предыдущая глава | содержание | следующая глава
- 10.1 «The server’s host key is not cached in the registry»
- 10.2 «WARNING — POTENTIAL SECURITY BREACH!»
- 10.3 «SSH protocol version 2 required by our configuration but remote only provides (old, insecure) SSH-1»
- 10.4 «The first cipher supported by the server is … below the configured warning threshold»
- 10.5 «Remote side sent disconnect message type 2 (protocol error): «Too many authentication failures for root»»
- 10.6 «Out of memory»
- 10.7 «Internal error», «Internal fault», «Assertion failed»
- 10.8 «Unable to use key file», «Couldn’t load private key», «Couldn’t load this key»
- 10.9 «Server refused our key», «Server refused our public key», «Key refused»
- 10.10 «Access denied», «Authentication refused»
- 10.11 «No supported authentication methods available»
- 10.12 «Incorrect MAC received on packet» or «Incorrect CRC received on packet»
- 10.13 «Incoming packet was garbled on decryption»
- 10.14 «PuTTY X11 proxy: various errors»
- 10.15 «Network error: Software caused connection abort»
- 10.16 «Network error: Connection reset by peer»
- 10.17 «Network error: Connection refused»
- 10.18 «Network error: Connection timed out»
- 10.19 «Network error: Cannot assign requested address»
This chapter lists a number of common error messages which PuTTY and its associated tools can produce, and explains what they mean in more detail.
We do not attempt to list all error messages here: there are many which should never occur, and some which should be self-explanatory. If you get an error message which is not listed in this chapter and which you don’t understand, report it to us as a bug (see appendix B) and we will add documentation for it.
10.1 «The server’s host key is not cached in the registry»
This error message occurs when PuTTY connects to a new SSH server. Every server identifies itself by means of a host key; once PuTTY knows the host key for a server, it will be able to detect if a malicious attacker redirects your connection to another machine.
If you see this message, it means that PuTTY has not seen this host key before, and has no way of knowing whether it is correct or not. You should attempt to verify the host key by other means, such as asking the machine’s administrator.
If you see this message and you know that your installation of PuTTY has connected to the same server before, it may have been recently upgraded to SSH protocol version 2. SSH protocols 1 and 2 use separate host keys, so when you first use SSH-2 with a server you have only used SSH-1 with before, you will see this message again. You should verify the correctness of the key as before.
See section 2.2 for more information on host keys.
10.2 «WARNING — POTENTIAL SECURITY BREACH!»
This message, followed by «The server’s host key does not match the one PuTTY has cached in the registry», means that PuTTY has connected to the SSH server before, knows what its host key should be, but has found a different one.
This may mean that a malicious attacker has replaced your server with a different one, or has redirected your network connection to their own machine. On the other hand, it may simply mean that the administrator of your server has accidentally changed the key while upgrading the SSH software; this shouldn’t happen but it is unfortunately possible.
You should contact your server’s administrator and see whether they expect the host key to have changed. If so, verify the new host key in the same way as you would if it was new.
See section 2.2 for more information on host keys.
10.3 «SSH protocol version 2 required by our configuration but remote only provides (old, insecure) SSH-1»
By default, PuTTY only supports connecting to SSH servers that implement SSH protocol version 2. If you see this message, the server you’re trying to connect to only supports the older SSH-1 protocol.
If the server genuinely only supports SSH-1, then you need to either change the «SSH protocol version» setting (see section 4.19.4), or use the -1 command-line option; in any case, you should not treat the resulting connection as secure.
You might start seeing this message with new versions of PuTTY (from 0.68 onwards) where you didn’t before, because it used to be possible to configure PuTTY to automatically fall back from SSH-2 to SSH-1. This is no longer supported, to prevent the possibility of a downgrade attack.
10.4 «The first cipher supported by the server is … below the configured warning threshold»
This occurs when the SSH server does not offer any ciphers which you have configured PuTTY to consider strong enough. By default, PuTTY puts up this warning only for Blowfish, single-DES, and Arcfour encryption.
See section 4.22 for more information on this message.
(There are similar messages for other cryptographic primitives, such as host key algorithms.)
10.5 «Remote side sent disconnect message type 2 (protocol error): «Too many authentication failures for root»»
This message is produced by an OpenSSH (or Sun SSH) server if it receives more failed authentication attempts than it is willing to tolerate.
This can easily happen if you are using Pageant and have a large number of keys loaded into it, since these servers count each offer of a public key as an authentication attempt. This can be worked around by specifying the key that’s required for the authentication in the PuTTY configuration (see section 4.23.8); PuTTY will ignore any other keys Pageant may have, but will ask Pageant to do the authentication, so that you don’t have to type your passphrase.
On the server, this can be worked around by disabling public-key authentication or (for Sun SSH only) by increasing MaxAuthTries in sshd_config.
10.6 «Out of memory»
This occurs when PuTTY tries to allocate more memory than the system can give it. This may happen for genuine reasons: if the computer really has run out of memory, or if you have configured an extremely large number of lines of scrollback in your terminal. PuTTY is not able to recover from running out of memory; it will terminate immediately after giving this error.
However, this error can also occur when memory is not running out at all, because PuTTY receives data in the wrong format. In SSH-2 and also in SFTP, the server sends the length of each message before the message itself; so PuTTY will receive the length, try to allocate space for the message, and then receive the rest of the message. If the length PuTTY receives is garbage, it will try to allocate a ridiculous amount of memory, and will terminate with an «Out of memory» error.
This can happen in SSH-2, if PuTTY and the server have not enabled encryption in the same way (see question A.7.3 in the FAQ).
This can also happen in PSCP or PSFTP, if your login scripts on the server generate output: the client program will be expecting an SFTP message starting with a length, and if it receives some text from your login scripts instead it will try to interpret them as a message length. See question A.7.4 for details of this.
10.7 «Internal error», «Internal fault», «Assertion failed»
Any error beginning with the word «Internal» should never occur. If it does, there is a bug in PuTTY by definition; please see appendix B and report it to us.
Similarly, any error message starting with «Assertion failed» is a bug in PuTTY. Please report it to us, and include the exact text from the error message box.
10.8 «Unable to use key file», «Couldn’t load private key», «Couldn’t load this key»
Various forms of this error are printed in the PuTTY window, or written to the PuTTY Event Log (see section 3.1.3.1) when trying public-key authentication, or given by Pageant when trying to load a private key.
If you see one of these messages, it often indicates that you’ve tried to load a key of an inappropriate type into PuTTY, Plink, PSCP, PSFTP, or Pageant.
You may have tried to load an SSH-2 key in a «foreign» format (OpenSSH or ssh.com) directly into one of the PuTTY tools, in which case you need to import it into PuTTY’s native format (*.PPK) using PuTTYgen – see section 8.2.12.
Alternatively, you may have specified a key that’s inappropriate for the connection you’re making. The SSH-2 and the old SSH-1 protocols require different private key formats, and a SSH-1 key can’t be used for a SSH-2 connection (or vice versa).
10.9 «Server refused our key», «Server refused our public key», «Key refused»
Various forms of this error are printed in the PuTTY window, or written to the PuTTY Event Log (see section 3.1.3.1) when trying public-key authentication.
If you see one of these messages, it means that PuTTY has sent a public key to the server and offered to authenticate with it, and the server has refused to accept authentication. This usually means that the server is not configured to accept this key to authenticate this user.
This is almost certainly not a problem with PuTTY. If you see this type of message, the first thing you should do is check your server configuration carefully. Common errors include having the wrong permissions or ownership set on the public key or the user’s home directory on the server. Also, read the PuTTY Event Log; the server may have sent diagnostic messages explaining exactly what problem it had with your setup.
Section 8.3 has some hints on server-side public key setup.
10.10 «Access denied», «Authentication refused»
Various forms of this error are printed in the PuTTY window, or written to the PuTTY Event Log (see section 3.1.3.1) during authentication.
If you see one of these messages, it means that the server has refused all the forms of authentication PuTTY has tried and it has no further ideas.
It may be worth checking the Event Log for diagnostic messages from the server giving more detail.
This error can be caused by buggy SSH-1 servers that fail to cope with the various strategies we use for camouflaging passwords in transit. Upgrade your server, or use the workarounds described in section 4.28.11 and possibly section 4.28.12.
10.11 «No supported authentication methods available»
This error indicates that PuTTY has run out of ways to authenticate you to an SSH server. This may be because PuTTY has TIS or keyboard-interactive authentication disabled, in which case see section 4.23.4 and section 4.23.5.
10.12 «Incorrect MAC received on packet» or «Incorrect CRC received on packet»
This error occurs when PuTTY decrypts an SSH packet and its checksum is not correct. This probably means something has gone wrong in the encryption or decryption process. It’s difficult to tell from this error message whether the problem is in the client, in the server, or in between.
In particular, if the network is corrupting data at the TCP level, it may only be obvious with cryptographic protocols such as SSH, which explicitly check the integrity of the transferred data and complain loudly if the checks fail. Corruption of protocols without integrity protection (such as HTTP) will manifest in more subtle failures (such as misdisplayed text or images in a web browser) which may not be noticed.
Occasionally this has been caused by server bugs. An example is the bug described at section 4.28.8, although you’re very unlikely to encounter that one these days.
In this context MAC stands for Message Authentication Code. It’s a cryptographic term, and it has nothing at all to do with Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) addresses, or with the Apple computer.
10.13 «Incoming packet was garbled on decryption»
This error occurs when PuTTY decrypts an SSH packet and the decrypted data makes no sense. This probably means something has gone wrong in the encryption or decryption process. It’s difficult to tell from this error message whether the problem is in the client, in the server, or in between.
If you get this error, one thing you could try would be to fiddle with the setting of «Miscomputes SSH-2 encryption keys» (see section 4.28.10) or «Ignores SSH-2 maximum packet size» (see section 4.28.5) on the Bugs panel.
10.14 «PuTTY X11 proxy: various errors»
This family of errors are reported when PuTTY is doing X forwarding. They are sent back to the X application running on the SSH server, which will usually report the error to the user.
When PuTTY enables X forwarding (see section 3.4) it creates a virtual X display running on the SSH server. This display requires authentication to connect to it (this is how PuTTY prevents other users on your server machine from connecting through the PuTTY proxy to your real X display). PuTTY also sends the server the details it needs to enable clients to connect, and the server should put this mechanism in place automatically, so your X applications should just work.
A common reason why people see one of these messages is because they used SSH to log in as one user (let’s say «fred»), and then used the Unix su command to become another user (typically «root»). The original user, «fred», has access to the X authentication data provided by the SSH server, and can run X applications which are forwarded over the SSH connection. However, the second user («root») does not automatically have the authentication data passed on to it, so attempting to run an X application as that user often fails with this error.
If this happens, it is not a problem with PuTTY. You need to arrange for your X authentication data to be passed from the user you logged in as to the user you used su to become. How you do this depends on your particular system; in fact many modern versions of su do it automatically.
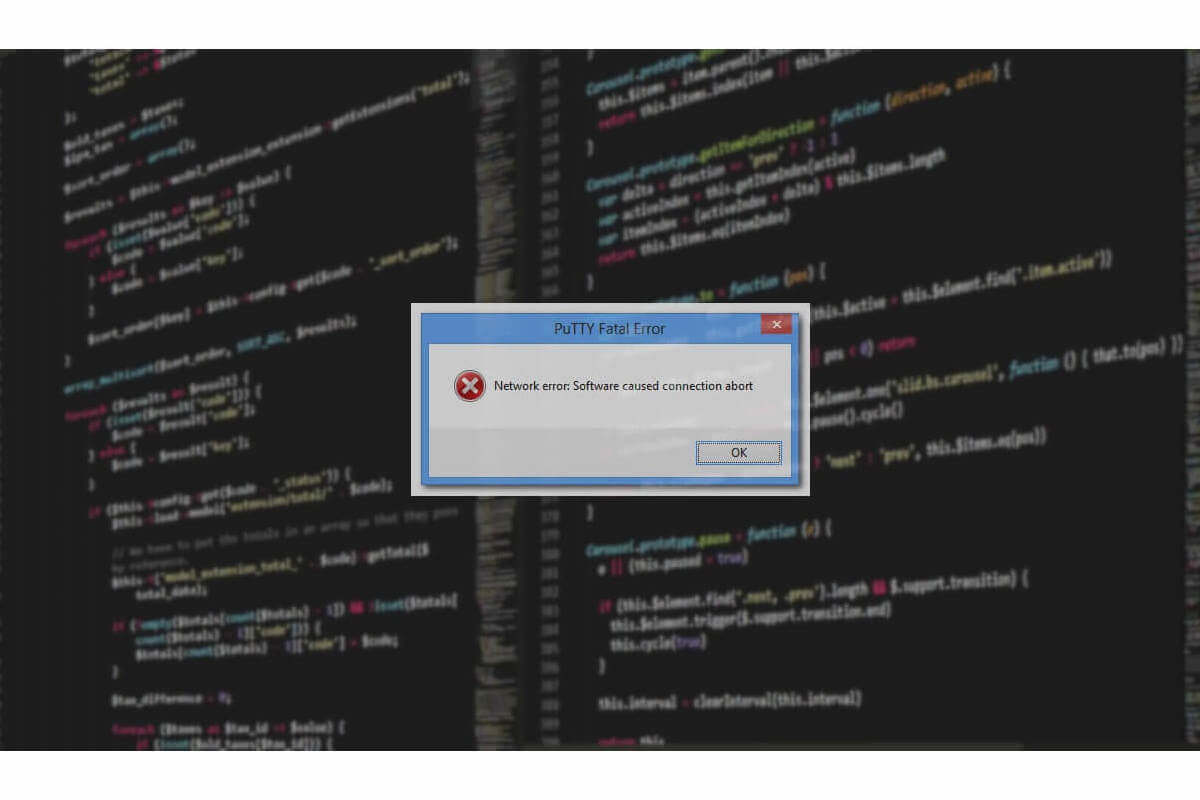
10.15 «Network error: Software caused connection abort»
This is a generic error produced by the Windows network code when it kills an established connection for some reason. For example, it might happen if you pull the network cable out of the back of an Ethernet-connected computer, or if Windows has any other similar reason to believe the entire network has become unreachable.
Windows also generates this error if it has given up on the machine at the other end of the connection ever responding to it. If the network between your client and server goes down and your client then tries to send some data, Windows will make several attempts to send the data and will then give up and kill the connection. In particular, this can occur even if you didn’t type anything, if you are using SSH-2 and PuTTY attempts a key re-exchange. (See section 4.20.2 for more about key re-exchange.)
(It can also occur if you are using keepalives in your connection. Other people have reported that keepalives fix this error for them. See section 4.14.1 for a discussion of the pros and cons of keepalives.)
We are not aware of any reason why this error might occur that would represent a bug in PuTTY. The problem is between you, your Windows system, your network and the remote system.
10.16 «Network error: Connection reset by peer»
This error occurs when the machines at each end of a network connection lose track of the state of the connection between them. For example, you might see it if your SSH server crashes, and manages to reboot fully before you next attempt to send data to it.
However, the most common reason to see this message is if you are connecting through a firewall or a NAT router which has timed the connection out. See question A.7.8 in the FAQ for more details. You may be able to improve the situation by using keepalives; see section 4.14.1 for details on this.
Note that Windows can produce this error in some circumstances without seeing a connection reset from the server, for instance if the connection to the network is lost.
10.17 «Network error: Connection refused»
This error means that the network connection PuTTY tried to make to your server was rejected by the server. Usually this happens because the server does not provide the service which PuTTY is trying to access.
Check that you are connecting with the correct protocol (SSH, Telnet or Rlogin), and check that the port number is correct. If that fails, consult the administrator of your server.
10.18 «Network error: Connection timed out»
This error means that the network connection PuTTY tried to make to your server received no response at all from the server. Usually this happens because the server machine is completely isolated from the network, or because it is turned off.
Check that you have correctly entered the host name or IP address of your server machine. If that fails, consult the administrator of your server.
Unix also generates this error when it tries to send data down a connection and contact with the server has been completely lost during a connection. (There is a delay of minutes before Unix gives up on receiving a reply from the server.) This can occur if you type things into PuTTY while the network is down, but it can also occur if PuTTY decides of its own accord to send data: due to a repeat key exchange in SSH-2 (see section 4.20.2) or due to keepalives (section 4.14.1).
10.19 «Network error: Cannot assign requested address»
This means that the operating system rejected the parameters of the network connection PuTTY tried to make, usually without actually trying to connect to anything, because they were simply invalid.
A common way to provoke this error is to accidentally try to connect to port 0, which is not a valid port number.
OpenSSH is an open-source version of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol that can be used to login remotely to a server and to control remote Linux-based systems.
OpenSSH provides secure encrypted communication between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network.
OpenSSH also provides sftp and sftp-server that implement an easier solution for file-transfer and is used in major network monitoring tools and web servers all around the world.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to troubleshoot “the SSH Connection Refused” error while connecting to Ubuntu/Linux.
Connecting to a Server Via SSH
There are two ways to connect to a server via SSH. You can either use SSH command or Putty (or any other SSH Client for that matter) to connect a server.
Connect to a Server with SSH command
The basic syntax of the SSH command is shown below:
ssh Username@Server-ip-address -p Port
Where:
- Username : user account on your server.
- Server-ip-address : IP address or Domain name of your server.
- Port : It is the port number of the OpenSSH server, usually 22, unless you’ve changed it.
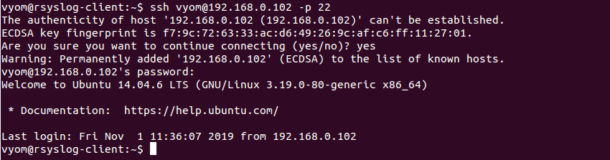
For example, let’s connect a remote server with username vyom, IP address 192.168.0.102 and Port number 22:
ssh vyom@192.168.0.102 -p 22
When your connecting your server via SSH for the first time, you should see the following message:
The authenticity of host '192.168.0.102 (192.168.0.102)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is f7:9c:72:63:33:ac:d6:49:26:9c:af:c6:ff:11:27:01.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Type yes and hit Enter, you will be asked to provide a password for user vyom. Provide a password and hit Enter to connect to a server. You should see the following output:
Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.6 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.19.0-80-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/
Last login: Fri Nov 1 11:36:07 2019 from 192.168.0.102
You should see the above output in the following screen:
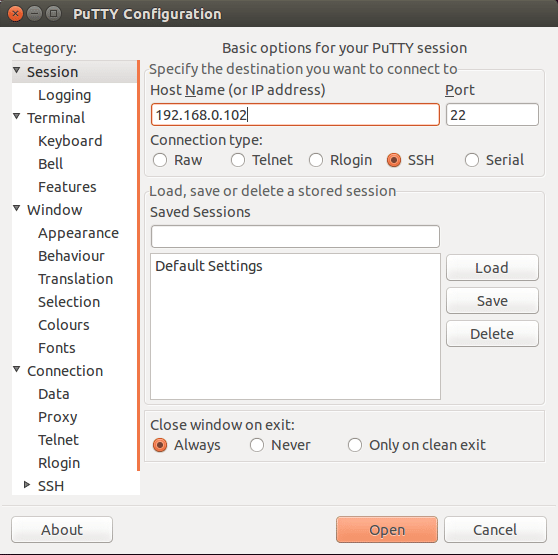
Connect a Server with Putty
Putty is open source SSH client software used to connect SSH server from Windows-based operating systems. You can download the Putty software from the Putty download page.
Once downloaded, double-click on the putty.exe program to launch the application. You should see the following screen:
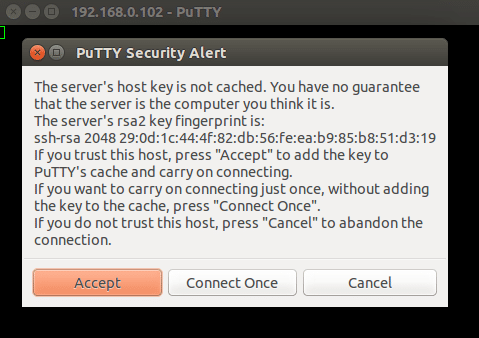
Now, provide your SSH server IP-address, Port number, Connection type and click on the Open button to start the SSH session. If you are connecting to this server first time. You should see the following screen:
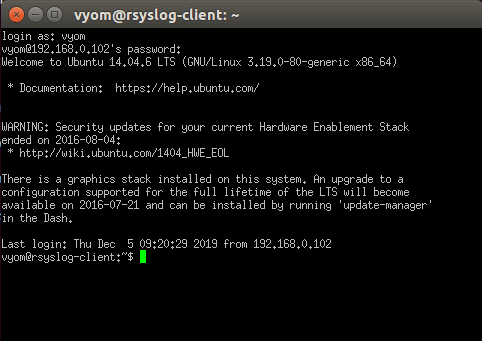
Click on the Accept button. You should see a terminal prompt asking for your username.
Provide your username, password and hit Enter to logged into your server.
Sometimes you receive an error like “Network error: Connection refused” while connecting to your server via SSH. There are a number of reasons for this error. In order to fix this error, you will need to identify the cause of the error by checking and ruling out each possibility. In this section, we will show you some troubleshooting steps to resolve this error.
Step 1
First, make sure the openssh-server package is installed on your server.
You can check it with the following command:
dpkg -l | grep openssh-server
If the openssh-server is installed, you should see the following output:
ii openssh-server 1:6.6p1-2ubuntu2.13 amd64 secure shell (SSH) server, for secure access from remote machines
If not installed, you can install it with the following command:
apt-get install openssh-server
Step 2
OpenSSH service uses sshd daemon to listen to the incoming connections and handles user authentication. If this service crashes, the connection fails and you will get the SSH Connection refused error.
You can check the status of OpenSSH service whether it is running or not with the following command:
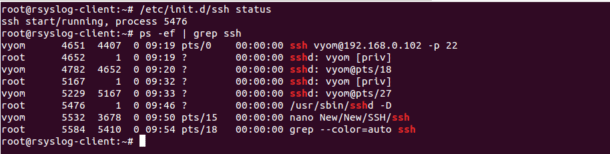
/etc/init.d/ssh status
If it is running, you should see the following output:
ssh start/running, process 5476
You can also check the SSH service with the following command:
ps -ef | grep ssh
You should see the following output:
vyom 4651 4407 0 09:19 pts/0 00:00:00 ssh vyom@192.168.0.102 -p 22
root 4652 1 0 09:19 ? 00:00:00 sshd: vyom [priv]
vyom 4782 4652 0 09:20 ? 00:00:00 sshd: vyom@pts/18
root 5167 1 0 09:32 ? 00:00:00 sshd: vyom [priv]
vyom 5229 5167 0 09:33 ? 00:00:00 sshd: vyom@pts/27
root 5476 1 0 09:46 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
vyom 5532 3678 0 09:50 pts/15 00:00:00 nano New/New/SSH/ssh
root 5584 5410 0 09:54 pts/18 00:00:00 grep --color=auto ssh
If an OpenSSH service is not running, you can start it with the following command:
/etc/init.d/ssh start
You should see the output of the above commands in the following screen:
Step 3
By default, OpenSSH is running on port 22 and is vulnerable to attack. Sometimes you’ll get the “Network error: Connection refused” error if your SSH server is listening on a different port.
First, you will need to find the open ports in your server with Nmap command:
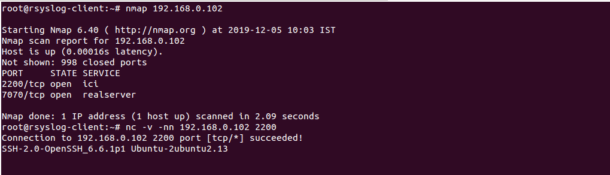
nmap 192.168.0.102
You should see the following output:
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2019-12-05 10:03 IST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.102
Host is up (0.00016s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
2200/tcp open ici
7070/tcp open realserver
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.09 seconds
In the above output, you should see that port 2200 and 7070 are open on your server.
Now, check which service is running on the given ports (2200, 7070) one by one:
nc -v -nn 192.168.0.102 2200
You should see that SSH service is running on port 2200:
Connection to 192.168.0.102 2200 port [tcp/*] succeeded!
SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_6.6.1p1 Ubuntu-2ubuntu2.13
You can also check the OpenSSH listening port by opening the file:
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
You should now be able to connect to your OpenSSH server using the port 2200 as shown below:
ssh vyom@192.168.0.102 -p 2200
You should see the output of all the commands in the following screen:
Step 4
Some times you will get the “Network error: Connection refused” error, if your OpenSSH server IP address is conflict with other systems in your network.
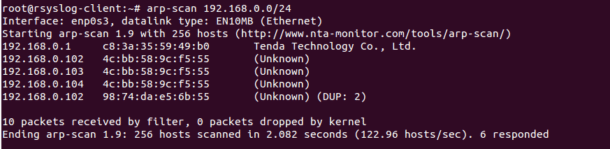
You can use arp-scan tool to check the duplicate IP address in your network as shown below:
arp-scan 192.168.0.0/24
You should see the following output:
Interface: enp0s3, datalink type: EN10MB (Ethernet)
Starting arp-scan 1.9 with 256 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/arp-scan/)
192.168.0.1 c8:3a:35:59:49:b0 Tenda Technology Co., Ltd.
192.168.0.102 4c:bb:58:9c:f5:55 (Unknown)
192.168.0.103 4c:bb:58:9c:f5:55 (Unknown)
192.168.0.104 4c:bb:58:9c:f5:55 (Unknown)
192.168.0.102 98:74:da:e5:6b:55 (Unknown) (DUP: 2)
10 packets received by filter, 0 packets dropped by kernel
Ending arp-scan 1.9: 256 hosts scanned in 2.082 seconds (122.96 hosts/sec). 6 responded
To resolve this error, you will need to change your server’s IP address.
Step 5
Similarly, SSH connectivity problems may occur due to improper firewall configurations. If a firewall is configured to deny SSH connection on your server, the connectivity can fail and lead to the error SSH connection refused.
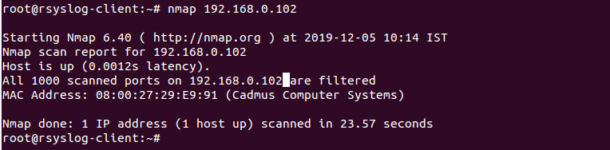
You can check whether your server is filtered with a firewall or not with the following command:
nmap 192.168.0.102
You should see that your server is filtered with a firewall:
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2019-12-05 10:14 IST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.102
Host is up (0.0012s latency).
All 1000 scanned ports on 192.168.0.102 are filtered
MAC Address: 08:00:27:29:E9:91 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 23.57 seconds
To resolve this error, you will need to allow your SSH port through the firewall on your server.
Conclusion
In the above article, we learned how to troubleshoot the “SSH connection refused” error with several examples. I hope you have now enough knowledge to resolve this type of error.
25 мая, 2017 11:40 дп
86 521 views
| Комментариев нет
Linux, SSH
В первой статье этой серии вы узнали о том, как и в каких ситуациях вы можете попробовать исправить ошибки SSH. Остальные статьи расскажут, как определить и устранить ошибки:
- Ошибки протокола: в этой статье вы узнаете, что делать, если сбрасываются клиентские соединения, клиент жалуется на шифрование или возникают проблемы с неизвестным или измененным удаленным хостом.
- Ошибки аутентификации: поможет устранить проблемы с парольной аутентификацией или сбросом SSH-ключей.
- Ошибки оболочки: это руководство поможет исправить ошибки ветвления процессов, валидации оболочки и доступа к домашнему каталогу.
Для взаимодействия SSH-клиента с SSH-сервером необходимо установить базовое сетевое подключение. Это руководство поможет определить некоторые общие ошибки подключения, исправить их и предотвратить их возникновение в будущем.
Требования
- Убедитесь, что можете подключиться к виртуальному серверу через консоль.
- Проверьте панель на предмет текущих проблем, влияющих на работу и состояние сервера и гипервизора.
Основные ошибки
Разрешение имени хоста
Большинство ошибок подключения возникает тогда, когда ссылка на хост SSH не может быть сопоставлена с сетевым адресом. Это почти всегда связано с DNS, но первопричина часто бывает не связана с DNS.
На клиенте OpenSSH эта команда:
ssh user@example.com
может выдать ошибку:
ssh: Could not resolve hostname example.com: Name or service not known
В PuTTY может появиться такая ошибка:
Unable to open connection to example.com Host does not exist
Чтобы устранить эту ошибку, можно попробовать следующее:
- Проверьте правильность написания имени хоста.
- Убедитесь, что вы можете разрешить имя хоста на клиентской машине с помощью команды ping. Обратитесь к сторонним сайтам (WhatsMyDns.net, например), чтобы подтвердить результаты.
Если у вас возникают проблемы с разрешением DNS на любом уровне, в качестве промежуточного решения можно использовать IP-адрес сервера, например:
ssh user@111.111.111.111
# вместо
ssh user@example.com.
Истечение времени соединения
Эта ошибка значит, что клиент попытался установить соединение с SSH-сервером, но сервер не смог ответить в течение заданного периода ожидания.
На клиенте OpenSSH следующая команда:
ssh user@111.111.111.111
выдаст такую ошибку:
ssh: connect to host 111.111.111.111 port 22: Connection timed out
В PuTTY ошибка выглядит так:
Network error: Connection timed out
Чтобы исправить ошибку:
- Убедитесь, что IP-адрес хоста указан правильно.
- Убедитесь, что сеть поддерживает подключение через используемый порт SSH. Некоторые публичные сети могут блокировать порт 22 или пользовательские SSH-порты. Чтобы проверить работу порта, можно, например, попробовать подключиться к другим хостам через этот же порт. Это поможет вам определить, не связана ли проблема с самим сервером.
- Проверьте правила брандмауэра. Убедитесь, что политика по умолчанию – не DROP.
Отказ в соединении
Эта ошибка означает, что запрос передается на хост SSH, но хост не может успешно принять запрос.
На клиенте OpenSSH следующая команда выдаст ошибку:
ssh user@111.111.111.111
ssh: connect to host 111.111.111.111 port 22: Connection refused
В PuTTY ошибка появится в диалоговом окне:
Network error: Connection refused
Эта ошибка имеет общие с ошибкой Connection Timeout причины. Чтобы исправить её, можно сделать следующее:
- Убедиться, что IP-адрес хоста указан правильно.
- Убедиться, что сеть поддерживает подключение через используемый порт SSH. Некоторые публичные сети могут блокировать порт 22 или пользовательские SSH-порты. Чтобы проверить работу порта, можно, например, попробовать подключиться к другим хостам через этот же порт.
- Проверить правила брандмауэра. Убедитесь, что политика по умолчанию – не DROP, и что брандмауэр не блокирует этот порт.
- Убедиться, что сервис запущен и привязан к требуемому порту.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибок подключения
Брандмауэр
Иногда проблемы с подключением возникают из-за брандмауэра. Он может блокировать отдельные порты или сервисы.
Читайте также: Что такое брандмауэр и как он работает?
В разных дистрибутивах используются разные брандмауэры. Вы должны научиться изменять правила и политики своего брандмауэра. В Ubuntu обычно используется UFW, в CentOS – FirewallD. Брандмауэр iptables используется независимо от системы.
Читайте также:
- Основы UFW: общие правила и команды фаервола
- Настройка брандмауэра FirewallD в CentOS 7
- Основы Iptables: общие правила и команды брандмауэра
Чтобы настроить брандмауэр, нужно знать порт сервиса SSH. По умолчанию это порт 22.
Чтобы запросить список правил iptables, введите:
iptables -nL
Такой вывод сообщает, что правил, блокирующих SSH, нет:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Если в выводе вы видите правило или политику по умолчанию REJECT или DROP, убедитесь, что цепочка INPUT разрешает доступ к порту SSH.
Чтобы запросить список правил FirewallD, введите:
firewall-cmd --list-services
Список, появившийся на экране, содержит все сервисы, которые поддерживаются брандмауэром. В списке должно быть правило:
dhcpv6-client http ssh
Если вы настроили пользовательский порт SSH, используйте опцию –list-ports. Если вы создали пользовательское определение сервиса, добавьте опцию –list-services, чтобы найти SSH.
Чтобы проверить состояние UFW, введите:
ufw status
Команда вернёт доступные порты:
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
22 LIMIT Anywhere
443 ALLOW Anywhere
80 ALLOW Anywhere
Anywhere ALLOW 192.168.0.0
22 (v6) LIMIT Anywhere (v6)
443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
В списке должен быть порт SSH.
Проверка состояния сервиса SSH
Если вы не можете подключиться к серверу по SSH, убедитесь, что сервис SSH запущен. Способ сделать это зависит от операционной системы сервера. В более старых версиях дистрибутивов (Ubuntu 14.04, CentOS 6, Debian 
Метод проверки состояния сервиса может варьироваться от системы к системе. В более старых версиях (Ubuntu 14 и ниже, CentOS 6, Debian 6) используется команда service, поддерживаемая системой инициализации Upstart, а в более современных дистрибутивах для управления сервисом используется команда systemctl.
Примечание: В дистрибутивах Red Hat (CentOS и Fedora) сервис называется sshd, а в Debian и Ubuntu – ssh.
В более старых версия используйте команду:
service ssh status
Если процесс работает должным образом, вы увидите вывод, который содержит PID:
ssh start/running, process 1262
Если сервис не работает, вы увидите:
ssh stop/waiting
В системах на основе SystemD используйте:
systemctl status sshd
В выводе должна быть строка active:
sshd.service - OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2017-03-20 11:00:22 EDT; 1 months 1 days ago
Process: 899 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd-keygen (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 906 (sshd)
CGroup: /system.slice/sshd.service
├─ 906 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
├─26941 sshd: [accepted]
└─26942 sshd: [net]
Если сервис не работает, вы увидите в выводе inactive:
sshd.service - OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2017-04-21 08:36:13 EDT; 2s ago
Process: 906 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 899 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd-keygen (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 906 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Чтобы перезапустить сервис, введите соответственно:
service ssh start
systemctl start sshd
Проверка порта SSH
Существует два основных способа проверить порт SSH: проверить конфигурационный файл SSH или просмотреть запущенный процесс.
Как правило, конфигурационный файл SSH хранится в /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Стандартный порт 22 может переопределяться любой строкой в этом файле, определяющей директиву Port.
Запустите поиск по файлу с помощью команды:
grep Port /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Читайте также: Использование Grep и регулярных выражений для поиска текстовых шаблонов в Linux
Команда вернёт:
Port 22
Если вы уже убедились, что сервис работает, теперь вы можете узнать, работает ли он на требуемом порте. Для этого используйте команду ss. Команда netstat –plnt выдаст аналогичный результат, но команду ss рекомендуется использовать для запроса информации сокета из ядра.
ss -plnt
В выводе должно быть указано имя программы и порт, который она прослушивает. Например, следующий вывод сообщает, что сервис SSH прослушивает все интерфейсы и порт 22.
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:(("sshd",pid=1493,fd=3))
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* users:(("sshd",pid=1493,fd=4))
Символ * и 0.0.0.0 указывает, что все интерфейсы сервера прослушиваются. Строка 127.0.0.1 значит, что сервис не является общедоступным. В sshd_config директива ListenAddress должна быть закомментирована, чтобы прослушивать все интерфейсы, или должна содержать внешний IP-адрес сервера.
Если у вас не получается самостоятельно настроить соединение SSH, вы можете обратиться за помощью к службе поддержки своего хостинг-провайдера.
Tags: firewalld, Iptables, OpenSSH, PuTTY, SSH, UFW
Secure Shell (SSH) is a key WordPress development tool. It grants advanced users access to key platforms and software that make coding and other tasks easier, faster, and more organized.
So if you attempt to use SSH only to see a “Connection refused” error, you may start to feel concerned. However, this is a common issue, and it’s entirely possible to fix it on your own with just a bit of troubleshooting. You’ll be back to running commands in no time flat.
In this post, we’ll discuss what SSH is and when to use it. Then we’ll explain some common reasons your connection may be refused, including in PuTTY. Finally, we’ll provide some troubleshooting tips.
Let’s dive in!
Prefer to watch the video version?
What Is SSH and When Should I Use It?
Secure Shell (SSH), also sometimes called Secure Socket Shell, is a protocol for securely accessing your site’s server over an unsecured network. In other words, it’s a way to safely log in to your server remotely using your preferred command-line interface:
Unlike File Transfer Protocol (FTP), which only enables you to upload, delete, and edit files on your server, SSH can accomplish a wide range of tasks. For instance, if an error locks you out of your WordPress site, you can use SSH to access it remotely.
This protocol also enables you to use several key developer tools, including:
- WP-CLI. The WordPress command line. You can use it for a variety of tasks, including new installations, bulk plugin updates, and media file imports.
- Composer. A PHP package manager. It enables you to implement several frameworks for use in your site’s code by pulling the necessary libraries and dependencies.
- Git. A version control system used to track changes in code. This is especially useful for teams of developers working together on a single project.
- npm. A JavaScript package manager. It includes a command-line and JavaScript software registry. Note: Kinsta customers will need an Enterprise plan in order to access this feature.
It’s important to note that using SSH is an advanced skill. Generally speaking, lay users of WordPress should contact their developers or hosting providers for help, rather than trying to resolve issues with SSH themselves.
Why Is My SSH Connection Refused? (5 Reasons for Connectivity Errors)
Unfortunately, there are many scenarios that could occur while you’re trying to connect to your server via SSH, which might result in an error reading “Connection refused”.
Below are some of the most common issues that might be causing problems for you.
1. Your SSH Service Is Down
In order to connect to your server with SSH, it must be running an SSH daemon – a program that runs in the background to listen for and accept connections.
If this service is down, you will not be able to successfully connect to your server and may receive a Connection refused error:
Your server’s SSH daemon may be down for a wide variety of reasons, including unexpected traffic spikes, resource outages, or even a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. In addition to the troubleshooting steps we’ll mention below, you may want to contact your hosting provider to determine the root cause of the issue.
If you suspect that your SSH service might be down, you can run this command to find out:
sudo service ssh statusIf the command line returns a status of down, then you’ve likely found the reason behind your connectivity error.
2. You Have the Wrong Credentials
Although it may seem too simple to be true, it’s possible that you’re just entering the wrong credentials when trying to connect to your server. There are four pieces of information needed to run SSH:
- Host name. The IP address of the server you’re trying to connect to or your domain name.
- Username. Your (S)FTP username.
- Password. Your (S)FTP password.
- Port. The default port is 22. However, some hosting providers (including Kinsta) change their SSH port number for security reasons. If this is the case, you should be able to find it by logging in to your MyKinsta dashboard.
You can also check to see which port is being used for SSH by running this command:
grep Port /etc/ssh/sshd_configThe command line should return the correct port.
Check to make sure you’re entering the right credentials and taking into account the possibility of typos or entering the wrong IP address or port.
3. The Port You’re Trying to Use Is Closed
A “port” is simply the endpoint to which you’re directed when connecting to your server. In addition to making sure you have the correct one, you’ll also want to check to see if the port you’re trying to use is open.
Any open port is a security vulnerability, as hackers can try to exploit it and gain access to the server. For this reason, unused ports are often closed to prevent attacks.
In the event that port 22, or the custom SSH port for your server, has been closed, you will likely see a Connection refused error. You can see all the ports listening on your server by running this command:
sudo lsof -i -n -P | grep LISTENThis command should return a list of ports with the LISTEN state. Ideally, you want to see port 22 or your server’s custom SSH port listed here. If it’s not, you’ll need to reopen the port in order to connect to your server.
4. SSH Isn’t Installed on Your Server
As we briefly mentioned earlier, servers use SSH daemons to listen for and accept connections. Therefore, if the server you’re trying to connect to doesn’t have one installed, you won’t be able to access it using SSH.
Generally speaking, almost all hosting providers will have SSH daemons installed on their servers by default. This particular issue is more common on localhost or dedicated servers.
5. Firewall Settings Are Preventing an SSH Connection
Since open ports present a security risk, firewalls installed to protect servers from hackers sometimes block connections to them. Unfortunately, this means that even harmless users who are trying to SSH into their servers may receive a Connection refused error as a result of firewall settings.
If your setup appears to be in order and you still can’t connect, take a look at your firewall’s rules. You can display them in your command-line interface with the following commands:
sudo iptables-save # display IPv4 rulessudo ip6tables-save # display IPv6 rulesYour results will vary, but you’ll want to look for these elements to determine if your firewall is blocking SSH connections:
- dport 22: This refers to the destination port, which for SSH is usually port 22 (reminder: Kinsta doesn’t use this port number).
- REJECT: This would indicate that connections are being refused from the specified destination.
- DROP: Like REJECT, this means that connections to the relevant port are being blocked.
If you search the results of the commands above for dport 22, you should be able to determine if your firewall is preventing an SSH connection. If so, you’ll have to change the rules to accept requests.
Why Does PuTTY Say Connection Refused?
PuTTY is an SSH client. If you’re familiar with FTP, this platform is the FileZilla equivalent to SSH on Windows machines. In other words, PuTTY enables users to input their credentials and launch an SSH connection:
If you’re a PuTTY user and see the Connection refused error, the cause is likely one of those listed above.
This is an SSH connectivity error like any other, and the troubleshooting tips below should work whether you’re using PuTTY, Terminal, or any other program for connecting to your server with SSH.
We’ve taken our knowledge of effective website management at scale, and turned it into an ebook and video course. Click to download The Guide to Managing 60+ WordPress Sites!
How Do I Troubleshoot SSH Connectivity Errors?
When you’re experiencing an SSH connectivity error, there are a few steps you can take to troubleshoot it depending on the cause. Here are some tips for troubleshooting the reasons for a Connection refused error that we covered above:
- If your SSH service is down. Contact your hosting provider to see why your SSH service isn’t running. For localhost or dedicated servers, you can use the command
sudo service ssh restartto try to get it running again. - If you entered the wrong credentials. Once you’ve double-checked the SSH port using the
grep Port /etc/ssh/sshd_configcommand, try connecting again with the correct details. - If your SSH port is closed. This is usually a side effect of one of the two reasons listed below. Either install an SSH daemon on the server you want to connect to or change your firewall rules to accept connections to your SSH port.
- If SSH isn’t installed on your server. Install an SSH tool such as OpenSSH on the server you want to connect to using the
sudo apt install openssh-servercommand. - If your firewall is blocking your SSH connection. Disable the firewall rules blocking your SSH connection by changing the destination port’s settings to ACCEPT.
If you’re attempting to connect to your hosting provider’s server, it may be wiser to contact support than to try troubleshooting the problem yourself. Users on localhost or dedicated servers may be able to find further support on more advanced forums if none of the above solutions works.
Are you getting the ‘Connection refused’ error over SSH? Learn why that’s happening and how to troubleshoot SSH connectivity errors thanks to this guide 🙅 ✋Click to Tweet
Summary
Being able to connect to your server with SSH is convenient in a wide range of situations. It can enable you to access your site when you’re locked out of your WordPress dashboard, run commands via WP-CLI, track changes in your site’s code with Git, and more.
Although there are several causes that could be behind your SSH connectivity error, these are a few of the most common:
- Your SSH service is down.
- You have the wrong credentials.
- The port you’re trying to use is closed.
- SSH isn’t installed on your server.
- Firewall settings are preventing an SSH connection.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Содержание
- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как исправить ошибку SSH Connection Refused
- Бесплатный вводный урок на онлайн курс по Linux
- Почему при использовании SSH возникает отказ в подключении?
- Клиент SSH не установлен
- Демон SSH не установлен на сервере
- Учетные данные неверны
- Служба SSH не работает
- Брандмауэр препятствует подключению SSH
- Порт SSH закрыт
- Отладка и ведение журнала SSH
- Бесплатный вводный урок на онлайн курс по Linux
- Полезно?
- Почему?
- CentOS
- SSH Access from 2nd NIC — «Network Error: Connection Refused»
- SSH Access from 2nd NIC — «Network Error: Connection Refused»
- Устранение неполадок SSH: проблемы с подключением к серверу
- Требования
- Основные ошибки
- Разрешение имени хоста
- Истечение времени соединения
- Отказ в соединении
- Рекомендации по исправлению ошибок подключения
- Брандмауэр
- Проверка состояния сервиса SSH
- Проверка порта SSH
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как исправить ошибку SSH Connection Refused
В соединении отказано
У вас проблемы с доступом к удаленному серверу через SSH? Если SSH отвечает сообщением «Connection Refused» (Соединение отклонено), возможно, вам придется изменить запрос или проверить настройки.
Бесплатный вводный урок на онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят начать карьеру администраторов Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг в DevOps
Почему при использовании SSH возникает отказ в подключении?
Существует множество причин, по которым вы можете получить ошибку «Connection Refused» при попытке подключения к серверу по SSH. Чтобы решить эту проблему, вам сначала нужно определить, почему система отказалась от вашего подключения через SSH.
Ниже вы найдете некоторые из наиболее распространенных причин, которые могут вызвать отказ в соединении SSH.
Клиент SSH не установлен
Прежде чем устранять другие проблемы, первым делом необходимо проверить, правильно ли установлен SSH. На машине, с которой вы получаете доступ к серверу, должен быть настроен клиент SSH. Без правильной настройки клиента вы не сможете подключиться к серверу.
Чтобы проверить, есть ли в вашей системе клиент SSH, введите в окне терминала следующее:
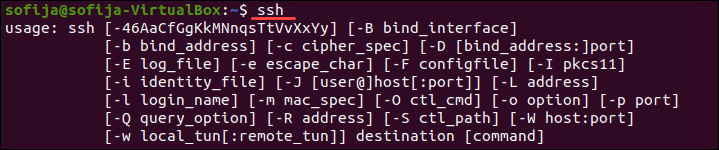
Если терминал предоставляет список параметров команды ssh, клиент SSH установлен в системе. Однако, если он ответит, что команда не найдена (command not found), вам необходимо установить клиент OpenSSH.
Решение: установить клиент SSH
Чтобы установить клиент SSH на свой компьютер, откройте терминал и выполните одну из команд, перечисленных ниже.
Для систем Ubuntu / Debian:
Для систем CentOS / RHEL:
Демон SSH не установлен на сервере
Так же, как вам нужна клиентская версия SSH для доступа к удаленному серверу, вам нужна версия сервера для прослушивания и приема соединений. Таким образом, сервер может отклонить входящее соединение, если SSH-сервер отсутствует или настройка неверна.
Чтобы проверить, доступен ли SSH на удаленном сервере, выполните команду:
Если на выходе отображается «Connection refused», переходите к установке SSH на сервере.
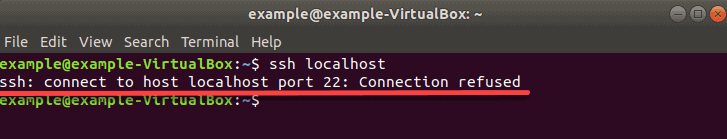
Решение: установите SSH на удаленный сервер
Чтобы решить проблему отсутствия сервера SSH, установите сервер OpenSSH.
Учетные данные неверны
Опечатки или неправильные учетные данные — частые причины отказа в SSH-соединении. Убедитесь, что вы не ошиблись при вводе имени пользователя или пароля.
Затем проверьте, правильно ли вы используете IP-адрес сервера.
Наконец, убедитесь, что у вас открыт правильный порт SSH. Вы можете проверить, запустив:
На выходе отображается номер порта, как на картинке ниже.

Служба SSH не работает
Служба SSH должна быть включена и работать в фоновом режиме. Если служба не работает, демон SSH не может принимать соединения.
Чтобы проверить статус службы, введите эту команду:
Вывод должен ответить, что служба активна. Если терминал отвечает, что служба не работает, включите его, чтобы решить проблему.
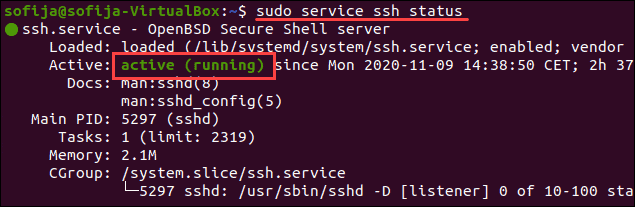
Решение: включить службу SSH
Если система показывает, что демон SSH не активен, вы можете запустить службу, выполнив:
Чтобы служба запускалась при загрузке, выполните команду:
Брандмауэр препятствует подключению SSH
SSH может отклонить соединение из-за ограничений брандмауэра. Брандмауэр защищает сервер от потенциально опасных подключений. Однако, если в системе настроен SSH, необходимо настроить брандмауэр, чтобы разрешить SSH-соединения.
Убедитесь, что брандмауэр не блокирует SSH-соединения, так как это может вызвать ошибку «Connection refused».
Решение: разрешить SSH-подключения через брандмауэр
Чтобы решить проблему, о которой мы упоминали выше, вы можете использовать ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall — несложный брандмауэр), инструмент интерфейса командной строки для управления конфигурацией брандмауэра.
Введите следующую команду в окне терминала, чтобы разрешить SSH-соединения:
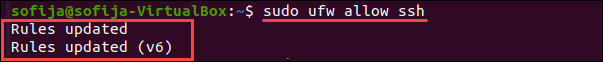
Порт SSH закрыт
Когда вы пытаетесь подключиться к удаленному серверу, SSH отправляет запрос на определенный порт. Чтобы принять этот запрос, на сервере должен быть открыт порт SSH.
Если порт закрыт, сервер отказывает в соединении.
По умолчанию SSH использует порт 22. Если вы не вносили никаких изменений в конфигурацию порта, вы можете проверить, прослушивает ли сервер входящие запросы.
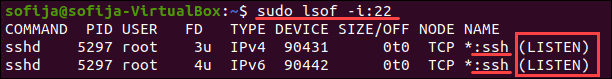
Чтобы вывести список всех прослушивающих портов, запустите:
Найдите порт 22 в выходных данных и проверьте, установлено ли для него STATE значение LISTEN .
Кроме того, вы можете проверить, открыт ли конкретный порт, в данном случае порт 22:
Решение: откройте порт SSH
Чтобы разрешить порту 22 слушать запросы, используйте команду iptables :
Вы также можете открывать порты через графический интерфейс, изменив настройки брандмауэра.
Отладка и ведение журнала SSH
Чтобы проанализировать проблемы SSH в Linux, вы можете включить подробный режим или режим отладки. Когда вы включаете этот режим, SSH выдает отладочные сообщения, которые помогают устранять проблемы с подключением, конфигурацией и аутентификацией.
Существует три уровня детализации:
Поэтому вместо доступа к удаленному серверу с использованием синтаксиса ssh [server_ip] добавьте параметр -v и выполните:
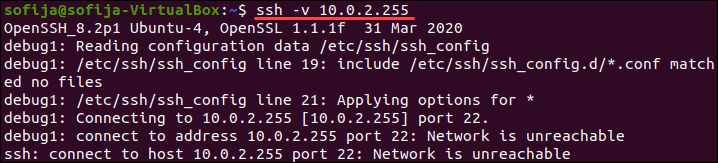
В качестве альтернативы вы можете использовать:
Бесплатный вводный урок на онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят начать карьеру администраторов Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг в DevOps
Полезно?
Почему?
😪 Мы тщательно прорабатываем каждый фидбек и отвечаем по итогам анализа. Напишите, пожалуйста, как мы сможем улучшить эту статью.
😍 Полезные IT – статьи от экспертов раз в неделю у вас в почте. Укажите свою дату рождения и мы не забудем поздравить вас.
Источник
CentOS
The Community ENTerprise Operating System
SSH Access from 2nd NIC — «Network Error: Connection Refused»
SSH Access from 2nd NIC — «Network Error: Connection Refused»
Post by Klio » 2012/05/24 18:13:47
Firstly I’m a Windows admin a few months into CentOS so excuse me if this is a simple issue.
I’ve got a server with 2 NIC on different ranges:
I can view web pages served by the server over both IP Addresses.
I can SSH into the server from the 192.168.100.x network to server address 192.168.100.245
I cannot SSH into the server from the 192.168.0.x network to the server address 192.168.0.245, I get the simple error: «Network Error: Connection Refused».
I’m using IP Tables and this is the result of iptables -L —line-numbers:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
num target prot opt source destination
1 RH-Firewall-1-INPUT all — anywhere anywhere
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
num target prot opt source destination
1 RH-Firewall-1-INPUT all — anywhere anywhere
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
num target prot opt source destination
Chain RH-Firewall-1-INPUT (2 references)
num target prot opt source destination
1 ACCEPT all — anywhere anywhere
2 ACCEPT icmp — anywhere anywhere icmp any
3 ACCEPT esp — anywhere anywhere
4 ACCEPT ah — anywhere anywhere
5 ACCEPT udp — anywhere 224.0.0.251 udp dpt:mdns
6 ACCEPT udp — anywhere anywhere udp dpt:ipp
7 ACCEPT tcp — anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ipp
8 ACCEPT all — anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
9 ACCEPT tcp — anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:smtp
10 ACCEPT tcp — anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:http
11 ACCEPT tcp — anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:https
12 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.100.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:netbios-ssn
13 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.100.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:microsoft-ds
14 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.100.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:mysql
15 ACCEPT tcp — cpc1-woki6-2-0-cust932.6-2.cable.virginmedia.com anywhere tcp spts:1024:65535 dpt:ssh state NEW
16 ACCEPT tcp — 188-39-44-176.static.enta.net/28 anywhere tcp spts:1024:65535 dpt:ssh state NEW
17 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.100.0/24 anywhere tcp spts:1024:65535 dpt:ssh state NEW
18 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:netbios-ssn
19 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:microsoft-ds
20 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:mysql
21 ACCEPT tcp — 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere tcp spts:1024:65535 dpt:ssh state NEW
22 REJECT all — anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
When I stop the iptables service and try again, PuTTY gives me the same error message.
I’ve added a test IP address into my hosts.allow file but that has not fixed the error.
I’ve checked /var/log/secure but can’t see any trace of the connection being attmpted.
I’m now at a loss of what to do, can anyone help? Happy to run tests if you give me commands to use.
Источник
Устранение неполадок SSH: проблемы с подключением к серверу
В первой статье этой серии вы узнали о том, как и в каких ситуациях вы можете попробовать исправить ошибки SSH. Остальные статьи расскажут, как определить и устранить ошибки:
- Ошибки протокола: в этой статье вы узнаете, что делать, если сбрасываются клиентские соединения, клиент жалуется на шифрование или возникают проблемы с неизвестным или измененным удаленным хостом.
- Ошибки аутентификации: поможет устранить проблемы с парольной аутентификацией или сбросом SSH-ключей.
- Ошибки оболочки: это руководство поможет исправить ошибки ветвления процессов, валидации оболочки и доступа к домашнему каталогу.
Для взаимодействия SSH-клиента с SSH-сервером необходимо установить базовое сетевое подключение. Это руководство поможет определить некоторые общие ошибки подключения, исправить их и предотвратить их возникновение в будущем.
Требования
- Убедитесь, что можете подключиться к виртуальному серверу через консоль.
- Проверьте панель на предмет текущих проблем, влияющих на работу и состояние сервера и гипервизора.
Основные ошибки
Разрешение имени хоста
Большинство ошибок подключения возникает тогда, когда ссылка на хост SSH не может быть сопоставлена с сетевым адресом. Это почти всегда связано с DNS, но первопричина часто бывает не связана с DNS.
На клиенте OpenSSH эта команда:
может выдать ошибку:
ssh: Could not resolve hostname example.com: Name or service not known
В PuTTY может появиться такая ошибка:
Unable to open connection to example.com Host does not exist
Чтобы устранить эту ошибку, можно попробовать следующее:
- Проверьте правильность написания имени хоста.
- Убедитесь, что вы можете разрешить имя хоста на клиентской машине с помощью команды ping. Обратитесь к сторонним сайтам (WhatsMyDns.net, например), чтобы подтвердить результаты.
Если у вас возникают проблемы с разрешением DNS на любом уровне, в качестве промежуточного решения можно использовать IP-адрес сервера, например:
ssh user@111.111.111.111
# вместо
ssh user@example.com.
Истечение времени соединения
Эта ошибка значит, что клиент попытался установить соединение с SSH-сервером, но сервер не смог ответить в течение заданного периода ожидания.
На клиенте OpenSSH следующая команда:
выдаст такую ошибку:
ssh: connect to host 111.111.111.111 port 22: Connection timed out
В PuTTY ошибка выглядит так:
Network error: Connection timed out
Чтобы исправить ошибку:
- Убедитесь, что IP-адрес хоста указан правильно.
- Убедитесь, что сеть поддерживает подключение через используемый порт SSH. Некоторые публичные сети могут блокировать порт 22 или пользовательские SSH-порты. Чтобы проверить работу порта, можно, например, попробовать подключиться к другим хостам через этот же порт. Это поможет вам определить, не связана ли проблема с самим сервером.
- Проверьте правила брандмауэра. Убедитесь, что политика по умолчанию – не DROP.
Отказ в соединении
Эта ошибка означает, что запрос передается на хост SSH, но хост не может успешно принять запрос.
На клиенте OpenSSH следующая команда выдаст ошибку:
ssh user@111.111.111.111
ssh: connect to host 111.111.111.111 port 22: Connection refused
В PuTTY ошибка появится в диалоговом окне:
Network error: Connection refused
Эта ошибка имеет общие с ошибкой Connection Timeout причины. Чтобы исправить её, можно сделать следующее:
- Убедиться, что IP-адрес хоста указан правильно.
- Убедиться, что сеть поддерживает подключение через используемый порт SSH. Некоторые публичные сети могут блокировать порт 22 или пользовательские SSH-порты. Чтобы проверить работу порта, можно, например, попробовать подключиться к другим хостам через этот же порт.
- Проверить правила брандмауэра. Убедитесь, что политика по умолчанию – не DROP, и что брандмауэр не блокирует этот порт.
- Убедиться, что сервис запущен и привязан к требуемому порту.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибок подключения
Брандмауэр
Иногда проблемы с подключением возникают из-за брандмауэра. Он может блокировать отдельные порты или сервисы.
В разных дистрибутивах используются разные брандмауэры. Вы должны научиться изменять правила и политики своего брандмауэра. В Ubuntu обычно используется UFW, в CentOS – FirewallD. Брандмауэр iptables используется независимо от системы.
Читайте также:
Чтобы настроить брандмауэр, нужно знать порт сервиса SSH. По умолчанию это порт 22.
Чтобы запросить список правил iptables, введите:
Такой вывод сообщает, что правил, блокирующих SSH, нет:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Если в выводе вы видите правило или политику по умолчанию REJECT или DROP, убедитесь, что цепочка INPUT разрешает доступ к порту SSH.
Чтобы запросить список правил FirewallD, введите:
Список, появившийся на экране, содержит все сервисы, которые поддерживаются брандмауэром. В списке должно быть правило:
dhcpv6-client http ssh
Если вы настроили пользовательский порт SSH, используйте опцию –list-ports. Если вы создали пользовательское определение сервиса, добавьте опцию –list-services, чтобы найти SSH.
Чтобы проверить состояние UFW, введите:
Команда вернёт доступные порты:
Status: active
To Action From
— —— —-
22 LIMIT Anywhere
443 ALLOW Anywhere
80 ALLOW Anywhere
Anywhere ALLOW 192.168.0.0
22 (v6) LIMIT Anywhere (v6)
443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
В списке должен быть порт SSH.
Проверка состояния сервиса SSH
Если вы не можете подключиться к серверу по SSH, убедитесь, что сервис SSH запущен. Способ сделать это зависит от операционной системы сервера. В более старых версиях дистрибутивов (Ubuntu 14.04, CentOS 6, Debian 
Метод проверки состояния сервиса может варьироваться от системы к системе. В более старых версиях (Ubuntu 14 и ниже, CentOS 6, Debian 6) используется команда service, поддерживаемая системой инициализации Upstart, а в более современных дистрибутивах для управления сервисом используется команда systemctl.
Примечание: В дистрибутивах Red Hat (CentOS и Fedora) сервис называется sshd, а в Debian и Ubuntu – ssh.
В более старых версия используйте команду:
service ssh status
Если процесс работает должным образом, вы увидите вывод, который содержит PID:
ssh start/running, process 1262
Если сервис не работает, вы увидите:
В системах на основе SystemD используйте:
systemctl status sshd
В выводе должна быть строка active:
sshd.service — OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2017-03-20 11:00:22 EDT; 1 months 1 days ago
Process: 899 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd-keygen (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 906 (sshd)
CGroup: /system.slice/sshd.service
├─ 906 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
├─26941 sshd: [accepted] └─26942 sshd: [net]
Если сервис не работает, вы увидите в выводе inactive:
sshd.service — OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2017-04-21 08:36:13 EDT; 2s ago
Process: 906 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 899 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd-keygen (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 906 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Чтобы перезапустить сервис, введите соответственно:
service ssh start
systemctl start sshd
Проверка порта SSH
Существует два основных способа проверить порт SSH: проверить конфигурационный файл SSH или просмотреть запущенный процесс.
Как правило, конфигурационный файл SSH хранится в /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Стандартный порт 22 может переопределяться любой строкой в этом файле, определяющей директиву Port.
Запустите поиск по файлу с помощью команды:
grep Port /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Если вы уже убедились, что сервис работает, теперь вы можете узнать, работает ли он на требуемом порте. Для этого используйте команду ss. Команда netstat –plnt выдаст аналогичный результат, но команду ss рекомендуется использовать для запроса информации сокета из ядра.
В выводе должно быть указано имя программы и порт, который она прослушивает. Например, следующий вывод сообщает, что сервис SSH прослушивает все интерфейсы и порт 22.
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:((«sshd»,pid=1493,fd=3))
LISTEN 0 128 . 22 . * users:((«sshd»,pid=1493,fd=4))
Символ * и 0.0.0.0 указывает, что все интерфейсы сервера прослушиваются. Строка 127.0.0.1 значит, что сервис не является общедоступным. В sshd_config директива ListenAddress должна быть закомментирована, чтобы прослушивать все интерфейсы, или должна содержать внешний IP-адрес сервера.
Если у вас не получается самостоятельно настроить соединение SSH, вы можете обратиться за помощью к службе поддержки своего хостинг-провайдера.
Источник
by Tashreef Shareef
Tashreef Shareef is a software developer turned tech writer. He discovered his interest in technology after reading a tech magazine accidentally. Now he writes about everything tech from… read more
Updated on December 13, 2022
- Connecting to a remote server for file transfers can be accomplished using a software like PuTTY. It is a very old software that continues to be updated and works very well.
- If a network error show with Connection Refused message, make sure that the server is configured, check if the port used is the same as your setup or look at your firewall and make sure PuTTY is not blocked.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
This software will repair common computer errors, protect you from file loss, malware, hardware failure and optimize your PC for maximum performance. Fix PC issues and remove viruses now in 3 easy steps:
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
PuTTy is a free and open-source terminal application that allows the system administrator to log in to a remote server over SSH. This small yet highly stable application is also used to transfer files securely via SCP and SFTP.
If you work in IT or have your own set of servers that need to be connected, PuTTy is not an alien concept to you. However, what can be an alien concept is the Putty Fatal error.
The error “Network error: connection refused” is one of the common PuTTY related errors that you may face while working with Putty. The error pops up when you try to connect to a remote server for the first time or the 100th time.
I have had my fair share of problems with PuTTy, but most of the time the errors are caused by small but not so obvious issues.
If you are one of those trying to diagnose a connection refused error, this article will help you to resolve the error.
In this article, I have listed all the possible solutions to the PuTTy connection refused error. Make sure you try each one of them a try until the issue is resolved.
What causes Network error: Connection Refused errors?
The error can occur due to several reasons. Some of them are listed below.
- The users may encounter “Network error: connection refused” error:
- If the application tries to access the services not offered/supported by the server
- If the application tries to connect to a telnet server not supported by the server.
- If your router blocks the connection due to security reasons.
- If the server does not support the default port used by the system administrator on PuTTy.
These are some of the common reasons for network error: connection refused error in PuTTy. Below are some common solutions that you can try to fix the issue.
How can I fix Network Error: Connection Refused errors?
Fix 1: Contact the system/network administrator
If you are not a system administrator, it is a better idea to start by contacting your system administrator.
System Administrators may change some permissions in the router if they notice any unknown device trying to connect or for other security reasons from time to time.
If that’s the case, you can easily resolve the issue by contacting the system admin before trying to resolve the issue on your end. While you are at it, you can also tell him about how NetCrunch Tools could help with their daily tasks.
Fix 2: Check if SSH connection is enabled
Depending on the device you are trying to connect, the network error – connection refused error may appear if the device settings have SSH disabled.
For example, if you are using Raspberry Pi to connect through your PC, make sure the ssh is enabled in the configuration. Here is how to do it.
In Raspberry Pi, go to Configuration > Interfaces > ssh. Enable the service and try again.
The settings may change depending on the device you are using, but the end result should be a working network connection through PuTTy.
Fix 3: Check if your domain records points to the server
If you are working with a new server and a fresh domain, the error can occur due to an incorrect DNS server address in the domain settings. All the domain registrar allows you to point your domain to you any third-party hosting provider using the name server.
If you have only installed a server and did not change the name server, you might end up with a network error: connection refused error.
To fix the problem, log in to your domain name provider and check the name server settings to see if the name servers are pointing to your hosting provider.
Fix 4: Check for Blacklisted and Whitelisted IP Address in the server
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
For security reasons system administrator may allow connection from only computers with known IP address and that is already whitelisted in the configuration file.
If your ISP IP address has changed or if you are new to the job, you probably need to ask the network admin to make an exception.
The same can also happen if your IP address is blacklisted by the network admin accidentally.
So, check with your network admin for both scenarios and see if that can help you resolve the issue.
Fix 5: Disable Firewall
If you are using Windows, your anti-virus or the default Windows Security firewall and network protection feature may block incoming connections resulting in a connection refused error.
Try disabling the firewall temporarily to see if that can resolve the connection refused error. If it does, you may need to tweak the firewall setting to fix the error completely.
Disable Firewall in Windows Security
Disable Anti-virus Firewall
If you have a third-party anti-virus program running, you may also need to disable the firewall offered by the application. You can disable the firewall from the anti-virus settings option.
Try to connect using PuTTy now. If the connection goes through, you need to tweak Firewall settings to fix the problem.
Even so, having a compatible antivirus solution installed on your PC keeps you safe and protected all the time, without interfering with your tasks or activities.
Therefore, we strongly recommend choosing the best antivirus for your PC, even though right now as a temporary workaround you had to disable the Firewall and fix this issue. It is not recommendable to be vulnerable to dangerous attacks throughout the network.
Other Fixes
If none of the fixes worked for you, you can try to restart the SSH server or reboot the servers.
If your server was set up by someone else, the possibility is that they may have moved the default port as per their convenience. Contact and ask for the configuration nodes to get a better idea of the ports.
If you are using a fully managed server, contact support. If the issue is from the hosting provider’s end, the system administrator will fix the issue.
Last but not the least, start using other alternatives to Putty such as other SH terminals can help you in case you encounter an error that is specific to PuTTY.
Conclusion
The Putty Fatal error “Network error: connection refused error can occur due to several reasons and I have tried to list the most common problems and solutions for the same.
However, if the fixes listed in this article don’t work for you, you may ask in forums related to your device or OS on which the error is appearing.
Do let us know if any of the fixes worked for you or if you have a solution that is not listed in the article in the comments below.