Появление сообщения об ошибке 401 Unauthorized Error («отказ в доступе») при открытии страницы сайта означает неверную авторизацию или аутентификацию пользователя на стороне сервера при обращении к определенному url-адресу. Чаще всего она возникает при ошибочном вводе имени и/или пароля посетителем ресурса при входе в свой аккаунт. Другой причиной являются неправильные настройки, допущенные при администрировании web-ресурса. Данная ошибка отображается в браузере в виде отдельной страницы с соответствующим описанием. Некоторые разработчики интернет-ресурсов, в особенности крупных порталов, вводят собственную дополнительную кодировку данного сбоя:
- 401 Unauthorized;
- Authorization Required;
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации.
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
- Идентификация – получение вашей учетной записи («identity») по username/login или email.
- Аутентификация («authentic») – проверка того, что вы знаете пароль от этой учетной записи.
- Авторизация – проверка вашей роли (статуса) в системе и решение о предоставлении доступа к запрошенной странице или ресурсу на определенных условиях.
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Проверьте в адресной строке правильность написания URL. Особенно это касается перехода на подстраницы сайта, требующие авторизации. Введите правильный адрес. Если переход на страницу осуществлялся после входа в аккаунт, разлогинитесь, вернитесь на главную страницу и произведите повторный вход с правильными учетными данными.
- При осуществлении входа с сохраненными данными пользователя и появлении ошибки сервера 401 проверьте их корректность в соответствующих настройках данного браузера. Возможно, авторизационные данные были вами изменены в другом браузере. Также можно очистить кэш, удалить cookies и повторить попытку входа. При удалении истории браузера или очистке кэша потребуется ручное введение логина и пароля для получения доступа. Если вы не помните пароль, пройдите процедуру восстановления, следуя инструкциям.
- Если вы считаете, что вводите правильные регистрационные данные, но не можете получить доступ к сайту, обратитесь к администратору ресурса. В этом случае лучше всего сделать скриншот проблемной страницы.
- Иногда блокировка происходит на стороне провайдера, что тоже приводит к отказу в доступе и появлению сообщения с кодировкой 401. Для проверки можно попробовать авторизоваться на том же ресурсе с альтернативного ip-адреса (например, используя VPN). При подтверждении блокировки трафика свяжитесь с провайдером и следуйте его инструкциям.
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.
Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
- Обращение в службу поддержки хостинга сайта. Как и в случае возникновения проблем с провайдером, лучше всего подробно описать последовательность действий, приведших к появлению ошибки 401, приложить скриншот.
- При отсутствии проблем на стороне хостинг-провайдера можно внести следующие изменения в настройки сайта с помощью строки Disallow:/адрес проблемной страницы. Запретить индексацию страницам с ошибкой в «rоbоts.txt», после чего добавить в файл «.htассеss» строку такого типа:
Redirect 301 /oldpage.html http://site.com/newpage.html.
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
- Если после выполнения предыдущих рекомендаций пользователи при попытках авторизации все равно видят ошибку 401, то найдите на сервере файл «php.ini» и увеличьте время жизни сессии, изменив значения следующих параметров: «session.gc_maxlifetime» и «session.cookie_lifetime» на 1440 и 0 соответственно.
- Разработчики веб-ресурсов могут использовать более сложные методы авторизации и аутентификации доступа для создания дополнительной защиты по протоколу HTTP. Если устранить сбой простыми методами администрирования не удается, следует обратиться к специалистам, создававшим сайт, для внесения соответствующих изменений в код.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
- 401, 1 – войти не удалось;
- 401, 2 – ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера;
- 401, 3 – несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс;
- 401, 501 – доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов и т.д.
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
- 400 Bad Request;
- 403 Forbidden;
- 404 Not Found;
- 408 Request Timeout.
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
Содержание
- How to Fix a 401 Unauthorized Error?
- Что делать с ошибкой 401 Unauthorized Error – методы исправления
- Как исправить ошибку 401
- Другие варианты ошибки 401
- Ошибки подобные 401
- How to fix the Web Error Code Error 401 Authorization Required
- Ошибка сервера 401: что это за ошибка и как ее исправить
- Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
- Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
- Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
The 401 Unauthorized Error is an HTTP status code error that represented the request sent by the client to the server that lacks valid authentication credentials. It may be represented as 401 Unauthorized, Authorization required, HTTP error 401- Unauthorized. It represents that the request could not be authenticated. It consists of a www-Authenticate header which contains the hint on how to authorize correctly.
401 Unauthorized Error Occur: This error may occur due to the reasons described below:
- It may occur client does not provide the proper authentication credentials to the server within the request time.
- It may occur when the server rejects the request of the client for some reason even though the client provides proper authentication credentials.
- When the client is banned for some reason by the server.
Methods to rectify the error: The 401 Unauthorized error can be fixed by using any of the following ways:
- Check The URL: Due to manual errors in typing the URL, the 401 unauthorized error may occur. Hence, checking the URL and rectifying the mistakes in it will fix the 401 error status.
- Flush the DNS: Errors in DNS also creates 401 error status sometimes. Therefore, clearing the DNS will also rectify this error. In Windows, the DNS can be flushed by typing ipconfig/flushdns in the command prompt and clicking on ENTER.
- Clear Browser Cookie: In some situations, the cookies may not work smoothly leading to improper server authentication. Thus, by clearing the cookies, the error can be rectified.
- Logging out and Logging in again: This error may also occur during the maintenance time of the websites. Therefore, visiting the website and logging in again by providing the credentials may also rectify this error.
- Website mistake: A few times all the above things are good or accurate but still you will get the 401 Unauthorized Error, which is a mistake of the website. That time you need to contact the webmaster of that website and inform that the server is down. You can email them at webmaster@webmaster.com replace the webmaster.com with the website, or you can see the contact us option on any website through that you can inform them.
Some other ways of 401 Authentication error: This error can occur in the below forms also:
Источник
Что делать с ошибкой 401 Unauthorized Error – методы исправления
Ошибка 401 Unauthorized Error – это код состояния HTTP, который означает, что страница, к которой вы пытались получить доступ, не может быть загружена, пока вы не войдете в систему с действительным идентификатором пользователя и паролем.
Если вы только что вошли в систему и получили 401 ошибку авторизации, это означает, что введенные вами учетные данные по какой-то причине недействительны.
Сообщения об ошибках 401 часто настраиваются на каждом веб-сайте индивидуально, особенно если это крупный портал, поэтому имейте в виду, что эта ошибка может проявляться многими способами, из которых самые распространенные:
- 401 Unauthorized
- Authorization Required
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации
401 ошибка авторизации отображается внутри окна веб-браузера, как обычная веб-страница. Как и большинство подобных ошибок, вы можете найти их во всех браузерах, работающих в любой операционной системе.
Как исправить ошибку 401
Проверьте на наличие ошибок в URL. Возможно, ошибка 401 Unauthorized возникла, потому что URL-адрес был введен неправильно, или выбранная ссылка указывает на неправильный URL-адрес, предназначенный только для авторизованных пользователей.
Если вы уверены, что URL-адрес действителен, посетите главную страницу веб-сайта и найдите ссылку с надписью «Логин» или «Безопасный доступ». Введите здесь свои учетные данные, а затем повторите попытку.
Если у вас нет учетных данных или вы забыли свои, следуйте инструкциям на веб-сайте для настройки учетной записи или изменения пароля.
Если вам трудно вспоминать свои, храните их в диспетчере паролей, чтобы приходилось помнить только один пароль.
Перезагрузите страницу. Как бы просто это не показалось, закрытия страницы и её повторное открытие может помочь исправить ошибку 401, но только если она вызвана ошибочно загруженной страницей.
Удалите кеш вашего браузера. Возможно, в вашем браузере хранится неверная информация для входа в систему, что нарушает процесс входа и выдает ошибку 401. Очистка кеша устранит все проблемы в этих файлах и даст странице возможность загружать свежие файлы прямо с сервера.
Другие варианты ошибки 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительную информацию об ошибке 401 Unauthorized, например:
| Коды ошибок Microsoft IIS 401 | |
|---|---|
| Ошибка | Объяснение |
| 401,1 | Войти не удалось. |
| 401,2 | Ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера. |
| 401,3 | Несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс. |
| 401,4 | Авторизация не пройдена фильтром. |
| 401,5 | Авторизация блокирована приложением ISAPI/CGI. |
| 401,501 | Доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; Ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов. |
| 401,502 | Запрещено: слишком много запросов с одного IP-адреса клиента; Ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут максимальный предел скорости запросов. |
| 401,503 | Отказ в доступе: IP-адрес включен в список запрещенных IP |
| 401,504 | Отказ в доступе: имя хоста включено в список запрещенных |
Ошибки подобные 401
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке: 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found и 408 Request Timeout.
Также существует ряд кодов состояния HTTP на стороне сервера, например, часто встречающийся 500 Internal Server Error.
Источник
How to fix the Web Error Code Error 401 Authorization Required
This article features error number Code 401, commonly known as Authorization Required described as The request header did not contain the necessary authentication codes, and the client is denied access.
Error Information
Error name: Authorization Required
Error number: Error 401
Applies to: Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP
Description: The request header did not contain the necessary authentication codes, and the client is denied access.
This repair tool can fix common computer errors like BSODs, system freezes and crashes. It can replace missing operating system files and DLLs, remove malware and fix the damage caused by it, as well as optimize your PC for maximum performance.
About Status Codes
When you receive web error codes, you may either be having client or server issues. The problem could be related to browser or settings that are blocking your connection, or it can be any other issues related to the server you are trying to access.
To explain the problem further, here are some useful information about web error codes, their symptoms, causes and repair methods.
Definitions (Beta)
Here we list some definitions for the words contained in your error, in an attempt to help you understand your problem. This is a work in progress, so sometimes we might define the word incorrectly, so feel free to skip this section!
- Access — DO NOT USE this tag for Microsoft Access, use [ms-access] instead
- Authentication — Authentication is the process of determining whether someone or something is, in fact, who or what it is declared to be.
- Authorization — Authorization is the process of determining whether a user, program or device is allowed to access a protected resource in a particular way
- Client — A client is an application or system that accesses a service made available by a server.
- Denied — Anything related to the refusal of a system to accomplish some operation requested by an user
- Header — This tag is deprecated because it lacks discriminating power
- Request — A request is a message sent by a source to another object.
- Required — Required is an HTML attribute of an input element that forces that the input be supplied.
- Access — Microsoft Access, also known as Microsoft Office Access, is a database management system from Microsoft that commonly combines the relational Microsoft JetACE Database Engine with a graphical user interface and software-development tools
Symptoms of Code 401 — Authorization Required
Web error codes are also known as http status codes. There are five different classes of http status codes and they always start with the following digits, depending on what kind of error was encountered by the user. These are also the symptoms of the error that the user is experiencing. To explain further, here are the status codes.
4xx: Client Error
This error is sent back to the user when it is a client-side error. The user receives notifications of a bad request, content not found or unauthorized access to the content or something to that effect.
400 — Bad Request
401 — Unauthorized
402 — Payment Required
403 — Forbidden
404 — Not Found
405 — Method Not Allowed
406 — Not Accepted
407 — Proxy Authentication Required
408 — Request Timeout
409 — Conflict
410 — Gone
411 — Length Required
412 — Precondition Failed
413 — Request Entity Too Large
414 — Request-URI Too Long
415 — Unsupported Media Type
416 — Request Range Not Satisfied
417 — Expectation Failed
(For illustrative purposes only)
Causes of Authorization Required — Error 401
4XX codes are caused by the user or settings from the user’s side. The request was not understood by the server because of wrong address bar entry, incorrect syntax, unstable connection or erroneous OS.
Repair Methods
There are particular troubleshooting steps for particular Web Error codes. However, there are also generalized repair methods users can perform when faced with these kinds of errors.
If a repair method works for you, please click the upvote button to the left of the answer, this will let other users know which repair method is currently working the best.
Источник
Ошибка сервера 401: что это за ошибка и как ее исправить
Появление сообщения об ошибке 401 Unauthorized Error («отказ в доступе») при открытии страницы сайта означает неверную авторизацию или аутентификацию пользователя на стороне сервера при обращении к определенному url-адресу. Чаще всего она возникает при ошибочном вводе имени и/или пароля посетителем ресурса при входе в свой аккаунт. Другой причиной являются неправильные настройки, допущенные при администрировании web-ресурса. Данная ошибка отображается в браузере в виде отдельной страницы с соответствующим описанием. Некоторые разработчики интернет-ресурсов, в особенности крупных порталов, вводят собственную дополнительную кодировку данного сбоя:
- 401 Unauthorized;
- Authorization Required;
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации.
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
- Идентификация – получение вашей учетной записи («identity») по username/login или email.
- Аутентификация («authentic») – проверка того, что вы знаете пароль от этой учетной записи.
- Авторизация – проверка вашей роли (статуса) в системе и решение о предоставлении доступа к запрошенной странице или ресурсу на определенных условиях.
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Проверьте в адресной строке правильность написания URL. Особенно это касается перехода на подстраницы сайта, требующие авторизации. Введите правильный адрес. Если переход на страницу осуществлялся после входа в аккаунт, разлогинитесь, вернитесь на главную страницу и произведите повторный вход с правильными учетными данными.
- При осуществлении входа с сохраненными данными пользователя и появлении ошибки сервера 401 проверьте их корректность в соответствующих настройках данного браузера. Возможно, авторизационные данные были вами изменены в другом браузере. Также можно очистить кэш, удалить cookies и повторить попытку входа. При удалении истории браузера или очистке кэша потребуется ручное введение логина и пароля для получения доступа. Если вы не помните пароль, пройдите процедуру восстановления, следуя инструкциям.
- Если вы считаете, что вводите правильные регистрационные данные, но не можете получить доступ к сайту, обратитесь к администратору ресурса. В этом случае лучше всего сделать скриншот проблемной страницы.
- Иногда блокировка происходит на стороне провайдера, что тоже приводит к отказу в доступе и появлению сообщения с кодировкой 401. Для проверки можно попробовать авторизоваться на том же ресурсе с альтернативного ip-адреса (например, используя VPN). При подтверждении блокировки трафика свяжитесь с провайдером и следуйте его инструкциям.
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.
Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
- Обращение в службу поддержки хостинга сайта. Как и в случае возникновения проблем с провайдером, лучше всего подробно описать последовательность действий, приведших к появлению ошибки 401, приложить скриншот.
- При отсутствии проблем на стороне хостинг-провайдера можно внести следующие изменения в настройки сайта с помощью строки Disallow:/адрес проблемной страницы. Запретить индексацию страницам с ошибкой в «rоbоts.txt», после чего добавить в файл «.htассеss» строку такого типа:
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
- Если после выполнения предыдущих рекомендаций пользователи при попытках авторизации все равно видят ошибку 401, то найдите на сервере файл «php.ini» и увеличьте время жизни сессии, изменив значения следующих параметров: «session.gc_maxlifetime» и «session.cookie_lifetime» на 1440 и 0 соответственно.
- Разработчики веб-ресурсов могут использовать более сложные методы авторизации и аутентификации доступа для создания дополнительной защиты по протоколу HTTP. Если устранить сбой простыми методами администрирования не удается, следует обратиться к специалистам, создававшим сайт, для внесения соответствующих изменений в код.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
- 401, 1 – войти не удалось;
- 401, 2 – ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера;
- 401, 3 – несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс;
- 401, 501 – доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов и т.д.
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
Источник
Methods to fix a 401 Unauthorized error
Updated on September 15, 2022
The 401 Unauthorized error is an HTTP status code that means the page you were trying to access cannot be loaded until you first log in with a valid user ID and password.
If you’ve just logged in and received the 401 Unauthorized error, it means that the credentials you entered were invalid for some reason.
401 Unauthorized error messages are often customized by each website, especially very large ones, so keep in mind that this error may present itself in more ways than these common ones:
- 401 Unauthorized
- Authorization Required
- HTTP Error 401 — Unauthorized
The 401 Unauthorized error displays inside the web browser window, just as web pages do. Like most errors like these, you can find them in all browsers that run on any operating system.
How to Fix the 401 Unauthorized Error
-
Check for errors in the URL. It’s possible that the 401 Unauthorized error appeared because the URL was typed incorrectly or the link that was selected points to the wrong URL—one that is for authorized users only.
-
If you’re sure the URL is valid, visit the website’s main page and look for a link that says Login or Secure Access. Enter your credentials here and then try the page again.
If you don’t have credentials or have forgotten yours, follow the instructions provided on the website for setting up an account or resetting your password.
Do you usually struggle to remember your passwords? Consider keeping them in a password manager so that you only have to remember one password.
-
Reload the page. As simple as it might seem, closing down the page and reopening it might be enough to fix the 401 error, but only if it’s caused by a misloaded page.
-
Delete your browser’s cache. There might be invalid login information stored locally in your browser that’s disrupting the login process and throwing the 401 error. Clearing the cache will remove any problems in those files and give the page an opportunity to download fresh files directly from the server.
-
If you’re sure the page you’re trying to reach shouldn’t need authorization, the 401 Unauthorized error message may be a mistake. At that point, it’s probably best to contact the website owner or other website contact and inform them of the problem.
The web site owner of some websites can be reached via email at webmaster@website.com, replacing website.com with the actual website name. Otherwise, find a Contact page for specific contact instructions.
Other Ways You Might See 401 Errors
Web servers running Microsoft IIS might give more information about the 401 Unauthorized error, such as the following:
| Microsoft IIS 401 Error Codes | |
|---|---|
| Error | Explanation |
| 401.1 | Logon failed. |
| 401.2 | Logon failed due to server configuration. |
| 401.3 | Unauthorized due to ACL on resource. |
| 401.4 | Authorization failed by filter. |
| 401.5 | Authorization failed by ISAPI/CGI application. |
| 401.501 | Access Denied: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Concurrent request rate limit reached. |
| 401.502 | Forbidden: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Maximum request rate limit reached. |
| 401.503 | Access Denied: the IP address is included in the Deny list of IP Restriction |
| 401.504 | Access Denied: the host name is included in the Deny list of IP Restriction |
You can learn more about IIS-specific codes on Microsoft’s the HTTP status code in IIS 7 and later versions page.
Errors Like 401 Unauthorized
The following messages are also client-side errors and so are related to the 401 Unauthorized error: 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found, and 408 Request Timeout.
A number of server-side HTTP status codes also exist, like the often-seen 500 Internal Server Error.
FAQ
-
What do I do if I receive a http 401 error in Zoom?
Double-check the URL to make sure it’s accurate, and if so reload the page. If that doesn’t work, log out and log back in again, and if you’re still having problems try turning off any themes or plugins that may be active. Clearing your browser cache might also fix the issue.
-
What’s the difference between 401 Unauthorized and 403 Forbidden?
A 401 Unauthorized code indicates some sort of issue tied to login credentials for a given web page, while 403 Forbidden errors mean the page has been blocked.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Assume your Web API is protected and a client attempts to access it without the appropriate credentials. How do you deal with this scenario? Most likely, you know you have to return an HTTP status code. But what is the more appropriate one? Should it be 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden? Or maybe something else?
As usual, it depends 🙂. It depends on the specific scenario and also on the security level you want to provide. Let’s go a little deeper.
If you prefer, you can watch a video on the same topic:
Web APIs and HTTP Status Codes
Before going into the specific topic, let’s take a quick look at the rationale of HTTP status codes in general. Most Web APIs are inspired by the REST paradigm. Although the vast majority of them don’t actually implement REST, they usually follow a few RESTful conventions when it comes to HTTP status codes.
The basic principle behind these conventions is that a status code returned in a response must make the client aware of what is going on and what the server expects the client to do next. You can fulfill this principle by giving answers to the following questions:
- Is there a problem or not?
- If there is a problem, on which side is it? On the client or on the server side?
- If there is a problem, what should the client do?
This is a general principle that applies to all the HTTP status codes. For example, if the client receives a 200 OK status code, it knows there was no problem with its request and expects the requested resource representation in the response’s body. If the client receives a 201 Created status code, it knows there was no problem with its request, but the resource representation is not in the response’s body. Similarly, when the client receives a 500 Internal Server Error status code, it knows that this is a problem on the server side, and the client can’t do anything to mitigate it.
In summary, your Web API’s response should provide the client with enough information to realize how it can move forward opportunely.
Let’s consider the case when a client attempts to call a protected API. If the client provides the appropriate credentials (e.g., a valid access token), its request is accepted and processed. What happens when the client has no appropriate credentials? What status code should your API return when a request is not legitimate? What information should it return, and how to guarantee the best security experience?
Fortunately, in the OAuth security context, you have some guidelines. Of course, you can use them even if you don’t use OAuth to secure your API.
«The basic principle behind REST status code conventions is that a status code must make the client aware of what is going on and what the server expects the client to do next»
Tweet This
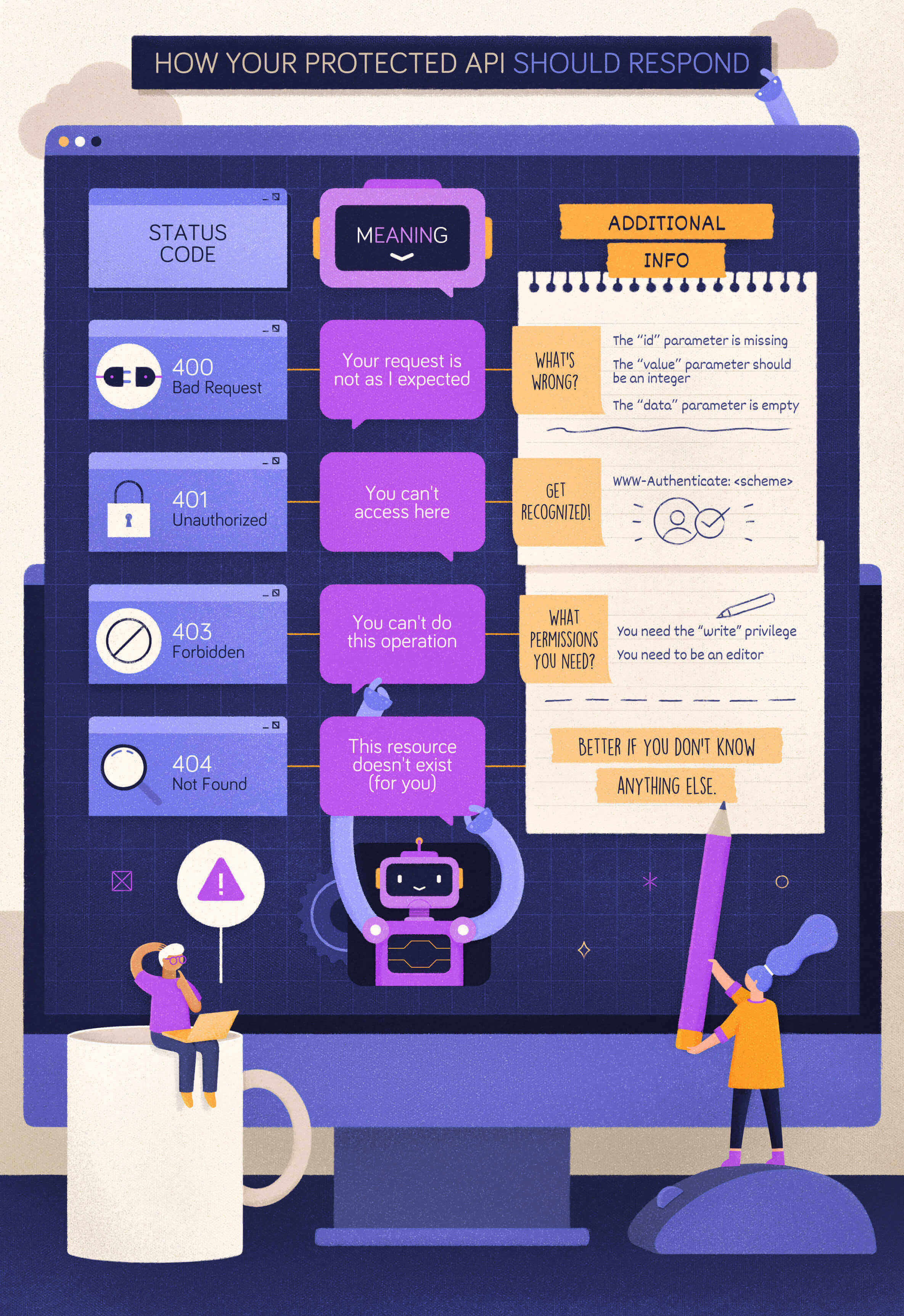
When to Use 400 Bad Request?
Let’s start with a simple case: a client calls your protected API, omitting a required parameter. In this case, your API should respond with a 400 Bad Request status code. In fact, if that parameter is required, your API can’t even process the client request. The client’s request is malformed.
Your API should return the same status code even when the client provides an unsupported parameter or repeats the same parameter multiple times in its request. In both cases, the client’s request is not as expected and should be refused.
Following the general principle discussed above, the client should be empowered to understand what to do to fix the problem. So, you should add in your response’s body what was wrong with the client’s request. You can provide those details in the format you prefer, such as simple text, XML, JSON, etc. However, using a standard format like the one proposed by the Problem Details for HTTP APIs specifications would be more appropriate to enable uniform problem management across clients.
For example, if your client calls your API with an empty value for the required data parameter, the API could reply with the following response:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/problem+json
Content-Language: en
{
"type": "https://myapi.com/validation-error",
"title": "Validation error",
"detail": "Your request parameters are not valid.",
"invalid-params": [
{
"name": "data",
"reason": "cannot be blank."
}
]
}When to Use 401 Unauthorized?
Now, let’s assume that the client calls your protected API with a well-formed request but no valid credentials. For example, in the OAuth context, this may fall in one of the following cases:
- An access token is missing.
- An access token is expired, revoked, malformed, or invalid for other reasons.
In both cases, the appropriate status code to reply with is 401 Unauthorized. In the spirit of mutual collaboration between the client and the API, the response must include a hint on how to obtain such authorization. That comes in the form of the WWW-Authenticate header with the specific authentication scheme to use. For example, in the case of OAuth2, the response should look like the following:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer realm="example"You have to use the Bearer scheme and provide the realm parameter to indicate the set of resources the API is protecting.
If the client request does not include any access token, demonstrating that it wasn’t aware that the API is protected, the API’s response should not include any other information.
On the other hand, if the client’s request includes an expired access token, the API response could include the reason for the denied access, as shown in the following example:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer realm="example",
error="invalid_token",
error_description="The access token expired"When to Use 403 Forbidden?
Let’s explore a different case now. Assume, for example, that your client sends a request to modify a document and provides a valid access token to the API. However, that token doesn’t include or imply any permission or scope that allows the client to perform the desired action.
In this case, your API should respond with a 403 Forbidden status code. With this status code, your API tells the client that the credentials it provided (e.g., the access token) are valid, but it needs appropriate privileges to perform the requested action.
To help the client understand what to do next, your API may include what privileges are needed in its response. For example, according to the OAuth2 guidelines, your API may include information about the missing scope to access the protected resource.
Try out the most powerful authentication platform for free.Get started →
Security Considerations
When you plan how to respond to your client’s requests, always keep security in mind.
How to deal with response details
A primary security concern is to avoid providing useful information to potential attackers. In other words, returning detailed information in the API responses to attempts to access protected resources may be a security risk.
For example, suppose your API returns a 401 Unauthorized status code with an error description like The access token is expired. In this case, it gives information about the token itself to a potential attacker. The same happens when your API responds with a 403 Forbidden status code and reports the missing scope or privilege.
In other words, sharing this information can improve the collaboration between the client and the server, according to the basic principle of the REST paradigm. However, the same information may be used by malicious attackers to elaborate their attack strategy.
Since this additional information is optional for both the HTTP specifications and the OAuth2 bearer token guidelines, maybe you should think carefully about sharing it. The basic principle on sharing that additional information should be based on the answer to this question: how would the client behave any differently if provided with more information?
For example, in the case of a response with a 401 Unauthorized status code, does the client’s behavior change when it knows that its token is expired or revoked? In any case, it must request a new token. So, adding that information doesn’t change the client’s behavior.
Different is the case with 403 Forbidden. By informing your client that it needs a specific permission, your API makes it learn what to do next, i.e., requesting that additional permission. If your API doesn’t provide this additional information, it will behave differently because it doesn’t know what to do to access that resource.
Don’t let the client know…
Now, assume your client attempts to access a resource that it MUST NOT access at all, for example, because it belongs to another user. What status code should your API return? Should it return a 403 or a 401 status code?
You may be tempted to return a 403 status code anyway. But, actually, you can’t suggest any missing permission because that client has no way to access that resource. So, the 403 status code gives no actual helpful information. You may think that returning a 401 status code makes sense in this case. After all, the resource belongs to another user, so the request should come from a different user.
However, since that resource shouldn’t be reached by the current client, the best option is to hide it. Letting the client (and especially the user behind it) know that resource exists could possibly lead to Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR), an access control vulnerability based on the knowledge of resources you shouldn’t access. Therefore, in these cases, your API should respond with a 404 Not Found status code. This is an option provided by the HTTP specification:
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
For example, this is the strategy adopted by GitHub when you don’t have any permission to access a repository. This approach avoids that an attacker attempts to access the resource again with a slightly different strategy.
How to deal with bad requests
When a client sends a malformed request, you know you should reply with a 400 Bad Request status code. You may be tempted to analyze the request’s correctness before evaluating the client credentials. You shouldn’t do this for a few reasons:
- By evaluating the client credentials before the request’s validity, you avoid your API processing requests that aren’t allowed to be there.
- A potential attacker could figure out how a request should look without being authenticated, even before obtaining or stealing a legitimate access token.
Also, consider that in infrastructures with an API gateway, the client credentials will be evaluated beforehand by the gateway itself, which doesn’t know at all what parameters the API is expecting.
The security measures discussed here must be applied in the production environment. Of course, in the development environment, your API can provide all the information you need to be able to diagnose the causes of an authorization failure.
Recap
Throughout this article, you learned that:
400 Bad Requestis the status code to return when the form of the client request is not as the API expects.401 Unauthorizedis the status code to return when the client provides no credentials or invalid credentials.403 Forbiddenis the status code to return when a client has valid credentials but not enough privileges to perform an action on a resource.
You also learned that some security concerns might arise when your API exposes details that malicious attackers may exploit. In these cases, you may adopt a more restricted strategy by including just the needed details in the response body or even using the 404 Not Found status code instead of 403 Forbidden or 401 Unauthorized.
The following cheat sheet summarizes what you learned:
Themeisle content is free. When you purchase through referral links on our site, we earn a commission. Learn More
Trying to access a website only to be met with a 401 error code? This could be happening on your own WordPress website or it could be happening on someone else’s site that you’re trying to visit.
If your WordPress site is showing the 401 error code to other visitors, it’s important to fix the problem so that your visitors can enjoy your site. And if you’re experiencing the 401 error code when you visit someone else’s site, you’ll want to understand the problem so you know what’s happening.
In a previous post we presented the most common HTTP error codes and status codes, but this post, we’ll explain what the 401 error is, what causes it, and how to fix the error 401 message.
What does the 401 error code mean?
A 401 Unauthorized error is an HTTP status code indicating that the server received an unauthenticated request. 401 error code responses are most often generated because of invalid credentials for a particular page or destination on your website. This status is typically sent with a WWW-authenticate header that contains information on how to authorize properly.
In human terms, this basically means that your client (e.g. your web browser) isn’t able to authenticate itself with the server and, as such, cannot view the resource. For example, a specific page might require a valid username and password to view.
The 401 error code, like other error codes in the 400-range, means there’s a problem on the client-side – AKA the problem lies on your web browser’s side (or another client), rather than the website you’re trying to visit.
401 error vs 403 error
People often confuse a 401 error with a 403, but the two are different. A 403 error means access to the page is forbidden, whereas a 401 error just means there’s a problem with authenticating access to the page. That is, a 401 means access is not necessarily forbidden, the server just cannot authenticate the request to grant access.
401 error code variations
The exact message that indicates a 401 error code varies depending on the server, but here are the typical 401 error code variations that you’ll see:
- 401 Unauthorized
- Authorization Required
- Access Denied
- HTTP Error 401 Unauthorized
What causes the 401 error code?
Here are some common causes of the 401 error code:
- Incorrect URL – sometimes the 401 error code is because of the wrong URL. Make sure that the URL for the site you want to access has been entered correctly.
- Invalid login credentials – some pages of a website require you to login in order to access the information. If you’re not logged in, you will very likely get a 401-error. Make sure that the login credentials you are entering are accurate.
- False login requirement – this occurs rarely but, in some cases, a website that should not require a login will still show a login page. This indicates an issue on the admin side and will often throw up a 401-error.
- DNS errors – occasionally, domain name system failures may result in a 401 response. DNS malfunctioning is less common.
- Security/firewall issues – some WordPress security plugins or firewalls can cause a 401 error if they detect malicious activity.
- Plugin issues – a WordPress plugin on your site might be triggering the 401 error code.
Often, 401-error codes can be fixed by simply hitting the refresh button. If refreshing your page doesn’t work, try the following fixes:
1. Check the URL for errors
It is possible that a 401 error occurs because you have typed the URL incorrectly or the login URL has been changed. Alternatively, you may have clicked on an outdated link in your web browser. In cases where a page no longer exists, the server might show a 401 code. Check the URL for spelling mistakes. You can also use a search engine to find the correct URL of the webpage you are trying to access.
2. Clear browser cache and cookies
Your browser’s cache helps improve your overall surfing experience by decreasing the loading time of websites. To do this, browsers store local copies of the content you visit most frequently. Your browser’s cache can sometimes overlap with the live version of your application, resulting in a 404 error code.
To fix this error, just clear the browser’s cache.
Similar to the cache, there are HTTP cookies which are basically tiny pieces of stored data. Invalid and/or corrupted cookies can cause an authentication error. Clear the cookies and try to open the page again.
3. Deactivate your WordPress plugins
Because WordPress plugins can alter how your site functions, they’re a typical cause of the 401 error code on WordPress.
In the case of WordPress security plugins, sometimes the plugin intends to do this. For example, some plugins will lock down your login page if the plugin thinks you’re under attack, which can trigger the 401 error code when you try to open your login page. Or the firewall in a plugin like Wordfence might cause the issue.
In this case, once you figure out the issue by deactivating the plugin, you can reach out to the plugin’s support to understand the issue.
Other times, it could be an unintended compatibility issue.
To figure out which plugin is causing the 401 error, try deactivating all of the plugins at your site and reactivating them one-by-one. Or, if the error only appeared after you installed a new plugin, try deactivating that plugin first.
4. Remove server-level password protection
If you’re using htaccess/htpasswd to protect parts of your WordPress site with an extra username/password, try deactivating this extra password protection.
Many web hosts also give you a tool to control such passwords from cPanel. Look for a tool named something like:
- Password protect directories
- Directory privacy
5. Flush your DNS
In rare cases, DNS errors can cause the server to show a 401-error code on your browser. To fix this, you need to flush your DNS. Although this is a fairly unusual cause, it is quite simple to repair.
For Windows users:
- Log in to your computer as an administrator
- Open a “search” window
- Type in CMD.exe in the search field to open Command Prompt
- Enter this little code in the CMD interface: “ipconfig/flushdns”
For macOS users:
- Open the Command Terminal
- Enter this code in terminal interface: “sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder”
6. Try waiting
Like security plugins, some WordPress hosting companies will temporarily block your IP if they think you’re doing something malicious – e.g. entering the wrong password. In this case, you can try waiting to see if that fixes the issue, as sometimes your site is only locked down for a short period of time.
Additionally, many WordPress websites need regular downtime for maintenance. If you’re seeing a 401-error on someone else’s site, there may be maintenance or construction going on at the backend causing temporary login issues. Try giving the admins some time and logging in a few minutes later.
Conclusion
A 401 error indicates a client-side problem with authentication. That is, your web browser is having issues authenticating itself with your WordPress site’s server.
Before you start digging into any in-depth troubleshooting, try a few quick fixes first. Make sure that the URL you’re using is correct, and don’t forget to clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
Also consider any security tools you may be using on your site, as well as any server-level passwords you might have added, like a password via htaccess and htpasswd. You can also try deactivating your plugins.
Do you have any questions about the 401 error code? Let us know in the comments!
Free guide
5 Essential Tips to Speed Up
Your WordPress Site
Reduce your loading time by even 50-80%
just by following simple tips.
Download free guide