# from lxml import etree;
import module2dbk;
print module2dbk.xsl_transform(etree.parse('test-ccap/col10614/index.cnxml'), []);
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token `('
Levon
135k33 gold badges198 silver badges188 bronze badges
asked May 20, 2012 at 18:32
Jessica BurnettJessica Burnett
7112 gold badges9 silver badges20 bronze badges
2
add #!/usr/bin/env python at the top of your script, or call your script using python myscript.py
answered May 20, 2012 at 18:34
1
Are you typing this at the unix command prompt? You should be doing this inside the python environment, ie. type python at the prompt and work from there.
Also, no ; needed at the end of the line in Python
answered May 20, 2012 at 18:35
LevonLevon
135k33 gold badges198 silver badges188 bronze badges
1
add
#!/usr/bin/env python
or but i will prefer to use the above one.
#!/usr/bin/python
In case you have installed python 2 and python 3 and python 2 is default you can run python 3 by using these command
#!/usr/bin/env python3
at top of the file
or run this way
python code.py
answered Jan 13, 2015 at 7:14
Well I had exactly the same problem. I had tried everything and nothing really worked. My program was running perfectly on Windows command prompt, and on my iPhone Python app interpreter, but not on my Macbook’s terminal, where I always got the following error whenever I tried to run the program:
bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
Finally the comment above from the user tripleee helped me come up with a solution; although his solution of adding !/usr/bin/python at the very start of my code didn’t do it for me it helped me understand as he wrote that:
The error message indicates that the script gets executed by bash, not python.
Then I noticed that my code(extra).py contained ‘(‘ apostrophes, I renamed to my codeextra.py and that was it, problem solved. 
shim
8,88511 gold badges72 silver badges104 bronze badges
answered Nov 14, 2018 at 19:15
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token '('in Python- Fix
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token '('in Python

Every time a Python code runs through a shell terminal such as Bash, it must point to an interpreter. If Bash cannot find a suitable way to run the file, then it will give out errors.
This guide will discuss Error: Bash: syntax error near unexpected token '('.
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token '(' in Python
Python needs to be installed on your computer for the interpreter to find and run the Python files. The interpreter works differently in different operating systems.
In Windows, when we install Python, a program called IDLE is installed on the computer, which comes with the interpreter. It runs Python codes.
In Linux, we can access Python using the shell terminal by typing the command python. It opens the Python environment where the code can be written and run.
If the code has trouble finding the Python interpreter, it will run on whichever shell it runs. If the user runs the code from the Bash terminal, then the shell will give an error that will resemble this:
#Python 3.x
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token '('
Bash is a Unix command and is the default shell for most Linux distributions. It cannot understand Python code, so it gives out this error.
It might not give an error on the first line of the code and will give the error later because it might interpret some of the code as a shell command.
Fix Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token '(' in Python
There are multiple ways to fix this error in Python. The fixes vary between Linux and Windows because these operating systems work differently.
Solutions for Linux
The path to the interpreter should be added to the code file so that the computer knows the interpreter has to run this file and not the shell terminal. We should add the following line at the top of the code file:
#Python 3.x
#!/usr/bin/env python
It runs the file from the Python interpreter, not the Bash shell. We have to note that this is not a Python comment.
Instead, this shell command starts the Python environment in the shell before running the code. The user can also run the code file on the shell by giving the python command before the file name, like python filename.py.
It also does the same and runs the file from the Python interpreter. If we have both Python 2 and 3 installed, we need to write python3 if we want to run the code using Python 3. And just python if we want to run the code using Python 2.
Example Code:
#Python 3.x
#!/usr/bin/env python
print("Hello World")
Output:
Solution for Windows
In Windows, the user can also use the python keyword in the terminal to run the code file, but before doing so, the path to the Python interpreter needs to add to the PATH variable of Windows. The steps to do that are:
- Search for
envin the Windows search bar and open theEdit the system environment variablesoption. - Now open the
Environment Variables. - Now, choose the
PATHvariable and click onEdit. - Paste the interpreter’s path in an empty field in this window.
- The path to the interpreter is now added to the user’s Windows, and we can use the
pythoncommand to run the code files from the shell.
Now we need to write the following in a terminal to run the code:
#Python 3.x
python filename.py
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and
privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub?
Sign in
to your account
Comments
-
I am on the latest Poetry version.
-
I have searched the issues of this repo and believe that this is not a duplicate.
-
If an exception occurs when executing a command, I executed it again in debug mode (
-vvvoption). -
OS version and name: macOS 10.14.6 Mojave
-
Poetry version: Poetry (version 1.2.0a2)
-
Link of a Gist with the contents of your pyproject.toml file: N/A
Issue
Generated a completion file for bash via poetry completions bash > /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion due to poetry completions bash > /etc/bash_completion.d/poetry.bash-completion not having the /etc/bash_completion.d directory on Mac. Sourced in .bashrc and wound up with a bunch of syntax errors that I had to comment out (i.e., not use.)
.bashrc
. /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion
/usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion
-bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: syntax error near unexpected token `clear' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: ` (cache clear)' $ which poetry /usr/local/bin/poetry $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 44: syntax error near unexpected token `list' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 44: ` (cache list)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 56: syntax error near unexpected token `info' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 56: ` (debug info)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 60: syntax error near unexpected token `resolve' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 60: ` (debug resolve)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 64: syntax error near unexpected token `info' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 64: ` (env info)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 68: syntax error near unexpected token `list' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 68: ` (env list)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 72: syntax error near unexpected token `remove' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 72: ` (env remove)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 76: syntax error near unexpected token `use' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 76: ` (env use)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 108: syntax error near unexpected token `add' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 108: ` (plugin add)' $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 112: syntax error near unexpected token `remove' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 112: ` (plugin remove)' $ !! source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 116: syntax error near unexpected token `show' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 116: ` (plugin show)' $ !! source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 136: syntax error near unexpected token `update' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 136: ` (self update)' $ $ !! source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 148: syntax error near unexpected token `add' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 148: ` (source add)' $ !! source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 152: syntax error near unexpected token `remove' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 152: ` (source remove)' $ !! source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 156: syntax error near unexpected token `show' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 156: ` (source show)' $ !! source ~/.bashrc $
Full poetry.bash-completion
Attached the generated completion file with commented out lines.
Hi,
Can you add the version of bash you are using and how you installed Poetry and bash ?
I have tested your file with bash 5.1.8 on High Sierra and it worked properly.
bash was installed via brew and poetry is pip.
$ bash --version GNU bash, version 5.0.11(1)-release (x86_64-apple-darwin18.6.0) Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html> This is free software; you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. $ pip list Package Version ------------------ --------- ... poetry 1.2.0a2 poetry-core 1.1.0a6
Updated bash to 5.1.8(1)-release. Re-ran the completion command and get this:
$ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: syntax error near unexpected token `clear' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: ` (cache clear)'
Did you check the value of $BASH_VERSION ?
IIRC, it’s used by bash completion to load its helper functions and if it’s too old it won’t but without a warning.
An mismatched value can happen for the following reason: your login shell is still configured to point on the macOS provided bash and your «Shell opens with» Terminal setting is set to «Default login shell».
You have two options here:
- Change «Shell opens with» to point to your brew bash
- Change the default shell used when you login keeping the «Shell opens with» default value
For number 2, you need to add your brew bash path to the list of available shells in /etc/shells (requires root access) and then use chsh -s <path/to/bash> as your current user.
Good catch with $BASH_VERSION. It was pointing to the old v3.x version of bash while the shell itself was up-to-date and the $PATH called the right one when checking the version 🤔
Set both the absolute path in iTerm (login shell to custom shell) to the brew bash and appending the same to /etc/shells, I’m now getting:
$ echo $BASH_VERSION 5.1.8(1)-release
Re-ran poetry completions bash > /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion, but no joy:
$ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: syntax error near unexpected token `clear' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: ` (cache clear)'
From the looks of it, you did not install the bash-completion package.
Do that first and then put the poetry completion file under /usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d/.
This is what I’ve been doing:
$ poetry completions bash > /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion $ ll /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion -rw-r--r-- 1 lance.stephens admin 4.4K Oct 6 12:56 /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion $ grep 'poetry.bash-completion' ~/.bashrc . /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion $ source ~/.bashrc -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: syntax error near unexpected token `clear' -bash: /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion: line 40: ` (cache clear)'
Which appears to be supported according to poetry help completions.
I’m getting the same issue here on Ubuntu using the exact same commands and when i try to run it as a bash script normally. I have updated my bash and bash-completions to no avail.
The problem seems to be that completions for subcommands are written like
(command subcommand)
opts="${opts} ..."
;;
which isn’t valid bash as far as i can tell. Separating the command and subcommand with a space doesn’t seem to work.
But i’m no expert so take that with a grain of salt.
This only is a problem with 1.2.0a2 and doesn’t exist in 1.1.0
I suspect this is an issue with cleo as we use it to handle the CLI ux, the issue seems to be how subcommands are being handled.
This one still fails accross all platforms.
$ poetry --version Poetry (version 1.2.0b2dev0) $ echo $BASH_VERSION 5.1.16(1)-release $ poetry completions bash | bash bash: line 40: syntax error near unexpected token `clear' bash: line 40: ` (cache clear)'
TentacleHorn, dgcnz, rjlasko, dapicester, and relaxdiego reacted with eyes emoji
abn
mentioned this issue
May 11, 2022
This was referenced
Sep 9, 2022
Can we reopen this issue as it is still a problem and the PR that was supposed to close it, did actually do it (see there)?
@LordFckHelmchen AFAIK, it should affect future release. You probably have to compare release dates and when pull request with fix was accepted (or git log for that release). I’ve been ranging first too (because it looked like maintainers have closed an open issue), until I’ve read full discussion. And, as always, patches are welcome.
Thanks to maintainers for the support.
The poetry maintainers are playing whack-a-mole with duplicate tickets. Poetry users will probably keep creating more issues for this bug as long as the bug still exists in the latest version of poetry, and an open issue for the bug doesn’t exist. Hand-waving at an upstream repo and closing all of the issues makes it extremely difficult to follow what’s going on.
Suggestion: leave 1 issue open for this bug in poetry and link it to the root cause issue in cleo.
Edit: This issue might be a good one to use, since it’s linked to the cleo PR
I personally haven’t looked at this issue for a minute (it merely lives in my ‘common duplicates’ doc) — looks like it was closed by mistake as the Cleo PR should have specified Relates-To or similar. This shouldn’t be closed in Poetry until after the Cleo release and subsequent bump of our constraint.
If anyone wants working bash completion for poetry now, I created a gist: https://gist.github.com/raffraffraff/36b7a8cd1a4308150d7f843724a19ff9
I wanted an excuse to learn the poetry syntax, plus having decent shell completion makes learning it much easier.
YMMV, but it’s working great for me. It’s able to complete commands, positional args and options, and even suggests package names, source names, config options and caches where appropriate (and I don’t think the official shell completion will do that).
@raffraffraff without pull request it will be lost in the internet for sure. (I have fixed completions with vim+macros in <1 min).
@koutoftimer I didn’t send a pull request because poetry uses cleo for bash completions, but my script is ‘hand made’. I’m just sharing here in case it’s useful to others.
This is well-known and universal; please refrain from «me too» as it only adds noise and distracts the people trying to get Cleo 1.0 over the finish line so we can ship the (already merged) fix 😄
Completion bugs are now fixed with the incoming release.
When is version 1.3.0 expected to be published?
When it’s ready/the maintainers have had time to finalize the changelog (including any late merges).
If you go to the «watch» dropdown for this repository in the upper right corner of the page and click «custom», you can select to be notified of releases, which should send you an alert when 1.3.0 is published.
Just wanted to close the loop here (know the issue is closed haha) — running bash 5.2.15 and poetry 1.3.2 appears to have resolved the completion errors after re-exporting the completion script via
poetry completions bash > /usr/local/etc/profile.d/poetry.bash-completion
Appreciate everyone’s help 🙏
|
triatri3 11 / 12 / 8 Регистрация: 16.11.2016 Сообщений: 892 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
07.01.2019, 20:14. Показов 15555. Ответов 5 Метки нет (Все метки)
Ошибки в строках 2 и 3: unexpected token ‘<newline>’
__________________
0 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
07.01.2019, 20:14 |
|
5 |
|
Catstail Модератор 33878 / 18905 / 3981 Регистрация: 12.02.2012 Сообщений: 31,695 Записей в блоге: 13 |
||||
|
07.01.2019, 21:38 |
2 |
|||
|
Найди одно отличие:
https://ideone.com/ZmmZdQ
0 |
|
triatri3 11 / 12 / 8 Регистрация: 16.11.2016 Сообщений: 892 |
||||
|
08.01.2019, 12:07 [ТС] |
3 |
|||
|
Извините, не то вставил. Вот полный код
Найди одно отличие: Да, я взял готовый код откуда-то на этом форуме. Возможно у Вас. Не разрешаете его использовать?
0 |
|
Модератор 33878 / 18905 / 3981 Регистрация: 12.02.2012 Сообщений: 31,695 Записей в блоге: 13 |
|
|
08.01.2019, 12:15 |
4 |
|
РешениеА этот код содержит две ошибки и не запустится. Подсказать, или сам найдешь?
0 |
|
Просто Лис 4832 / 3155 / 991 Регистрация: 17.05.2012 Сообщений: 9,201 Записей в блоге: 9 |
|
|
08.01.2019, 13:43 |
5 |
|
РешениеЯ подскажу. Пропущено два двоеточия. Добавлено через 30 секунд
1 |
|
Dax Модератор 1351 / 648 / 207 Регистрация: 23.03.2014 Сообщений: 3,053 |
||||
|
09.01.2019, 11:07 |
6 |
|||
0 |
Содержание
- Error: Bash: Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token ‘(‘ in Python
- Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token ‘(‘ in Python
- Fix Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token ‘(‘ in Python
- Solutions for Linux
- Solution for Windows
- bash: синтаксическая ошибка рядом с неожиданным токеном `(‘ — Python
- 4 ответы
- Bash Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token: How to Fix It
- One Approach to Fix Them All
- Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token ‘(‘
- Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Then (Example 1)
- Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Then (Example 2)
- Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Done
- Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token fi
- Conclusion
- Исправить синтаксическую ошибку Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном
- Как исправить синтаксическую ошибку Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном
- Способ 1: исправить ошибки в каждой командной строке вручную
- Шаг I: Чтение содержимого файла
- Шаг II. Удалите разрывы строк Windows
- Шаг III: Установите разрешения для вновь созданного файла
- Шаг IV: форматирование кода в файле
- Способ 2: переписать код
- Способ 3: используйте команду Dos2unix.exe
Error: Bash: Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token ‘(‘ in Python
Every time a Python code runs through a shell terminal such as Bash, it must point to an interpreter. If Bash cannot find a suitable way to run the file, then it will give out errors.
This guide will discuss Error: Bash: syntax error near unexpected token ‘(‘ .
Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token ‘(‘ in Python
Python needs to be installed on your computer for the interpreter to find and run the Python files. The interpreter works differently in different operating systems.
In Windows, when we install Python, a program called IDLE is installed on the computer, which comes with the interpreter. It runs Python codes.
In Linux, we can access Python using the shell terminal by typing the command python . It opens the Python environment where the code can be written and run.
If the code has trouble finding the Python interpreter, it will run on whichever shell it runs. If the user runs the code from the Bash terminal, then the shell will give an error that will resemble this:
Bash is a Unix command and is the default shell for most Linux distributions. It cannot understand Python code, so it gives out this error.
It might not give an error on the first line of the code and will give the error later because it might interpret some of the code as a shell command.
Fix Error: bash: syntax error near unexpected token ‘(‘ in Python
There are multiple ways to fix this error in Python. The fixes vary between Linux and Windows because these operating systems work differently.
Solutions for Linux
The path to the interpreter should be added to the code file so that the computer knows the interpreter has to run this file and not the shell terminal. We should add the following line at the top of the code file:
It runs the file from the Python interpreter, not the Bash shell. We have to note that this is not a Python comment.
Instead, this shell command starts the Python environment in the shell before running the code. The user can also run the code file on the shell by giving the python command before the file name, like python filename.py .
It also does the same and runs the file from the Python interpreter. If we have both Python 2 and 3 installed, we need to write python3 if we want to run the code using Python 3. And just python if we want to run the code using Python 2.
Solution for Windows
In Windows, the user can also use the python keyword in the terminal to run the code file, but before doing so, the path to the Python interpreter needs to add to the PATH variable of Windows. The steps to do that are:
- Search for env in the Windows search bar and open the Edit the system environment variables option.
- Now open the Environment Variables .
- Now, choose the PATH variable and click on Edit .
- Paste the interpreter’s path in an empty field in this window.
- The path to the interpreter is now added to the user’s Windows, and we can use the python command to run the code files from the shell.
Now we need to write the following in a terminal to run the code:
I am Fariba Laiq from Pakistan. An android app developer, technical content writer, and coding instructor. Writing has always been one of my passions. I love to learn, implement and convey my knowledge to others.
Источник
bash: синтаксическая ошибка рядом с неожиданным токеном `(‘ — Python
задан 20 мая ’12, 19:05
Сообщение об ошибке указывает, что скрипт выполняется bash, а не python. Попробуйте добавить #!/usr/bin/python как первая строка файла. — tripleee
почему ваша первая строка закомментирована? — zmo
4 ответы
Добавить #!/usr/bin/env python в верхней части вашего сценария или вызовите свой сценарий, используя python myscript.py
ответ дан 20 мая ’12, 19:05
Это должен был быть принятый ответ. Я совершал эту ошибку более чем несколько раз. — Вилли Чалмерс III
Вы вводите это в командной строке unix? Вы должны делать это внутри среды Python, т.е. тип python по подсказке и работать оттуда.
Кроме того, нет ; нужно в конце строки в Python
@Эрри, не надо чувствовать себя глупо, мы все были там 🙂 — Левон
или, но я предпочту использовать вышеуказанный.
Если вы установили python 2 и python 3 и python 2 по умолчанию, вы можете запустить python 3 с помощью этой команды
ответ дан 27 мар ’20, в 08:03
Ну у меня была точно такая же проблема. Я пробовал все, и ничего действительно не работало. Моя программа отлично работала в командной строке Windows и на моем интерпретаторе приложения Python для iPhone, но не на терминале моего Macbook, где я всегда получал следующую ошибку всякий раз, когда пытался запустить программу:
bash: синтаксическая ошибка рядом с неожиданным токеном `(‘
Наконец, комментарий выше от пользователя тройной помог мне найти решение; хотя его решение добавления !/usr/bin/python в самом начале моего кода это не помогло мне понять, как он написал это:
Сообщение об ошибке указывает, что скрипт выполняется bash, а не python.
Источник
Bash Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token: How to Fix It
Have you ever seen the message “syntax error near unexpected token” while running one of your Bash scripts?
In this guide I will show you why this error occurs and how to fix it.
Why the Bash unexpected token syntax error occurs?
As the error suggests this is a Bash syntax error, in other words it reports bad syntax somewhere in your script or command. There are many things that can go wrong in a Bash script and cause this error. Some common causes are missing spaces next to commands and lack of escaping for characters that have a special meaning for the Bash shell.
Finding the syntax error reported when you execute your script is not always easy. This process often requires you to change and retest your script multiple times.
To make your life easier I have analysed different scenarios in which this syntax error can occur. For every scenario I will show you the script or command with the error and the fix you need to apply to solve the problem.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
One Approach to Fix Them All
Considering that this syntax error can occur in multiple scenarios you might not be able to find your exact error in the list below.
Don’t worry about it, what matters is for you to learn the right approach to identify what’s causing the error and knowing how to fix it.
And going through the examples below you will learn how to do that.
In some of the examples I will show you how to fix this error if it happens while executing a single command in a Bash shell.
In other examples we will look at Bash scripts that when executed fail with the “unexpected token” error.
To fix the error in a single command it’s usually enough to add or remove some incorrect characters that cause the syntax error in the command.
Knowing how to fix the error in a script can take a bit more time, and for that I will use the following 5-step process:
- Run the script that contains the syntax error.
- Take note of the line mentioned by the Bash error.
- Execute the line with the error in a Bash shell to find the error fast (without having to change the script and rerun it multiple times).
- Update your script with the correct line of code.
- Confirm the script works.
It’s time for the first scenario.
Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token ‘(‘
Let’s say I have the following file on my Linux system:
And I want to rename it to report_july.csv.
I can use the following command, right?
When I run it I get the following error:
Because parentheses () are used in Bash to create a subshell. In other words they are special characters.
And Bash special character need to be escaped if used as normal characters in a command. The backslah is used to escape characters.
I will update the command to include the backslash before both parentheses:
No errors this time:
Lesson 1: Remember to escape Bash special characters when you use them as normal characters (literals) in a filename or string in general.
First error fixed!
Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Then (Example 1)
And here is the second scenario.
When I run the following script:
I get back the error below:
Can you see why?
The error is caused by the missing space between if and the open square bracket ( [ ).
And the reason is the following:
if is a shell builtin command and you might be thinking you are using if here. But in reality the shell sees if[ that is not a known command to the shell.
At that point the shell doesn’t know how to handle then given that it hasn’t found if before, and it stops the script with the error above.
The correct script is:
I have just added a space between if and [ so the shell can see the if command.
And the output of the script is correct:
Lesson 2: Spaces are important in Bash to help the shell identify every command.
Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Then (Example 2)
While writing Bash scripts, especially at the beginning, it’s common to do errors like the one below:
When you run this one-liner here’s what you get:
Let’s find out why…
The syntax of a for loop in Bash is:
And using a single line:
So, as you can see the semicolon is used in Bash to separate commands when you want to write them on a single line.
The reason why the semicolons were not required in the first version of the script is that the newline is a command separator too.
Now, let’s go back to our error…
The one-liner that was failing with an error contains the then statement that as you can see is not part of the structure of a for loop.
The error is telling us:
- There is a syntax error.
- The token ‘then‘ is unexpected.
Let’s confirm the one-liner runs well after removing then:
Lesson 3: When you see a syntax error verify that you are using Bash loops or conditional constructs in the right way and you are not adding any statements that shouldn’t be there.
Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token Done
I have created a simple script in which an if statement is nested inside a while loop. It’s a very common thing to do in Bash.
This script might seem ok, but when I run it I get the following…
The done and fi statements are correctly used to close the while loop and the if conditional statement. But they are used in the wrong order!
The if statement is nested into the while loop so we should be closing the if statement first, using fi. And after that we can close the while loop using done.
Let’s try the script:
Lesson 4: Nested loops and conditional statements need to be closed in the same order in which they are opened.
Syntax Error Near Unexpected Token fi
Let’s look at another scenario in which this syntax error can occur with the fi token:
And this is what I get when I run it:
In this case the Bash shell identifies the if statement and because of that it expects then after it.
As you can see then is there, so what’s the problem?
There is no command separator between the [ ] command (yes….it’s a command) and the then statement.
So, what’s the fix?
Add a command separator immediately after the closing square bracket. We will use the semicolon ( ; ) as command separator.
Our script becomes:
And if I run it I get the correct output:
Lesson 5: Remember to specify command separators in your Bash scripts. Either the semicolon or the newline.
Conclusion
You now have what you need to understand what causes this syntax error in your scripts. You can apply the 5 lessons I have explained in this guide to find a fix.
Take the time to review the lessons at the end of each section so they become part of your Bash knowledge.
If you have any questions please feel free to write them in the comments below.
Now, let’s say you have saved your Bash script using Windows.
And when you run it in Linux you are seeing a syntax error that you can’t really explain because the script looks correct to you.
You might be having the problem explained in this article.
Enjoy your scripting!
Related FREE Course : Decipher Bash Scripting
Источник
Исправить синтаксическую ошибку Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном
Кодирование в терминале Linux Bash стало преобладающей практикой в секторе кодирования. Инженеры-программисты и студенты, изучающие язык программирования, сталкиваются с различными ошибками. Если вы неоднократно сталкивались с такими ошибками, как Синтаксическая ошибка рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘ или Синтаксическая ошибка Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном, вы можете попробовать использовать методы, описанные в статье, и стать опытным программистом. Прочитайте методы, описанные в статье, в разделе порядок описан и исправьте ошибки в командных строках вашего файла.
Как исправить синтаксическую ошибку Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном
Linux Bash — интерпретатор командной строки для системы на базе Linux, заменяющий Bourne Shell или sh. Файлы именуются в формате .sh в сценариях Linux Bash. Если в коде сценария оболочки есть проблемы с форматированием, вы можете столкнуться с синтаксической ошибкой. Если ошибка близка к символу (, оболочка подскажет вам ошибку в строке и отобразит ошибку в соответствующей строке. Поскольку Linux Bash является интерпретатором, строка с ошибкой будет возвращена вам в Терминал, и он прекратит сканирование остальных команд в сценарии. Следовательно, вам необходимо исправить ошибку в конкретной командной строке и перейти к следующей, чтобы исправить непредвиденную ошибку токена в сценарии оболочки. Причины синтаксиса ошибка рядом с неожиданным токеном в Linux Bash перечислены ниже в этом разделе, как показано ниже:
Кодирование с помощью escape-последовательностей. Если вы написали код в сценарии Bash, escape-последовательности или кавычки в сценарии могут вызвать ошибки. Чтобы исправить ошибку, управляющие последовательности и кавычки должны быть записаны в правильном формате.
Неправильный синтаксис в файле кодирования. Синтаксис в коде может привести к синтаксической ошибке, если команда написана с неправильным синтаксисом, например, с изменением порядка циклов.
Неправильное использование команды. Если вы неправильно используете команду, например, присваиваете неверное значение, у вас может возникнуть синтаксическая ошибка.
Несовместимая ОС в системах. Если оболочка для сценария кодирования несовместима между системами Unix и DOS, у вас может возникнуть непредвиденная ошибка.
Проблемы в сценарии оболочки bash. Проблемы, выполняемые в сценарии оболочки bash в файле, скопированном из другой системы, могут привести к непредвиденной ошибке токена.
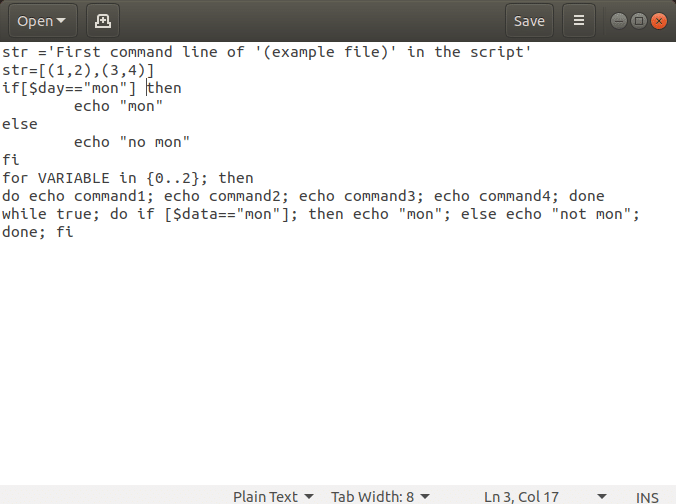
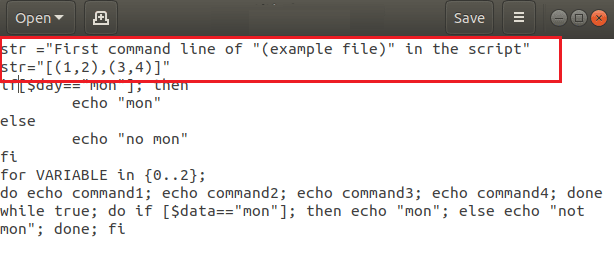
Рассмотрим файл с именем example.sh, созданный в сценариях Linux Bash со следующими командными строками для пояснений. Файл примера допускает синтаксические ошибки и включает все возможные команды, которые можно использовать в сценарии оболочки.
Способ 1: исправить ошибки в каждой командной строке вручную
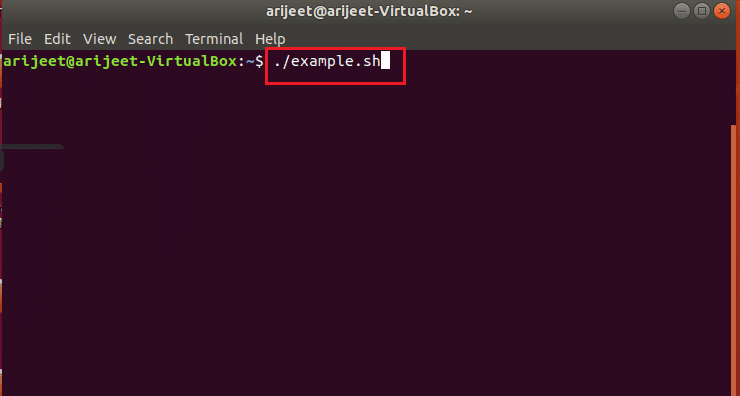
Первый способ исправить ошибки — исправить синтаксическую ошибку вручную в каждой командной строке скрипта. В этом разделе обсуждаются шаги по устранению синтаксических ошибок рядом с неожиданным токеном в командных строках. Процесс исправления непредвиденной ошибки токена в Терминале описан ниже. Запустите файл в Терминале, введя команду ./example.sh и нажав клавишу Enter.
2. Обратите внимание на строки с непредвиденной ошибкой токена в командных строках результата ниже.
3. Исправьте ошибку в каждой строке, следуя описанным ниже методам по отдельности и сохранив файл.
4. После внесения изменений снова запустите файл и проверьте, устранена ли синтаксическая ошибка в файле.
Шаг I: Чтение содержимого файла
Первым шагом к устранению синтаксической ошибки в командной строке является чтение файла в Терминале. ЕСЛИ есть проблемы с файлом, возможно, вы не сможете просмотреть файл. Обычная практика просмотра файла заключается в запуске файла с помощью команды ./example.sh, но вы не можете изменить содержимое файла. Варианты просмотра содержимого файла и изменения командных строк для исправления синтаксической ошибки рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘ обсуждаются ниже.
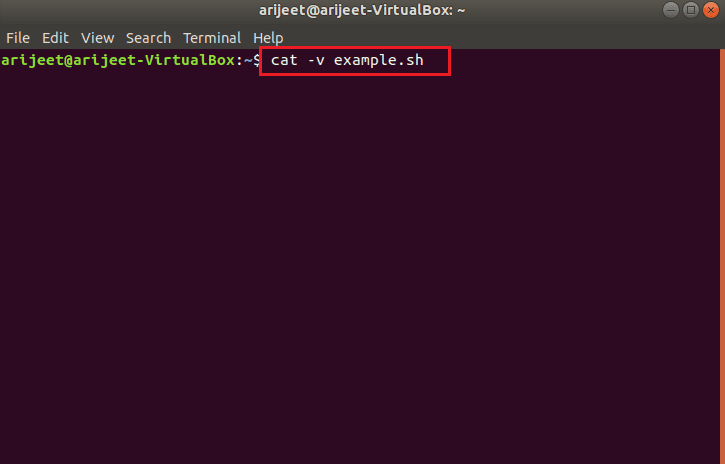
Вариант 1: через CAT-команду
Первый вариант — использовать команду cat для просмотра файла в сценарии оболочки. Прочтите содержимое файла с неожиданной ошибкой токена с помощью команды cat, введя команду cat –v example.sh в Терминале.
Примечание 1. Файл example.sh используется в пояснительных целях, и вам необходимо ввести имя файла с непредвиденной ошибкой токена.
Примечание 2. Команда cat –v используется для отображения всех невидимых символов, которые могут представлять собой возврат каретки или пробел без разрыва.
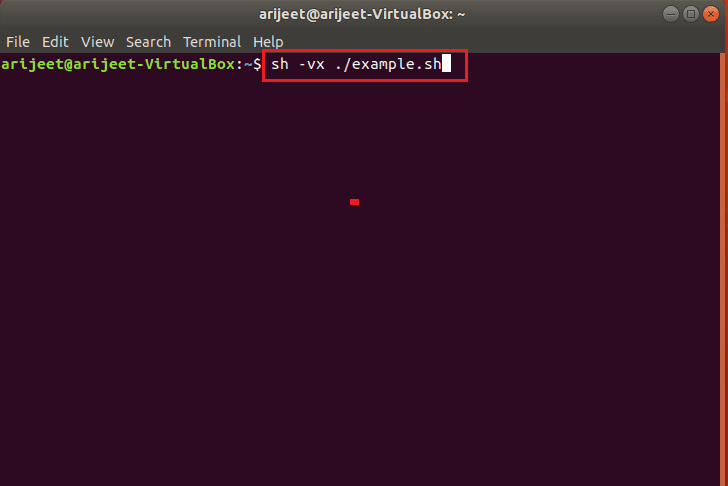
Вариант 2: Через команду VX
Если вы не можете использовать команду cat, вы можете попробовать использовать команду vx для просмотра и изменения команд в файле, используя шаг, указанный ниже. Введите команду sh –vx ./example.sh в Терминале, чтобы открыть файл.
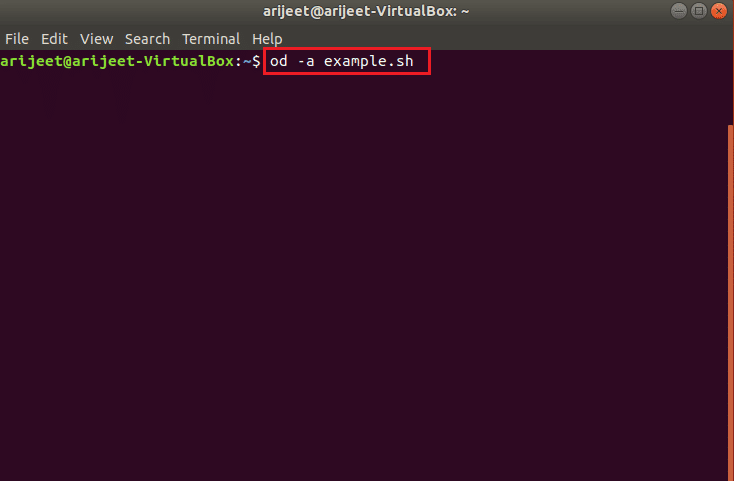
Вариант 3: Через od –a Command
3. Если в командной строке есть несколько невидимых символов, вы можете использовать команду od –a для просмотра файла. Если содержимое файла не видно в файле кода, вы можете попробовать прочитать файл, используя команду od –a example.sh для изменения кода.
Шаг II. Удалите разрывы строк Windows
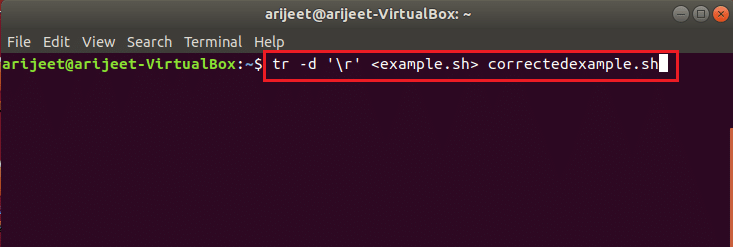
Если в сценарии оболочки есть разрывы строк Windows, вы можете использовать консольные команды, чтобы удалить разрывы строк и скопировать строки кода в новый файл, чтобы исправить ошибку.
Введите следующую команду в Терминале, чтобы сохранить содержимое файла в другой файл с именем correctedexample.sh, чтобы удалить разрывы строк Windows в сценарии.
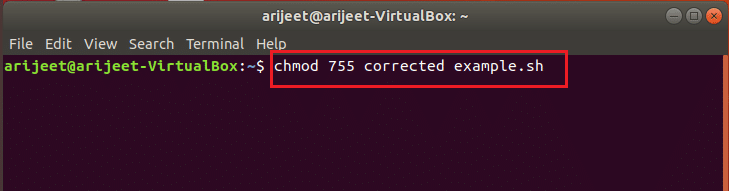
Шаг III: Установите разрешения для вновь созданного файла
Вам необходимо установить разрешение для вновь созданного файла для редактирования файла, чтобы файл можно было выполнить в оболочке. Введите команду как chmod 755 correctedexample.sh в Терминале, чтобы предоставить права доступа к файлу и запустить файл. Теперь вы можете просмотреть исправленный файл и исправить проблемы с форматированием, а также исправить синтаксическую ошибку рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘ в файле.
Шаг IV: форматирование кода в файле
Второй шаг — отформатировать строки кода по отдельности и вручную изменить командные строки в файле. Варианты форматирования файла для исправления синтаксической ошибки рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘ обсуждаются ниже в этом разделе.
Вариант 1: заменить одинарные кавычки двойными кавычками
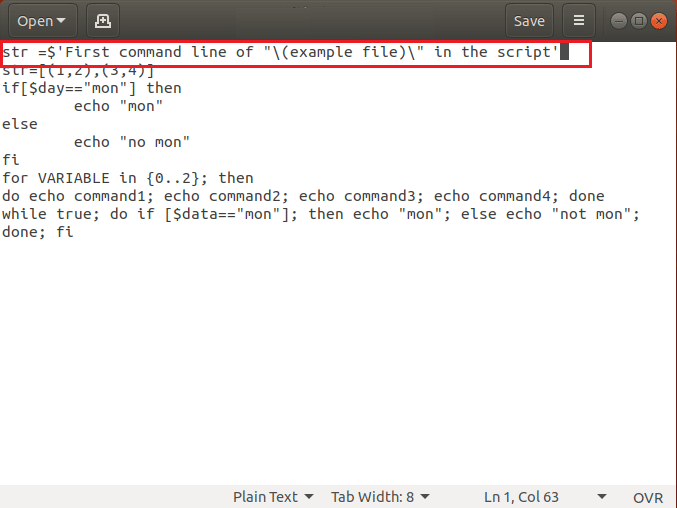
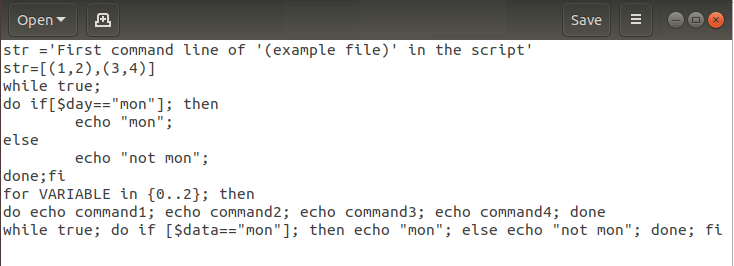
Если вы используете одинарные кавычки в командной строке, вам нужно изменить команду, заменив одинарную кавычку двойными, чтобы исправить синтаксическую ошибку. В файле example.sh удалите строки кода, содержащие ‘ и ‘ или одинарные кавычки в команде, и замените одинарные кавычки двойными кавычками или » и ». Здесь, в файле примера, вам нужно изменить код как str= «Первая командная строка «(файл примера)» в скрипте»
Примечание. Двойные кавычки необходимы для команд типа параметра, таких как str= “[(1,2),(3,4)]».
Вариант 2: добавить $ к строковым строкам
Если вы добавили строковые значения в скрипт, вам нужно добавить $ к строковым значениям, чтобы исправить синтаксическую ошибку в скрипте. Добавьте $ для командных строк со строковыми значениями, чтобы исправить непредвиденную ошибку. Здесь, в файле примера, измените командную строку как;
Примечание. Если вы используете $ в строковом значении, вы можете обойти escape-последовательность обратной косой черты, поскольку командные строки декодируются по стандарту ANSI C. Другими словами, используя $ для строкового значения, вы можете избежать использования двойных кавычек вместо одинарных в командных строках.
Вариант 3: преобразовать вкладки в пробелы
Пробелы, которые вы оставили между двумя операторами в команде, должны быть пробелами, а не табуляцией, чтобы исправить синтаксическую ошибку в сценарии. Если вы получаете ошибку на Cygwin, вы можете попробовать преобразовать вкладки в кодах в пробелы, чтобы исправить ошибку. Командная строка представлена ниже как;
Приведенную выше команду следует переписать, как показано ниже, чтобы исправить ошибку.
Вариант 4. Используйте escape-символы
Если вы используете символ bash, важно использовать escape-символ вместе с символом bash, чтобы исправить синтаксическую ошибку. Круглые скобки или () являются специальными символами bash в файле, поэтому вам нужно будет использовать escape-символ или обратную косую черту в командной строке, чтобы экранировать обычные символы для выполнения команды. Команда str= ‘Первая командная строка ‘(пример файла)’ в команде script’ не выдаст ошибку в Терминале, поскольку используется escape-символ.
Вариант 5. Используйте пробелы между символами
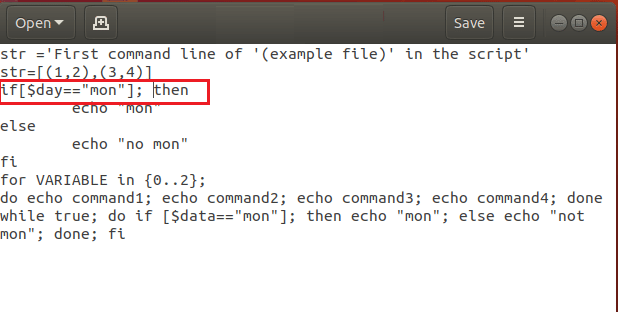
Сценарий оболочки распознает команды и операторы в сценарии по значениям по умолчанию. Вам необходимо обеспечить правильное использование пробелов между символами, чтобы оболочка могла идентифицировать команду, указанную в сценарии. Пробел — это символ, который используется для различения двух символов в командной строке. В коде нет пробела между if и [, which gives the unexpected token error as the if[ command is not identified by the shell. If the code is changed to if [ $ day == “mon” ]; тогда ошибка может быть решена с помощью команды бюллетеня оболочки, если она идентифицируется оболочкой.
Вариант 6. Используйте разделитель команд для операторов
Различные команды в сценарии оболочки должны быть разделены на операторы, чтобы Терминал мог идентифицировать отдельные команды. Вам нужно использовать разделитель команд, чтобы исправить синтаксическую ошибку в Linux Bash. Операторы в команде должны быть разделены разделителем команд, таким как точка с запятой или ; или новую строку, нажав клавишу Enter. Например, команда в коде if [ $ day == “mon” ] тогда нужно изменить, как если бы [ $ day == “mon” ]; затем исправить ошибку. Поскольку точка с запятой используется в качестве разделителя команд между символами [ and then, you can fix this error.
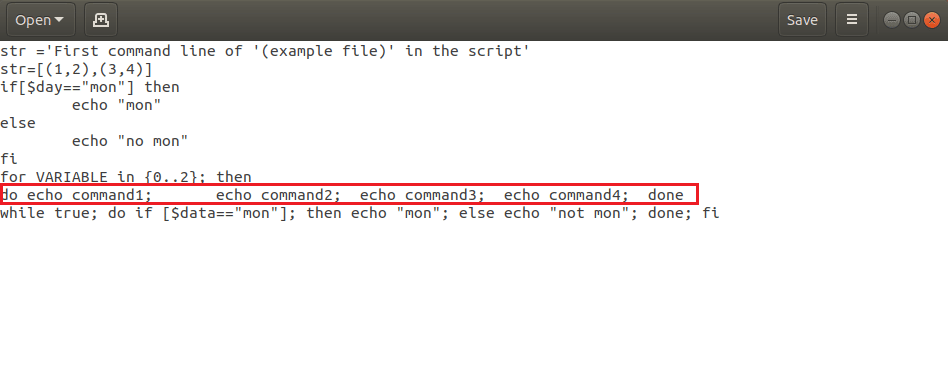
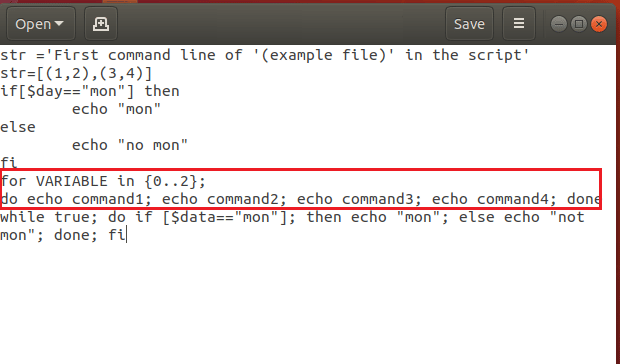
Option 7: Remove Additional Statements
Sometimes, you may have added additional statements or may have mixed up the codes in case of multiple nested loops. You need to remove the additional statements on the command lines to fix the Syntax error near unexpected token ‘(’ in the Linux Bash. The bash loops for…done or and the constructional constructs if… fi needs to be in the correct syntax. The example file has the wrong syntax in the for loop has the term then which is used in the if statement. Modifying the code as the following code will fix the unexpected token error. The statement then is an additional statement in the code and removing the term will fix the error.
Option 8: Ensure Order of Closing of Statements is Correct
If you are using many nested or conditional construct statements in the shell script, you have to ensure that the loops are closed in the order they are opened. You can use a new line separator to avoid conflicts with the loops. The order of closing the nested loops and conditional statements should be correct and must not be altered. The loops in the code while true; do if [ $ day == “mon” ]; затем эхо «мон»; иначе эхо «не пн»; Выполнено; fi нужно закрывать в правильном порядке. Изменение кода, как показано ниже, может исправить непредвиденную ошибку токена, поскольку порядок закрытия операторов исправлен.
Способ 2: переписать код
Если вы скопировали код и вставили его в новый файл в Терминале, вы можете попробовать переписать код вручную, чтобы исправить ошибку. Ошибки в коде можно исправить, если вы написали код без каких-либо ошибок формата в сценарии оболочки. Это связано с тем, что скрытые символы и проблемы с форматированием в текстовом редакторе, таком как Microsoft Word, которые вы могли использовать для копирования и вставки кода, могли привести к ошибке.
Способ 3: используйте команду Dos2unix.exe
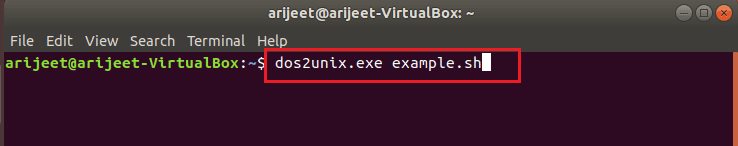
Если вы используете операционную систему Unix, вы можете писать коды с символом перевода строки как n, чтобы перейти к следующей строке в файле. Однако, если вы используете ОС Windows, вам нужно перейти к следующей строке в коде, используя возврат каретки и перевод строки или rn в файле. Если вы выполняете код, написанный в ОС Windows, в Cygwin, вы можете получить синтаксическую ошибку рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘.
Чтобы исправить ошибку, вам нужно очистить символы возврата каретки, используя инструмент командной строки DOS в Unix в качестве конвертера формата текстового файла. Введите следующую команду как dos2unix.exe example.sh в терминале, и вы сможете преобразовать файл в формат Unix.
В статье обсуждались основные методы исправления синтаксической ошибки Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном ‘(‘ в сценарии. Если вы используете Linux Bash, вы можете использовать методы, описанные в этом разделе, для исправления синтаксической ошибки Bash рядом с неожиданным токеном. Если вы Если вы прочитали всю статью и нашли ее содержание полезным, сообщите нам о своих предложениях и вопросах в разделе комментариев.
Источник



 Сообщение было отмечено triatri3 как решение
Сообщение было отмечено triatri3 как решение