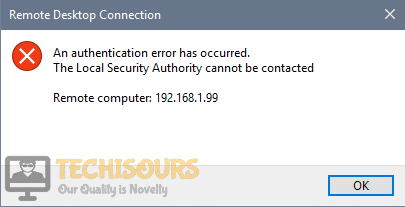
This error appears when users try to login to other computers via a remote desktop connection. The problem prevents them from connecting and it displays the “The Local Security Authority Cannot be Contacted” error message. The problem often appears after an update has been installed on either the client or the host PC and it causes plenty of problems on many different versions of Windows.
There have been many unofficial fixes for the problem which were created by the users who had the same unfortunate experience. We have gathered the working methods in this article so make sure you follow it in order to resolve the problem.
Pinpointing the correct cause for the problem is one of the most important steps when it comes to resolving one. That is why we have created a list of possible causes for the problem so make sure you check it out below:
- DNS addresses may be wrongly configured – If this is indeed the case, try using the DNS addresses provided by Google or OpenDNS
- Remote Desktop connections may be disabled by default on either the host or the client PC – Make sure you turn the option on to connect properly without errors.
- IP and DNS address conflicts – Running a certain command may help you resolve the problem
Solution 1: Change Your DNS Address
The problem is often caused by a faulty DNS setup which is simply not accepted by the host or its service. The problem can be resolved easily by changing your default DNS settings to use the ones provided by OpenDNS or Google. This can be done easily in Control Panel so make sure you follow the steps below carefully.
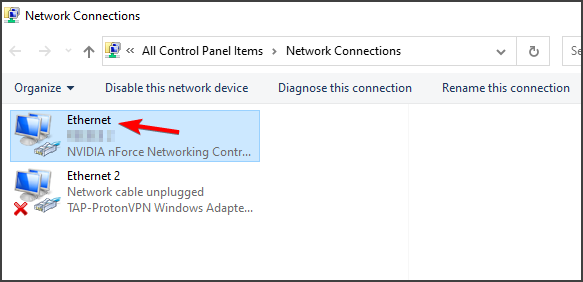
- Use the Windows + R key combo which should immediately open the Run dialog box where you should type ‘ncpa.cpl’ in the bar and click OK in order to open the Internet Connection Settings item in Control Panel.
- The same process can also be done by manually opening Control Panel. Switch the View by setting at the top right section of the window to Category and click on Network and Internet at the top. Click the Network and Sharing Center button in order to open it. Try to locate the Change adapter settings button at the left menu and click on it.
- Now that the Internet Connection window is open using any method above, double-click on your active network adapter and click on the Properties button below if you have admin permissions.
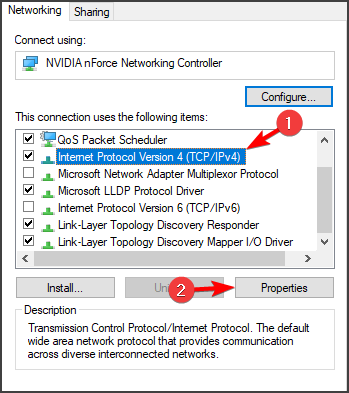
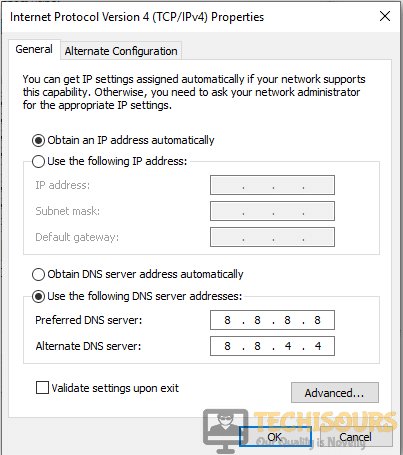
- Locate the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) item on the list. Click on it in order to select it and click the Properties button below.
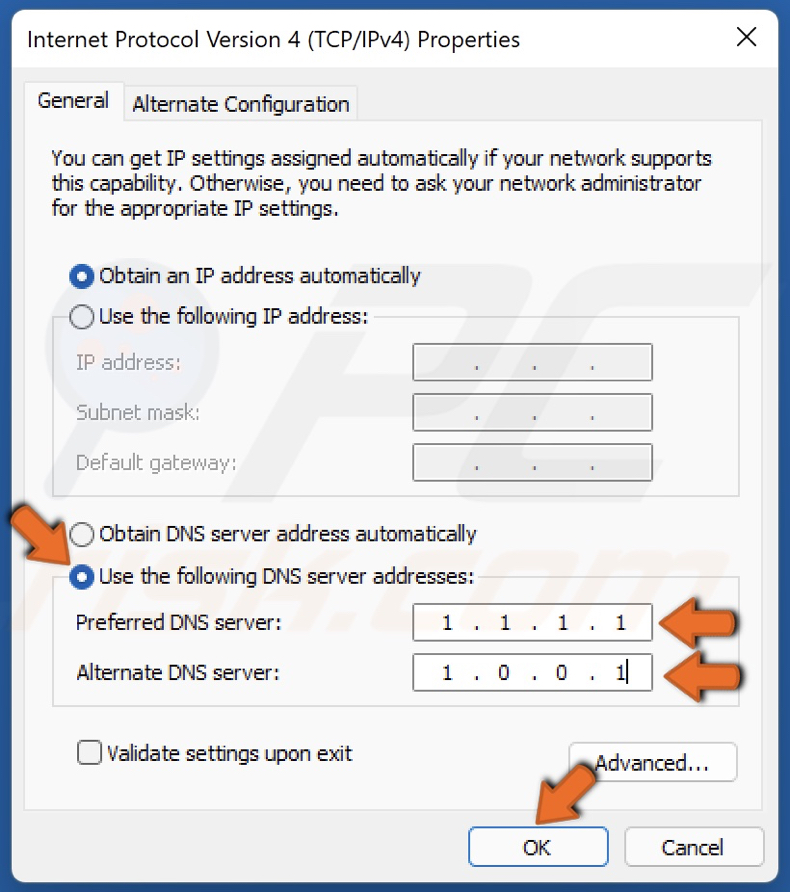
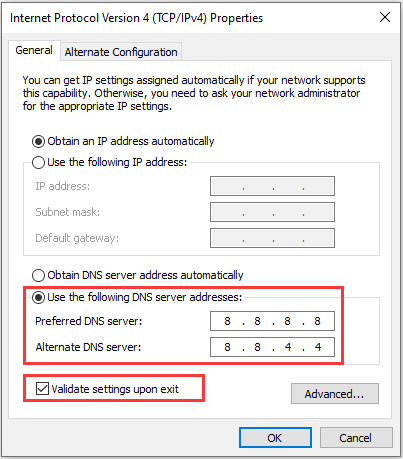
- Stay in the General tab and switch the radio button in the Properties window to “Use the following DNS server addresses” if it was set to something else.
- Set Preferred DNS server to be 8.8.8.8 and the Alternate DNS server to be 8.8.4.4
- Keep the “Validate settings upon exit” option checked and click OK in order to apply the changes immediately. Check to see if the same problem still appears!
Solution 2: Enable Remote Connections in Group Policy Editor
Sometimes the Group Policy on the client computer is preventing the remote Desktop connection completely. This can be changed quite easily in Group Policy Editor if you are running any version of Windows besides Windows Home. Follow the steps below in order to enable remote connections in Group Policy Editor.
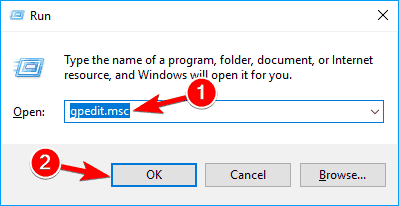
- Use the Windows Key + R key combination (tap the keys simultaneously) to open the Run dialog box. Enter “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog box, and press the OK button in order to open the Local Group Policy Editor tool. On Windows 10, you can try simply type Group Policy Editor in the Start menu and click the top result.
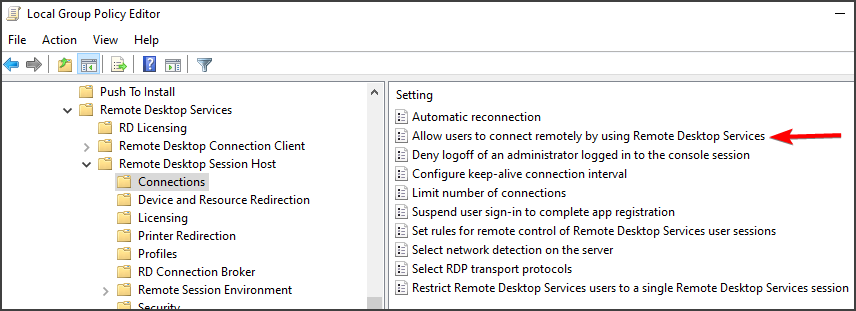
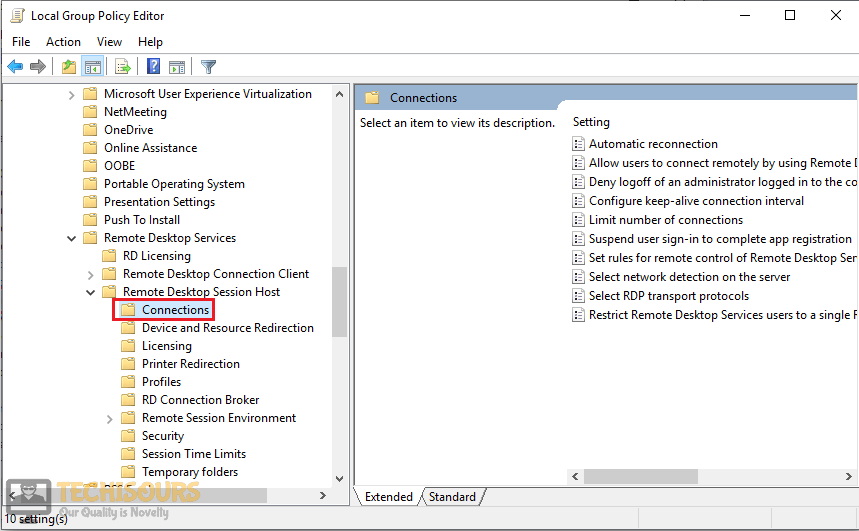
- On the left navigation pane of Local Group Policy Editor, under Computer Configuration, double click on Administrative Templates, and navigate to the Windows Components>> Remote Desktop Services >> Remote Desktop Session Host >> Connections.
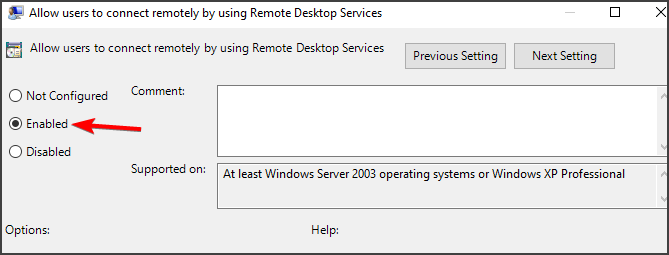
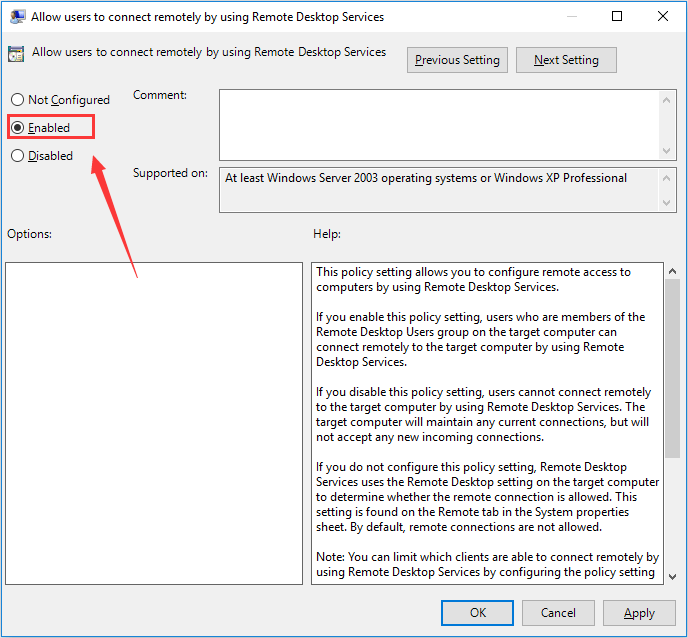
Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services - Select the Connections folder by left-clicking on it and check out its right side section.
- Double click on the “Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services” policy and check the radio button next to the “Enabled” option.
- Apply the changes you have made before exiting. The changes won’t be applied until you restart.
- Finally, reboot the computer to save the changes and check to see if you are still being targeted with the error.
Solution 3: Allow the Connection inside System Properties
The most common cause for the problem is the fact that remote access is, in one way or another, blocked on either the host or the client PC. This time, the problem may be with the host PC which may not be accepting connections from other PCs or the ones with another version of Remote Desktop running. Follow the steps below in order to fix this.
- Right-click either on My Computer/This PC depending on the version of Windows you have installed on your computer and choose the Properties
- After that, locate the Change settings button at the left side of the Properties window, under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings, and click on it.
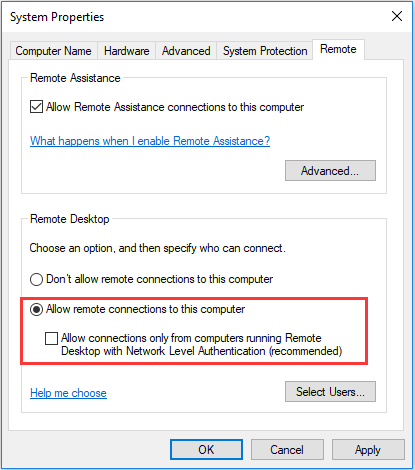
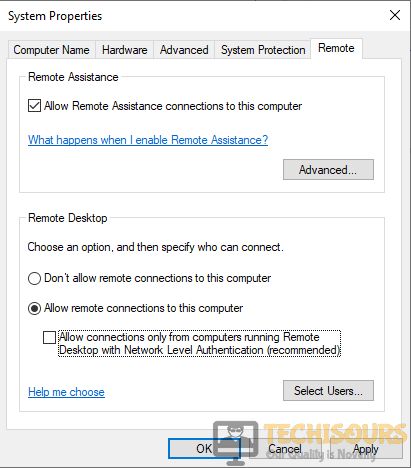
- In the Remote tab of System properties, check under Remote Desktop and click the radio button next to Allow remote connections to this computer. Also, uncheck the box next to the Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (recommended).
- Apply the changes you have made and check to see if the problem still appears.
Solution 4: Run a Helpful Command on the Host
This method is quite popular for its simplicity and plenty of people use it in order to fix most things related to connectivity issues. The funny thing is that it works and users have commented saying that this is the only step it took to resolve the problem. Try it out now!
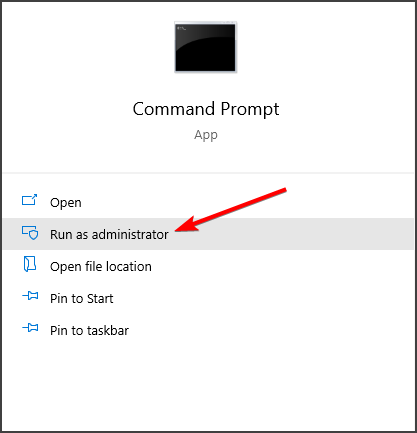
- Search for “Command Prompt” by typing it right in the Start menu or by pressing the search button right next to it. Right-click the first entry which will pop up as a search result and select the “Run as administrator” option from the context menu.
- Additionally, you can also use the Windows Logo Key + R key combination in order to bring up the Run dialog box. Type in “cmd” in the dialog box which appears and use the Ctrl + Shift + Enter key combination for administrative Command Prompt.
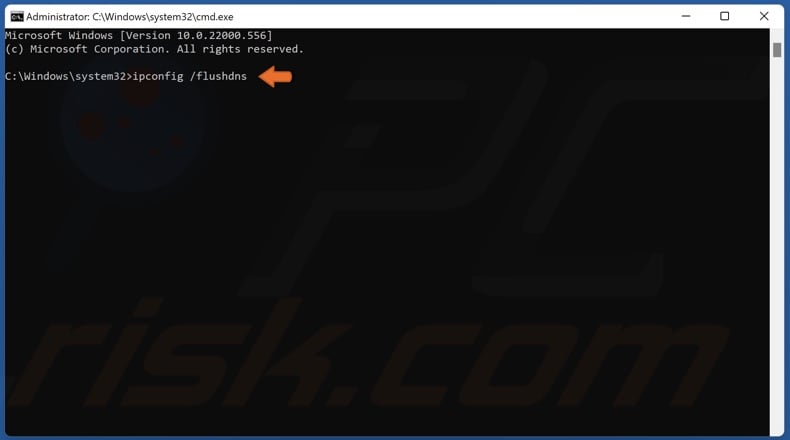
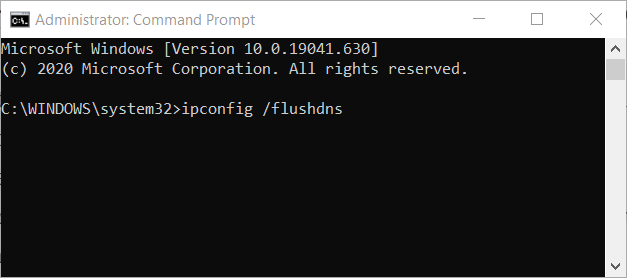
- Type in the following command in the window and make sure you press Enter after typing it out. Wait for the “Operation completed successfully” message or something similar to know that the method worked.
ipconfig/flushdns
- Try to reset the connection and check to see if the error still appears.
Solution 5: Set to Allow Connections from All Versions
Microsoft released an update to Windows 10 and Windows server to fix certain vulnerabilities and didn’t end up releasing one for Windows 7. Therefore, Windows 7 users were stuck on a different version. Therefore, you have to set up the connection in such a way that it allows connecting from any and all versions of Remote Desktop. However, keep in mind that this is much less secure than the latter option.
Kevin Arrows
Kevin is a dynamic and self-motivated information technology professional, with a Thorough knowledge of all facets pertaining to network infrastructure design, implementation and administration. Superior record of delivering simultaneous large-scale mission critical projects on time and under budget.
A very common error that states ” An Authentication Error Has Occurred. The local security authority cannot be contacted“, appears when a user tries to access another computer by logging into it through a remote desktop connection. This error mostly arises if the OS is updated on either the host or the client computer. To resolve this issue, go through this article and follow the steps explained.
What prevents you from contacting the Local Security Authority?
There are so many reasons that cause this error to pop up. Some of these reasons are listed below:
- The System Properties might be blocking the connection.
- This error can occur if the Remote connections are disabled in the group policies.
- If the DNS address is not configured correctly then this error message might pop up.
Pre Tips
This is a common error and is very easy to resolve. If you come across this error, before going to any major solution, follow some basic troubleshooting steps and check if the error s resolved.
- Remove your computer from the domain.
- Log in again as a local admin.
- Re-join the domain.
What to do if you get the “The Local Security Authority Cannot Be Contacted” Error?
Solution 1: Edit System Properties
Sometimes this error occurs because the access through remote connection is denied in the system properties. We can allow access through remote connections by following some simple steps.
- Click and pen This PC from the desktop.
- Right-click anywhere in the window and click Properties.
Properties - Now click Change settings from the right pane, under the Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings section.
Change Setting - Locate and open the Remote Tab.
- Check the radio button parallel to Allow remote connections to this computer.
Allow Remote Connections - Make sure you uncheck the box parallel to Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication.
- Click Apply and restart your PC.
Solution 2: Update your DNS Address
Sometimes changing the DNS address can resolve this issue. Follow the steps given below to change the DNS address of your machine.
- Click the search button in the taskbar. Type Control Panel and open it.
Control Panel - Click Network and Internet.
Network and Internet - Now click the Network and Sharing Center button.
Network and Sharing Center - Now click Change adapter settings button in the left pane.
Change adapter setting - Now Locate the network you are connected to, Right-click it and open properties.
Properties - Now locate and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4). After this click Properties.
IPv4 - Check the radio button parallel to Use the following DNS server addresses.
- Set the Preferred DNS server to 8.8.8.8 and Alternate DNS server to 8.8.4.4.
DNS address
Solution 3: Enable Remote Connections
If this error message still pops up, try to enable the remote connections in the group policies. To do this, follow the steps below:
- Click the search button in the taskbar and type gpedit.
Search - Click and open the Group Policies Editor.
- Under the Computer Configuration on the left pane, Locate and click Administrative Templates.
Administrative Templates - Locate and Click Windows Components.
Windows Components - Now Locate and click Remote Desktop Sevices to expand its components.
- Now click Remote Desktop Session Host and then click Connections.
Connections - On the right pane, double click Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.
Allow Users to Connect Remotely - A window will appear. Click the Enable button and then click OK.
Solution 4: Flush DNS using Command Prompt
If you still can’t get rid of this message, then try to flush DNS and check if the issue is resolved or not. Follow the steps below to carry this task out:
- In the taskbar, click the search button and type Command Prompt.
- Right-click the icon and click Run as Administrator.
Command Prompt - Type the following command and restart the PC.
ipconfig/flushdns
If you want further assistance, contact here. You can also contact Microsoft Support here.
Back to top button
-
Question
-
So I keep getting this error but I’m not sure why. Both machines are running Win 7 Ultimate using the Network Authentication Layer option for added security. I have exceptions in the firewall for remote desktop and yet it will not work.
Does someone know why? Is there something I need to do in local security to get this enabled?
Answers
-
-
Marked as answer by
Ronnie VernonMVP
Wednesday, October 14, 2009 11:22 AM
-
Marked as answer by
All replies
-
I’m having the same problem. I’m trying to connect to my Vista machine from my Win7 machine. If I log into the Vista machine once locally, then I’m able to connect from the Win7 Machine.
-
Proposed as answer by
Vendenberg
Friday, May 22, 2015 6:31 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
-
Marked as answer by
Ronnie VernonMVP
Wednesday, October 14, 2009 11:22 AM
-
Marked as answer by
-
Check that the account does not have an expired password, and that the account itself is not expired. In my case, the account password had expired, causing this error.
As soon as I changed the password, the error was no longer present.
-
Proposed as answer by
DavidRa
Sunday, November 15, 2009 3:36 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I had the same issue connecting to a machine that was part of a domain. The password of the domain account I was trying to connect was not expired.
What worked for me eventually was removing the computer from the domain logged in as a local admin (by changing it back to a workgroup), and then re-join the domain. [I did the join workgroup, re-join domain without a restart, and only did a restart at the
end].After that I was able to login via RDP using the domain account again.
-
Proposed as answer by
Chris1234567891
Thursday, August 13, 2015 5:45 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
That may work for one pc but I have many that are having this problem as I rollout Windows 7. Has anyone actually found a fix for this problem?
-
I’m having this problem as well. Or at least one related. I have a single physical server (not on domain), about 8 virtual servers all on a domain (including the domain controller), about 8 physical client machines (all on domain) and another
4 or so virtual machines (running «client OS» over remote desktop). Everything is Server2KR2 or Win7Ultimate. One of my physical Win7 machines and one of my virtual Win7 machines are somehow «different» in that if one attempts from either of
them to connect via remote desktop to any of the other Win7 machines in the house (the second machine can be P or V)
using an account that is not an administrator on the second machine I get the «Local security authority cannot be contacted» error. The account with which I’ve logged onto the first machine (admin or not on first machine, admin or not on second
machine) doesn’t appear to make a difference. -
I also have the «An authentication error has occurred. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» issue. I’m not very technical and I could not follow the info at the link in the above post marked «Answer.»
In looking at the other possible remedies, I don’t think a password is required on my account — if a password were required, would that mean I would have to use password every time I start Windows? And how do I know if my PC is part of a domain?
As a non-technical person, I hesitated to infiltrate a technical forum, but I have been trying everywhere to find a remedy for this issue so I would be very grateful for anyone’s help.
-
Proposed as answer by
Jaysam Thanki
Wednesday, November 28, 2012 6:05 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I had this issue pop up on my 2008 R2 server after importing group policy settings to the Default Domain Controller Policy
Basically it seems to have something to do with security rights.
The parts edited were under computer policy «User Rights Assignments» or «Security Options»
I’m not sure the exact one, but I’m guessing it has to do with logging in remotely.
-
Proposed as answer by
Osman A
Wednesday, July 21, 2010 12:23 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
Hello everybody!
Yesterday I spent my time on solving this issue. Thankfully I solved it. Now with great pleasure I would like to share with you.
First:
Go to System — Remote setting (in the left pane of the window) — under
Remote Desktop select Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure)
and click OK.Then you will set a password for you account, this is a required procedure. To set password go to:
Start — type User Accounts select Create a password . I recommend to make a strong password because your computer now allow remote connections.Next, unblock the Remote Desktop in your Firewall. Open your firewall (depending which security software is installed on your computer) find
Remote Desktop and set it to By application rule
or Allow .OK, first preparation step is ready.
Now, let’s go to second final step.
Run Remote Desktop Connection .
In the Experience tab select your connection speed. Go back to
General tab, in the Computer: type the full name of a remote computer to which you going connect, and then click
Connect button. (You can view a computer full name in System properties
under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings. )Then the new window will pop-up (Windows Security) here you must enter you credentials.
Please READ further instructions carefully.
In the new (Windows Security) window select Use another account , then type the
User name and Password OF your remote computer and click OK button. Probably then you will receive the Warning message select OK
or Allow.Wait a little bit and then you will see you Remote Desktop.
That’s it.
I hope this instructions will help you to solve Your problems of Remote Desktop setup.
So, Good Luck to You!
Best regards,
Osman.
-
Proposed as answer by
wrighti
Monday, June 6, 2016 4:12 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I was getting the «The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» when connecting from XP to a Windows 7 machine. I had updated the Remote Desktop client software through KB 969084. Don’t make this update if you need to access win2000 systems as they
are not supported.I have the firewall turned off for testing purposes, so that wasnt the issue. I applied the CSSP Fix under XP(listed in the KB) and rebooted the XP system, though that may not have been necessary.
It turns out I had almost everything correct.
After reading Osman’s solution above, I connected to the remote system though an alternate remote connection method, and added a password to the account.
There should be a note added that the destination account must have a password for RDP to work under Windows 7.
Once the password was added I was able to connect using the Enhanced Security with no errors.
-
Are you on a domain network? If so, I had this error. Found out someone else had changed the DNS servers to OpenDNS and not the IP of the AD/DNS server. Problem fixed!
-
Proposed as answer by
DerBachmannRocker
Friday, July 20, 2012 8:18 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
This might also happen when the remote user account is brand new. I had to logon to the server locally and make the mandatory first-login password change before it worked with RDP.
-
Proposed as answer by
Radu Dorneanu
Tuesday, May 1, 2012 3:18 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I ran into this tonight but was able to solve it.
symptom:
From vpn based Windows 7 64-bit (Laptop/remote). I attempted to login to Windows 7 32-bit desktop (Office) using a specific domain account intended for the office computer only.
An Authentication error has occurred. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted. Remote computer: Office
Solution:
Use a domain account that does not have a «Log onTo…» specified in the Account settings. Alternately add both Laptop/remote and Office to the domain user account intended for the office computer only.
-
Proposed as answer by
lavee45
Thursday, May 31, 2012 8:45 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
hi
im having same issues, i have 2 pc local both windows 7 ultimate. pc1 is not on domain, pc2 was on the domain, uses password which is saved in the rdp.
from pc1 trying to rdp pc2, was able to do for long time but not recently. tried all kind of tricks,
i ve installed teamviewer so i can check if really i can connect,so with teamviewr (tv as short) from pc1 to pc2 i can logon.
as soon i connect with tv from pc1, then i try rdp from pc1 to pc2 and Bingo! it works. i close tv, rdp connection stays. i can rdp again and again AS LONGER I dont switch off pc2!!! if i do,im unable to connect via rdp!
looks like security issues, but establishing a connection with tv, it removes these issues and then rdp works! (tried every time!)
need a permanent solution though…
thanks.
-
Sounds to me like Group Policy might be the issue. Team Viewer perhaps changes a security setting in order to work and when you reboot Group Policy resets the security. Try gpupdate /force on the machine once you have it working using your teamviewer workaround
to confirm. -
I ran into this issue when i had «do not connect if authentication fails» enabled, which from what i’ve read tries to connect through TLS, which if you dont have a compatible certificate installed on both ends, gets automatically rejected.
This can also be set in group policy settings, which i believe overrides the RDP setting.
-
I encountered this trying to RDP into a new Windows 7 install. The destination computer is a laptop. It turns out that I just have to do the initial log in from the laptop itself, then subsequent attempts to RDP into it work fine. It’s
a minor inconvenience now and I can deal with it since the laptop is always a few feet away.-
Proposed as answer by
JAB-RTE
Wednesday, January 23, 2019 7:47 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
Add the Remote Desktop Users group to the group policy setting Access This Computer From the Network.
By default only Administrators are allowed this right. If you are using the Network Level Authentication option then the Remote Desktop Users group must have this right for logon to work.
-
Edited by
GNCA
Wednesday, April 25, 2012 6:53 PM
-
Edited by
-
Just remove the machine from Domain and remove the system name from AD computer list after all you just restart the system then add the system again in the domain.
-
Hi AndyD77,
Please go to AD and check the particular computer account is enabled or disabled. Most probably it is disabled, so please enable that computer account.
-
Here is another solution, looks like this issue is caused by different scenarios, in my case I was still able to logon with my Domain Admin account to a locked down machine(with very tight Domain Security Policies), the issue started happening on another
account that was a local admin on the machine but I had flagged that account on the domain to prompt for a password change on the next logon, my guess is due to the security policies applied to this specific machine, the Security Authority was being blocked
from properly communicating with the Domain Controller and it could not initiate the password change procedure and it was returning that error. All I had to do was uncheck the «User must change password on next logon» checkbox in the domain account and then
it allowed me to logon with it.Again this might be in my case, but in other cases it could be due to different configurations, I personally believe that for the most part this issue is due to security policies being applied to the machine, if you are not sure if that is the case and have
tried all these solutions, you can always try to restore the machine security policies to the default state.Hope this helps.
-
Proposed as answer by
BlackHawk816
Thursday, June 28, 2012 5:47 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
For what it is worth I was having this issue with a Windows 7 SP1 x64 machine RDPing to a Window Server 2008 R2 SP1 Datacentre. I could logon locally, but not with a domain account.
The domain account was not locked, RDP was set to use Network Level Authentication, routing was set correctly, etc.
The issue was related to the cached account on the server. As soon as I deleted the cached credentials I could login without issue.
-
Exactly. Thanks a bunch! In my case I used Core Configurator 2.0 on Server Core 2008 R2. I did not intend to change any DNS settings, maybe it’s a bug in Core Configurator. Anyways: if you try to log on to a domain joined machine and get this error, make
sure the DNS settings on that machine point to an Active Directory server.-
Proposed as answer by
Mindaugas Balsevicius
Monday, April 8, 2013 12:44 PM -
Unproposed as answer by
Mindaugas Balsevicius
Monday, April 8, 2013 12:44 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
We just needed to set «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)»… instead of the NLA option.
-
That is a workaround, but NLA is normally fine until this problem pops up.
-
Well, the solution for my issue was to reset the user account password eventhough it is not expiring. This seems to be the work around so far.
/* Server Support Specialist */
-
Make sure you can ping the FQDN. I had this issue and was unable to ping DevDomainSrv.Dev.Local, but I could ping DevDomainSrv. When I took a look at the network adapter properties, the DNS setting was set to obtain automatically. I set
it so the primary DNS was the DNS domain server for my dev domain, and the secondar DNS server was external to my dev domain. Once I did this, it worked like a champ.Good Luck
-
Proposed as answer by
Mark Dykun
Thursday, April 4, 2013 3:05 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I had this problem on a Windows 8 RTM installation in a domain environment. A domain user was able to log on locally but not through Remote desktop. Another domain user was able to logon both locally and through Remote desktop. Computer has Network Authentication
Layer (NLA) enabled. I turn of NLA, and both users can logon Remote desktop.The first user had a «Allow only logon to these workstations» setting on the user object in the domain. Even if the computer name was added to the list, in a Remote desktop scenario it would not allow logon.
So I changed the user object in the domain and allowed the user to logon to any computer. Now he’s able to logon using Remote Desktop, even with NLA turned on.
Guess it’s a bug in Windows 8 RTM.
Regards,
Krug-
Proposed as answer by
Kruger44
Friday, October 19, 2012 5:56 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
Hi Guys,
I got the same issue when I do a remote desktop to Server 2012 Hyper-V Core,
I reset the password — It didn’t work for me.
I rebooted after reset the password — It didn’t work
I disabled the remote desktop after reset the password and enabled — It didn’t work
It worked for me when I reassign the internal DNS server IPs where I put the static host record in the local DNS servers manually.
I had to create dns records manually for this hyper-v core as it is not added to domain. Previously I had the public DNS for network interface as I wanted to do the updates only.
Hope it may help to anyone.
-
Edited by
Karan.T
Thursday, March 28, 2013 9:29 AM
-
Edited by
-
I had this same problem. 2 accounts. Both could log in locally only one could RDP. The one that could not was station restricted. Turned off NLA and then it could log right in.
-
I fixed it with running the command «ipconfig /flushdns» in the CMD.exe on the server.
-
try find the solution here
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2493594
-
It worked for me. You could write {machinename}{localusername} in user name bracket instead.
-
@Smarcell: You sir, are a savior. Thank you! Can’t believe a bug like this passed right under MS’s nose.
-
Edited by
naashkyr
Thursday, August 8, 2013 1:31 PM
-
Edited by
-
I got this error when I was decommishioning some old domain controllers, the server I was trying to connect to had a static IP set with static DNS server entries. Once the last DNS server was powered off I could no longer connect. Updated the
DNS server entries and was able to log on. -
This did it for me after a good few hours of research. Thanks very much!
-
Unjoin, then re-Join the server to the domain.
The server even will show «joined to the domain» (if you look in computer/properties), BUT, for some reason, mine was not completely joined. Go figure. I think it’s a feature (LOL) … BUT, note that my server previously existed in the domain, and I was
giving a new physical box that same name; i.e. moving Server1 to new hardware, AND I never reallycleanly removed the previous server. I guess you can call it an «unclean join» and, even though no errors were evident, well, you get the picture — stuff wasn’t
working. So, double-check, especially if you have remote DCs over slow links, the domain might not have had time to «catch up» all the AD/DNS info regarding whatever new box you are putting in.Tried it 5 minutes ago and it worked.
So, YES, multiple things can cause this error and, NO, switching to a lower security setting (Allowing connections from ANY RDP) is not the real solution.
Old thread, but still valid.
Please remember to Mark as Answer if I helped resolve your issue. Thanks.
tnjman
-
I created this same error message by renaming an account. I created the account originally just for remote access and immediately did not like the name I picked so I renamed it.
I attempted to access the remote machine via the updated account for the very first time and the error appeared.
To correct the issue, I accessed the server [win server 2008]
Right clicked computer off the start menu and chose «Properties» to Access the «System»
Clicked «Remote Settings» then «Remote» Tab
Clicked button for «Select User» and attempted to confirm the account I was trying to use had permission. It was then I discovered that the account still had the original name.
To confirm this was the issue, I was able to gain remote access using the original account name
-
I had the same problem in my domain home lab, even i restarted the server I wanted to RDP.
What i did is to shutdown all my servers, including domain controller.
I started the domain controller. I waited until it was reachable and all services were up.
Then i started the server with rdp problems, giving it some time too to start properly
Problem fixed.
I hope you don’t need to reboot your DC, but at least, I wanted to give the tip that, in my case, the problem was in the domain controller side.
Sys Admin
-
Radu,
Thanks for this comment which helped me solve my problem. My user was logging onto their pc with their normal credentials and then using different credentials to RDP to a server. This was not an issue until I forced stronger authentication by
configuring «Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication…» on the server they were trying to RDP to. This occurred even though the user’s pc was Windows 7.As soon as I set the higher security setting
they could no longer RDP.To solve the problem I had the user log onto their pc using the same credentials that they would later use to RDP to the server. Once they did that they could RDP to the server, regardless of the credentials used to log on to their pc.
Andrew
-
Hi,
I had the same problem and the same resolution!
-
I just had the same message «The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» happen in the following scenario. Windows 7 user using Remote Desktop to log in to a newly upgraded Windows Server 2012. The issue was related to the username using a capital
letter at the beginning. I do not remember Windows Server 2008 ever minding about the case-sensitiveness of the username but I could be wrong. Anyways, that’s how we got around that. -
In my case, it was easier to solve than I thought…
I reset the user password from the domain controller. Then, in Active Directory I selected the user and opened the user properties window. In the tab «Account» I unchecked the option «User must change password at next logon». That’s it!
Hope it helps to anyone!
Regards!
-
Proposed as answer by
Manolo Vivero-PM-Financial Aplications Coordinator
Tuesday, October 7, 2014 12:56 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
Additionally to this particular answer, user forgot to mention that the Domain Policy password expiration ask the user to change password. I ask the user to restart the PC, and once the user change the old password everything went back to normal.
Good day…
-
After I read the answer by DavidRa I went to the Server 2008 R2 gave me the your password has expired and needs to be changed. I changed it and got in. The 2012 box was the one that gave me the «Local Security Authority could not be contacted»
message. Strange that it would not let me change pw on 2012 server box… -
This one works great. I disabled the check mark on the profile asking for password expires; etc.. and works great.
Then I asked the user to come to my desk and changed the password! -
I would have this issue when trying to RDP into a DC after it was rebooted (not very often). I could log into them locally with no errors and would have to do so to «nudge» the server back into letting me RDP. This led me to my solution which
was adding the /admin switch to my RDP connection (to try and simulate «local»). Voila! No «local security» error when I RDP. Not entirely sure why that solved my issue…but it did. -
Assuming you have RDP setup correctly on the client and server:
My solution was to UNCHECK the ‘Allow connections only from computers….’ in System properties , Remote tab.
Working now.
Less secure? Yes. Less frustrating? Definitely.
-
I’ve run in this problem after inplace upgrade of W2k3 into w2k8
What I’ve found is that when You set «Log On To» to the user account and add a few computers remember to add the one that user is running mstsc from.
In other case You will get «The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted»
-
This worked for me too. My original issue was caused by removal of one DC and addition of another, while having the new one seize the Schema Master and Domain Naming Master fsmo roles.
-
I had the same error on my Azure virtual machine and a local virtual machine. I resolved this error by following the under given URL:
An authentication error has occurred. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted.
-
Hi
In my humble opinion, I think the the issue comes from the local accounts
I think that the local account is set to «User must change password at next logon»
Hope it will help some folks !
-
I had the same problem which was easily mitigated by disabling NLA for the remote connection (which is a trivial workaround) but the true reason for this error message was that the server could not reach the domain controller properly and would only
log me in with the cached credentials but the server could not verify the credentials with the domain.This is what the NLA actually is supposed to do and it worked perfectly to the detriment of functionality.
Soultion: Please check the server for full connectivity to the domain (domain controllers).
-
I know this is a really old thread. But I *finally* figured this out with what for me is the DEFINITIVE solution. I get the «local security authority could not be contacted» error too, when attempting to connect via RDP over the internet from a
computer that is NOT a member of the domain. Removing NLA is just not an option, as I am just flat out not willing to sacrifice security for convenience. So here’s the solution, assuming the user is NOT authorized to log onto every computer on the domain.That is to say, you have identified in the user’s account properties the specific computers they are allowed to log on to. If you change this to «all computers» the problem goes away. But it also sacrifices your internal security by allowing the
user to log on to any domain computer — probably not desired. So what to do?If remoting in from a computer that is not a domain member (such as your personal computer at home) then on the AD DS domain server open the AD Computers and Users applet. Then in the users container select/open the specific user account being used.
In the user account dialog under the Account tab, click the «Log On To» button. Now add the name of the non-domain computer they are remoting in from, and that solves this problem without sacrificing NLA or any other security.
If you’re using health policies on the NPS, that just adds another layer of security, and I highly recommend it if you’re going to allow users to log into domain computers remotely, from non-domain computers.
-
Proposed as answer by
John Deeman
Tuesday, February 14, 2017 9:42 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
-
I have the same issue, So I unchecked the «user must change password at next logon» option and It worked for me.
-
Hi all,
For me, it was on a tiny network that had two domain controllers, but one crashed a while ago, and I had no plans to replace it. I hadn’t removed it from Active Directory, though. I was working remotely and logged in to the one remaining DC,
and (thankfully) also logged in to my admin workstation as the domain administrator, with RSAT.I had to reboot the DC, and when it came back up, I got this error trying to connect with RDP. From my admin workstation, I removed the old DC from Active Directory Users and Computers, and from Sites and Services. I also inspected DNS, and found
that the IP address for the old server was listed under gc._msdcs.domain, so I removed that.The problem was instantly fixed. What had happened, was the LSA was finding the missing DC when looking for a GC/ADDS server.
Hope this helps.
-
Hi All Osman’s steps solved this issue but I will like to make it very simple.C
Right click on Computer/ This Computer,
Select Properties
On the Top Left, Select Remote SettingsThis will Take you to Remote assistance panel.
From the three Options,
uncheck the following:
Don’t Allow remote connection to this Computer.
And Check: Allow Connection from Computers Running any version of Remote Desktop.(Less Secured)
Make sure the last Option is Unchecked: Allow connection only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (More Secured).
Click Apply and OK.
Hope this helps.
-
It has literally taken me days to figure out my specific issue for my specific setup. First the setup.
Runnint a Server 2012 Standard domain controller with Group Policy and Hyper-V.
In AD DS some users are set up to only be allowed logon to specific computers both locally and remotely via RDP.
The Hyper-V is running a Windows 10 Pro virtual machine also joined to the domain.
Then I have another box with Server 2008 R2 that is a member server jointed to the domain. This box is running NPS and is also set up as the RD Gateway server.
Only users that are allowed to log on to specific computers locally, can also do so remotely via RDP.
When remoting in to VM01 from either the 2012 or 2008 server systems, it was no problem. However, when they tried to remote in from their home computer, the following error was generated.
An authentication error has occurred. The local security policy can not be contactedThere’s no way I’m undoing the requirement for Network Level Communication. So I dug, and I dug, and I dug. I finally found the gold at the bottom of this hole.
The solution for my specific situation was to go into AD DS and add the name of the remote computer to the list of computers the user is authorized to log on to. It doesn’t matter that the computer they are connecting from is not on the
domain and is sitting in their living room at their house 30 miles away. Their domain login has to be authorized to log on to their personal computer at their house — even though of course, it never will. So if they try to remotely log in from another
computer, they can’t. If they get a new computer and it does not have the same network name as their old computer, then they can not connect to their domain computer at work over the internet via RDP with Network Level Authentication.Of course, there is another option that for me I won’t use. It’s to allow the user to log on to any computer.
-
For me I couldn’t even do a reset of the password.
I had to check the box that says «Password Never Expires».
If it is checked my user can login
If it is not checked …. An authentication error has occurred the local security authority cannot be contacted.
Weird….!!!!!
-
I starting having this issue after I updated to Windows CU 1703 from Windows 10 Anniversary edition.
The PC is NOT part of a domain.
I can’t figure it out.
—— Sean J Vreeland Seattle, WA
-
i had the same issue pop up, though mine is on a domain. The problem was the comcast router that was recently replaced, which has no ability to turn off DHCP for ipv6, handing out incorrect IPV6 addresses. I had to isolate it behind a router, which immediately
resolved my issue.Check your logs for a termDD error and it will list the IP address, that may lead you somewhere.
-
I had this issue with a 2008 R2 Server after it rebooted after updates. I remotely logged on using the local credentials, and found that the nework adapter was saying private network instead of domain. I then founf that the dns server IP address was missing/had
disappeared from the static IPv4 settings on the network controller — I re-added this then rebooted, and the issue went away. -
if you renew the IP on the remote machine, it should work :
— open command prompt
— type «ipconfig /release»
— type «ipconfig /renew»
-
Just Uninstall KB4480968(patch
date year 2019) Windows security patch.after uninstall patch just restart your server. -
I dont have that patch and have the same issue.
-
Check that the account does not have an expired password, and that the account itself is not expired. In my case, the account password had expired, causing this error.
As soon as I changed the password, the error was no longer present.
10 years later, Windows 2016 Server… Same issue. This helped me resolve it. It was a new User with «User must change password at next login» set. Once I cleared the «must change password» flag, the user was able to connect
to remote desktop. -
Same fix for an old Windows Server 2008 x86 server.
I also found that if I added the remote PC’s hostname to the list it worked.
Don
-
In Local Security Policy/Local Policies/User Rights Assignment, remove Guest from «Deny access to this computer from the network». As mentioned by another person on this thread, you might also need to add Guest to «Access to this computer
from the network».
How to Fix “The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted” Error in Windows 11/10
“The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted” error occurs when logging in to another computer via a remote desktop connection. This article is dedicated to helping you resolve this problem.
When attempting to connect to a remote computer (such as Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012) using the Remote Desktop client (mstsc.exe), you may receive the following error message:
An authentication error has occurred.
The Local Security Authority cannot be contactedRemote computer: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
This could be due to an expired password.
Please update your password if it has expired.
For assistance, contact your administrator or technical support.
What Causes “The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted” Error
- Remote desktop connections may be disabled on the host or client PC. The solution is to turn the remote desktop feature on.
- DNS address misconfiguration. The solution is to set up another DNS server address.
- IP and DNS address conflicts.
- An update to fix Windows 10 and Windows Server remote desktop vulnerability prevents connecting to older Windows versions.
Video Guide on How to Fix «The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» Error
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Method 1. Allow the Connection in System Properties
- Method 2. Allow the Connection in Group Policy Editor
- Method 3. Change Your DNS Server Address
- Method 4. Perform a DNS Flush
- Video Guide on How to Fix «The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» Error
Method 1. Allow the Connection in System Properties
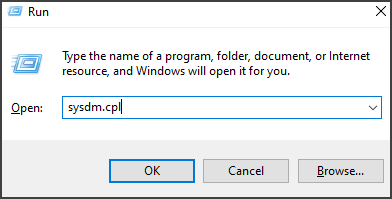
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
2. In the Run dialog box, type in sysdm.cpl and click OK.
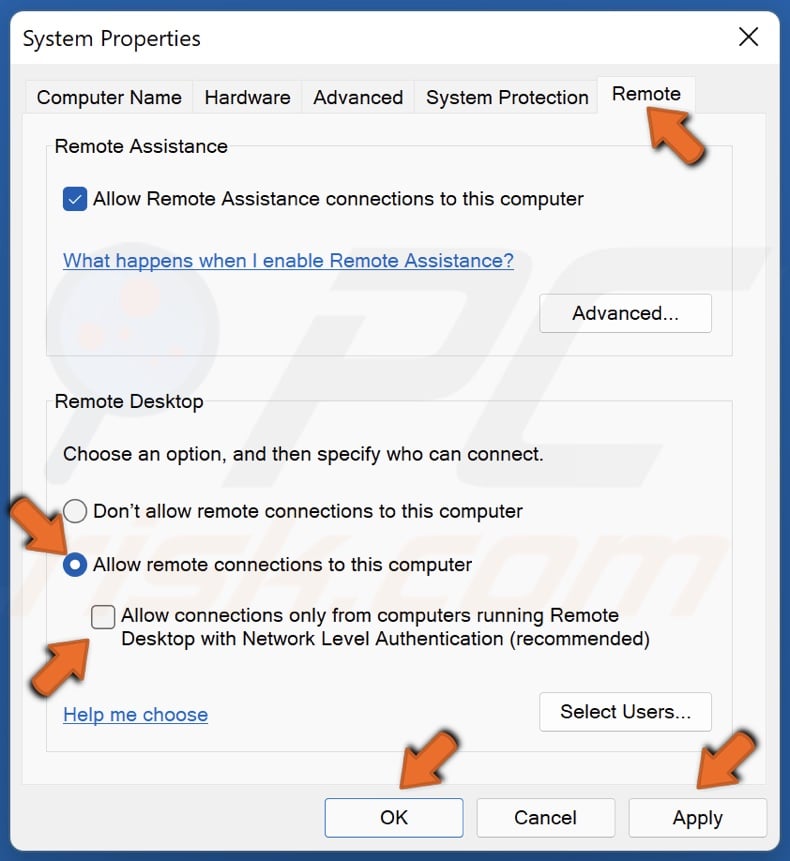
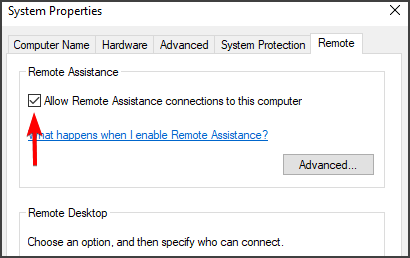
3. Navigate to the Remote tab.
4. Mark the Allow remote connections to this computer checkbox.
5. Deselect Allow connections only from running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (recommended) option.
6. Click Apply and click OK.
[Back to Table of Contents]
Method 2. Allow the Connection in Group Policy Editor
Note that This solution is not applicable to Windows 10 Home Edition since the Home Edition does not have the Group Policy Editor.
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
2. In the Run dialog box, type in gpedit.msc and click OK to open the Group Policy Editor.
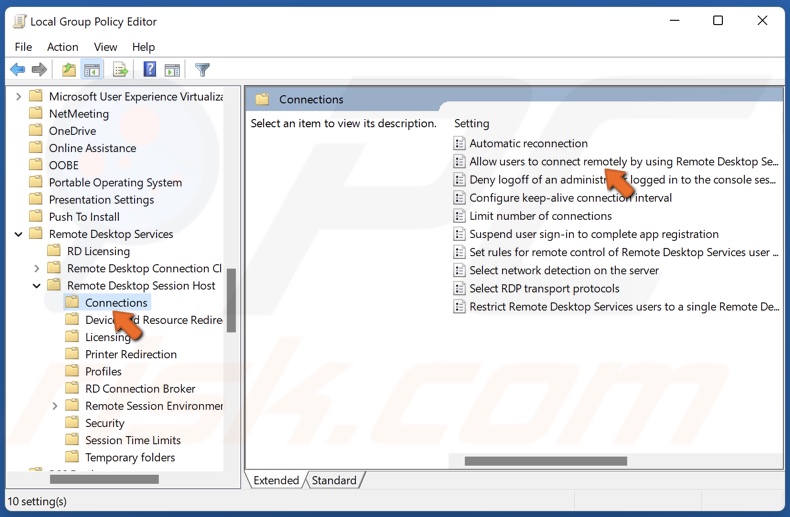
3. Navigate to Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop ServicesRemote Desktop Session HostConnections
4. In the right pane, double-click Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.
5. Tick Enabled.
6. Click Apply and click OK.
[Back to Table of Contents]
Method 3. Change Your DNS Server Address
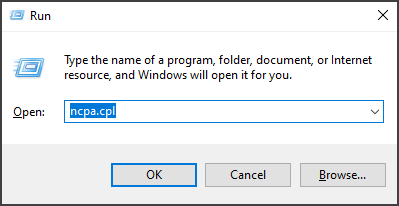
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
2. In the Run dialog box, type in ncpa.cpl and click OK.
3. Right-click the network adapter and select Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
5. Tick the Use the following DNS server addresses option.
6. Enter the following addresses (or your preferred DNS addresses):
- In the Preferred DNS server, type in 1.1.1.1
- In the Alternate DNS server, type in 1.0.0.1
7. Click OK to save settings.
8. Restart your PC for the changes to take effect.
[Back to Table of Contents]
Method 4. Perform a DNS Flush
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
2. In the Run dialog box, type in CMD and hold down Ctrl+Shift+Enter keys to open the elevated Command Prompt.
3. In the Command Prompt window, type in ipconfig /flushdns and press the Enter key. Running this command will clear the DNS cache files and reset the DNS resolver cache.
4. Close the Command Prompt.
[Back to Top]
Содержание
- How to Fix ‘The Local Security Authority Cannot be Contacted’ Error on Windows
- What Causes “The Local Security Authority Cannot be Contacted” Error on Windows?
- Solution 1: Change Your DNS Address
- Solution 2: Enable Remote Connections in Group Policy Editor
- Solution 3: Allow the Connection inside System Properties
- Solution 4: Run a Helpful Command on the Host
- Solution 5: Set to Allow Connections from All Versions
- Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
- Asked by:
- Question
- Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
- Asked by:
- Question
- Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
- Asked by:
- Question
This error appears when users try to login to other computers via a remote desktop connection. The problem prevents them from connecting and it displays the “The Local Security Authority Cannot be Contacted” error message. The problem often appears after an update has been installed on either the client or the host PC and it causes plenty of problems on many different versions of Windows.

There have been many unofficial fixes for the problem which were created by the users who had the same unfortunate experience. We have gathered the working methods in this article so make sure you follow it in order to resolve the problem.
What Causes “The Local Security Authority Cannot be Contacted” Error on Windows?
Pinpointing the correct cause for the problem is one of the most important steps when it comes to resolving one. That is why we have created a list of possible causes for the problem so make sure you check it out below:
- DNS addresses may be wrongly configured – If this is indeed the case, try using the DNS addresses provided by Google or OpenDNS
- Remote Desktop connections may be disabled by default on either the host or the client PC – Make sure you turn the option on to connect properly without errors.
- IP and DNS address conflicts – Running a certain command may help you resolve the problem
Solution 1: Change Your DNS Address
The problem is often caused by a faulty DNS setup which is simply not accepted by the host or its service. The problem can be resolved easily by changing your default DNS settings to use the ones provided by OpenDNS or Google. This can be done easily in Control Panel so make sure you follow the steps below carefully.
- Use the Windows + R key combo which should immediately open the Run dialog box where you should type ‘ncpa.cpl’ in the bar and click OK in order to open the Internet Connection Settings item in Control Panel.
- The same process can also be done by manually opening Control Panel. Switch the View by setting at the top right section of the window to Category and click on Network and Internet at the top. Click the Network and Sharing Center button in order to open it. Try to locate the Change adapter settings button at the left menu and click on it.

- Now that the Internet Connection window is open using any method above, double-click on your active network adapter and click on the Properties button below if you have admin permissions.
- Locate the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) item on the list. Click on it in order to select it and click the Properties button below.

- Stay in the General tab and switch the radio button in the Properties window to “Use the following DNS server addresses” if it was set to something else.
- Set Preferred DNS server to be 8.8.8.8 and the Alternate DNS server to be 8.8.4.4

- Keep the “Validate settings upon exit” option checked and click OK in order to apply the changes immediately. Check to see if the same problem still appears!
Solution 2: Enable Remote Connections in Group Policy Editor
Sometimes the Group Policy on the client computer is preventing the remote Desktop connection completely. This can be changed quite easily in Group Policy Editor if you are running any version of Windows besides Windows Home. Follow the steps below in order to enable remote connections in Group Policy Editor.
- Use the Windows Key + R key combination (tap the keys simultaneously) to open the Run dialog box. Enter “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog box, and press the OK button in order to open the Local Group Policy Editor tool. On Windows 10, you can try simply type Group Policy Editor in the Start menu and click the top result.

- On the left navigation pane of Local Group Policy Editor, under Computer Configuration, double click on Administrative Templates, and navigate to the Windows Components>> Remote Desktop Services >> Remote Desktop Session Host >> Connections.
Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services
- Select the Connections folder by left-clicking on it and check out its right side section.
- Double click on the “Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services” policy and check the radio button next to the “Enabled” option.

- Apply the changes you have made before exiting. The changes won’t be applied until you restart.
- Finally, reboot the computer to save the changes and check to see if you are still being targeted with the error.
Solution 3: Allow the Connection inside System Properties
The most common cause for the problem is the fact that remote access is, in one way or another, blocked on either the host or the client PC. This time, the problem may be with the host PC which may not be accepting connections from other PCs or the ones with another version of Remote Desktop running. Follow the steps below in order to fix this.
- Right-click either on My Computer/This PC depending on the version of Windows you have installed on your computer and choose the Properties
- After that, locate the Change settings button at the left side of the Properties window, under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings, and click on it.

- In the Remote tab of System properties, check under Remote Desktop and click the radio button next to Allow remote connections to this computer. Also, uncheck the box next to the Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (recommended).

- Apply the changes you have made and check to see if the problem still appears.
Solution 4: Run a Helpful Command on the Host
This method is quite popular for its simplicity and plenty of people use it in order to fix most things related to connectivity issues. The funny thing is that it works and users have commented saying that this is the only step it took to resolve the problem. Try it out now!
- Search for “Command Prompt” by typing it right in the Start menu or by pressing the search button right next to it. Right-click the first entry which will pop up as a search result and select the “Run as administrator” option from the context menu.
- Additionally, you can also use the Windows Logo Key + R key combination in order to bring up the Run dialog box. Type in “cmd” in the dialog box which appears and use the Ctrl + Shift + Enter key combination for administrative Command Prompt.

- Type in the following command in the window and make sure you press Enter after typing it out. Wait for the “Operation completed successfully” message or something similar to know that the method worked.
- Try to reset the connection and check to see if the error still appears.
Solution 5: Set to Allow Connections from All Versions
Microsoft released an update to Windows 10 and Windows server to fix certain vulnerabilities and didn’t end up releasing one for Windows 7. Therefore, Windows 7 users were stuck on a different version. Therefore, you have to set up the connection in such a way that it allows connecting from any and all versions of Remote Desktop. However, keep in mind that this is much less secure than the latter option.
Источник
Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Asked by:
Question
We have an application that accesses a SQL server and we are experiencing very slow performance of the application and it also sometimes just doesn’t return any information. I understand that this is not a great deal of information regarding the application but it is all I have available at the moment (I am trying to get more details from developers).
The users of the application are located in separate domain to the domain the SQL server is a member of (different subnets etc). There is a one way external trust between the domain of the SQL server and the domain the users of the application reside in.
We think this error we see in the logs of the SQL server may be related.
«SSPI handshake failed with error code 0x80090304, state 14 while establishing a connection with integrated security; the connection has been closed. Reason: AcceptSecurityContext failed. The Windows error code indicates the cause of failure. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted [CLIENT: 10.133.21.73]»
After following a troubleshooting guide for the above error part of the guide states to verify the SQL server is using Kerberos authentication. After running a query the SQL server seems to be using NTLM. I don’t know whether this would cause this issue or not.
Any help or insight that anyone could provide, even if it just gets me started, would be very useful.
Источник
Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Asked by:
Question
We have an application that accesses a SQL server and we are experiencing very slow performance of the application and it also sometimes just doesn’t return any information. I understand that this is not a great deal of information regarding the application but it is all I have available at the moment (I am trying to get more details from developers).
The users of the application are located in separate domain to the domain the SQL server is a member of (different subnets etc). There is a one way external trust between the domain of the SQL server and the domain the users of the application reside in.
We think this error we see in the logs of the SQL server may be related.
«SSPI handshake failed with error code 0x80090304, state 14 while establishing a connection with integrated security; the connection has been closed. Reason: AcceptSecurityContext failed. The Windows error code indicates the cause of failure. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted [CLIENT: 10.133.21.73]»
After following a troubleshooting guide for the above error part of the guide states to verify the SQL server is using Kerberos authentication. After running a query the SQL server seems to be using NTLM. I don’t know whether this would cause this issue or not.
Any help or insight that anyone could provide, even if it just gets me started, would be very useful.
Источник
Error 0x80090304 the local security authority cannot be contacted
This forum has migrated to Microsoft Q&A. Visit Microsoft Q&A to post new questions.
Asked by:
Question
It’s interesting that I have searched for days now, and still can not find an answer to this. Hopefully someone can look over what I have and recommend a solution.
The situation:
There is a VPN tunnel that connects the various locations. I have a user that connects to the corporate network via VPN, and uses RDP to connect to their workstation in a different location than the entry point. User receives the following error when trying to use RDP:
Authentication error has occurred.
The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted.
Remote computer xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
This could be due to an expired password .
Please update your password if it has expired.
If I am physically within the network, but attempt to RDP to any of the workstations on the other side of the tunnel, I receive the same error.
I am able to successfully RDP into any system on my side of the tunnel, and RDP into a server on the other side of the tunnel. If I were to connect to the remote server and RDP into any workstation that resides within that network, I receive the following error:
An authentication error has occurred (Code: 0x80090304)
Remote computer: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
What I have tried:
- Error code 0x80090304 is linked to error SEC_E_INTERNAL_ERROR. The Microsoft Hotfix for this error returned a message stating that it did not apply to this system. The server is x64 and the hotfix was for an x64 system. This error message also seems to be link to the error in the workstations Event Viewer TermDD Event ID 56
- In the Terminal Services Configurations settings on that server, the Security Layer is correctly set to RDP Security Layer and «Allow connections only form computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication» is unchecked in the System Properties under the Remote tab.
- In the registry, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Terminal Server > WinStations > RDP-Tcp the UserAuthentication value was changed it to 1 and system was restarted to apply registry changes.
- GPO already disables Network Level Authentication.
- — Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment
«Access this computer from the network» is set to correctly - Also tried logging in with the following schemes with no success:
. - Even with firewall disabled, RDP attempts to remote workstation were unsuccessful
- RDP connecting to workstations using domain admin credentials or users credentials.
- Users credentials was reset, user does not have to log in to change password and password is set to never expire.
Is there anything else that could cause this issue that I should check?
Источник
by Matthew Adams
Matthew is a freelancer who has produced a variety of articles on various topics related to technology. His main focus is the Windows OS and all the things… read more
Updated on July 28, 2021
- The local security authority cannot be contacted message will prevent you from using Remote Desktop on your PC.
- Fix this issue easily by switching to reliable and secure remote control software.
- Check your Remote Desktop settings and make sure that all required settings are enabled.
- Adjusting your DNS settings is another method that you can use to fix this issue on your PC.
Windows 10’s Remote Desktop enables users to connect with a remote PC. However, a local security authority error can arise for some users when they try to set up, or log in to, a remote desktop connection.
The full error message states:
An authentication error has occurred. The local security authority cannot be contacted.
As a consequence, a remote connection can’t be established.
1. Check that Remote Desktop is enabled
- First, check that the basic Remote Desktop setting is enabled.
- To do that, click Windows 10’s Type here to search taskbar button.
- Input the keyword remote desktop settings in the search box.
- Click Remote Desktop settings to open further options.
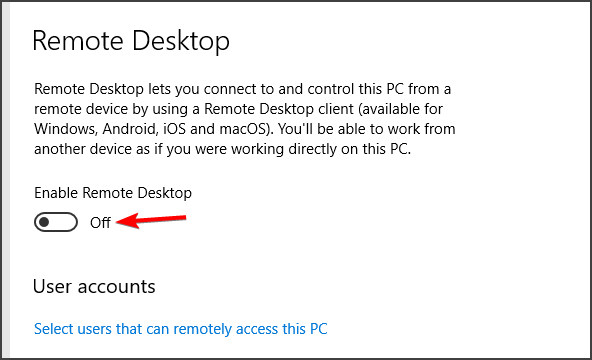
- Then toggle the Enable Remote Desktop setting on if it’s off.
2. Unblock remote access
- Right-click the Start menu and select Run.
- Input sysdm.cpl and click OK.
- Click the Remote tab.
- Then select the Allow remote connections to this computer setting if you need to .
- Deselect the Allow connections only form computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (recommended) option if it’s checked.
- Click the Apply option.
- Click OK to exit the window.
Users have confirmed they’ve fixed the local security authority error by deselecting the Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication setting.
3. Switch to Google DNS
- Open Run window.
- Input ncpa.cpl in the Open box and click OK to open Network and Sharing Center.
- Double-click your Internet adapter to open its window.
- Click the Properties button.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4, and then click the Properties button.
- Select the Use the following DNS server address radio button.
- Enter the value 8.8.8.8 in the Preferred DNS server box.
- Then input 8.8.4.4 in the Alternative DNS server box.
- Click the OK button.
Some users might need to switch to Google DNS to resolve the local security authority error, so be sure to try that.
4. Check Group Policy’s Remote Desktop Services settings
- Launch the Run accessory.
- Enter gpedit.msc and click OK to open Group Policy Editor.
- Click Administrative Templates on the left side of Group Policy Editor.
- Then click on Windows Components and go to Remote Desktop Services.
- Expand Remote Desktop Services and choose. Remote Desktop Session Host. Now select Connections.
- Double-click Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services to open the window for that policy.
- Select the Enabled radio button.
- Click Apply to save the new settings.
- Click OK to close the policy window.
- Restart Windows after enabling Remote Desktop Services.
Some users might need to enable Remote Desktop Services with the Group Policy Editor on client PCs.
5. Flush DNS Cache
- Some users have also resolved this issue by flushing the DNS cache. To do that, enter cmd in Windows 10‘s search box.
- Select Run as administrator on the menu.
- Click Yes if a UAC dialog box opens.
- Input this command:
ipconfig/flushdns - Press Enter to initiate that command.
If the error keeps occurring, we recommend switching to alternative software. Here’s a list of some of the best remote management software.
Those are some of the resolutions users have fixed the local security authority error with. So, there’s a good chance that they’ll fix the same issue for you.
Let us know which of the solutions solved this issue for you by leaving us a message in the comments section below.
Newsletter
When you are trying to log into other computer via remote desktop connections, you might receive an error message that the Local Security Authority cannot be contacted. How to fix it? In this post from MiniTool Partition Wizard, you will learn about several solutions.
It is convenient for users to access another computer via the remote desktop connection. However, they might be stopped from connecting the remote computer by the error message the Local Security Authority cannot be contacted.
This error message comes up with a Remote Desktop Connection windows, prompting that an authentication error has occurred. Why does this issue occur? The reasons could be various, including improper DNS address, Remote Desktop connections disabled, and conflictions between IP and DNS address.
If you come across the same problem, just keep on your reading to get some feasible solutions to it. Let’s check them out one by one.
Fix 1: Keep Remote Connections Enabled
If the remote desktop connections feature is disabled, you will be definitely unable to log into the remote computer. So, if you are prompting that an authentication error has occurred during the process, you should make sure the remote connections feature is enabled on both the host and the client PC.
Here are 2 methods to enable remote connections on a computer, and you can choose either one to have a try.
Enable Remote Connections in System Properties
Step 1: Right-click This PC and choose Properties.
Step 2: Click Change settings in the right pane to open System Properties.
Step 3: Switch to Remote tab, check Allow remote connections to this computer under Remote Desktop section. Uncheck Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication option.
Step 4: Click Apply and OK to save the changes.
Enable Remote Connections in Group Policy Editor
The Group Policy Editor is only provided in the Pro and Enterprise editions of Windows 10. If this tool is available in your Windows, you can also use this method to enable remote connections.
Step 1: Press Windows + R, input gpedit.msc and click OK button to open Group Policy Editor.
Step 2: Now, go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections.
Step 3: Select Connections folder and double-click Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services policy in the right pane.
Step 4: In the new window, choose Enabled and click Apply and OK to save changes.
After that, restart your computer and check if you are able to connect to the remote PC.
Fix 1: Change DNS Address
If your DNS address is wrongly configured, it might not be accepted by the host or the client computer. As a result, you will receive the remote desktop connection error and fail to log into the remote computer.
In this case, you can try changing your DNS address. If you don’t know how to do that, just follow the steps below.
Step 1: Press Windows + R, input ncpa.cpl and click OK to open Network Connections interface in Control Panel.
Step 2: Right-click the network adapter you are using and choose Properties.
Step 3: Under Networking tab, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Step 4: In General tab, choose Use the following DNS server addresses and input the following value:
- Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8
- Alternate DNS server: 8.8.4.4
Step 5: Check Validate stings upon exit option and click OK to apply the changes. Then, check if the issue is fixed.
Fix 3: Flush DNS Cache
If the DNS cache gets corrupted or broken, you might also encounter “the Local Security Authority cannot be contacted” error. In this case, you just need to flush DNS cache with a simple command. Here’s how to do it.
Step 1: Press Windows + R, input cmd and press Enter to open Command Prompt.
Step 2: Type the command ipconfig/flushdns and press Enter to execute it.
Step 3: After the operation completed successfully, reset the connection and check if the issue has been resolved.
I’m trying to define logonHours for Remote Desktop users on Windows Server 2012; Network Level Authentication is required for remote connections. When an account with restricted logonHours (defined in ActiveDirectory) tries to connect at a denied time, the client (Remote Desktop Connection) responds with:
An authentication error has occurred.
The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted.
If the account tries to login at allowed times, everything works fine. If Network Level Authentication is not required, then the client connects to the server, which denies the logon, but displays the much nicer error message «Your account has time restrictions…»
Is there some way to still require NLA, but present the friendlier notice about time restrictions? Am I missing a policy setting or some other configuration?
asked Nov 16, 2013 at 16:12
1
The RDP client will display a nice, usable error message if you run it from a machine that is joined to a trusting domain, and the RDP client must be able to resolve the hostname of the RDP server (session host).
- The RDP client must be joined to a domain that trusts the domain that the RDP server is in
- Date and time must be synchronized
- Connect to the RDP server using the host name or FQDN, not its IP address
This error will occur if any of the above requirements are not met.
In this case, this is actually caused by the additional security provided by NLA. This is a feature. A computer that is not trusted by the domain of the RDP server should not be able to gain any kind of information on the account being used.
The error message «Local Security Authority cannot be contacted» prevents information being leaked on whether the user account is invalid, expired, untrusted, time-restricted, or anything else an attacker may use to identify valid accounts, to untrusted computers running the RDP client.
answered Mar 2, 2016 at 18:37
PatrickPatrick
3641 silver badge6 bronze badges
Found same message appeared from a failed Win 7 RDP connection to a Win 2012 R2 server.
I tested a connection to same server using the same account from my macbook using Royal TSX for RDP and got a warning that the password had expired.
Reset password and the user was able to log on via their Win 7 RDP session.
answered Nov 15, 2017 at 1:35
You are asking for an application-layer error message but you want a network-layer security feature. You can’t have your cake and eat it too.
The network layer cannot connect to the application layer. So the message you receive is completely accurate.
answered Apr 30, 2016 at 2:53
Ryan RiesRyan Ries
55.2k10 gold badges140 silver badges199 bronze badges
This means your Workstation service has been disabled.
Re-enable it and you should be good to go.
Fire up a command line with Administrator privileges run the following command:
sc config LanmanWorkstation start= auto
sc start LanmanWorkstation
Please note there is a space after start= auto
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 18:18

















 cleanly removed the previous server. I guess you can call it an «unclean join» and, even though no errors were evident, well, you get the picture — stuff wasn’t
cleanly removed the previous server. I guess you can call it an «unclean join» and, even though no errors were evident, well, you get the picture — stuff wasn’t