In my Ruby on Rails application I tried to upload an image through the POSTMAN REST client in Base64 format. When I POST the image I am getting a 406 Not Acceptable Response. When I checked my database, the image was there and was successfully saved.
What is the reason for this error, is there anything I need to specify in my header?
My request:
URL — http://localhost:3000/exercises.json
Header:
Content-Type - application/json
Raw data:
{
"exercise": {
"subbodypart_ids": [
"1",
"2"
],
"name": "Exercise14"
},
"image_file_name": "Pressurebar Above.jpg",
"image":"******base64 Format*******"
}
ekad
14.3k26 gold badges44 silver badges45 bronze badges
asked Jan 10, 2013 at 6:13
1
406 Not Acceptable
The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities which have content characteristics not
acceptable according to the accept headers sent in the request.
406 happens when the server cannot respond with the accept-header specified in the request.
In your case it seems application/json for the response may not be acceptable to the server.
answered Jan 10, 2013 at 6:17
ashutosh rainaashutosh raina
9,16811 gold badges43 silver badges80 bronze badges
1
You mentioned you’re using Ruby on Rails as a backend. You didn’t post the code for the relevant method, but my guess is that it looks something like this:
def create
post = Post.create params[:post]
respond_to do |format|
format.json { render :json => post }
end
end
Change it to:
def create
post = Post.create params[:post])
render :json => post
end
And it will solve your problem. It worked for me 
answered Aug 3, 2014 at 8:41
itamaryuitamaryu
3263 silver badges5 bronze badges
«Sometimes» this can mean that the server had an internal error, and wanted to respond with an error message (ex: 500 with JSON payload) but since the request headers didn’t say it accepted JSON, it returns a 406 instead. Go figure. (in this case: spring boot webapp).
In which case, your operation did fail. But the failure message was obscured by another.
answered May 8, 2018 at 22:08
rogerdpackrogerdpack
60.5k35 gold badges260 silver badges379 bronze badges
You can also receive a 406 response when invalid cookies are stored or referenced in the browser — for example, when running a Rails server in Dev mode locally.
If you happened to run two different projects on the same port, the browser might reference a cookie from a different localhost session.
This has happened to me…tripped me up for a minute. Looking in browser > Developer Mode > Network showed it.
answered Jul 31, 2016 at 22:50
etusmetusm
3,9821 gold badge31 silver badges26 bronze badges
const request = require('request');
const headers = {
'Accept': '*/*',
'User-Agent': 'request',
};
const options = {
url: "https://example.com/users/6",
headers: headers
};
request.get(options, (error, response, body) => {
console.log(response.body);
});
answered Dec 9, 2016 at 19:56
JP VenturaJP Ventura
5,4465 gold badges51 silver badges69 bronze badges
1
Changing header to Accept: */* resolved my issue and make sure you don’t have any other Accept Header
answered Jun 6, 2022 at 12:11
Kunal TyagiKunal Tyagi
1,42313 silver badges23 bronze badges
0
In my case, I added:
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
solved my problem completely.
answered Aug 29, 2016 at 23:10
If you are using ‘request.js’ you might use the following:
var options = {
url: 'localhost',
method: 'GET',
headers:{
Accept: '*/*'
}
}
request(options, function (error, response, body) {
...
})
answered Jul 1, 2019 at 12:48
0
In my case for a API in .NET-Core, the api is set to work with XML (by default is set to response with JSON), so I add this annotation in my Controller :
[Produces("application/xml")]
public class MyController : ControllerBase {...}
Thank you for putting me on the path !
answered Sep 16, 2019 at 6:55
It could also be due to a firewall blocking the request. In my case the request payload contained string properties — «like %abc%» and ampersand symbol «&» — which caused the firewall to think it is a security risk (eg. a sql injection attack) and it blocked the request. Note here the request does not actually go to the server but is returned at the firewall level itself.
In my case, there were no application server logs generated so I knew that the request did not actually reach the server and was blocked before that. The logs that helped me were Web application firewall (WAF) logs.
answered Jul 8, 2022 at 11:58
singh_vsingh_v
741 silver badge12 bronze badges
In my Ruby on Rails application I tried to upload an image through the POSTMAN REST client in Base64 format. When I POST the image I am getting a 406 Not Acceptable Response. When I checked my database, the image was there and was successfully saved.
What is the reason for this error, is there anything I need to specify in my header?
My request:
URL — http://localhost:3000/exercises.json
Header:
Content-Type - application/json
Raw data:
{
"exercise": {
"subbodypart_ids": [
"1",
"2"
],
"name": "Exercise14"
},
"image_file_name": "Pressurebar Above.jpg",
"image":"******base64 Format*******"
}
ekad
14.3k26 gold badges44 silver badges45 bronze badges
asked Jan 10, 2013 at 6:13
1
406 Not Acceptable
The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities which have content characteristics not
acceptable according to the accept headers sent in the request.
406 happens when the server cannot respond with the accept-header specified in the request.
In your case it seems application/json for the response may not be acceptable to the server.
answered Jan 10, 2013 at 6:17
ashutosh rainaashutosh raina
9,16811 gold badges43 silver badges80 bronze badges
1
You mentioned you’re using Ruby on Rails as a backend. You didn’t post the code for the relevant method, but my guess is that it looks something like this:
def create
post = Post.create params[:post]
respond_to do |format|
format.json { render :json => post }
end
end
Change it to:
def create
post = Post.create params[:post])
render :json => post
end
And it will solve your problem. It worked for me 
answered Aug 3, 2014 at 8:41
itamaryuitamaryu
3263 silver badges5 bronze badges
«Sometimes» this can mean that the server had an internal error, and wanted to respond with an error message (ex: 500 with JSON payload) but since the request headers didn’t say it accepted JSON, it returns a 406 instead. Go figure. (in this case: spring boot webapp).
In which case, your operation did fail. But the failure message was obscured by another.
answered May 8, 2018 at 22:08
rogerdpackrogerdpack
60.5k35 gold badges260 silver badges379 bronze badges
You can also receive a 406 response when invalid cookies are stored or referenced in the browser — for example, when running a Rails server in Dev mode locally.
If you happened to run two different projects on the same port, the browser might reference a cookie from a different localhost session.
This has happened to me…tripped me up for a minute. Looking in browser > Developer Mode > Network showed it.
answered Jul 31, 2016 at 22:50
etusmetusm
3,9821 gold badge31 silver badges26 bronze badges
const request = require('request');
const headers = {
'Accept': '*/*',
'User-Agent': 'request',
};
const options = {
url: "https://example.com/users/6",
headers: headers
};
request.get(options, (error, response, body) => {
console.log(response.body);
});
answered Dec 9, 2016 at 19:56
JP VenturaJP Ventura
5,4465 gold badges51 silver badges69 bronze badges
1
Changing header to Accept: */* resolved my issue and make sure you don’t have any other Accept Header
answered Jun 6, 2022 at 12:11
Kunal TyagiKunal Tyagi
1,42313 silver badges23 bronze badges
0
In my case, I added:
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
solved my problem completely.
answered Aug 29, 2016 at 23:10
If you are using ‘request.js’ you might use the following:
var options = {
url: 'localhost',
method: 'GET',
headers:{
Accept: '*/*'
}
}
request(options, function (error, response, body) {
...
})
answered Jul 1, 2019 at 12:48
0
In my case for a API in .NET-Core, the api is set to work with XML (by default is set to response with JSON), so I add this annotation in my Controller :
[Produces("application/xml")]
public class MyController : ControllerBase {...}
Thank you for putting me on the path !
answered Sep 16, 2019 at 6:55
It could also be due to a firewall blocking the request. In my case the request payload contained string properties — «like %abc%» and ampersand symbol «&» — which caused the firewall to think it is a security risk (eg. a sql injection attack) and it blocked the request. Note here the request does not actually go to the server but is returned at the firewall level itself.
In my case, there were no application server logs generated so I knew that the request did not actually reach the server and was blocked before that. The logs that helped me were Web application firewall (WAF) logs.
answered Jul 8, 2022 at 11:58
singh_vsingh_v
741 silver badge12 bronze badges
Server and client-side errors happen occasionally, and we commonly refer to them as HTTP responses or status codes. The “406 error” or “406 Not Acceptable” error is one such HTTP response.
You may see the 406 error while visiting a site. Or worse, on your website. While It may irritate the average internet user, it can be borderline terrifying for a website or application owner. Besides looking somewhat unprofessional and confusing, any HTTP response code, including the 406 error, can lose sales and users.
This article will explain the basics of the “406 Not Acceptable” error, its causes, how to fix it, and steps to avoid it in the future.
Check Out Our Guide to Fixing a 406 Error and Find the Source of the Problem
What Is 406 Error?
The good news is that the HTTP error “406 Not Acceptable” message is not nearly as common as the 404 server error (which usually indicates a non-existent webpage), or even 301 or 500 HTTP errors. Therefore, you definitely shouldn’t see this one as much.
Although it’s rare, it’s still possible that the 406 error may come into play as a problem for your website. It usually looks like this:
The message typically reads:
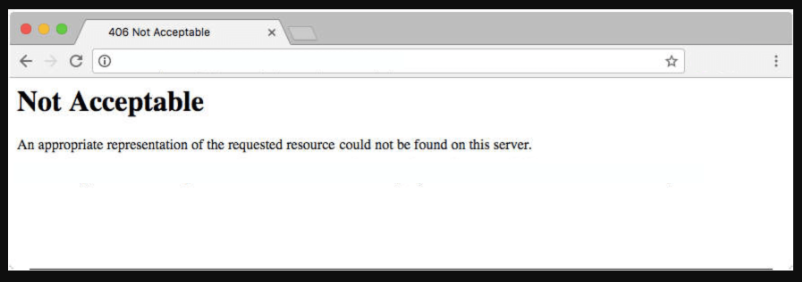
Not Acceptable
An appropriate representation of the requested resource could not be found on this server.
It then sometimes identifies the “requested resource” where the problem lies, with other messages or server information mentioned at the end:
The appearance and text within the 406 error message depending on the website, host, and browser used to access the website. The 406 error may reveal where the errors stem from. Other times you may find that it’s a simple “406 Not Acceptable” error without any information helping you solve the problem.
Now, let’s pretend browsers spoke in plain English and not these cryptic messages. In that case, the browser would be saying something like this:
Hello, I’m a browser. I tried to show this webpage, but one of the two problems occurred:
- The website’s server sent me the wrong file format, so I can’t accept it.
- The website’s server violates some settings or security requirements.
Therefore, please resolve the violation or have the server use one of the file formats I accept. In case you’re wondering, here are the file formats I know how to read.
If only browsers were that friendly!
Essentially, there’s a miscommunication between the server and the browser or machine used to present the web application. The browser either can’t read what’s coming in or verify the data because it didn’t meet some requirements.
Now we have to answer some questions to figure out the cause of that miscommunication.
Server and client-side errors happen from time to time, but that doesn’t make them any less frustrating 😅 Learn how to fix one common error in this in-depth guide 👇Click to Tweet
What Causes the 406 Error?
Every time you open a web page, your browser (like Safari, Firefox, Brave, Chrome, or Internet Explorer) sends a request to the page’s server to obtain site content and database files. The browser acts as the messenger between you and the server — it tells the server what the user wants to see, and hopefully, the correct information comes back.
During that first request, the browser tells the server all about the file formats it can accept. It’s called an Accept- header request, which prompts the server to deliver the files in the proper formats to produce the entire website or web application, starting with the header.
Sometimes the server sends a reply that’s not in the suitable format or violates a rule set forth by the browser or client machine. In this situation, a 406 error appears in the browser window, indicating the server isn’t delivering the appropriate data.
Here are some examples of “bad formats” and “rule violations” that can come up with the header requests:
- Accept-ranges: Some servers have security measures set in place or only allow a specific file size range in the response. If the response attempts to send too many bytes outside the allowable range, you’ll see the 406 error.
- Accept-encoding: Here’s an area of the header meant to compress files, so they move quickly from the server to the browser. Some compression methods and formats aren’t accepted, rendering a 406 error code.
- Accept-charset: Refers to a character set or how site file tables take code (like CSS and HTML) and turn it into understandable characters. There are so many characters, languages, and symbols in the world that it’s challenging to cover them all. The standard table is called ISO-8859, but there are other complementary tables as well. New character tables occasionally get released to keep up with language and character additions.
- Accept-language: This is usually a different name for Accept-charset that references its focus on international languages.
- MIME type violation: Sometimes, the browser requests a specific MIME type from the server. MIME types are content elements like JPEG images, specific video formats, or simple text. If the server can’t provide a requested MIME type, like JPEG images, you’ll see a 406 error.
The primary way to address and fix a 406 error is by checking the source code for issues in the Accept-, Request-, and Response- headers.
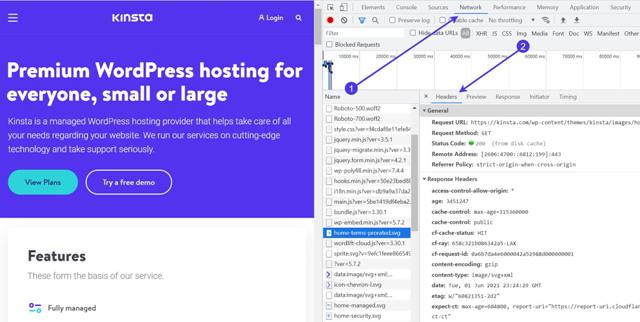
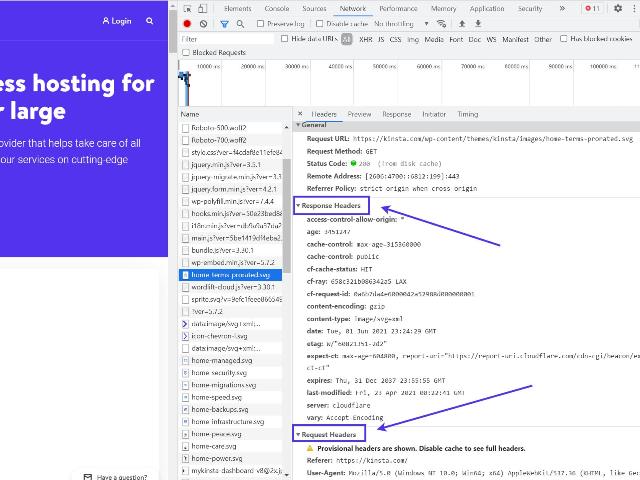
The easiest way to review Accept- and Response- headers is to open a webpage in your browser, right-click, and select Inspect.
Go to Network > Headers to reveal all requests from this webpage.
You can typically select any request from the long list to see the Request- and Response- headers for that particular request.
Or, you can contact your web developer to take a look into the source code. However, checking the source code is much easier when you have tools for debugging and cleaning your database, which we’ll discuss later in this article.
As mentioned before, a “406 Not Acceptable” error tells us that the client has sent a valid request to the server, but the request included a unique requirement for the server to follow. That special requirement in the initial request was in the form of an HTTP Accept- header.
That leaves us with a few potential causes:
- The server didn’t provide the requested MIME type or proper formats, like a JPEG or mp4 video.
- The server didn’t return with the correct language (Accept-language). For instance, it may have sent back a response in German when the browser asked for French.
- The server used the wrong compression method or format in response to the Accept-encoding request.
- The server sent back too many bytes that didn’t align with the Accept-ranges request.
- The server failed to provide understandable characters, which would result in a problem with the Accept-charset request from the browser.
There are other reasons you may see the 406 error, but they’re not nearly as common. The above list is from the most common reasons to the least common. The first two come into play far more often than the others, so there’s a good chance you should usually focus on troubleshooting the potential for a MIME type violation or an Accept-language problem.
Overall, website owners should know about these format problems and violations, seeing how something within your site files may cause problems. Such situations often occur because of human error, like accidentally typing in the wrong code, deleting necessary code, or misconfiguring the server. The 406 error also appears when specific security settings or rules block content transmission from the server.
How to Fix the 406 Error
It’s prudent to run a website or application backup before completing any steps to resolve a 406 error. There’s always the potential for causing further problems by going into your site’s source code, so you’ll want to have a database and site file backup to restore if necessary.
Make sure you complete a full backup with everything from the database to the application and the media elements to the site files. If you’re a Kinsta user, you can do this with the MyKinsta backup feature, which logs your entire website in a separate file and has a Restore button for later use:
Now that we have a deeper understanding of why the 406 error occurs, it’s time to talk about the best methods to troubleshoot the error and prevent it from happening again.
These tactics include client-side causes (where a user makes an error or the machine isn’t working correctly), server-side causes, and platform-based causes like faulty plugins.
Make Sure the URL Is Correct
Our first piece of advice may sound simple, but it’s the quickest troubleshooting option, and it puts a focus on issues with the client-side of things (i.e., your computer).
A 404 error is far more likely than a 406 error in this situation, but you may end up seeing a “406 Not Acceptable” error if the website URL is valid. Yet, there’s something odd about the way your browser translates the request. For instance, adding “JSON” or “PHP” to the end of URLs could be misinterpreted as a request for those particular formats, even though the client doesn’t need them.
To resolve the issue, double-check the previously used URL that produced the error. Try typing it in again or opting for a different subdomain on the website to see if it’s only one page that isn’t rendering.
A 406 message is technically considered a client-side error code (even though it’s often a platform or server issue), so this is the first course of action to determine if something’s wrong on the client side.
Reset Your Devices and Networks
Another client-side problem occasionally involves those same Accept- headers sent from the user’s computer to a platform that can’t satisfy the request. Many of these platforms include gaming- or media-oriented systems like Hulu or music marketplaces like Spotify.
In simpler terms, you may log into a platform like Hulu, try to watch your favorite TV show, and receive a 406 error message. In this example, the problem is almost always on the client-side. It’s usually your computer, network, or another device you’ve used to launch the platform.
Although it can happen with any platform, some platforms that commonly report 406 errors include:
- Hulu
- Google Play
- Square Enix Games
- Netflix
- Xbox
- Windows (usually for gaming)
This list is far from complete, but it gives you an idea of where the 406 error may occur.
Media and gaming platforms are complicated with many restrictions, and those restrictions depend on your location or network configuration. There’s a chance you might encounter an error like this due to all the moving pieces.
Although we can’t help you troubleshoot every specific platform, consider walking through the following recommendations and checking to see if the error resolves:
- Go online to check the status of your platform’s server. It may simply be a problem with the company’s server.
- Restart your computer, gaming system, streaming device, or other machines.
- Disconnect all devices from their cables, wait a few minutes before reconnecting them all, and check to see if the error is gone.
- Check if the app is running the most current version. Also, see if any of your machines have firmware updates available.
- Reset your home or office network (the WiFi or internet connection through your router).
- Consider switching from a wireless network to a wired network connection if you’re still having trouble.
- Although this isn’t always a possibility, consider duplicating the error with a completely different machine. Make sure that the device is on the same network. If you can’t replicate the error, look into your network and the original machine.
If all else fails, go to your search engine and type in the name of your platform along with “+ 406 error code” for platform-specific troubleshooting advice. That often reveals forums and support documentation to guide you through the process.
Rollback Your Recent CMS Changes
Next, it’s time to explore the system used for your websites or applications. You may find that your content management system, such as WordPress, is the direct cause of a “406 Not Acceptable” error due to a complication with something inside your site files.
Whether using WordPress or any other content management system, look into when your last update occurred. WordPress has a sturdy default infrastructure meant to avoid these types of errors, no matter what.
However, specific plugins, themes, or manually adjusted coding could produce situations where the site files violate client or server requests. A simple upgrade to your CMS’s latest version can solve the problem right away.
To figure out if it’s your CMS, start by rolling back any recent upgrades that occurred to the core files. As you may already know, WordPress sends out updates to its system regularly. Most of these updates happen automatically, but older versions still require you to click a button.
Furthermore, WordPress and other CMSs utilize several moving parts like plugins, themes, and extensions. Those also get updated regularly, so you might need to roll back some of them.
For all systems outside of WordPress, search for “platform name + how to downgrade.”
If you use WordPress, you can easily downgrade your WordPress website, effectively rolling it back to one of the previous versions:
That guide outlines the following methods for downgrading your WordPress site, most of which only take a few minutes:
- Manually downgrading your WordPress site.
- Using a plugin to complete the WordPress system downgrade.
- Restoring a previous backup to bring back an old version, or at least the content and files from before.
- Manually downgrading a theme or plugin.
- Downgrading a plugin or theme with a separate plugin.
- Switching to an older version of PHP.
Uninstall and Reinstall Plugins, Themes, and Extensions
WordPress plugins and themes add extra code to your site files that interact with the core WordPress files. Reputable plugins typically don’t cause any problems, but occasionally a conflict occurs. A plugin, theme, or third-party extension may be the reason for the 406 error.
The tried-and-true method for identifying a troublesome plugin or theme is to deactivate your plugins and themes one by one. After disabling each, check to see if the 406 error has vanished. If so, you’ve found the problem. If it doesn’t go away, reinstall the plugin or theme and continue uninstalling the next one.
Analyze the Status of Your Database for Changes and Conflicts
Unfortunately, a removed “problem” plugin could still affect your WordPress database since plugins get full access to the database to work well. Therefore, you should still check the status of your database even if it appears the removal of a plugin has made the 406 error go away. Otherwise, you may still run the risk of seeing further issues in the future.
If a plugin or theme wasn’t the culprit, you should also check your database if it’s the primary source of the error. Sometimes a database change, whether accidental or purposeful, becomes the primary reason a 406 error appears.
To scan and fix your database, consider these solutions:
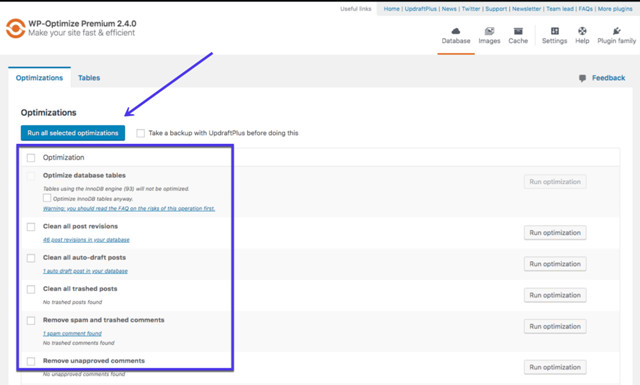
- Install a database scanner and cleaner that removes useless and troublesome tables and assets. Some options include WP Optimize and the Advanced Database Cleaner. Much of this process involves deleting old or orphaned items like trash posts, revisions, and metadata. It’s a solid first step to cleaning up your database and potentially eliminating that 406 error.
- Scan the database and look for records and tables potentially changed by a problematic plugin or ones that look out of place or unnecessary.
- If you have an idea of what’s wrong with your database, go to a search engine and seek out help from forums and other discussions online. There’s a good chance someone else has experienced the same problem.
Analyze Your Server Logs
The previous recommendations focus on client-side and CMS-oriented troubleshooting. Now we’ll consider all server-side issues. This tip, and the ones following, are best if you aren’t using a CMS or know that the 406 error has no connection to your CMS or client machine.
The first step in troubleshooting the server is checking the logs. It doesn’t matter what type of web application, CMS, or web design system you use; they all have server-side logs.
The application logs store that web application’s entire (or recent) history, with information about each database inquiry, results provided, pages requested, and much more. On the other hand, the server logs contain information about the health and status of the server or hardware used to run the web application.
For Kinsta users, you can find error and server logs in the MyKinsta dashboard. Check all logs that may be causing the 406 error:
- The error.log file
- The kinsta-cache-perf.log file
- The access.log file
You can also check raw access and WordPress error log files with an FTP client. Other options include enabling error logs in wp-config.php and going through the debug mode in the MyKinsta dashboard.
If you have problems finding the error logs or don’t know how to interpret them, contact the Kinsta customer support team for assistance.
Debug the Web Application (Like WordPress)
Like most web applications have server and error logs, they also typically provide information about debugging the application itself. Debugging involves going through the application’s code to find and eliminate minor errors (or bugs).
One of the best ways to run a complete scan of WordPress (and any web application for that matter) is to debug the database and website files. Luckily, debugging doesn’t mean you have to read through every line of code and pick out the bugs yourself. Programs are available for this specific purpose, and as we mentioned earlier, Kinsta even has its debugging tool within the MyKinsta dashboard.
Start the debugging process by learning the basics of debugging WordPress with the Kinsta Debug Mode, WordPress Debug plugins, or a more manual process:
Preventing the 406 Error in the Future
The problem with the 406 error is that it can pop up in many different situations. You might see the “406 Not Acceptable HTTP” error while browsing through Hulu or Netflix as a regular consumer.
That isn’t very pleasant, but nothing a little troubleshooting can’t fix. The more concerning occurrence of the 406 error is when it happens on your website or application. For those instances, you’ll need to check the server and CMS site files.
If it’s your website, you’ll want to prevent the error from ever happening again. Plugins, themes, and human error can always come into play, but we have a few suggestions to keep your databases and site files clean into the future:
- Only install necessary and reputable plugins, themes, and extensions. Always keep these elements to a minimum.
- Don’t ever modify the core WordPress files unless you absolutely must and know what you’re doing.
- Run a database cleaner and site optimizer regularly. We recommend completing this process every month and ideally finding a cleaner plugin that runs automatically in the background.
- Make a habit of debugging your server and web application. As mentioned, Kinsta offers a Debugging feature in its dashboard. Many other applications have this type of functionality as well.
- Set automated backups of your website or application. This way, a code conflict or error won’t cause you much stress since you can restore a previous version of the website and start from there.
- Run a manual backup of your site before you plan on updating WordPress and any plugins, even if you already run automated backups (better safe than sorry). It’s also wise to run backups before editing any files or adding new code to your site.
In addition to looking unprofessional and causing confusion, the 406 error can cause you to lose sales or users 💸 Learn how to fix it here ⬇️Click to Tweet
Summary
You can fix the 406 error in several ways. As long as you know what you are seeing and where to look for the fix, you should be able to clear the error up.
While this is not one of the more common WordPress errors, it is one you will see from time to time if your configuration is not correct.
Do you have any other recommendations for resolving “406 Not Acceptable” errors? Please share them in the comments section below!
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Иногда возникают ошибки на стороне сервера и на стороне клиента, обычно их называют HTTP-ответами или кодами состояния. Одним из таких HTTP-ответов является ошибка «406 error» или «406 Not Acceptable».
Эту ошибку можно увидеть при посещении сайта. Или, что еще хуже, на собственном сайте. Это может раздражать обычного пользователя Интернета, но для владельца веб-сайта или приложения это на грани ужаса. Любой код ответа HTTP, включая ошибку 406, может не только выглядеть непрофессионально и сбивать с толку, но и приводит к потере продаж и пользователей.

В этой статье будут объяснены основные сведения об ошибке «406 Not Acceptable», ее причины, способы исправления и шаги по профилактике ее появления в будущем.
Что такое ошибка 406
Хорошая новость заключается в том, что сообщение об ошибке HTTP «406 Not Acceptable» встречается не так часто, как ошибка сервера 404 (которая обычно указывает на несуществующую веб-страницу) или даже ошибки 301 или 500 HTTP.
Чаще всего появляется во время редактирования постов, страниц, товаров, меток и других таксономий в WordPress. При этом отредактировать контент невозможно.
Хотя это случается редко, все же возможно, что ошибка 406 может стать проблемой для веб-сайта. Обычно это выглядит так:
An appropriate representation of the requested resource /wp-admin/post.php could not be found on this server.
Сообщение обычно гласит (в переводе на русский):
Недопустимо
Соответствующее представление запрошенного ресурса /wp-admin/post.php не может быть найдено на этом сервере.
Иногда «запрошенный ресурс», в котором заключается проблема, определяется и выводится с другими сообщениями или информацией о сервере:
Внешний вид и текст сообщения об ошибке 406 зависит от веб-сайта, хоста и браузера, которые использовались для доступа к веб-сайту. Ошибка 406 может показать, где произошли ошибки. В других случаях отображается простая ошибка «406 Not Acceptable» без какой-либо информации о проблеме.
А теперь давайте представим, что браузеры говорят на простом английском, а не в этих загадочных сообщениях. В этом случае браузер скажет что-то вроде этого:
Здравствуйте, я браузер. Я попытался показать эту веб-страницу, но возникла одна из двух проблем:
- Сервер веб-сайта отправил мне файл неправильного формата, поэтому я не могу его принять.
- Сервер веб-сайта нарушает некоторые настройки или требования безопасности.
Поэтому устраните нарушение или попросите сервер использовать один из приемлемых мной форматов файлов. Если вам интересно, вот форматы файлов, которые я умею читать.
Если бы только браузеры были такими дружелюбными!
По сути, существует недопонимание между сервером и браузером или компьютером, используемым для представления веб-приложения. Браузер либо не может прочитать, что поступает, либо проверить данные, потому что они не соответствуют некоторым требованиям.
Теперь нужно ответить на несколько вопросов, чтобы выяснить причину этого недопонимания.
Смотрите также:
Наиболее распространенные ошибки SSL-соединения и методы их исправления
Что вызывает ошибку 406
Каждый раз, когда вы открываете веб-страницу, ваш браузер (например, Safari, Firefox, Brave, Chrome или Internet Explorer) отправляет запрос на сервер страницы для получения содержимого сайта и файлов базы данных. Браузер действует как посредник между вами и сервером – он сообщает серверу, что пользователь хочет видеть, и, надеюсь, верная информация возвращается.
Во время этого первого запроса браузер сообщает серверу все форматы файлов, которые он может принимать. Это называется Accept- header запросом, который побуждает сервер доставить файлы в надлежащих форматах для создания всего веб-сайта или веб-приложения, начиная с заголовка.
Иногда сервер отправляет ответ в неподходящем формате или нарушает правило, установленное браузером или клиентским компьютером. В этой ситуации в окне браузера появляется ошибка 406, указывающая, что сервер не предоставляет соответствующие данные.
Вот несколько примеров «плохих форматов» и «нарушений правил», которые могут возникать при запросах заголовков:
- Accept-ranges: на некоторых серверах установлены меры безопасности или разрешен только определенный диапазон размера файла в ответе. Если ответ пытается отправить слишком много байтов за пределы допустимого диапазона, вы увидите ошибку 406.
- Accept-encoding: это область заголовка, предназначенная для сжатия файлов, поэтому они быстро перемещаются с сервера в браузер. Некоторые методы и форматы сжатия не принимаются, что приводит к отображению кода ошибки 406.
- Accept-charset: относится к набору символов или к тому, как таблицы файлов сайта принимают код (например, CSS и HTML) и превращают его в понятные символы. В мире так много персонажей, языков и символов, что сложно охватить их все. Стандартная таблица называется ISO-8859, но есть и другие дополнительные таблицы. Время от времени выпускаются новые таблицы символов.
- Accept-language: обычно это другое имя для Accept-charset, которое ссылается на его ориентацию на международные языки.
- Нарушение типа MIME: иногда браузер запрашивает у сервера определенный тип MIME. Типы MIME – это элементы содержимого, такие как изображения JPEG, определенные видеоформаты или простой текст. Если сервер не может предоставить запрошенный тип MIME, например изображения JPEG, вы увидите ошибку 406.
Основной способ исправить ошибку 406 – проверить исходный код на наличие проблем в заголовках Accept-, Request- и Response- .
Самый простой способ просмотреть заголовки «Accept» и «Response» – открыть веб-страницу в браузере, щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши и выбрать « Inspect» (Проверить).
Перейдите в Сеть> Заголовки, чтобы отобразить все запросы с этой веб-страницы.
Обычно выбирают любой запрос из длинного списка, чтобы увидеть заголовки запроса и ответа для этого конкретного запроса.
Или можете обратиться к своему веб-разработчику. Однако проверка исходного кода намного проще, если есть инструменты для отладки и очистки базы данных, которые обсудим позже в этой статье.
Ошибка «406 Not Acceptable» сообщает, что клиент отправил действительный запрос на сервер, но запрос включал уникальное требование для сервера. Это специальное требование в первоначальном запросе было в форме HTTP Accept— заголовка.
Это оставляет нам несколько потенциальных причин:
- Сервер не предоставил запрошенный тип MIME или правильные форматы, такие как видео в формате JPEG или mp4.
- Сервер не вернулся с правильным языком (Accept-language). Например, он мог отправить ответ на немецком языке, когда браузер запросил французский.
- Сервер использовал неправильный метод или формат сжатия в ответ на запрос Accept-encoding.
- Сервер отправил обратно слишком много байтов, которые не совпадают с запросом Accept-ranges.
- Серверу не удалось предоставить понятные символы, что привело бы к проблеме с запросом Accept-charset из браузера.
Есть и другие причины, по которым вы можете увидеть ошибку 406, но они не так распространены. Приведенный выше список — от наиболее распространенных причин до наименее распространенных. Первые два используются гораздо чаще, чем другие, поэтому есть большая вероятность, что вам обычно следует сосредоточиться на устранении потенциальных проблем с нарушением типа MIME или проблемой языка принятия.
В целом, владельцы веб-сайтов должны знать об этих проблемах и нарушениях формата, чтобы знать, как что-то в файлах вашего сайта может вызывать проблемы. Такие ситуации часто возникают из-за человеческой ошибки, например, случайного ввода неправильного кода, удаления необходимого кода или неправильной настройки сервера. Ошибка 406 также появляется, когда определенные настройки или правила безопасности блокируют передачу контента с сервера.
Как исправить ошибку 406
Перед выполнением каких-либо действий по устранению ошибки 406 разумно запустить резервную копию веб-сайта или приложения. Всегда есть вероятность вызвать дальнейшие проблемы, войдя в исходный код сайта. Поэтому может понадобится резервная копия базы данных и файлов сайта для восстановления в случае необходимости.
Убедитесь, что создана полная резервная копия всего, от базы данных и мультимедийных элементов до файлов сайта.
Теперь, когда у нас есть более глубокое понимание того, почему возникает ошибка 406, пришло время поговорить о лучших методах устранения ошибки и предотвращения ее повторения.
Эти тактики включают причины на стороне клиента (когда пользователь совершает ошибку или машина работает некорректно), причины на стороне сервера и причины на основе платформы, такие как неисправные плагины.
Убедитесь, что URL-адрес правильный
Первый совет может показаться простым, но это самый быстрый способ устранения неполадок, и он фокусируется на проблемах, связанных с клиентской стороной (то есть с вашим компьютером).
Ошибка 404 гораздо более вероятна, чем ошибка 406 в этой ситуации. Но если URL-адрес веб-сайта действителен, то можно увидеть и ошибку «406 Not Acceptable». Тем не менее, есть что-то странное в том, как браузер переводит запрос. Например, добавление «JSON» или «PHP» в конец URL-адресов может быть неверно истолковано как запрос для этих конкретных форматов, даже если клиенту они не нужны.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, дважды проверьте ранее использованный URL-адрес, вызвавший ошибку. Попробуйте ввести его еще раз или выберите другой субдомен на веб-сайте, чтобы проверить, не отображается ли таким образом только одна страница.
Сообщение 406 технически считается кодом ошибки на стороне клиента (даже если это часто проблема платформы или сервера), поэтому это первый шаг, позволяющий определить, что на стороне клиента что-то не так.
Сбросьте свои устройства и сети
Другая проблема на стороне клиента иногда связана с теми же заголовками Accept, отправленными с компьютера пользователя на платформу, которая не может удовлетворить запрос. Многие из этих платформ включают игровые или медиа-ориентированные системы, такие как Hulu, или музыкальные торговые площадки, такие как Spotify.
Проще говоря, можно войти на такую платформу, как Hulu, попробовать посмотреть свое любимое телешоу и получить сообщение об ошибке 406. В этом примере проблема почти всегда на стороне клиента. Обычно это компьютер, сеть или другое устройство, которое вы использовали для запуска платформы.
Хотя это может произойти с любой платформой, некоторые платформы, которые обычно сообщают об ошибках 406:
- Hulu
- Гугл игры
- Игры Square Enix
- Netflix
- Xbox
- Windows (обычно для игр)
Этот список далеко не полный, но он дает представление о том, где может возникнуть ошибка 406.
Медиа и игровые платформы имеют множество ограничений, и эти ограничения зависят от вашего местоположения или конфигурации сети.
Хотя трудно помочь вам устранить неполадки для каждой конкретной платформы, рассмотрите следующие рекомендации и проверьте, устранена ли ошибка:
- Войдите в Интернет, чтобы проверить статус сервера платформы. Это может быть просто проблема с сервером компании.
- Перезагрузите компьютер, игровую систему, потоковое устройство или другие машины.
- Отсоедините все устройства от кабелей, подождите несколько минут, прежде чем снова их все подключить, и проверьте, исчезла ли ошибка.
- Убедитесь, что в приложении установлена самая последняя версия. Также проверьте, доступны ли обновления прошивки для какой-либо из ваших машин.
- Сбросьте настройки домашней или офисной сети (Wi-Fi или подключение к Интернету через маршрутизатор).
- Если проблема не исчезнет, подумайте о переключении с беспроводной сети на проводное сетевое соединение.
- Хотя это не всегда возможно, рассмотрите возможность дублирования ошибки на совершенно другом компьютере. Убедитесь, что устройство находится в той же сети. Если вы не можете воспроизвести ошибку, проверьте свою сеть и исходный компьютер.
Если все это не помогло, перейдите в свою поисковую систему и введите название своей платформы вместе с «кодом ошибки + 406», чтобы получить рекомендации по устранению неполадок для конкретной платформы. Этот запрос часто открывает форумы и вспомогательную документацию, которая поможет определиться.
Откат последних изменений в CMS
Пришло время изучить систему, используемую для ваших веб-сайтов или приложений. Может случится так, что система управления контентом, такая как WordPress, является прямой причиной ошибки «406 Not Acceptable» из-за сложностей внутри файлов сайта.
Независимо от того, используете ли WordPress или любую другую систему управления контентом, узнайте, когда было последнее обновление. Несмотря ни на что WordPress имеет надежную поддержку по умолчанию, предназначенную для предотвращения подобных ошибок.
Однако определенные плагины, темы или код, настроенные вручную, могут привести к ситуациям, когда файлы сайта нарушают запросы клиента или сервера. Простое обновление до последней версии CMS может сразу решить проблему.
Чтобы выяснить, не CMS ли все портит, начните с отката всех недавних обновлений, которые произошли с файлами ядра. WordPress регулярно рассылает обновления своей системы. Большинство этих обновлений происходит автоматически, но более старые версии по-прежнему требуют нажатия кнопки для обновления.
Кроме того, WordPress и другие CMS используют несколько сторонних частей, таких как плагины, темы и расширения. Они также регулярно обновляются, поэтому может потребоваться откатить некоторые из них.
Для всех систем, не относящихся к WordPress, выполните поиск по запросу «название платформы + как перейти на более раннюю версию».
Если вы используете WordPress, можете легко понизить версию своего веб-сайта WordPress, эффективно откатив его до одной из предыдущих версий:
Удалите и переустановите плагины, темы и расширения
Плагины и темы WordPress добавляют дополнительный код к файлам сайта, который взаимодействует с основными файлами WordPress. Авторитетные плагины обычно не вызывают никаких проблем, но с некачественным ПО иногда возникают конфликты. Плагин, тема или стороннее расширение могут быть причиной ошибки 406.
Проверенный метод определения проблемного плагина или темы — один за другим деактивировать плагины и темы. После отключения каждого проверьте, исчезла ли ошибка 406. Если да, то вы нашли проблему. Если ошибка не исчезнет, переустановите плагин или тему и продолжите удаление следующего.
Важно!
Начните с плагинов, если ничего не найдете – перейдите к теме.
Анализируйте состояние БД на предмет изменений и конфликтов
К сожалению, удаленный «проблемный» плагин все еще может повлиять на базу данных WordPress, поскольку плагины для правильной работы получают полный доступ к БД. Поэтому все равно следует проверять статус базы данных, даже если кажется, что удаление плагина привело к исчезновению ошибки 406. В противном случае можно столкнуться с дополнительными проблемами в будущем.
Если плагин или тема не были причиной ошибки, следует проверить базу данных: является ли основным источником ошибки. Иногда изменение базы данных, случайное или целенаправленное, становится основной причиной появления ошибки 406.
Чтобы просканировать и исправить БД, рассмотрите следующие решения:
- Установите сканер и очиститель базы данных, который удаляет бесполезные и проблемные таблицы и активы. Некоторые параметры включены в плагины WP Optimize и Advanced Database Cleaner. Большая часть этого процесса включает в себя удаление старых или потерянных элементов, таких как мусорные записи, исправления и метаданные. Это надежный первый шаг к очистке БД и потенциальному устранению ошибки 406.
- Просканируйте базу данных и найдите записи и таблицы, которые могут быть изменены проблемным плагином или выглядят неуместными или ненужными.
- Если у вас есть представление о том, что не так с базой данных, перейдите в поисковую систему и обратитесь за помощью на форумы и в другие обсуждения в Интернете. Есть большая вероятность, что кто-то другой столкнулся с той же проблемой.
Анализируйте журналы вашего сервера
Предыдущие рекомендации сосредоточены на устранении неполадок на стороне клиента и CMS. Теперь рассмотрим проблемы на стороне сервера. Этот и следующие советы лучше всего подходят, если вы не используете CMS или знаете, что ошибка 406 не связана с CMS или клиентским компьютером.
Первым шагом в устранении неполадок сервера является проверка журналов. Неважно, какой тип веб-приложения, CMS или системы веб-дизайна вы используете; все они имеют журналы на стороне сервера.
Журналы приложений хранят всю (или недавнюю) историю этого веб-приложения с информацией о каждом запросе к базе данных, предоставленных результатах, запрошенных страницах и многом другом. С другой стороны, журналы сервера содержат информацию о работоспособности и состоянии сервера или оборудования, используемых для запуска веб-приложения.
Отладка веб-приложения (например, WordPress)
Подобно большинству веб-приложений, у которых есть журналы серверов и ошибок, они обычно предоставляют информацию об отладке самого приложения. Отладка включает просмотр кода приложения для поиска и устранения мелких ошибок.
Один из лучших способов запустить полное сканирование WordPress (или любого веб-приложения) – отладить файлы базы данных и веб-сайта. К счастью, отладка не означает, что вам нужно читать каждую строчку кода и самостоятельно выявлять ошибки. Для этой конкретной цели доступны программы, и многие хостинги предоставляют их на панели управления сайтами.
Предотвращение ошибки 406 в будущем
Проблема с ошибкой 406 заключается в том, что она может появляться в различных ситуациях. Можно увидеть ошибку «406 Not Acceptable HTTP» при просмотре Hulu или Netflix в качестве обычного пользователя.
Это не очень приятно, но все можно исправить с помощью небольшого устранения неполадок. Более опасно появление ошибки 406, когда она происходит на вашем веб-сайте или в приложении. В таких случаях необходимо проверить файлы сервера и сайта CMS.
Если это ваш веб-сайт, то нужно предотвратить повторение ошибки. Плагины, темы и человеческий фактор всегда могут сыграть роль, но у нас есть несколько советов, как сохранить базы данных и файлы сайта в чистоте в будущем:
- Устанавливайте только необходимые и проверенные плагины, темы и расширения. Всегда сводите эти элементы к минимуму.
- Никогда не изменяйте основные файлы WordPress, если вы в этом не уверены и не знаете, что делаете.
- Запускайте регулярно очистители/оптимизаторы базы данных и сайта. Рекомендуем выполнять этот процесс каждый месяц, а в идеале найти чистый плагин, который автоматически запускается в фоновом режиме.
- Возьмите за привычку отлаживать сервер и веб-приложение. Многие ресурсы имеют такую функциональность.
- Установите автоматическое резервное копирование сайта или приложения. Таким образом, конфликт кода или ошибка не вызовут у вас особого стресса, поскольку можно восстановить предыдущую версию веб-сайта и начать с нее.
- Выполните ручное резервное копирование сайта, прежде чем планировать обновление WordPress и любых плагинов, даже если уже запущено автоматическое резервное копирование (лучше перестраховаться, чем сожалеть). Также разумно выполнить резервное копирование перед редактированием любых файлов или добавлением нового кода на сайт.
Исправить ошибку 406 можно несколькими способами. Хотя это не одна из наиболее распространенных ошибок WordPress, вы будете время от времени встречаться с ней, если конфигурация неверна.
Источник: kinsta.com
Смотрите также:


Изучает сайтостроение с 2008 года. Практикующий вебмастер, специализирующий на создание сайтов на WordPress. Задать вопрос Алексею можно на https://profiles.wordpress.org/wpthemeus/

Aug 17, 2022 11:00:00 AM |
406 Not Acceptable: What It Is and How to Fix It
An in-depth overview of what a 406 Not Acceptable response is, including troubleshooting tips to help you resolve this error in your own application.
The 406 Not Acceptable is an HTTP response status code indicating that the client has requested a response using Accept- headers that the server cannot fulfill.
The 406 Error is the result of the user agent (i.e., browser) specifying an acceptable character set (via Accept-Charset), language (via Accept-Language), etc. that needs a response and the server is unable to provide such a response.
This article will examine what causes a 406 Not Acceptable error and how to fix it. Using a Content Management System (CMS)? Not a problem! We’ll also review how these systems generate 406 Not Acceptable errors.
And, with that, let’s get started!
Server- or Client-Side?
All HTTP response status codes in the 4xx category are considered client error responses. This category contrasts with 5xx classification errors, such as the 504 Gateway Timeout Error, which are considered server error responses.
That said, the appearance of a 4xx error doesn’t necessarily mean the issue is on the client side, where the «client» is the web browser or device used to access an application.
In some cases, the server could be responsible for the 406 Error since it’s the network object producing the error. Perhaps the server is misconfigured and can’t handle the request correctly. Maybe it’s a traffic routing issue.
We’ll look at both client and server-side issues within this article, but first, let’s make sure you’re set up to diagnose and debug your application.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
Before attempting to fix any errors, you should perform a complete backup of your application, database, and all other components of your website or application.
Even better, create a complete copy of the application and stick the copy on a secondary staging server that isn’t accessible to the public. A staging server will give you a clean testing ground to test all potential fixes to resolve the issue without threatening the sanctity of your live application.
Diagnosing a 406 Not Acceptable
As discussed in the introduction, a 406 Not Acceptable Error means that the user agent (the web browser, in most cases) has requested a valid resource; however, the request included a special Accept- header. The Accept- header indicates to the server a valid response can only contain certain types of information.
Here are a few examples of such scenarios:
- The user agent may be localized to a particular locale or language the server cannot provide. For example, a user agent may use the Accept-Language request header to specify a valid language of French (Accept-Language: fr). Still, if the server cannot serve a response in French, a 406 code may be the only proper response.
- The user agent may request a specific type of content to be returned by the server. These content types, commonly known as MIME types, define things like plain text (text/plain), PNG images (image/png), mp4 videos (video/mp4), etc. Thus, the client may include the Accept header in the request and define an explicit MIME type that the server should provide (e.g., Accept: application/XML). If the server cannot respond with the matching content type requested, a 406 Not Acceptable response may be necessary.
There are a handful of other Accept- headers that can be provided in HTTP requests. Still, the vast majority of scenarios are similar to the above: The user agent wants an explicit type of response, and the server either provides it or returns a 406 code indicating it cannot fulfill the request.
Troubleshooting on the Client-Side
Since the 406 Not Acceptable is a client error response code, it’s best to troubleshoot any potential client-side issues first. Here are a few tips to try on the browser or device throwing the error.
Check the Requested URL
The most common cause of a 406 Not Acceptable is inputting an incorrect URL. Servers tend to be tightly secured against unexpected requests to resources that a client/user agent should not have access to. It may be that the requested URL is slightly incorrect, which is causing the user agent to request a specific type of response.
For example, a request to the URI https://airbrake.io?json might indicate to the server that a JSON response is required. Since 406 codes are not as common as 404 codes, the appearance of a 406 could mean that the requested URL is valid, but the browser may misinterpret the intended request type. Either way, it’s a good idea to double-check the exact URL that is returning the 406 Not Acceptable error to make sure it is the intended resource.
Debugging Common Platforms
Suppose you’re running common software packages on the server responding with the 406 Not Acceptable. In that case, you may want to start by first looking into those platforms’ stability and functionality.
The most common content management systems (CMS) — like WordPress, Joomla!, and Drupal — are all typically well-tested out of the box. Once you start making modifications to the underlying extensions or PHP code, it’s too easy to cause an unforeseen issue that results in a 406 Not Acceptable.
Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot some of these popular software platforms.
Rollback Recent Upgrades
If you recently updated the content management system before the 406 Not Acceptable appeared, consider rolling back to the previous version you had installed.
Similarly, any extensions or modules you recently upgraded can also cause server-side issues, so reverting to previous versions of those may also help.
In some cases, however, certain CMSs don’t have a version downgrade capability. This is likely because they consider the base application and each new version released to be highly stable and bug-free.
Uninstall New Extensions, Modules, or Plugins
Depending on the content management system you use, the exact names of these components will be different. Still, they all serve the same purpose across every system: improving the capabilities and features of the platform beyond what it’s typically capable of out of the box.
Be warned: such extensions can, more or less, take complete control of the system and make virtually any changes to the CMS’s code. As such, it may be wise to uninstall any new extensions you recently added.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
Even if you uninstall an extension through the CMS dashboard, this doesn’t guarantee that changes made by the extension will fully revert.
This is particularly true for many WordPress extensions. WordPress extensions are given carte blanche within the application, including full access rights to the database. That means they can modify database records that don’t «belong» to the extension but are created and managed by other extensions (or even the base CMS).
Unfortunately, the extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records so that it will ignore such things during uninstallation.
Diagnosing such problems can be tricky, but I’ve personally encountered such scenarios multiple times. Your best course of action, assuming you’re reasonably convinced an extension is a likely culprit for the 406 Not Acceptable Error, is to open the database and manually look through tables and records that were likely modified by the extension.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
If you aren’t running a CMS application or you’re confident the 406 Not Acceptable Error isn’t related to that — here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot what might be causing the issue on the server-side.
Confirm Your Server Configuration
Your application is likely running on a server using one of the two most popular web server software, Apache or Nginx. One of the first steps you can take to determine what might be causing these 406 Not Acceptable response codes is to check the configuration files for your web server software for unintentional redirect or request handling instructions.
To determine your application’s web server, you’ll want to look for a key file.
Apache Server
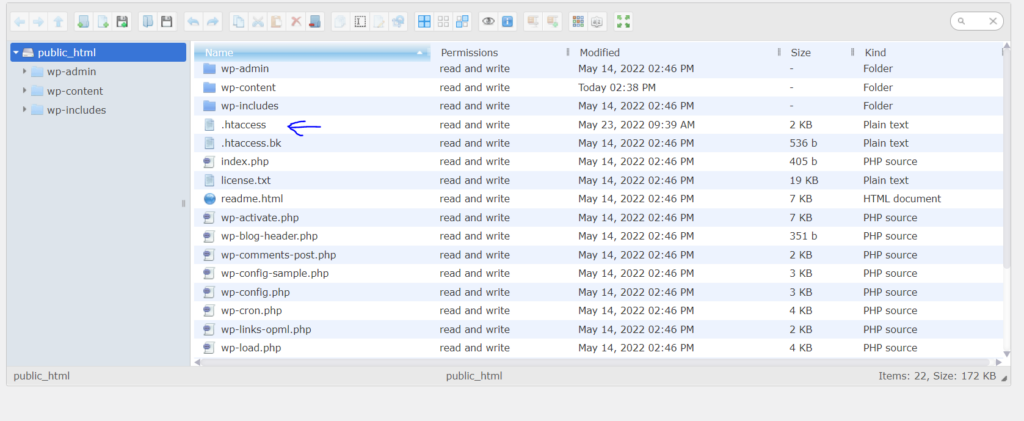
If your web server is Apache, look for a .htaccess file within the root directory of your website file system.
For example, if your application is on a shared host, you’ll likely have a username associated with the hosting account. The application root directory is typically found at the path of:
/home/<username>/public_html/, so the .htaccessfile would be at /home/<username>/public_html/.htaccess.
If you located the .htaccess file, open it in a text editor and look for lines that use RewriteXXX directives, which are part of the mod_rewrite module in Apache. Covering exactly how these rules work is well beyond the scope of this article; however, the basic concept is that a RewriteCond directive defines a text-based pattern that will be matched against entered URLs.
Suppose a visitor requests a matching URL to the site. In that case, the RewriteRule directive that follows one or more RewriteCond directives is used to perform the actual redirection of the request to the appropriate URL.
For example, a RewriteRule matches all incoming requests to https://airbrake.io/users/json that do not contain an Accept: application/JSON request header.
The result is a redirection and 406 Not Acceptable response error code:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} ^/users/json/?.*$
RewriteCond %{HTTP_ACCEPT} !application/json
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://airbrake.io/users/json$1 [R=406,L]
Notice the R=406 flag at the end of the RewriteRule, which explicitly states that the response code should be 406. This tells the user agents that the resource exists, but the explicit Accept- headers could not be fulfilled.
If you find any strange RewriteCondor RewriteRule directives in the .htaccess file that don’t seem to belong, try temporarily commenting them out (using the # character prefix) and restarting your web server to see if this resolves the issue.
Nginx
On the other hand, if your server is running on Nginx, you’ll need to look for a completely different configuration file. By default this file is named nginx.conf and is located in one of a few common directories: /usr/local/nginx/conf, /etc/nginx, or /usr/local/etc/nginx.
Once located, open nginx.conf in a text editor and look for directives using the 406 response code flag.
For example, here is a block directive (i.e., a named set of directives) that configures a virtual server for airbrake.io and ensures that, similar to above, a request to
https://airbrake.io/users/json that doesn’t include an Accept: application/JSON request header will fail and is met with a 406 response code:
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name airbrake.io;
location /users/json {
if ($http_accept != application/json) {
return 406 https://airbrake.io/users/json$request_uri;
}
}
}
Have a look through your nginx.conf file for any abnormal directives or lines that include the 406 flags. Comment out any abnormalities before restarting the server to see if the issue was resolved.
Configuration options for each different type of web server can vary dramatically, so we’ll list a few popular ones to give you some resources to look through, depending on what kind of server your application is running on:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
- Node.js
- Apache Tomcat
Look Through the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs. Application logs are typically the history of the application’s actions, including requested pages, connected servers, database results, etc.
Server logs are related to the actual hardware running the application and will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services or the server itself.
Google «logs [PLATFORM_NAME]» if you’re using a CMS, or «logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]» and «logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]» if you’re running a custom application, to get more information on finding the logs in question.
Debug Your Application Code or Scripts
If all else fails, you might have a problem with some custom code within your application. Try to diagnose where the issue may come from by manually debugging your application and parsing through application and server logs.
Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process, which will allow you to recreate the exact scenario in which the 406 Not Acceptable occurred and view the application code at the moment something goes wrong.
Prevent an future unexpected 406 Not Acceptable Error from impacting users by implementing an error monitoring solution. Error Monitoring will help you automatically detect errors and will alert you the very moment they occur.
Airbrake’s Error and Performance Monitoring software provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your development projects. Airbrake’s state-of-the-art web dashboard ensures you receive round-the-clock status updates on your application’s health and error rates. No matter what you’re working on, Airbrake easily integrates with all the most popular languages and frameworks. Plus, Airbrake makes it easy to customize exception parameters while giving you complete control of the active error filter system, so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out Airbrake’s error monitoring software today and see why so many of the world’s best engineering teams use Airbrake to revolutionize their exception handling practices!
Browse by Categoy
- 404 Error
- 406 Error
- Affiliate Marketing
- Amazon EC2
- Apache
- AWS
- Cache
- Cloud
- Cloudflare
- Conversion Rate Optmization
- CRO
- Cron Jobs
- CyberPanel
- Database
- Dedicated Server
- DigitalOcean
- DKIM
- DMARC
- DNS
- Elementor
- Git
- Google Cloud
- IP Address
- LAMP
- Linux
- LiteSpeed Cache
- Mailgun
- Malware
- Marketing
- Mautic
- Multisite
- MySQL
- News
- NGINX
- OpenLiteSpeed
- Oxygen Builder
- Performance Test
- Permalinks
- PHP
- PHPMyAdmin
- Postfix
- Processes
- Query Monitor
- rDNS
- Redis
- SCP
- Security
- Server
- Shared Hosting
- SMTP
- SPF
- SSH
- Telnet
- Uptime Monitoring
- Varnish
- Video Marketing
- WooCommerce
- Wordfence
- WordPress
- WordPress Builder
Posted on June 3rd, 2022
by Editorial Team
Errors on the client and server side can happen (such as 406 error), and these are commonly referred to as HTTP responses or status codes. This HTTP response code is known as the «406 error».
When visiting a site, you might encounter a 406 error. If you have a website, it might be even worse. Internet users may find it irritating, but website or application owners might find it absolutely terrifying. Any HTTP response code, including the 406 error, can make an otherwise professional website seem unprofessional and confusing.
What is 406 error?
«406 Not Acceptable» HTTP error messages aren’t as common as «404 Not Found» errors (which usually indicate that URLs don’t exist) or even the 301 or 500 HTTP problems. As a result, you shouldn’t expect to see much of this one.
The status code 406 Not Acceptable is an HTTP response code. When user agents (web browsers) request information from the server, they provide an Accept header that notifies the server which data types the browser may accept. If the server is unable to transmit data in any of the codecs specified in the Accept header, a 406 Not Acceptable error will be returned.
Although the 406 error is uncommon, it is possible that it will cause an issue for your website.
The message usually goes like this:
Not Acceptable
An appropriate representation of the requested resource could not be found on this server.
Additional messages or server information are mentioned at the end, and it sometimes indicates the «requested resource» where the problem is.
Is 406 error a server-side or a client-side error?
A client-side error is the 406 Not Acceptable status code. It belongs to the 4xx (The 4xx status code class is for situations where the client appears to have made a mistake) category of HTTP response status codes, which are client error responses.
HTTP status codes in the 4xx category include:
- 400 Bad Request
- 401 Unauthorized Error
- 403 Forbidden
- 404 Not Found
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- 410 Gone
- 429 Too Many Requests
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
4xx errors imply that the intended page was not located and that the request was incomplete. The problem is something that is occurring on the client’s end.
They differ from the 5xx category of status codes, which are considered server-side faults. These errors are not the fault of the client, but they do indicate a problem on the server-side
A 406 Not Acceptable error can sometimes be traced back to the server. It can, for example, result in a 406 code response and other significant traffic routing issues if it is misconfigured and handling requests incorrectly.
What are the causes of 406 error?
Your browser (such as Safari, Firefox, Brave, Chrome, or Internet Explorer) requests site files and content whenever you open a web page. By communicating with the server, the browser notifies the server what the user wants to see, and hopefully, the server replies with the correct information.
When the browser sends its first request, it informs the server what file types it can accept. Essentially it’s an Accept-Header request, which tells the server to deliver the files in the proper formats in order to produce the entire website or web application, beginning with the header.
A server’s response may not respect a browser’s or a client’s rule when it is not in the appropriate format. This error indicates that the server isn’t delivering the required data, as indicated by a 406 error.
In header requests, there can be some «bad formats» and «rule violations». Here are some examples:
- Accept-ranges: Some servers use security measures or only allow a specified file size limit in the response. You’ll get a 406 error if the answer tries to send too many bytes outside the allowed range.
- Accept-encoding: This section of the header is used to compress files so they can be sent from the server to the browser fast. A 406 error code is generated when certain encoding methods and formats aren’t accepted.
- Accept-language: Accept-language is a nickname for Accept-charset that refers to its emphasis on worldwide languages.
- MIME type violation: The browser may occasionally ask the server for a certain MIME type. JPEG photos, particular video formats, and basic text are examples of MIME types. You’ll get a 406 error if the server can’t offer a specified MIME type, such as JPEG images.
- Accept-charset: This is a character set that describes how site file tables convert code (such as CSS and HTML) into readable characters. It’s difficult to cover all of the characters, languages, and symbols that exist around the globe. The ISO-8859 table is the standard, although there are also various complementing tables. To keep up with language and character additions, new character tables are released on a regular basis.
The «406 Not Acceptable» error indicates that the client provided a legitimate request to the web server, but that the request included a special criterion that the server must comply with. The initial request included a particular need in the form of an HTTP Accept- header.
That leaves us just a few possibilities or causes:
- The desired MIME type or suitable formats, such as JPEG or mp4 video, were not provided by the server.
- The server did not provide the appropriate language (Accept-language).
- In accordance with the Accept-encoding request, the server utilized the incorrect compression method or format.
- The server returned an excessive number of bytes that did not match the Accept-ranges request.
- The server failed to deliver comprehensible characters, resulting in an issue with the browser’s Accept-charset request.
The 406 error can be caused by other things, but they aren’t as common. The first two are more prevalent than the others, so it’s likely you should start by looking into the possibility of a MIME type violation or an Accept-language issue.
Seeing how something within your site files might cause problems is key information for website owners regarding these format issues and violations. Human error, such as entering in the wrong code, removing vital code, or misconfiguring the server, frequently results in such scenarios. When specific security settings or regulations prevent content delivery from the server, the 406 error arises.
What are some preventative measures for 406 error?
The issue with the 406 error is that it might appear in a variety of circumstances.
That’s not ideal, but it’s nothing that a little troubleshooting can’t fix. When the 406 error occurs on your website or app, it is much more problematic.
If it’s your website, you’ll want to make sure it doesn’t happen again. Plugins, themes, and human mistakes can all play a role, so here are some additional recommendations.
- Keep plugins, themes, and extensions to a minimum. Only install the necessary and reputable elements.
- Unless you know what you are doing and absolutely must, you should never edit the core files of WordPress.
- It is recommended to perform a database cleaner and site optimizer regularly. We recommend that this process is completed every month and that a cleaner plugin is used that will run automatically in the background.
- Debugging your server and web application should become a habit.
- Backup your website or application regularly. This will prevent code conflicts or errors from causing too much anxiety since you can easily restore a previous version of the site.
- Even if you already run automated backups, run a manual backup of your site before updating WordPress and any plugins. It’s also a good idea to take a backup before editing any files or adding new code to your site.
How to fix 406 error?
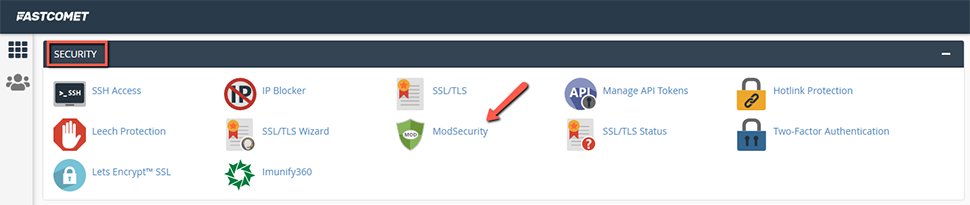
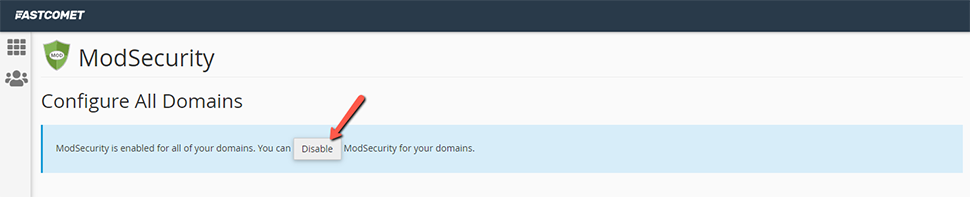
Go into your WordPress site’s file manager. Enter the publi_html and right click on .htaccess to edit
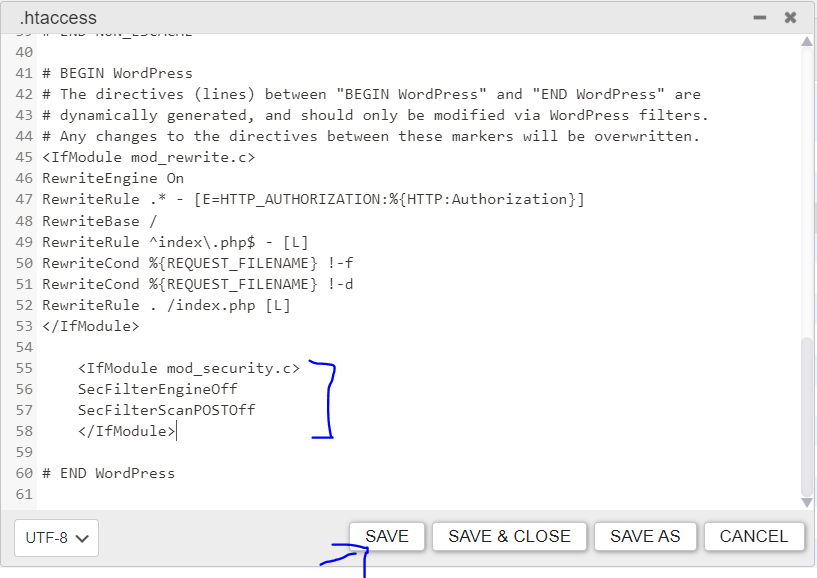
Enter the following code at the end of the file and click save. This will resolve the 406 error, please note that for below solution to work you either need to have your site on LiteSpeed Enterprise or Apache, even on NGINX this below solution will not work.
<IfModule mod_security.c>
SecFilterEngineOff
SecFilterScanPOSTOff
</IfModule>Conclusion
When browsing a website, you may see the 406 error. Or, in the worst-case scenario, on your website. While it may annoy the typical internet user, it can be downright frightening for the owner of a website or service. Any HTTP response code, even the 406 error, might lose sales and users in addition to seeming unprofessional and unclear.
There are various methods for resolving the 406 error. You should be able to clear up the mistake as long as you know what you’re seeing and where to seek for the solution.
While this isn’t one of the most common WordPress issues, it is one that you may encounter if your configuration is incorrect.
You might be interested in
Web browsers make a request for information from the server whenever one visits your website. If the Web server detects that the data it wants to return is not acceptable to the client, it returns a header containing the 406 error code. In practice, this error is very rarely used compared to the “404-Page not found” but it refrains you from accessing a site. You need to learn about its cause and the solution. In this tutorial, you’re going to learn about what might cause the 406 Not Acceptable error, along with a handful of tips for diagnosing and debugging within your own application.
Table of Contents:
- What is the 406 Error?
- Server-side or Client-side?
- Begin with a Thorough Backup
- Client-side Causes of 406 Not Acceptable
- Debug Common Platforms
- Rollback Recent Updates
- Uninstall Plugins, Extensions, or Modules
- Check for Unexpected Database Changes
- Server-side Causes of Error 406 — Not Acceptable
- How To Prevent Error 406 Not Acceptable
What is the 406 Error?
The 406 Not Acceptable is an HTTP response status code. When user agents (web browsers) make a request for information from the server, they send an Accept header, which tells the server the specific formats in which the browser can accept data. If the server is unable to send data in any of the formats requested in the Accept header, the result would be a 406 Not Acceptable error.
There are more than 50 status codes, representing the complicated relationship between client, web application, web server, and sometimes even multiple third-party web services. That said, it’s not easy to determine what’s causing a specific status code, at least not without some proper diagnostics and troubleshooting.
Server-side or Client-side?
All HTTP response status codes in the 4xx category are considered client error responses. The category contrasts with 5xx classification errors, such as the 504 Gateway Timeout Error, which are considered server error responses. However, the appearance of a 4xx error does not necessarily mean the issue is on the client-side, where the “client” is the web browser or device being used to access the application. If you’re trying to diagnose an issue within your own application, you can immediately ignore most client-side code and components, such as HTML, CSS, client-side JavaScript, etc. This doesn’t apply only to websites, either. There are many smartphone apps that implement a modern-looking user interface. Those are actually powered by a normal web app behind the scenes that is simply hidden from the user.
On the other hand, the root cause of a 406 Not Acceptable error could be the server. There are known cases where the server is misconfigured and handling requests improperly, which can result in 406 code responses and other problematic traffic routing issues.
Begin with a Thorough Backup
As always, it’s best to play it safe from the start. Create a full backup of your website or application, database, as well as all other components. Doing that is crucial, especially if you are about to perform a certain task (fix, change, update) for the first time. It’s always a good idea to create a full copy and stick it on a secondary server (your personal computer) if you have one. You can use it as an environment to test all potential fixes for the issue, without risking the security of your live application.
Furthermore, you can implement the staging environment via cPanel’s Softaculous.
Client-side Causes of 406 Not Acceptable
The 406 Not Acceptable is a client error response. That’s why it’s best to start with the troubleshooting of any potential client-side problems which might be causing the error.
Debug Common Platforms
In case you are running some of the common software packages and getting the 406 Not Acceptable, you should look into the stability of your platform(s). The most commonly used Content Management Systems (CMSs) such as WordPress or Joomla!, are considered to be well-tested out of the box. However, there is never a guarantee that once you start making changes (installing plugins, themes, extensions, etc.) everything will go perfectly. It’s not too hard to cause an unforeseen issue, which may result in a 406 Not Acceptable.
There are some helpful tips that might help you pinpoint the issue and resolve it.
Rollback Recent Updates
If you have recently updated your CMS, and then started getting the 406 Not Acceptable, you should consider rolling back to the previous version. When it comes to WordPress, we have a thorough guide on How to Downgrade WordPress. For assistance with other CMS downgrades, just Google “how to downgrade” and put the name of your platform at the end. Keep in mind that some platforms don’t offer downgrade capabilities. If that’s the case, you should know that such platforms consider themselves to be stable and as bug-free as possible.
Similar to the platform itself, you might have recently updated some modules or extensions, which may also lead to the 406 error. Reverting to older versions of those extensions may also resolve your issue. If not, you can try to deactivate or uninstall them.
Uninstall Plugins, Extensions, or Modules
Depending on the CMS you are using for your application, the exact names of plugins, extensions, or modules, could be different. However, every system has components of that type and they serve the same purpose everywhere. Such tools are used for improving the capabilities and features of the platform beyond what it’s normally capable of out of the box.
However, keep in mind that those extensions could potentially take full control of the system and start making all types of changes (to the PHP code, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or database). In such cases, it’s best if you uninstall the most recent additions to your extensions list.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
Note that even if you uninstall an extension through the CMS dashboard, you are not guaranteed that changes made by the extension will be fully reverted. This is especially true for many WordPress extensions, which are given permissions within the application, including full access rights to the database. Unless the extension author explicitly codes such things in, there are scenarios where an extension may modify database records that don’t “belong” to the extension itself but are instead created and managed by other extensions (or even the base CMS itself).
In those scenarios, the extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records, so it will ignore such things during uninstallation. Diagnosing such problems can be tricky, but I’ve personally encountered such scenarios multiple times, so your best course of action, assuming you’re reasonably convinced an extension is a likely culprit for the 406 Not Acceptable, is to open the database and manually look through tables and records that were likely modified by the extension.
Most importantly, you should not be afraid to Google your issue. Try searching for specific terms related to your issue, such as the name of your application’s CMS, along with the 406 Not Acceptable. Chances are, you are going to find someone who has experienced the same issue.
Server-side Causes of Error 406 — Not Acceptable
If you are experiencing the error 406 Not Acceptable, you have most likely triggered a security rule, and thus your request got blocked. At FastComet, we make sure to optimize our security rules in order to minimize the chance of false-positive blocks. However, you might end up with the 406 error due to one of the following reasons:
- The page you are attempting to request contains renders about the hosting environment (e.g., Kernel version). That’s one of the common issues with apps that have Server Information sections in their admin panels or directly render the output of the
phpinfo()function. - The request or the response body is too large. This often happens when your page is attempting to reply with a body that’s larger than the maximum allowed on the server. The limit is set high enough to process almost any “healthy” page, and thus it’s not common to run into 406 Not Acceptable because of the page size.
- The requested page includes known malware or phishing content like a PayPal scam.
- The request is matching any of the security rules we have set, and thus the request is being blocked.
How To Prevent Error 406 Not Acceptable
To prevent the 406 error from happening mod_security can be turned off. Additionally, you may just disable specific ModSecurity rules, as well as disable ModSecurity for each domain individually. Turning mod_security off is a 3-step process. All you have to do is:
- Log into your cPanel;
- Find ModSecurity and click on it:
- Once you’re in, just click on Disable:
You may not be able to enable or disable mod_security in your cPanel on VPS or Dedicated CPU Servers. To disable mod_security in accounts that do not have that option in cPanel, you would need to use CLI via SSH.
However, the best thing to do here is to contact our technical support by opening a new ticket. They will assist you as quickly as possible, making sure everything is done properly. Additionally, you can ask for the mod_security to be turned off only for specific domains.
We hope you find this article useful. Discover more about FastCloud — the top-rated Hosting Solutions for personal and small business websites in four consecutive years by the HostAdvice Community!
- Код ошибки 406 Not Acceptable
- Ошибка 410 Gone
- Код ошибки 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Если ошибки 404 и 520 встречаются часто и многие знакомы с решениями таких проблем, то ошибки 406, 410, 505 встречаются редко и иногда приводят пользователя в недоумение. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, почему появляются эти ошибки и как их исправить.
Код ошибки 406 Not Acceptable
Ошибка HTTP 406 Not Acceptable говорит о том, что формат или кодировка страницы не поддерживается у пользователя. Чаще всего причины этой ошибки на стороне владельца сайта. Проблемы могут быть разные:
- Проблемы с заголовками Content-Language, Content-Encoding или Content-Type.
- Запрос браузера заблокирован брандмауэром ModSecurity. Этот брандмауэр фильтрует все поступающие к сайту запросы: принимает корректные запросы и блокирует нежелательные. С его помощью блокируются нежелательные запросы, которые нацелены на выявление уязвимостей в CMS.
Как отключить ModSecurity
Иногда добавленный код на сайт может восприниматься ModSecurity как опасный. Особенно такое встречается с кодами от рекламных сервисов. Чтобы исправить ошибку 406, вызванную ModSecurity, откройте файл .htaccess и вставьте этот фрагмент кода:
<IfModule mod_security.c>
SecFilterEngine Off
SecFilterScanPOST Off
</IfModule>Код отключит фильтры брандмауэра ModSecurity по отношению к вашему сайту.
3. Если у вас сайт на WordPress, HTTP 406 ошибка может появиться из-за установленных плагинов. Чтобы найти плагин, который нарушает работу, деактивируйте плагины по очереди. Когда нежелательный плагин будет найден, удалите его.
Как деактивировать плагин в WordPress
- Войдите в панель управления WordPress.
- Перейдите в раздел Плагины ― Установленные.
- Нажмите Деактивировать рядом с плагином, который хотите отключить:
Чтобы деактивировать все плагины, поставьте галочку напротив строки Плагин. Автоматически отметятся все установленные плагины. В выпадающем списке выберите Деактивировать. Нажмите Применить:
Что может сделать пользователь
В основном проблема встречается на стороне владельца сайта, но бывают ситуации, когда проблема с устройством пользователя. Чтобы устранить ошибку:
- Почистите cookies и кэш браузера. Даже если доступ к сайту уже восстановлен, эти файлы могут отображать старую версию сайта с ошибкой.
- Проверьте, не мешают ли работе сайта расширения браузера. Для этого в браузере перейдите в режим «Инкогнито». Если сайт начал запускаться, проблема с расширениями. Удалите недавно установленные расширения.
- Проверьте работоспособность браузера. Откройте сайт в другом браузере. Если веб-ресурс загрузился, проблема с браузером. Переустановите его.
- Обновите драйверы устройства. Многие программы на ПК работают с помощью драйверов. Устаревшие драйверы могут перестать выполнять свои функции. Обновите драйверы и попробуйте запустить сайт заново.
- Откатите последние изменения. Если у вас Windows и недавно произошло обновление системы, можно попробовать вернуть прежнюю версию системы, при которой сбоев в работе не наблюдалось.
Ошибка 410 Gone
Ошибка 410 ― что значит? Ошибка 410 Gone значит, что страница или запрашиваемый файл был удалён. Если вы пользователь и видите эту ошибку, сделать вы ничего не можете. Эта проблема только на стороне владельца сайта. Если вы владелец сайта, исправление ошибки зависит от того, что вы хотите сделать со страницей:
- Если вы хотите вернуть страницу, можно восстановить её из резервной копии (если она есть).
- Если вы планировали удалить страницу, настройте редирект старой страницы на любую другую (например, на главную страницу сайта). Благодаря редиректу вы сможете сохранить поисковые позиции удалённой страницы и пользователи не увидят ошибку 410.
Отличие от ошибки 404
Может показаться, что ошибка 410 похожа на 404. Действительно, по некоторым параметрам они похожи, но есть и существенные отличия. Ошибка 404 говорит о том, что страница совсем не существует либо временно не найдена, так как она скрыта от пользователя. То есть нельзя точно сказать, что страница удалена и никогда не появится по этому URL. Ошибка 410 говорит о том, что страница раньше существовала и сейчас 100% была удалена.
Для поисковых систем эти ошибки дают два разных сценария действий. Если поисковые роботы видят 410 ошибку, они сразу удаляют эту страницу из индексации и больше никогда не вернуться на неё. При 404 ошибке поисковые системы подразумевают, что страница будет открыта позже, и отмечают, что к ней нужно будет вернуться и проиндексировать.
Код ошибки 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Что означает ошибка 505? Как все ошибки, которые начинаются на 5, ошибка 505 ― серверная ошибка. Она означает, что версия протокола HTTP, которую использует пользователь, не поддерживается на сервере с сайтом. Такая проблема может возникнуть как на стороне владельца сайта, так и на стороне пользователя.
Как исправить ошибку 505 на стороне пользователя:
- Обновите программное обеспечение. Сюда входит обновление операционной системы, драйверов (особенно для сетевых устройств) и веб-приложений.
- Дайте больше прав браузеру, который вы используете, в брандмауэре и антивирусе.
- Очистите cookies и кэш браузера.
- Полностью удалите и снова установите браузер.
- Если код 505 отображается во всех браузерах и веб-приложениях, обратитесь за помощью к интернет-провайдеру. Вероятно, проблема на его стороне.
Что может сделать владелец сайта:
- Проверьте, с каким протоколом работает ваш сервер. Если нужно, обновите версию протокола до нужного. Например, серверы 2DOMAINS работают с протоколом HTTP 1.1.
- Проверьте, нет ли ошибок в CGI-скриптах, директивах .htaccess или в конфигурационном файле веб-сервера. Увидеть ошибки можно в логах сервера.
В прикладном смысле сайт — это набор файлов. Файлы каждого сайта находятся на том или ином физическом сервере. Чтобы пользователь мог перейти на нужный ресурс в интернете, нужно запросить эти файлы у сервера.
Сразу после того, как пользователь вбивает какой-то запрос в поисковик, браузер делает запрос на сервер. После этого сервер дает ответ и искомый сайт открывается в браузере. Однако иногда вместо ответа на запрос появляется ошибка.
Каждая ошибка имеет свой код. По коду можно определить возможные причины её появления. Рассмотрим, что означают ошибки 406, 410 и 505, из-за чего они появляются и как их можно исправить.
Ошибка 406 Not Acceptable
Если веб-сервер выдаёт код ошибки 406, значит запрос был заблокирован брандмауэром веб-приложений (WAF) ModSecurity. Брандмауэр ModSecurity — это программное обеспечение для веб-сервера Apache, которое фильтрует все поступающие к сайту запросы (веб-трафик). Он принимает корректные запросы и блокирует нежелательные. Например, защищает веб-ресурс от нелегитимных запросов, с помощью которых можно найти уязвимости CMS и затем взломать её.
ModSecurity по умолчанию подключают все хостинг-провайдеры для защиты сайтов клиентов. Подробнее о работе брандмауэра ModSecurity читайте на modsecurity.org.
HTTP 406 ошибка чаще всего имеет локальный характер и возникает на стороне клиента. В редких случаях, чтобы исправить проблему, необходимы действия со стороны владельца.
Основные причины
- Брандмауэр ошибочно блокирует корректные запросы.
- Временная проблема идентификации IP-адреса при подключении к Wi-Fi.
- Ваш браузер поврежден вирусами. К заражению могли привести установленные для браузера расширения или поврежденные файлы операционной системы.
- Поврежден реестр Windows. Нередко такое происходит в результате последних обновлений программного обеспечения или после удаления тех или иных его компонентов.
- Когда клиенты жалуются, что видят страницу с 406, самая вероятная причина — некорректная работа плагинов CMS. Чаще всего такое бывает на Wordpress-сайтах.
Как исправить HTTP 406 Not Acceptable
Если вы пользователь:
- Почистите файлы cookies. Если при повторном подключении вы снова увидите ошибку, попробуйте очистить кэш браузера. Возможно, доступ уже восстановлен, но ваш браузер обращается к старой версии страницы.
- Отключите дополнительные расширения. Запустите браузер в режиме «Инкогнито». В этом режиме браузер задействует только базовые настройки. Если веб-ресурс доступен в этом режиме, значит причина ошибки в одном из дополнительных расширений, которые вы используете.
- Переустановите браузер. Если вы отключили расширения, но доступ к сайту не появился, попробуйте ввести аналогичный запрос через другой поисковик. Если страница открывается, значит есть критические нарушения в работе текущего браузера.
- Обновите драйверы компьютера. Иногда драйверы устройства отключаются и перестают автоматически работать. Это может спровоцировать нарушение в подключении. Для восстановления работы достаточно обновить драйверы.
- Отмените последние изменения, если у вас Windows. Восстановление системы позволит вернуть программы и системные файлы вашего компьютера в то состояние, когда не было сбоев в работе.
- Просканируйте системные файлы. Благодаря этому можно обнаружить поврежденные файлы и восстановить их. Это поможет оптимизировать работу компьютера и, возможно, устранить проблему.
Если указанные способы не помогли, вероятно, проблема связана с настройками сайта.
Если вы владелец сайта:
1) Если ваш сайт создан на WordPress, проверьте работу плагинов. Чтобы убедиться, что проблема именно в них, можно отключить сразу все плагины и проверить соединение.
Если вы уверены, что на работу влияет конкретный плагин — отключите его. Если не уверены, то отключайте плагины по очереди, пока не вычислите нужный. Для этого:
-
1.
Войдите в панель управления WordPress. Если вы пользуетесь услугой REG.Site, войти в панель управления CMS можно прямо из Личного кабинета.
-
2.
Перейдите на Плагины ― Установленные.
-
3.
Нажмите Деактивировать для плагина, который хотите отключить:
2) Если ваш сайт создан не на WordPress или отключение плагинов не дало результата, чтобы исправить ошибку 406, напишите заявку в техническую поддержку.
Ошибка 410 Gone
Иногда при переходе на одну из страниц сайта может встретится ошибка 410, что значит, что этой страницы больше не существует. Следовательно, проблема возникла на стороне владельца сайта.
Этим 410 похожа на ошибку 404 (страница не найдена). Их основное отличие в том, что при ошибке 404 страница либо не существовала, либо наоборот — существует, но временно не найдена (например, потому что скрыта от пользователей). Ошибка 410 же сообщает, что страница точно существовала раньше, но затем её удалили.
Также ошибки по-разному обрабатывают поисковые роботы. Если роботы встретят страницу с ошибкой 404, они перенесут индексацию сайта на 24 часа. Если сервер выдаст страницу с 410, роботы сразу отметят её как удаленную и больше не будут индексировать. Для владельца сайта это не очень хороший сценарий, поскольку не индексируемые страницы негативно влияют на позиции сайта в поисковых системах.
Как исправить
Способ исправить ошибку 410 HTTP зависит от намерений владельца.
- Если страница удалена по ошибке, можно попробовать восстановить её из резервной копии.
- Если страницу удалили намеренно, лучше всего настроить редирект. Редирект помогает сделать перенаправление одной страницы на другую. Это позволит сохранить поисковые позиции.
Ошибка 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Код ошибки 505 говорит нам о том, что проблема возникла на уровне сервера. Вот что означает ошибка 505: с её помощью сервер сообщает, что не может установить соединение по той версии HTTP-протокола, с помощью которой к нему хотят подключиться.
Основные причины
- Пользователь использует устаревший браузер, который не поддерживает новые версии протокола. То есть в этом случае браузер подключается по версии HTTP 1.1, а сервер работает по версии HTTP 2.
- Сервер не поддерживает HTTP-протокол, с помощью которого пытается подключиться клиент. Например, он работает по версии HTTP 1.1, а запрос поступает из браузера с версии HTTP 2.
- Неверные директивы, указанные в файле .htaccess.
- Неполадки в работе скриптов ресурса.
Как исправить ошибку 505
Если вы пользователь:
- Почистите файлы cookies и кэш браузера.
- Обновите версию браузера.
- Обновите операционную систему и драйверы.
- Обратитесь к интернет-провайдеру. Если все страницы показывают 505 в любых браузерах, обратитесь в службу поддержки вашего провайдера.
Если вы владелец сайта:
- Узнайте, по какой версии протокола работает ваш сайт. Обновите её до актуальной, если необходимо. Например, серверы REG.RU работают с протоколом HTTP 1.1.
- Проверьте логи веб-сервера. Определите, где кроется ошибка (в работе CGI-скриптов, директивах .htaccess или файле конфигурации веб-сервера) и исправьте её.
- Если проблема в скриптах, обратитесь к разработчику сайта.