Модераторы: Trinity admin`s, Free-lance moderator`s
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Купили в августе 2013 платформу SuperMicro 1U 5018D-MTLN4F и все вроде работало, пока сегодня сервер не завис. Начали разбираться и увидели, что с самого начала в Event Log (IPMI) много ошибок:
Код: Выделить всё
1 2013/08/20 11:02:29 Chassis Intru Physical Security (Chassis Intrusion) General Chassis Intrusion - Asserted
2 2013/08/21 08:20:06 Chassis Intru Physical Security (Chassis Intrusion) General Chassis Intrusion - Asserted
3 2013/08/22 06:48:38 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMB1(CPU1) - Asserted
4 2013/08/22 07:27:17 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMB1(CPU1) - Asserted
5 2013/08/22 07:34:47 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMB1(CPU1) - Asserted
6 2013/08/22 08:18:26 Chassis Intru Physical Security (Chassis Intrusion) General Chassis Intrusion - Asserted
7 2013/08/30 14:21:44 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1) - Asserted
8 2013/09/01 05:57:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1) - Asserted
9 2013/09/01 22:12:37 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1) - Asserted
10 2013/09/07 08:01:50 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1) - Asserted
11 2013/09/08 20:20:13 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1) - Asserted
12 2013/09/11 19:04:47 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1) - Asserted
13 2013/09/11 23:16:25 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
14 2013/09/11 23:16:25 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
15 2013/09/13 06:21:32 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
16 2013/09/14 01:17:29 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
17 2013/09/14 11:06:30 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
18 2013/09/15 01:46:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
19 2013/09/15 12:52:32 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
20 2013/09/17 01:07:16 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
21 2013/09/17 01:49:20 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
22 2013/09/17 02:32:00 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
23 2013/09/19 02:59:14 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
24 2013/10/07 07:03:01 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
25 2013/10/19 06:17:15 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
26 2013/10/27 16:33:37 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
27 2013/11/12 18:04:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
28 2013/11/25 01:06:12 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
29 2013/11/25 08:36:41 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
30 2013/11/29 01:52:10 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
31 2013/11/29 01:52:10 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
32 2013/11/29 01:52:11 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
33 2013/11/29 01:52:11 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
34 2013/11/29 01:52:11 Session Audit Invalid Username or Password
35 2014/01/27 03:46:19 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
36 2014/01/28 00:57:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
37 2014/01/29 04:22:46 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
38 2014/01/29 18:13:15 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
39 2014/02/01 17:59:22 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
40 2014/02/01 18:06:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
41 2014/02/01 18:06:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
42 2014/02/01 18:06:07 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
43 2014/02/01 18:06:14 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
44 2014/02/02 04:44:55 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
45 2014/02/02 16:39:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
46 2014/02/05 11:10:56 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
47 2014/02/06 07:23:49 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
48 2014/02/09 07:24:20 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
49 2014/02/09 07:24:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
50 2014/02/09 07:24:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
51 2014/02/09 07:24:26 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
52 2014/02/09 07:24:28 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
53 2014/02/09 07:24:32 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
54 2014/02/10 04:22:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
55 2014/02/10 04:22:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
56 2014/02/12 12:17:30 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
57 2014/02/14 20:54:02 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
58 2014/02/18 14:12:33 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
59 2014/02/19 22:36:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
60 2014/02/25 02:00:27 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
61 2014/02/26 12:58:57 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
62 2014/02/26 12:58:57 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
63 2014/02/26 21:44:29 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
64 2014/02/27 02:51:03 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
65 2014/02/28 05:35:55 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
66 2014/03/01 21:06:47 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
67 2014/03/02 14:41:01 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
68 2014/03/02 17:31:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
69 2014/03/06 08:33:50 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
70 2014/03/08 02:09:46 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
71 2014/03/08 20:39:48 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
72 2014/03/09 00:47:00 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
73 2014/03/09 14:51:31 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
74 2014/03/09 17:02:56 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
75 2014/03/10 10:19:30 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
76 2014/03/10 10:19:31 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
77 2014/03/10 21:00:41 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
78 2014/03/11 04:36:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
79 2014/03/11 04:36:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
80 2014/03/12 08:45:22 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
81 2014/03/13 02:27:47 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
82 2014/03/13 09:43:43 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
83 2014/03/14 08:19:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
84 2014/03/15 11:18:55 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
85 2014/03/16 08:06:38 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
86 2014/03/16 09:51:34 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
87 2014/03/19 07:00:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
88 2014/03/22 08:02:24 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
89 2014/03/22 12:06:37 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
90 2014/03/23 20:33:31 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
91 2014/03/24 05:32:14 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
92 2014/03/24 08:17:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
93 2014/03/28 02:48:11 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
94 2014/04/02 21:26:48 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
95 2014/04/02 22:18:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
96 2014/04/02 22:18:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
97 2014/04/02 22:18:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
98 2014/04/02 22:18:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
99 2014/04/02 22:18:05 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
100 2014/04/02 22:18:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
101 2014/04/02 22:18:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
102 2014/04/04 13:55:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
103 2014/04/05 10:06:36 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
104 2014/04/06 01:42:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
105 2014/04/06 06:29:36 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
106 2014/04/07 04:46:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
107 2014/04/07 13:49:24 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
108 2014/04/07 13:49:26 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
109 2014/04/08 16:27:42 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
110 2014/04/08 17:19:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
111 2014/04/09 02:29:00 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
112 2014/04/09 09:21:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
113 2014/04/09 09:21:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
114 2014/04/09 09:21:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
115 2014/04/09 09:21:52 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
116 2014/04/09 09:21:53 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
117 2014/04/09 09:21:53 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
118 2014/04/09 09:21:53 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
119 2014/04/10 03:22:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
120 2014/04/10 11:13:22 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
121 2014/04/10 11:13:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
122 2014/04/11 13:34:51 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
123 2014/04/11 14:44:17 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
124 2014/04/11 14:44:18 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
125 2014/04/12 08:12:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
126 2014/04/12 08:12:21 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
127 2014/04/12 08:51:38 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
128 2014/04/12 19:02:11 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
129 2014/04/14 11:53:56 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
130 2014/04/14 22:07:02 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
131 2014/04/15 12:20:00 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
132 2014/04/18 04:28:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
133 2014/04/18 06:17:24 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
134 2014/04/19 07:45:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
135 2014/04/19 07:46:02 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
136 2014/04/19 07:46:03 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
137 2014/04/19 07:46:03 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
138 2014/04/19 07:46:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
139 2014/04/19 07:46:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
140 2014/04/19 07:46:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
141 2014/04/19 07:46:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
142 2014/04/19 07:46:04 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
143 2014/04/19 07:46:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
144 2014/04/19 07:46:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
145 2014/04/19 07:46:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
146 2014/04/19 07:46:07 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
147 2014/04/19 07:46:07 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
148 2014/04/19 07:46:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
149 2014/04/19 07:46:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
150 2014/04/19 07:46:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
151 2014/04/19 07:46:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
152 2014/04/19 07:46:08 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
153 2014/04/19 07:46:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
154 2014/04/19 07:46:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
155 2014/04/19 07:46:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
156 2014/04/19 07:46:09 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
157 2014/04/19 07:48:59 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
158 2014/04/19 07:52:16 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
159 2014/04/21 07:11:39 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
160 2014/04/22 14:29:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
161 2014/04/23 17:36:58 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
162 2014/04/24 12:40:47 OEM Memory Uncorrectable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
163 2014/04/26 09:52:33 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
164 2014/04/27 17:09:15 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
165 2014/04/27 17:56:32 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
166 2014/04/27 21:11:31 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
167 2014/04/27 21:11:31 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
168 2014/04/29 09:37:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
169 2014/04/30 11:22:11 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
170 2014/05/02 01:27:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
171 2014/05/02 01:27:06 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
172 2014/05/02 20:06:24 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
173 2014/05/04 15:27:23 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
174 2014/05/05 11:13:51 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
175 2014/05/07 07:20:33 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
176 2014/05/07 13:16:35 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
177 2014/05/08 00:35:13 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
178 2014/05/09 13:17:57 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)
179 2014/05/16 18:44:45 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
180 2014/05/17 11:48:47 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
181 2014/05/18 01:15:36 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
182 2014/05/19 14:54:33 OEM Memory Correctable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)
183 2014/05/20 15:14:03 OEM Memory Uncorrectable Memory ECC @ DIMMA1(CPU1)И последняя четко в то время, когда сервер завис. Смущают следующие вещи:
1) Ошибки не только в DIMMA1, но и в DIMMA2 (а ведь это другой канал?)
2) В апреле уже было «Uncorrectable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)», но тогда сервер на завис.
3) В самом начале были ошибки в DIMMB1, но это было во время тестов сервера в офисе, а не ДЦ и возможно планки переставлялись.
Первая мысль поменять местами DIMMA1 и DIMMB1, DIMMA2 и DIMMB2.
Подскажите что делать?
-
Stranger03
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 12979
- Зарегистрирован: 14 ноя 2003, 16:25
- Откуда: СПб, Екатеринбург
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
Stranger03 » 21 май 2014, 11:16
ServerMan писал(а):Подскажите что делать?
Проверьте мемтестом на ночь, там видно будет. И поправьте город в профиле.
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
ServerMan » 21 май 2014, 12:06
На что похоже вообще это поведение по вашему опыту?
И само наличие Correctable Memory ECC это уже не нормально?
-
Stranger03
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 12979
- Зарегистрирован: 14 ноя 2003, 16:25
- Откуда: СПб, Екатеринбург
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
Stranger03 » 21 май 2014, 12:24
ServerMan писал(а):На что похоже вообще это поведение по вашему опыту?
И само наличие Correctable Memory ECC это уже не нормально?
Ну само их наличие не так критично, коррекции ошибок. Все-таки прогоните тесты, поставьте на ночь часов на 6-ть. Если там что будет, то менять по гарантии.
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
ServerMan » 21 май 2014, 12:28
А наличие Uncorrectable Memory ECC нормально или нет?
Просто на сервере 5017C-MTF с такой же памятью нет таких ошибок вообще.
Вообще на что больше похоже: на мать или память? Просто я к первому варианту больше склоняюсь пока…
На тест ночью стремно ставить, вдруг зависнет…
-
gs
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 16650
- Зарегистрирован: 23 авг 2002, 17:34
- Откуда: Москва
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
gs » 21 май 2014, 12:48
Корректабл ошибки — это сбои, которые способна исправить ЕСС. Это плохо. Не смертельно (как анкорректабл), но при регулярном появлении очень плохо.
Виноваты могут быть как модули памяти, так и мамка/слоты, даже контакт в процессорном сокете или сам процессор (хотя последнее очень редко бывает).
В общем, запускайте мемтест, а там видно будет.
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
ServerMan » 24 май 2014, 13:51
Просто сервер рабочий и останавливать его в режим синглмод и тестить память — нет возможности…
BIOS Version : 1.1
BIOS Build Time : 07/19/2013
А биос не может быть проблемой?
-
Stranger03
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 12979
- Зарегистрирован: 14 ноя 2003, 16:25
- Откуда: СПб, Екатеринбург
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
Stranger03 » 26 май 2014, 09:55
ServerMan писал(а):А биос не может быть проблемой?
Врядли
-
gs
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 16650
- Зарегистрирован: 23 авг 2002, 17:34
- Откуда: Москва
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
gs » 26 май 2014, 14:12
А если он просто сломается — тоже будете говорить, что остановить нет возможности?
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
ServerMan » 02 июн 2014, 16:45
Прошло 9 дней, больше ошибок не было. Что я сделал: вынул из сервера DIMMA1 и DIMMA2, отдав сотруднику на тест (memtest86 запущенный на 8 часов и сделавший 4 прохода ошибок не выявил!).
DIMMB1 поставил на DIMMA1, DIMMB2 на DIMMB1 — переставил чтобы исключить проблемы плохо вставленных контактов. И я правильно вставил две планки в DIMMA1 и DIMMB1, чтобы на одном канале было?
Возникает вопрос, что было? Память тесты на другом компе прошла, а та что осталась (частично в тех же слотах) проблем больше не вызывала…
PS: обновил IPMI.
-
gs
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 16650
- Зарегистрирован: 23 авг 2002, 17:34
- Откуда: Москва
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
gs » 02 июн 2014, 16:59
Ну так может просто неконтакт?
-
ServerMan
- Junior member
- Сообщения: 6
- Зарегистрирован: 20 май 2014, 21:54
- Откуда: МСК
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
ServerMan » 02 июн 2014, 17:05
Сейчас сервер хорошо справляется и на в два раза меньшем количестве памяти, имеет ли смысл после тестов вернуть память на место или лучше не рисковать?
-
Stranger03
- Сотрудник Тринити
- Сообщения: 12979
- Зарегистрирован: 14 ноя 2003, 16:25
- Откуда: СПб, Екатеринбург
- Контактная информация:
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение
Stranger03 » 03 июн 2014, 08:27
ServerMan писал(а):Сейчас сервер хорошо справляется и на в два раза меньшем количестве памяти, имеет ли смысл после тестов вернуть память на место или лучше не рисковать?
Это вам решать.
Вернуться в «Серверы — Решение проблем»
Перейти
- Серверы
- ↳ Серверы — Конфигурирование
- ↳ Конфигурации сервера для 1С
- ↳ Серверы — Решение проблем
- ↳ Серверы — ПО, Unix подобные системы
- ↳ Серверы — ПО, Windows система, приложения.
- ↳ Серверы — ПО, Базы Данных и их использование
- ↳ Серверы — FAQ
- Дисковые массивы, RAID, SCSI, SAS, SATA, FC
- ↳ Массивы — RAID технологии.
- ↳ Массивы — Технические вопросы, решение проблем.
- ↳ Массивы — FAQ
- Майнинг, плоттинг, фарминг (Добыча криптовалют)
- ↳ Proof Of Work
- ↳ Proof Of Space
- Кластеры — вычислительные и отказоустойчивые ( SMP, vSMP, NUMA, GRID , NAS, SAN)
- ↳ Кластеры, Аппаратная часть
- ↳ Deep Learning и AI
- ↳ Кластеры, Программное обеспечение
- ↳ Кластеры, параллельные файловые системы
- Медиа технологии, и цифровое ТВ, IPTV, DVB
- ↳ Станции видеомонтажа, графические системы, рендеринг.
- ↳ Видеонаблюдение
- ↳ Компоненты Digital TV решений
- ↳ Студийные системы, производство ТВ, Кино и рекламы
- Инфраструктурное ПО и его лицензирование
- ↳ Виртуализация
- ↳ Облачные технологии
- ↳ Резервное копирования / Защита / Сохранение данных
- Сетевые решения
- ↳ Сети — Вопросы конфигурирования сети
- ↳ Сети — Технические вопросы, решение проблем
- Общие вопросы
- ↳ Обсуждение общих вопросов
- ↳ Приколы нашего IT городка
- ↳ Регистрация на форуме
Содержание
- Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
- Uncorrectable ecc error dimm
- Uncorrectable DIMM Errors
- Correctable DIMM Errors
- DIMM Fault LEDs
- Troubleshoot DIMM Memory Issues in UCS
- Available Languages
- Download Options
- Bias-Free Language
- Contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Requirements
- Components Used
- Troubleshoot Methodology
- Terms and Acronyms
- Memory Placement
- Memory Errors
- Correctable vs. Uncorrectable Errors
- Troubleshoot DIMM’s via UCSM and CLI
- To Check Errors from GUI
- To Check Errors from CLI
- Log Files to Check in Tech Support
- DIMM Blacklisting
Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение ServerMan » 20 май 2014, 22:05
И последняя четко в то время, когда сервер завис. Смущают следующие вещи:
1) Ошибки не только в DIMMA1, но и в DIMMA2 (а ведь это другой канал?)
2) В апреле уже было «Uncorrectable Memory ECC @ DIMMA2(CPU1)», но тогда сервер на завис.
3) В самом начале были ошибки в DIMMB1, но это было во время тестов сервера в офисе, а не ДЦ и возможно планки переставлялись.
Первая мысль поменять местами DIMMA1 и DIMMB1, DIMMA2 и DIMMB2.
Подскажите что делать?
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение Stranger03 » 21 май 2014, 11:16
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение ServerMan » 21 май 2014, 12:06
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение Stranger03 » 21 май 2014, 12:24
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение ServerMan » 21 май 2014, 12:28
А наличие Uncorrectable Memory ECC нормально или нет?
Просто на сервере 5017C-MTF с такой же памятью нет таких ошибок вообще.
Вообще на что больше похоже: на мать или память? Просто я к первому варианту больше склоняюсь пока.
На тест ночью стремно ставить, вдруг зависнет.
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение gs » 21 май 2014, 12:48
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение ServerMan » 24 май 2014, 13:51
Просто сервер рабочий и останавливать его в режим синглмод и тестить память — нет возможности.
BIOS Version : 1.1
BIOS Build Time : 07/19/2013
А биос не может быть проблемой?
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение Stranger03 » 26 май 2014, 09:55
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение gs » 26 май 2014, 14:12
Re: Uncorrectable Memory ECC
Сообщение ServerMan » 02 июн 2014, 16:45
Прошло 9 дней, больше ошибок не было. Что я сделал: вынул из сервера DIMMA1 и DIMMA2, отдав сотруднику на тест (memtest86 запущенный на 8 часов и сделавший 4 прохода ошибок не выявил!).
DIMMB1 поставил на DIMMA1, DIMMB2 на DIMMB1 — переставил чтобы исключить проблемы плохо вставленных контактов. И я правильно вставил две планки в DIMMA1 и DIMMB1, чтобы на одном канале было?
Возникает вопрос, что было? Память тесты на другом компе прошла, а та что осталась (частично в тех же слотах) проблем больше не вызывала.
Источник
Uncorrectable ecc error dimm
This chapter describes how to detect and correct problems with the server’s Dual Inline Memory Modules (DIMMs). It includes the following sections:
Note — Refer to the service manual or service label for the system that you are servicing for information on DIMM population rules.
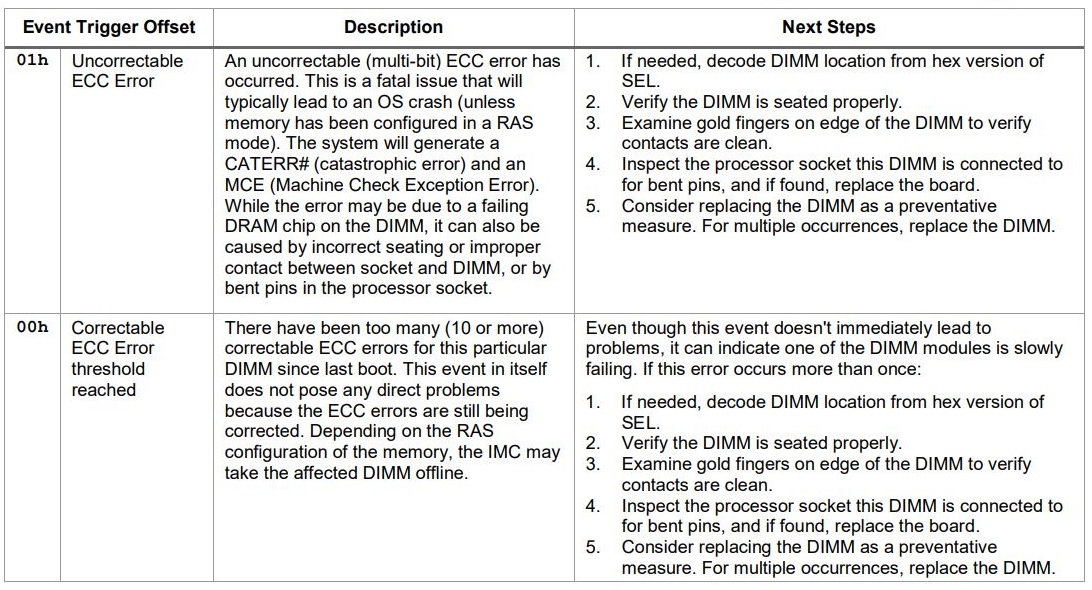
Replace a DIMM when one of the following events takes place:
- The DIMM fails memory testing under BIOS due to Uncorrectable Memory Errors (UCEs).
UCEs occur and investigation shows that the errors originated from memory.
More than 24 Correctable Errors (CEs) originate in 24 hours from a single DIMM and no other DIMM is showing further CEs.
Note — If more than one DIMM has experienced multiple CEs, other possible causes of CEs must be ruled out by a qualified Sun Support specialist before replacing any DIMMs.
Retain copies of the logs showing the memory errors to send to Sun for verification prior to calling Sun.
This section describes the following topics:
Uncorrectable DIMM Errors
For all operating systems, the behavior is the same for uncorrectable errors (UCEs):
1. When a UCE occurs, the memory controller causes an immediate reboot of the system.
2. During reboot, the BIOS checks the Machine Check registers and determines that the previous reboot was due to a UCE.
The uncorrectable ECC error is displayed in the service processor’s system event log (SEL) as shown here:
Memory | Uncorrectable ECC | Asserted | DIMM A0
Correctable DIMM Errors
If a DIMM has 24 or more correctable errors (CE)s in 24 hours, it is considered defective and should be replaced.
CEs will be captured in the SEL and light the fault LED after 24 single bit errors are detected in 24 hours. They are reported or handled in the supported operating systems as follows:
a. A Machine Check error-message bubble appears on the task bar.
b. Open the Event Viewer to view errors.
Access the Event Viewer through this menu path:
Start—>Administration Tools—>Event Viewer
c. View individual errors (by time) to see the details of the error.
Solaris FMA reports and sometimes retires memory with correctable Error Correction Code (ECC) errors. See your Solaris documentation for details.
To view ECC errors, use the following command:
DIMM Fault LEDs
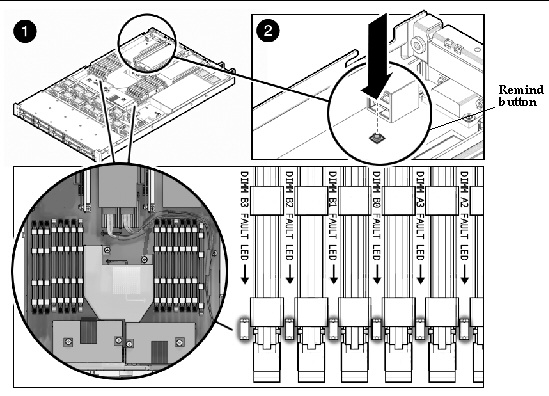
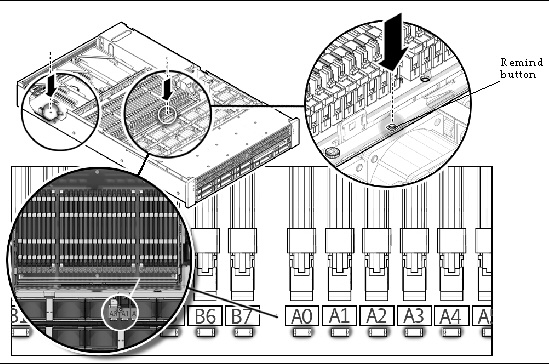
When you press the Remind button on the motherboard (or memory tray for x4450), the LEDs next to the DIMMs flash to indicate that the system has detected 24 or more CEs in a 24-hour period on that DIMM.
- DIMM fault LED is off: The DIMM is operating properly.
DIMM fault LED is flashing (amber): At least one of the DIMMs in this DIMM pair has reported 24 CEs within a 24-hour period or a UE (uncorrectable error).
See FIGURE 2-1 and FIGURE 2-2 for the locations of the Remind button and LEDs on the motherboard.
FIGURE 2-1 DIMMs and LEDs on Motherboard (X4150 and X4250)
FIGURE 2-2 . DIMMs and LEDs on Mezzanine (x4450)
If your log files report an Error Correction Code (ECC) error or a problem with a DIMM, complete the following steps until you can isolate the fault.
In this example, the log file reports an error with the DIMM in D0. The fault LED on DIMM D0 is on.
To isolate and correct DIMM ECC errors:
1. If you have not already done so, shut down your server to standby power mode and remove the cover.
2. Inspect the installed DIMMs to ensure that they comply with the DIMM population rules in your product service manual.
3. Press the Remind button and inspect the DIMM fault LEDs. See FIGURE 2-1 and FIGURE 2-2.
For CEs and UCEs, a flashing LED identifies the DIMM where the error is located.
4. Disconnect the AC power cords from the server.
 |
Caution — Before handling components, attach an antistatic wrist strap to a chassis ground (any unpainted metal surface). The system’s printed circuit boards and hard disk drives contain components that are extremely sensitive to static electricity. |
Note — To recover fault information, look in the SP SEL, as described in the Sun Integrated Lights Out Manager 2.0 User’s Guide .
5. Remove the DIMMs from the DIMM slots.
Refer to your server’s service manual for details.
6. Visually inspect the DIMMs for physical damage, dust, or any other contamination on the connector or circuits.
7. Visually inspect the DIMM slot for physical damage. Look for cracked or broken plastic on the slot.
8. Dust off the DIMMs, clean the contacts, and install them.
 |
Caution — Use only compressed air to dust DIMMs. |
9. If there is no obvious damage, replace any failed DIMMs.
For UCEs, if the LEDs indicate a fault with the pair, replace both DIMMs. Ensure that they are inserted correctly with ejector latches secured.
10. Reconnect AC power cords to the server.
11. Power on the server and run the diagnostics test again.
12. Review the log file.
If the tests identify the same error, the problem is in the CPU, not the DIMMs.
| Sun Fire X4150, X4250, and X4450 Servers Diagnostics Guide | 820-4213-11 |     |
Copyright © 2009 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Источник
Troubleshoot DIMM Memory Issues in UCS
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot memory modules and related issues in the Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) solution.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends knowledge of Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) .
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
However, this document addresses:
- Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers
- UCS Manager
- UCS uses Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM) as RAM modules.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Troubleshoot Methodology
This section covers several parts of UCS memory issues.
- Memory placement
- Troubleshoot DIMMs via UCSM and CLI
- Logs to check in technical support
Terms and Acronyms
| DIMM | Dual In-line Memory Module |
| ECC | Error Correcting Code |
| LVDIMM | Low Voltage DIMM |
| MCA | Machine Check Architecture |
| MEMBIST | Memory Built-in Self Test |
| MRC | Memory Reference Code |
| POST | Power On Self Test |
| SPD | Serial Presence Detect |
| DDR | Double Data Rate |
| RAS | Reliability, Availability and Serviceability |
Memory Placement
Memory placement is one of the most notable physical aspects of the UCS solution.
Typically the server comes with memory pre-populated with a requested amount.
However, when in doubt, refer to the hardware installation guide.
For memory population rules, refer to B-series technical specifications for the specific platform.
B-series technical specifications link:
Memory Errors
- DIMM Error
- Multibit = Uncorrectable
- POST is mapped by BIOS; OS does not see DIMM
- Runtime usually causes OS reboot
- Singlebit = Correctable
- OS continues to see the DIMM
- ECC ( Error Correcting Code) Error
- Parity Error
- SPD (Serial Presence Detect) Error
- Multibit = Uncorrectable
- Configuration Error
- Not supported DIMMs
- Not supported DIMM population
- Unpaired DIMMs
- Mismatch errors
- Identity unestablishable error
- Check and update the catalog
Correctable vs. Uncorrectable Errors
Whether a particular error is correctable or uncorrectable depends on the strength of the ECC code employed within the memory system.
Dedicated hardware is able to fix correctable errors when they occur with no impact on program execution.
The DIMMs with correctable errors are not disabled and are available for the OS to use. The Total Memory and Effective Memory are the same.
These correctable errors are reported in the UCSM operability state as Degraded while overall operability is Operable with correctable errors.
Uncorrectable errors make it impossible for the application or operating system to continue execution.
The DIMMs with uncorrectable errors are disabled and OS does not see them. UCSM operState change to Inoperable in this case.
Troubleshoot DIMM’s via UCSM and CLI
To Check Errors from GUI
| UCSM | Logs | Description | |
| DIMM Status | Operability | SEL | Comments |
| Operable | Operable | Check SEL log for DIMM related errors | A DIMM is installed and functional. |
| Operable | Degraded | Check SEL for ECC errors | A correctable ECC DIMM error is detected during run time. |
| Removed | N/A | No logs | A DIMM is not installed or corrupted SPD data. |
| Disabled | Operable | Check SEL for Identity unestablishable errors | Check and update capability catalog |
| Disabled | N/A | Check SEL if another DIMM in failed in the same channel | A DIMM is healthy but disabled because configuration rule could not be maintained by a failed DIMM in the same channel. |
| Disabled | N/A | No logs | Failed memory configuration rule because of missed DIMMs. |
| Inoperable | Inoperable/Replacement required | UE ECC Error was detected. | |
| Degraded | Inoperable | Check SEL for ECC errors | DIMM status and Operability changed due to ECC errors were detected before host rebooted. |
| Degraded | Inoperable/Replacement required | Check SEL for ECC error during POST/MRC | Uncorrectable ECC error was detected during runtime, DIMM remains available to OS, OS crashes and comes back up but still can use this DIMM. Error can occur again later. DIMM must be replaced in most situations. |
To obtain statistics navigate to Equipment > Chassis > Server > Inventory > Memory, then right-click Memory and select show navigator .
To Check Errors from CLI
These commands are useful when troubleshooting errors from CLI.
From memory array scope, you can also get access to DIMM.
scope server X/Y > scope memory-array Z > scope DIMM N
From there, then you can obtain per-DIMM statistics or reset the error counters.
If you see a correctable error that matches this information, the problem can be corrected by resetting the BMC instead of resetting the blade server.
Use these Cisco UCS Manager CLI commands:
(Resetting the BMC does not impact the OS running on the blade.)
With UCS releases 2.27, and 3.1 and above, the thresholds for memory corrected errors has been removed.
Therefore, memory modules are no longer reported as Inoperable or Degraded solely due to corrected memory errors.
Industry demands for greater capacity, greater bandwidth, and lower operating voltages lead to increased memory error rates.
Traditionally, the industry has treated correctable errors in the same way as uncorrectable errors, requiring the module to be replaced immediately upon alert.
Given extensive research that correctable errors are not correlated with uncorrectable errors, and that correctable errors do not degrade system performance, the Cisco UCS team recommends against immediate replacement of modules with correctable errors.
Customers who experience a Degraded memory alert for correctable errors are advised to reset the memory error and resume operation.
This recommendation helps to avoid unnecessary server disruption.
Future enhancements to error management distinguish among various types of correctable errors and identify the appropriate actions, if any, needed.
At minimum, use version 2.1(3c) or 2.2(1b) which has enhancement with UCS memory error management
Log Files to Check in Tech Support
UCSM_X_TechSupport > sam_techsupportinfo provides information about DIMM and memory array.
Chassis/server tech support
Based on the platform/version, navigate to the files in tech support bundle.
var/nuova/BIOS > RankMarginTest.txt
var/nuova/BIOS > MemoryHob.txt
var/nuova/var/nuova/ BIOS > MrcOut_*.txt
These files provide information about memory as seen from BIOS level.
Information there can be cross-referenced again with DIMM states report tables.
/var/nuova/BIOS/RankMarginTest.txt
- Useful for showing the test results from BIOS Training test MEMBIST
- Look for errors
- Look to see if any DIMMs are mapped out
- show DIMM specific information (Vendor/speed/PID)
The first column has two values:
DIMM locator (F2)
Here is a brief description for each status:
0x00 // Not Installed (No DIMM)
0x01 // Installed (Working)
0x10 // Failed Training
0x11 // Failed Clock Training
0x18 // Failed MemBIST
0x20 // Ignored (Disabled from debug console)
0x21 // Ignored (SPD Error reported by BMC)
0x22 // Ignored (Non-RDIMM)
0x23 // Ignored (Non-ECC)
0x24 // Ignored (Non-x4)
0x25 // Ignored (Other PDIMM in same LDIMM failed)
0x26 // Ignored (Other LDIMM in same channel failed)
0x27 // Ignored (Other channel in LockStep or Mirror failed)
0x28 // Ignored (Invalid PDIMM population)
0x29 // Ignored (PDIMM Organization Mismatch)
0x2A // Ignored (PDIMM Register Vendor Mismatch)
var/nuova/BIOS > MemoryHob.txt
shows effective and failed memory installed on the server
18h — DIMM status is marked as failed when it fails in MemBist test. Replace with a known good DIMM.
DIMM Status Description
00h Not Installed (No DIMM)
01h Installed (Working)
10h Failed (Training)
11h Failed (Clock training)
18h Failed (MemBIST)
20h Ignored (Disabled from debug console)
21h Ignored (SPD Error reported by BMC)
22h Ignored (Non-RDIMM)
23h Ignored (Non-ECC)
24h Ignored (Non-x4)
25h Ignored (Other PDIMM in same LDIMM failed)
26h Ignored (Other LDIMM in same channel failed)
27h Ignored (Other channel in LockStep or Mirror)
28h Ignored (Invalid memory population)
29h Ignored (Organization mismatch)
2Ah Ignored (Register vendor mismatch)
2Bh- 7Fh Reserved
80h Ignored ( Workaround -Looping)
81h Ignored (Stuck I2C bus)
82h – FFh Reserved
DIMM Blacklisting
In Cisco UCS Manager , the state of the Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM) is based on SEL event records.
When the BIOS encounters a noncorrectable memory error during memory test execution, the DIMM is marked as faulty.
A faulty DIMM is a considered a nonfunctional device.
If you enable DIMM blacklisting, Cisco UCS Manager monitors the memory test execution messages and blacklists any DIMMs that encounter memory errors in the DIMM SPD data.
DIMM Blacklisting was introduced as an optional global policy in UCSM 2.2(2).
Server firmware must be 2.2(1)+ for B-series blades and 2.2(3)+ for C-series rack servers to properly implement this feature.
In UCSM 2.2(4), the DIMM, Blacklisting is enabled.
Open the tech support file …/var/log/DimmBL.log
Open the file /var/nuova/BIOS/MrcOut.txt if it is available
Find the DIMM Status table. Look for “DIMM Status:”
DIMM Blacklisted = 1E
Find the DIMM Status table. Look for “DIMM Status:”
00 — Not Installed
10 — Failed (Training failure)clear
1E — Failed (DIMM Blacklisted by BMC)
1F — Failed (SPD Error)
25 — Disabled (Other DIMM failed in same channel)
Источник
The browser version you are using is not recommended for this site.
Please consider upgrading to the latest version of your browser by clicking one of the following links.
- Safari
- Chrome
- Edge
- Firefox
Basic Diagnostics for Correctable/Uncorrectable ECC Memory Errors with Intel® Server Boards
Documentation
Content Type
Troubleshooting
Article ID
000024007
Last Reviewed
01/10/2023
What am I seeing?
Correctable and/or Uncorrectable Error Correcting Code (ECC) events for memory modules. For example:
Mmry ECC Sensor SMI Handler Warning Memory CPU: 1, DIMM: D0 DIMM Rank: 1. — Correctable ECC / other correctable memory error — Asserted.
What is Memory Error Correction Code (ECC) Correctable Error Event?
ECC correctable error represents a threshold overflow for a given Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMM) within a given timeframe.
How to fix it:
Memory data errors are logged as correctable or uncorrectable. Refer to the instructions below, based on the error type you encounter:
| Notes |
|
- If there is no catastrophic issue (Purple Screen of Death (PSOD) or unexpected restart) and the correctable ECC error, including Adaptative Double Device Data Correction (ADDDC) error, is less than 10 events every 24 hours for each DIMM location, which is within the threshold limit, the recommendation is to monitor the server for any recurrence of ECC error each DIMM location that triggers the event.
- If there is a catastrophic issue (Purple Screen of Death (PSOD) or unexpected restart) and the correctable ECC error, including Adaptative Double Device Data Correction (ADDDC) error, is less than 10 events every 24 hours for each DIMM location, it is recommended to re-seat each DIMM location by following the steps below:
- Power OFF the system and remove the AC power cable.
- Identify the DIMM location to re-seat. Refer to the Technical Product Specifications for your server platform to identify the DIMM location.
- Perform the re-seat of identified DIMM.
- Insert the AC power cable and power back ON the system.
- Observe for 24 hours for any recurrence of ECC error.
- If the ECC error persists with the same DIM location that was re-seated, then generate and send the SEL and Debug logs, both generated from the BMC Web Console to Intel Customer Support
- The advanced memory test (AMT) features were introduced in the BIOS and firmware stack starting with the BIOS revision 02.01.0014 for the Intel® Server Systems S2600BP, S2600WF, and S2600ST; and starting with the BIOS revision 22.01.0097 for the Intel® Server System S9200WK. For these products, recommend to enable the advanced memory test (AMT) and post package repair (PPR) features through the BIOS setup utility to perform a full check of the memory health. Refer to Chapter 5 in Memory Replacement Guideline and Advanced Memory Test for Intel® Server Products Based on Intel® 62X Chipset – White Paper for detail steps.
|
Notes |
The Error Correction Code (ECC) errors are self-correcting. Depending on the Reliability Availability Serviceability (RAS) configuration of the memory, the Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) may take the affected DIMM offline. |
|
For different Intel server platforms, there are some differences in their event definition, refer to System Event Log Troubleshooting Guide for your server platform |
|
|
Intel recommends downloading and updating the system BIOS to the latest available version for your server platform. |
|
|
If the system is an Intel® Data Center Block for Nutanix* Enterprise Cloud, rather, visit the Nutanix* Life Cycle Manager page. For a list of hardware and firmware compatibility, visit the Nutanix* Hardware and Firmware compatibility page. |
Related Products
This article applies to 221 products.
Discontinued Products
Need more help?
Give Feedback
Статистика отказов в серверной памяти
Время прочтения
5 мин
Просмотры 46K
В 2009 году, на ежегодной научной конференции SIGMETRICS, группа исследователей, работавших в Университете Торонто с данными, собранными и предоставленными для изучения компанией Google, опубликовала крайне интересный документ «DRAM Errors in the Wild: A Large-Scale Field Study» посвященный статистике отказов в серверной оперативной памяти (DRAM). Хотя подобные исследования и проводились ранее (например исследование 2007 года, наблюдавшее парк в 300 компьютеров), это было первое исследование, охватившее такой значительный парк серверов, исчисляемый тысячами единиц, на протяжении свыше двух лет, и давшее столь всеобъемлющие статистические сведения.
Отмечу также, что та же группа исследователей, во главе с аспирантом, а ныне профессором Университета Торонто, Бианкой Шрёдер (Bianca Shroeder) ранее, в 2007 году публиковала не менее интересное исследование, посвященное статистике отказов жестких дисков в датацентрах Google (краткую популярную выжимку из работы Failure Trends in a Large Disk Drive Population (pdf 242 KB), если вам скучно читать весь отчет, можно найти здесь: http://blog.aboutnetapp.ru/archives/tag/google). Кроме того, их перу принадлежит еще несколько работ, в частности об влиянии температуры и охлаждении, и о статистике отказов в оперативной памяти, вызываемой, предположительно, космическими лучами высоких энергий. Ссылки на публикации можно найти на домашней странице Шрёдер, на сервере университета.
Кратко о том, как именно происходила сборка статистических данных. Дело в том, что на протяжении довольно продолжительного времени (в опубликованной работе проанализирован период около 2,5 лет), в датацентрах Google собираются разнообразные данные мониторинга и иных событий в жизни оборудования в большой базе, данные которой в дальнейшем можно анализировать за любой желаемый промежуток времени.
(на фото, кстати, подлинный вид серверной платформы Google, именно из таких «кирпичиков» собираются гугловские кластеры, размером в многие тысячи узлов, впрочем, про них тут уже писалось)
Результаты такого анализа и представлены в опубликованной работе. И результаты во многом удивительные, заставляющие по-иному смотреть на вопросы надежности и привычные допущения в области надежности серверного оборудования.
Исследование со всей убедительностью продемонстрировало, что влияние отказов в оперативной памяти существенно недооценивается, что отказы оперативной памяти случаются куда чаще, чем до этого это было принято считать, наконец, многие допущения, например что оперативная память практически не «стареет», как «стареют», повышая вероятность отказов, компоненты с движущимися частями, такие как, например, жесткие диски, или что перегрев губительно сказывается на работе ОЗУ, являются неверными, и требуют пересмотра.
Несомненно тот факт, что в последние несколько лет, в связи со сравнительным удешевлением DRAM, и широким распространением систем серверной виртуализации, крайне охочих до объемов памяти, концентрация в одной серверной системе все больших и больших объемов ОЗУ, повышает и требования к ее надежности.
Исследование показало, что примерно каждый третий сервер (или 8% модулей памяти) в наблюдаемых датацентрах на протяжении 2,5 лет исследования встречался со сбоем в оперативной памяти. Число сбоев, зарегистрированных системой мониторинга составило свыше 4000 в год! Большая часть из них конечно была устранена использованием ECC (Error Correction Code), используемого в оперативной памяти, и более сложными его вариантами, такими как Chipkill (позволяет устранить многобитовые ошибки, например сразу в группе ячеек). Тем не менее, Uncorrectable Errors, то есть ошибки, которые не удалось исправить, и которые, почти наверняка привели к фатальным последствмяи типа BSOD или kernel panic встречаются куда чаще, чем это принято считать. А в случае использования памяти без ECC каждая из таких ошибок — это почти наверняка BSOD или kernel panic, или серьезный сбой в работе приложения. Ведь, например, очень многие хранят данные баз в памяти для ускорения ее работы.
В сравнении с ранее опубликованным исследованием, работа группы Шрёдер резко повысила «ожидания» сбоев. Так, они оценили события отказов в 25-70 тысяч сбоев на миллиард часов работы сервера, что почти в пятнадцать раз превышает более раннюю оценку, сделанную на меньшей популяции.
С отказами в результате неисправимых (uncorrectable, неисправленных ECC или Chipkill) встретились 1,3% серверов в год, или около 0,22% DIMM.
Системы, использующие «многобитные» механизмы, такие как Chipkill, имели число отказов в 4-10 раз меньше, по сравнению с обычным ECC.
Другие интересные выводы, сделанные в опубликованной работе это:
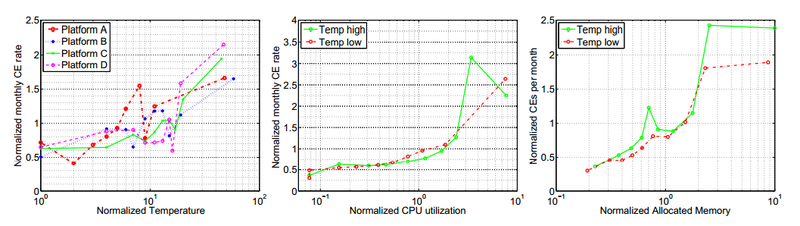
Рабочая температура, и ее повышение крайне мало коррелирует с вероятностью сбоя в DRAM. Это еще один факт, который указывает, что бытующее до сих пор в индустрии мнение о губительности повышенной температуры на полупроводники и компьютерное оборудование (мнение, основанное на исследовании 80-х годов) на сегодняшний день следует радикально пересмотреть. Это еще одно подтверждение этому факту, который уже был установлен, например в работе о жестких дисках. Парадоксальным образом там было установлено, что наименьшее количество отказов HDD наблюдалось при температурах в районе 40-45 градусов, а ее понижение количество отказов увеличивало (!).
В случае DRAM кореляция между температурой (в наблюдавшемся диапазоне около 20 градусов между самой низкой и самой высокой) и отказами была крайне незначительной.
(здесь и далее на слайдах: CE — correctable errors, ошибки, зарегистрированные, но исправленные ECC, UE — uncorrectable errors)
Однако существенно коррелировали отказы с загрузкой памяти и интенсивностью обмена с ней (отчасти высокая загрузка памяти влияет и на ее температуру, конечно, но не всегда). Вполне вероятно, что интенсивный обмен и большой относительный объем заполненных данными памяти значительно повышает вероятность быстрого обнаружения сбоя.
Было установлено, что вероятность получить повторный сбой в уже ранее сбоившем модуле памяти в сотни раз выше, по сравнению с не сбоившем ранее. Это может быть вызвано как наличием плохо выявляемого технологического брака, так и тем, что отказ, например пробой заряженной частицей космических лучей, не проходит для памяти бесследно, даже если ошибка была скорректирована ECC.
70-80% случаях, когда регистрировалась неисправимая ошибка в модуле памяти, это модуль уже имел исправимый ECC или Chipkill отказ в этом или предыдущем месяце.
Было установлено, что сравнительно новые модули, выполненные с более высокой плотностью и более тонкими техпроцессами, не показывают более высокого уровня отказов. По-видимому пока в технологии DRAM технологический предел, близ которого начинаются проблемы с надежностью, пока не достигнут. В наблюдаемом парке модулей было примерно шесть разных типов и поколений памяти (DDR1, DDR2 и FBDIMM разных типов), и корреляции между высокой плотностью и числом отказов и сбоев выявлено не было.
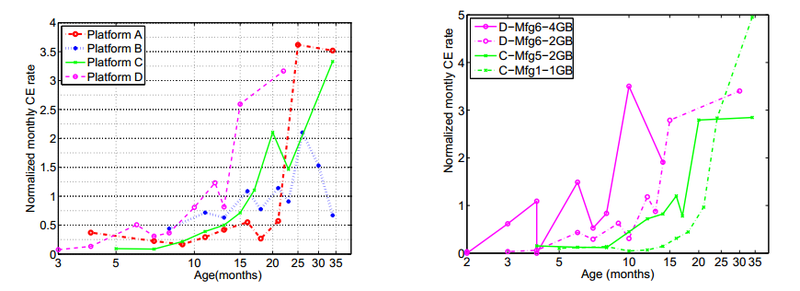
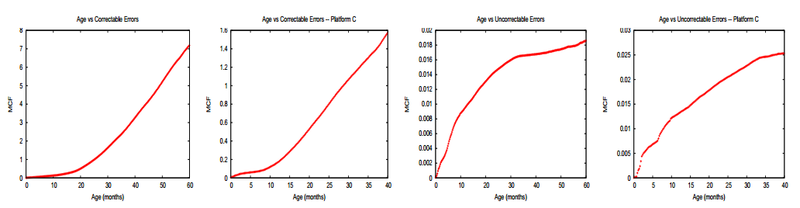
Наконец, с пугающей ясностью был продемонстрирован эффект «старения» в модулях DRAM. Более того, в памяти он проявился куда более явно, чем, напрмер, в HDD, где порог, после которого отказы растут в разы, составил примерно 3-4 года.
Парадоксальным образом статистика демонстрирует увеличивающиеся темпы роста correctable errors с увеличением возраста модулей, но снижающийся темп для Uncorrectable errors, однако скорее всего это просто результат плановой замены памяти в серверах, которые были замечены за сбоями.
Удивительным образом, DRAM, лишенная каких-либо движущихся частей, показывает существенный и продолжающийся рост correctable отказов уже после года-полутора эксплуатации.
Подводя итоги, хотелось бы отметить, что приведенные статистические данные заставляют пересмотреть привычные для многих, основанные на «житейском опыте» принципы построения серверных платформ и эксплуатации датацентров, и позиция «чем холоднее — тем лучше», «память не изнашивается», «если север правильно собран, то он не ломается» и «ECC DRAM — ненужная трата денег, ведь у меня десктоп работает без ECC, и ничего». И чем скорее будут изжиты подобные шапкозакидательские настроения в столь серьезной области, как построение датацентров, тем, в итоге, будет лучше.
А занимающимся темой хочу порекомендовать неизбывный источник сладости, интеллектуального упражнения и пищи для мозгов, как публикации ежегодных конференций группы USENIX, это вам, господа, не маркетинговый булшит, столь привычный нам уже всем, а настоящая серьезная наука, от которой не отмахнешься.
О LENOVO
+
О LENOVO
-
Наша компания
-
Новости
-
Контакт
-
Соответствие продукта
-
Работа в Lenovo
-
Общедоступное программное обеспечение Lenovo
КУПИТЬ
+
КУПИТЬ
-
Где купить
-
Рекомендованные магазины
-
Стать партнером
Поддержка
+
Поддержка
-
Драйверы и Программное обеспечение
-
Инструкция
-
Инструкция
-
Поиск гарантии
-
Свяжитесь с нами
-
Поддержка хранилища
РЕСУРСЫ
+
РЕСУРСЫ
-
Тренинги
-
Спецификации продуктов ((PSREF)
-
Доступность продукта
-
Информация об окружающей среде
©
Lenovo.
|
|
|
|