Тема: Обновление прошивки Panasonic KX-HDV130 — Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
depcadastre
(156/04.09.08)
Приветствую участников форума.
Аппарат KX-HDV130 версия ПО 08.101. Не могу обновить до версии 11.100 — ошибка Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
Вставляю ссылку, всё как по инструкции, но идет ошибка. До версии 08.101 обновил, а до последней никак
http://XXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1
По ссылке перехожу, файл скачивается.
Что не так делаю?
Спасибо.
Mike_K
EXPERT
ошибка Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
Что не так делаю?
Установили запрет на обновление и пытаетесь обновляться.
Сбросьте аппарат в заводские установки и обновите ПО.
Без сброса — не помню где, эта установка активирована.
depcadastre
(156/04.09.08)
В файле конфигурации, что касается обновления указано только
## Firmware Update Settings
FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“N”
FIRM_FILE_PATH=“http://XXXXXXXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1”
FIRM_VERSION=“11.100”
Когда указывал параметр FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“Y”, телефон перегружался циклично и не мог установить прошивку.
Согласно Вашей рекомендации сбросил настройки, указал путь к обновлению, ошибка не появилась, телефон перегрузился, но телефон не прошился.
depcadastre
(156/04.09.08)
В файле конфигурации, что касается обновления указано только
## Firmware Update Settings
FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“N”
FIRM_FILE_PATH=“http://XXXXXXXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1”
FIRM_VERSION=“11.100”
Когда указывал параметр FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“Y”, телефон перегружался циклично и не мог установить прошивку.
Согласно Вашей рекомендации сбросил настройки, указал путь к обновлению, ошибка не появилась, телефон перегрузился, но телефон не прошился.
Mike_K
EXPERT
Установите в локальной сети http сервер, к примеру hfs.
На него выложите две части 11.100.fw.part1 и 11.100.fw.part2.
Выключите всякие антивирусы и фаерволы. Должно обновится.
Не помню ни разу, чтоб были проблемы с обновлением ПО.
depcadastre
(156/04.09.08)
Всё получилось!
Спасибо!!!!!!!!!!!!1
Mike_K
EXPERT
Получилось обновить ПО из локальной сети?
depcadastre
(156/04.09.08)
Да.
Содержание
- Upgrade firmware error firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter
- Как обновить прошивку на телефонах Panasonic серии KX-HDV
- Тема: Обновление прошивки Panasonic KX-HDV130 — Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
- What should I do if fail to upgrade the firmware of my TP-Link router?
- Looking for More
- Upgrade firmware error firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
- How to Upgrade the Firmware on the TP-Link Wi-Fi Routers
- Case 1. If your TP-Link router cannot support TP-Link Cloud service, please upgrade the firmware manually.
- Case 2. If your TP-Link router supports Cloud service, you do not have to manually download and install the firmware any longer. Simply click the Upgrade icon and the router itself will complete the whole process automatically.
- Online upgrade through web management page:
Upgrade firmware error firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter
Как обновить прошивку на телефонах Panasonic серии KX-HDV
Прежде чем приступать к прошивке данных аппаратов удостоверьтесь, что ссылки на скачивание работают.
Для аппаратов KX-HDV100 или KX-HDV130 (обе ссылки):
Для аппаратов KX-HDV230:
Для аппаратов KX-HDV330:
Для аппаратов KX-HDV430:
Для аппаратов KX-TGP600RU:
Доступ на веб-интерфейс телефона по умолчанию выключен, поэтому его нужно включить через экранное меню телефона. Такое поведение характерно для SIP-телефонов Panasonic.
Включим русский язык в экранном меню: Menu –> Basic Settings –> Display Option –> Language –> РУССКИЙ и ОК.
Определим IP адрес, который получил телефон по DHCP:
Mеню –> Системные Настр. –> Статус –> Настройки IPV4 –> IP-Адрес
Для открытия веб-интерфейса нажмите Mеню –> Базовые Настр. –> Прочее –> Встроенный Web, выберете “Включить” для “Встроенный Web”, затем нажмите ОК.
Для доступа в веб-интерфейс телефона предусмотрено два уровня доступа “пользователь” — для просмотра и изменения некоторых настроек и полный доступ уровня “администратор”, который может настраивать любые параметры устройства, нас интересует уровень администратора. Для доступа к веб-интерфейсу телефона просто откройте IP-адрес в веб-браузере
В открывшемся окне авторизации введите следующие данные:
Имя пользователя: admin
Мы попадаем на страницу статуса телефона, где содержится информация о модели телефона и версии встроенного ПО телефона.
Для обновления программного обеспечения Вам необходимо выбрать пункт верхнего меню Maintenance.
Внимание! Телефон должен иметь доступ к интернету!
В левом меню выбираем пункт Upgrade Firmware:
В поле Firmware File URL указать адрес ссылки:
Для аппаратов KX-HDV100 или KX-HDV130 (обе ссылки):
Для аппаратов KX-HDV230:
Для аппаратов KX-HDV330:
Для аппаратов KX-HDV430:
Для аппаратов KX-TGP600RU:
и нажать кнопку Update Firmware
Дальше телефон перезагрузится и начнётся процедура обновления прошивки.
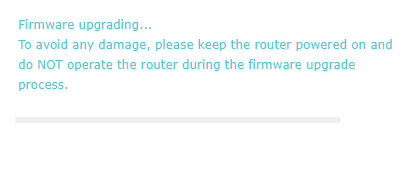
Процесс обновления может занять некоторое время. На протяжении данного времени НИ В КОЕМ СЛУЧАЕ не отключайте оборудование от электропитания!
По техническим вопросам обращайтесь на наш e-mail (master@ats.by)
ПрофТелеком — Как обновить прошивку на телефонах Panasonic KX-HDV100RU | KX-HDV130RU | KX-HDV230RU | KX-HDV330RU | KX-HDV430RU Официальный дилер в РБ!
Источник
Тема: Обновление прошивки Panasonic KX-HDV130 — Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
Приветствую участников форума.
Аппарат KX-HDV130 версия ПО 08.101. Не могу обновить до версии 11.100 — ошибка Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
Вставляю ссылку, всё как по инструкции, но идет ошибка. До версии 08.101 обновил, а до последней никак
http://XXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1
По ссылке перехожу, файл скачивается.
Что не так делаю?
Спасибо.
ошибка Error : Firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter.
Установили запрет на обновление и пытаетесь обновляться.
Сбросьте аппарат в заводские установки и обновите ПО.
Без сброса — не помню где, эта установка активирована.
В файле конфигурации, что касается обновления указано только
## Firmware Update Settings
FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“N”
FIRM_FILE_PATH=“http://XXXXXXXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1”
FIRM_VERSION=“11.100”
Когда указывал параметр FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“Y”, телефон перегружался циклично и не мог установить прошивку.
Согласно Вашей рекомендации сбросил настройки, указал путь к обновлению, ошибка не появилась, телефон перегрузился, но телефон не прошился.
В файле конфигурации, что касается обновления указано только
## Firmware Update Settings
FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“N”
FIRM_FILE_PATH=“http://XXXXXXXXXXXXXX.ru/panasonic/firmware/HDV130-11.100.fw.part1”
FIRM_VERSION=“11.100”
Когда указывал параметр FIRM_UPGRADE_ENABLE=“Y”, телефон перегружался циклично и не мог установить прошивку.
Согласно Вашей рекомендации сбросил настройки, указал путь к обновлению, ошибка не появилась, телефон перегрузился, но телефон не прошился.
Источник
What should I do if fail to upgrade the firmware of my TP-Link router?
This article will show you how we can handle the case of failing to upgrade the firmware on TP-Link devices.
Part I: Online Upgrade
Step 1: Check whether the TP-Link device supports online upgrades or not. Only devices which support the TP-Link Cloud service have an online upgrade function. You may check the following compatibility list:
Step 2: Confirm the internet connectivity of the TP-Link device. Only devices which connect to the internet successfully could upgrade the firmware online smoothly.
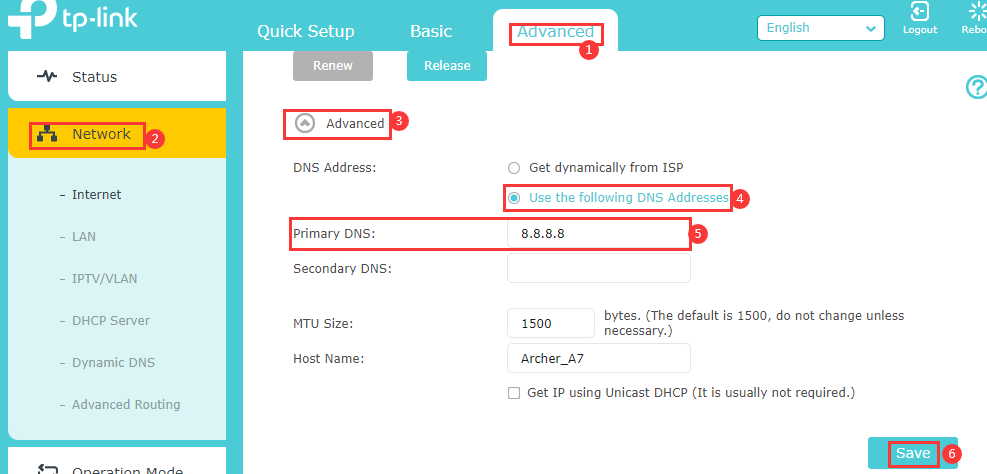
Step3: Change the DNS Server manually. Try manually assigning a static DNS server to the router WAN/Internet. You may try some popular public DNS servers, such as Google’s 8.8.8.8 or CloudFlare’s 1.1.1.1. Please refer to the following screenshot.
Step 4: Try to upgrade firmware locally or manually by downloading the latest firmware on the computer. Please refer to How to upgrade the firmware on TP-Link devices?
Part II: Manual/Local Upgrade
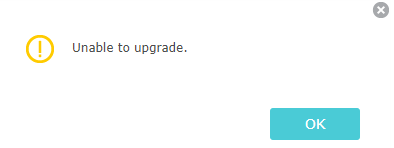
Case1. The error message “unable to upgrade”.
Step 1: Verify the format of the latest firmware. After downloading the latest firmware from the TP-Link official website, you should extract that folder first. The correct format of firmware should be a bin file.
Step 2: check whether you have downloaded the correct firmware version for your TP-Link device.
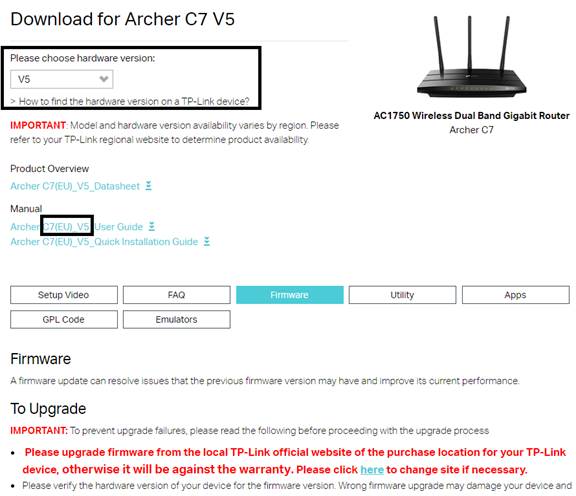
1. Check the model number, hardware version, EU or US version of TP-Link device by referring to How to find the hardware version on a TP-Link device?
Reminder: Please upgrade firmware/software from the local TP-Link official website of the purchase location for your TP-Link device, otherwise it may cause upgrade failure or mistakes and be against the warranty.
2. Select the corresponding hardware version on the download website.
Case2. The progress bar is stuck
1. We suggest you wait for 5minutes to see if the progress is finished.
2. Try to refresh the web page first. Then upgrade again.
3. Try to change another web browser(Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Chrome and etc) to upgrade.
Notes: If there is a sudden power outage during the upgrade, there is a high chance that the router will become a bridge. At this point, you may refer to How to use webpage firmware recovery if the router become brick (new logo)?
If the above suggestions cannot help you out, please contact TP-Link technical support with the following info:
1. The model number, hardware version, current firmware version of TP-Link device;
2. The firmware version downloaded from TP-Link official website;
3. The screenshot of error info is displayed on the firmware upgrade page.
To get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.
Looking for More
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
What’s your concern with this article?
- Dissatisfied with product
- Too Complicated
- Confusing Title
- Does not apply to me
- Too Vague
- Other
We’d love to get your feedback, please let us know how we can improve this content.
Thank you
We appreciate your feedback.
Click here to contact TP-Link technical support.
Источник
Upgrade firmware error firmware version is fixed by configuration parameter
Sun Feb 16, 2020 6:49 am
MikroTik Routerboard displays the following information:
Factory Firmware: 3.36
Current Firmware: 3.36
Upgrade Firmware: 3.33
As we can see «Upgrade Firmware» version is low than «Current Firmware» when try to upgrade it displays this error «Can not chnage firmware to this version»
I tried to upgrade by downloading a newer version and upgrade but it fails.
I have already upgraded many other routers but this one appear to be having a fault, any idea how to fix this?
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Sun Feb 16, 2020 12:56 pm
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Sun Feb 16, 2020 7:25 pm
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Mon Feb 17, 2020 5:07 pm
Based on you old firmware you must also have a old and vulnerable ROS.
First update ROS System > Packages >> Check for Update and upgrade. Now this can be somewhat of a risky business depending on what version you are on so make a backup and export config before doing this!
After you have upgraded ROS you can upgrade the firmware by clicking upgrade, check the log and then reboot.
Just out of curiosity, what version of ROS are you running?
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Tue Feb 18, 2020 7:48 am
Thank you for the replys,
I already tried updating the Router OS first as suggested by @Kindis but after reboot Router wasn’t updated (there is nothin in the log regarding the upgrade) so both methods fails, any other method or suggession?
Below is the Router OS Version and Package Details:
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Tue Feb 18, 2020 9:59 am
Re: Can’t Upgrade Firmware
Tue Feb 18, 2020 11:21 am
Oo this is a big update and also the version you have have several security issues that are more or less very critical.
I would go for a export of configuration and perform a Netinstall but otherwise do as mentioned above.
You will also get the new bridge setup and a lot of other features so as I said before this is a big risk upgrade and for that reason I would netinstall and then rebuild config.
Longer path for upgrading but you can be more confident that the final result will work fine.
Источник
How to Upgrade the Firmware on the TP-Link Wi-Fi Routers
This article will guide you to upgrade firmware on TP-Link Wi-Fi routers step by step.
First of all, please check whether your TP-Link router supports TP-Link Cloud service or not. You may click here to check the Cloud Compatibility list.
Case 1. If your TP-Link router cannot support TP-Link Cloud service, please upgrade the firmware manually.
B e f o r e upg r adi ng :
1. Please v er i f y the ha r d w a r e v er sion of y our d e vice f or the f ir m w a r e v er sio n . W r ong f ir m w a r e upg r adi n g m ay d a m age your d e vice and v oid the w a rr ant y .
2. Please upgrade firmware from the local TP-Link official website of the purchase location for your TP-Link device, otherwise it will be against the warranty. (The firmware of EU and US are different.)
3. Backup the configuration in order to restore it after upgrading. O r, write down all the settings you changed from the default values, you may need to re-enter them manually.
4. It ’ s r ec o mme nd e d th a t us er s stop all Inte r n e t Ap p li c ations on the c o m pute r , or s i m ply d iscon n ec t the Internet line f r o m the de v ice b e f o r e upg r adi n g.
During upg r adin g :
DO NOT upg r ade the f ir m w a r e th r ough w i r e less c onn e c tion unl e ss there is no LAN/Ethernet port on your TP-Link device.
DO NOT tu r n off the po w e r or disconnect the Eth er n e t c able du r i n g the firmware upg r ade.
Steps about upgrading:
Step 1 Find and navigate to the zip file from which you want to extract the content. Right-click on the file and select Extract All from the context menu. (Google Chrome & Windows system as example)
S tep 2 L o g into the T P- L ink device b y t y pi n g http://tpli n kwifi.net in the a ddress b a r of any web brows e r (such a s Chrome , Firefo x ). The d e f a ult username a n d p a sswo r d a r e both a d m i n in lower case, or you need to create a new local password by yourself.
S tep 3 Click Advanced ->System -> Firmware Upgrade, click BROWSE to choose the firmware you already extracted in the folder. The firmware type is usually BIN File.
Note: Please double-check the firmware and hardware version.
S tep 4 Cli c k Upgrade. The pop window will ask you to confirm the operated. Please double-check if all the previous steps are fine.
Step 5 The d e vi c e will reboot a utom a ti ca l l y a fter up g r a di n g. Pl ea se w a it a bout 3 minut e s.
S tep 6 Verify that the router’s firmware has been upgraded successfully or not in the same page.
1. Check f r om m anag e me nt page.
Log into the device, at the bottom of the interface, the firmware and hardware version will be shown as the following picture:
(As an example, in the following picture, the hardware version is «V2»). Or go the Advanced->System->Firmware Upgrade, you can see them too.
2. Check f r om bottom la b e l.
Turn over the device, you can see a label at the back of the device, there is a character string «Ver:X.Y» (for example, Ver:1.0) and the number X.Y is the hardware version of the device. If the string is «Ver: 1.2», it means that the hardware version is V1.2. (Normally V1.x=V1).
How to Backup & Restore configuration of TP-Link Wireless Router?
Log i nto the d e vice, Click Advanced->System — > Backup & Restore . Click BACK UP and save the file. The f ile na m e is config.bin by default.
If the release note of the firmware version you want to upgrade will reset your settings. After firmware upgrading, click BROWSE to upload the previous backup configuration file.
Finally, click RESTORE and confirm, wait 3 minute you can see configuration uploaded successfully. Then the device will reboot automatically.
Case 2. If your TP-Link router supports Cloud service, you do not have to manually download and install the firmware any longer. Simply click the Upgrade icon and the router itself will complete the whole process automatically.
Note:
1. During the online upgrade, please DON’T power off the router, unplug the Ethernet or disconnect from the wireless.
2. If you fail to download the firmware online, you can download it directly from the TP-Link official website. And manually upgrade the firmware as Case 1.
Online upgrade through web management page:
Step 1. Connect your device to the TP-Link wireless router either via Ethernet or wirelessly. Then open a browser and type http://tplinkwifi.net in the address bar. Press Enter and login the router.
Step 2. If there is an update available, you will be notified by the Update icon in the upper right corner (if there is no update, the icon will not appear). Click Update and you will redirect to the Firmware Upgrade page on which you can check the latest firmware version and release notes.
Step 3. Click on the Upgrade button to begin the upgrade. Then wait until the router finishes the upgrade process, which will include a router reboot at the end.
*Note: Please make sure that you have a stable internet connection during the download process. Loss of connection during the process can damage the router.
Online upgrade through the Tether APP:
Step 1. Connect your smartphone to the Wi-Fi of the router. Then open the Tether APP and login the router. Please tap the management icon at the bottom right corner, and you will see a red point in the System area which indicates there is new firmware for the router.
Step 2. Tap Tools > System > Firmware Update, and you will find the new version of firmware.
Tap Learn More to learn the release logs of the new firmware (recommended).
Note: Please pay attention to the release logs. If it mentions a reset after the upgrade, your previous configuration on the router including internet access and wireless settings will be reset to factory defaults, and you will need to connect your smartphone to the router with the default SSID and password printed on the bottom label and configure the device again.
Step 3. Tap Update to begin the upgrade process.
Get to know more details of each function and configuration please go to Download Center to download the manual of your product.
Источник
18 января 2017
На новых SIP-телефонах Panasonic KX-HDV100, KX-HDV130, KX-HDV230, KX-HDV330, KX-HDV430 была изменена система обновления прошивки. Вместо привычной для аппаратов Panasonic схемы — скачать прошивку с сайта и загрузить её на телефон — предлагается схема в стиле компании Grandstream — аппарату необходимо указать ссылку на сайт, откуда он сам скачает прошивку. Но, к сожалению, компания Panasonic предлагает нам самостоятельно поднять web-сервер и правильно расположить на нём файлы. Мы же, люди ленивые и решили сделать простую и понятную инструкцию без «всех этих заморочек».
Итак поехали.
Здесь представлены самые свежие на данный момент версии прошивок (03.105) для России и Казахстана, предоставленные компанией Panasonic, вы можете их скачать и использовать для обновления через свой сервер.
- На самом аппарате необходимо включить web-интерфейс. Для этого:
- нажимаем клавишу под экраном, которая подписана на экране как Меню(Menu)
- пролистать меню и выбрать пункт Базовые Настр.(Basic Settings)
- пролистать и выбрать пункт ПРОЧЕЕ(Other Options)
- выбрать пункт Встроенный Web(Embended Web)
- и в нём выбрать пункт ВКЛ.(On).
- Заходим на web-интрефейс телефона. Если вы не знаете каким образом зайти на web-интерфейс — то вы можете посмотреть адрес телефона пройдя по следующему пути: Системн. Настр.(System settings) — Статус(Status) — Настройки IPV4(IPv4 Settings) -IP-Адрес(IP Address), а после этого в адресной строке браузера набрать http://XXX.XXX.X.XX , где вместо X будут цифры, отображенные на экране телефона.
- Зайдя по ссылке вы увидите следующий экран:
- Нам необходимо выбрать пункт верхнего меню Maintenance.
- В левом меню выбираем пункт Upgrade Firmware:
- В поле Firmware File URL указать адрес ссылки
Для аппаратов KX-HDV100 или KX-HDV130:
http://fw.tatris.ru/HDV130-06.000.fw.part1Для аппаратов KX-HDV230:
http://fw.tatris.ru/HDV230-06.000.fwДля аппаратов KX-HDV330:
http://fw.tatris.ru/HDV330-06.000.fwДля аппаратов KX-HDV430:
http://fw.tatris.ru/HDV430-06.001.fw - Дальше телефон потупит несколько секунд (до 20), перезагрузится и начнётся процедура обновления прошивки. Она выглядит примерно следующим образом:
- Поздравляем, ваш телефон обновлён.
и нажать кнопку Update Firmware:
-
kitsa_nik
- Без страха и упрёка
- Сообщения: 95
- Зарегистрирован: 03 июл 2019, 12:28
- Благодарил (а): 2 раза
- Поблагодарили: 1 раз
Обновление KX-HDV130
Коллеги есть желание обновить телефоны до 11 версии.
Я правильно понимаю что для этого необходимо поднять http сервер.
Может есть у кого ссылка для обновления прошивки, а то больно неохота с сервером заморачиваться.
-
vda
- Патриарх
- Сообщения: 917
- Зарегистрирован: 14 май 2019, 11:04
- Откуда: Ташкент
- Благодарил (а): 182 раза
- Поблагодарили: 175 раз
Re: Обновление KX-HDV130
Сообщение
vda » 29 окт 2019, 14:17
kitsa_nik писал(а): ↑
29 окт 2019, 13:29
Коллеги есть желание обновить телефоны до 11 версии.
Я правильно понимаю что для этого необходимо поднять http сервер.
Может есть у кого ссылка для обновления прошивки, а то больно неохота с сервером заморачиваться.
Смотри. SIP телефоны от панасоника это бытовуха. А все что связано с бытовухой есть на официальном сайте в открытом доступе.
https://panasonic.net/cns/pcc/support/s … V1/ru.html
-
kitsa_nik
- Без страха и упрёка
- Сообщения: 95
- Зарегистрирован: 03 июл 2019, 12:28
- Благодарил (а): 2 раза
- Поблагодарили: 1 раз
Re: Обновление KX-HDV130
Сообщение
kitsa_nik » 30 окт 2019, 05:20
Эта ссылка у меня есть. Вопрос не в этом был.
Согласно (for_Web_portal)_02-022_Technical_Notification_HDV130_and_HDV100_upgrade_to_Firmware_V02.081
Для обновления необходимо в Upgrade Firmware ссылку вводить в формате
http://XX.XX.XX.XX/HDV130-11.050.fw.part1
А у меня нет возможности поднять http
-
shkiper516
- Инквизиция
- Сообщения: 956
- Зарегистрирован: 29 окт 2019, 02:01
- Откуда: Владивосток
- Благодарил (а): 177 раз
- Поблагодарили: 188 раз
- Контактная информация:
Re: Обновление KX-HDV130
Сообщение
shkiper516 » 30 окт 2019, 06:40
kitsa_nik писал(а): ↑
30 окт 2019, 05:20
Эта ссылка у меня есть. Вопрос не в этом был.
Согласно (for_Web_portal)_02-022_Technical_Notification_HDV130_and_HDV100_upgrade_to_Firmware_V02.081
Для обновления необходимо в Upgrade Firmware ссылку вводить в формате
http://XX.XX.XX.XX/HDV130-11.050.fw.part1
А у меня нет возможности поднять http
Дык скачай и залей вручную
-
vda
- Патриарх
- Сообщения: 917
- Зарегистрирован: 14 май 2019, 11:04
- Откуда: Ташкент
- Благодарил (а): 182 раза
- Поблагодарили: 175 раз
Re: Обновление KX-HDV130
Сообщение
vda » 30 окт 2019, 07:19
kitsa_nik писал(а): ↑
30 окт 2019, 05:20
А у меня нет возможности поднять http
Религия не позволяет
Берешь любой говноутбук или самый старый ПК с любой виндой. Ставишь бесплатный HFS с интуитивно понятным интерфейсом и вперед. Даже ребенок шимпанзе разберется
-
kitsa_nik
- Без страха и упрёка
- Сообщения: 95
- Зарегистрирован: 03 июл 2019, 12:28
- Благодарил (а): 2 раза
- Поблагодарили: 1 раз
Re: Обновление KX-HDV130
Сообщение
kitsa_nik » 30 окт 2019, 07:25
Да не вопрос, если у вас в организации разрешена установка любого приложения или нет port security
Ладно развели тему не о чем. Сказали бы сразу что нет ссылки.
О альтернативных вариантах я в курсе.
Куратор(ы):
DeathBringer
ingviowarr
CodeRush
LS_29
| Автор | Сообщение | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
Полезные статьи (автор: CodeRush) Открыть для чтения «Устройство файла UEFI BIOS» «Устройство NVRAM в UEFI-совместимых прошивках» «Модификация UEFI BIOS в UEFITool» Софт UEFITool — просмотрщик и редактор UEFI BIOS’ов UEFI утилиты Management Engine ME (Обсуждение), FW и Утилиты Скачать последние версии на GitHub: Обновления для видеоадаптеров 02.01.2019 — В коллекцию добавлены VBIOS + BSF SKL/KBL 1062 Перенос настроек OROM Intel VBIOS — Новая редакция 23.10.2021 GOPUpd v1.9.6.5.k_mod_v0.4.9 — Добавление/обновление EFI GOP Driver для видеокарт на базе AMD и NVIDIA UEFI BIOS Updater — комплект для автоматического обновления EFI, OROM и mCode в UEFI BIOS Все изменения тут [1.79.3] [1,75] [1.70] [Предыдущие версии] Сохраненные статьи с Win-Raid Forum:
• Intel (Converged Security) Trusted Execution Engine: Drivers, Firmware and Tools • Which are the «best» Intel AHCI/RAID drivers? Другие интересности по теме:
• CPUID — CodeName новых процессоров • Добавление NVMe module в BIOS (6-8 Series) • FFS. Считаем контрольные суммы сами (Новое) • FAQ по прошивке и редактор индивидуальных данных BIOS плат ASUS P8xxx и их ROG-аналогов • Потрошим структуру меню Aptio BIOS • Модификация материнских плат 100/200 для поддержки процессоров Coffee Lake 8xxx/9xxx • ASUS Flashback (Новое) Доска объявлений Актуальное 1) В послденее время опять участились жалобы на наличии вируса в пакете UBU, якобы МСЕ,ехе содержит вирус. Поэтому принято решение, что вместо ехе файла теперь будет py исхотдный Пайтона. Чтобы была корректная работа с микодами вам необходимо установить пакет Ptyhon версии 3.7 или выше. А также две библиотеки: https://mega.nz/#F!MSRDxSqR!5etS-te7ZqRQX9Zb25es_A 3) На данный момент рекомендуется использовать UEFITool v0.25.0 (и не выше), до выяснения Мешающие чтению картинки и видео убирайте под спойлер.
|
| Реклама | |
|
Партнер |
|
LS_29 |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
Точно. Почти у всех и во всех обновках летних эта опция и расписывалась, сверился со своим Асроком х570м про4.. Но вот что странно если на 1507 10-ка грузится, а после уже толпа обновок была, текущая то вообще 56хх, то вроде жалобы в ТП должны были быть, а значит и поправки.. |
|
Jo-Jo |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Люди, помогите прошить биос на МСИ Z490(в подписи), тулзой AFUWINx64. Ниже цитата, которую прислали чуваку якобы с мси. : Цитата: not flash the bios by M-Flash or LiveUpdate, if you want to flash the bios in the future, we can provide you a tool to update the bios. Я вот один раз запорол биос, теперь мфлэшью боязно, хочу попробовать AFUWINx64. Кто что подскажет? https://drive.google.com/file/d/1QrxbGe … sp=sharing https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Zgnqkb … sp=sharing |
|
Jo-Jo |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
dart_raiden писал(а): Модификация UEFI BIOS. Софт для работы. #17440584 Я так понял, эта инфа из ссылки, так же и для интел подходит, по мимо биосов амд, и объясняет почему 32мб не видит прога? Ну я 16 мегов зашил, вроде ещё 16 не просит))). Сейчас ввел команду в батник без всяких аргументов, D:1AFUWINx64.exe D:1E7C76IMS.2B0. В итоге прошилось только MAIN по ходу. Перезагрузил, прошка поменялась. Но я не очень понял, там есть нврам и бут. Надо их прошивать, если майн от новой прошивки, а всё остальное от старой осталось или новая прошка, туда запишет свои данные, какие ей нужны, сама? Или прошить надо? |
|
Michael_Code |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Я так понял, эта инфа из ссылки, так же и для интел подходит, помимо биосов амд Jo-Jo, dart_raiden, |
|
Jo-Jo |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Michael_Code писал(а): AFUWIN снял только BIOS redgion 16 MB, а биос с офф. сайта целиком, с дескриптором и МЕ. Спасибо, прошил, теперь и так работает. Остальные 16 мб видимо, которые МЕ с дескриптором, можно обновить другой прогой? |
|
DeathBringer |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
win-raid.com закрывают: Цитата: Global Announcement |
|
Michael_Code |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Остальные 16 мб видимо, которые МЕ с дескриптором, можно обновить другой прогой? Jo-Jo, не остальные 16, а биос целиком. Вестимо, для интела с помощью FPT, Flash Programming Tool своей версии. win-raid.com закрывают DeathBringer, да, увы, когда выскочило сообщение — сердце чуть не встало. Оччень, очень жаль. |
|
Voyager777 |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
о, а причины закрытия озвучить? |
|
LS_29 |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
Наисано что всяинфа о закрытии будет тут https://www.win-raid.com/f2-News-Announcements.html но там пока ничего. Полагаю что всё упирается в финансы (фрпум живет только за счет пожертвований, рекламы со стороны никакой), по моим наблюдениеям с начала ёпидемии посещяемость упала, новых и интересных проектов тоже почти нет. Добавлено спустя 6 часов 17 минут 10 секунд: |
|
Jo-Jo |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
LS_29 писал(а): Станно, но МСИ позволяла прошивать моды через встроенный M-Flash… Видимо политика поменялась. Да, сравнил регион МЕ в родных прошивках от апреля до октября, он не меняется, поэтому его можно и не обновлять. Но я обновляю не мод, а оригинал. Я мфлешем запорол мать наглухо. Тут неделю назад ещё один запорол мфлешем. В отзывах днс несколько запороли. На сайте мси тема людей, где с мая по сейчас, больше сотни людей запороли мфлешем материнки. Восстановление только программатор. Поэтому я и прошивал не мфлешем. |
|
LS_29 |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
При прошивке встроенным флэшером настройки биввиса, особенно оверные, по дефолту были сброшены? |
|
Jo-Jo |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
LS_29 писал(а): При прошивке встроенным флэшером настройки биввиса, особенно оверные, по дефолту были сброшены? Да сбросил по дефолту. Дело явно не в оверклокерах). https://forum-en.msi.com/index.php?thre … es.367575/ А вот тема от 2015 года. МСИ уже тогда жгла матери своим мфлэшером: https://forum-ru.msi.com/index.php?topic=90326.0 |
|
Mercury127 |
|
|
Junior Статус: Не в сети |
https://www.win-raid.com/t9784f2-Win-Ra … ement.html перевод мой Цитата: Привет всем. Я пришел сказать вам пренеприятнейшее известие для сообщества Винрейд — мы планируем закрыть форум в конце года. У администрации больше нет возможности поддерживать и сопровождать его. Из-за изменившихся жизненных и рабочих обстоятельств, мы больше не можем уделять форуму столько времени и сил, как в минувшие годы. Кроме того, оказалось, что сообщество, созданное Дитером в 2013, нынче уже не то. Задачей форума всегда было привлечение опытных участников, желающих изучать, оптимизировать и улучшать свои системы, как это заявлено на странице Приветствия. Это означало изучать новые штуковины и писать руководства для других, желающих им следовать и учиться. Обе эти задачи требуют много времени и знающих людей, которые могут и хотят тратить на это свое время и силы. К сожалению, большинство таких людей сейчас ушли в иные места, и теперь у нас самые активные топики — про «Памагите». Более того, общие тенденции развитие Интернета привели к тому, что классические форумы вымирают как класс. Всё больше и больше сообществ превращаются в соцсети или переходят к общению на их базе. И как вишенка на торте, хостер нашего конкретного частного форума не предоставляет ни регулярных обновлений, ни исправлений долгоживущих багов, ни модераторской защиты. В целом, мы не управляли форумом полностью, никогда не имели никакого дохода от назойливой рекламы, которую вы видели, и не имеем возможности управлять ее содержимым, положением или частотой. Все это не соответствует духу форума, заявленному изначально, и мы решили закрыть его, чтобы не дать ему превратиться в то, чего мы никогда не желали — в переполненную рекламой неуправляемую мусорку. Спасобо вам за участие и поддержку на протяженни чудесных восьми лет! Если вам есть что сказать — пожалйуста, пишите здесь, чтоб все видели. Plato (a.k.a. plutomaniac) |
|
Michael_Code |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
у МСИ как то раньше не было никогда проблем с прошивкой через M-Flash LS_29, была проблема, решал её на win-raid online с линуксоидом. Модбиос, только микрокоды новые, упорно не хотел шиться через M-Flash. Т.е. шился, но без GUID 17088572-….. с микрокодами |
|
DeathBringer |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
Michael_Code и LS_29 |
|
Michael_Code |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Может какие-то посты с win-raid.com перевести в формат этого форума и сохранить у нас ветке? DeathBringer, ох, как много на win-raid, там, конечно, много пустого, но ценного….. Немерянно. Это какой объём? |
|
DeathBringer |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
#77 Fernando @ all users with an Intel AHCI or RAID system Preliminary note: Which are the «best» Intel AHCI/RAID drivers? Since there is no Intel AHCI/RAID driver available, which is suitable or may be even perfect for all different Intel SATA Controllers, Operating Systems and driver installation/integration procedures, I am offering a variety of Intel AHCI/RAID drivers, which belong to different development branches (MSM, RST and RSTe). To make the selection of the appropriate driver for your special system easier for you, I have tried to list the advantages/disadvantages of the different Intel AHCI/RAID drivers development branches:
General personal statements:
My favorite Intel AHCI/RAID drivers Recommended for all Intel Chipset AHCI/RAID systems (except X79/X99/X299 Chipsets running in RSTe mode):
Remark: Recommended for Intel 600/600+ Chipset series AHCI/RAID systems running in RSTe mode:
To make is easier for you to find the Intel RST/RSTe driver, which I recommend for your special AHCI or RAID system, here is a table: Recommended Intel AHCI & RAID drivers: ICH7R/M, ICH8R/M and ICH9R/M AHCI: RST v11.2.0.1006 P45 and X58 Chipset/ICH10R AHCI: RST(e) v11.7.4.1001 5-Series Chipsets (e.g. P55) AHCI: RST(e) v11.7.4.1001 or v12.9.4.1000 6-Series Chipsets (e.g. P67+Z68) AHCI: RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 7-Series Desktop systems (e.g. Z77) AHCI: RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 or v13.2.8.1002 7-Series Mobile systems (e.g. QM77) AHCI: RST(e) v12.9.4.1000 or v13.2.8.1002 8-/9-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z87/Z97) AHCI: RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 100-/200-Series (e.g. Z170/Z270) AHCI: Intel RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 or v14.8.18.1066 300-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z370) AHCI: latest RST v16/17 platform drivers 400/500-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z470) AHCI: latest RST v18 platform drivers X79 Chipset RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 WHQL X99 Chipset RST(e) v14.8.18.1066 resp. RSTe v5.5.4.1036 X299 Chipset and up AHCI: latest RST v17 resp. RSTe v6/v7 platform drivers) Have fun! (c) win-raid.com |
|
dart_raiden |
|
|
Member Статус: Не в сети |
Я пока заливаю всё сюда, главное — спасти файлы и информацию, а потом уже можно подумать, как и где это красиво развернуть. Там тупо html + все архивы с обменников, упоминающиеся в тексте. Последний раз редактировалось dart_raiden 14.11.2021 22:14, всего редактировалось 1 раз. |
|
DeathBringer |
|
|
Куратор темы Статус: Не в сети |
#77 plutomaniac Intel (Converged Security) Management Engine: Last Updated: 2021-10-08 Intel Management Engine Introduction: Built into many Intel-based platforms is a small, low power computer subsystem called the Intel Management Engine (Intel ME). This can perform various tasks while the system is booting, running or sleeping. It operates independently from the main CPU, BIOS and OS but can interact with them if needed. The ME is responsible for many parts of an Intel-based system. Such functionality extends, but it’s not limited, to Platform Clocks Control (ICC), Thermal Monitoring, Fan Control, Power Management, Overclocking, Silicon Workaround (resolves silicon bugs which would have otherwise required a new cpu stepping), Identity Protection Technology, Boot Guard, Rapid Start Technology, Smart Connect Technology, Sensor Hub Controller (ISHC), Active Management Technology (AMT), Small Business Advantage (SBA), Wireless Display, PlayReady, Protected Video/Audio Path etc. For certain advanced/corporate features (i.e. AMT, SBA) the ME uses an out-of-band (OOB) network interface to perform functions even when the system is powered down, the OS and/or hard drivers are non-functional etc. Thus it is essential for it to be operational in order for the platform to be working properly, no matter if the advanced/corporate features are available or not. Intel Converged Security Engine Introduction: The evolution of Intel Management Engine into a unified security co-processor, running x86 code under a Minix-based Operating System. It was first introduced in 2015 with the release of Skylake CPUs working alongside 100-series Sunrise Point Platform Controller Hub (PCH). The CSE hardware can run Management Engine (ME) 11+, Trusted Execution Engine (TXE) 3+ or Server Platform Services (SPS) 4+ firmware. So there are a total of three families of CSE-based firmware: CSME (CSE ME), CSTXE (CSE TXE) and CSSPS (CSE SPS). The CSE hardware is also capable of running other types of firmware such as Power Management Controller (PMC), Integrated Sensor Hub (ISH), Imaging Unit (iUnit), Clear Audio Voice Speech (cAVS), Wireless Microcode (WCOD) etc. Intel Power Management Controller Introduction: Handles all Platform Controller Hub (PCH) power management related activities, running ARC code on top of the CSE hardware. PMC administers power management functions of the PCH including interfacing with other logic and controllers on the platform to perform power state transitions, configure, manage and respond to wake events, aggregate and report latency tolerance information for devices and peripherals connected to and integrated into the PCH etc. It was first introduced in 2018 with the release of Coffee/Cannon Lake CPUs working alongside 300-series Cannon Point PCH. Disclaimer: All the software and firmware below comes only from official updates which were provided and made public by various manufacturers! The System Tools are gathered and provided with the sole purpose of helping people who are out of other viable solutions. Thus, they can be extremely helpful to those who have major problems with their systems for which their manufacturer refuses to assist due to indifference and/or system age. Getting Started: Intel (CS)ME is a Hardware platform which runs Firmware, is monitored/configured by Tools and interfaces with the user via Drivers. To get started, you need at the very least to know what (CS)ME firmware major and minor version your system is running. Such info can be retrieved in various ways but you can use the free system information and diagnostics tool HWiNFO > Motherboard > Intel ME > Intel ME Version. The format is Major.Minor, Build, Hotfix. Once you determine the system’s (CS)ME firmware major and minor version, you can install the latest Drivers from section A and update the (CS)ME Firmware by following sequentially the relevant steps at Section B using the required Tools from Section C. A. Intel MEI Drivers The latest v15.0 DCH drivers are usable with (CS)ME 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 systems running under Windows 10 >= 1709. The latest v15.0 MSI drivers are usable with (CS)ME 10, 11 and 12 systems running under Windows 8, 10 <= 1703 or (CS)ME 10 and 11 systems running under Windows 7. Users of systems with ME <= 9, must check Section D to find the driver they need. In order to check your current installed version, use Intel MEInfo tool as instructed below. Note: To extract the files below you need to use programs which support RAR5 compression! A1. Intel MEI Drivers and Software These packages contain the Intel MEI drivers with their respective software and system services. It is advised to install these to enable all the Engine-related functionality. Since the Intel MEI Drivers and Software are OS version dependent, search and run «winver.exe» to determine your own.
Note: MEI Drivers and Software v2137.15.0.2461 DCH includes MEI v2120.100.0.1085. MEI Drivers and Software v2112.15.0.2221 MSI includes MEI v2108.100.0.1053. A2. Intel MEI Driver Only These packages contain only the Intel MEI Drivers without any additional software or system services. Installing these allow only very basic Engine-related functionality. Since the Intel MEI Driver is OS version dependent, search and run «winver.exe» to determine your own.
Note: The MEI Drivers listed above are part of the complete Drivers and Software packages found at section A1. A newer Drivers and Software package has newer Software but the actual MEI Driver may still be an older version. B. Intel (CS)ME, PMC, PCHC and PHY Firmware SPI/BIOS Regions (FD/Engine/BIOS): The SPI/BIOS chip firmware is divided into regions which control different aspects of an Intel-based system. The mandatory regions are the Flash Descriptor (FD), the (Converged Security) Management Engine (CSME/ME or Engine) and the BIOS. The FD controls read/write access between the SPI/BIOS chip regions and holds certain system hardware settings. The (CS)ME holds the system’s Engine firmware. For security reasons, the FD and Engine regions of the SPI/BIOS chip are usually locked so that no read/write access is allowed via software means. Since the FD controls that read/write access, it must be locked/protected so that it is not manually overwritten to allow unauthorized access to the firmware regions of the system’s SPI/BIOS chip. The Engine region at the system’s SPI/BIOS chip is also locked/protected due to the nature of the CSE/ME co-processor, as explained at the Introductions above. Engine Firmware Attributes (Family/Platform/SKU/Version): Intel (CS)ME or Engine firmware is mainly categorized based on its target Chipset Family (i.e. Cougar Point, Cannon Point, Lake Field, Tiger Point), Chipset Platform (H = Halo, LP = Low Power, N = Nano, V = Value), Type/SKU (i.e. Consumer, Corporate, Slim, Lite, 1.5MB, 5MB) and Version (i.e. 12.0.6.1120 = Major.Minor.Hotfix.Build). Be careful of what firmware your download relevant to your system. To understand your exact Chipset Family, Chipset Platform, (CS)ME Type/SKU and (CS)ME Version, you can usually run MEInfo or MEManuf tools with «-verbose» parameter. Otherwise, ME Analyzer can show you all the relevant information, after loading your SPI/BIOS image (Flash Descriptor + Engine + BIOS), when the latter is available. If a SPI/BIOS image is not available, run FWUpdate tool with parameter «-save fw.bin» and load the resulting «fw.bin» image into ME Analyzer instead. All the firmware below correspond to a specific Platform which runs a specific (CS)ME firmware version (example: For systems running CSME Corporate H v11.0 — v11.8). Engine Firmware Regions (RGN/EXTR): The Type of each Engine/(CS)ME firmware Region can be either Stock (RGN) or Extracted (EXTR). Stock are clean/stock/unconfigured images provided by Intel to OEMs. Extracted are dirty/extracted/configured images from various SPI/BIOS. The Engine firmware at the system’s SPI/BIOS chip is always EXTR, generated by the OEM after configuring the equivalent RGN with the appropriate system settings. Engine Firmware Configuration (CODE/DATA): The Engine Firmware Regions (RGN/EXTR) consist of two sections: CODE and DATA. CODE is the actual Engine firmware whereas DATA is where all the system-specific settings are stored, as configured by the OEM at the factory via Intel Flash Image Tool. The Engine firmware is not static as it holds system-specific configuration and can additionally be configured by the Engine co-processor itself while the system is running in order to provide the proper support and functionality. Any such changes are written into the DATA section of the Engine Region and the firmware is considered Initialized. That means that the DATA section can be in one of three states: Unconfigured, Configured or Initialized. Unconfigured means that the Engine firmware image is the stock one Intel provides and not configured by the OEM at all (RGN). Configured means that the OEM has applied model specific settings and the Engine region is ready for deployment (EXTR). Initialized means that the Engine region comes from a system which was already running and thus the Engine co-processor has further configured the DATA section to suit that particular system better (system specific or dirty EXTR). FWUpdate Update Images (UPD): FWUpdate images (UPD) are partial RGN/EXTR firmware regions which contain only ME CODE without any DATA. They are created and used only by Intel’s FWUpdate tool. Thus, they can neither be opened nor configured by Intel Flash Image Tool (FIT). Never flash UPD images via anything other than Intel FWUpdate tool. UPD images are not needed for 7-series (ME Independent Update Partitions (IUP): The Engine firmware consists of multiple Partitions (sections) and each one is responsible for different features/capabilities. For example, the Fault Tolerant Partition (FTPR) contains CODE which is essential for the (CS)ME operation whereas the File System Partition (MFS, EFFS) contains the Configured and/or Initialized DATA. Some (CS)ME firmware Partitions target auxiliary CSE/ME co-processor devices or capabilities and can also be updated independently of the main (CS)ME firmware. These are called Independent Update Partitions (IUP) with the most notable/important ones being Power Management Controller (PMC), Platform Controller Hub Configuration (PCHC) and USB Type C Physical (PHY). Starting from CSME 12+, the main CSME firmware must first be combined/stitched with one or more obligatory IUPs, before initiating an update procedure via FWUpdate tool. Whenever CSME + IUP merging is required, equivalent instructions and firmware are provided below. The following CSME/IUP Table lists the CSME 12+ firmware Major.Minor versions which require the presence of IUP(s) and their respective versions or SKUs. You’ll need to consult this table while following the update instructions below to choose the correct CSME + IUP combination for your system. #77 Engine Security Version Number (SVN): All (CS)ME >= 8 and all IUP firmware are defined by a Security Version Number (SVN) like 1,2,3 etc which is used to control the possible upgrade/downgrade paths provided by Intel’s FWUpdate tool. The SVN gets incremented if there is a high or critical security fix that requires a Trusted Computing Base (TCB) recovery operation, a significant event in the life cycle of the firmware which requires renewal of the security signing keys in use. A downgrade to a lower SVN value via FWUpdate tool is prohibited whereas an upgrade to the same or higher SVN is allowed. For example if your current firmware has a SVN of 2, you can update to another firmware with SVN >= 2 (for example 3) but you cannot downgrade to another firmware with SVN < 2 (for example 1). Trying to flash a firmware with lower SVN will result in the error «The image provided is not supported by the platform» or similar. To view the SVN value of any (CS)ME or PMC firmware, you can use ME Analyzer tool. Engine Version Control Number (VCN): All (CS)ME >= 8 and all IUP firmware are defined by a Version Control Number (VCN) like 1,2,45,193 etc which is used to control the possible upgrade/downgrade paths provided by Intel’s FWUpdate tool. The VCN gets incremented if there is a security fix, a significant firmware change or a new feature addition. A downgrade to a lower VCN value via FWUpdate tool is prohibited whereas an upgrade to the same or higher VCN is allowed. For example if your current firmware has a VCN of 176, you can update to another firmware with VCN >= 176 (for example 193) but you cannot downgrade to another firmware with VCN < 176 (for example 174). Trying to flash a firmware with lower VCN will result in the error «The image provided is not supported by the platform» or similar. To view the VCN value of any (CS)ME firmware, you can use ME Analyzer tool. Engine Production Ready Status (PV): All (CS)ME >= 8 and all IUP firmware are defined by a Production Version/Ready Status (PV) which can be either Yes or No and is used to control the possible upgrade/downgrade paths provided by Intel’s FWUpdate tool. The PV status is set to Yes when a firmware is validated/ready for use at Production platforms, thus when its status is Stable and not Beta, Alpha etc. An upgrade/downgrade from PV to non-PV firmware via FWUpdate tool is prohibited whereas upgrades/downgrades to the same PV or from non-PV to PV are allowed. For example if your current firmware has PV set to Yes, you can upgrade/downgrade to another firmware with PV set to Yes but you cannot upgrade/downgrade to another firmware with PV set to No. Trying to flash a firmware with incompatible PV will result in the error «The image provided is not supported by the platform» or similar. To view the PV status of any (CS)ME firmware, you can use ME Analyzer tool. Power Down Mitigation (PDM): At CSME v11 LP firmware, make sure to mind the PDM status which is distinguished between YPDM (Yes) and NPDM (No). PDM is some sort of erratum, which is only relevant to 100-series PCH-LP systems. Thus, it is an attribute of every CSME v11.0 — v11.8 firmware which supports 100-series PCH-LP systems. The PDM status of a firmware can be detected by ME Analyzer by loading either your SPI/BIOS image (Flash Descriptor + Engine + BIOS) or an Engine Firmware Recovery image which can be generated via FWUpdate tool parameter «-save recovery.bin». Power Management Controller (PMC) IUP: PMC firmware always targets a specific Chipset Family/Codename (i.e. CNP, ICP, LKF, CMP), Chipset Platform (i.e. H, LP, N, V) and Chipset Stepping/Revision (i.e. A, B, C, D). For example, a CSME 12.0 Corporate H B system must use PMC CNP H B 300.2 firmware, a CSME 15.0 Consumer LP B system must use PMC TGP LP B 150.1 firmware etc. The PMC firmware can only be updated after being merged with a compatible CSME firmware via Flash Image Tool. Platform Controller Hub Configuration (PCHC) IUP: PCHC firmware always targets a specific Chipset Family/Codename (i.e. ICP, CMP, TGP). For example, a CSME 13.0 Consumer LP D system must use PCHC ICP 13.0 firmware, a CSME 15.40 Server LP B system must use PCHC EHL 15.0 firmware etc. The PCHC firmware can only be updated after being merged with a compatible CSME firmware via Flash Image Tool. USB Type C Physical (PHY) IUP: PHY firmware always targets a specific Chipset Family/Codename (i.e. LKF, CMP, TGP) and PHY Type/SKU (i.e. S, N, P). For example, a CSME 14.1 Consumer H A system must use PHY P CMP firmware, a CSME 13.30 Lite LP B SPI system must use PHY S LKF firmware etc. The PHY firmware can only be updated after being merged with a compatible CSME firmware via Flash Image Tool. How to update Engine firmware: There are two ways to upgrade or downgrade the Engine firmware: either via Intel FWUpdate tool or manually.
How to use FWUpdate Tool at CSME v13+: At CSME 13 or newer, FWUpdate tool requires CSME firmware which has been combined/stitched with its equivalent IUP firmware (i.e. PMC, PCHC, PHY) via Flash Image Tool (FIT). To proceed, you must first learn your system’s Chipset Family/Codename (i.e. ICP, LKF, JSP, CMP, TGP, EHL), Chipset Platform (i.e. H, LP, N, V), Chipset Type (i.e. Consumer, Corporate, Slim, Value, Atom, Server) and Chipset Stepping/Revision (i.e. A, B, C, D).
How to use FWUpdate Tool at CSME v12: At CSME v12, FWUpdate tool requires CSME firmware which has been combined/stitched with its equivalent IUP firmware (PMC) via Flash Image Tool (FIT). To proceed, you must first learn your system’s Chipset Platform (H, LP), Chipset Type (Consumer, Corporate, Slim) and Chipset Stepping/Revision (i.e. A, B, C).
Note: To extract the files below you need to use programs which support RAR5 compression! B1. (Converged Security) Management Engine — (CS)ME
B2. Power Management Controller — PMC
B3. Platform Controller Hub Configuration — PCHC
B4. USB Type C Physical — PHY
C. Intel (CS)ME System Tools The Intel (CS)ME System Tools are used for creating, modifying, and writing binary image files, manufacturing testing, Intel (CS)ME setting information gathering and Intel (CS)ME firmware configuration and updating. These tools are not released to end-users but only to OEMs. The software below comes only from official updates which were provided and made public by various OEMs. Flash Image Tool: Creates and configures a complete SPI image file which includes regions such as Flash Descriptor (FD), BIOS/UEFI, Intel Integrated LAN (GbE), Intel (CS)ME etc. The user can manipulate the completed SPI image via a GUI and change the various chipset parameters to match the target hardware. Flash Programming Tool: Used to program a complete SPI image into the SPI flash device(s). FPT can program each region individually or it can program all of the regions with a single command. The user can also use FPT to perform various functions such as view the contents of the flash on the screen, write the contents of the flash to a log file, perform a binary file to flash comparison, write to a specific address block, program fixed offset variables etc. Manifest Extension Utility: Used to generate a 3rd party Independent Update Partitions (IUP) which are compressed and signed by an external signing tool, such as OpenSSL. The signed contents may then be stitched into a SPI/BIOS image using the Intel Flash Image Tool (FIT). Notice: Avoid using the Windows builds of very old (CS)ME System Tools which either retrieve info (MEInfo, MEManuf, Flash Programming Tool) or modify the platform (FWUpdate, Flash Programming Tool, Integrated Clock Controller) as they may not work properly on newer operating system versions. When available, it is advised to use either the DOS or EFI builds of said very old tools. Notice: Avoid running the System Tools from paths which include non-English characters (i.e. Cyrillic, Chinese, Arabic, Greek) as it may cause them to crash or behave unpredictably. C1. Identifying, Updating and Diagnosing Intel (CS)ME Firmware Those who are looking to update/downgrade their firmware should use MEInfo, FWUpdate and MEManuf tools for status information, updating and functionality checking accordingly. The information and instructions below apply to these three tools only and can be found inside the full Intel ME System Tools Packages. MEInfo: Shows (CS)ME and IUP info and checks that the Engine co-processor is operating properly on the software/firmware level. Make sure it doesn’t report any errors. You can use «-verbose» parameter to get status info in more detail. The «GBE Region does not exist» warning is normal for systems that don’t have an Intel GbE Controller, you can safely ignore it. MEManuf: Diagnostic tool which runs various manufacturing-line tests to ensure that the Engine co-processor is operating properly on the hardware level. It should report a «MEManuf Operation Passed» or similar success message. You can use «-verbose» parameter to get diagnostic info in more detail. FWUpdate: Used to effortlessly upgrade or downgrade the (CS)ME and IUP (i.e PMC, PCHC, PHY) Engine firmware. Read more about FWUpdate tool at Section B. C2. (CS)ME System Tools Note: To extract the files below you need to use programs which support RAR5 compression!
D. Old Intel MEI Drivers You should always install the latest drivers for all 8-series Broadwell mobile and up systems, which can be found at section A. The driver versions linked below are the latest of each older Engine major branch. Note: To extract the files below you need to use programs which support RAR5 compression! D1. Old Intel MEI Drivers and Software These packages contain the Intel MEI/SOL drivers with their respective software and system services. It is advised to install these to enable all the Engine-related functionality. It is important to install the correct package depending on your Consumer/1.5MB or Corporate/5MB system.
Note: MEI Drivers and Software v11.7.0.1069 includes MEI v11.7.0.1057. MEI Drivers and Software v11.0.6.1194 includes MEI v11.0.5.1189. MEI Drivers and Software v6.2.50.1062 includes MEI Driver v6.2.50.1050. MEI Drivers and Software v3.2.50.1059 includes MEI Driver v3.2.20.1046. MEI Drivers and Software v2.6.30.1051 includes MEI Driver v2.6.30.1046. D2. Old Intel SOL «Drivers» and Software
D3. Old Intel TPM Drivers and Software
D4. Old Intel MEI Driver Only These packages contain only the Intel MEI Driver without any additional software or system services. Installing these allow only very basic Engine-related functionality. They are compatible with both Consumer/1.5MB and Corporate/5MB systems. The MEI Installer is the setup file from Intel which includes the MEI Driver but also allows easy installation and adds a Control Panel entry for quick driver removal.
Note: The MEI Drivers listed above are part of the complete Drivers and Software packages found at section D1. A newer Drivers and Software package has newer Software but the actual MEI Driver may still be an older version. Note: The MEI Installer includes the MEI Driver but allows easy installation of it. However, since we cannot always find the latest MEI Installer, it is advised to manually install the MEI Driver in case its version is newer. MEI Installer v11.7.0.1069 includes MEI Driver v11.7.0.1057. MEI Installer v11.0.6.1194 includes MEI Driver v11.0.5.1189. D5. Old Intel SOL «Driver» Only These packages contain only the Intel SOL «Driver» without any additional software or system services. It is compatible only with Corporate/5MB systems. If the software and system services are required in case of remote management etc, users of such systems should install the equivalent complete Drivers and Software package (section D1).
Note: The SOL «Drivers» for ME 2-5 listed above are part of the complete Drivers and Software packages found at section D2. A newer Drivers and Software package has newer Software but the actual SOL «Driver» may still be an older version. Note: The SOL «Driver» is not really a driver but rather a placeholder INF file which assigns a correct device name at Device Manager and prevents the latter from showing the yellow exclamation mark of «No driver was found for this device». D6. Old Intel TPM Driver Only
(c) win-raid.com |
—
Кто сейчас на конференции |
|
Сейчас этот форум просматривают: aoxoa1, Home_135 и гости: 16 |
| Вы не можете начинать темы Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения Вы не можете добавлять вложения |

























 на винрайде появилось разъяснение о причинах закрытия:
на винрайде появилось разъяснение о причинах закрытия:  AFU /GAN спас.
AFU /GAN спас. or newer systems. However, all 6-series (ME 7) or older systems must use UPD images in order to initiate a ME firmware update. Thus, at section B1 below, only RGN/EXTR images are provided for 7-series (ME
or newer systems. However, all 6-series (ME 7) or older systems must use UPD images in order to initiate a ME firmware update. Thus, at section B1 below, only RGN/EXTR images are provided for 7-series (ME