 10061 | 10061 | 10061 |
| .NET Core | 10061 | 61 | 61 |
Here, Mono is completely Windows-compatible again, but .NET Core returns 61 for ErrorCode and NativeErrorCode.
In the IBM Knowledge Center, we can find a few more values for the connection refused error code from the Unix world (also known as ECONNREFUSED):
- AIX: 79
- HP-UX: 239
- Solaris: 146
For a better understanding of what’s going on, let’s check out the source code of all the properties.
SocketErrorCode
SocketException.SocketErrorCode returns a value from the SocketError enum. The numerical values of the enum elements are the same on all the runtimes (see its implementation in .NET Framework, .NET Core 3.1.3, and Mono 6.8.0.105):
public enum SocketError
{
SocketError = -1, // 0xFFFFFFFF
Success = 0,
OperationAborted = 995, // 0x000003E3
IOPending = 997, // 0x000003E5
Interrupted = 10004, // 0x00002714
AccessDenied = 10013, // 0x0000271D
Fault = 10014, // 0x0000271E
InvalidArgument = 10022, // 0x00002726
TooManyOpenSockets = 10024, // 0x00002728
WouldBlock = 10035, // 0x00002733
InProgress = 10036, // 0x00002734
AlreadyInProgress = 10037, // 0x00002735
NotSocket = 10038, // 0x00002736
DestinationAddressRequired = 10039, // 0x00002737
MessageSize = 10040, // 0x00002738
ProtocolType = 10041, // 0x00002739
ProtocolOption = 10042, // 0x0000273A
ProtocolNotSupported = 10043, // 0x0000273B
SocketNotSupported = 10044, // 0x0000273C
OperationNotSupported = 10045, // 0x0000273D
ProtocolFamilyNotSupported = 10046, // 0x0000273E
AddressFamilyNotSupported = 10047, // 0x0000273F
AddressAlreadyInUse = 10048, // 0x00002740
AddressNotAvailable = 10049, // 0x00002741
NetworkDown = 10050, // 0x00002742
NetworkUnreachable = 10051, // 0x00002743
NetworkReset = 10052, // 0x00002744
ConnectionAborted = 10053, // 0x00002745
ConnectionReset = 10054, // 0x00002746
NoBufferSpaceAvailable = 10055, // 0x00002747
IsConnected = 10056, // 0x00002748
NotConnected = 10057, // 0x00002749
Shutdown = 10058, // 0x0000274A
TimedOut = 10060, // 0x0000274C
ConnectionRefused = 10061, // 0x0000274D
HostDown = 10064, // 0x00002750
HostUnreachable = 10065, // 0x00002751
ProcessLimit = 10067, // 0x00002753
SystemNotReady = 10091, // 0x0000276B
VersionNotSupported = 10092, // 0x0000276C
NotInitialized = 10093, // 0x0000276D
Disconnecting = 10101, // 0x00002775
TypeNotFound = 10109, // 0x0000277D
HostNotFound = 11001, // 0x00002AF9
TryAgain = 11002, // 0x00002AFA
NoRecovery = 11003, // 0x00002AFB
NoData = 11004, // 0x00002AFC
}
These values correspond to the Windows Sockets Error Codes.
NativeErrorCode
In .NET Framework and Mono, SocketErrorCode and NativeErrorCode always have the same values:
public SocketError SocketErrorCode {
//
// the base class returns the HResult with this property
// we need the Win32 Error Code, hence the override.
//
get {
return (SocketError)NativeErrorCode;
}
}
In .NET Core, the native code is calculated in the constructor (see SocketException.cs#L20):
public SocketException(int errorCode) : this((SocketError)errorCode)
// ...
internal SocketException(SocketError socketError) : base(GetNativeErrorForSocketError(socketError))
The Windows implementation of GetNativeErrorForSocketError is trivial (see SocketException.Windows.cs):
private static int GetNativeErrorForSocketError(SocketError error)
{
// SocketError values map directly to Win32 error codes
return (int)error;
}
The Unix implementation is more complicated (see SocketException.Unix.cs):
private static int GetNativeErrorForSocketError(SocketError error)
{
int nativeErr = (int)error;
if (error != SocketError.SocketError)
{
Interop.Error interopErr;
// If an interop error was not found, then don't invoke Info().RawErrno as that will fail with assert.
if (SocketErrorPal.TryGetNativeErrorForSocketError(error, out interopErr))
{
nativeErr = interopErr.Info().RawErrno;
}
}
return nativeErr;
}
TryGetNativeErrorForSocketError should convert SocketError to the native Unix error code.
Unfortunately, there exists no unequivocal mapping between Windows and Unix error codes. As such, the .NET team decided to create a Dictionary that maps error codes in the best possible way (see SocketErrorPal.Unix.cs):
private const int NativeErrorToSocketErrorCount = 42;
private const int SocketErrorToNativeErrorCount = 40;
// No Interop.Errors are included for the following SocketErrors, as there's no good mapping:
// - SocketError.NoRecovery
// - SocketError.NotInitialized
// - SocketError.ProcessLimit
// - SocketError.SocketError
// - SocketError.SystemNotReady
// - SocketError.TypeNotFound
// - SocketError.VersionNotSupported
private static readonly Dictionary<Interop.Error, SocketError> s_nativeErrorToSocketError = new Dictionary<Interop.Error, SocketError>(NativeErrorToSocketErrorCount)
{
{ Interop.Error.EACCES, SocketError.AccessDenied },
{ Interop.Error.EADDRINUSE, SocketError.AddressAlreadyInUse },
{ Interop.Error.EADDRNOTAVAIL, SocketError.AddressNotAvailable },
{ Interop.Error.EAFNOSUPPORT, SocketError.AddressFamilyNotSupported },
{ Interop.Error.EAGAIN, SocketError.WouldBlock },
{ Interop.Error.EALREADY, SocketError.AlreadyInProgress },
{ Interop.Error.EBADF, SocketError.OperationAborted },
{ Interop.Error.ECANCELED, SocketError.OperationAborted },
{ Interop.Error.ECONNABORTED, SocketError.ConnectionAborted },
{ Interop.Error.ECONNREFUSED, SocketError.ConnectionRefused },
{ Interop.Error.ECONNRESET, SocketError.ConnectionReset },
{ Interop.Error.EDESTADDRREQ, SocketError.DestinationAddressRequired },
{ Interop.Error.EFAULT, SocketError.Fault },
{ Interop.Error.EHOSTDOWN, SocketError.HostDown },
{ Interop.Error.ENXIO, SocketError.HostNotFound }, // not perfect, but closest match available
{ Interop.Error.EHOSTUNREACH, SocketError.HostUnreachable },
{ Interop.Error.EINPROGRESS, SocketError.InProgress },
{ Interop.Error.EINTR, SocketError.Interrupted },
{ Interop.Error.EINVAL, SocketError.InvalidArgument },
{ Interop.Error.EISCONN, SocketError.IsConnected },
{ Interop.Error.EMFILE, SocketError.TooManyOpenSockets },
{ Interop.Error.EMSGSIZE, SocketError.MessageSize },
{ Interop.Error.ENETDOWN, SocketError.NetworkDown },
{ Interop.Error.ENETRESET, SocketError.NetworkReset },
{ Interop.Error.ENETUNREACH, SocketError.NetworkUnreachable },
{ Interop.Error.ENFILE, SocketError.TooManyOpenSockets },
{ Interop.Error.ENOBUFS, SocketError.NoBufferSpaceAvailable },
{ Interop.Error.ENODATA, SocketError.NoData },
{ Interop.Error.ENOENT, SocketError.AddressNotAvailable },
{ Interop.Error.ENOPROTOOPT, SocketError.ProtocolOption },
{ Interop.Error.ENOTCONN, SocketError.NotConnected },
{ Interop.Error.ENOTSOCK, SocketError.NotSocket },
{ Interop.Error.ENOTSUP, SocketError.OperationNotSupported },
{ Interop.Error.EPERM, SocketError.AccessDenied },
{ Interop.Error.EPIPE, SocketError.Shutdown },
{ Interop.Error.EPFNOSUPPORT, SocketError.ProtocolFamilyNotSupported },
{ Interop.Error.EPROTONOSUPPORT, SocketError.ProtocolNotSupported },
{ Interop.Error.EPROTOTYPE, SocketError.ProtocolType },
{ Interop.Error.ESOCKTNOSUPPORT, SocketError.SocketNotSupported },
{ Interop.Error.ESHUTDOWN, SocketError.Disconnecting },
{ Interop.Error.SUCCESS, SocketError.Success },
{ Interop.Error.ETIMEDOUT, SocketError.TimedOut },
};
private static readonly Dictionary<SocketError, Interop.Error> s_socketErrorToNativeError = new Dictionary<SocketError, Interop.Error>(SocketErrorToNativeErrorCount)
{
// This is *mostly* an inverse mapping of s_nativeErrorToSocketError. However, some options have multiple mappings and thus
// can't be inverted directly. Other options don't have a mapping from native to SocketError, but when presented with a SocketError,
// we want to provide the closest relevant Error possible, e.g. EINPROGRESS maps to SocketError.InProgress, and vice versa, but
// SocketError.IOPending also maps closest to EINPROGRESS. As such, roundtripping won't necessarily provide the original value 100% of the time,
// but it's the best we can do given the mismatch between Interop.Error and SocketError.
{ SocketError.AccessDenied, Interop.Error.EACCES}, // could also have been EPERM
{ SocketError.AddressAlreadyInUse, Interop.Error.EADDRINUSE },
{ SocketError.AddressNotAvailable, Interop.Error.EADDRNOTAVAIL },
{ SocketError.AddressFamilyNotSupported, Interop.Error.EAFNOSUPPORT },
{ SocketError.AlreadyInProgress, Interop.Error.EALREADY },
{ SocketError.ConnectionAborted, Interop.Error.ECONNABORTED },
{ SocketError.ConnectionRefused, Interop.Error.ECONNREFUSED },
{ SocketError.ConnectionReset, Interop.Error.ECONNRESET },
{ SocketError.DestinationAddressRequired, Interop.Error.EDESTADDRREQ },
{ SocketError.Disconnecting, Interop.Error.ESHUTDOWN },
{ SocketError.Fault, Interop.Error.EFAULT },
{ SocketError.HostDown, Interop.Error.EHOSTDOWN },
{ SocketError.HostNotFound, Interop.Error.EHOSTNOTFOUND },
{ SocketError.HostUnreachable, Interop.Error.EHOSTUNREACH },
{ SocketError.InProgress, Interop.Error.EINPROGRESS },
{ SocketError.Interrupted, Interop.Error.EINTR },
{ SocketError.InvalidArgument, Interop.Error.EINVAL },
{ SocketError.IOPending, Interop.Error.EINPROGRESS },
{ SocketError.IsConnected, Interop.Error.EISCONN },
{ SocketError.MessageSize, Interop.Error.EMSGSIZE },
{ SocketError.NetworkDown, Interop.Error.ENETDOWN },
{ SocketError.NetworkReset, Interop.Error.ENETRESET },
{ SocketError.NetworkUnreachable, Interop.Error.ENETUNREACH },
{ SocketError.NoBufferSpaceAvailable, Interop.Error.ENOBUFS },
{ SocketError.NoData, Interop.Error.ENODATA },
{ SocketError.NotConnected, Interop.Error.ENOTCONN },
{ SocketError.NotSocket, Interop.Error.ENOTSOCK },
{ SocketError.OperationAborted, Interop.Error.ECANCELED },
{ SocketError.OperationNotSupported, Interop.Error.ENOTSUP },
{ SocketError.ProtocolFamilyNotSupported, Interop.Error.EPFNOSUPPORT },
{ SocketError.ProtocolNotSupported, Interop.Error.EPROTONOSUPPORT },
{ SocketError.ProtocolOption, Interop.Error.ENOPROTOOPT },
{ SocketError.ProtocolType, Interop.Error.EPROTOTYPE },
{ SocketError.Shutdown, Interop.Error.EPIPE },
{ SocketError.SocketNotSupported, Interop.Error.ESOCKTNOSUPPORT },
{ SocketError.Success, Interop.Error.SUCCESS },
{ SocketError.TimedOut, Interop.Error.ETIMEDOUT },
{ SocketError.TooManyOpenSockets, Interop.Error.ENFILE }, // could also have been EMFILE
{ SocketError.TryAgain, Interop.Error.EAGAIN }, // not a perfect mapping, but better than nothing
{ SocketError.WouldBlock, Interop.Error.EAGAIN },
};
internal static bool TryGetNativeErrorForSocketError(SocketError error, out Interop.Error errno)
{
return s_socketErrorToNativeError.TryGetValue(error, out errno);
}
Once we have an instance of Interop.Error, we call interopErr.Info().RawErrno. The implementation of RawErrno can be found in Interop.Errors.cs:
internal int RawErrno
{
get { return _rawErrno == -1 ? (_rawErrno = Interop.Sys.ConvertErrorPalToPlatform(_error)) : _rawErrno; }
}
[DllImport(Libraries.SystemNative, EntryPoint = "SystemNative_ConvertErrorPalToPlatform")]
internal static extern int ConvertErrorPalToPlatform(Error error);
Here we are jumping to the native function SystemNative_ConvertErrorPalToPlatform that maps Error to the native integer code that is defined in errno.h. You can get all the values using the errno util. Here is a typical output on Linux:
$ errno -ls
EPERM 1 Operation not permitted
ENOENT 2 No such file or directory
ESRCH 3 No such process
EINTR 4 Interrupted system call
EIO 5 Input/output error
ENXIO 6 No such device or address
E2BIG 7 Argument list too long
ENOEXEC 8 Exec format error
EBADF 9 Bad file descriptor
ECHILD 10 No child processes
EAGAIN 11 Resource temporarily unavailable
ENOMEM 12 Cannot allocate memory
EACCES 13 Permission denied
EFAULT 14 Bad address
ENOTBLK 15 Block device required
EBUSY 16 Device or resource busy
EEXIST 17 File exists
EXDEV 18 Invalid cross-device link
ENODEV 19 No such device
ENOTDIR 20 Not a directory
EISDIR 21 Is a directory
EINVAL 22 Invalid argument
ENFILE 23 Too many open files in system
EMFILE 24 Too many open files
ENOTTY 25 Inappropriate ioctl for device
ETXTBSY 26 Text file busy
EFBIG 27 File too large
ENOSPC 28 No space left on device
ESPIPE 29 Illegal seek
EROFS 30 Read-only file system
EMLINK 31 Too many links
EPIPE 32 Broken pipe
EDOM 33 Numerical argument out of domain
ERANGE 34 Numerical result out of range
EDEADLK 35 Resource deadlock avoided
ENAMETOOLONG 36 File name too long
ENOLCK 37 No locks available
ENOSYS 38 Function not implemented
ENOTEMPTY 39 Directory not empty
ELOOP 40 Too many levels of symbolic links
EWOULDBLOCK 11 Resource temporarily unavailable
ENOMSG 42 No message of desired type
EIDRM 43 Identifier removed
ECHRNG 44 Channel number out of range
EL2NSYNC 45 Level 2 not synchronized
EL3HLT 46 Level 3 halted
EL3RST 47 Level 3 reset
ELNRNG 48 Link number out of range
EUNATCH 49 Protocol driver not attached
ENOCSI 50 No CSI structure available
EL2HLT 51 Level 2 halted
EBADE 52 Invalid exchange
EBADR 53 Invalid request descriptor
EXFULL 54 Exchange full
ENOANO 55 No anode
EBADRQC 56 Invalid request code
EBADSLT 57 Invalid slot
EDEADLOCK 35 Resource deadlock avoided
EBFONT 59 Bad font file format
ENOSTR 60 Device not a stream
ENODATA 61 No data available
ETIME 62 Timer expired
ENOSR 63 Out of streams resources
ENONET 64 Machine is not on the network
ENOPKG 65 Package not installed
EREMOTE 66 Object is remote
ENOLINK 67 Link has been severed
EADV 68 Advertise error
ESRMNT 69 Srmount error
ECOMM 70 Communication error on send
EPROTO 71 Protocol error
EMULTIHOP 72 Multihop attempted
EDOTDOT 73 RFS specific error
EBADMSG 74 Bad message
EOVERFLOW 75 Value too large for defined data type
ENOTUNIQ 76 Name not unique on network
EBADFD 77 File descriptor in bad state
EREMCHG 78 Remote address changed
ELIBACC 79 Can not access a needed shared library
ELIBBAD 80 Accessing a corrupted shared library
ELIBSCN 81 .lib section in a.out corrupted
ELIBMAX 82 Attempting to link in too many shared libraries
ELIBEXEC 83 Cannot exec a shared library directly
EILSEQ 84 Invalid or incomplete multibyte or wide character
ERESTART 85 Interrupted system call should be restarted
ESTRPIPE 86 Streams pipe error
EUSERS 87 Too many users
ENOTSOCK 88 Socket operation on non-socket
EDESTADDRREQ 89 Destination address required
EMSGSIZE 90 Message too long
EPROTOTYPE 91 Protocol wrong type for socket
ENOPROTOOPT 92 Protocol not available
EPROTONOSUPPORT 93 Protocol not supported
ESOCKTNOSUPPORT 94 Socket type not supported
EOPNOTSUPP 95 Operation not supported
EPFNOSUPPORT 96 Protocol family not supported
EAFNOSUPPORT 97 Address family not supported by protocol
EADDRINUSE 98 Address already in use
EADDRNOTAVAIL 99 Cannot assign requested address
ENETDOWN 100 Network is down
ENETUNREACH 101 Network is unreachable
ENETRESET 102 Network dropped connection on reset
ECONNABORTED 103 Software caused connection abort
ECONNRESET 104 Connection reset by peer
ENOBUFS 105 No buffer space available
EISCONN 106 Transport endpoint is already connected
ENOTCONN 107 Transport endpoint is not connected
ESHUTDOWN 108 Cannot send after transport endpoint shutdown
ETOOMANYREFS 109 Too many references: cannot splice
ETIMEDOUT 110 Connection timed out
ECONNREFUSED 111 Connection refused
EHOSTDOWN 112 Host is down
EHOSTUNREACH 113 No route to host
EALREADY 114 Operation already in progress
EINPROGRESS 115 Operation now in progress
ESTALE 116 Stale file handle
EUCLEAN 117 Structure needs cleaning
ENOTNAM 118 Not a XENIX named type file
ENAVAIL 119 No XENIX semaphores available
EISNAM 120 Is a named type file
EREMOTEIO 121 Remote I/O error
EDQUOT 122 Disk quota exceeded
ENOMEDIUM 123 No medium found
EMEDIUMTYPE 124 Wrong medium type
ECANCELED 125 Operation canceled
ENOKEY 126 Required key not available
EKEYEXPIRED 127 Key has expired
EKEYREVOKED 128 Key has been revoked
EKEYREJECTED 129 Key was rejected by service
EOWNERDEAD 130 Owner died
ENOTRECOVERABLE 131 State not recoverable
ERFKILL 132 Operation not possible due to RF-kill
EHWPOISON 133 Memory page has hardware error
ENOTSUP 95 Operation not supported
Note that errno may be not available by default in your Linux distro. For example, on Debian, you should call sudo apt-get install moreutils to get this utility.
Here is a typical output on macOS:
$ errno -ls
EPERM 1 Operation not permitted
ENOENT 2 No such file or directory
ESRCH 3 No such process
EINTR 4 Interrupted system call
EIO 5 Input/output error
ENXIO 6 Device not configured
E2BIG 7 Argument list too long
ENOEXEC 8 Exec format error
EBADF 9 Bad file descriptor
ECHILD 10 No child processes
EDEADLK 11 Resource deadlock avoided
ENOMEM 12 Cannot allocate memory
EACCES 13 Permission denied
EFAULT 14 Bad address
ENOTBLK 15 Block device required
EBUSY 16 Resource busy
EEXIST 17 File exists
EXDEV 18 Cross-device link
ENODEV 19 Operation not supported by device
ENOTDIR 20 Not a directory
EISDIR 21 Is a directory
EINVAL 22 Invalid argument
ENFILE 23 Too many open files in system
EMFILE 24 Too many open files
ENOTTY 25 Inappropriate ioctl for device
ETXTBSY 26 Text file busy
EFBIG 27 File too large
ENOSPC 28 No space left on device
ESPIPE 29 Illegal seek
EROFS 30 Read-only file system
EMLINK 31 Too many links
EPIPE 32 Broken pipe
EDOM 33 Numerical argument out of domain
ERANGE 34 Result too large
EAGAIN 35 Resource temporarily unavailable
EWOULDBLOCK 35 Resource temporarily unavailable
EINPROGRESS 36 Operation now in progress
EALREADY 37 Operation already in progress
ENOTSOCK 38 Socket operation on non-socket
EDESTADDRREQ 39 Destination address required
EMSGSIZE 40 Message too long
EPROTOTYPE 41 Protocol wrong type for socket
ENOPROTOOPT 42 Protocol not available
EPROTONOSUPPORT 43 Protocol not supported
ESOCKTNOSUPPORT 44 Socket type not supported
ENOTSUP 45 Operation not supported
EPFNOSUPPORT 46 Protocol family not supported
EAFNOSUPPORT 47 Address family not supported by protocol family
EADDRINUSE 48 Address already in use
EADDRNOTAVAIL 49 Can`t assign requested address
ENETDOWN 50 Network is down
ENETUNREACH 51 Network is unreachable
ENETRESET 52 Network dropped connection on reset
ECONNABORTED 53 Software caused connection abort
ECONNRESET 54 Connection reset by peer
ENOBUFS 55 No buffer space available
EISCONN 56 Socket is already connected
ENOTCONN 57 Socket is not connected
ESHUTDOWN 58 Can`t send after socket shutdown
ETOOMANYREFS 59 Too many references: can`t splice
ETIMEDOUT 60 Operation timed out
ECONNREFUSED 61 Connection refused
ELOOP 62 Too many levels of symbolic links
ENAMETOOLONG 63 File name too long
EHOSTDOWN 64 Host is down
EHOSTUNREACH 65 No route to host
ENOTEMPTY 66 Directory not empty
EPROCLIM 67 Too many processes
EUSERS 68 Too many users
EDQUOT 69 Disc quota exceeded
ESTALE 70 Stale NFS file handle
EREMOTE 71 Too many levels of remote in path
EBADRPC 72 RPC struct is bad
ERPCMISMATCH 73 RPC version wrong
EPROGUNAVAIL 74 RPC prog. not avail
EPROGMISMATCH 75 Program version wrong
EPROCUNAVAIL 76 Bad procedure for program
ENOLCK 77 No locks available
ENOSYS 78 Function not implemented
EFTYPE 79 Inappropriate file type or format
EAUTH 80 Authentication error
ENEEDAUTH 81 Need authenticator
EPWROFF 82 Device power is off
EDEVERR 83 Device error
EOVERFLOW 84 Value too large to be stored in data type
EBADEXEC 85 Bad executable (or shared library)
EBADARCH 86 Bad CPU type in executable
ESHLIBVERS 87 Shared library version mismatch
EBADMACHO 88 Malformed Mach-o file
ECANCELED 89 Operation canceled
EIDRM 90 Identifier removed
ENOMSG 91 No message of desired type
EILSEQ 92 Illegal byte sequence
ENOATTR 93 Attribute not found
EBADMSG 94 Bad message
EMULTIHOP 95 EMULTIHOP (Reserved)
ENODATA 96 No message available on STREAM
ENOLINK 97 ENOLINK (Reserved)
ENOSR 98 No STREAM resources
ENOSTR 99 Not a STREAM
EPROTO 100 Protocol error
ETIME 101 STREAM ioctl timeout
EOPNOTSUPP 102 Operation not supported on socket
ENOPOLICY 103 Policy not found
ENOTRECOVERABLE 104 State not recoverable
EOWNERDEAD 105 Previous owner died
EQFULL 106 Interface output queue is full
ELAST 106 Interface output queue is full
Hooray! We’ve finished our fascinating journey into the internals of socket error codes. Now you know where .NET is getting the native error code for each SocketException from!
ErrorCode
The ErrorCode property is the most boring one, as it always returns NativeErrorCode.
.NET Framework, Mono 6.8.0.105:
public override int ErrorCode {
//
// the base class returns the HResult with this property
// we need the Win32 Error Code, hence the override.
//
get {
return NativeErrorCode;
}
}
In .NET Core 3.1.3:
public override int ErrorCode => base.NativeErrorCode;
Writing cross-platform socket error handling
Circling back to the original method we started this post with, we rewrote ShouldRetryConnection as follows:
protected virtual bool ShouldRetryConnection(Exception ex)
{
if (ex is SocketException sx)
return sx.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.ConnectionRefused;
return false;
}
There was a lot of work involved in tracking down the error code to check against, but in the end, our code is much more readable now. Adding to that, this method is now also completely cross-platform, and works correctly on any runtime.
Overview of the native error codes
In some situations, you may want to have a table with native error codes on different operating systems. We can get these values with the following code snippet:
var allErrors = Enum.GetValues(typeof(SocketError)).Cast<SocketError>().ToList();
var maxNameWidth = allErrors.Select(x => x.ToString().Length).Max();
foreach (var socketError in allErrors)
{
var name = socketError.ToString().PadRight(maxNameWidth);
var code = new SocketException((int) socketError).NativeErrorCode.ToString().PadLeft(7);
Console.WriteLine("| {name} | {code} |");
}
We executed this program on Windows, Linux, and macOS. Here are the aggregated results:
| SocketError | Windows | Linux | macOS |
| Success | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OperationAborted | 995 | 125 | 89 |
| IOPending | 997 | 115 | 36 |
| Interrupted | 10004 | 4 | 4 |
| AccessDenied | 10013 | 13 | 13 |
| Fault | 10014 | 14 | 14 |
| InvalidArgument | 10022 | 22 | 22 |
| TooManyOpenSockets | 10024 | 23 | 23 |
| WouldBlock | 10035 | 11 | 35 |
| InProgress | 10036 | 115 | 36 |
| AlreadyInProgress | 10037 | 114 | 37 |
| NotSocket | 10038 | 88 | 38 |
| DestinationAddressRequired | 10039 | 89 | 39 |
| MessageSize | 10040 | 90 | 40 |
| ProtocolType | 10041 | 91 | 41 |
| ProtocolOption | 10042 | 92 | 42 |
| ProtocolNotSupported | 10043 | 93 | 43 |
| SocketNotSupported | 10044 | 94 | 44 |
| OperationNotSupported | 10045 | 95 | 45 |
| ProtocolFamilyNotSupported | 10046 | 96 | 46 |
| AddressFamilyNotSupported | 10047 | 97 | 47 |
| AddressAlreadyInUse | 10048 | 98 | 48 |
| AddressNotAvailable | 10049 | 99 | 49 |
| NetworkDown | 10050 | 100 | 50 |
| NetworkUnreachable | 10051 | 101 | 51 |
| NetworkReset | 10052 | 102 | 52 |
| ConnectionAborted | 10053 | 103 | 53 |
| ConnectionReset | 10054 | 104 | 54 |
| NoBufferSpaceAvailable | 10055 | 105 | 55 |
| IsConnected | 10056 | 106 | 56 |
| NotConnected | 10057 | 107 | 57 |
| Shutdown | 10058 | 32 | 32 |
| TimedOut | 10060 | 110 | 60 |
| ConnectionRefused | 10061 | 111 | 61 |
| HostDown | 10064 | 112 | 64 |
| HostUnreachable | 10065 | 113 | 65 |
| ProcessLimit | 10067 | 10067 | 10067 |
| SystemNotReady | 10091 | 10091 | 10091 |
| VersionNotSupported | 10092 | 10092 | 10092 |
| NotInitialized | 10093 | 10093 | 10093 |
| Disconnecting | 10101 | 108 | 58 |
| TypeNotFound | 10109 | 10109 | 10109 |
| HostNotFound | 11001 | -131073 | -131073 |
| TryAgain | 11002 | 11 | 35 |
| NoRecovery | 11003 | 11003 | 11003 |
| NoData | 11004 | 61 | 96 |
| SocketError | -1 | -1 | -1 |
This table may be useful if you work with native socket error codes.
Summary
From this investigation, we’ve learned the following:
SocketException.SocketErrorCodereturns a value from theSocketErrorenum. The numerical values of the enum elements always correspond to the Windows socket error codes.SocketException.ErrorCodealways returnsSocketException.NativeErrorCode.SocketException.NativeErrorCodeon .NET Framework and Mono always corresponds to the Windows error codes (even if you are using Mono on Unix). On .NET Core,SocketException.NativeErrorCodeequals the corresponding native error code from the current operating system.
A few practical recommendations:
- If you want to write portable code, always use
SocketException.SocketErrorCodeand compare it with the values ofSocketError. Never use raw numerical error codes. - If you want to get the native error code on .NET Core (e.g., for passing to another native program), use
SocketException.NativeErrorCode. Remember that different Unix-based operating systems (e.g., Linux, macOS, Solaris) have different native code sets. You can get the exact values of the native error codes by using the errno command.
References
- Microsoft Docs: Windows Sockets Error Codes
- IBM Knowledge Center: TCP/IP error codes
- MariaDB: Operating System Error Codes
- gnu.org: Error Codes
- Stackoverflow: Identical Error Codes
У меня есть серверно-клиентское приложение, в котором сервер находится в сети в случайное время, но клиенту необходимо периодически отправлять широковещательные сообщения, чтобы зарегистрироваться на сервере, когда он находится в сети. Поэтому я хочу, чтобы мое приложение игнорировало указанную выше ошибку и продолжало делать то, что оно делает, пока не получит определенный управляющий триггер с сервера.
Пример кода:
import socket,sys
cs = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
cs.connect((HOST, CPORT))
cs.send("REGS " + hostname)
cs.close()
Есть идеи ?
1 ответы
ответ дан 14 апр.
Не тот ответ, который вы ищете? Просмотрите другие вопросы с метками
python
exception
or задайте свой вопрос.