Зачастую после установки SSL-сертификатов многие пользователи сталкиваются с ошибками, которые препятствуют корректной работе защищенного протокола HTTPS.
Предлагаем разобраться со способами устранения подобных ошибок.
Что такое SSL?
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) — это интернет-протокол для создания зашифрованного соединения между пользователем и сервером, который гарантирует безопасную передачу данных.
Когда пользователь заходит на сайт, браузер запрашивает у сервера информацию о наличии сертификата. Если сертификат установлен, сервер отвечает положительно и отправляет копию SSL-сертификата браузеру. Затем браузер проверяет сертификат, название которого должно совпадать с именем сайта, срок действия сертификата и наличие корневого сертификата, выданного центром сертификации.
Причины возникновения ошибок SSL-соединения
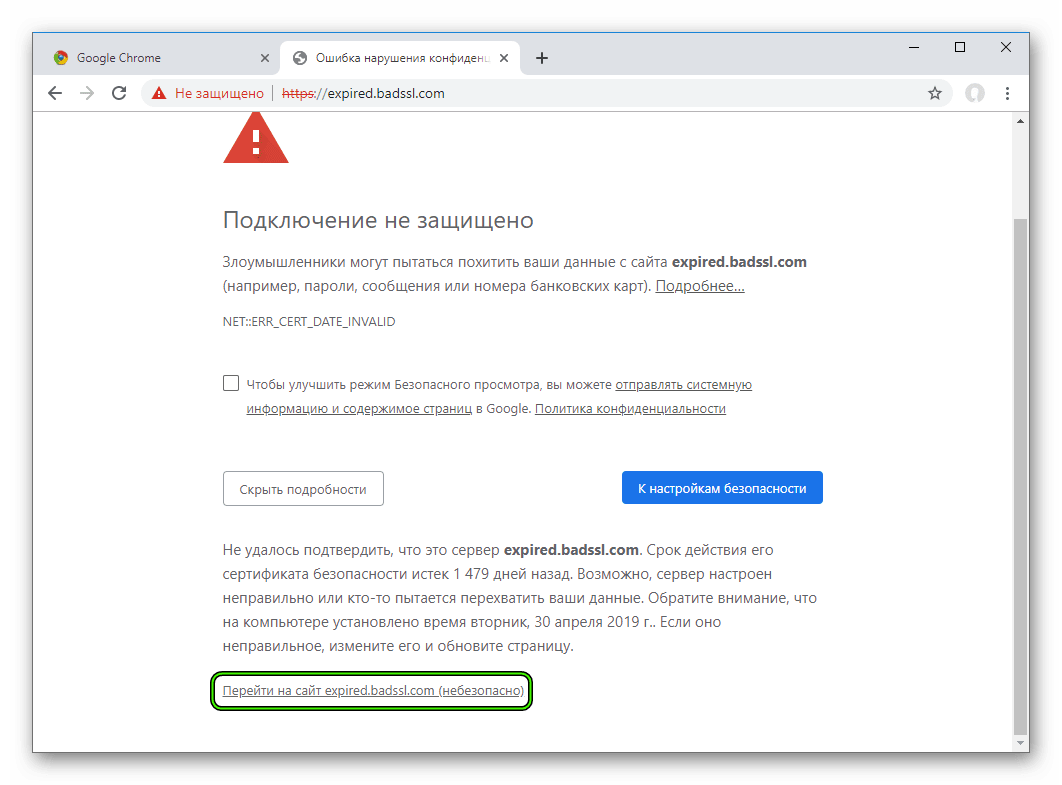
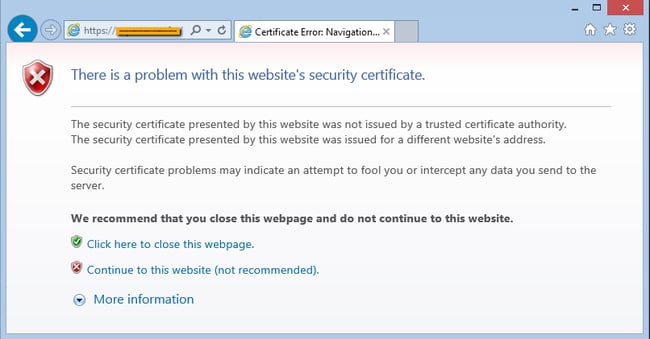
Когда сертификат работает корректно, адресная строка браузера выглядит примерно так:
Но при наличии ошибок она выглядит несколько иначе:
Существует множество причин возникновения таких ошибок. К числу основных можно отнести:
- Некорректную дату и время на устройстве (компьютер, смартфон, планшет и т.д.);
- Ненадежный SSL-сертификат;
- Брандмауэр или антивирус, блокирующие сайт;
- Включенный экспериментальный интернет-протокол QUIC;
- Отсутствие обновлений операционной системы;
- Использование SSL-сертификата устаревшей версии 3.0;
- Появление ошибки «Invalid CSR» при генерации сертификата из панели управления облачного провайдера.
Давайте рассмотрим каждую из них подробнее.
Проблемы с датой и временем
Если на устройстве установлены некорректные дата и время, ошибка SSL-соединения неизбежна, ведь при проверке сертификата происходит проверка срока его действия. Современные браузеры умеют определять такую ошибку самостоятельно и выводят сообщение о неправильно установленной дате или времени.
Для исправления этой ошибки достаточно установить на устройстве актуальное время. После этого необходимо перезагрузить страницу или браузер.
Ненадежный SSL-сертификат
Иногда при переходе на сайт, защищенный протоколом HTTPS, появляется ошибка «SSL-сертификат сайта не заслуживает доверия».
Одной из причин появления такой ошибки, как и в предыдущем случае, может стать неправильное время. Однако есть и вторая причина — браузеру не удается проверить цепочку доверия сертификата, потому что не хватает корневого сертификата. Для избавления от такой ошибки необходимо скачать специальный пакет GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority, содержащий корневые сертификаты. После скачивания переходим к установке. Для этого:
- Нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R и вводим команду certmgr.msc, жмем «Ок». В Windows откроется центр сертификатов.
- Раскрываем список «Доверенные корневые центры сертификации» слева, выбираем папку «Сертификаты», кликаем по ней правой кнопкой мышки и выбираем «Все задачи — импорт».
- Запустится мастер импорта сертификатов. Жмем «Далее».
- Нажимаем кнопку «Обзор» и указываем загруженный ранее сертификат. Нажимаем «Далее»:
- В следующем диалоговом окне указываем, что сертификаты необходимо поместить в доверенные корневые центры сертификации, и нажимаем «Далее». Импорт должен успешно завершиться.
После вышеперечисленных действий можно перезагрузить устройство и проверить отображение сайта в браузере.
Брандмауэр или антивирус, блокирующие сайт
Некоторые сайты блокируются брандмауэром Windows. Для проверки можно отключить брандмауэр и попробовать зайти на нужный сайт. Если SSL-сертификат начал работать корректно, значит дело в брандмауэре. В браузере Internet Explorer вы можете внести некорректно работающий сайт в список надежных и проблема исчезнет. Однако таким образом вы снизите безопасность своего устройства, так как содержимое сайта может быть небезопасным, а контроль сайта теперь отключен.
Также SSL может блокировать антивирусная программа. Попробуйте отключить в антивирусе проверку протоколов SSL и HTTPS и зайти на сайт. При необходимости добавьте сайт в список исключений антивируса.
Включенный экспериментальный протокол QUIC
QUIC — это новый экспериментальный протокол, который нужен для быстрого подключения к интернету. Основная задача протокола QUIC состоит в поддержке нескольких соединений. Вы можете отключить этот протокол в конфигурации вашего браузера.
Показываем как отключить QUIC на примере браузера Google Chrome:
- Откройте браузер и введите команду chrome://flags/#enable-quic;
- В появившемся окне будет выделен параметр: Experimental QUIC protocol (Экспериментальный протокол QUIC). Под названием этого параметра вы увидите выпадающее меню, в котором нужно выбрать опцию: Disable.
- После этого просто перезапустите браузер.
Этот способ работает и в Windows и в Mac OS.
Отсутствие обновлений операционной системы
Проблемы с SSL-сертификатами могут возникать и из-за того, что на вашей операционной системе давно не устанавливались обновлений. Особенно это касается устаревших версий Windows (7, Vista, XP и более ранние). Установите последние обновления и проверьте работу SSL.
Использование SSL-сертификата версии 3.0
Некоторые сайты используют устаревший SSL-протокол версии 3.0, который не поддерживают браузеры. По крайней мере, по умолчанию. Чтобы браузер поддерживал устаревший SSL необходимо сделать следующее (на примере браузера Google Chrome):
- Откройте браузер и перейдите в раздел «Настройки».
- Прокрутите страницу настроек вниз и нажмите «Дополнительные».
- В разделе «Система» найдите параметр «Настройки прокси-сервера» и кликните на него.
- Откроется окно. Перейдите на вкладку «Дополнительно».
- В этой вкладке вы увидите чекбокс «SSL 3.0».
- Поставьте галочку в чекбоксе, нажмите кнопку «Ок» и перезагрузите браузер.
Ошибки «Invalid CSR» при генерации сертификата из панели управления облачного провайдера
В процессе активации сертификата можно столкнуться с ошибкой «Invalid CSR». Такая ошибка возникает по следующим причинам:
- Неправильное имя FQDN (полное имя домена) в качестве Common Name (в некоторых панелях управления это поле может также называться Host Name или Domain Name). В этом поле должно быть указано полное доменное имя вида domain.com или subdomain.domain.com (для субдоменов). Имя домена указывается без https://. В качестве данного значения нельзя использовать интранет-имена (text.local). В запросе для wildcard-сертификатов доменное имя необходимо указывать как *.domain.com.
- В CSR или пароле есть не латинские буквы и цифры. В CSR поддерживаются только латинские буквы и цифры – спецсимволы использовать запрещено. Это правило распространяется и на пароли для пары CSR/RSA: они не должны содержать спецсимволов.
- Неверно указан код страны. Код страны должен быть двухбуквенным ISO 3166-1 кодом (к примеру, RU, US и т.д.). Он указывается в виде двух заглавных букв.
- В управляющей строке не хватает символов. CSR-запрос должен начинаться с управляющей строки ——BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST—— и заканчиваться управляющей строкой ——END CERTIFICATE REQUEST——. С каждой стороны этих строк должно быть по 5 дефисов.
- В конце или начале строки CSR есть пробелы. Пробелы на концах строк в CSR не допускаются.
- Длина ключа меньше 2048 бит. Длина ключа должна быть не менее 2048 бит.
- В CRS-коде для сертификата для одного доменного имени есть SAN-имя. В CSR-коде для сертификата, предназначенного защитить одно доменное имя, не должно быть SAN (Subject Alternative Names). SAN-имена указываются для мультидоменных (UCC) сертификатов.
- При перевыпуске или продлении сертификата изменилось поле Common Name. Это поле не должно меняться.
What do you think of a website that displays SSL/TLS certificate errors when you visit it? Most people abandon it in disappointment. A certain amount of trust and respect for the service is lost. After investing a lot of effort and time in getting users to visit your site, and the user finds the site down or shows a warning, it will result in having dissatisfied users.
Moreover, if the downtime or warning is due to a security issue, it will also hurt your brand image.
As we worked on improving the SSL certificate monitoring functionality in Sematext Synthetics, our synthetic monitoring solution, we learned a lot about how browsers and other clients handle SSL certificates and the errors caused by invalid certificates. So in this post, I will share a list of the most common SSL certificate errors that can cause the browser to block your website and tips on how to prevent or fix them. I will also show how to use Sematext Synthetics to monitor the SSL certificates of your website.
What Is an SSL/TLS Certificate?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a standard security protocol that enables encrypted communication between a client (web browser) and a server (webserver). Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the successor protocol to SSL.
SSL certificates are data files hosted by the server that makes SSL encryption possible. They contain the server’s public key and identity. The SSL certificates are digital certificates issued by a legitimate third-party Certificate Authority, confirming the identity of the certificate owner.
Whenever you visit a website whose URL starts with HTTPS, it means the server has SSL enabled. Before the web browser fetches the data from the server, it fetches the SSL certificates to verify the identity of the server.
Why Do You Need an SSL Certificate?
SSL helps to keep sensitive information like usernames, passwords, credit cards, etc. secure by encrypting the data between the client and the server. You need SSL for three reasons: privacy, integrity, and identification.
An SSL certificate helps a browser verify the identity of a website. By using the SSL certificates, the browser can ensure that it is connected to the exact website the user intended to. SSL certificates guarantee that you are the legitimate and verified owner of the website.
Needless to say, you should always stay on top of any SSL error messages you or your site visitors may receive errors concerning your website certificate.
What Is an SSL Certificate Error?
When the browser connects to your secure website, the webserver returns a list of SSL certificates to prove its identity. The browser performs various checks on these SSL certificates. Only when all the checks pass the browser will proceed to show the website to the user.
An SSL certificate error occurs when the browser cannot verify the SSL certificates returned by the server. When the error happens, the browser blocks the website and warns the user that the website cannot be trusted as shown below. These warnings will negatively impact the user’s trust in your website.
The exact checks and error messages shown to the user might vary depending on the browser.
SSL certificate errors can be caused by a variety of reasons. Here are the most common types of SSL errors and how to prevent or fix them:
1. Expired Certificate
This is the most common cause of SSL certificate errors. This error means that the validity period of the SSL certificate has expired. Every certificate has a validity period. The client will reject certificates that are not within its validity period. The validity periods are usually around one year long. So it is easy to forget to update the certificates before expiry.
The browser performs this check on all the certificates in your chain (leaf, intermediate, and root) for expiry. You should make sure both leaf and intermediate certificates are not expired.
This could also happen when the browser machine’s time is incorrect.
Fix: Update the SSL certificates of your web server with new valid certificates.
Tip: To prevent errors due to expired certificates, make sure you monitor the SSL certificate expiry date and renew the certificates before they expire. Use a certificate manager like AWS Certificate Manager or Let’s Encrypt to automatically update the certificates before expiry.
2. Inactive Certificate
The inactive certificate error occurs when the browser receives an SSL certificate whose validity period has not yet started. Nowadays it is common to use a certificate manager to manage the certificates for your server. The manager will automatically deploy the new certificates whose validity period starts at the time of deployment. If the client machine’s time is 5 minutes behind due to misconfiguration or other reasons, the client will reject the certificate. This is most common in the case of API clients when the client machine’s clock is not in sync.
Fix: Replace the SSL certificate with a new certificate with a valid start time. Make sure the client machine’s clock is in sync with the server.
Tip: To avoid deploying certificates that are not yet active, check the validity start time before deploying the certificate in the server. Also, when using a certificate manager to manage your certificate make sure you get notified about the certificate change along with the details of the new certificate.
3. Certificate lifetime greater than 398 days
Earlier this year, to ensure a secure web environment for the user, CA/B Forum, decided to limit the lifespan of all newly issued certificates to 398 days. Starting from September 1st, 2020, all the major browsers (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari) will reject certificates issued after this date with a validity period of more than 398 days.
Fix: Replace the certificate with a new certificate, whose validity is less than 398 days.
Tip: With a decreased lifetime of the certificates, you will have to replace the certificates more often. It is recommended to use a certificate manager to manage your certificates. Monitoring your certificate expiry time will help by alerting you before it occurs.
4. Missing Hostname
This error indicates that the hostname of the website is missing from the certificate. To prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, the browser checks if it is talking to the correct server. The browser checks the hostname of the website against the list of hostnames present in the leaf certificate. If there is no match, then the client will assume it is talking to the wrong server, will reject the certificate, and block the connection. The hostname details are present in commonName and subjectAltName (SAN) fields of the leaf certificate.
Fix: While reusing a certificate across multiple websites or sub-domains, make sure the certificates cover the domain names of all the websites.
Tip: Use a wildcards certificate to cover all your subdomains or a SAN certificate to cover multiple hostnames.
5. Invalid/Incomplete Certificate Chain
The invalid or incomplete certificate chain error happens when the browser is not able to establish a valid chain of trust between the certificates of your browser and the list of trusted root certificates.
Every browser maintains a set of trusted root certificates. When the browser receives the certificates from the server, it starts chaining your website certificates until it reaches any of the trusted root certificates. It will try to establish an SSL Chain of Trust – an ordered list of certificates that permit the browser to certify that the website’s server and the certificate authority are trustworthy. If the browser is not able to establish the chain for your certificates, say for example due to missing intermediate certificates, it will reject the certificates.
Fix: Deploy and configure your webserver to return the leaf certificate and all intermediate certificates.
Tip: To prevent certificate chain error due to missing intermediate certificates, always deploy the leaf and all the intermediate certificates in your server.
6. Revoked Certificate
This error happens when any of the leaf or intermediate certificates of your website is revoked and present in the revoked certificates list.
The certificate authority will revoke certificates that are compromised before their expiry. The Certificate Authority maintains a list of revoked certificates in the Certificate Revocation List (CRL). While loading the website, the browser checks if any of the certificates in the chain is present in CRL. If any of the certificates in your chain is present in CRL, the browser will reject your certificates. Each browser has a different mechanism to verify the revocation status of the certificates.
To check the revocation status of your certificates, you need to either periodically query the CRL or use Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to check for the certificate status. These mechanisms are difficult to implement.
Fix: Replace the revoked certificate with a new certificate. Also, investigate the reason for certificate revocation.
Tip: You can use SSL certificate monitoring tools like the Sematext Synthetics Browser monitor that uses a real Google Chrome browser to monitor your website. The browser checks the revocation status of your website certificates and alerts you when the certificate is present in the browser’s CRL.
This error means that the browser cannot find the root certificate in the local trusted certificate store. While establishing the SSL Chain of Trust if the browser cannot find any locally trusted root certificates, then it will not trust the server’s certificate. Using self-signed certificates will also cause this issue since the browser cannot trust them.
Fix: If you want to use a self-signed certificate for your website then manually add the certificate to the browser’s trust store.
Tip: To avoid this always ensure you buy your certificates from a reliable certificate authority. For example, at Sematext we used to get them from Digicert, and then we switched to AWS Certificate Manager. Digicert worked flawlessly for us, but we switched to AWS Certificate Manager. Given that we already use AWS this simplified our management by eliminating one extra vendor, plus it was completely free.
8. Insecure Signature Algorithm
The insecure SSL warning appears when any of the SSL certificates returned by your web server uses the old deprecated SHA-1 hashing algorithm.
The strength of the hashing function used to sign the certificate plays an important role in the strength of the certificate security. Some of the older certificates rely on the SHA-1 hashing function, which is now considered insecure. Modern browsers block websites with leaf and intermediate certificates that have the SHA-1 hashing signature.
Fix: SHA-1 certificates are no longer issued by certificate authorities. If you have any servers running with SHA-1 certificates it is recommended to get a new certificate.
9. Missing/Incorrect Certificate Transparency Information
Certificate Transparency is a mechanism that makes it possible to detect SSL certificates that have been mistakenly issued by a certificate authority or maliciously acquired from an otherwise unimpeachable certificate authority. It also makes it possible to identify certificate authorities that have gone rogue and are maliciously issuing certificates. The certificate authority updates the certificate transparency log whenever they issue a certificate.
When a client connects, the server responds with the certificates and the Signed Certificate Timestamp (SCT) for the certificate. SCT is the record for the certificate in the certificate transparency log. If SCT is missing, or incorrect, the browser will reject the certificate.
Tip: To prevent certificate transparency issues, make sure you buy the certificate from a reliable certificate authority.
Monitoring Your SSL Certificates
The best thing you can do to avoid SSL certificate issues is to monitor them.
We learned about all these SSL certificate errors while adding SSL certificate monitoring functionality to Sematext Synthetics, our synthetic monitoring solution that measures the functionality, availability, and performance of your APIs and websites. If you want to see how it compares to other similar services available on the market, check out our SSL monitoring tools comparison.
You can monitor the SSL certificates of your websites using the Sematext Synthetics Browser monitor. The Browser monitor performs the following SSL certificate checks on all the certificates in the chain – the leaf, intermediate, and root certificates.
- Certificate Validation – Check the validity of the SSL certificates of your websites. The monitor uses an actual Google Chrome browser to load your websites like your user. This will catch all the errors mentioned above and will alert you immediately before your end-user sees it.
- Certificate Expiry – Check the expiry time of the certificates every day and alert you 28, 14, 7, and 3 days before the expiry.
- Certificate Change – Check for certificate change every 10 minutes and alert you on detecting any changes, with a detailed change report.
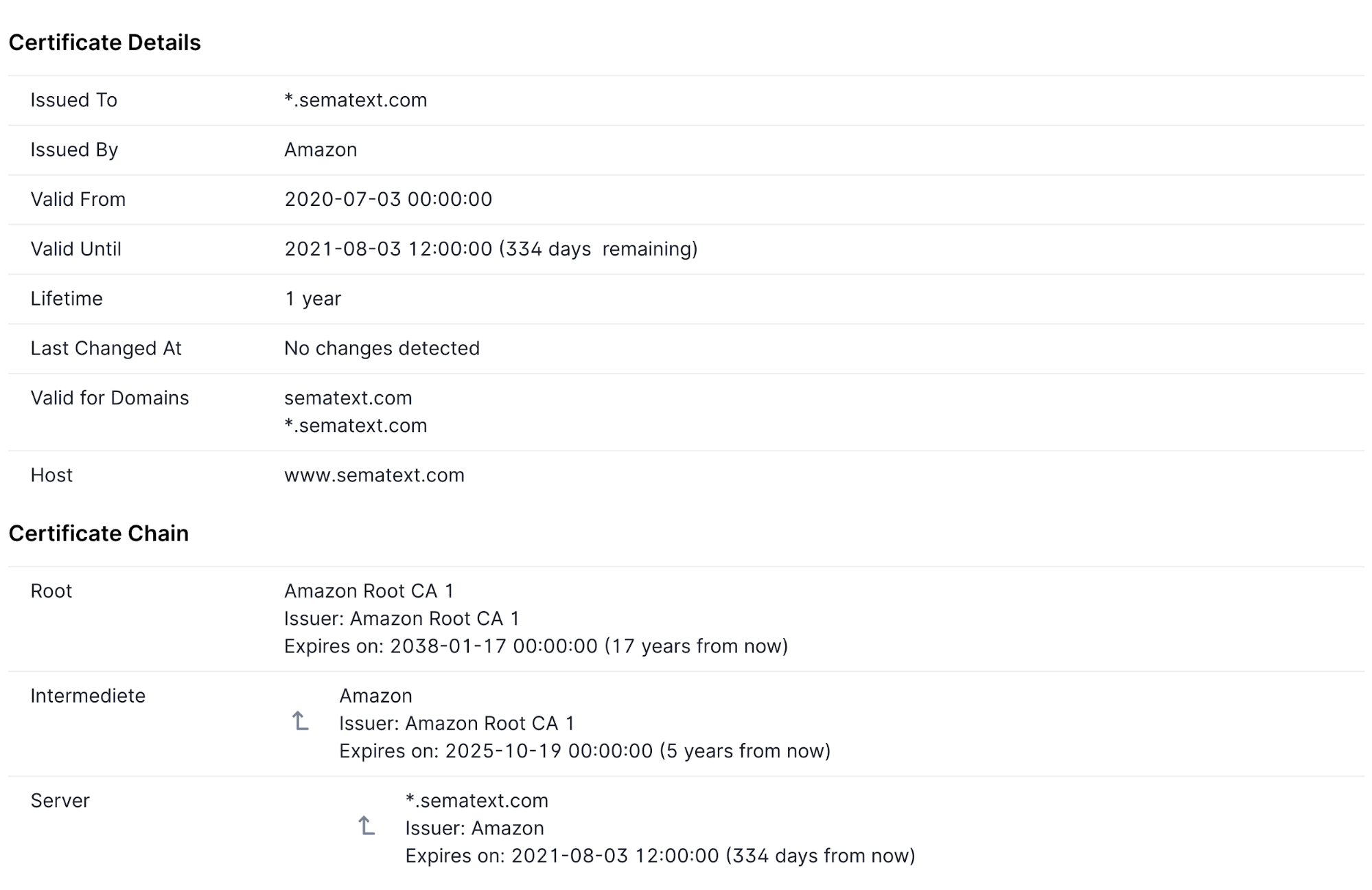
Synthetics also provides an SSL certificate report, with details of all the certificates in the chain, as seen below.
Sematext Synthetics alerts you via multiple channels like PageDuty, Telegram, Slack, Email, etc.
For more information on Sematext Synthetics SSL certificate monitoring capabilities, check out our SSL/TLS certificate monitoring documentation. Or, you can check out our short video on Synthetic Monitoring with Sematext below.
If you’re interested in improving the overall performance of your website and ensuring the absolute best experience for your users, we recommend you go beyond monitoring your SSL certificates and opt for a tool with multiple functionalities. Here are a few blog posts that we wrote to help you out:
- Best Website Performance Monitoring Tools
- Best Website Speed Testing Tools
- Best Website Uptime Monitoring Tools
- Best Synthetic Monitoring Tools
It’s never been easier to obtain a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate for your website and set it up. But you can still run into SSL connection errors even after installing your certificate correctly and forcing traffic through HTTPS. In many cases, these error messages can drive users away.
Understanding what causes SSL errors will help you prevent them from popping up on your website. You’ll also know what to do if you run into one, depending on the message you see and the browser or OS you’re using.
In this article, we’ll explore what SSL connection errors are and their leading causes. We’ll also discuss their most common types and how you can troubleshoot them.
Let’s get to it!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Fixing SSL Connection Errors
What Is an SSL Connection Error?
There are several types of SSL connection errors that you may encounter while browning the web. Some of these errors are due to server-side issues, whereas others are because of local configuration problems.
In broad terms, SSL connection errors will prevent you from browsing a website securely over Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). Your browser may allow you to proceed with the connection, but in most cases, it’ll tell you that you’re doing so at your own risk. Without a valid SSL certificate, malicious parties can intercept any data you exchange with the website you’re trying to view.
Some of the most common SSL connection errors that you may run into include:
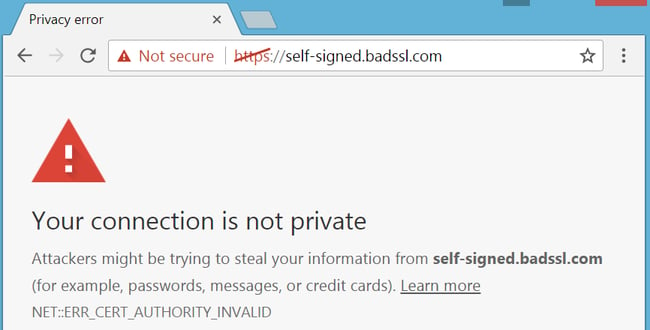
- NET:ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
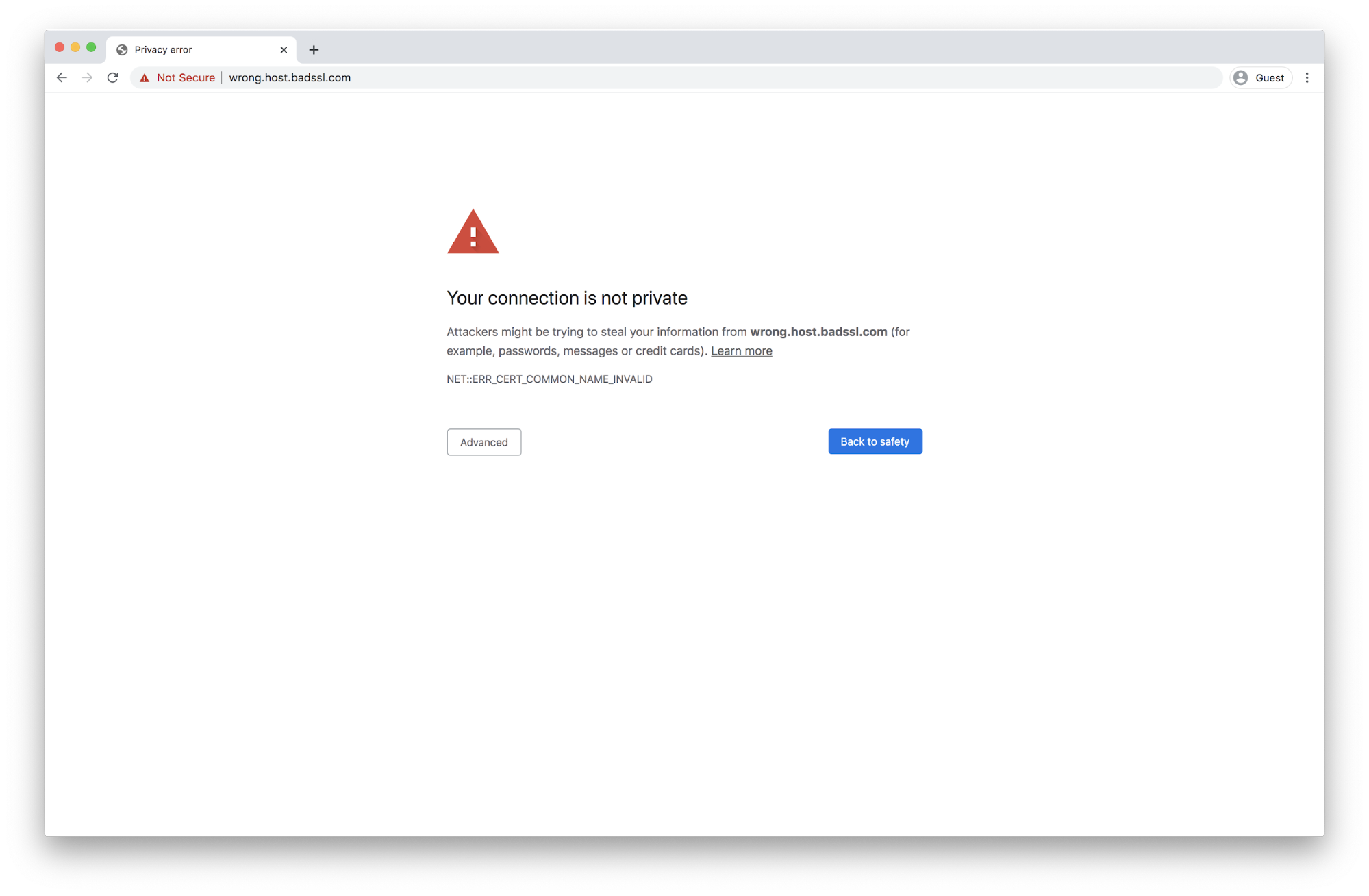
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_REVOKED
- SSL Handshake Failed
- ERR_SSL_OBSOLETE_VERSION
- ERR_SLL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
Each type of SSL connection error points towards a different cause. When you run into such a problem, your browser will display a specific message that gives you information about why you see it:
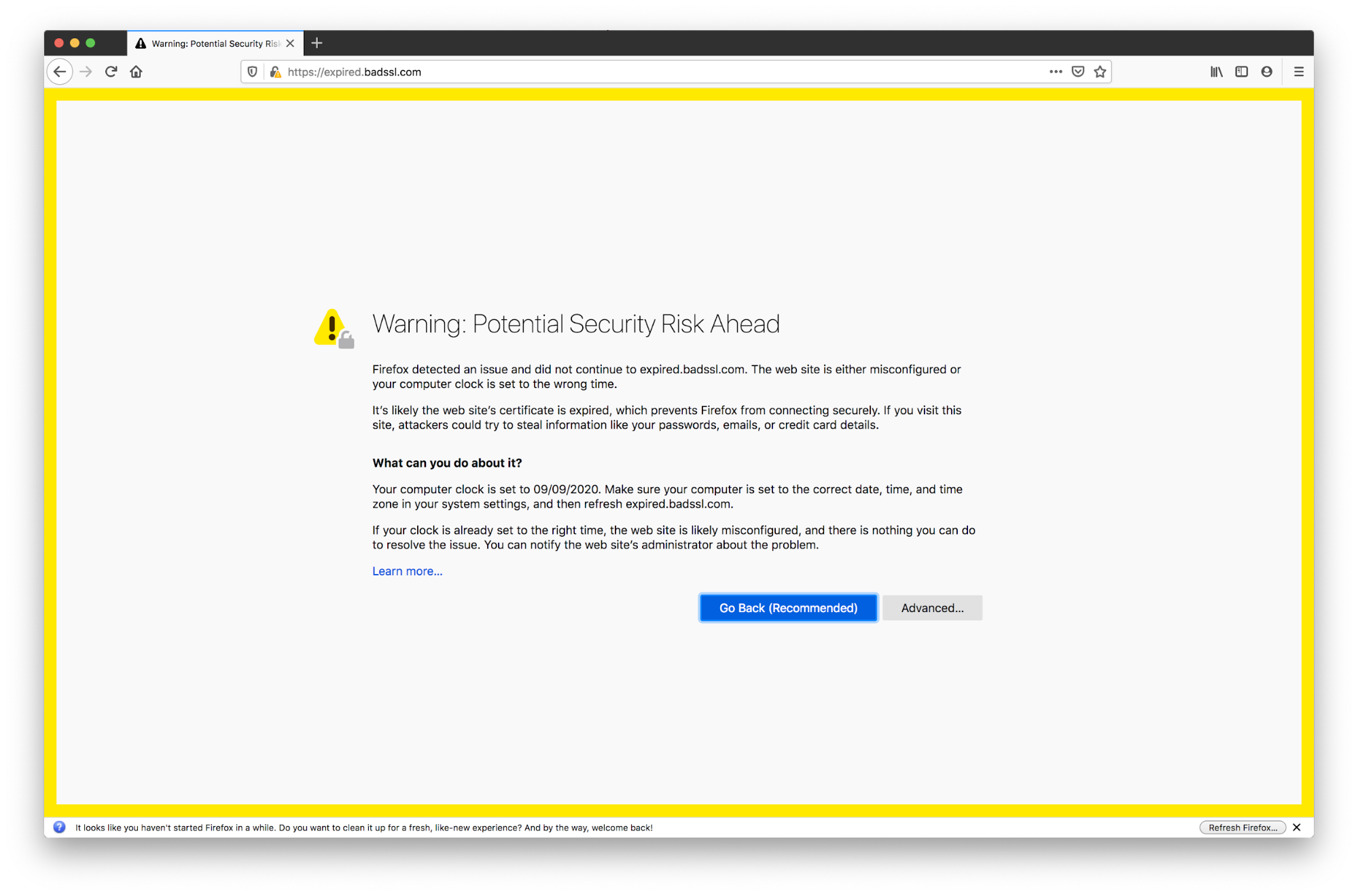
It’s important to note that error messages can vary from one browser to another. The one pictured above comes from Firefox, whereas the one below pops up when we open the same website using Chrome:
As mentioned before, not all SSL connection errors stem from problems with your server configuration. Your website can have a perfectly valid SSL certificate, but users might still run into errors when accessing it.
Throughout the following few sections, we’ll show you what to do if you’re trying to access a website and you run into SSL connection issues.
It’s never been easier to obtain an SSL certificate for your website and set it up… but errors can still occur. 😅 Learn how to fix them with this guide ⬇️Click to Tweet
How to Fix SSL Connection Errors (8 Methods)
If you’re not in charge of a website, there’s little that you can do when it comes to fixing server-side SSL connection errors. However, some issues can occur due to problems with your local device or browser configuration.
We’ll show you how to fix local issues that cause SSL connection errors using various browsers, mobile OSs, and social media platforms.
Let’s get fixing!
1. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Google Chrome
If you run into an SSL connection error in Google Chrome, there are several quick fixes that you can implement.
First off, make sure you’re running the latest version of Chrome. You can update Chrome from within the browser itself, or you can download and install the most recent version from Google Chrome’s website.
Next, check if your system’s time and date are synchronized. If your device’s time is not correct, you may run into SSL connection issues throughout the web because some SSL certificates rely on internal system clocks for validation. An incorrect time or date on your computer can lead to errors as your browser can’t verify these certificates.
On Windows, you can fix the time and date by opening the Settings menu and selecting the Time & Language option:
On the next screen, make sure that both the Set the time automatically and Set the time zone automatically options are enabled. Alternatively, you can select your time zone manually and enable the Set the date and time manually option:
If you’re using Chrome on macOS, open the System Preferences menu by clicking on the Apple icon in the top left corner of the screen. Select the Date & Time option and enable the Set date and time automatically setting:
Once you fix the date and time, try accessing the website that showed an SSL connection error in Chrome. If the problem persists, move on to clearing your Chrome cache and cookies. To do so, open the Settings menu and click on Clear browsing data.
A window will pop up, enabling you to select what data you want to clear. If you’re using the Basic settings, select Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files, then hit the Clear data button:
Another fix that you can try is to clear the SSL slate in your operating system. To do so in Windows, open the start menu and search for Internet Options. Click on the result that comes up, and an Internet Properties window will pop up. Jump to Content and click on Clear SSL slate:
Clearing the SSL slate will remove all of the certificates stored locally on your computer. The next time you reload the website giving you SSL connection errors, the browser will attempt to re-validate its certificate and, in doing so, might clear the error.
If you’re using macOS, clearing your SSL slate works a bit differently. Open your Utilities menu and go to Keychain Access. Select the System option under Keychains in the left-hand menu, and you’ll see an overview of all the SSL certificates that your system stores locally:
You can select certificates individually and delete them manually. If you spot a certificate for the website you’re trying to access, delete that one first, then check to see if the SSL connection error persists.
At this stage, if all else fails, temporarily disable your antivirus software and firewall. We suggest this as a last resort because, in most cases, your antivirus software won’t cause issues with SSL connections.
If you try every fix and nothing works, you can assume that the SSL connection problem lies with the server.
2. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Firefox
Fixing SSL connection errors in Firefox works much the same as with other browsers. You can follow the instructions in the last section to implement the following fixes:
- Check your system’s date and time and adjust them.
- Clear your local SSL slate.
If neither of those solutions works, then it’s time to clear your Firefox cookies and cache. To do so, go to the Options menu and jump to the Privacy & Security tab. Then click on the Clear Data button under Cookies and Site Data:
Try accessing the website with the SSL connection error once more. If your browser fails to establish a connection, check to see whether there’s a new version of Firefox that you can update.
3. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Safari
So far, we’ve covered multiple fixes for the SSL connection error that work across OSs. If you’re using Safari, start by following the same instructions given under the Google Chrome section:
- Check your system’s date and time and adjust them.
- Clear your local SSL slate in macOS.
If the SSL connection error persists, you can move forward and clear your Safari cookies and cache. If you’re using an iMac, Macbook, iPhone, or iPad, the exact instructions apply here:
- Open the Safari Settings menu.
- Click on Clear History.
With that out of the way, try to access the website that gave you an SSL connection error before. The error should be gone now unless you’re dealing with a server-side configuration issue.
4. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on iPhones and iPads
The process for fixing the SSL connection error on an iPhone or an iPad is identical to doing so on macOS. First, you need to check if your device’s date and time are synchronized. To access your mobile device’s date and time settings:
- Open the Settings app and select General > Date & Time.
- Check if the Set Automatically option is enabled. If it isn’t, turn it on.
- Manually check if your device is using the correct time zone.
After updating your date and time settings, you can move on to clearing your browser’s cookies and cache. To do so, open the Settings app and select Safari > Clear History and Website Data:
If you’ve installed a different browser on your iOS device, the process should still be similar.
Unfortunately, the most recent versions of iOS have removed the option to clear your SSL slate on your iPhone or iPad, so this is not a viable solution. If none of the fixes above work, you can assume the problem is server-side.
5. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Android
Fixing the SSL connection error on Android is relatively simple. First, go ahead and check your time and date settings to see if they’re accurate.
Open the Settings app and tap on General Management > Date and time. Then check if the Automatic date and time setting is enabled:
It’s important to note that, like iOS, Android doesn’t include an option for clearing your SSL slate or deleting individual certificates. What you can do to fix SSL connection errors is to clear your Chrome browsing data. To do so:
- Open the Chrome browser and access its Settings menu.
- Go to Privacy and security.
- Tap on Clear browsing data.
- Select your browser’s Cookies and site data and Cached images and files options, then tap on Clear data.
After clearing your Chrome website data, check if the SSL connection error persists. If it does, the chances are that it’s a server-side configuration issue.
6. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Facebook
If you run into an SSL connection error on Facebook, you can be sure that it’s not a server-side issue. That means you’re dealing with a local configuration problem. Here are the fixes that you should implement:
- Adjust your local time and date settings.
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates for Facebook.
You can find instructions about adjusting your date and time settings on Windows and macOS within the Google Chrome section of this article. We also have instructions on clearing your browser’s cookies and cache for Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
7. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Gmail
You won’t run into SSL connection errors while trying to access Gmail using mobile apps. However, SSL errors might pop up if you’re using Chrome, Firefox, or Safari to access Gmail’s web service. In that case, you should:
- Adjust your local time and date settings (check the Google Chrome section above for instructions).
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates for Gmail.
If everything else fails, you can access Gmail using a mobile app while you try disabling your firewall temporarily or updating your browser to its latest version.
8. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on YouTube
SSL connection errors on YouTube are likely due to local configuration errors within your OS or browser. If you run into an SSL error in YouTube:
- Adjust your local time and date settings (check the Google Chrome section above for instructions).
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates from YouTube.
We provided instructions on clearing your browser’s cache and cookies for Chrome, Firefox, and Safari earlier in this post. Likewise, you can find step-by-step guides on how to clear your SSL slate by checking the Chrome and Safari instructions in the previous sections.
Don’t let SSL errors bring you down 🙅♂️ Learn how to quickly troubleshoot them right here ✅Click to Tweet
Summary
SSL connection errors can come in a lot of shapes and sizes. If you’re dealing with a server-side error, there’s often little that you can do except wait for the site’s owner to fix it or proceed with an unsafe connection.
That said, you can attempt several local configuration fixes that may solve this issue, including:
- Adjusting your time and date settings.
- Clearing your browser’s cookies and cache.
- Clearing your OS’s SSL slate.
If you’re still facing SSL connection errors with your website, please leave a comment below. Kinsta clients can also reach out to our support team to get any SSL errors fixed.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
It’s never been easier to obtain a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate for your website and set it up. But you can still run into SSL connection errors even after installing your certificate correctly and forcing traffic through HTTPS. In many cases, these error messages can drive users away.
Understanding what causes SSL errors will help you prevent them from popping up on your website. You’ll also know what to do if you run into one, depending on the message you see and the browser or OS you’re using.
In this article, we’ll explore what SSL connection errors are and their leading causes. We’ll also discuss their most common types and how you can troubleshoot them.
Let’s get to it!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Fixing SSL Connection Errors
What Is an SSL Connection Error?
There are several types of SSL connection errors that you may encounter while browning the web. Some of these errors are due to server-side issues, whereas others are because of local configuration problems.
In broad terms, SSL connection errors will prevent you from browsing a website securely over Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). Your browser may allow you to proceed with the connection, but in most cases, it’ll tell you that you’re doing so at your own risk. Without a valid SSL certificate, malicious parties can intercept any data you exchange with the website you’re trying to view.
Some of the most common SSL connection errors that you may run into include:
- NET:ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_REVOKED
- SSL Handshake Failed
- ERR_SSL_OBSOLETE_VERSION
- ERR_SLL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
Each type of SSL connection error points towards a different cause. When you run into such a problem, your browser will display a specific message that gives you information about why you see it:
It’s important to note that error messages can vary from one browser to another. The one pictured above comes from Firefox, whereas the one below pops up when we open the same website using Chrome:
As mentioned before, not all SSL connection errors stem from problems with your server configuration. Your website can have a perfectly valid SSL certificate, but users might still run into errors when accessing it.
Throughout the following few sections, we’ll show you what to do if you’re trying to access a website and you run into SSL connection issues.
It’s never been easier to obtain an SSL certificate for your website and set it up… but errors can still occur. 😅 Learn how to fix them with this guide ⬇️Click to Tweet
How to Fix SSL Connection Errors (8 Methods)
If you’re not in charge of a website, there’s little that you can do when it comes to fixing server-side SSL connection errors. However, some issues can occur due to problems with your local device or browser configuration.
We’ll show you how to fix local issues that cause SSL connection errors using various browsers, mobile OSs, and social media platforms.
Let’s get fixing!
1. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Google Chrome
If you run into an SSL connection error in Google Chrome, there are several quick fixes that you can implement.
First off, make sure you’re running the latest version of Chrome. You can update Chrome from within the browser itself, or you can download and install the most recent version from Google Chrome’s website.
Next, check if your system’s time and date are synchronized. If your device’s time is not correct, you may run into SSL connection issues throughout the web because some SSL certificates rely on internal system clocks for validation. An incorrect time or date on your computer can lead to errors as your browser can’t verify these certificates.
On Windows, you can fix the time and date by opening the Settings menu and selecting the Time & Language option:
On the next screen, make sure that both the Set the time automatically and Set the time zone automatically options are enabled. Alternatively, you can select your time zone manually and enable the Set the date and time manually option:
If you’re using Chrome on macOS, open the System Preferences menu by clicking on the Apple icon in the top left corner of the screen. Select the Date & Time option and enable the Set date and time automatically setting:
Once you fix the date and time, try accessing the website that showed an SSL connection error in Chrome. If the problem persists, move on to clearing your Chrome cache and cookies. To do so, open the Settings menu and click on Clear browsing data.
A window will pop up, enabling you to select what data you want to clear. If you’re using the Basic settings, select Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files, then hit the Clear data button:
Another fix that you can try is to clear the SSL slate in your operating system. To do so in Windows, open the start menu and search for Internet Options. Click on the result that comes up, and an Internet Properties window will pop up. Jump to Content and click on Clear SSL slate:
Clearing the SSL slate will remove all of the certificates stored locally on your computer. The next time you reload the website giving you SSL connection errors, the browser will attempt to re-validate its certificate and, in doing so, might clear the error.
If you’re using macOS, clearing your SSL slate works a bit differently. Open your Utilities menu and go to Keychain Access. Select the System option under Keychains in the left-hand menu, and you’ll see an overview of all the SSL certificates that your system stores locally:
You can select certificates individually and delete them manually. If you spot a certificate for the website you’re trying to access, delete that one first, then check to see if the SSL connection error persists.
At this stage, if all else fails, temporarily disable your antivirus software and firewall. We suggest this as a last resort because, in most cases, your antivirus software won’t cause issues with SSL connections.
If you try every fix and nothing works, you can assume that the SSL connection problem lies with the server.
2. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Firefox
Fixing SSL connection errors in Firefox works much the same as with other browsers. You can follow the instructions in the last section to implement the following fixes:
- Check your system’s date and time and adjust them.
- Clear your local SSL slate.
If neither of those solutions works, then it’s time to clear your Firefox cookies and cache. To do so, go to the Options menu and jump to the Privacy & Security tab. Then click on the Clear Data button under Cookies and Site Data:
Try accessing the website with the SSL connection error once more. If your browser fails to establish a connection, check to see whether there’s a new version of Firefox that you can update.
3. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error in Safari
So far, we’ve covered multiple fixes for the SSL connection error that work across OSs. If you’re using Safari, start by following the same instructions given under the Google Chrome section:
- Check your system’s date and time and adjust them.
- Clear your local SSL slate in macOS.
If the SSL connection error persists, you can move forward and clear your Safari cookies and cache. If you’re using an iMac, Macbook, iPhone, or iPad, the exact instructions apply here:
- Open the Safari Settings menu.
- Click on Clear History.
With that out of the way, try to access the website that gave you an SSL connection error before. The error should be gone now unless you’re dealing with a server-side configuration issue.
4. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on iPhones and iPads
The process for fixing the SSL connection error on an iPhone or an iPad is identical to doing so on macOS. First, you need to check if your device’s date and time are synchronized. To access your mobile device’s date and time settings:
- Open the Settings app and select General > Date & Time.
- Check if the Set Automatically option is enabled. If it isn’t, turn it on.
- Manually check if your device is using the correct time zone.
After updating your date and time settings, you can move on to clearing your browser’s cookies and cache. To do so, open the Settings app and select Safari > Clear History and Website Data:
If you’ve installed a different browser on your iOS device, the process should still be similar.
Unfortunately, the most recent versions of iOS have removed the option to clear your SSL slate on your iPhone or iPad, so this is not a viable solution. If none of the fixes above work, you can assume the problem is server-side.
5. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Android
Fixing the SSL connection error on Android is relatively simple. First, go ahead and check your time and date settings to see if they’re accurate.
Open the Settings app and tap on General Management > Date and time. Then check if the Automatic date and time setting is enabled:
It’s important to note that, like iOS, Android doesn’t include an option for clearing your SSL slate or deleting individual certificates. What you can do to fix SSL connection errors is to clear your Chrome browsing data. To do so:
- Open the Chrome browser and access its Settings menu.
- Go to Privacy and security.
- Tap on Clear browsing data.
- Select your browser’s Cookies and site data and Cached images and files options, then tap on Clear data.
After clearing your Chrome website data, check if the SSL connection error persists. If it does, the chances are that it’s a server-side configuration issue.
6. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Facebook
If you run into an SSL connection error on Facebook, you can be sure that it’s not a server-side issue. That means you’re dealing with a local configuration problem. Here are the fixes that you should implement:
- Adjust your local time and date settings.
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates for Facebook.
You can find instructions about adjusting your date and time settings on Windows and macOS within the Google Chrome section of this article. We also have instructions on clearing your browser’s cookies and cache for Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
7. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on Gmail
You won’t run into SSL connection errors while trying to access Gmail using mobile apps. However, SSL errors might pop up if you’re using Chrome, Firefox, or Safari to access Gmail’s web service. In that case, you should:
- Adjust your local time and date settings (check the Google Chrome section above for instructions).
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates for Gmail.
If everything else fails, you can access Gmail using a mobile app while you try disabling your firewall temporarily or updating your browser to its latest version.
8. How to Fix the SSL Connection Error on YouTube
SSL connection errors on YouTube are likely due to local configuration errors within your OS or browser. If you run into an SSL error in YouTube:
- Adjust your local time and date settings (check the Google Chrome section above for instructions).
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Clear your OS’s SSL slate or delete any local certificates from YouTube.
We provided instructions on clearing your browser’s cache and cookies for Chrome, Firefox, and Safari earlier in this post. Likewise, you can find step-by-step guides on how to clear your SSL slate by checking the Chrome and Safari instructions in the previous sections.
Don’t let SSL errors bring you down 🙅♂️ Learn how to quickly troubleshoot them right here ✅Click to Tweet
Summary
SSL connection errors can come in a lot of shapes and sizes. If you’re dealing with a server-side error, there’s often little that you can do except wait for the site’s owner to fix it or proceed with an unsafe connection.
That said, you can attempt several local configuration fixes that may solve this issue, including:
- Adjusting your time and date settings.
- Clearing your browser’s cookies and cache.
- Clearing your OS’s SSL slate.
If you’re still facing SSL connection errors with your website, please leave a comment below. Kinsta clients can also reach out to our support team to get any SSL errors fixed.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Today there are over 170 million websites with an SSL certificate on the Internet — and this number is expected to increase as more search engines and consumers show preference to these sites.
An SSL certificate makes your site look more trustworthy. An SSL error does the opposite. And if customers no longer trust you, you can expect them to look to a competitor they can actually trust.
In this post, we’ll discuss what this error means and what could be causing it. Then we’ll walk through the different steps you can take to resolve the error and get your site up and running again. Or you can choose a CMS that includes an SSL certificate — like the Free CMS Hub does.
What is an SSL certificate error?
An SSL certificate error occurs when a web browser can’t verify the SSL certificate installed on a site. Rather than connect users to your website, the browser will display an error message, warning users that the site may be insecure.
An SSL certificate is a standard security technology for encrypting information between a visitor’s browser and your website. Because it helps keep sensitive information like passwords and payment information safe, visitors feel safer on sites that are encrypted with SSL. You can identify encrypted sites by the HTTPS in their URLs and the padlock icon in the address bar.
Sites that aren’t encrypted may see hits to their traffic or conversion rates. Not only are these sites flagged as “Not secure” in Google Chrome, they’re also avoided by 85% of online shoppers.
Thankfully, many hosted platforms like CMS Hub and Squarespace will include an SSL certificate in their plans, so you don’t have to worry about installing or renewing it.
If you opt for a self-hosted platform like WordPress.org, most hosting providers will include an SSL in their plans as well. HostGator, for example, includes an SSL certificate in its lowest-tiered plans. If your solution does not include SSL, then you can acquire one from an SSL certificate provider.
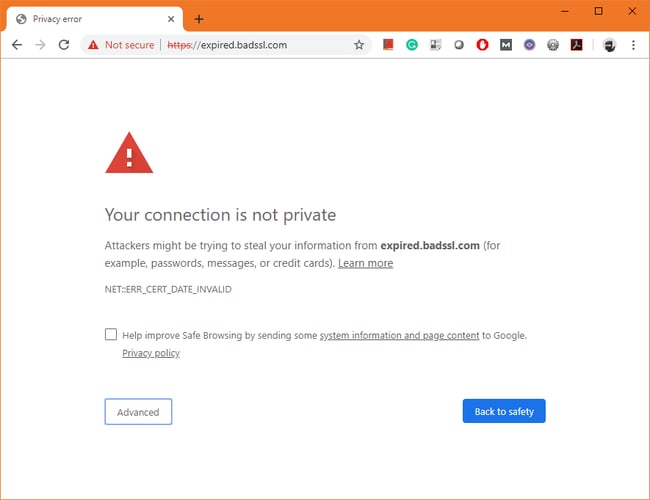
Let’s say you’ve chosen a plan that includes SSL certification or installed a certificate on your site. Then you open up Google Chrome and try to visit a page on your site and, instead of the page loading, you get an “ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR” message. What gives?
Image Source
This is an SSL error.
This message will look different depending on two factors. The first is the browser you’re using. The previous screenshot shows an error message on Google Chrome. The screenshot below is a message you’ll see on Internet Explorer.
Image Source
The second factor is the type of SSL Certificate error occurring. Let’s take a look at these different types below.
There are several different types of SSL certificate errors that might occur on your site. Let’s take a look at the most common ones.
1. SSL Certificate Not Trusted Error
This error indicates that the SSL certificate is signed or approved by a company that the browser does not trust. That means either the company, known as the certificate authority (CA), is not on the browser’s built-in list of trusted certificate providers or that the certificate was issued by the server itself. Certificates issued by the server are often referred to as self-signed certificates.
Image Source
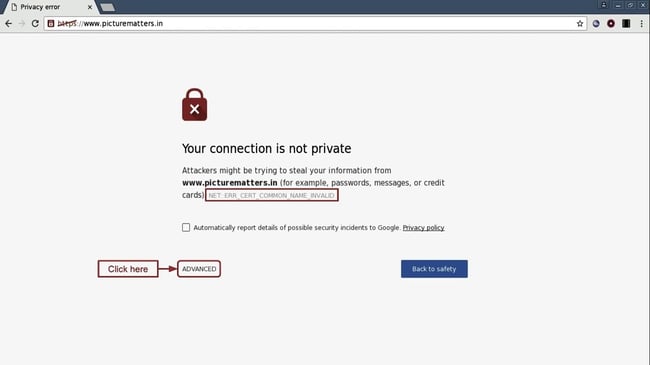
2. Name Mismatch Error
This error indicates that the domain name in the SSL certificate doesn’t match the URL that was typed into the browser. This message can be caused by something as simple as “www.” Say the certificate is registered for www.yoursite.com and you type in https://yoursite.com. Then you’ll get an SSL certificate name error.
Image Source
3. Mixed Content Error
This error indicates that a secure page (one that is loaded with HTTPS in the address bar) contains an element that’s being loaded from an insecure page (one that is loaded with HTTP in the address bar). Even if there’s only one insecure file on a page — often, an image, iframe, Flash animation, or snippet of JavaScript — your browser will display an error message instead of loading the page.
Image Source
4. Expired SSL Certificate Error
This error occurs when the site’s SSL certificate expires. According to industry standards, SSL certificates cannot have a lifespan longer than 398 days. That means that every website needs to renew or replace its SSL certificate at least once every two years.
Otherwise when you try to load your site, you’ll see an error that looks something like this:
Image Source
5. SSL Certificate Revoked Error
This error indicates that the CA has canceled or revoked the website’s SSL certificate. This could be because the website acquired the certificate with false credentials (whether by accident or on purpose), the key was compromised, or the wrong key was issued. These issues result in the following error message:
Image Source
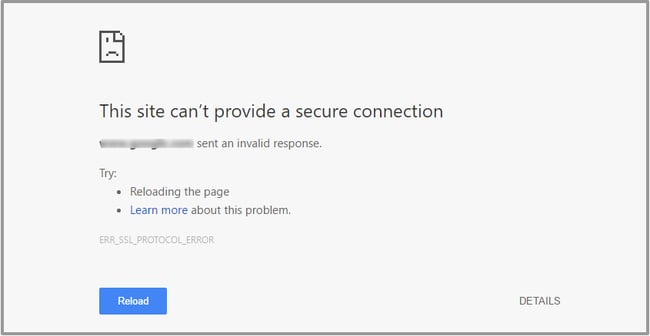
6. Generic SSL Protocol Error
This error is particularly tricky to resolve because there are multiple potential causes, including:
- an improperly formatted SSL certificate that the browser cannot parse.
- a certificate that is not properly installed on the server.
- a faulty, unverified, or lack of digital signature.
- the use of an outdated encryption algorithm.
- a firewall or other security software interfering with the SSL protection.
- a problem in the certificate’s chain of trust, the series of certifications that make up your site’s SSL encryption.
In these cases, you’ll see a generic SSL message like this one:
How to Fix SSL Certificate Error
- Diagnose the problem with an online tool.
- Install an intermediate certificate on your web server.
- Generate a new Certificate Signing Request.
- Upgrade to a dedicated IP address.
- Get a wildcard SSL certificate.
- Change all URLS to HTTPS.
- Renew your SSL certificate.
1. Diagnose the problem with an online tool.
2. Install an intermediate certificate on your web server.
If the problem is that your CA is not trusted, then you may need to install at least one intermediate certificate on your web server. Intermediate certificates help browsers establish that the website’s certificate was issued by a valid root certification authority.
Some web hosting providers, such as GoDaddy, offer information on installing intermediate certificates. So first, double-check that your web host offers the option or a tool to obtain an intermediate certificate.
If not, you’ll want to double-check your website’s server and find instructions for your server. Let’s say you installed an SSL certificate from the popular provider, Namecheap, on your Microsoft Windows Server. Then you can follow this step-by-step tutorial to install an intermediate certificate.
If you’re not on a Windows Server, you can find instructions for your server here.
3. Generate a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
If you’re still getting a certificate not trusted error, then you could have installed the certificate incorrectly. In that case, you can generate a new CSR from your server and reissue it from your certificate provider. Steps will vary depending on your server. You can check out this link hub for generating a CSR on different servers.
4. Upgrade to a dedicated IP address.
If you’re getting a name mismatch error, then the problem may be your IP address.
When you type your domain name into your browser, it first connects to your site’s IP address and then goes to your site. Usually, a website has its own IP address. But if you use a type of web hosting other than dedicated hosting, your site may be sharing an IP address with multiple sites. If one of those websites does not have an SSL certificate installed, then a browser might not know which site it’s supposed to visit and display a mismatch name error message. To resolve the issue, you can upgrade to a dedicated IP address for your site.
5. Get a wildcard SSL certificate.
If you’re still getting a name mismatch error, then you might need to get a wildcard SSL certificate. This type of certificate will allow you to secure multiple subdomain names as well as your root domain. For example, you could get one Multi-Domain SSL Certificate to cover all of the following names:
- mysite.com
- mail.mysite.com
- autodiscover.mysite.com
- blog.mysite.com
6. Change all URLS to HTTPS.
If you’re getting a mixed content error on one of your web pages, then copy and paste the URL into WhyNoPadLock.com to identify the insecure elements. Once you’ve identified the elements, edit the source code of the page and change the URLs of the insecure elements to HTTPS. Alternatively, you can take a look at the results and see if you need additional support from your web hosting provider.
7. Renew your SSL certificate.
If your SSL certificate is expired, you’ll have to renew it immediately. The details of the renewal process change depending on the web host or CA you’re using, but the steps remain the same. You’ll need to generate a CSR, activate your certificate, and install it.
Resolving an Invalid SSL Certificate
As we’ve seen, there are several possible explanations for an SSL certificate that doesn’t work. However, the end result is the same for your visitors — they’ll see a warning in their browser window explaining that the website they’re about to enter is not secure.
Of course, this is far from the best thing for your reputation, so be sure to address the lack of encryption as soon as possible. If the methods above don’t work, we recommend getting in touch with your hosting provider to help you troubleshoot. Chances are, they’ve seen problems like yours before.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in April 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Техническая оптимизация — основа основ в продвижении сайта. Если у вашего ресурса есть проблемы с безопасностью и защитой данных, вам будет очень сложно двигаться в ТОП выдачи.
Ранее мы писали о базовых правилах безопасности сайта и важности перехода на HTTPS. В этой статье мы расскажем о настройке SSL-/TLS-сертификата и типичных ошибках, которые могут навредить сайту.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) и TLS (Transport Layer Security) — стандартизированная технология шифрования, которая защищает передаваемые сайтом и сайту данные. Она напрямую связана с HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): если сайт использует HTTPS-подключение, это значит, что данные передаются по протоколу SSL или TLS.
SSL была представлена в 1995 году и обновлена до TLS в 1999-м — технология видоизменялась, реагируя на новые уязвимости. Протоколы постоянно обновляются и большинство их предыдущих версий считаются устаревшими. Важно следить за обновлениями и использовать самую актуальную версию SSL/TLS.
Как SSL/TLS влияет на продвижение
Для Google безопасность всегда среди главных приоритетов: поисковик учитывает наличие HTTPS при ранжировании с 2014 года и постоянно обновляет требования к SSL-/TLS-сертификатам.
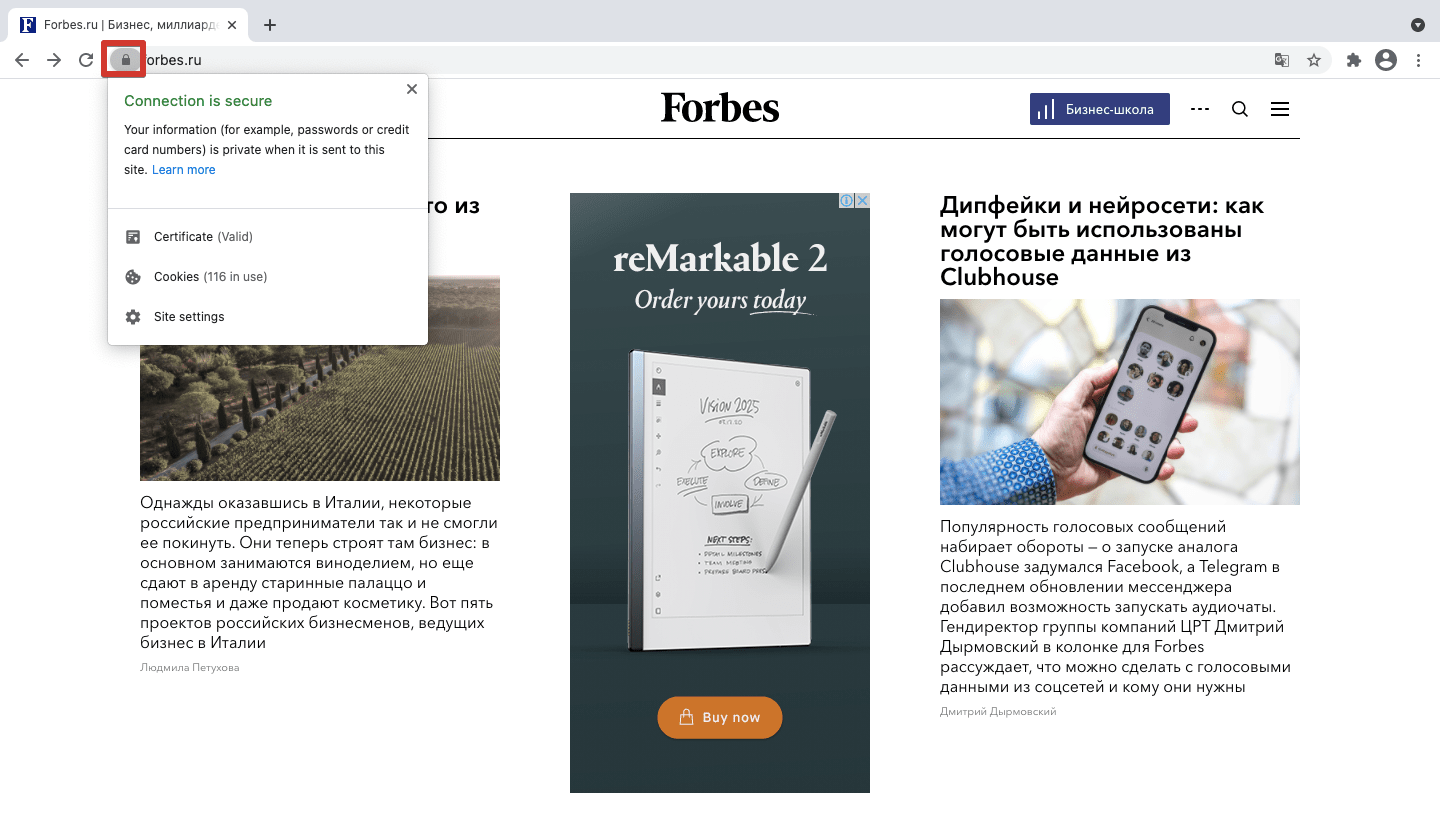
Большинство браузеров маркируют незащищенные страницы — проверить безопасность соединения можно по значку замка в адресной строке. Safari показывает этот значок, только если сайт использует адекватное шифрование; Firefox показывает перечеркнутый замок при недостаточном уровне защиты на сайтах, которые используют пользовательские данные; Chrome показывает красный треугольник при проблемах с безопасностью и значок замка при безопасном соединении.
Хоть преимущества технологии SSL/TLS довольно очевидны, многие сайты до сих пор не перешли на HTTPS или же используют недостаточно надежные версии протоколов. Статистика 2019 года говорит о том, что 20% крупнейших сайтов в мире не используют безопасный протокол, а по данным на начало 2020 года, только 18% доменных имен в зоне .ru используют узлы HTTPS.
Многие владельцы сайтов не хотят заморачиваться с покупкой и обновлением SSL-/TLS-сертификата или считают, что он им не нужен, если ресурс не собирает пользовательские данные. Но в современных реалиях ваш сайт будет попросту терять клиентов и позиции в поиске, если вы не перейдете на HTTPS и не будете следить за актуальностью шифрования. Для вашего удобства существует множество инструментов для настройки и мониторинга SSL-/TLS-сертификатов, в том числе бесплатные, как Let’s Encrypt.
Как исправлять типичные ошибки SSL/TLS
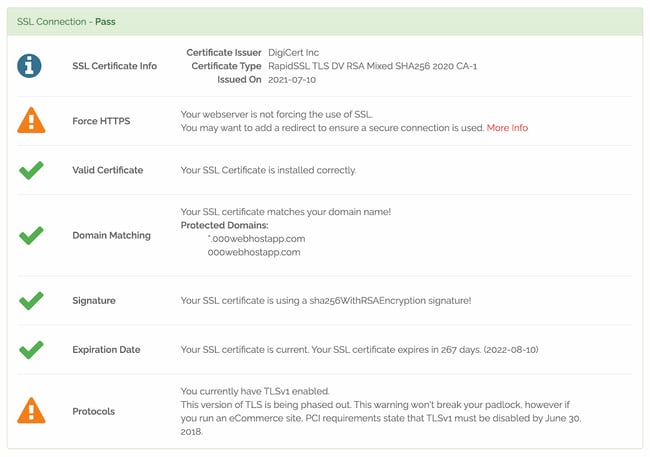
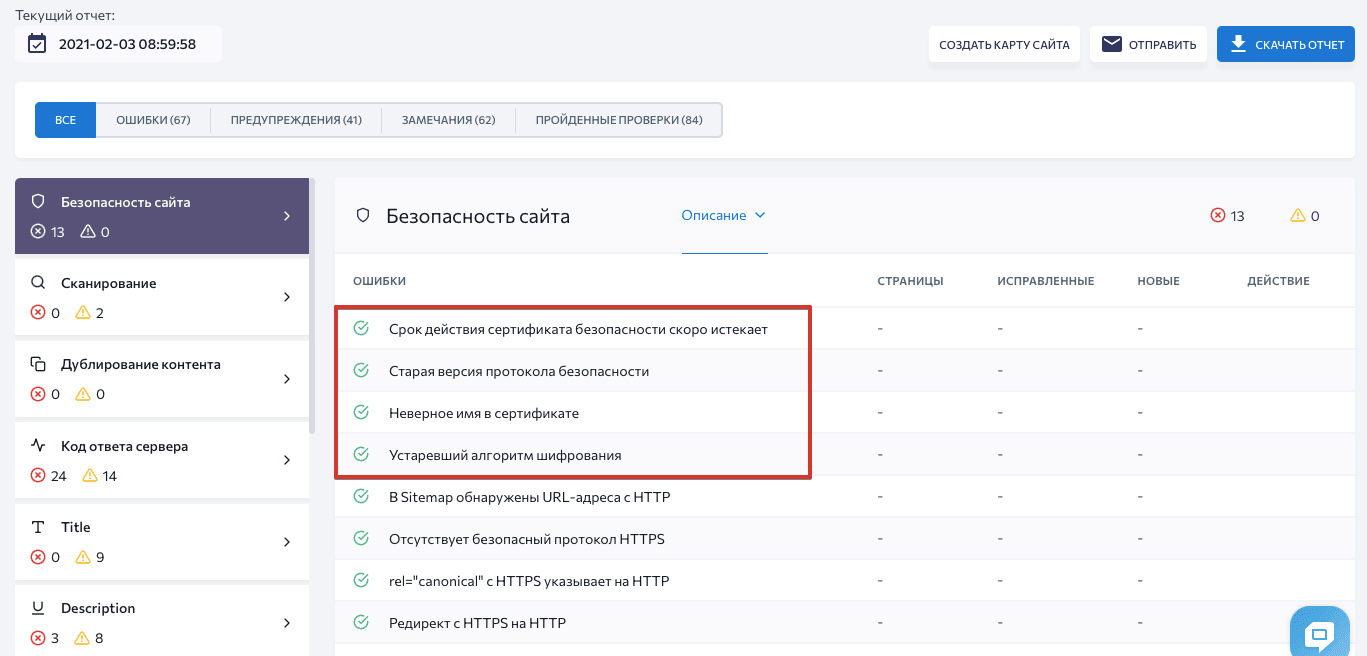
Если у вас уже есть SSL-/TLS-сертификат, он требует регулярного обновления и мониторинга. Чтобы избежать ошибок, проверяйте свой сайт на наличие проблем с SSL/TLS. Вы можете быстро обнаружить возможные ошибки с помощью «Аудита сайта» SE Ranking — для этого перейдите в раздел «Отчет об ошибках» и секцию «Безопасность сайта»:
Давайте рассмотрим 4 частые ошибки SSL-/TLS-сертификатов и объясним, как их исправить.
1. Недействительный сертификат
У сертификата безопасности есть определенный срок действия. Он постоянно уменьшался: до 5 лет в 2011-м, до 3 лет в 2015-м, до 2 лет в 2018-м. Сейчас сертификаты действительны только 398 дней (13 месяцев) — с 2020 года Safari, Chrome и Mozilla прекратили поддержку сертификатов с большим сроком действия.
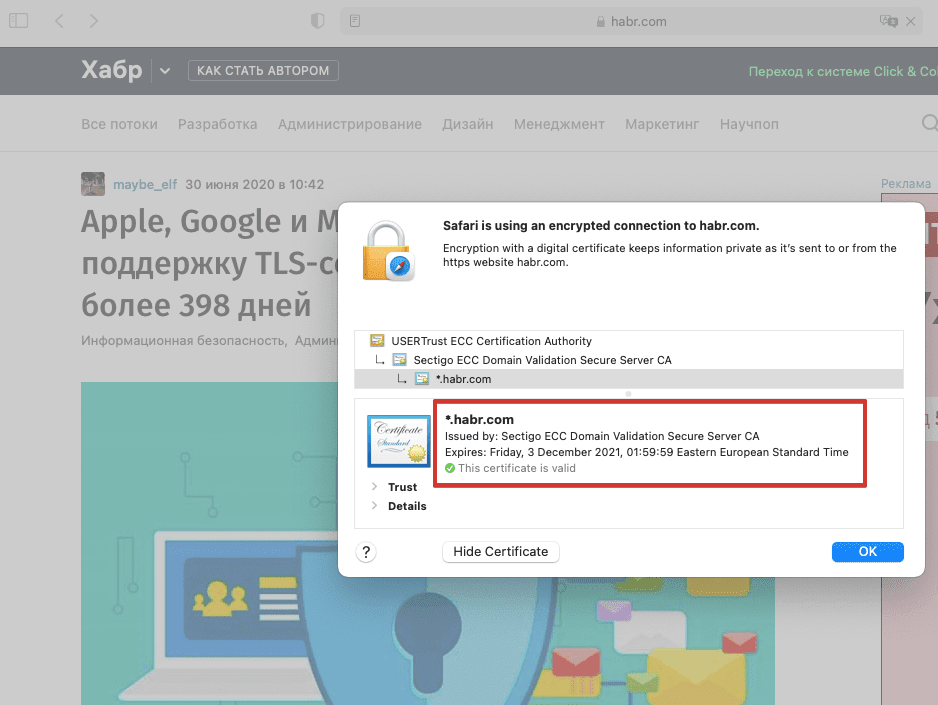
Информация о дате истечения действия сертификата доступна в браузере:
Что же происходит, если SSL-/TLS-сертификат устаревает? Сайт становится недоступен — пользователи увидят сообщение о небезопасности в браузере. Результат — существенные потери трафика и, соответственно, прибыли.
Поэтому стоит знать дату истечения действия сертификата и вовремя его обновлять. Помогут вам в этом автоматизированные решения типа Let’s Encrypt, AWS Certificate Manager. Также существуют инструменты, которые несколько раз оповещают вас перед окончанием срока действия сертификата. Иногда и вовсе ничего делать не нужно, ведь многие центры сертификации предлагают автоматическое обновление.
Если вы все же оказались в ситуации недействительного сертификата, нужно вручную его обновить или приобрести новый. Что именно нужно сделать:
- Выбрать тип сертификата. Большинство центров сертификации предлагает несколько вариантов, покрывающих потребности сайтов разного масштаба. Если вы только обновляете существующий сертификат и не хотите поменять его тип, этот шаг у вас уже выполнен (иногда логично переключиться на более мощный тип сертификата — например, приобрести Wildcard-сертификат, если у вашего сайта появились поддомены). Покупая новый сертификат, внимательно проверяйте авторитетность производителя. Вы можете настроить CAA-запись, чтобы ограничить круг удостоверяющих центров, имеющих право выпускать сертификаты для вашего домена. Среди самых популярных центров сертификации — GlobalSign, Digicert, Sectigo, Thawte.
- Сгенерировать запрос на получение сертификата. После покупки нужно сгенерировать CSR (certificate signing request) у хостинг-провайдера. В результате вы получите файл ключа и сам запрос для загрузки в настройках сертификата.
- Активировать и валидировать сертификат. Далее нужно подтвердить свои права на домен через email, CNAME-запись или подтверждающий файл. Как и в предыдущем процессе, особенности настройки зависят от выбранного провайдера.
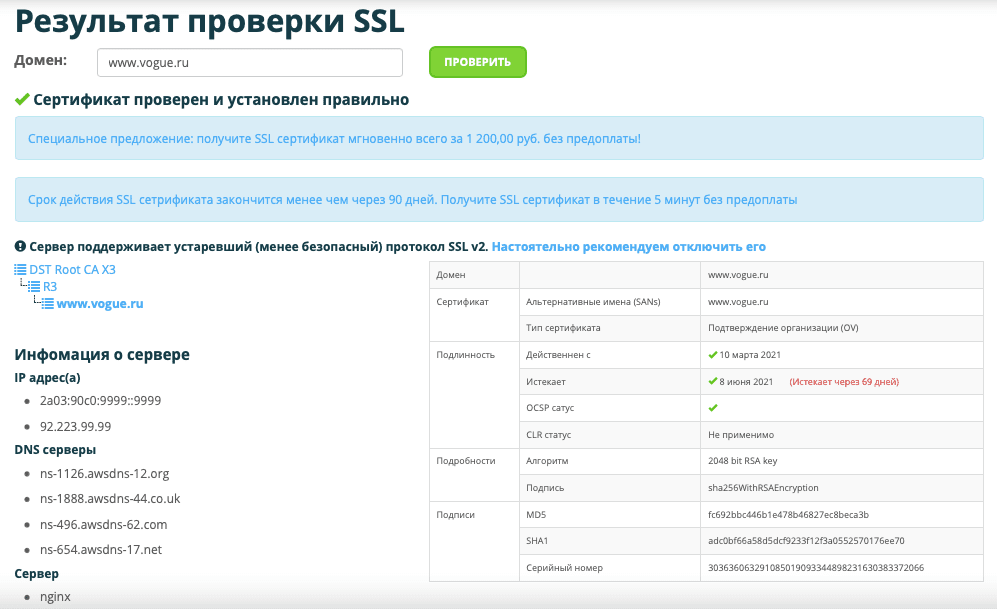
- Проверить корректность работы сертификата. После установки сертификата проверьте его с помощью онлайн-инструмента. Например:
Если это ваша первая покупка SSL-/TLS-сертификата, вам также следует добавить HTTPS-версию сайта в сервисы для вебмастеров и перенаправить на нее HTTP-трафик. Узнайте больше о правильном переезде на HTTPS из нашей статьи.
Рекомендуем использовать инструменты мониторинга и настраивать напоминания об окончании срока действия — так вам не придется разбираться с последствиями, если срок действия сертификата истечет.
2. Устаревшая версия протокола безопасности
Технологии шифрования совершенствуются, но и хакерские атаки становятся все изощреннее. Постоянно растущие риски — одна из причин сокращения срока действия SSL-/TLS-сертификатов и обновления протокола.
Протокол TLS был представлен как апгрейд SSL (версии 3.0 на тот момент), поэтому любая версия TLS более безопасна чем SSL. Самый актуальный протокол — TLS 1.3, выпущенный в 2018 году, — имеет усовершенствованный криптографический алгоритм и позволяет браузеру быстрее подсоединиться к серверу сайта. С 2020 года все основные браузеры не поддерживают устаревшие версии TLS (1.0 и 1.1), а значит не пускают пользователей на сайты, использующие эти версии.
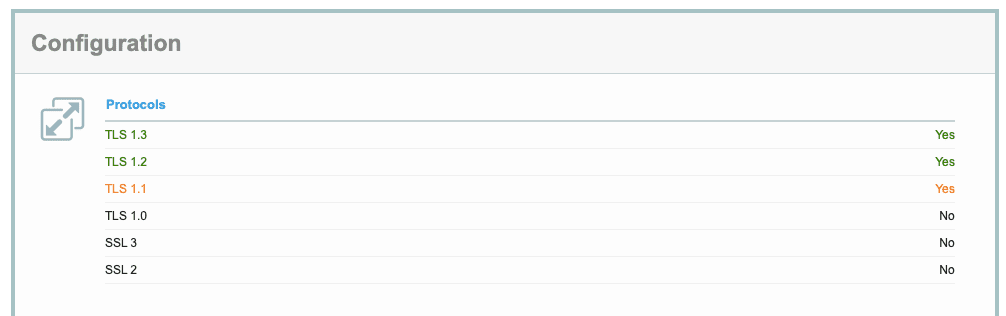
Важно использовать актуальную версию протокола безопасности и отключать все предыдущие версии. Существует несколько способов проверить, какой протокол у сайта:
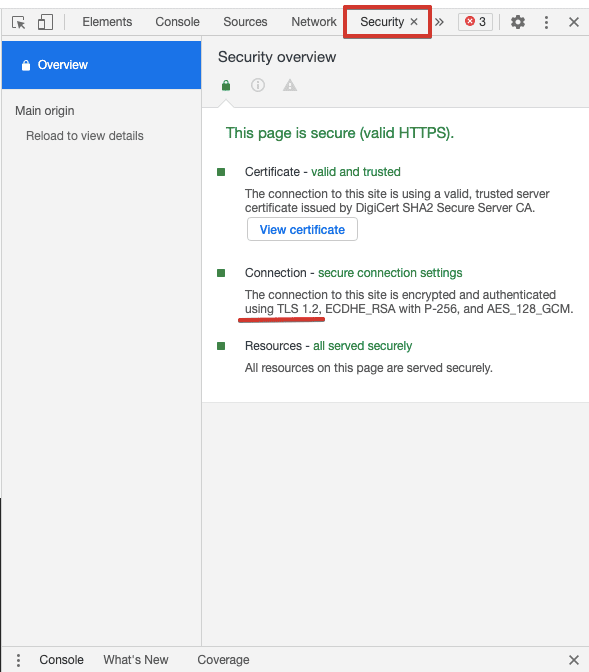
- Во вкладке Security в Chrome DevTools:
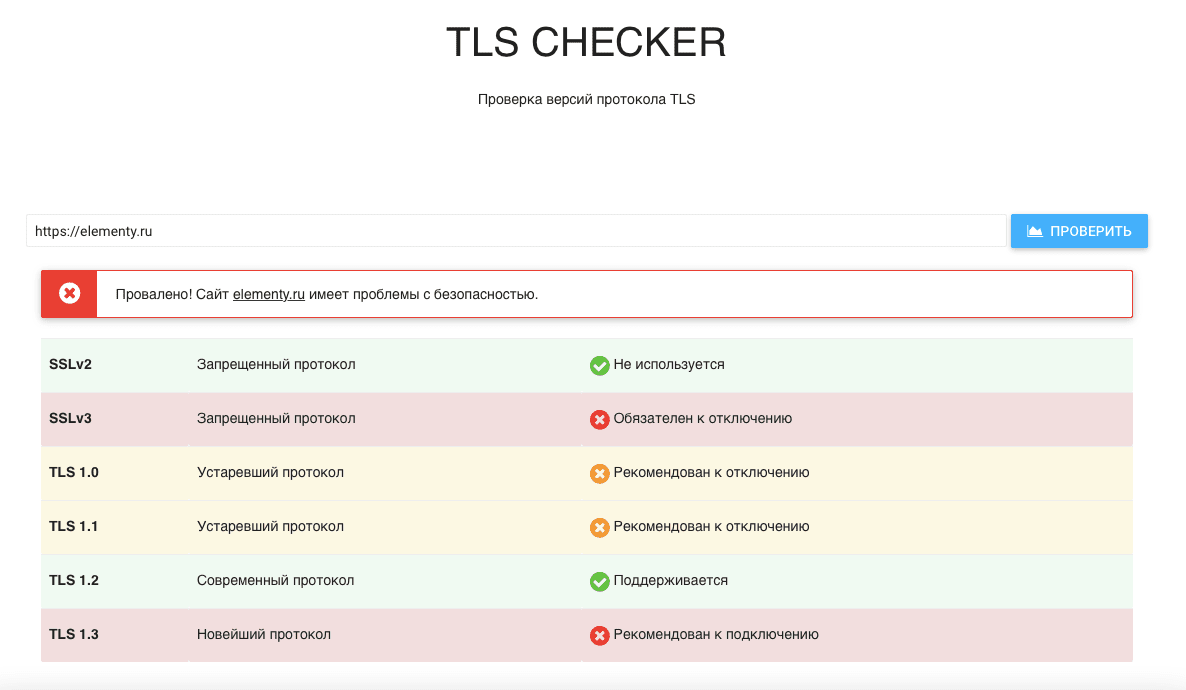
- В онлайн-инструментах, проверяющих, какие версии TLS и SSL включены на сайте. Например:
Чтобы включить последнюю версию TLS, прежде всего убедитесь, что ваш сайт поддерживает ее. Запустите серверную проверку — например, в SSL Labs — и просмотрите результаты конфигурации:
После этого свяжитесь со своим хостинг-провайдером, чтоб узнать, как именно подключить актуальную версию протокола. Вам нужно будет указать правильную версию в файле конфигураций сервера.
Скажем, ваш сайт размещен на сервере Nginx. Вам нужно отредактировать файл nginx.conf, указав в нем установленную версию TLS. Также удалите из файла все ранее используемые версии, которые признаны устаревшими. Строка конфигурации будет выглядеть так:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
Если же окажется, что ваш сайт не поддерживает TLS 1.2 или 1.3, стоит обратиться к провайдеру и по возможности сменить тариф (или провайдера).
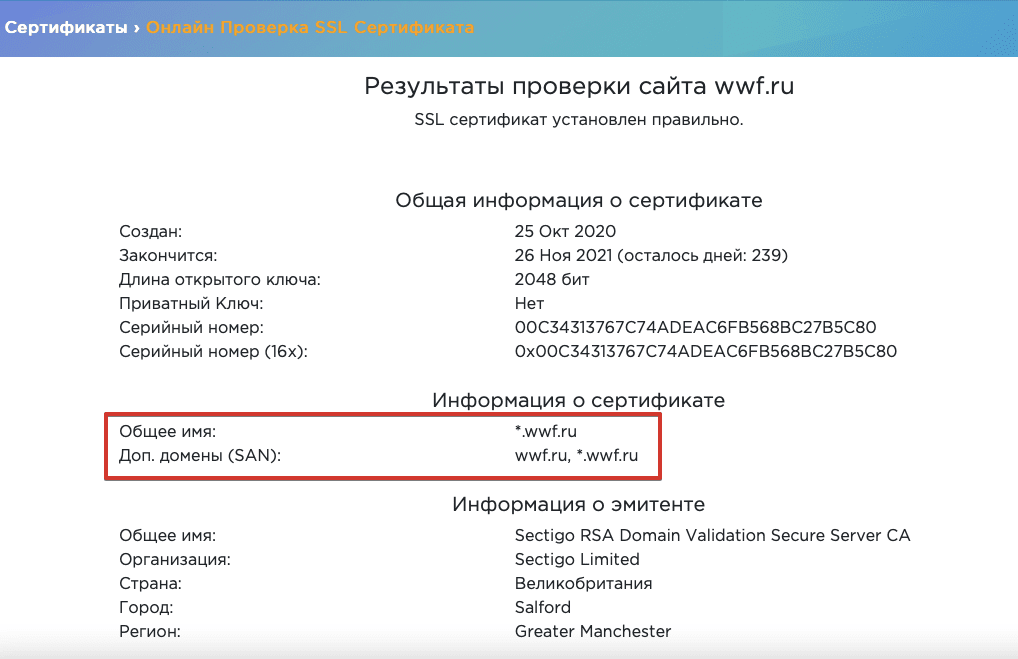
3. Несоответствие имени сертификата
Ошибка неверного имени сертификата вызвана тем, что доменное имя, указанное в SSL-/TLS-сертификате, не соответствует введенному в адресной строке. Пользователи в таком случае не смогут зайти на сайт.
Причины несоответствия имени SSL-/TLS-сертификата:
- На сайт заходят через внутреннее доменное имя, не указанное в сертификате. Например, вы вводите в адресную строку vashsajt.localhost, тогда как ваш сертификат содержит только vashsajt.com. Вы можете решить эту проблему с помощью сертификата с альтернативным именем субъекта SAN — такой тип позволяет включать целый ряд имен хостов. Проверяйте наличие сертификатов SAN у разных удостоверяющих центров.
- Сайт доступен и с префиксом www, и без, тогда как в сертификате указана только одна версия. Вам нужно решить, хотите ли вы использовать www в доменном имени, перенаправить весь трафик сайта на соответствующую версию и указать ее в SSL-/TLS-сертификате. Мы детальнее разбираем этот вопрос в статье о префиксе www и его влиянии на SEO.
- Сайт делит IP-адрес с другими и не имеет отдельного протокола. Для большинства сайтов необязателен отдельный IP-адрес, а использование совместного экономит бюджет. Если у вашего сайта общий IP, укажите доменное имя в расширении протокола SNI. С помощью SNI сервер будет выбирать уникальный для вашего имени хоста TLS-сертификат и соответствующий ключ. Без такого расширения сервер будет использовать шаблонный сертификат, общий для нескольких сайтов, и он может быть слабее установленного вами протокола.
- Хостинг-провайдер сайта использует шаблонные настройки, которые предопределяют SSL/TLS для доменного имени. Чтобы решить эту проблему, нужно связаться с провайдером и узнать, как заменить их сертификат на ваш, или же поменять провайдера.
В онлайн-инструментах можно проверить, какие доменные имена включены в ваш SSL-/TLS-сертификат:
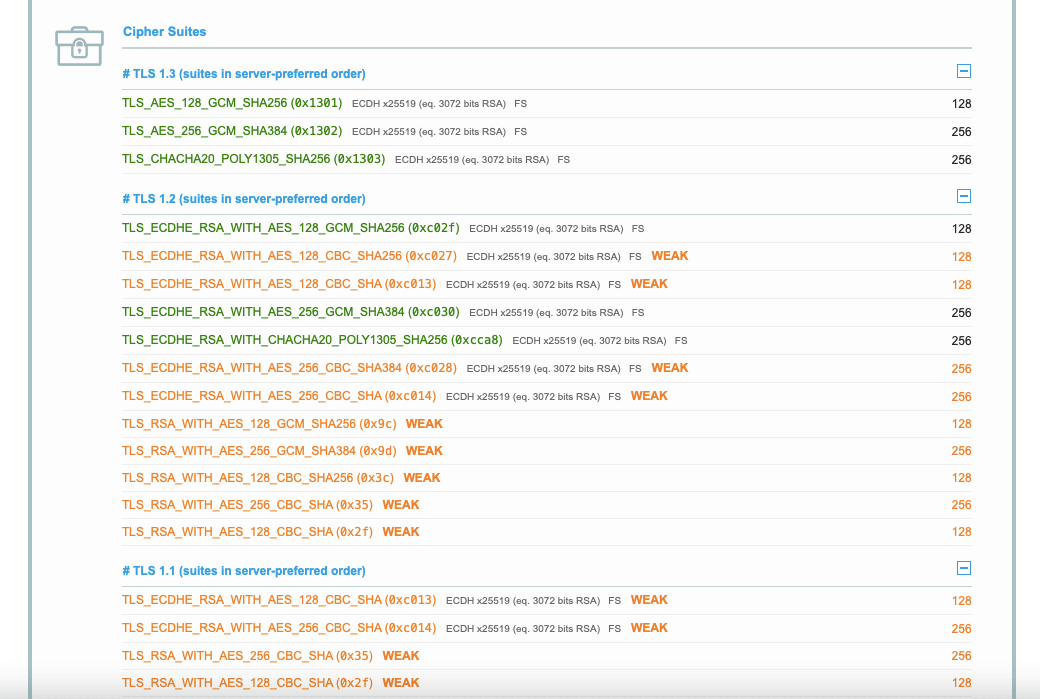
4. Устаревший алгоритм шифрования
Когда пользователь заходит на сайт, происходит процесс «рукопожатия»: клиент (браузер) и сервер идентифицируют друг друга, браузер при этом проверяет подлинность SSL-/TLS-сертификата. Набор алгоритмов шифрования очень важен для этого процесса: браузер сообщает, какие комбинации шифров он поддерживает, и сервер выбирает лучшую из подходящих. Если набор алгоритмов шифрования, используемый в конкретном сертификате, недостаточно надежный, браузер выдаст предупреждение об устаревшей криптографии.
Набор алгоритмов шифрования состоит из нескольких шифров, отвечающих за разные функции. Перед разработкой TLS 1.3 самой надежной была такая комбинация:
- Алгоритм для обмена ключами между сервером и браузером (ECDHE)
- Цифровая подпись, удостоверяющая сертификат (ECDSA)
- Шифр для обмена данными (AES-256-GCM)
- Алгоритм для аутентификации сообщений (SHA384)
Комбинация в TLS 1.3 содержит только два последних шифра и по умолчанию не поддерживает устаревшие алгоритмы для обмена ключами и аутентификации сертификата.
Версия TLS 1.2 до сих пор считается достаточно надежной, но у нее есть уязвимости из-за большей вариативности алгоритмов шифрования и их качества. С TLS 1.3 выбор шифров ограничен самыми безопасными и весь процесс «рукопожатия» происходит проще и быстрее.
Если вы не знаете, какие шифры поддерживаются вашим сертификатом, стоит проверить их актуальность. Можно запустить онлайн-тест:
Если вы обнаружите устаревшие алгоритмы, нужно отключить их в настройках сервера. Кроме того, можно проанализировать рейтинг шифров и указать приоритетный порядок, чтобы браузеры выбирали самый надежный из поддерживаемых в вашем сертификате.
Обеспечьте сайту бескомпромиссную защиту
Продвигать сайт без заботы о его безопасности не получится. Чтобы защитить свой сайт от кибератак и уязвимости данных, нужен надежный SSL-/TLS-сертификат с самыми актуальными настройками. Мы рекомендуем использовать последнюю версию TLS, поставить напоминания о дате истечения срока действия, подключить самые надежные алгоритмы шифрования и регулярно проверять состояние протокола.
Анастасия — контент-маркетолог и редактор в SE Ranking, пишет про SEO, маркетинг и цифровые технологии. Кроме текстов для блога SE Ranking, Анастасия пишет музыку, а также любит старые фильмы и свою собаку.



























.png?width=650&name=fix%20ssl%20certificate%20error%20(update).png)