Содержание
- Troubleshooting cloning errors
- In this article
- Help us make these docs great!
- Bitbucket Support
- Knowledge base
- Products
- Jira Software
- Jira Service Management
- Jira Work Management
- Confluence
- Bitbucket
- Resources
- Documentation
- Community
- Suggestions and bugs
- Marketplace
- Billing and licensing
- Viewport
- Confluence
- Git Commands Return Error Code 400
- Related content
- Still need help?
- Symptoms
- Problem #1:
- Problem #2:
- Problem #1:
- Problem #2:
- Resolution
- Problem #1:
- Problem #2:
- 400 error on heroku git:clone
- GIT ERROR 403 как исправить?
- Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
- Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
Troubleshooting cloning errors
In this article
If you’re having trouble cloning a repository, check these common errors.
HTTPS cloning errors
There are a few common errors when using HTTPS with Git. These errors usually indicate you have an old version of Git, or you don’t have access to the repository.
Here’s an example of an HTTPS error you might receive:
Check your Git version
There’s no minimum Git version necessary to interact with GitHub, but we’ve found version 1.7.10 to be a comfortable stable version that’s available on many platforms. You can always download the latest version on the Git website.
Ensure the remote is correct
The repository you’re trying to fetch must exist on GitHub.com, and the URL is case-sensitive.
You can find the URL of the local repository by opening the command line and typing git remote -v :
Alternatively, you can change the URL through our GitHub Desktop application.
Provide an access token
To access GitHub, you must authenticate with a personal access token instead of your password. For more information, see «Creating a personal access token.»
If you are accessing an organization that uses SAML SSO and you are using a personal access token (classic), you must also authorize your personal access token to access the organization before you authenticate. For more information, see «About authentication with SAML single sign-on» and «Authorizing a personal access token for use with SAML single sign-on.»
Check your permissions
When prompted for a username and password, make sure you use an account that has access to the repository.
Tip: If you don’t want to enter your credentials every time you interact with the remote repository, you can turn on credential caching. If you are already using credential caching, please make sure that your computer has the correct credentials cached. Incorrect or out of date credentials will cause authentication to fail.
Use SSH instead
If you’ve previously set up SSH keys, you can use the SSH clone URL instead of HTTPS. For more information, see «About remote repositories.»
Error: Repository not found
If you see this error when cloning a repository, it means that the repository does not exist or you do not have permission to access it. There are a few solutions to this error, depending on the cause.
Check your spelling
Typos happen, and repository names are case-sensitive. If you try to clone git@github.com:user/repo.git , but the repository is really named User/Repo you will receive this error.
To avoid this error, when cloning, always copy and paste the clone URL from the repository’s page. For more information, see «Cloning a repository.»
To update the remote on an existing repository, see «Managing remote repositories».
Checking your permissions
If you are trying to clone a private repository but do not have permission to view the repository, you will receive this error.
Make sure that you have access to the repository in one of these ways:
- The owner of the repository
- A collaborator on the repository
- A member of a team that has access to the repository (if the repository belongs to an organization)
Check your SSH access
In rare circumstances, you may not have the proper SSH access to a repository.
You should ensure that the SSH key you are using is attached to your personal account on GitHub. You can check this by typing the following into the command line:
If the repository belongs to an organization and you’re using an SSH key generated by an OAuth App, OAuth App access may have been restricted by an organization owner. For more information, see «About OAuth App access restrictions.»
Check that the repository really exists
If all else fails, make sure that the repository really exists on GitHub.com! If you’re trying to push to a repository that doesn’t exist, you’ll get this error.
Error: Remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout
This error occurs if the default branch of a repository has been deleted on GitHub.com.
Detecting this error is simple; Git will warn you when you try to clone the repository:
To fix the error, you’ll need to be an administrator of the repository on GitHub.com. You’ll want to change the default branch of the repository.
After that, you can get a list of all the available branches from the command line:
Then, you can just switch to your new branch:
Help us make these docs great!
All GitHub docs are open source. See something that’s wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
Источник
Bitbucket Support
Knowledge base
Products
Jira Software
Project and issue tracking
Jira Service Management
Service management and customer support
Jira Work Management
Manage any business project
Confluence
Bitbucket
Git code management
Resources
Documentation
Usage and admin help
Answers, support, and inspiration
Suggestions and bugs
Feature suggestions and bug reports
Marketplace
Billing and licensing
Frequently asked questions
Viewport
Confluence
Git Commands Return Error Code 400
Related content
Still need help?
The Atlassian Community is here for you.
Symptoms
Problem #1:
When trying to create repositories, Git commands return error code 400:
The following can be seen in the atlassian-bitbucket.log :
Problem #2:
When running git commands on your CI applications (i.e. Jenkins), with Bitbucket server DEBUG logs on — refer to Enable debug logging.
The following can be seen on your CI system:
The following can be seen on your Bitbucket Server atlassian-bitbucket.log :
Problem #1:
This happens because the Git server is trying to use the git «dumb» HTTP protocol, which is not supported by Bitbucket Server. Bitbucket Server supports only the «smart» HTTP protocol, which was introduced in Git 1.6.6.
Problem #2:
Resolution
Problem #1:
Update the Git on the system running your Bitbucket server to a supported one (1.6.6 and above).
Problem #2:
Update the Git client to something higher the Git 1.7.1. Although Git dumb protocol is supposed to be used on any Git client above 1.6.6 (see 4.1 Git on the Server — The Protocols). Please upgrade upgrade your Git client to the most of recent supported one as described on our Supported Platforms.
Источник
400 error on heroku git:clone
Photo by jacobian
I’m working on an estimate for changes to a heroku hosted web application.
I was trying to run heroku git:clone —app appname after adding myself as a collaborator. I was running this on a new vagrant box running ubuntu.
However, I kept getting this error message:
$ heroku git:clone —app appname
Cloning from app ‘appname’.
Cloning into ‘appname’.
error: The requested URL returned error: 400 while accessing https://git.heroku.com/appname.git/info/refs
fatal: HTTP request failed
And I couldn’t understand why.
After some fiddling, I determined that first you need to have an ssh key generated:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
And then you can run:
$ heroku git:clone —app appname —ssh-git
Cloning from app ‘appname’.
Cloning into ‘appname’.
Warning: Permanently added the RSA host key for IP address ‘ipaddress’ to the list of known hosts.
Fetching repository, done.
remote: Counting objects: 902, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (473/473), done.
remote: Total 902 (delta 433), reused 826 (delta 379)
Receiving objects: 100% (902/902), 28.06 MiB | 556 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (433/433), done.
Источник
GIT ERROR 403 как исправить?
вот такая ошибочка после PUSH , логин и пароль не запрашивает.
ранее пользовался гитом, но через другой акк гитхаба.
- Вопрос задан более трёх лет назад
- 51004 просмотра
Оценить 1 комментарий
Здравствуйте.
—
1) Вы пытаетесь загрузить с другого аккаунта, выйти из него я не знаю как, но зато, при установке git на ваш компьютер, создаётся файл .githistory , обычно пихается в пользовательскую папку, как и данные по composer. (for Windows) — для других систем не узнавал.
2) Если вы нашли .githistory — и используете другой аккаунт, удалите его. Возможно другие файлы со словом git так же стоит удалить.
3) Убедитесь, что вы после удаления истории сделали новую регистрацию:
4) Когда создаёте репозиторий на GitHub , клонируйте его на свой компьютер.
Чтобы убедится, что вы открыли консоль [Git Bash] в нужном месте, просто сделайте команду
$ git status
Если репозиторий и директория верны, он красным подсветит файлы, которые нужно добавить.
Если он пишет, что такой директории не существует, значит перейдите в вашу папку.
$ cd your_folder — ещё раз проверьте статус.
Если git увидел ваш склонированный репозиторий, значит делайте запрос:
$ git add .
или
$ git add —all
Почему я не начал с
$ git init ?
Если вы склонировали, то папка .git там уже есть.
Закидывайте к этой папке и файлу README.md ваши файлы, и делайте
$ git add .
Только теперь можно делать коммиты
$ git commit -m «your commit»
высветились все файлы? Тогда пропускаете
$ git remote add origin. — потому что ветка уже создана, при создании репозитория на сайте.
Теперь мы загружаем:
$ git push -u origin master
Если не ошибаюсь, дописать записанное можно через команду:
$ git pull
—-
Самое главное, это сменить пользователя на того, у которого есть права, иначе вам не поможет удаление программы и установка новой. Есть команда, которая чистит кеш истории
$ git credential-cache exit
Но она почему-то в последнее время бесполезная и нерабочая, так что ищите способ очистить кеш.
Что касается ключей и ssh — их можно и не создавать, но как показывает практика, не только git , но и composer не дадут вам работать.
Источник
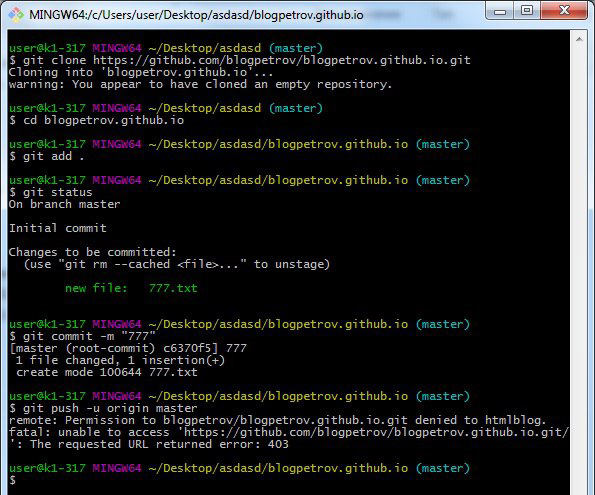
Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
В данном уроке рассмотрим варианты решения данной оишбки:
remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Возникает она чаще всего у новичков при попытке выполнить команду:
Пример ошибки на скриншоте ниже.
Данная ошибка возникает довольно часто при работе с Git в терминале Windows. Суть ошибка довольно таки простая, но почему-то в интернете постоянно создаются темы с вопросом на данную тему и нет внятного ответа на русском языке.
Ошибка говорит нам о том, что мы пытаемся отправить данные в чужой репозиторий. И о том, что текущий пользователь Git не имеет прав для отправки данных в указанный в команде репозиторий.
Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
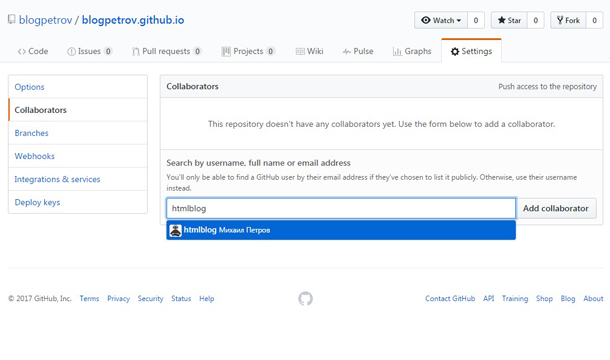
Вариант 1. Дать текущему пользователю права для работы с репозиторием
Данный способ подойдет, если вы являетесь владельцем обеих учетных записей указанных в ошибке. Необходимо зайти на GitHub под именем того пользователя, в чей репозиторий вы не можете отправить данные. В настройках репозитория указать необходимого соавтора. Ему на почту отправится приглашение, которое необходимо подтвердить, перейдя по ссылке в письме.
После этого вы сможете работать с репозиторием как со своим и ошибка больше не появится.
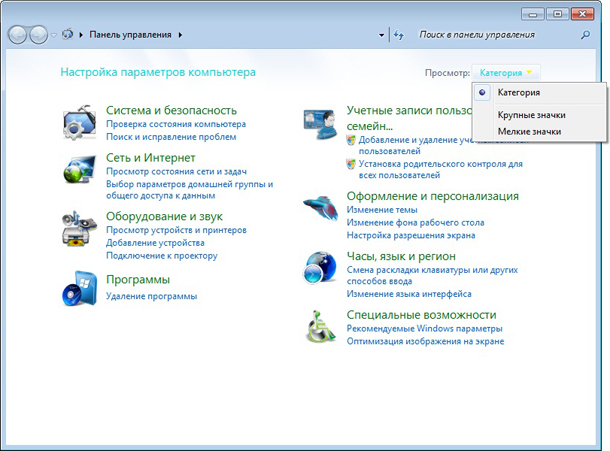
Вариант 2. Назначить в системе текущим пользователем Git ту учетную запись, в которую не можете отправить данные
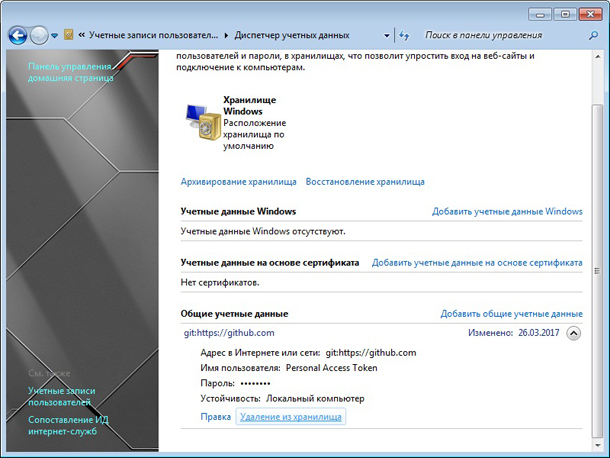
Для этого необходимо перейти в Панель управления Windows. Выбрать отображение в виде категорий.
Перейти в раздел “Учетные записи пользователей и семейная безопасность”. Далее в раздел “Диспетчер учетных данных”. В самом низу будет блок “Общие учетные данные”. Нажмите в нем ссылку “Удаление из хранилища”.
После этого при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push -u origin master
Терминал запросит у вас пароль от учетной записи на Github в чей репозиторий вы пытаетесь отправить данные.
После ввода пароля система установит данного пользователя как основного и будет использовать его в дальнейшем при работе с Git.
Надеюсь данный пост поможет вам решить ошибку, с которой я разбирался почти сутки.
Источник
HTTPS cloning errors
There are a few common errors when using HTTPS with Git. These errors usually indicate you have an old version of Git, or you don’t have access to the repository.
Here’s an example of an HTTPS error you might receive:
> error: The requested URL returned error: 401 while accessing
> https://github.com/USER/REPO.git/info/refs?service=git-receive-pack
> fatal: HTTP request failed> Error: The requested URL returned error: 403 while accessing
> https://github.com/USER/REPO.git/info/refs
> fatal: HTTP request failed> Error: https://github.com/USER/REPO.git/info/refs not found: did you run git
> update-server-info on the server?Check your Git version
There’s no minimum Git version necessary to interact with GitHub, but we’ve found version 1.7.10 to be a comfortable stable version that’s available on many platforms. You can always download the latest version on the Git website.
Ensure the remote is correct
The repository you’re trying to fetch must exist on GitHub.com, and the URL is case-sensitive.
You can find the URL of the local repository by opening the command line and
typing git remote -v:
$ git remote -v
# View existing remotes
> origin https://github.com/ghost/reactivecocoa.git (fetch)
> origin https://github.com/ghost/reactivecocoa.git (push)
$ git remote set-url origin https://github.com/ghost/ReactiveCocoa.git
# Change the 'origin' remote's URL
$ git remote -v
# Verify new remote URL
> origin https://github.com/ghost/ReactiveCocoa.git (fetch)
> origin https://github.com/ghost/ReactiveCocoa.git (push)Alternatively, you can change the URL through our
GitHub Desktop application.
Provide an access token
To access GitHub, you must authenticate with a personal access token instead of your password. For more information, see «Creating a personal access token.»
If you are accessing an organization that uses SAML SSO and you are using a personal access token (classic), you must also authorize your personal access token to access the organization before you authenticate. For more information, see «About authentication with SAML single sign-on» and «Authorizing a personal access token for use with SAML single sign-on.»
Check your permissions
When prompted for a username and password, make sure you use an account that has access to the repository.
Tip: If you don’t want to enter your credentials every time you interact with the remote repository, you can turn on credential caching. If you are already using credential caching, please make sure that your computer has the correct credentials cached. Incorrect or out of date credentials will cause authentication to fail.
Use SSH instead
If you’ve previously set up SSH keys, you can use the SSH clone URL instead of HTTPS. For more information, see «About remote repositories.»
Error: Repository not found
If you see this error when cloning a repository, it means that the repository does not exist or you do not have permission to access it. There are a few solutions to this error, depending on the cause.
Check your spelling
Typos happen, and repository names are case-sensitive. If you try to clone git@github.com:user/repo.git, but the repository is really named User/Repo you will receive this error.
To avoid this error, when cloning, always copy and paste the clone URL from the repository’s page. For more information, see «Cloning a repository.»
To update the remote on an existing repository, see «Managing remote repositories».
Checking your permissions
If you are trying to clone a private repository but do not have permission to view the repository, you will receive this error.
Make sure that you have access to the repository in one of these ways:
- The owner of the repository
- A collaborator on the repository
- A member of a team that has access to the repository (if the repository belongs to an organization)
Check your SSH access
In rare circumstances, you may not have the proper SSH access to a repository.
You should ensure that the SSH key you are using is attached to your personal account on GitHub. You can check this by typing
the following into the command line:
$ ssh -T git@github.com
> Hi USERNAME! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not
> provide shell access.If the repository belongs to an organization and you’re using an SSH key generated by an OAuth App, OAuth App access may have been restricted by an organization owner. For more information, see «About OAuth App access restrictions.»
For more information, see Adding a new SSH key to your GitHub account.
Check that the repository really exists
If all else fails, make sure that the repository really exists on GitHub.com!
If you’re trying to push to a repository that doesn’t exist, you’ll get this error.
Error: Remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout
This error occurs if the default branch of a repository has been deleted on GitHub.com.
Detecting this error is simple; Git will warn you when you try to clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/USER/REPO.git
# Clone a repo
> Cloning into 'repo'...
> remote: Counting objects: 66179, done.
> remote: Compressing objects: 100% (15587/15587), done.
> remote: Total 66179 (delta 46985), reused 65596 (delta 46402)
> Receiving objects: 100% (66179/66179), 51.66 MiB | 667 KiB/s, done.
> Resolving deltas: 100% (46985/46985), done.
> warning: remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout.To fix the error, you’ll need to be an administrator of the repository on GitHub.com.
You’ll want to change the default branch of the repository.
After that, you can get a list of all the available branches from the command line:
$ git branch -a
# Lists ALL the branches
> remotes/origin/awesome
> remotes/origin/more-work
> remotes/origin/new-mainThen, you can just switch to your new branch:
$ git checkout new-main
# Create and checkout a tracking branch
> Branch new-main set up to track remote branch new-main from origin.
> Switched to a new branch 'new-main'Symptoms
Problem #1:
When trying to create repositories, Git commands return error code 400:
The following can be seen in the atlassian-bitbucket.log:
2012-10-08 15:04:10,147 INFO [http-7990-32] blah 904x33x1 ky07q7 143.88.25.110 "POST /projects/TEST/repos HTTP/1.1" c.a.s.internal.scm.git.CreateCommand Repository t1 has been created and configured successfully 2012-10-08 15:04:26,327 ERROR [http-7990-8] blah 904x38x1 1e7prrh 143.88.25.110 "GET /scm/TEST/t1.git/info/refs HTTP/1.1" c.a.s.i.scm.git.web.GitSmartRequest Request for repo 't1' of project 'TEST' from 'IP' failed: read process '/usr/local/bin/git http-backend /info/refs' caused an exception Process's error output: warning: unable to access '/root/etc/gitconfig': Permission denied warning: unable to access '/root/etc/gitconfig': Permission denied warning: unable to access '/root/etc/gitconfig': Permission denied warning: unable to access '/root/etc/gitconfig': Permission denied git: 'http-backend' is not a git command. See 'git --help'.Problem #2:
When running git commands on your CI applications (i.e. Jenkins), with Bitbucket server DEBUG logs on — refer to Enable debug logging.
The following can be seen on your CI system:
Failed to connect to repository : Command "/usr/bin/git -c core.askpass=true ls-remote -h http://jenkins@mybitbucketserver.com:7990/scm/TT/test.git HEAD" returned status code 128:
stdout:
stderr: error: The requested URL returned error: 400 Bad Request while accessing http://jenkins@mybitbucketserver.com:7990/scm/TT/test.git/info/refsThe following can be seen on your Bitbucket Server atlassian-bitbucket.log:
2016-08-26 14:48:20,317 DEBUG [http-nio-7990-exec-3117] @H5FYGBx888x863255x0 10.138.28.33 "GET /scm/TT/test.git/info/refs HTTP/1.1" c.a.s.i.s.g.p.h.DefaultGitHttpScmRequestHandler It looks like we've received a 'dumb' protocol git request. service=null, pathInfo=/TT/test.git/info/refs<IP> | http | i@H5FYGBx888x863255x0 | - | 2016-08-26 14:48:20,310 | "GET /scm/TT/test.git/info/refs HTTP/1.1" | "" "git/1.7.1" | - | - | - |
<IP> | http | o@H5FYGBx888x863255x0 | - | 2016-08-26 14:48:20,318 | "GET /scm/TT/test.git/info/refs HTTP/1.1" | "" "git/1.7.1" | - | 8 | - |Cause
Problem #1:
This happens because the Git server is trying to use the git «dumb» HTTP protocol, which is not supported by Bitbucket Server. Bitbucket Server supports only the «smart» HTTP protocol, which was introduced in Git 1.6.6.
Problem #2:
The Git client is performing a dumb protocol request because it is an old version.
Resolution
Problem #1:
Update the Git on the system running your Bitbucket server to a supported one (1.6.6 and above).
Problem #2:
Update the Git client to something higher the Git 1.7.1. Although Git dumb protocol is supposed to be used on any Git client above 1.6.6 (see 4.1 Git on the Server — The Protocols). Please upgrade upgrade your Git client to the most of recent supported one as described on our Supported Platforms.
Ответ на:
комментарий
от damix9 15.02.22 21:44:28 MSK
Server: 127.0.0.53
Address: 127.0.0.53#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: linux.org.ru
Address: 178.248.233.6
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от a1batross 15.02.22 22:00:29 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:03:41 MSK
Тогда отметь тему как решено.
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:03:41 MSK
Что сделать-то хотите? Кто вам сказал клонировать именно git.example.org? Может вы не правильно инструкции поняли?
- Показать ответ
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от a1batross 15.02.22 22:13:27 MSK
Я не клонирую git.example.org, я клонирую свой репозиторий (с github), а он мне эту ошибку выдаёт
- Показать ответы
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:15:11 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:15:11 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от Jameson 15.02.22 22:20:18 MSK
Там написано, что :
Опять же, затрагиваются только пользователи, подключающиеся через SSH или git://. Если ваши Git-пульты начинаются с https://, ничто здесь не повлияет на вас.
Если я всё правильно поняла, то на меня это не должно повлиять, так как мой пульт начинается с https://.
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от a1batross 15.02.22 22:17:29 MSK
Я работаю в vscode (установлено расширение GitHub Pull Requests and Issues). Создаю репозиторий на github, пытаюсь склонировать его на свой компьютер через git clone, выдаёт эту ошибку (тоже самое при попытке сделать push). Извините, я не знаю, как ещё объяснить
- Показать ответ
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:37:58 MSK
Просто Could not resolve host говорит о том, что Git не смог преобразовать github.com в IP адрес. Прямым текстом именно это и пишется.
Если вам так стыдно выложить лог, что вы даже github.com подменяете на какую-то бессмыслицу типа example.com, наврядли вам вообще кто-то поможет.
- Показать ответ
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от a1batross 15.02.22 22:41:31 MSK
Я ничего не подменяю… Это
> git push -u origin main
fatal: unable to access 'https://git.example.com/example.git (you can omit this URL)/': Could not resolve host: git.example.com
в точности то, что мне выдаёт vscode при попытке клонирования репозитория…
- Показать ответ
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 15.02.22 22:49:00 MSK
Точнее то, что выше это на попытку сделать push, а при клонировании это
> git clone https://github.com/BlackKubIsI/WEB_flask_wtf.git /home/blackkub/Music/WEB_flask_wtf --progress
fatal: unable to access 'https://git.example.com/example.git (you can omit this URL)/': Could not resolve host: git.example.com
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от token_polyak 15.02.22 22:50:10 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от token_polyak 15.02.22 22:50:10 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от BlackKub 17.02.22 20:14:07 MSK
Ответ на:
комментарий
от damix9 17.02.22 22:25:27 MSK
По глупости вставила это
[remote "origin"]
url = https://git.example.com/example.git (you can omit this URL)
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
в
git config -e --global
- Ссылка
Ответ на:
комментарий
от damix9 17.02.22 22:25:27 MSK
Удалила эту фигню + git fetch –all и всё заработало
- Ссылка
Troubleshooting cloning errors
In this article
If you’re having trouble cloning a repository, check these common errors.
HTTPS cloning errors
There are a few common errors when using HTTPS with Git. These errors usually indicate you have an old version of Git, or you don’t have access to the repository.
Here’s an example of an HTTPS error you might receive:
Check your Git version
There’s no minimum Git version necessary to interact with GitHub, but we’ve found version 1.7.10 to be a comfortable stable version that’s available on many platforms. You can always download the latest version on the Git website.
Ensure the remote is correct
The repository you’re trying to fetch must exist on GitHub.com, and the URL is case-sensitive.
You can find the URL of the local repository by opening the command line and typing git remote -v :
Alternatively, you can change the URL through our GitHub Desktop application.
Provide an access token
To access GitHub, you must authenticate with a personal access token instead of your password. For more information, see «Creating a personal access token.»
If you are accessing an organization that uses SAML SSO and you are using a personal access token (classic), you must also authorize your personal access token to access the organization before you authenticate. For more information, see «About authentication with SAML single sign-on» and «Authorizing a personal access token for use with SAML single sign-on.»
Check your permissions
When prompted for a username and password, make sure you use an account that has access to the repository.
Tip: If you don’t want to enter your credentials every time you interact with the remote repository, you can turn on credential caching. If you are already using credential caching, please make sure that your computer has the correct credentials cached. Incorrect or out of date credentials will cause authentication to fail.
Use SSH instead
If you’ve previously set up SSH keys, you can use the SSH clone URL instead of HTTPS. For more information, see «About remote repositories.»
Error: Repository not found
If you see this error when cloning a repository, it means that the repository does not exist or you do not have permission to access it. There are a few solutions to this error, depending on the cause.
Check your spelling
Typos happen, and repository names are case-sensitive. If you try to clone git@github.com:user/repo.git , but the repository is really named User/Repo you will receive this error.
To avoid this error, when cloning, always copy and paste the clone URL from the repository’s page. For more information, see «Cloning a repository.»
To update the remote on an existing repository, see «Managing remote repositories».
Checking your permissions
If you are trying to clone a private repository but do not have permission to view the repository, you will receive this error.
Make sure that you have access to the repository in one of these ways:
- The owner of the repository
- A collaborator on the repository
- A member of a team that has access to the repository (if the repository belongs to an organization)
Check your SSH access
In rare circumstances, you may not have the proper SSH access to a repository.
You should ensure that the SSH key you are using is attached to your personal account on GitHub. You can check this by typing the following into the command line:
If the repository belongs to an organization and you’re using an SSH key generated by an OAuth App, OAuth App access may have been restricted by an organization owner. For more information, see «About OAuth App access restrictions.»
Check that the repository really exists
If all else fails, make sure that the repository really exists on GitHub.com! If you’re trying to push to a repository that doesn’t exist, you’ll get this error.
Error: Remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout
This error occurs if the default branch of a repository has been deleted on GitHub.com.
Detecting this error is simple; Git will warn you when you try to clone the repository:
To fix the error, you’ll need to be an administrator of the repository on GitHub.com. You’ll want to change the default branch of the repository.
After that, you can get a list of all the available branches from the command line:
Then, you can just switch to your new branch:
Help us make these docs great!
All GitHub docs are open source. See something that’s wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
Источник
Bitbucket Support
Knowledge base
Products
Jira Software
Project and issue tracking
Jira Service Management
Service management and customer support
Jira Work Management
Manage any business project
Confluence
Bitbucket
Git code management
Resources
Documentation
Usage and admin help
Community
Answers, support, and inspiration
Suggestions and bugs
Feature suggestions and bug reports
Marketplace
Billing and licensing
Frequently asked questions
Viewport
Confluence
Git Commands Return Error Code 400
Related content
Still need help?
The Atlassian Community is here for you.
Symptoms
Problem #1:
When trying to create repositories, Git commands return error code 400:
The following can be seen in the atlassian-bitbucket.log :
Problem #2:
When running git commands on your CI applications (i.e. Jenkins), with Bitbucket server DEBUG logs on — refer to Enable debug logging.
The following can be seen on your CI system:
The following can be seen on your Bitbucket Server atlassian-bitbucket.log :
Problem #1:
This happens because the Git server is trying to use the git «dumb» HTTP protocol, which is not supported by Bitbucket Server. Bitbucket Server supports only the «smart» HTTP protocol, which was introduced in Git 1.6.6.
Problem #2:
Resolution
Problem #1:
Update the Git on the system running your Bitbucket server to a supported one (1.6.6 and above).
Problem #2:
Update the Git client to something higher the Git 1.7.1. Although Git dumb protocol is supposed to be used on any Git client above 1.6.6 (see 4.1 Git on the Server — The Protocols). Please upgrade upgrade your Git client to the most of recent supported one as described on our Supported Platforms.
Источник
Ошибка 400 Bad Request: что это означает и как ее исправить
Ошибка 400 Bad Request – это код ответа HTTP , который означает, что сервер не смог обработать запрос, отправленный клиентом из-за неверного синтаксиса. Подобные коды ответа HTTP отражают сложные взаимоотношения между клиентом, веб-приложением, сервером, а также зачастую сразу несколькими сторонними веб-сервисами. Из-за этого поиск причины появления ошибки может быть затруднён даже внутри контролируемой среды разработки.
В этой статье мы разберём, что значит ошибка 400 Bad Request ( переводится как « Неверный запрос »), и как ее исправить
На стороне сервера или на стороне клиента?
Все коды ответа HTTP из категории 4xx считаются ошибками на стороне клиента. Несмотря на это, появление ошибки 4xx не обязательно означает, что проблема как-то связана с клиентом, под которым понимается веб-браузер или устройство, используемое для доступа к приложению. Зачастую, если вы пытаетесь диагностировать проблему со своим приложением, можно сразу игнорировать большую часть клиентского кода и компонентов, таких как HTML , каскадные таблицы стилей ( CSS ), клиентский код JavaScript и т.п. Это также применимо не только к сайтам. Многие приложения для смартфонов, которые имеют современный пользовательский интерфейс, представляют собой веб-приложения.
С другой стороны, ошибка 400 Bad Request означает, что запрос, присланный клиентом, был неверным по той или иной причине. Пользовательский клиент может попытаться загрузить слишком большой файл, запрос может быть неверно сформирован, заголовки HTTP запроса могут быть неверными и так далее.
Мы рассмотрим некоторые из этих сценариев ( и потенциальные решения ) ниже. Но имейте в виду: мы не можем однозначно исключить ни клиент, ни сервер в качестве источника проблемы. В этих случаях сервер является сетевым объектом, генерирующим ошибку 400 Bad Request и возвращающим её как код ответа HTTP клиенту, но возможно именно клиент ответственен за возникновение проблемы.
Начните с тщательного резервного копирования приложения
Важно сделать полный бэкап вашего приложения, базы данных и т.п. прежде , чем вносить какие-либо правки или изменения в систему. Ещё лучше, если есть возможность создать полную копию приложения на дополнительном промежуточном сервере, который недоступен публично.
Подобный подход обеспечит чистую тестовую площадку, на которой можно отрабатывать все возможные сценарии и потенциальные изменения, чтобы исправить или иную проблему без угрозы безопасности или целостности вашего « живого » приложения.
Диагностика ошибки 400 Bad Request
Ошибка 400 Bad Request означает, что сервер ( удалённый компьютер ) не может обработать запрос, отправленный клиентом ( браузером ), вследствие проблемы, которая трактуется сервером как проблема на стороне клиента.
Существует множество сценариев, в которых ошибка 400 Bad Request может появляться в приложении. Ниже представлены некоторые наиболее вероятные случаи:
- Клиент случайно ( или намеренно ) отправляет информацию, перехватываемую маршрутизатором ложных запросов. Некоторые веб-приложения ищут особые заголовки HTTP , чтобы обрабатывать запросы и удостовериться в том, что клиент не предпринимает ничего зловредного. Если ожидаемый заголовок HTTP не найден или неверен, то ошибка 400 Bad Request – возможный результат.
- Клиент может загружать слишком большой файл. Большинство серверов или приложений имеют лимит на размер загружаемого файла, Это предотвращает засорение канала и других ресурсов сервера. Во многих случаях сервер выдаст ошибку 400 Bad Request , когда файл слишком большой и поэтому запрос не может быть выполнен.
- Клиент запрашивает неверный URL . Если клиент посылает запрос к неверному URL ( неверно составленному ), это может привести к возникновению ошибки 400 Bad Request .
- Клиент использует недействительные или устаревшие куки. Это возможно, так как локальные куки в браузере являются идентификатором сессии. Если токен конкретной сессии совпадает с токеном запроса от другого клиента, то сервер/приложение может интерпретировать это как злонамеренный акт и выдать код ошибки 400 Bad Request .
Исправление проблем на стороне клиента
Устранение ошибки 400 Bad Request ( попробуйте позже ) лучше начать с исправления на стороне клиента. Вот несколько советов, что следует попробовать в браузере или на устройстве, которые выдают ошибку.
Проверьте запрошенный URL
Наиболее частой причиной ошибки 400 Bad Request является банальный ввод некорректного URL . Доменные имена ( например, internet-technologies.ru ) нечувствительны к регистру, поэтому ссылка, написанная в смешанном регистре, такая как interNET-technologies.RU работает так же, как и нормальная версия в нижнем регистре internet-technologies.ru. Но части URL , которые расположены после доменного имени, чувствительными к регистру. Кроме случаев, когда приложение/сервер специально осуществляет предварительную обработку всех URL и переводит их в нижний регистр перед исполнением запроса.
Важно проверять URL на неподходящие специальные символы, которых в нем не должно быть. Если сервер получает некорректный URL , он выдаст ответ в виде ошибки 400 Bad Request .
Очистите соответствующие куки
Одной из потенциальных причин возникновения ошибки 400 Bad Request являются некорректные или дублирующие локальные куки. Файлы куки в HTTP – это небольшие фрагменты данных, хранящиеся на локальном устройстве, которые используются сайтами и веб-приложениями для « запоминания » конкретного браузера или устройства. Большинство современных веб-приложений использует куки для хранения данных, специфичных для браузера или пользователя, идентифицируя клиента и позволяя делать следующие визиты быстрее и проще.
Но куки, хранящие информацию сессии о вашем аккаунте или устройстве, могут конфликтовать с другим токеном сессии от другого пользователя, выдавая кому-то из вас ( или вам обоим ) ошибку 400 Bad Request .
В большинстве случаев достаточно рассматривать только ваше приложение в отношении файлов куки, которые относятся к сайту или веб-приложению, выдающему ошибку 400 Bad Request .
Куки хранятся по принципу доменного имени веб-приложения, поэтому можно удалить только те куки, которые соответствуют домену сайта, сохранив остальные куки не тронутыми. Но если вы не знакомы с ручным удалением определённых файлов куки, гораздо проще и безопаснее очистить сразу все файлы куки.
Это можно сделать разными способами в зависимости от браузера, который вы используете:
- Google Chrome;
- Internet Explorer;
- Microsoft Edge;
- Mozilla Firefox;
- Safari.
Загрузка файла меньшего размера
Если вы получаете ошибку 400 Bad Request при загрузке какого-либо файла, попробуйте корректность работы на меньшем по размеру файле, Это включает в себя и «загрузки» файлов, которые не загружаются с вашего локального компьютера. Даже файлы, отправленные с других компьютеров, считаются «загрузками» с точки зрения веб-сервера, на котором работает ваше приложение.
Выйдите и войдите
Попробуйте выйти из системы и войти обратно. Если вы недавно очистили файлы куки в браузере, это приводит к автоматическому выходу из системы при следующей загрузке страницы. Попробуйте просто войти обратно, чтобы посмотреть, заработала ли система корректно.
Также приложение может столкнуться с проблемой, связанной с вашей предыдущей сессией, являющейся лишь строкой, которую сервер посылает клиенту, чтобы идентифицировать клиента при будущих запросах. Как и в случае с другими данными, токен сессии ( или строка сессии ) хранится локально на вашем устройстве в файлах куки и передаётся клиентом на сервер при каждом запросе. Если сервер решает, что токен сессии некорректен или скомпрометирован, вы можете получить ошибку 400 Bad Request .
В большинстве веб-приложений выход повторный вход приводит к перегенерации локального токена сессии.
Отладка на распространённых платформах
Если вы используете на сервере распространённые пакеты программ, которые выдают ошибку 400 Bad Request , изучите стабильность и функциональность этих платформ. Наиболее распространённые системы управления контентом, такие как WordPress , Joomla! и Drupal , хорошо протестированы в своих базовых версиях. Но как только вы начинаете изменять используемые ими расширения PHP , очень легко спровоцировать непредвиденные проблемы, которые выльются в ошибку 400 Bad Request .
Откатите последние изменения
Если вы обновили систему управления контентом непосредственно перед появлением ошибки 400 Bad Request , рассмотрите возможность отката к предыдущей версии, которая была установлена, как самый быстрый и простой способ убрать ошибку 400 bad request .
Аналогично, любые расширения или модули, которые были обновлены, могут вызывать ошибки на стороне сервера, поэтому откат к предыдущим версиям этих расширений также может помочь.
Но в некоторых случаях CMS не предоставляют возможности отката к предыдущим версиям. Так обычно происходит с популярными платформами, поэтому не бойтесь, если вы не можете найти простой способ вернуться к использованию старой версии той или иной программной платформы.
Удалите новые расширения, модули или плагины
В зависимости от конкретной CMS , которую использует приложение, имена этих компонентов будут различаться. Но во всех системах они служат одной и той же цели: улучшение возможностей платформы относительно её стандартной функциональности.
При этом имейте в виду, что расширения могут так или иначе получать полный контроль над системой, вносить изменения в код PHP , HTML , CSS , JavaScript или базу данных. Поэтому мудрым решением может быть удаление любых новых расширений, которые были недавно добавлены.
Проверьте непреднамеренные изменения в базе данных
Даже если удалили расширение через панель управления CMS , это не гарантирует, что внесенные им изменения были полностью отменены. Это касается многих расширений WordPress , которым предоставляется полный доступ к базе данных.
Расширение может изменить записи в базе данных, которые «не принадлежат» ему, а созданы и управляются другими расширениями ( или даже самой CMS ). В подобных случаях модуль может не знать, как откатить назад изменения, внесенные в записи базы данных.
Я лично сталкивался с такими случаями несколько раз. Поэтому лучшим путём будет открыть базу данных и вручную просмотреть таблицы и записи, которые могли быть изменены расширением.
Поиск проблем на стороне сервера
Если вы уверены, что ошибка 400 Bad Request не связана с CMS , вот некоторые дополнительные советы, которые могут помочь найти проблему на стороне сервера.
Проверка на неверные заголовки HTTP
Ошибка, которую вы получаете от приложения, является результатом недостающих или некорректных специальных заголовков HTTP , которые ожидает получить приложение или сервер. В подобных случаях нужно проанализировать заголовки HTTP , которые отправляются на сторону сервера.
Просмотрите логи
Почти любое веб-приложение будет вести логи на стороне сервера. Они представляют собой историю того, что делало приложение. Например, какие страницы были запрошены, к каким серверам оно обращалось, какие результаты предоставлялись из базы данных и т.п.
Логи сервера относятся к оборудованию, на котором выполняется приложение, и зачастую представляют собой детали о статусе подключённых сервисов или даже о самом сервере. Поищите в интернете “ логи [ИМЯ_ПЛАТФОРМЫ] ”, если вы используете CMS , или “ логи [ЯЗЫК_ПРОГРАММИРОВАНИЯ] ” и “ логи [ОПЕРАЦИОННАЯ_СИСТЕМА] ”, если у вас собственное приложение, чтобы получить подробную информацию по поиску логов.
Отладьте код приложения или скриптов
Если это не помогло, проблема может быть в исходном коде, который выполняется внутри приложения. Попытайтесь диагностировать, откуда может исходить проблема, отлаживая приложение вручную и параллельно просматривая логи приложения и сервера.
Создайте копию всего приложения на локальном устройстве для разработки и пошагово повторите тот сценарий, который приводил к возникновению ошибки 400 Bad Request . А затем просмотрите код приложения в тот момент, когда что-то пойдёт не так.
Независимо от причины возникновения ошибки, даже если вам удалось исправить её в этот раз, появление в вашем приложении такой проблемы — это сигнал для того, чтобы внедрить инструмент обработки ошибок, который поможет автоматически обнаруживать их и оповещать в момент возникновения.
Сергей Бензенко автор-переводчик статьи « 400 Bad Request Error What It Is and How to Fix It »
Источник