Let’s learn about the Whitelabel error page in Spring Boot and how to customize or disable them. White label error pages are default behavior from Spring Boot. Like any other feature, We can customize this feature to great extent.
What are Whitelabel error pages in Spring Boot?
Depending on API client request or browser request, spring boot provides an error JSON response or a full HTML error page. For example, let’s create a simple /hello endpoint that throws an exception always.
Code language: Java (java)
@RequestMapping("/hello") String hello() { throw new IntrovertException("Don't bother me please..!"); }
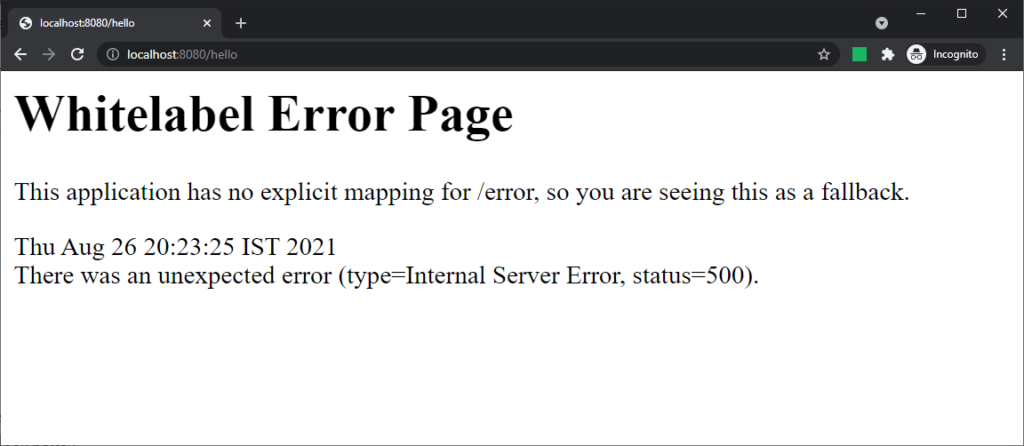
Even though this page looks simple, you can add details to it using the following configuration.
Code language: Properties (properties)
server.error.include-message=always server.error.include-exception=true server.error.include-stacktrace=always server.error.include-binding-errors=always
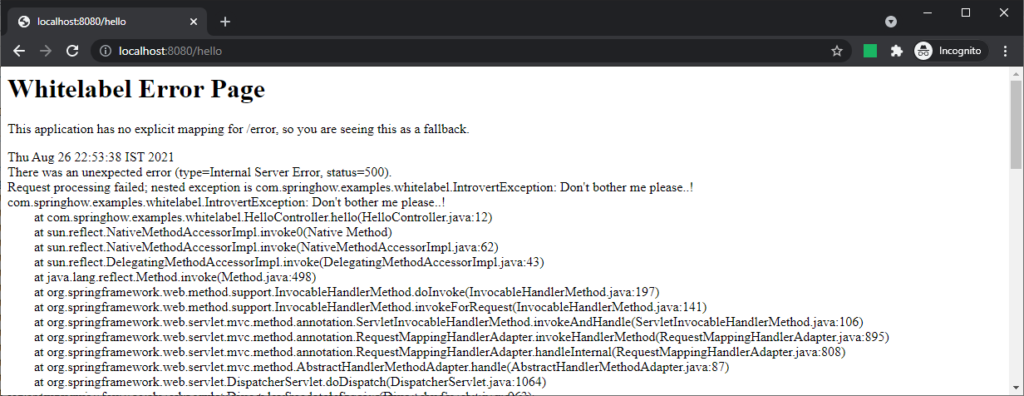
Even though the messages are helpful, this page may not fit well with your other page designs. So if you want to override this page with your own design, you are in luck.
Overriding Whitelabel Error Pages
Spring boot provides a /error mapping at a global servlet container level. This mapping handles requests and sends back JSON or HTML view as a response with error codes/messages. But the view that we saw above looks default. If you notice the first line of the error page, it says “This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.”
Here, the spring boot is trying to hint to you that you need to provide your own template to handle these error requests. So let’s see how to do that.
As we know, The handler mapped for /error expects a view to show the HTML response. If it doesn’t find a view matching “error” it will use the placeholder we have seen above. So we first need to add a template called error.html. But the template alone will not work. You also need to add one of the spring boot supported template engines. In our case, we are adding thymeleaf.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
Next, you need to add the error.html template into your src/main/resources/templates directory.
With the above in place, the following MVC attributes will be available for you to access in the templates.
- message – Return value of exception.getMessage()
- exception – A string that contains the canonical exception name.
- trace – The complete stacktrace of the exception that caused this error.
- errors – A list of validation failures that occured during the request.
Along with these, there is also a status attribute that gives the HTTP status code for the error response. With that in place, we can rewrite our template file to show all these attributes.
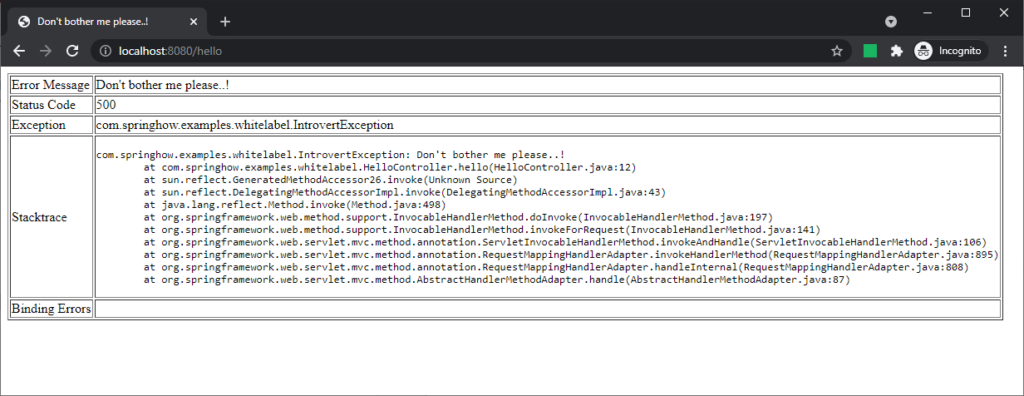
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title th:text="${message}"></title> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <tr><td>Error Message</td><td th:text="${message}"></td></tr> <tr><td>Status Code</td><td th:text="${status}"></td></tr> <tr><td>Exception</td><td th:text="${exception}"></td></tr> <tr><td>Stacktrace</td><td><pre th:text="${trace}"></pre></td></tr> <tr><td>Binding Errors</td><td th:text="${errors}"></td></tr> </table> </body> </html>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
This simple template will yield the following error page when we access /hello.
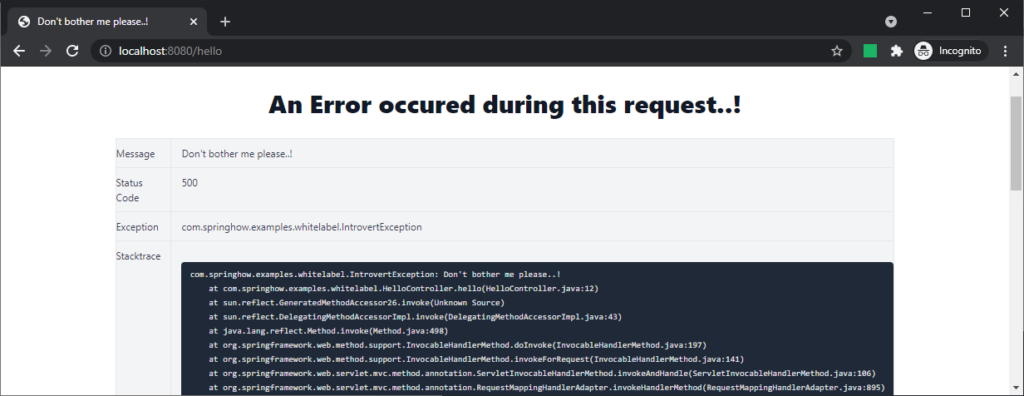
With a little bit of CSS, we can get this page to look better and more appealing.
Disabling Whitelabel error page altogether /Tomcat whitelabel
Spring boot also provides a way to disable the Whitelabel error page altogether using server.error.whitelabel.enabled setting. When set to false, the server will show an error page specific to the servlet container(tomcat). For example, the below error page from tomcat will be visible if the Whitelabel is disabled and no error template is available.
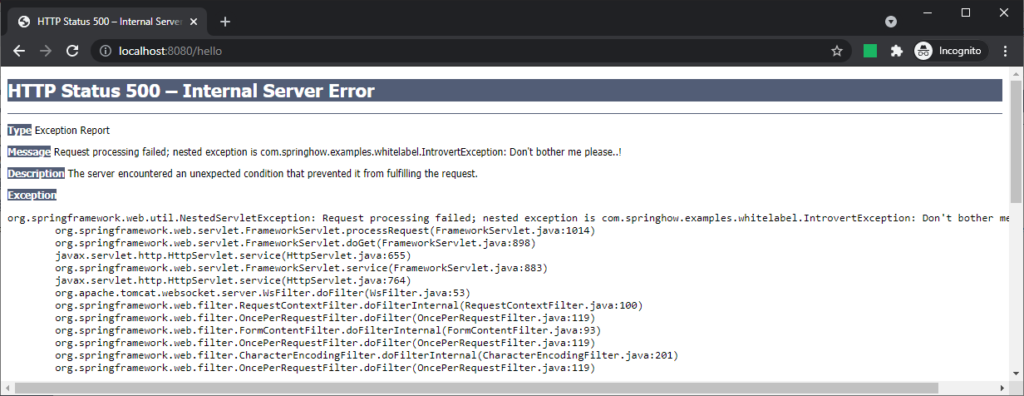
You can swap tomcat with jetty and you will still see an error page like this offered by the jetty runtime. And undertow currently doesn’t provide a view. But it does send response codes.
Important things to note
Always use a custom error.html page for the following reasons.
- Default whitelabel page lets hackers know you are using spring boot. This means they only need to try the exploits for spring boot.
- Never show exceptions in your production servers. Exceptions are great info for hackers.
- A custom error page with proper CSS will blend in to your other pages. You can even provide links and search boxes that can redirect users back to your site.
You can hide specific error attributes based on the configuration we saw earlier. Also, all these configurations are also applicable for the JSON response as well. If your request contains Accept: application/json header, then the response will be in the form of JSON. Even here, you can access all these attributes. For example, take a look at the below request.
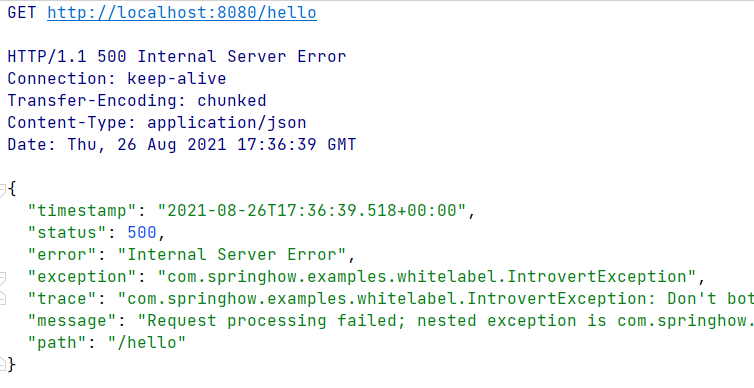
Here you can see the trace, exception, and message attributes being available as JSON.
Summary
To sum it up, we learned about white label error pages and how to customize them. We found out how to override the default Whitelabel with our own error.html. You can check out all these examples at our GitHub Repository.
Related
My Controller
@Controller
//@RequestMapping("/")
//@ComponentScan("com.spring")
//@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class HomeController {
@Value("${framework.welcomeMessage}")
private String message;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
String home(ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("hittin the controller...");
model.addAttribute("welcomeMessage", "vsdfgfgd");
return "Hello World!";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/indexPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
String index(ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("hittin the index controller...");
model.addAttribute("welcomeMessage", message);
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/indexPageWithModel", method = RequestMethod.GET)
ModelAndView indexModel(ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("hittin the indexPageWithModel controller...");
model.addAttribute("welcomeMessage", message);
return new ModelAndView("welcome", model);
}
}
My JSP (welcome.jsp) inside /WEB-INF/jsp (parent folder is WebContent)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Welcome to Spring Boot</title>
</head>
<body>
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
Message: ${message}
</body>
</html>
My pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>SpringBootPlay</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootPlay</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jcabi</groupId>
<artifactId>jcabi-log</artifactId>
<version>0.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<start-class>com.spring.play.BootLoader</start-class>
<main.basedir>${basedir}/../..</main.basedir>
<m2eclipse.wtp.contextRoot>/</m2eclipse.wtp.contextRoot>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<useSystemClassLoader>false</useSystemClassLoader>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
My App Initializer
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan({ "com.spring.controller" })
@PropertySources(value = { @PropertySource("classpath:/application.properties") })
public class BootLoader extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
final static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(BootLoader.class);
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(BootLoader.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootLoader.class, args);
}
}
I even added thymeleaf dependency to my pom. It still didn’t work. When ever I hit localhost:8080/hello or /indexPage or /indexPageWithModel it always says
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
Wed Sep 21 21:34:18 EDT 2016
There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found, status=404).
]/WEB-INF/jsp/welcome.jsp
My application.properties
spring.mvc.view.prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix: .jsp
framework.welcomeMessage=Welcome to Dashboard
Please help me. Thanks!
Содержание
- Русские Блоги
- Основная причина страницы ошибки SpringBoot Whitelabel, три решения и их характеристики
- 0, краткое описание
- 1. Страница ошибки Whitelabel
- 2. Решите проблему с белой страницей.
- Whitelabel error page что это за ошибка
- Spring выдает ошибку Whitelabel error page, что не так?
- В этом приложении нет явного сопоставления для / error
- Проблемы с простым проектом с Spring Framework
Русские Блоги
Основная причина страницы ошибки SpringBoot Whitelabel, три решения и их характеристики
0, краткое описание
Перед изучением этой заметки лучше всего иметь некоторое представление о Spring mvc и Tomcat, чтобы было удобнее понимать.Если вам нужно знать наиболее прямое решение, перетащите его вниз, чтобы увидеть образец кода.
Вводится настоящая причина появления белой страницы Springboot. Основная причина заключается в том, что нет подходящей ситуации соответствия и возникает ситуация 404. Затем перейдите к системной по умолчанию сначала ErrorPage, которая представляет собой содержимое белой страницы, а затем с трех точек зрения в соответствии с его спецификой. , 1. Перехватчик, 2. Новая страница ошибок, 3. Пользовательская маршрутизация / маршрутизация ошибок для решения проблемы, а также знакомство с преимуществами и недостатками каждого метода, включая основные причины ошибок страницы цикла и т. Д.
1. Страница ошибки Whitelabel
То, что называется страницей ошибок Whitelabel (также называемой белой страницей), является страницей описания аномального HTTP-запроса в SpringBoot, как показано ниже.
Содержимое белой страницы будет отображать код состояния, путь и причину ошибки, но реальная среда публикации онлайн-генерации обычно не допускает такой ситуации, и больше — это настраиваемые страницы 404 или 500 страниц.
Итак, теперь мы пришли к пониманию, в какой ситуации будут появляться белые страницы и как решить эту проблему. Давайте воспользуемся случаем 404, чтобы понять причину.
Перейти непосредственно к классу DispatcherServlet protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception Метод, содержащий фрагменты кода
В методе getHandler будет выполняться обход HandlerMapping в текущем веб-контейнере, чтобы найти соответствующий обработчик
Из приведенного выше рисунка очевидно, что текущий удобный обработчик — SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, потому что URL-адрес содержит /** , Все URL-адреса могут быть сопоставлены, Не войдет в noHandlerFound позади , Обработчик адаптации HandlerAdapter — это объект, созданный HttpRequestHandlerAdapter.
Не удается найти соответствующий ресурс в mv = ha.handle (loadedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler ()), установите код состояния ответа на 404Подробнее см. Метод handleRequest класса ResourceHttpRequestHandler.
Теперь это эквивалентно установке кода состояния запроса на 404, больше ничего не делается, mv также равно null
В это время вам нужно вернуться к процессу вызова Tomcat. Если вы запрашиваете процесс вызова Tomcat, вы должны знать, что когда Tomcat получает запрос сокета Socket на соединителе, он упаковывается в запрос, ответ и другую информацию, которая будет отправлена в Engine-> Host и другие компоненты. Он доставляется слой за слоем, затем принимается конвейером каждого компонента, а затем фильтруется соответствующим клапаном (клапаном) слой за слоем.
На этот раз дошел до класса StandardHostValve private void status(Request request, Response response) метод
Объедините код и диаграмму, а затем внимательно прочтите белую страницу. This application has no explicit mapping for /error , Маршрут error, причина отсюда, а затем переход вперед, адрес маршрута error
Белая страница mv, предоставляемая SpringBoot, используется позже для визуализации содержимого белой страницы, которую мы видим.
Пока что весь процесс выполнен,Подводя итог, это запрос несуществующей ссылки, которая перенаправляется в запрос / error после того, как обнаруживается, что это запрос 404.
Тогда решение очень простое, есть три решения, но эти три решения под разными углами, чтобы решить проблему.
- Добавить перехватчик
- Добавить ErrorPage
- Добавить / путь ошибки
2. Решите проблему с белой страницей.
2.1, добавить перехватчик
После того, как перехватчик перехватит запрос / error, он вынужден изменить mv, так что последний отрендеренный mv для пробного использования является нашей настраиваемой настройкой, а не содержимым белой страницы, где mv самой белой страницы будет проходить Анализатор представления ContentNegotiating Обработка становится ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration
Обратите внимание, что все это истечение фактически было обработано 3 HTTP-запросами,На следующем рисунке показана информация журнала, распечатанная с использованием мониторинга событий HTTP.
Пройдите через / abc ==> jump / err ==> jump / error (содержимое не отображается, потому что содержимое, отправленное в браузер, было отображено с помощью / err
Реальный поток обработки вызовов состоит в том, что / abc не находит подходящий обработчик, а затем решает передать его на путь / error для обработки, но он перехватывается перехватчиком и перенаправляется в / err для обработки.
Недостатки: все запросы для этого маршрута будут перехвачены, включая статические файлы ресурсов, что не оказывает большого влияния на внутренние службы, которые предоставляют чистые интерфейсы. Другие службы будут иметь влияние
2.2, добавьте ErrorPage
Добавление подходящей ErrorPage не приведет к переходу к пути по умолчанию / ошибке перехватчика, а перейдет к настраиваемой ErrorPage. Причина этого была указана в методе статуса выше.
В приведенном выше коде добавлено несколько путей перехода к странице ошибки ErrorPage и соответствующие им коды ошибок HTTP. В нашем текущем примере должен быть выполнен переход к соединению / 404, а затем как я могу получить сообщение об ошибке после его выполнения? В принципе, он должен отображать 404 Содержимое файла .html и классическая страница ошибок Tomcat отображаются одновременно, как показано на следующей странице, и содержимое вывода журнала.
Это проблема скачка петли
Когда в системе не указан преобразователь четкого представления, система будет использовать свой собственный преобразователь по умолчанию. InternalResourceView , Он проверит текущий URL-адрес перед отображением. Если обнаружится, что запрошенный URL-адрес соответствует целевому URL-адресу, он будет определен Вперед сам появляются Circular view path Эта проблема
Итак, как ее решить, нужно исходить из фундаментальной цели
- Добавьте синтаксический анализатор шаблона, чтобы синтаксический анализатор по умолчанию не использовался
- Изменить путь перехода
Вы можете понять конкретные решения самостоятельно.В этой статье не используется отрисовка механизма шаблонов, а непосредственно отображаются основные данные.
2.3, путь добавления / ошибки
Как вы знаете выше, поскольку система по умолчанию переходит к / error и завершает рендеринг данных, недостаточно настроить маршрут / error и избежать проблемы отсутствия статических ресурсов, но обратите внимание, что есть Один вопрос, подробности см. На рисунке ниже
Во-первых, я добавил и определил очень простой метод обработки пути ошибки, но при запуске Springboot есть 3 метода обработки пути ошибки, и они одновременно принадлежат одному и тому же дескриптору. Правила маршрутизации URL Обработка, выберите ручку в автоконфигурации,Это должно было привести к тому, что наш заказ / ошибка недействительны
После тестирования он действительно недействителен, и белая страница все еще отображается, так как это решить? Есть несколько способов сделать то же самое
- В соответствии с правилами сопоставления маршрутизации измените соответствующий контент, чтобы при окончательном выборе процессора он достиг нашего пользовательского процессора, но это очень сложно. Вам необходимо очень четко понимать правила сопоставления маршрутизации самого Spring mvc, чтобы гарантировать, что сопоставление URL-адресов Приоритетные вопросы, требующие решения, и т. Д.
Мы уже знаем, что эти три / ошибки находятся в картографе маршрутов RequestMappingHandlerMapping.Мы можем сделать так, чтобы пользовательский процессор не сохранялся в карте маршрутов, и сделать Spring приоритетом согласованного преобразователя маршрутов при опросе. Да, но на самом деле BeanNameUrlMapping в handlerMapping все еще находится после RequestMappingHandlerMapping, если вы измените порядок, это также очень сложно
EndpointHandlerMapping — это конечная точка в исполнительном модуле Springboot. Настроить конечную точку сложно, и она не подходит для текущего проекта.
Использование SimpleUrlHandlerMapping не подходит для Springboot. Если вы используете конфигурацию xml, вы можете напрямую установить ее URL-адрес. Это будет очень удобно. Если вы применяете метод аннотации в springboot, требуется дополнительная настройка, как показано в следующем коде
Хотя / error вводится в SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, он все равно будет отображаться, даже если добавлена дополнительная конфигурация Нет ошибки адаптера ,Этот метод не применим
Оглядываясь назад на наблюдение BasicErrorController, мы можем унаследовать интерфейс ErrorController сами.
Источник
Whitelabel error page что это за ошибка
Spring выдает ошибку Whitelabel error page, что не так?
давай читать то, что написано вместе за ручку =)
«это приложение не имеет эксплицитного (явного) маппинга для /error, поэтому ты видишь это»
добавь какой-то любой маппинг напр
@RestController
public class MyController
@GetMapping(«/error»)
public String smth() return «Error world»;
>
>
пробегись по spring boot in action. сам не читал, но говорят годная, странич всего ничего
в пропертях добавь
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false
ну или нарисуй свою страничку error.html
закинь в resources/templates
создай свой контроллер чтоб перехватить дефолтовое поведение
@Controller
public class MyErrorController implements ErrorController
@RequestMapping(«/error»)
public String handleError() //do something like logging
return «error»;
>
@Override
public String getErrorPath() return «/error»;
>
>
можешь под каждую свою ошибку свою error страничку сделать
типа error404.html error500.html
и переписать метод вот так
@RequestMapping(«/error»)
public String handleError(HttpServletRequest request) Object status = request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE);
if (status != null) Integer statusCode = Integer.valueOf(status.toString());
if(statusCode == HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value()) return «error404»;
>
else if(statusCode == HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()) return «error500»;
>
>
return «error»;
>
тогда будет подгружать нужную тебе страничку ошибки.
но как ты уже понял. это всё лишь чтоб настроить что показывать.
почему именно у тебя ошибка происходит — это ты уж в своём аппе копайся.
В этом приложении нет явного сопоставления для / error
Я использовал maven для создания учебника https://spring.io/guides/gs/uploading-files/
Все используемые мной коды были скопированы.
Приложение может работать, но я получаю сообщение об ошибке:
Whitelabel Error Page This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback. Tue Jun 30 17:24:02 CST 2015 There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found, status=404). No message available
Как я могу это исправить?
Убедитесь, что ваш основной класс находится в корневом пакете над другими классами.
Когда вы запускаете приложение Spring Boot (т. Е. Класс, помеченный @SpringBootApplication), Spring будет сканировать только классы, расположенные ниже вашего основного пакета классов.
Когда мы создаем загрузочное приложение Spring, мы аннотируем его @SpringBootApplication аннотациями. Эта аннотация «завершает» многие другие аннотации, необходимые для работы приложения. Одна из таких аннотаций — @ComponentScan аннотация. Эта аннотация сообщает Spring искать компоненты Spring и настраивать приложение для запуска.
Класс вашего приложения должен быть на вершине иерархии пакетов, чтобы Spring мог сканировать подпакеты и находить другие необходимые компоненты.
Ниже фрагмент кода работает, поскольку пакет контроллера находится в com.test.spring.boot пакете
Ниже фрагмент кода НЕ работает, поскольку пакет контроллера НЕ находится в com.test.spring.boot пакете
Из документации Spring Boot:
Many Spring Boot developers always have their main class annotated with @Configuration , @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan . Since these annotations are so frequently used together (especially if you follow the best practices above), Spring Boot provides a convenient @SpringBootApplication alternative.
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is equivalent to using @Configuration , @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan with their default attributes
Вы можете решить эту проблему, добавив ErrorController в свое приложение. Вы можете заставить контроллер ошибок возвращать нужное вам представление.
Контроллер ошибок в моем приложении выглядит так:
Вышеупомянутый класс основан на классе Springs BasicErrorController .
Вы можете создать экземпляр вышеуказанного ErrorController в @Configuration файле следующим образом:
Вы можете переопределить значение ErrorAttributes по умолчанию , реализовав ErrorAttributes . Но в большинстве случаев атрибутов DefaultErrorAttributes должно быть достаточно.
В моем случае класс контроллера был аннотирован @Controller . Изменив это, чтобы @RestController решить проблему. В основном @RestController это @Controller + @ResponseBody так либо использовать @RestController , либо @Controller с @ResponseBody аннотацией к каждому методу.
в моем случае это из-за позиции пакета, то есть пакет контроллера должен быть выше пакета основного класса
если мой пакет основного класса — это package co.companyname.spring.tutorial; любой пакет контроллера, package co.companyname.spring.tutorial.WHAT_EVER_HERE;
после завершения кодирования нажмите кнопку загрузки приборной панели
последнее, что нужно, чтобы убедиться, что ваш контроллер отображает или не только консоль, вы должны увидеть что-то smilliar
Это происходит, когда явная страница ошибки не определена. Чтобы определить страницу ошибки, создайте сопоставление / error с представлением. например, приведенный ниже код сопоставляется со строковым значением, возвращаемым в случае ошибки.
Попробуйте добавить зависимость.
По умолчанию весенняя загрузка будет сканировать текущий пакет на предмет определения bean-компонента. Поэтому, если ваш текущий пакет, в котором определен основной класс, а пакет контроллера не совпадает, или пакет контроллера не является дочерним пакетом вашего основного пакета приложения, он не будет сканировать контроллер. Чтобы решить эту проблему, можно включить список пакетов для определения bean-компонента в основной пакет.
или создать иерархию пакетов, в которой дочерний пакет является производным от основного пакета
Я разрабатываю приложение Spring Boot в течение нескольких недель .. И я получил ту же ошибку, что и ниже;
Whitelabel Error Page This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback. Thu Jan 18 14:12:11 AST 2018 There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found, status=404). No message available
Когда я получаю это сообщение об ошибке, я понял, что мой контроллер или класс контроллера отдыха не определен в моем проекте. Я имею в виду, что все наши пакеты контроллеров не являются одним и тем же пакетом с основным классом, который включает аннотацию @SpringBootApplication .. Я имею в виду, что вам нужно добавить имя вашего пакета контроллера в аннотацию @ComponentScan к вашему основному классу, который включает аннотацию @SpringBootApplication. Если вы напишете приведенные ниже коды, ваша проблема будет решена . Самое главное, вы должны добавить весь пакет вашего контроллера в аннотацию @ComponentScan, как я сделал в приведенном ниже
Я надеюсь, что эти коды помогут кому-то .
Если вы найдете другой способ решить эту ошибку или у вас есть предложения для меня, напишите в комментарии . спасибо .
Проблемы с простым проектом с Spring Framework
Пытаюсь написать приложение по https://www.toptal.com/spring/beginners-guide-to-mvc-with-spring-framework Запускается успешно, но на localhost пишет:
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
Как исправить ее в данном проекте?
В HTML в строке по типу
выделяется как ошибка. Почему?
При работе Spring Boot + Freemarker если появляется страница:
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
В версии spring-boot-starter-parent 2.2.1.RELEASE не работает freemarker :
- переименуйте файлы Freemarker c .ftl на .ftlh
Добавьте в application.properties :
spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=true
spring.freemarker.suffix= .ftl
Проблема #1: на / ничего не замаплено, поэтому при открытии сайта вы видите подобную ошибку.
Проблема #2: если обратиться по адресу /students , то появляется еще одна ошибка, но уже другая: Exception evaluating SpringEL expression: «student.forename + ‘ ‘ + student.surame» (students:16) . Если очень внимательно посмотреть, то уже ясно в чем дело, но на всякий случай можно посмотреть в консоль на исключение: org.springframework.expression.spel.SpelEvaluationException: EL1008E:(pos 33): Property or field ‘surame’ cannot be found on object of type ‘wenti.entity.Student’ — maybe not public? Причина в банальной опечатке — вы обращаетесь к полю surame , вместо surname .
В ошибке написано, что неверный мапинг по адресу /error . Spring перенаправляет вас на страницу /error когда по вашему GET запросу произошла ошибка на сервере.
Какие есть варианты 1. Ошибка при получении/обработке данных на сервере (как пример NullPointerException ). Пройтись дебагом по коду, посмотреть не выпадает ли где exception. 2. Ошибка при парсинге страницы thymeleaf.
Посмотрите лог, скорее всего ваша ошибка выше, чем то, что вы указали в отрывке.
В дополнение к ответу о том, что:
При работе Spring Boot + Freemarker если появляется страница:
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
У меня версия spring-boot-starter-parent 2.5.3 чтобы работал freemarker сделал следующее:
Источник
In the previous article, we have learned how to make your spring boot application files structure correct to avoid the Whitelabel error page ( Spring Boot Resolve Whitelabel Error Page Example ). But when your spring boot application has errors in source code, it still shows the Whitelabel error page, and you can not see the real error message on the page. This article will tell you how to customize the Whitelabel error page and display related error data to the client users.
1. Disable Whitelabel Error Page.
If you do not like the Whitelabel error page, you can disable it with the following method.
- Add below content in spring boot project src / main / resources / application.properties file.
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false
- You can also add the below content in the above application.properties file to exclude ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration class.
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
- Now when you run the spring boot application again, you will see the below familiar tomcat HTTP status 500 error page instead of the Whitelabel error page. But the below error page is not user-friendly, so we will tell you how to customize the error page.
HTTP Status 500 — Internal Server Error
2. Customize Spring Boot Application Error Page.
You have two ways to customize the error page in spring boot.
2.1 Create error.html page in src / main / resources / templates folder like below.
- Then when your spring boot app runs into an error, the error.html page will be displayed. Below is the error.html file content.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Web Site Error Page</title> </head> <body> This is web site error page. </body> </html>
2.2 Create a more detailed custom error page.
- The above error Html page is too general, if you want to display more detailed error information on the error page, please follow the below steps.
- Create a class that extends org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController
- Override the getErrorPath() method to return the error page url mapping path.
- Create a method that will process the /error page url mapping path. You can return either an error page template file’s name or an error data content string using the
@ResponseBodyannotation. - In the below example, the CustomErrorController class extends ErrorController class. It overrides the method getErrorPath, and adds a method processError.
- It adds the
@ResponseBodyannotation on the processError method when you want to return the error content directly from the processError method. If you want to return a specified template error page, just remove the@ResponseBodyannotation from the method. - There is also an error-500.html file added in the src/main/resources/templates folder. This error template file will be used in the custom error controller.
- CustomErrorController.java
package com.dev2qa.example.controller; import java.util.Map; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorAttributes; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest; @Controller public class CustomErrorController implements ErrorController { // ErrorAttributes object is used to save all error attributes value. private final ErrorAttributes errorAttributes; @Autowired public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) { Assert.notNull(errorAttributes, "ErrorAttributes must not be null"); this.errorAttributes = errorAttributes; } /* Return the error page path. */ @Override public String getErrorPath() { return "/error"; } // Handle the /error path invoke. @RequestMapping("/error") /* @ResponseBody annotation will return the error page content instead of the template error page name. */ @ResponseBody public String processError(HttpServletRequest request, WebRequest webRequest) { // Get error status code. Integer statusCode = (Integer)request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE); if(statusCode.intValue() == 500) { // If you want to return template error page, then remove the @ResponseBody annotation of this method. return "error-500.html"; }else { // Get error message. String message = (String)request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_MESSAGE); // Get exception object. Exception exception = (Exception)request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); // Get error stack trace map object. Map<String, Object> body = errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, true); // Extract stack trace string. String trace = (String) body.get("trace"); StringBuffer retBuf = new StringBuffer(); retBuf.append("<pre>"); if(statusCode != null) { retBuf.append("Status Code : "); retBuf.append(statusCode); } if(message != null && message.trim().length() > 0) { retBuf.append("nrError Message : "); retBuf.append(message); } if(trace != null){ retBuf.append("nrStack Trace : "); retBuf.append(trace); } retBuf.append("</pre>"); return retBuf.toString(); } } } - error-500.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Web Site Error Page</title> </head> <body> This is internal server error page, error status code is 500. </body> </html> - Below is the custom error page that removes the annotation
@ResponseBodyfrom the processError method. Then when the server 500 error occurred, it will display the error-500.html file content.This is internal server error page, error status code is 500.
- Below is the error page that uses
@ResponseBodyannotation on processError method, then it will display the processError method returned string on the web page.if(statusCode.intValue() == 500) { // If you want to return template error page, then remove the @ResponseBody annotation of this method. return "error-500.html"; }else { }
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback. error can be resolved in three ways, Identify the loading issue of the controller or method, disable the error page from the browser, and customize the error page to display the appropriate error message. There was an unexpected error Whitelabel Error page. It returns a 404 page not found error.
In this post, we will see about this error “Whitelabel Error page, This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.”. You see this error, because something went wrong in the application. For some reason, Spring boot can not server the web page
If the url invokes a rest call or a jsp call to the spring boot application, the spring boot will not be able to serve the request. Instead, the “Whitelable Error Page” page will be displayed in the browser.
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
Fri Apr 10 22:45:19 IST 2020
There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found, status=404).
No message available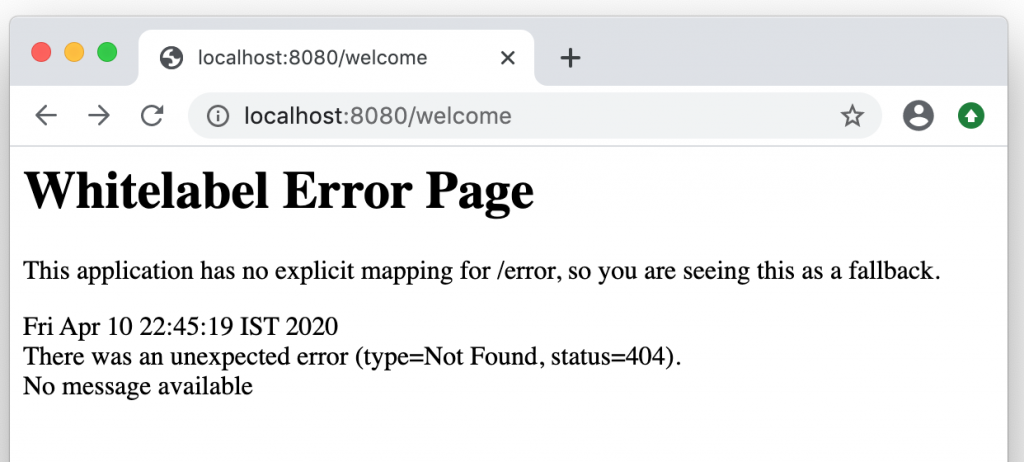
How to reproduce this Whitelabel Error Page
Create a web-based spring boot application in the spring tool suite. In the pom.xml file, add spring-boot-starter-web dependency. The maven dependence will be as shown in the code below.
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>The spring boot main class will be created in the “com.yawintutor.application” package. The main class will be shown in the code below.
Application.java
package com.yawintutor.application;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}A rest controller class is created to serve a rest call. The controller class “TestController.java” is created in the controller package “com.yawintutor.controller.”
TestController.java
package com.yawintutor.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/welcome")
public String welcomepage() {
return "Welcome to Yawin Tutor";
}
}To reproduce this error page, run the Spring Boot Application. The spring boot application starts the tomcat server and listens to port 8080. Open a web browser, type the “http:/localhost:8080/welcome” url. The “Whitelabel error page” will be shown in the browser.
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.Root Cause
If the url invokes a rest call or a jsp call to the spring boot application, the spring boot will not be able to serve the request. There are two reasons for failing to serve the request. Either the controller class is not loaded in the spring boot context or the rest call is not available.
There are three ways to solve this problem. Identify the loading issue of the controller or method, disable the error page from the browser, and customize the error page to display the appropriate error message.
Solution 1 – Root Package
The main class “Application.java” and the controller class “TestController.java” are in packages of parallel level (com.yawintutor.application, com.yawintutor.controller). Make sure your main class is in the root package. The other classes should be in the root sub package. The spring boot application scans the package from the root package where the main class exist with annotation @SpringBootApplication and sub packages.
com
+-- yawintutor
+-- application
| +-- Application.java (Main class)
|
+-- controller
+-- TestController.javaSolution 2 – @ComponentScan
In the spring boot application, if the main class package is not a root package, the other package beans will not be loaded in the spring boot context. The @ComponentScan annotation in the main class informs the bean packages to be loaded at startup.
package com.yawintutor.application;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan({"com.yawintutor.controller"})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}Solution 3 – Typo Error
If the main class package is a root package, still if you see the error, check the rest controller’s method signature. The rest call url and the configured request mapping url should match. Check the rest call url for any typo error. If anything exists, correct the error. Check the RequestMapping configuration in the rest controller and correct the request mapping url.
Make sure the rest call url and the request mapping url in the rest controller should match. In the example below, “/welcome” should match in both rest url and request mapping url.
http://localhost:8080/welcome @RequestMapping("/welcome")
public String welcomepage() {
return "Welcome to Yawin Tutor";
}Solution 4 – Disable the Error Page
The default Whitelabel Error page can be disabled with the configuration of “server.error.whitelabel.enabled” in the application.properties. This is not a valid solution as it appears as a blank page that does not transmit any information to the end user.
Add the following line to the application.properties, restart the spring boot application. The default Whitelable error page will disappear and the blank page will be displayed.
application.properties
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=falseThis can be configured using application.yml file as like below
application.yml
server:
error:
whitelabel:
enabled:falseThe error page can be disabled using the annotation @EnableAutoConfiguration with ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration in the main class. The code below shows how to disable using the annotation.
Application.java
package com.yawintutor.application;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}Solution 5 – Customize using Thymeleaf Error Page
The another way of removing Whitelabel error page is replace with customized error page. The error page can be customized by adding a error.html file in resources/templates directory. This error page is rendered using Thymeleaf template engine if any error is occurred.
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>resources/templates/error.html
<html>
<body>
<center>
<h1>Error occurred</h1>
<h2>Please contact website admin</h2>
<a href="/">Home</a>
</center>
</body>
</html>Solution 6 – Customize using ErrorController
If the error occurs, redirect the user to a custom error page showing the generic error message to intimate something that went wrong with the application, To take action, please contact the respective privileged person to resolve this problem. Create a customized error page that will overwrite the default error page as like below
ErrorHandlerController.java
package com.yawintutor.application;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ErrorHandlerController implements ErrorController{
@Override
@RequestMapping("/error")
@ResponseBody
public String getErrorPath() {
return "<center><h1>Something went wrong</h1></center>";
}
}Summary
In this post, we saw an error on the “Whitelabel error page” error. In most cases, this error page is due to controller bean loading issue or method signature issue. If the error is in a valid scenario, the customization of the error message is preferred to show the appropriate error message to the end user.
0, краткое описание
Перед изучением этой заметки лучше всего иметь некоторое представление о Spring mvc и Tomcat, чтобы было удобнее понимать.Если вам нужно знать наиболее прямое решение, перетащите его вниз, чтобы увидеть образец кода.
Вводится настоящая причина появления белой страницы Springboot. Основная причина заключается в том, что нет подходящей ситуации соответствия и возникает ситуация 404. Затем перейдите к системной по умолчанию сначала ErrorPage, которая представляет собой содержимое белой страницы, а затем с трех точек зрения в соответствии с его спецификой. , 1. Перехватчик, 2. Новая страница ошибок, 3. Пользовательская маршрутизация / маршрутизация ошибок для решения проблемы, а также знакомство с преимуществами и недостатками каждого метода, включая основные причины ошибок страницы цикла и т. Д.
1. Страница ошибки Whitelabel
То, что называется страницей ошибок Whitelabel (также называемой белой страницей), является страницей описания аномального HTTP-запроса в SpringBoot, как показано ниже.
image
Содержимое белой страницы будет отображать код состояния, путь и причину ошибки, но реальная среда публикации онлайн-генерации обычно не допускает такой ситуации, и больше — это настраиваемые страницы 404 или 500 страниц.
Итак, теперь мы пришли к пониманию, в какой ситуации будут появляться белые страницы и как решить эту проблему. Давайте воспользуемся случаем 404, чтобы понять причину.
Перейти непосредственно к классу DispatcherServletprotected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ExceptionМетод, содержащий фрагменты кода
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// находим подходящий обработчик запроса
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
// В принципе, если вы его не найдете, введите здесь и установите код статуса ответа 404
// Но после отладки так и не вошел сюда
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
В методе getHandler будет выполняться обход HandlerMapping в текущем веб-контейнере, чтобы найти соответствующий обработчик
image
image
Из приведенного выше рисунка очевидно, что текущий удобный обработчик — SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, потому что URL-адрес содержит/**, Все URL-адреса могут быть сопоставлены,Не войдет в noHandlerFound позади, Обработчик адаптации HandlerAdapter — это объект, созданный HttpRequestHandlerAdapter.
Не удается найти соответствующий ресурс в mv = ha.handle (loadedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler ()), установите код состояния ответа на 404Подробнее см. Метод handleRequest класса ResourceHttpRequestHandler.
Теперь это эквивалентно установке кода состояния запроса на 404, больше ничего не делается, mv также равно null
В это время вам нужно вернуться к процессу вызова Tomcat. Если вы запрашиваете процесс вызова Tomcat, вы должны знать, что когда Tomcat получает запрос сокета Socket на соединителе, он упаковывается в запрос, ответ и другую информацию, которая будет отправлена в Engine-> Host и другие компоненты. Он доставляется слой за слоем, затем принимается конвейером каждого компонента, а затем фильтруется соответствующим клапаном (клапаном) слой за слоем.
На этот раз дошел до класса StandardHostValveprivate void status(Request request, Response response)метод
private void status(Request request, Response response) {
int statusCode = response.getStatus();
// Просмотр текущего кода состояния, текущий пример - 404
// Получить текущий контекст
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
return;
}
if (!response.isError()) {
// Текущий запрос верен
// это атомарный класс AtomicInteger errorState, если он больше 0, это считается ошибкой
return;
}
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(statusCode);
// Об этом месте поговорим позже, это решение, устанавливаем страницу ошибки
if (errorPage == null) {
// Look for a default error page
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(0);
}
if (errorPage != null && response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
...
image
Объедините код и диаграмму, а затем внимательно прочтите белую страницу.This application has no explicit mapping for /error, Маршрут error, причина отсюда, а затем переход вперед, адрес маршрута error
image
Белая страница mv, предоставляемая SpringBoot, используется позже для визуализации содержимого белой страницы, которую мы видим.
Пока что весь процесс выполнен,Подводя итог, это запрос несуществующей ссылки, которая перенаправляется в запрос / error после того, как обнаруживается, что это запрос 404.
Тогда решение очень простое, есть три решения, но эти три решения под разными углами, чтобы решить проблему.
- Добавить перехватчик
- Добавить ErrorPage
- Добавить / путь ошибки
2. Решите проблему с белой страницей.
2.1, добавить перехватчик
public class CustomHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
// Должно быть истиной, иначе перехватчик не сработает
// Конечно, вы можете перехватывать любые URL-адреса по желанию
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
if (modelAndView != null) {
// Предотвращаем нулевые указатели
// Если это страница с ошибкой в springboot, определенно не будет отображаться, что mv имеет значение null
modelAndView.setViewName("/err");
// Примечание: этот запрос является всего лишь пробным и не имеет практического значения
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter customMvcConfigurerAdapter (){
return new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new CustomHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
// добавляем перехватчик
super.addInterceptors(registry);
}
};
}
После того, как перехватчик перехватит запрос / error, он вынужден изменить mv, так что последний отрендеренный mv для пробного использования является нашей настраиваемой настройкой, а не содержимым белой страницы, где mv самой белой страницы будет проходитьАнализатор представления ContentNegotiatingОбработка становитсяErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration
Обратите внимание, что все это истечение фактически было обработано 3 HTTP-запросами,На следующем рисунке показана информация журнала, распечатанная с использованием мониторинга событий HTTP.
image
Пройдите через / abc ==> jump / err ==> jump / error (содержимое не отображается, потому что содержимое, отправленное в браузер, было отображено с помощью / err
Реальный поток обработки вызовов состоит в том, что / abc не находит подходящий обработчик, а затем решает передать его на путь / error для обработки, но он перехватывается перехватчиком и перенаправляется в / err для обработки.
Недостатки: все запросы для этого маршрута будут перехвачены, включая статические файлы ресурсов, что не оказывает большого влияния на внутренние службы, которые предоставляют чистые интерфейсы. Другие службы будут иметь влияние
2.2, добавьте ErrorPage
Добавление подходящей ErrorPage не приведет к переходу к пути по умолчанию / ошибке перехватчика, а перейдет к настраиваемой ErrorPage. Причина этого была указана в методе статуса выше.
@Bean
public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer containerCustomizer() {
return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer configurableEmbeddedServletContainer) {
ErrorPage errorPage400 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST,"/400");
ErrorPage errorPage404 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND,"/404");
ErrorPage errorPage500 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,"/500");
configurableEmbeddedServletContainer.addErrorPages(errorPage400,errorPage404,errorPage500);
}
};
}
// ======= разделительная линия
@ApiOperation («запрос 404»)
@GetMapping("404")
public String e404() {
return "404";
}
В приведенном выше коде добавлено несколько путей перехода к странице ошибки ErrorPage и соответствующие им коды ошибок HTTP. В нашем текущем примере должен быть выполнен переход к соединению / 404, а затем как я могу получить сообщение об ошибке после его выполнения? В принципе, он должен отображать 404 Содержимое файла .html и классическая страница ошибок Tomcat отображаются одновременно, как показано на следующей странице, и содержимое вывода журнала.
image
image
Это проблема скачка петли
Когда в системе не указан преобразователь четкого представления, система будет использовать свой собственный преобразователь по умолчанию.InternalResourceView, Он проверит текущий URL-адрес перед отображением. Если обнаружится, что запрошенный URL-адрес соответствует целевому URL-адресу, он будет определенВперед сампоявляютсяCircular view pathЭта проблема
protected String prepareForRendering(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
String path = getUrl();
if (this.preventDispatchLoop) {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
if (path.startsWith("/") ? uri.equals(path) : uri.equals(StringUtils.applyRelativePath(uri, path))) {
throw new ServletException("Circular view path [" + path + "]: would dispatch back " +
"to the current handler URL [" + uri + "] again. Check your ViewResolver setup! " +
"(Hint: This may be the result of an unspecified view, due to default view name generation.)");
}
}
return path;
}
Итак, как ее решить, нужно исходить из фундаментальной цели
- Добавьте синтаксический анализатор шаблона, чтобы синтаксический анализатор по умолчанию не использовался
- Изменить путь перехода
Вы можете понять конкретные решения самостоятельно.В этой статье не используется отрисовка механизма шаблонов, а непосредственно отображаются основные данные.
@RequestMapping("/")
@RestController
public class ErrorController {
@ApiOperation («запрос 404»)
@GetMapping("404")
public String e404() {
System.out.println("404............");
return "Это действительно страница 404, посмотрите на нее";
}
image
2.3, путь добавления / ошибки
Как вы знаете выше, поскольку система по умолчанию переходит к / error и завершает рендеринг данных, недостаточно настроить маршрут / error и избежать проблемы отсутствия статических ресурсов, но обратите внимание, что есть Один вопрос, подробности см. На рисунке ниже
image
image
Во-первых, я добавил и определил очень простой метод обработки пути ошибки, но при запуске Springboot есть 3 метода обработки пути ошибки, и они одновременно принадлежат одному и тому же дескриптору.Правила маршрутизации URLОбработка, выберите ручку в автоконфигурации,Это должно было привести к тому, что наш заказ / ошибка недействительны
image
После тестирования он действительно недействителен, и белая страница все еще отображается, так как это решить? Есть несколько способов сделать то же самое
- В соответствии с правилами сопоставления маршрутизации измените соответствующий контент, чтобы при окончательном выборе процессора он достиг нашего пользовательского процессора, но это очень сложно. Вам необходимо очень четко понимать правила сопоставления маршрутизации самого Spring mvc, чтобы гарантировать, что сопоставление URL-адресов Приоритетные вопросы, требующие решения, и т. Д.
-
Мы уже знаем, что эти три / ошибки находятся в картографе маршрутов RequestMappingHandlerMapping.Мы можем сделать так, чтобы пользовательский процессор не сохранялся в карте маршрутов, и сделать Spring приоритетом согласованного преобразователя маршрутов при опросе. Да, но на самом деле BeanNameUrlMapping в handlerMapping все еще находится после RequestMappingHandlerMapping, если вы измените порядок, это также очень сложно
image
EndpointHandlerMapping — это конечная точка в исполнительном модуле Springboot. Настроить конечную точку сложно, и она не подходит для текущего проекта.
Использование SimpleUrlHandlerMapping не подходит для Springboot. Если вы используете конфигурацию xml, вы можете напрямую установить ее URL-адрес. Это будет очень удобно. Если вы применяете метод аннотации в springboot, требуется дополнительная настройка, как показано в следующем коде
@RequestMapping("/")
@Controller
public class SimpleUrlController {
private static final String ERROR_PATH = "/error";
@Resource
private SimpleUrlHandlerMapping simpleUrlHandlerMapping;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(ERROR_PATH, this);
simpleUrlHandlerMapping.setUrlMap(map);
simpleUrlHandlerMapping.initApplicationContext();
// Вызываем отображение simpleurl
}
@GetMapping("/error")
@ResponseBody
public String error(HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("SimpleUrlController");
Enumeration<String> attributes = request.getAttributeNames();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
while (attributes.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = attributes.nextElement();
if (name.startsWith("java")) {
// Помните, что свойства самой пружины не должны быть выставлены снаружи!
Object value = request.getAttribute(name);
map.put(name, value);
}
}
return JSON.toJSONString(map);
}
}
image
Хотя / error вводится в SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, он все равно будет отображаться, даже если добавлена дополнительная конфигурацияНет ошибки адаптера,Этот метод не применим
Оглядываясь назад на наблюдение BasicErrorController, мы можем унаследовать интерфейс ErrorController сами.
@RequestMapping("")
@Controller
public class CustomErrorController implements ErrorController {
private static final String ERROR_PATH = "/error";
@GetMapping(ERROR_PATH)
@ResponseBody
public String error(HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("CustomErrorController");
Enumeration<String> attributes = request.getAttributeNames();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
while (attributes.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = attributes.nextElement();
if (name.startsWith("java")) {
// Помните, что свойства самой пружины не должны подвергаться воздействию извне!
Object value = request.getAttribute(name);
map.put(name, value);
}
}
return JSON.toJSONString(map);
}
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return ERROR_PATH;
}
}
In this article, we will cover the famous Spring Boot Whitelabel error page. We are covering how to disable the default error page and how we can customize the Whitelabel error page in your Spring Boot application.
Introduction
Spring Boot uses a default Whitelabel error page in case server error. This is not very helpful and we may want to give more relevant information to the customer in a production environment. This article focuses on the Spring Boot whitelabel error page. We will learn how to disable this default behavior and how we can use our own custom error page to align with our UI.
1. Disabling Whitelabel Error Page
There are multiple ways to disable this behavior in your Spring Boot application. Let’s cover common options to do this.
1.1 Using Properties File
Spring Boot provides an application.properties (or YAML) file to easily configure/change your application. We can use the same property file to disable this error page globally. Set server.error.whitelabel.enabled to false to achieve this.
# Whether to enable the default error page displayed in browsers in case of a server error.
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false Please know that using the above configuration will restore the default of the servlet container you are using. This means that if you are not using any custom error page, the default servlet container error page shown to the customer (like default tomcat server error page).
Another option is to exclude ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration from your application using application.properties file.
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfigurationFor Spring Boot 1.x application use ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration in exclude the list.
1.2 Exclude using @EnableAutoConfiguration
In case you like to exclude using the code, you have the option to pass exclude configuration list to the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class
})
public class SpringBootApplication { //application code
}2. Custom Error Page
As suggested, one of the first options is to Overriding the error page with your own template. For this post, we are taking Thymeleaf as our underlying templating engine. We create a custom error page with name error.html and save it under resources/templates directory. In case of error, Spring Boot system will automatically pick this custom error page. Let’s see how the page looks like before customizing error page.
Let’s create our custom error.html and place it under the <em>resources/templates</em> directory.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>We've got some trouble</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cover">
<h1>Our apologies.</h1>
<p class="lead">This page stepped out for a quick ride.</p>
<p>Please go back to our homepage to restart your browsing experience.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>If we run our application, this is how the output shown to the customer.
Once we add the error.html in the templates directory, Spring Boot BasicErrorController automatically pick our custom template.
3. Custom ErrorController
If the above options are not suitable for your need or if we want to have a better control on the error handling mechanism, we have the option to extend Spring’s ErrorController with our own implementation. We need to implement the ErrorController interface and overrides its getErrorPath()to return a custom path.
package com.javadevjournal.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class CustomErrorController implements ErrorController {
private static final String PATH = "/error";
@RequestMapping(value = PATH)
public String error() {
return "customError";
}
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return PATH;
}
}Let’s have a look at the above code.
- Our controller creates a mapping for the path as returned by
getErrorPath()method. - ErrorController interface shows that a
@Controlleris used to render errors. - We have the option to use
getErrorPath()to return different error pages based on the error type.
Let’s create a new error page which we will use in this new controller method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>We've got some trouble</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cover">
<h1>Our apologies For Custom Page.</h1>
<p class="lead">This page stepped out for a quick ride.</p>
<p>Please go back to our homepage to restart your browsing experience.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>When we run our application this time, we will have a different error page displayed to the customer.
Summary
In this post, we cover how to disable Spring Boot Whitelabel error page and how we can customize the Whitelabel error page in your Spring Boot application. We learned how to extend the error handling mechanism by implementing ErrorController in the custom error handling controller.
Advertisements












