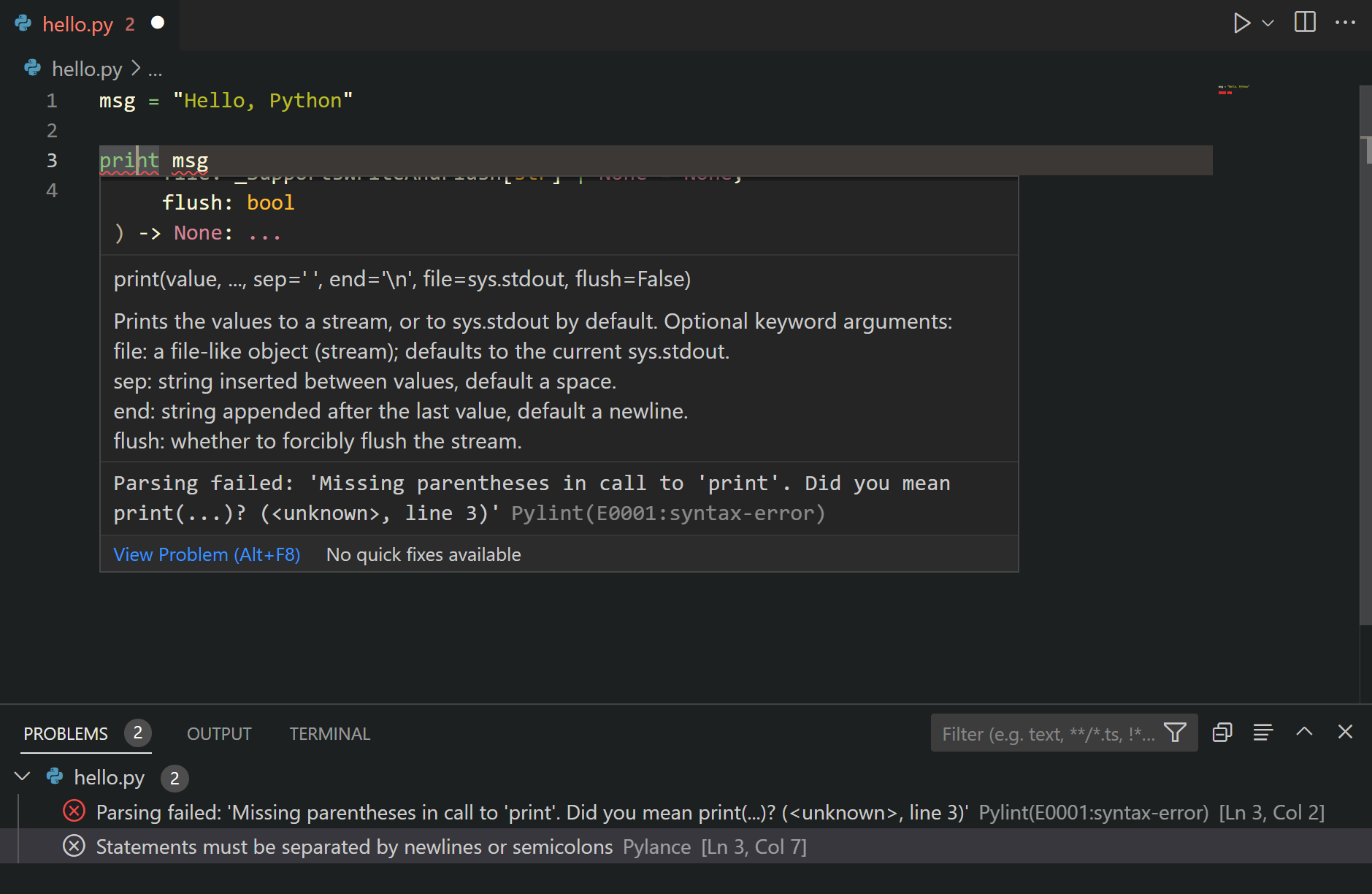
1. Unable to import (pylint)
- Scenario: You have a module installed, however the linter in the IDE is complaining about; not being able to import the module, hence error messages such as the following are displayed as linter errors:
.. unable to import 'xxx' ..
- Cause: The Python extension is most likely using the wrong version of Pylint.
Solution 1: (configure workspace settings to point to fully qualified python executable):
- Open the workspace settings (settings.json)
- Identify the fully qualified path to the python executable (this could even be a virtual environment)
- Ensure Pylint is installed for the above python environment
- Configure the setting “pythonPath” to point to (previously identified) the fully qualified python executable.
"python.pythonPath": "/users/xxx/bin/python"
Solution 2: (open VS Code from an activated virtual environment):
- Open the terminal window
- Activate the relevant python virtual environment
- Ensure Pylint is installed within this virtual environment
pip install pylint - Close all instances of VS Code
- Launch VS Code from within this terminal window
(this will ensure the VS Code process will inherit all of the Virtual Env environment settings)
2. Linting with xxx failed. …
Listing could fail due to a number of reasons. Please check each of the following.
Cause: The path to the python executable is incorrect
Solution: Configure the path to the python executable in the settings.json
Cause: The linter has not been installed in the Python environment being used
Solution: Identify the Python environment (executable) configured in settings.json. Next install the linter(s) against this Python environment (use the corresponding Pip).
Cause: The Path to the linter is incorrect
Solution: If you have provided a custom path to the linter in settings.json, then ensure this file path exist.
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
3. Ignore certain messages
It is possible you would like to ignore certain linter messages. This could be done easily.
Generally most linters support configuration files, hence all you need to do is create the relevant configuration file and ignore the appropriate error message.
If on the other hand the linters support the ability to ignore certain messages via command line args, this can be done as well.
Solution: Add relevant command line args to ignore certain messages
Here we’ll assume you use a TAB character as indentation of python code instead of 4 or 2 spaces.
Pylint would generally display a warning for this with the error code W0312.
In order to disable this particular message all one needs to do is as follows in the settings.json file:
"python.linting.pylintArgs": [
"--disable=W0312"
],
Note: You could apply the above configuration settings in your user settings file, so that it applies to all workspaces.
This saves you from having to define these settings for every single workspace (every time).
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
Содержание
- Linting
- 1. Unable to import (pylint)
- 2. Linting with xxx failed. …
- 3. Ignore certain messages
- Linting
- 1. Unable to import (pylint)
- 2. Linting with xxx failed. …
- 3. Ignore certain messages
- Linting Python in Visual Studio Code
- Enable linting
- Disable linting
- Run linting
- General linting settings
- Specific linters
- Pylint
- Command-line arguments and configuration files
- pydocstyle
- Command-line arguments and configuration files
- Message category mapping
- pycodestyle (pep8)
- Command-line arguments and configuration files
- Message category mapping
- Prospector
- Command-line arguments and configuration files
- Message category mapping
- Flake8
- Command-line arguments and configuration files
- Message category mapping
- Message category mapping
Linting
1. Unable to import (pylint)
- Scenario: You have a module installed, however the linter in the IDE is complaining about; not being able to import the module, hence error messages such as the following are displayed as linter errors:
- Cause: The Python extension is most likely using the wrong version of Pylint.
Solution 1: (configure workspace settings to point to fully qualified python executable):
- Open the workspace settings (settings.json)
- Identify the fully qualified path to the python executable (this could even be a virtual environment)
- Ensure Pylint is installed for the above python environment
- Configure the setting “pythonPath” to point to (previously identified) the fully qualified python executable.
Solution 2: (open VS Code from an activated virtual environment):
- Open the terminal window
- Activate the relevant python virtual environment
- Ensure Pylint is installed within this virtual environment pip install pylint
- Close all instances of VS Code
- Launch VS Code from within this terminal window
(this will ensure the VS Code process will inherit all of the Virtual Env environment settings)
2. Linting with xxx failed. …
Listing could fail due to a number of reasons. Please check each of the following.
Cause: The path to the python executable is incorrect
Solution: Configure the path to the python executable in the settings.json
Cause: The linter has not been installed in the Python environment being used
Solution: Identify the Python environment (executable) configured in settings.json. Next install the linter(s) against this Python environment (use the corresponding Pip).
Cause: The Path to the linter is incorrect
Solution: If you have provided a custom path to the linter in settings.json, then ensure this file path exist.
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
3. Ignore certain messages
It is possible you would like to ignore certain linter messages. This could be done easily.
Generally most linters support configuration files, hence all you need to do is create the relevant configuration file and ignore the appropriate error message.
If on the other hand the linters support the ability to ignore certain messages via command line args, this can be done as well.
Solution: Add relevant command line args to ignore certain messages
Here we’ll assume you use a TAB character as indentation of python code instead of 4 or 2 spaces. Pylint would generally display a warning for this with the error code W0312.
In order to disable this particular message all one needs to do is as follows in the settings.json file:
Note: You could apply the above configuration settings in your user settings file, so that it applies to all workspaces.
This saves you from having to define these settings for every single workspace (every time).
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
Linting
1. Unable to import (pylint)
- Scenario: You have a module installed, however the linter in the IDE is complaining about; not being able to import the module, hence error messages such as the following are displayed as linter errors:
- Cause: The Python extension is most likely using the wrong version of Pylint.
Solution 1: (configure workspace settings to point to fully qualified python executable):
- Open the workspace settings (settings.json)
- Identify the fully qualified path to the python executable (this could even be a virtual environment)
- Ensure Pylint is installed for the above python environment
- Configure the setting “pythonPath” to point to (previously identified) the fully qualified python executable.
Solution 2: (open VS Code from an activated virtual environment):
- Open the terminal window
- Activate the relevant python virtual environment
- Ensure Pylint is installed within this virtual environment pip install pylint
- Close all instances of VS Code
- Launch VS Code from within this terminal window
(this will ensure the VS Code process will inherit all of the Virtual Env environment settings)
2. Linting with xxx failed. …
Listing could fail due to a number of reasons. Please check each of the following.
Cause: The path to the python executable is incorrect
Solution: Configure the path to the python executable in the settings.json
Cause: The linter has not been installed in the Python environment being used
Solution: Identify the Python environment (executable) configured in settings.json. Next install the linter(s) against this Python environment (use the corresponding Pip).
Cause: The Path to the linter is incorrect
Solution: If you have provided a custom path to the linter in settings.json, then ensure this file path exist.
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
3. Ignore certain messages
It is possible you would like to ignore certain linter messages. This could be done easily.
Generally most linters support configuration files, hence all you need to do is create the relevant configuration file and ignore the appropriate error message.
If on the other hand the linters support the ability to ignore certain messages via command line args, this can be done as well.
Solution: Add relevant command line args to ignore certain messages
Here we’ll assume you use a TAB character as indentation of python code instead of 4 or 2 spaces. Pylint would generally display a warning for this with the error code W0312.
In order to disable this particular message all one needs to do is as follows in the settings.json file:
Note: You could apply the above configuration settings in your user settings file, so that it applies to all workspaces.
This saves you from having to define these settings for every single workspace (every time).
For further information on configuring Linters can be found here.
Источник
Linting Python in Visual Studio Code
Linting highlights syntactical and stylistic problems in your Python source code, which often helps you identify and correct subtle programming errors or unconventional coding practices that can lead to errors. For example, linting detects use of an uninitialized or undefined variable, calls to undefined functions, missing parentheses, and even more subtle issues such as attempting to redefine built-in types or functions. Linting is thus distinct from Formatting because linting analyzes how the code runs and detects errors whereas formatting only restructures how code appears.
Note: Stylistic and syntactical code detection is enabled by the Language Server. To enable third-party linters for additional problem detection, you can enable them by using the Python: Select Linter command and selecting the appropriate linter.
Enable linting
To enable linters, open the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) and select the Python: Select Linter command. The Select Linter command adds «python.linting.
Enabling a linter prompts you to install the required packages in your selected environment for the chosen linter.
Note: If you’re using a global environment and VS Code is not running elevated, linter installation may fail. In that case, either run VS Code elevated, or manually run the Python package manager to install the linter at an elevated command prompt for the same environment: for example sudo pip3 install pylint (macOS/Linux) or pip install pylint (Windows, at an elevated prompt).
Disable linting
You can easily toggle between enabling and disabling your linter. To switch, open the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) and select the Python: Enable/Disable Linting command.
This will populate a dropdown with the current linting state and options to Enable or Disable Python linting.
Run linting
To perform linting, open the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ), filter on «linting», and select Python: Run Linting. Linting will run automatically when you save a file.
Issues are shown in the Problems panel and as wavy underlines in the code editor. Hovering over an underlined issue displays the details:
General linting settings
You can add any of the linting settings to your user settings.json file (opened with the File > Preferences > Settings command ⌘, (Windows, Linux Ctrl+, ) ). Refer to User and Workspace settings to find out more about working with settings in VS Code.
To change the linting behavior across all enabled linters, modify the following settings:
| Feature | Setting (python.linting.) |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Linting in general | enabled | true |
| Linting on file save | lintOnSave | true |
| Maximum number of linting messages | maxNumberOfProblems | 100 |
| Exclude file and folder patterns | ignorePatterns | [«.vscode/*.py», «**/site-packages/**/*.py»] |
When enabling lintOnSave , you might also want to enable the generic files.autoSave option (see Save / Auto Save). The combination provides frequent linting feedback in your code as you type.
Specific linters
The following table provides a summary of available Python linters and their basic settings. For descriptions of individual settings, see the Linter settings reference.
| Linter | Package name for pip install command | True/false enable setting (python.linting.) |
Arguments setting (python.linting.) |
Custom path setting (python.linting.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pylint | pylint | pylintEnabled | pylintArgs | pylintPath |
| Flake8 | flake8 | flake8Enabled | flake8Args | flake8Path |
| mypy | mypy | mypyEnabled | mypyArgs | mypyPath |
| pycodestyle (pep8) | pycodestyle | pycodestyleEnabled | pycodestyleArgs | pycodestylePath |
| prospector | prospector | prospectorEnabled | prospectorArgs | prospectorPath |
| pylama | pylama | pylamaEnabled | pylamaArgs | pylamaPath |
| bandit | bandit | banditEnabled | banditArgs | banditPath |
Note: If you don’t find your preferred linter in the table above, you can add support via an extension. The Python Extension Template makes it easy to integrate new Python tools into VS Code.
To select a different linter, use the Python: Select Linter command. You can also edit your settings manually to enable multiple linters. Note, that using the Select Linter command overwrites those edits.
Custom arguments are specified in the appropriate arguments setting for each linter. Each top-level element of an argument string that’s separated by a space on the command line must be a separate item in the args list. For example:
If a top-level element is a single value (delineated by quotation marks or braces), it still appears as a single item in the list even if the value itself contains spaces.
A custom path is generally unnecessary as the Python extension resolves the path to the linter based on the Python interpreter being used (see Environments). To use a different version of a linter, specify its path in the appropriate custom path setting. For example, if your selected interpreter is a virtual environment but you want to use a linter that’s installed in a global environment, then set the appropriate path setting to point to the global environment’s linter.
Note: The following sections provide additional details for the individual linters linked in the Specific linters table above. In general, custom rules must be specified in a separate file as required by the linter you’re using.
Pylint
Pylint messages fall into the categories in the following table with the indicated mapping to VS Code categories. You can change the setting to change the mapping.
| Pylint category | Description | VS Code category mapping | Applicable setting (python.linting.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convention (C) | Programming standard violation | Information (underline) | pylintCategorySeverity.convention |
| Refactor (R) | Bad code smell | Hint (light bulbs) | pylintCategorySeverity.refactor |
| Warning (W) | Python-specific problems | Warning | pylintCategorySeverity.warning |
| Error (E) | Likely code bugs | Error (underline) | pylintCategorySeverity.error |
| Fatal (F) | An error prevented further Pylint processing | Error | pylintCategorySeverity.fatal |
Command-line arguments and configuration files
You can easily generate an options file using different methods. See Pylint command-line arguments for general switches.
If you’re using command-line arguments:
Command-line arguments can be used to load Pylint plugins, such as the plugin for Django:
If you’re using a pylintrc file:
Options can also be specified in a pylintrc or .pylintrc options file in the workspace folder, as described on Pylint command line arguments.
To control which Pylint messages are shown, add the following contents to an options file:
If you’re using Pylint:
You can create an options file using Pylint itself, by running the command below.
If you are running Pylint in PowerShell, you have to explicitly specify a UTF-8 output encoding. This file contains sections for all the Pylint options, along with documentation in the comments.
pydocstyle
Command-line arguments and configuration files
See pydocstyle Command Line Interface for general options. For example, to ignore error D400 (first line should end with a period), add the following line to your settings.json file:
A code prefix also instructs pydocstyle to ignore specific categories of errors. For example, to ignore all Docstring Content issues (D4XXX errors), add the following line to settings.json :
More details can be found in the pydocstyle documentation.
Options can also be read from a [pydocstyle] section of any of the following configuration files:
- setup.cfg
- tox.ini
- .pydocstyle
- .pydocstyle.ini
- .pydocstylerc
- .pydocstylerc.ini
For more information, see Configuration Files.
Message category mapping
The Python extension maps all pydocstyle errors to the Convention (C) category.
pycodestyle (pep8)
Command-line arguments and configuration files
See pycodestyle example usage and output for general switches. For example, to ignore error E303 (too many blank lines), add the following line to your settings.json file:
pycodestyle options are read from the [pycodestyle] section of a tox.ini or setup.cfg file located in any parent folder of the path(s) being processed. For details, see pycodestyle configuration.
Message category mapping
The Python extension maps pycodestyle message categories to VS Code categories through the following settings. If desired, change the setting to change the mapping.
| pycodestyle category | Applicable setting (python.linting.) |
VS Code category mapping |
|---|---|---|
| W | pycodestyleCategorySeverity.W | Warning |
| E | pycodestyleCategorySeverity.E | Error |
Prospector
Command-line arguments and configuration files
See Prospector Command Line Usage for general options. For example, to set a strictness level of «very high,» add the following line to your settings.json file:
It’s common with Prospector to use profiles to configure how Prospector runs. By default, Prospector loads the profile from a .prospector.yaml file in the current folder.
Because Prospector calls other tools, such as Pylint, any configuration files for those tools override tool-specific settings in .prospector.yaml . For example, suppose you specify the following, in .prospector.yaml :
If you also have a .pylintrc file that enables the too-many-arguments warning, you continue to see the warning from Pylint within VS Code.
Message category mapping
The Python extension maps all Prospector errors and warnings to the Error (E) category.
Flake8
Command-line arguments and configuration files
See Invoking Flake8 for general switches. For example, to ignore error E303 (too many blank lines), use the following setting:
By default, Flake8 ignores E121, E123, E126, E226, E24, and E704.
Flake8 user options are read from the C:Users .flake8 (Windows) or
/.config/flake8 (macOS/Linux) file.
At the project level, options are read from the [flake8] section of a tox.ini , setup.cfg , or .flake8 file.
Message category mapping
The Python extension maps flake8 message categories to VS Code categories through the following settings. If desired, change the setting to change the mapping.
| Flake8 category | Applicable setting (python.linting.) |
VS Code category mapping |
|---|---|---|
| F | flake8CategorySeverity.F | Error |
| E | flake8CategorySeverity.E | Error |
| W | flake8CategorySeverity.W | Warning |
Message category mapping
The Python extension maps mypy message categories to VS Code categories through the following settings. If desired, change the setting to change the mapping.
Источник
Environment data
- VS Code version: 1.20.0
- Extension version (available under the Extensions sidebar): 2018.2.1
- OS and version: macOS Sierra version 10.12.6
- Python version (& distribution if applicable, e.g. Anaconda): Anaconda custom (64 bit) Python 3.6.4
- Type of virtual environment used (N/A | venv | virtualenv | conda | …): conda
- Relevant/affected Python packages and their versions:
Actual behavior
This program works fine from the command line. I wrote this using the Python extension approx. 6 months ago on another mac. I recently picked up this program again and it shows me the import errors as shown in the attached screenshot. I know that it is pylint related. I am also attaching my user settings and workspace settings screenshots
Expected behavior
It should not show errors for import
Steps to reproduce:
See the screenshorts
Logs
Output for Python in the Output panel (View→Output, change the drop-down the upper-right of the Output panel to Python)
6,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_common’
7,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_anis’
8,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_brz’
10,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_inf’
11,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_mrp’
12,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_nmr’
13,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_op’
14,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_re’
15,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_ssk’
16,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_txc’
17,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_xrd’
##########Linting Output — pylint##########
No config file found, using default configuration
************* Module vglabs_uploader
6,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_common’
7,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_anis’
8,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_brz’
10,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_inf’
11,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_mrp’
12,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_nmr’
13,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_op’
14,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_re’
15,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_ssk’
16,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_txc’
17,0,error,E0401:Unable to import ‘vglabs_xrd’
59,0,refactor,R0912:Too many branches (15/12)
107,0,refactor,R0912:Too many branches (15/12)
5,0,warning,W0611:Unused import psycopg2
XXX
Output from `Console` under the `Developer Tools` panel (toggle Developer Tools on under `Help`)
XXX