Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Python offers multiple options for developing GUI (Graphical User Interface). Out of all the GUI methods, tkinter is the most commonly used method. It is a standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit shipped with Python. Python with tkinter is the fastest and easiest way to create the GUI applications. Creating a GUI using tkinter is an easy task.
Note: For more information, refer to Python GUI – tkinter
MessageBox Widget
Python Tkinter – MessageBox Widget is used to display the message boxes in the python applications. This module is used to display a message using provides a number of functions.
Syntax:
messagebox.Function_Name(title, message [, options])
Parameters:
There are various parameters :
- Function_Name: This parameter is used to represents an appropriate message box function.
- title: This parameter is a string which is shown as a title of a message box.
- message: This parameter is the string to be displayed as a message on the message box.
- options: There are two options that can be used are:
- default: This option is used to specify the default button like ABORT, RETRY, or IGNORE in the message box.
- parent: This option is used to specify the window on top of which the message box is to be displayed.
Function_Name:
There are functions or methods available in the messagebox widget.
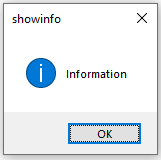
- showinfo(): Show some relevant information to the user.
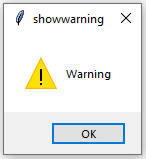
- showwarning(): Display the warning to the user.
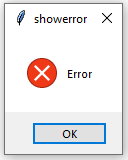
- showerror(): Display the error message to the user.
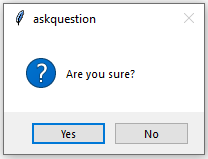
- askquestion(): Ask question and user has to answered in yes or no.
- askokcancel(): Confirm the user’s action regarding some application activity.
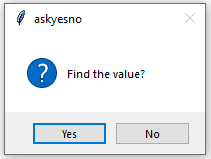
- askyesno(): User can answer in yes or no for some action.
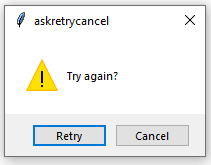
- askretrycancel(): Ask the user about doing a particular task again or not.
Example:
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import messagebox
root = Tk()
root.geometry("300x200")
w = Label(root, text ='GeeksForGeeks', font = "50")
w.pack()
messagebox.showinfo("showinfo", "Information")
messagebox.showwarning("showwarning", "Warning")
messagebox.showerror("showerror", "Error")
messagebox.askquestion("askquestion", "Are you sure?")
messagebox.askokcancel("askokcancel", "Want to continue?")
messagebox.askyesno("askyesno", "Find the value?")
messagebox.askretrycancel("askretrycancel", "Try again?")
root.mainloop()
Output:
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to show various message boxes using the tkinter.messagebox module.
Introduction to tkinter.messagebox module
When developing a Tkinter application, you often want to notify users about the events that occurred.
For example, when users click the save button, you want to notify them that the record has been saved successfully.
If an error occurred, for example, the database server is not reachable, you can notify users of the error.
When the update has been completed but the record already exists, you may want to show a warning.
To cover all of these scenarios, you can use various functions from the tkinter.messagebox module:
showinfo()– notify that an operation completed successfully.showerror()– notify that an operation hasn’t completed due to an error.showwarrning()– notify that an operation completed but something didn’t behave as expected.
All of these functions accept two arguments:
Code language: Python (python)
showinfo(title, message) showerror(title, message) showwarrning(title, message)
- The
titleis displayed on the title bar of the dialog. - The
messageis shown on the dialog.
To span the message multiple lines, you can add the new line character 'n'.
Tkinter messagebox examples
The following program consists of three buttons. When you click a button, the corresponding message box will display.
Code language: Python (python)
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo # create the root window root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter MessageBox') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150') # options = {'fill': 'both', 'padx': 10, 'pady': 10, 'ipadx': 5} ttk.Button( root, text='Show an error message', command=lambda: showerror( title='Error', message='This is an error message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an information message', command=lambda: showinfo( title='Information', message='This is an information message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an warning message', command=lambda: showwarning( title='Warning', message='This is a warning message.') ).pack(**options) # run the app root.mainloop()
How it works.
First, import the tkinter, tkinter.ttk, and tkinter.messagebox modules:
Code language: Python (python)
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo
Second, create the root window and initialize its properties:
Code language: Python (python)
# create the root window root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter MessageBox') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150')
Third, create three buttons and assign a lambda expression to the command option of each button. Each lambda expression shows a corresponding message box.
Code language: Python (python)
ttk.Button( root, text='Show an error message', command=lambda: showerror( title='Error', message='This is an error message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an information message', command=lambda: showinfo( title='Information', message='This is an information message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an warning message', command=lambda: showwarning( title='Warning', message='This is a warning message.') ).pack(**options)
Finally, display the root window.
Code language: Python (python)
root.mainloop()
Summary
- Use
showinfo(),showerror(),showwarrning()functions from thetkinter.messageboxmodule to show an information, error, and warning message.
Did you find this tutorial helpful ?
Последнее обновление: 24.09.2022
Окна сообщений
Tkinter имеет ряд встроенных окон для разных ситуаций, в частности, окна сообщений, функционал которых заключен в модуле tkinter.messagebox.
Для отображения сообщений этот модуль предоставляет следующие функции:
-
showinfo(): предназначена для отображения некоторой информации
-
showerror(): предназначена для отображения ошибок
-
showwarrning(): предназначена для отображения предупреждений
Все эти функции принимают три параметра:
showinfo(title, message, **options) showerror(title, message, **options) showwarrning(title, message, **options)
-
title: заголовок окна
-
message: отображаемое сообщение
-
options: настройки окна
В реальности различие между этими типами сообщений заключается лишь в изображении, которое отображается рядом с текстом сообщения:
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def open_info():
showinfo(title="Информация", message="Информационное сообщение")
def open_warning():
showwarning(title="Предупреждение", message="Сообщение о предупреждении")
def open_error():
showerror(title="Ошибка", message="Сообщение об ошибке")
info_button = ttk.Button(text="Информация", command=open_info)
info_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
warning_button = ttk.Button(text="Предупреждение", command=open_warning)
warning_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
error_button = ttk.Button(text="Ошибка", command=open_error)
error_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
Здесь по нажатию на каждую из трех кнопок отображается соответствующее сообщение:
Окна подтверждения операции
Модуль tkinter.messagebox также предоставляет ряд функций для подтверждения операции, где пользователю предлагается
нажать на одну из двух кнопок:
-
askyesno()
-
askokcancel()
-
askretrycancel()
Все эти функции принимают те же три параметра title, message и options. Отличие между ними только в том, что кнопки имеют разный текст. В случае нажатия на кнопку подтверждения, функция возвращает значение True, иначе возвращается False
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo, askyesno
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
result = askyesno(title="Подтвержение операции", message="Подтвердить операцию?")
if result: showinfo("Результат", "Операция подтверждена")
else: showinfo("Результат", "Операция отменена")
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
В данном случае по нажатию на кнопку вызывается функция askyesno(), которая отображает диалоговое окно с двумя кнопками «Да» и «Нет».
В зависимости от того, на какую кнопку нажмет пользователь, функция возвратит True или False. Получив результат функции, мы можем проверить его и выполнить те или иные действия.
Особняком стоит функция askquestion — она также отображает две кнопки для подтверждения или отмены действия (кнопки «Yes»(Да) и «No»(Нет)),
но в зависимости от нажатой кнопки возвращает строку: «yes» или «no».
Также отдельно стоит функция askyesnocancel() — она отображает три кнопки: Yes (возвращает True), No (возвращает False) и Cancel
(возвращает None):
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo, askyesnocancel
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
result = askyesnocancel(title="Подтвержение операции", message="Подтвердить операцию?")
if result==None: showinfo("Результат", "Операция приостановлена")
elif result: showinfo("Результат", "Операция подтверждена")
else : showinfo("Результат", "Операция отменена")
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
В этом случае диалоговое окно предоставит выбор из трех альтернатив
Настройка окон
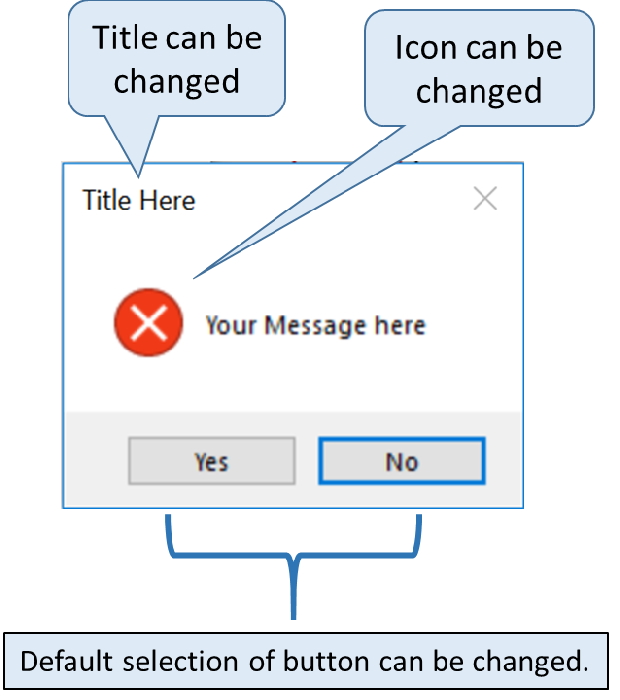
Дополнительно все вышерассмотренные функции принимают ряд параметров, которые могут применяться для настройки окон. Некоторые из них:
-
detail: дополнительный текст, который отображается под основным сообщением -
icon: иконка, которая отображается рядом с сообщением. Должна представлять одно из втроенных изображений: info, error, question или warning -
default: кнопка по умолчанию. Должна представлять одно из встроенных значений: abort, retry, ignore, ok, cancel, no, yes
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import OK, INFO, showinfo
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
showinfo(title="METANIT.COM", message="Добро пожаловать на сайт METANIT.COM",
detail="Hello World!", icon=INFO, default=OK)
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
При нажатии на кнопку отобразится следующее окно:
What is Tkinter Messagebox?
Tkinter Messagebox is a module in python which provides a different set of dialogues that are used to display message boxes, showing errors or warnings, widgets to select files or change colors which is a pop-up box with a relevant message being displayed along with a title based on the requirement in python applications with an icon and interrupts the user flow to take input from the user is called Tkinter Messagebox and has different functions that are used to display the relevant messages based on the application requirements like info message, warning message, error message, or taking input from the user.
Syntax:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
messagebox.functionname(title, message [,options])Explanation: In the above syntax, we have imported the Tkinter library, and from that, we imported the messagebox module using which we can call different functions and display the relevant messages along with title based on the application requirement.
Attributes of Tkinter Messagebox
In the previous section, we have discussed the syntax of the Tkinter messagebox. Now we will discuss in detail the parameters or attributes being used in the syntax. There are four attributes in the syntax: function name, title, message, and options.
- Function name: The function name represents the proper name for the message box function.
- Title: Title is a message which will be displayed in the dialogue box of the message in the title bar.
- Message: Messages is a text used to display a message to the appropriate function name.
- Options: Options are like a choice by which we can customize the message box, which is standard. Some of the options are default and parent. The default option is used to mention default operations or message boxes buttons such as ABORT, IGNORE or RETRY in the message box. Parent option is used to mention a parental window on top of which message box will be displayed.
Methods of Tkinter Messagebox
Let’s have a look at different functions available with Tkinter messagebox such as showinfo(), showwarning(), showerror(), askquestion(), askokcancel(), askyesno(), and, askretrycancel(). The above functions used to show appropriate message boxes, and all the functions have the same kind of syntax but with different functionalities. All the functions which we are going to discuss are with python3 and above.
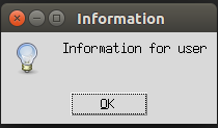
1. showinfo()
We use this messagebox function when we want to show some related or relevant information to the user. Let us try to create an information message box with an example below.
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.showinfo("Information","Information for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with showinfo() function to display the information message.
Output:
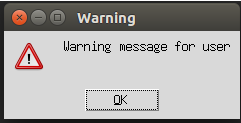
2. showwarning()
We use this messagebox function when we want to display a warning message to the user. Let us create a warning message to the user by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.showwarning("Warning","Warning message for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with a showwarning() function to display the user’s warning message.
Output:
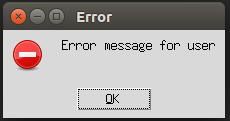
3. showerror()
We use this messagebox function when we want to display an error message to the user. Let us create an error message to the user by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.showerror("Error","Error message for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with showerror() function to display the user’s warning message.
Output:
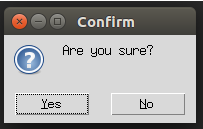
4. askquestion()
We use this messagebox function when we want to ask the user some questions, which can be answered by using yes or no. Let us create a program to ask the user a question whether the user wants to confirm it or not by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.askquestion("Confirm","Are you sure?")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with askquestion() function to ask the user a question Confirm with a message Are you sure?
Output:
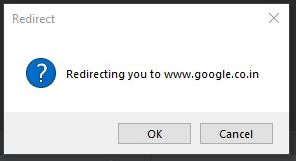
5. askokcancel()
We use this messagebox function when we want to confirm the user’s responses regarding the application behavior or activity. Let us create a program to confirm users response regarding an application by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.askokcancel("Redirect","Redirecting you to www.google.co.in")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using Tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with the askokcancel() function to get the user’s response regarding the application activity.
Output:
6. askyesno()
We use this messagebox function when we want to ask the user regarding some question that can be answered by using yes or no. Let us create a program to ask user regarding some question, and the user will answer by saying yes or no by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
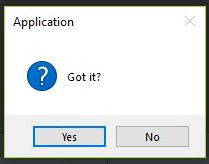
messagebox.askyesno("Application","Got it?")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with askyesno() function to ask the user regarding some question with a message Got it?
Output:
Examples to Implement Tkinter Messagebox
Let us create an application using labels, grid, and Entry class to take input from it and apply the action after a button click as the below example.
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import *
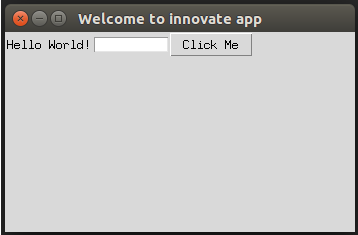
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.title("Welcome to innovate app")
top.geometry("350x200")
labl = Label(top, text=”Hello World!”)
labl.grid(column=0, row=0)
txt = Entry(top, width=10)
txt.grid(column=1, row=0)
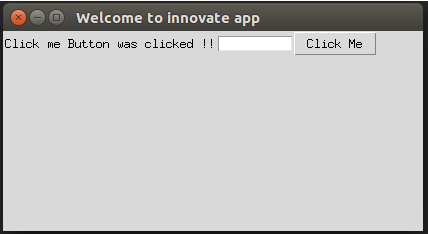
def click():
labl.configure(text="Click me Button was clicked ! !")
btn = Button(top, text ="Click Me", command=click)
btn.grid(column=2, row=0)
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we have created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and the function click() where we are configuring the label with the text “Click me Button was clicked!!” and we have created a title to the Tkinter object, created a grid to display the output as below:
Output:
Conclusion
Finally, it’s an overview of the Tkinter messagebox module in python. So far, we have discussed what messagebox, its syntax, its attributes, and functions supported in the module, describing functions in detail, and finally explaining with an example using showinfo() function using the pack() method. I hope after reading this article, you will have a good understanding of the Tkinter messagebox module, its functions, and how to use them based on the application requirement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tkinter Messagebox. Here we discuss Syntax, the attributes, different methods and examples to implement with appropriate syntax and sample code. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Tkinter Scrollbar
- Python Tkinter Label
- Tkinter Listbox
- Tkinter Menubutton
Basics of Python Tkinter
Tkinter Message box to show info & to take confirmation choice as input by showing options to user
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
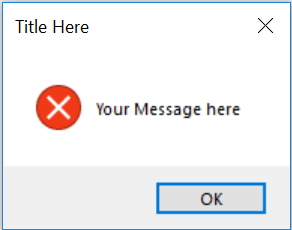
msg.showinfo("Title Here","Your Message here")
#messagebox.showerror("error","Error")
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openAbove window shows information only, we can collect user selection also.
Let us learn different type of message boxes we can use and basic syntax
tkMessageBox.typeofmessage(title, message [, options]).Show Message only :
showerror, showinfo,showwarning
Show Message and get user selection :
askokcancel,askyesno,askquestion,askretrycancel,askyesnocancel
showerror
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
msg.showerror("Title Here ","Your Message here ")
my_w.mainloop()showinfo
#showinfo
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
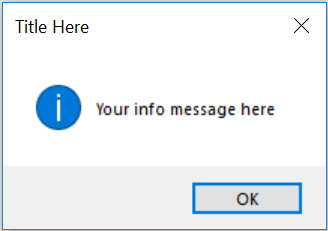
msg.showinfo("Title Here ","Your info message here ")
my_w.mainloop()showwarning
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
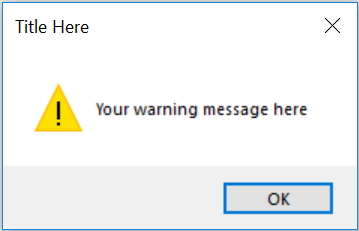
msg.showwarning("Title Here ","Your warning message here ")
my_w.mainloop()We will ask user to select choice and we will capture the selected option through a variable.
askokcancel
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
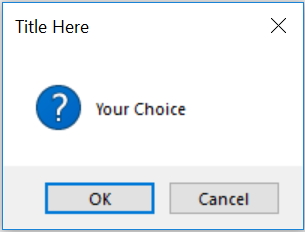
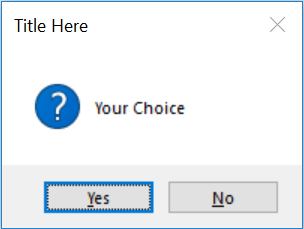
my_var=msg.askokcancel("Title Here ","Your Choice ")
print(my_var) # Output True or False
my_w.mainloop()askyesno
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_var=msg.askyesno("Title Here ","Your Choice ")
print(my_var) # Output True or False
my_w.mainloop()askretrycancel
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
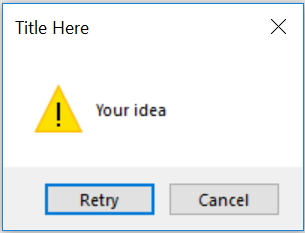
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_var=msg.askretrycancel("Title Here ","Your idea")
print(my_var) # Output True or False
my_w.mainloop()askyesnocancel
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
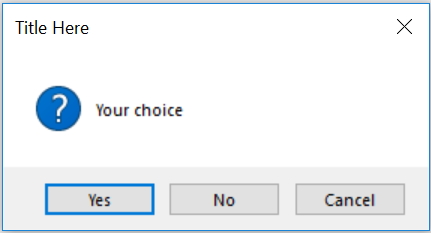
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_var=msg.askyesnocancel("Title Here ","Your choice")
print(my_var) # Output True or False or None
my_w.mainloop()Default button ( Optional )
We can’t change the text in button but we can change the default selection of buttons.
default value can be yes , no or cancel
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
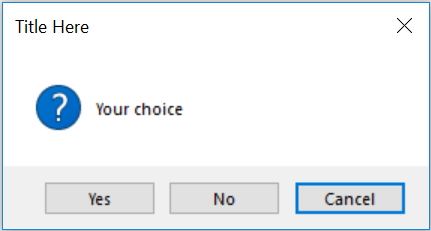
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_var=msg.askyesnocancel("Title Here ","Your choice",default='cancel')
# default = yes or no or cancel
print(my_var)
my_w.mainloop()icon ( Optional )
We can change the default icon comes with the different types of message boxes.
icon = warning or info or question or error
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_var=msg.askyesnocancel("Title Here ","Your choice",icon='warning')
# icon = warning or error or information or question
print(my_var)
my_w.mainloop()Displaying response in window
On click of a Button the message will be displayed. The user response will be collected and displayed through one Label.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox as msg
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("300x200") # Size of the window
#my_var=tk.StringVar(my_w)
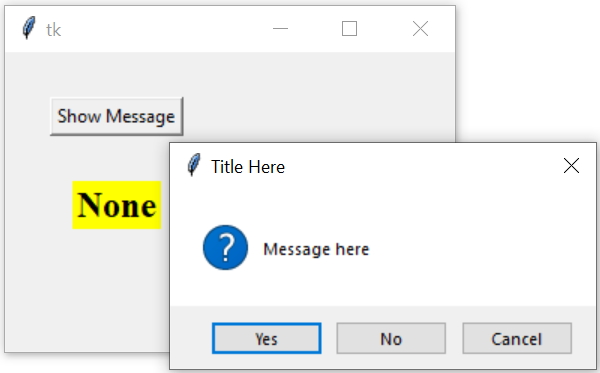
def show_msg(): # on click of the button b1
my_var=msg.askyesnocancel('Title Here', 'Message here')
print(my_var) # print at console
l1.config(text=str(my_var)) # display at Label
b1=tk.Button(my_w,text='Show Message',command=show_msg)
b1.grid(row=1,column=1,padx=30,pady=30)
my_font=('times',18,'bold')
l1=tk.Label(my_w,text='Output here',font=my_font,bg='yellow')
l1.grid(row=2,column=1)
my_w.mainloop()The output will show as 0 or 1, to display as string saying True, False , None , yes, no We have to convert the same to string by using str()
l1.config(text=str(my_var)) # display at Label Customizing message
We can change the message part here and show message by using variables.
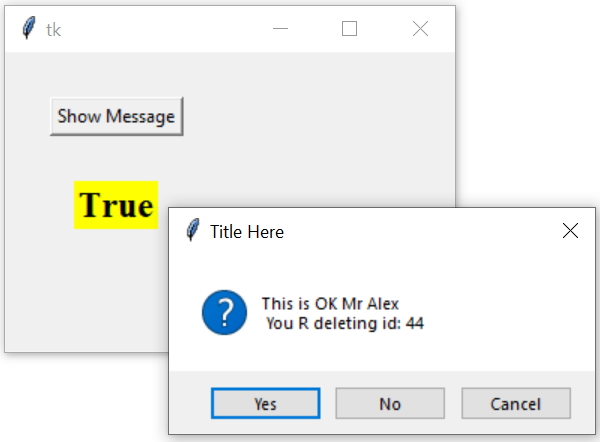
def show_msg():
str1='Alex'
str2=44
m1="This is OK Mr {0} n You R deleting id: {1}".format(str1,str2)
my_var=msg.askyesnocancel('Title Here', m1)
print(my_var)
l1.config(text=str(my_var))- Exercise on MessageBox
- Enter a series of radio button and then show matching messagebox based on the selection and then take input from user and show the value of user selected choice
- We can set the optional parameters icon to four different values ( info, question, warning, error ) . Create four radio buttons and on click of each button will display one showinfo() messagebox with selected type of icon. Inside the message box you can set the matching title and body message while displaying the different icons.
- In a message box we can set default selection of button by setting default value. Create three radio buttons which on select will set the value of default selection of buttons. The message box should display matching title and body message while setting the default button
Solution
simpledialog to take user inputs