Служба Windows Error Reporting (WER) служит для сбора и отправки отладочной информации о падении системных и сторонних приложений в Windows на сервера Microsoft. По задумке Microsoft, эта информация должна анализироваться и при наличии решения, вариант исправления проблемы должен отправляется пользователю через Windows Error Reporting Response. Но по факту мало кто пользуется этим функционалом, хотя Microsoft настойчиво оставляет службу сбора ошибок WER включенной по умолчанию во всех последних версиях Windows. В большинстве случае о службе WER вспоминают, когда каталог C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue начинает занимать много места на системном диске (вплоть до нескольких десятков Гб), даже не смотря на то что на этом каталоге по умолчанию включена NTFS компрессия.
Содержание:
- Служба Windows Error Reporting
- Очистка папки WERReportQueue в Windows
- Отключение Window Error Reporting в Windows Server
- Отключаем сбор и отправки отчетов об ошибках в Windows 10
- Отключение Windows Error Reporting через GPO
Служба Windows Error Reporting
Служба Windows Error Reporting при появлении ошибки показывает диалоговое окно, предлагающее отправить отчет об ошибке в корпорацию Microsoft. Когда в Windows вы видите сообщение об ошибке
YourApp has stop working
, в это время в служба Windows Error Reporting запускает утилиту WerFault.exe для сбора отладочных данных (могут включать в себя дамп памяти).
Данные пользователя сохраняются в профиль пользователя:
%USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowswer
Системные данные – в системный каталог:
%ALLUSERSPROFILE%MicrosoftWindowsWER
Служба Windows Error Reporting представляет собой отдельный сервис Windows. Вы можете проверить состояние службы командой PowerShell:
Get-Service WerSvc
Внутри каталога WERReportQueue содержится множество каталогов, с именами в формате:
- Critical_6.3.9600.18384_{ID}_00000000_cab_3222bf78
- Critical_powershell.exe_{ID}_cab_271e13c0
- Critical_sqlservr.exe__{ID}_cab_b3a19651
- NonCritical_7.9.9600.18235__{ID}_0bfcb07a
- AppCrash_cmd.exe_{ID}_bda769bf_37d3b403
Как вы видите, имя каталога содержит степень критичности события и имя конкретного exe файла, который завершился аварийно. Во всех каталогах обязательно имеется файл Report.wer, который содержит описание ошибок и несколько файлов с дополнительной информацией.
Очистка папки WERReportQueue в Windows
Как правило, размер каждой папки в WER незначителен, но в некоторых случаях для проблемного процесса генерируется дамп памяти, который занимает довольно много места. На скриншоте ниже видно, что размер файла дампа memory.hdmp составляет около 610 Мб. Парочка таким дампов – и на диске исчезло несколько свободных гигибайт.
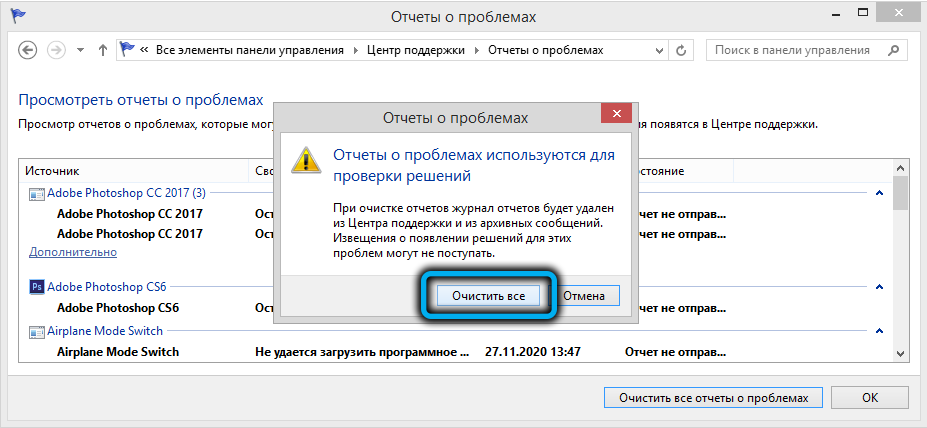
Чтобы очистить все эти ошибки и журналы штатными средствами, откройте панель управления и перейдите в раздел ControlPanel -> System and Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance -> View reliability history -> View all problem reports (Control PanelSystem and SecuritySecurity and MaintenanceProblem Reports) и нажмите на кнопку Clear all problem reports.
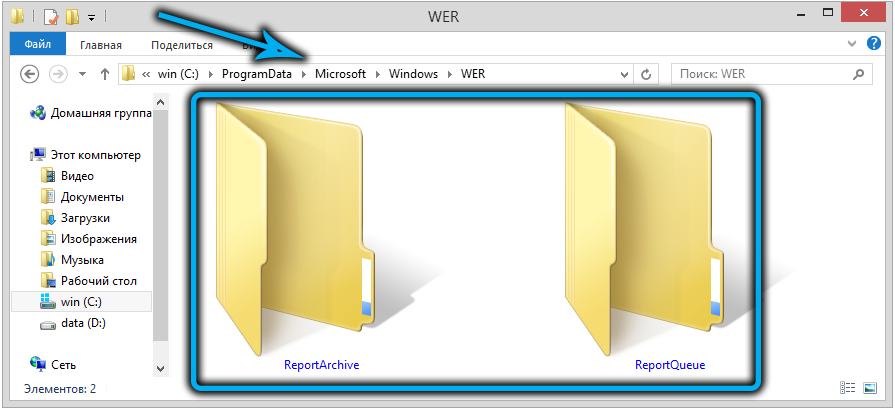
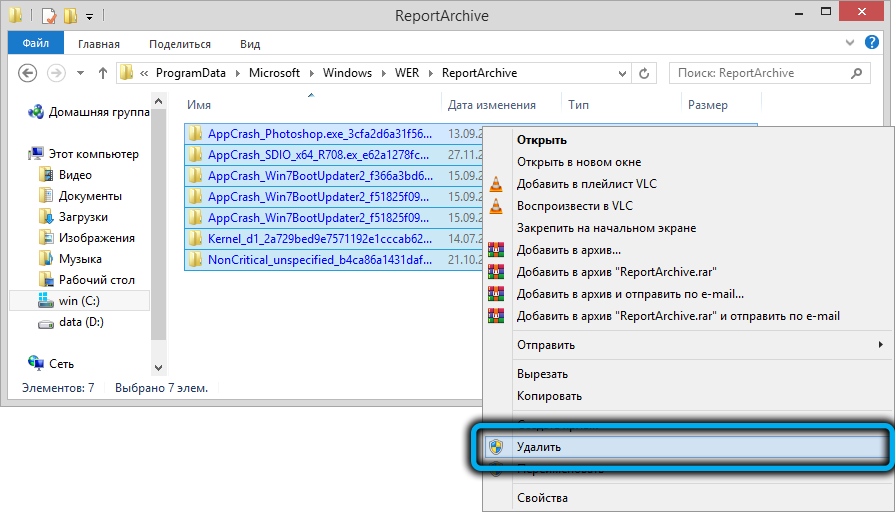
Для быстрого освобождения места на диске от файлов отладки, сгенерированных службой WER, содержимое следующих каталогов можно безболезненно очистить вручную.
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue
Следующие команды PowerShell удалят из каталога каталогов WER все файлы, старше 15 дней:
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-15) | Remove-Item -force -Recurse
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-15) | Remove-Item -force –Recurse
Для очистки каталогов WER в пользовательских профилях используйте такой скрипт:
$users = Get-ChildItem c:users|where{$_.name -notmatch 'Public|default'}
foreach ($user in $users){
Get-ChildItem "C:Users$UserAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsWER " –Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Remove-Item –force –Recurse
}
Отключение Window Error Reporting в Windows Server
В Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2 вы можете управлять состоянием WER с помощью PowerShell. Вы можете отключить службу Windows Error Reporting:
Get-Service WerSvc| stop-service –passthru -force
Set-Service WerSvc –startuptype manual –passthru
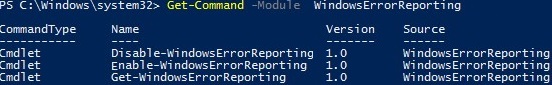
Но есть более корректные способы отключения WER в Windows. В версии PowerShell 4.0 добавлен отдельный модуль WindowsErrorReporting из трех командлетов:
Get-Command -Module WindowsErrorReporting
Проверить состояние службы Windows Error Reporting можно командой:
Get-WindowsErrorReporting
Для отключения WER, выполните:
Disable-WindowsErrorReporting
В Windows Server 2012 R2 можно отключить запись информации об ошибках Windows Error Reporting через панель управления (Control Panel -> System and Security -> Action Center -> раздел Maintenance -> Settings -> выберите опцию I don’t want to participate, and don’t ask me again
Отключаем сбор и отправки отчетов об ошибках в Windows 10
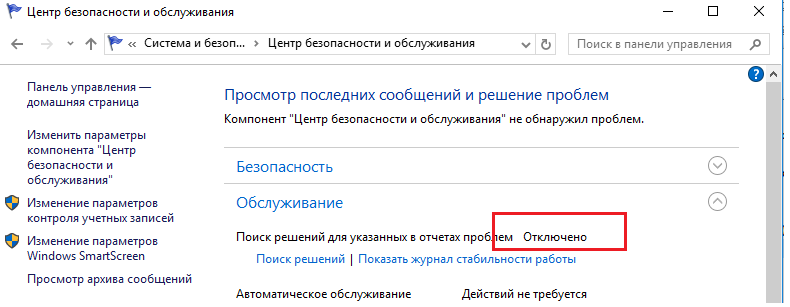
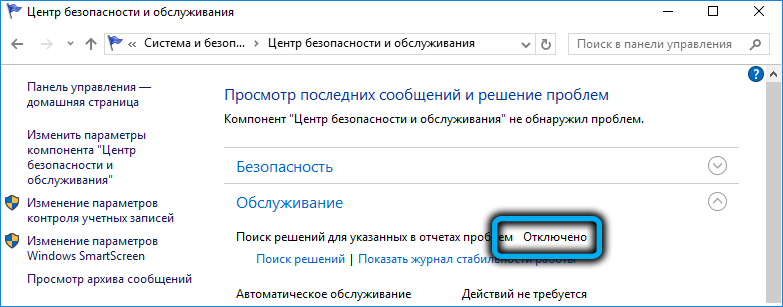
В Windows 10 нельзя отключить Error Reporting через панель управления. В графическогм интерфейсе можно только проверить ее статус (Система и безопасность ->Центр безопасности и обслуживания -> секция Обслуживание). Как вы видите, по умолчанию параметр Поиск решения для указанных в отчетах проблем включен (Control Panel -> System and Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance -> Report problems = On).
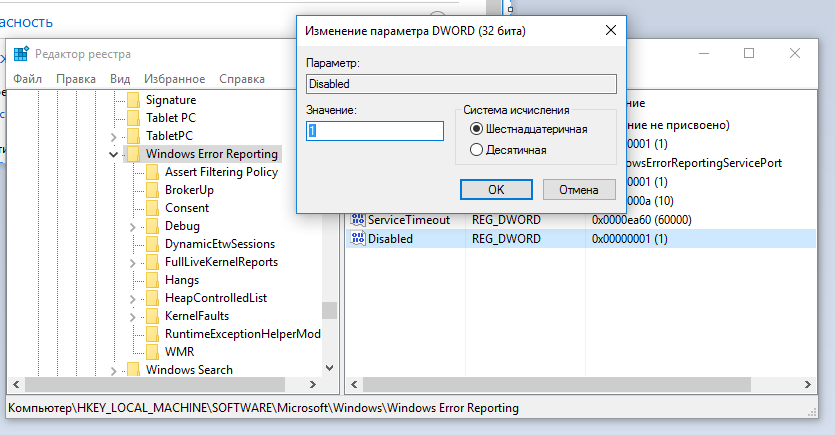
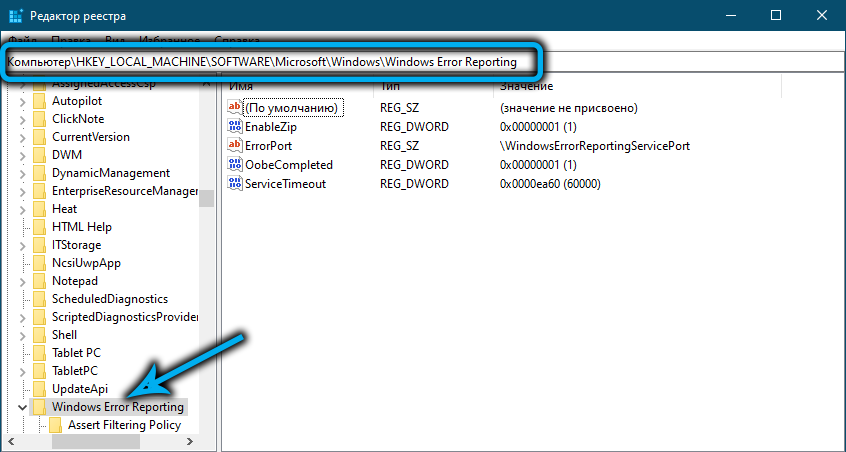
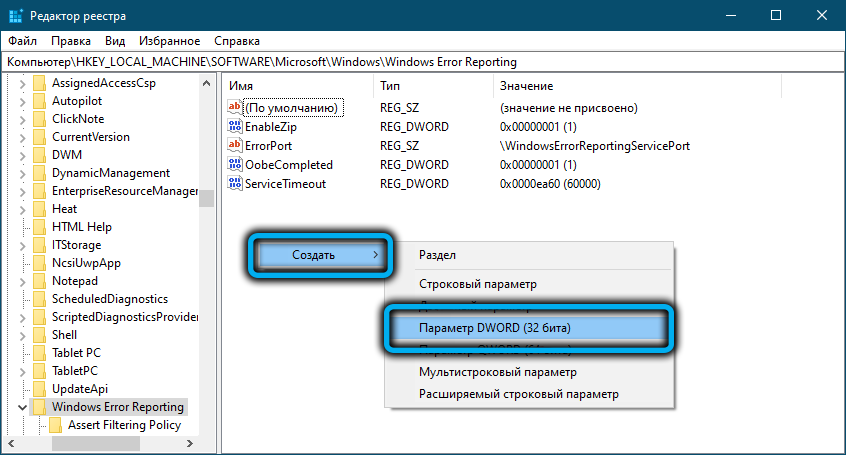
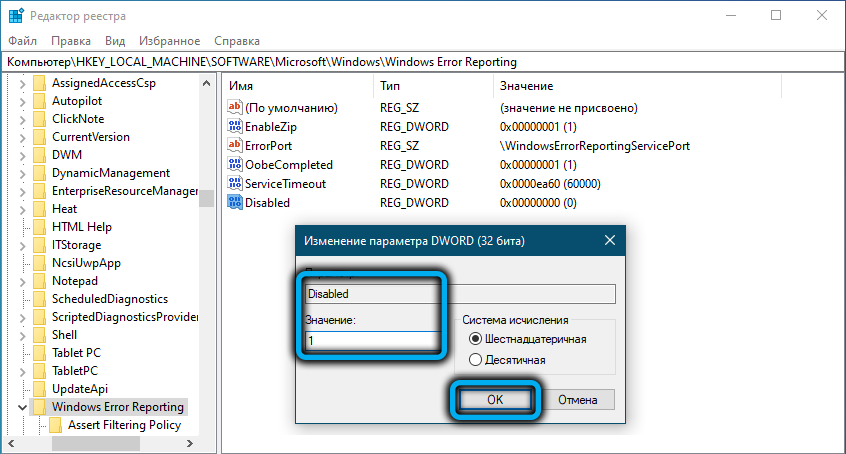
HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting нужно создать новый параметр типа DWORD (32 бита) с именем Disabled и значением 1.
Можно отключить сбор ошибок WER для конкретных пользователей:
reg add "HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Или отключить WER для всех:
reg add "HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Измените параметр реестра и проверьте статус параметра Поиск решения для указанных в отчетах проблем в панели управления. Его статус должен изменится на Отключено.
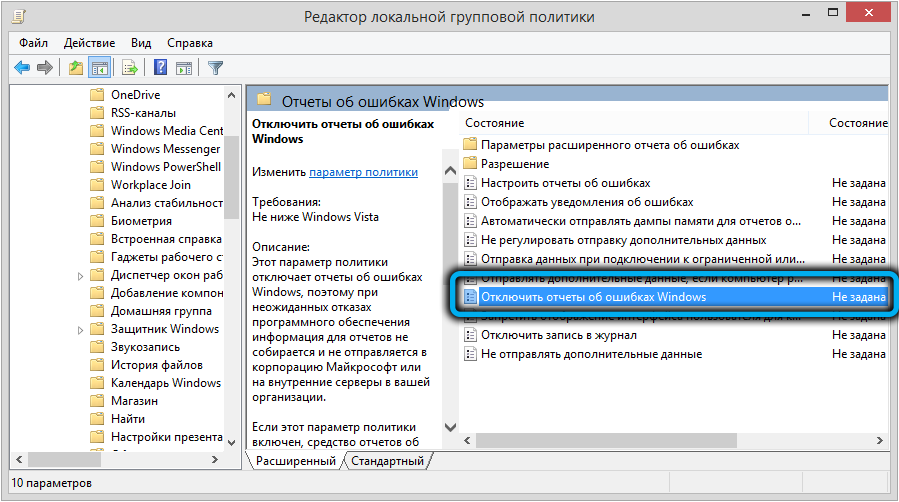
Отключение Windows Error Reporting через GPO
Также вы можете управлять настройками службы Windows Error Reporting через групповые политики.
Запустите редактор локальной (
gpedit.msc
) или доменной GPO (
gpmc.msc
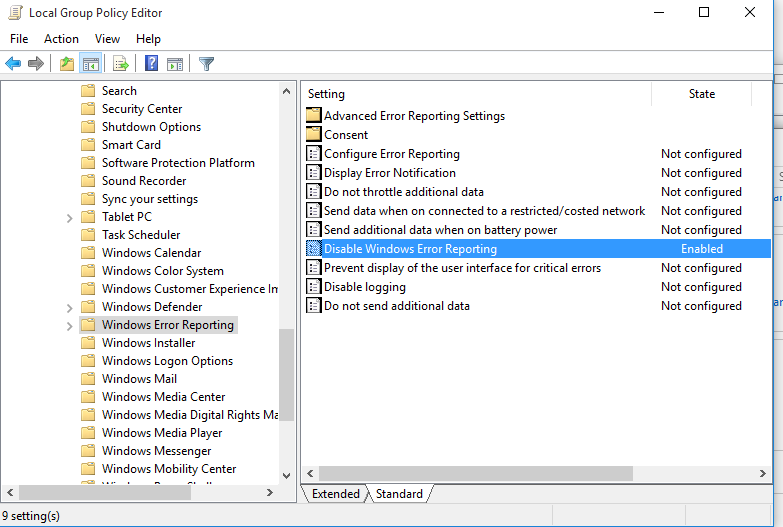
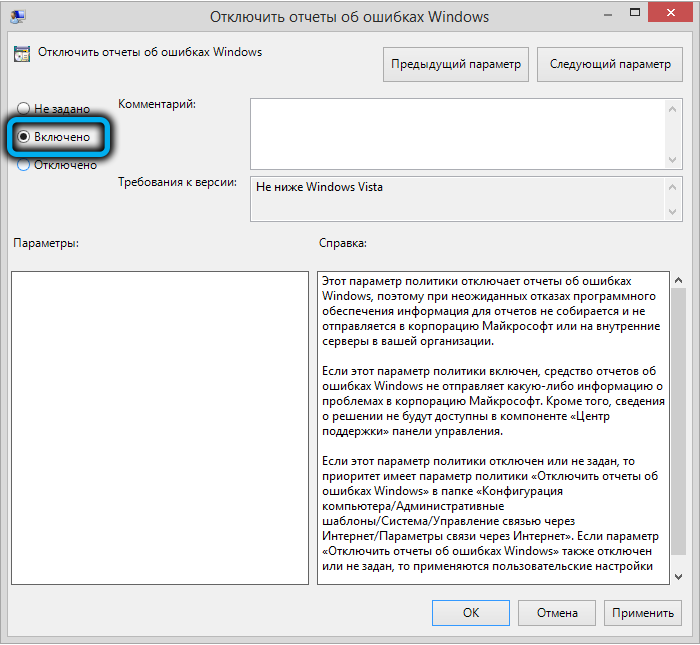
) и перейдите в ветку реестра Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Error Reporting (Компоненты Windows -> Отчеты об ошибках Windows). Для отключения сбора и отправки ошибок через WER включите политику Disable Windows Error Reporting (Отключить отчеты об ошибках Windows).
Аналогичная политика есть в пользовательском разделе политик (User Configuration).
Обновите GPO (перезагрузка не потребуется).
В результате в Windows перестанут формироваться сообщения об ошибках Windows и отправляться в Microsoft.
| title | description | ms.author | author | ms.date | ms.topic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting |
Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using WER Reports, with specific details on how to gather reports and diagnose common issues. |
johnmar |
JohnMarlin-MSFT |
10/21/2021 |
troubleshooting |
Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server, Azure Stack HCI, versions 21H2 and 20H2
Windows Error Reporting (WER) is a flexible event-based feedback infrastructure designed to help advanced administrators or Tier 3 support gather information about the hardware and software problems that Windows can detect, report the information to Microsoft, and provide users with any available solutions. This reference provides descriptions and syntax for all WindowsErrorReporting cmdlets.
The information on troubleshooting presented below will be helpful for troubleshooting advanced issues that have been escalated and that may require data to be sent to Microsoft for triaging.
Enabling event channels
When Windows Server is installed, many event channels are enabled by default. But sometimes when diagnosing an issue, we want to be able to enable some of these event channels since it will help in triaging and diagnosing system issues.
You could enable additional event channels on each server node in your cluster as needed; however, this approach presents two problems:
- You have to remember to enable the same event channels on every new server node that you add to your cluster.
- When diagnosing, it can be tedious to enable specific event channels, reproduce the error, and repeat this process until you root cause.
To avoid these issues, you can enable event channels on cluster startup. The list of enabled event channels on your cluster can be configured using the public property EnabledEventLogs. By default, the following event channels are enabled:
PS C:Windowssystem32> (get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs
Here’s an example of the output:
Microsoft-Windows-Hyper-V-VmSwitch-Diagnostic,4,0xFFFFFFFD
Microsoft-Windows-SMBDirect/Debug,4
Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer/Analytic
Microsoft-Windows-Kernel-LiveDump/Analytic
The EnabledEventLogs property is a multistring, where each string is in the form: channel-name, log-level, keyword-mask. The keyword-mask can be a hexadecimal (prefix 0x), octal (prefix 0), or decimal number (no prefix) number. For instance, to add a new event channel to the list and to configure both log-level and keyword-mask you can run:
(get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic,2,321"
If you want to set the log-level but keep the keyword-mask at its default value, you can use either of the following commands:
(get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic,2" (get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic,2,"
If you want to keep the log-level at its default value, but set the keyword-mask you can run the following command:
(get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic,,0xf1"
If you want to keep both the log-level and the keyword-mask at their default values, you can run any of the following commands:
(get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic" (get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic," (get-cluster).EnabledEventLogs += "Microsoft-Windows-WinINet/Analytic,,"
These event channels will be enabled on every cluster node when the cluster service starts or whenever the EnabledEventLogs property is changed.
Gathering Logs
After you have enabled event channels, you can use the DumpLogQuery to gather logs. The public resource type property DumpLogQuery is a mutistring value. Each string is an XPATH query as described here.
When troubleshooting, if you need to collect additional event channels, you can a modify the DumpLogQuery property by adding additional queries or modifying the list.
To do this, first test your XPATH query using the get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet:
get-WinEvent -FilterXML "<QueryList><Query><Select Path='Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy/Operational'>*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) >= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>"
Next, append your query to the DumpLogQuery property of the resource:
(Get-ClusterResourceType -Name "Physical Disk".DumpLogQuery += "<QueryList><Query><Select Path='Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy/Operational'>*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) >= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>"
And if you want to get a list of queries to use, run:
(Get-ClusterResourceType -Name "Physical Disk").DumpLogQuery
Gathering Windows Error Reporting reports
Windows Error Reporting Reports are stored in %ProgramData%MicrosoftWindowsWER
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsQueue folder contains reports that are waiting to be uploaded to Watson.
PS C:Windowssystem32> dir c:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue
Here’s an example of the output:
Volume in drive C is INSTALLTO
Volume Serial Number is 4031-E397
Directory of C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue
<date> <time> <DIR> .
<date> <time> <DIR> ..
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_02d10a3f
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_0588dd06
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_10d55ef5
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_13258c8c
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_13a8c4ac
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_13dcf4d3
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_1721a0b0
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_1839758a
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_1d4131cb
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_23551d79
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_2468ad4c
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_255d4d61
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_1cbd8ffecbc8a1a0e7819e4262e3ece2909a157a_00000000_cab_08289734
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_64acaf7e4590828ae8a3ac3c8b31da9a789586d4_00000000_cab_1d94712e
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_ae39f5243a104f21ac5b04a39efeac4c126754_00000000_003359cb
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_ae39f5243a104f21ac5b04a39efeac4c126754_00000000_cab_1b293b17
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_Physical Disk_b46b8883d892cfa8a26263afca228b17df8133d_00000000_cab_08abc39c
<date> <time> <DIR> Kernel_166_1234dacd2d1a219a3696b6e64a736408fc785cc_00000000_cab_19c8a127
0 File(s) 0 bytes
20 Dir(s) 23,291,658,240 bytes free
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsArchive folder contains reports that have already been uploaded to Watson. Data in these reports is deleted, but the Report.wer file persists.
PS C:Windowssystem32> dir C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive
Here’s an example of the output:
Volume in drive C is INSTALLTO
Volume Serial Number is 4031-E397
Directory of c:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive
<date> <time> <DIR> .
<date> <time> <DIR> ..
<date> <time> <DIR> Critical_powershell.exe_7dd54f49935ce48b2dd99d1c64df29a5cfb73db_00000000_cab_096cc802
0 File(s) 0 bytes
3 Dir(s) 23,291,658,240 bytes free
Windows Error Reporting provides many settings to customize the problem reporting experience. For further information, please refer to the Windows Error Reporting documentation.
Troubleshooting using Windows Error Reporting reports
Physical disk failed to come online
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder:
PS C:Windowssystem32> dir C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchiveCritical_PhysicalDisk_b46b8883d892cfa8a26263afca228b17df8133d_00000000_cab_08abc39c
Here’s an example of the output:
Volume in drive C is INSTALLTO
Volume Serial Number is 4031-E397
<date> <time> <DIR> .
<date> <time> <DIR> ..
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_1.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_10.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_11.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_12.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_13.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_14.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_15.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_16.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_17.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_18.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_19.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_2.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_20.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_21.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_22.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_23.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_24.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_25.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_26.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_27.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_28.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_29.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_3.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_30.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_31.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_32.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_33.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_34.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_35.evtx
<date> <time> 2,166,784 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_36.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_37.evtx
<date> <time> 33,194 Report.wer
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_38.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_39.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_4.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_40.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_41.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_5.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_6.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_7.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_8.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_ERROR_8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a_9.evtx
<date> <time> 7,382 WERC263.tmp.WERInternalMetadata.xml
<date> <time> 59,202 WERC36D.tmp.csv
<date> <time> 13,340 WERC38D.tmp.txt
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what failed.
EventType=Failover_clustering_resource_error
<skip>
Sig[0].Name=ResourceType
Sig[0].Value=Physical Disk
Sig[1].Name=CallType
Sig[1].Value=ONLINERESOURCE
Sig[2].Name=RHSCallResult
Sig[2].Value=5018
Sig[3].Name=ApplicationCallResult
Sig[3].Value=999
Sig[4].Name=DumpPolicy
Sig[4].Value=5225058577
DynamicSig[1].Name=OS Version
DynamicSig[1].Value=10.0.17051.2.0.0.400.8
DynamicSig[2].Name=Locale ID
DynamicSig[2].Value=1033
DynamicSig[27].Name=ResourceName
DynamicSig[27].Value=Cluster Disk 10
DynamicSig[28].Name=ReportId
DynamicSig[28].Value=8d06c544-47a4-4396-96ec-af644f45c70a
DynamicSig[29].Name=FailureTime
DynamicSig[29].Value=2017//12//12-22:38:05.485
Since the resource failed to come online, no dumps were collected, but the Windows Error Reporting report did collect logs. If you open all .evtx files using Microsoft Message Analyzer, you will see all of the information that was collected using the following queries through the system channel, application channel, failover cluster diagnostic channels, and a few other generic channels.
PS C:Windowssystem32> (Get-ClusterResourceType -Name "Physical Disk").DumpLogQuery
Here’s an example of the output:
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Kernel-PnP/Configuration">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-ReFS/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Ntfs/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Ntfs/WHC">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Storport/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Storport/Health">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Storport/Admin">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-ClassPnP/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-ClassPnP/Admin">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-ScmBus/Certification">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 86400000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-ScmBus/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-PmemDisk/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-NvdimmN/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-INvdimm/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-PersistentMemory-VirtualNvdimm/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Disk/Admin">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Disk/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-ScmDisk0101/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Partition/Diagnostic">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Volume/Diagnostic">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-VolumeSnapshot-Driver/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-FailoverClustering-Clusport/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-FailoverClustering-ClusBflt/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-StorageSpaces-Driver/Diagnostic">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-StorageManagement/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 86400000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-StorageSpaces-Driver/Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Storage-Tiering/Admin">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Hyper-V-VmSwitch-Operational">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select Path="Microsoft-Windows-Hyper-V-VmSwitch-Diagnostic">*[System[TimeCreated[timediff(@SystemTime) <= 600000]]]</Select></Query></QueryList>
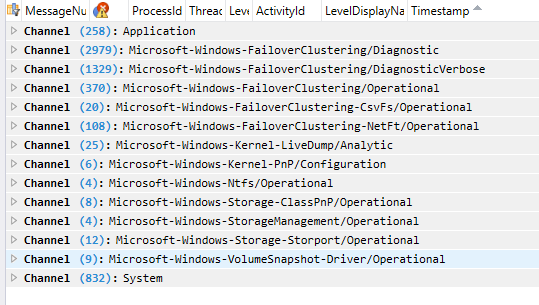
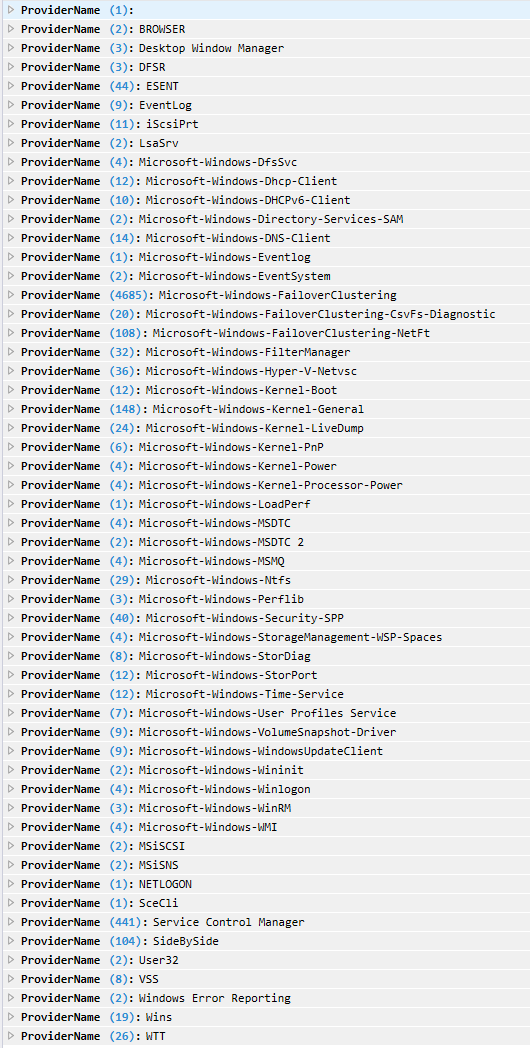
Message Analyzer enables you to capture, display, and analyze protocol messaging traffic. It also lets you trace and assess system events and other messages from Windows components. You can download Microsoft Message Analyzer from here. When you load the logs into Message Analyzer, you will see the following providers and messages from the log channels.
You can also group by providers to get the following view:
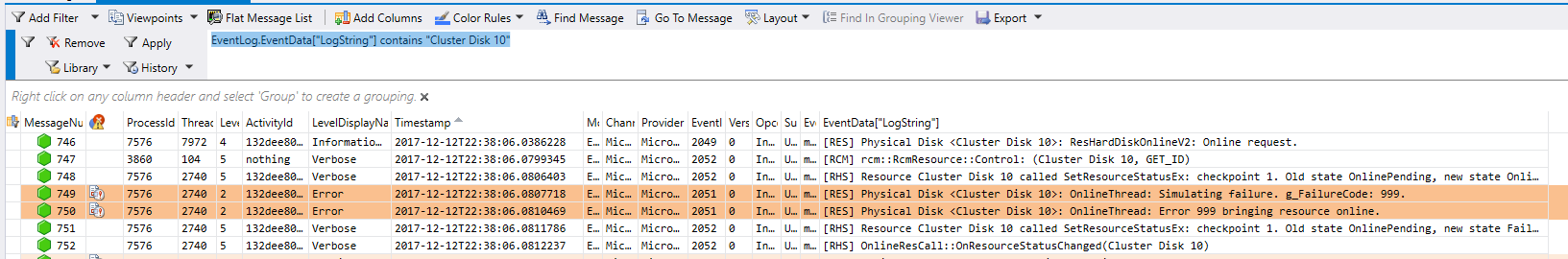
To identify why the disk failed, navigate to the events under FailoverClustering/Diagnostic and FailoverClustering/DiagnosticVerbose. Then run the following query: EventLog.EventData[«LogString»] contains «Cluster Disk 10». This will give you give you the following output:
Physical disk timed out
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder. The folder contains log files and dump files for RHS, clussvc.exe, and of the process that hosts the «smphost» service, as shown below:
PS C:Windowssystem32> dir C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchiveCritical_PhysicalDisk_64acaf7e4590828ae8a3ac3c8b31da9a789586d4_00000000_cab_1d94712e
Here’s an example of the output:
Volume in drive C is INSTALLTO
Volume Serial Number is 4031-E397
<date> <time> <DIR> .
<date> <time> <DIR> ..
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_1.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_10.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_11.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_12.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_13.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_14.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_15.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_16.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_17.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_18.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_19.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_2.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_20.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_21.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_22.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_23.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_24.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_25.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_26.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_27.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_28.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_29.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_3.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_30.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_31.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_32.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_33.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_34.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_35.evtx
<date> <time> 2,166,784 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_36.evtx
<date> <time> 1,118,208 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_37.evtx
<date> <time> 28,340,500 memory.hdmp
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_38.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_39.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_4.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_40.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_41.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_5.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_6.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_7.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_8.evtx
<date> <time> 69,632 CLUSWER_RHS_HANG_75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224_9.evtx
<date> <time> 4,466,943 minidump.0f14.mdmp
<date> <time> 1,735,776 minidump.2200.mdmp
<date> <time> 33,890 Report.wer
<date> <time> 49,267 WER69FA.tmp.mdmp
<date> <time> 5,706 WER70A2.tmp.WERInternalMetadata.xml
<date> <time> 63,206 WER70E0.tmp.csv
<date> <time> 13,340 WER7100.tmp.txt
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what call or resource is hanging.
EventType=Failover_clustering_resource_timeout_2
<skip>
Sig[0].Name=ResourceType
Sig[0].Value=Physical Disk
Sig[1].Name=CallType
Sig[1].Value=ONLINERESOURCE
Sig[2].Name=DumpPolicy
Sig[2].Value=5225058577
Sig[3].Name=ControlCode
Sig[3].Value=18
DynamicSig[1].Name=OS Version
DynamicSig[1].Value=10.0.17051.2.0.0.400.8
DynamicSig[2].Name=Locale ID
DynamicSig[2].Value=1033
DynamicSig[26].Name=ResourceName
DynamicSig[26].Value=Cluster Disk 10
DynamicSig[27].Name=ReportId
DynamicSig[27].Value=75e60318-50c9-41e4-94d9-fb0f589cd224
DynamicSig[29].Name=HangThreadId
DynamicSig[29].Value=10008
The list of services and processes that we collect in a dump is controlled by the following property: PS C:Windowssystem32> (Get-ClusterResourceType -Name «Physical Disk»).DumpServicesSmphost
To identify why the hang happened, open the dump files. Then run the following query: EventLog.EventData[«LogString»] contains «Cluster Disk 10» This will give you give you the following output:
We can cross-examine this with the thread from the memory.hdmp file:
# 21 Id: 1d98.2718 Suspend: 0 Teb: 0000000b`f1f7b000 Unfrozen
# Child-SP RetAddr Call Site
00 0000000b`f3c7ec38 00007ff8`455d25ca ntdll!ZwDelayExecution+0x14
01 0000000b`f3c7ec40 00007ff8`2ef19710 KERNELBASE!SleepEx+0x9a
02 0000000b`f3c7ece0 00007ff8`3bdf7fbf clusres!ResHardDiskOnlineOrTurnOffMMThread+0x2b0
03 0000000b`f3c7f960 00007ff8`391eed34 resutils!ClusWorkerStart+0x5f
04 0000000b`f3c7f9d0 00000000`00000000 vfbasics+0xed34
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hello,
I need to configure Windows server 2016 WER or a memory dump for a specific application / executable (*.exe). The applications runs as a service and fails unexpected some times and we want to gather and analyze a memory dump and / or WER information.
We don’t want to configure a default memory dump only for that singele application.
Thank you in advance for your help
Stephan (Germany)
regards Stephan
-
Edited by
Wednesday, January 9, 2019 12:59 PM
additions. OS = 2016
-
Edited by
Answers
-
Hi Stephan,
Thanks for your replying.
Have you gone through the link that I provided? It explains clearly. WER do can capture a dump for a specific application.
You can also provide per-application settings that override the global settings. To create a per-application setting, create a new key for your application under
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error ReportingLocalDumps(for example,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error ReportingLocalDumpsMyApplication.exe). Add your dump settings under the
MyApplication.exekey. If your application crashes, WER will first read the global settings, and then will override any of the settings with your application-specific settings.As for the memory dump, it is usually used for the situation like blue screen, system hang.
Best regards,
Please remember to mark the replies as answers if they help.
If you have feedback for TechNet Subscriber Support, contact
tnmff@microsoft.com.-
Edited by
cora ZhouMicrosoft contingent staff
Tuesday, January 15, 2019 6:04 AM -
Marked as answer by
Stephan-L
Wednesday, January 16, 2019 10:11 AM
-
Edited by
The Windows Error Reporting service (WER) is used to collect the debug information about system and third-party app failures and send error reports to Microsoft servers. This information should be analyzed by MSFT and if there is a solution, it will be sent to a user through Windows Error Reporting Response. Actually, few people use this feature, although Microsoft always leaves WER service enabled by default in the latest Windows versions. In most cases, people remember about WER when they see that C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue occupies much space on the system drive (up to several dozens of GB) even though NTFS compression is enabled for this directory by default.
Contents:
- Windows Error Reporting Service
- How to Clear the WERReportQueue Folder on Windows?
- Disable Windows Error Reporting on Windows Server
- How to Disable or Enable Error Reporting on Windows 10?
- How to Disable Automatic Windows Error Reporting via GPO?
Windows Error Reporting Service
Windows Error Reporting displays a dialog box when an application error occurs, prompting you to submit an error report to Microsoft. When you see the “YourAppName.exe has stopped working, Windows is collecting more information about the problem” error message in Windows, the Windows Error Reporting service runs the WerFault.exe tool to collect debug data (may include a memory dump).
User data is saved to the user profile:
%USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsWER
And the system data goes to the ProgramData directory:
%ALLUSERSPROFILE%MicrosoftWindowsWER
The Windows Error Reporting service is a separate Windows service. You can check the status of the service using the PowerShell command:
Get-Service WerSvc
In the WERReportQueue directory there are a lot of folders with the names in the following format:
- Critical_6.3.9600.11285_{ID}_00000000_cab_3212dd23
- Critical_powershell.exe_{ID}_cab_332a45c5
- Critical_sqlservr.exe__{ID}_cab_b3a200181
- NonCritical_7.9.9600.11285__{ID}_0bfab19a
- AppCrash_cmd.exe_{ID}_dba332ad_12eb5425
As you can see, the directory name contains the severity level of an event and the name of the specific EXE file that has crashed. In all folders, there is a file called Report.wer, which contains the description of the errors and some files with the additional information.
How to Clear the WERReportQueue Folder on Windows?
Typically, the size of each folder is small, but in some cases a memory dump is generated for a problem process that occupies much space. The screenshot below shows that the size of memory.hdmp is about 610 MB. A couple of such dumps can occupy several gigabytes on the system drive.
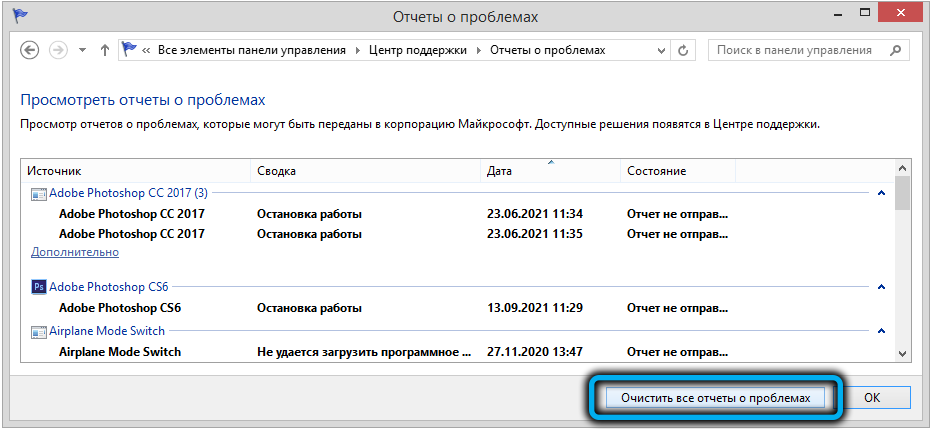
To clear all these errors and logs using the built-in tools, open the Control Panel and go to System and Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance -> View reliability history -> View all problem reports, then click Clear all problem reports.
To free up some disk space quickly, you can manually delete debug and log files generated by the WER service in the following folders:
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue
The following PowerShell commands will remove all files older than 30 days from the WER directories:
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30) | Remove-Item -Force -Recurse
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30) | Remove-Item -Force –Recurse
To clean up the WER directories in all user profiles, use the following PowerShell script:
$users = Get-ChildItem c:users|where{$_.name -notmatch 'Public|default'}
foreach ($user in $users){
Get-ChildItem "C:Users$UserAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsWER " –Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Remove-Item –force –Recurse
}
Disable Windows Error Reporting on Windows Server
On Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2, you can manage WER service state using PowerShell. You can disable Windows Error Reporting service:
Get-Service WerSvc| stop-service –passthru -force
Set-Service WerSvc –startuptype manual –passthru
But there are better ways to disable WER on Windows. The PowerShell version 4.0 adds a separate WindowsErrorReporting module:
Get-Command -Module WindowsErrorReporting
You can check the status of the Windows Error Reporting service with the command:
Get-WindowsErrorReporting
To disable WER, run:
Disable-WindowsErrorReporting
On Windows Server 2012 R2 you can disable Windows Error Reporting via the control panel (Control Panel -> System and Security -> Action Center -> Maintenance -> Settings -> select I don’t want to participate, and don’t ask me again.
How to Disable or Enable Error Reporting on Windows 10?
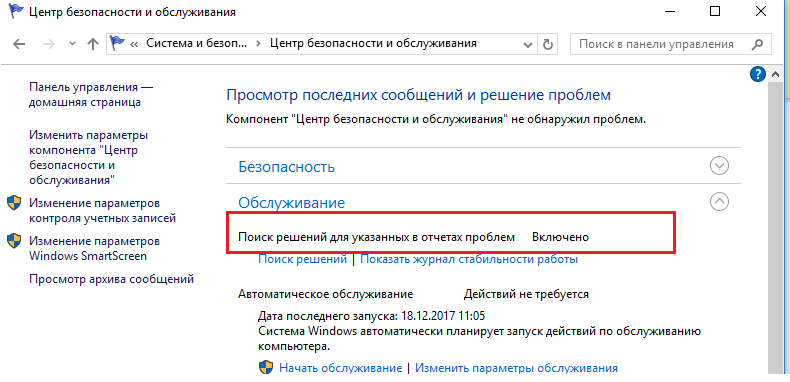
In Windows 10 you cannot disable the Error Reporting through the Control Panel. You can check the component status in the Control Panel -> System & Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance. As you can see, the Report problems parameter is enabled.
You can disable Windows Error Reporting on Windows 10 via the registry. To do it, create a new DWORD (32-bit) parameter with the name Disabled and the value 1 under the registry key HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting.
You can disable Windows error collection for specific users with the command:
reg add "HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Or disable WER for everyone:
reg add "HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Now let’s check the status of the Report problems parameter in the Control Panel again. It should be Off.
How to Disable Automatic Windows Error Reporting via GPO?
You can disable logging by the Windows Error Reporting service through Group Policy. Open the local (gpedit.msc) or domain GPO (gpmc.msc) editor and go to the following GPO section Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Error Reporting. Find the policy named Disable Windows Error Reporting and set it to Enabled. This will disable Windows data collection and error reporting.
There is a similar policy in the User Configuration section.
Update the GPO settings (no reboot required).
As a result, Windows will no longer generate application and system error messages and will no longer be sent to Microsoft.
Windows 10: Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting
Discus and support Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting in Windows 10 Customization to solve the problem; Some report application (C++) exes occasionally fail during an overnight batch. Some of these failures cause a popup like «… has stopped working»…
Discussion in ‘Windows 10 Customization’ started by GerardIE, Nov 29, 2018.
-
Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting
Some report application (C++) exes occasionally fail during an overnight batch. Some of these failures cause a popup like «… has stopped working» which is from the WerFault.exe. The batch controller should decide what to do with failed jobs not the server operating system.
We have tried the settings below we still get the annoying popups.
1. The Windows Error reporting Service is NOT RUNNING.
2. The exes have been added using the Local Group Policy Editor to be excluded from error reporting:
User Configuration ->Administrative Templates ->Windows ComponentsWindows Error Reporting->Advanced Error Reporting settings->List of applications to be excluded
Computer Configuration ->Administrative Templates ->Windows ComponentsWindows Error Reporting->Advanced Error Reporting settings->List of applications to be excluded
Computer Configuration ->Administrative Templates ->Windows ComponentsWindows Error Reporting->Advanced Error Reporting settings->List of applications to never report errors for
The server has been rebooted.
-
FIXED!! Windows 7 sp1 never ends searching for updatesThey made it part of the WU client then, or it’s two different things doing the same. Too bad you can’t download it separately.
-
Unable to disable subtitles in Windows Media Player
Hi folks,
I rented Shutter Island last night and was unable to disable the subtitles in Windows Media Player. Is this something to do with regional playback protection? Does anybody have a workaround to fix this issue?
Thanks in advance.
-
Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting
Questions about Windows Server 2016 and 2012 R2
Hey guys, hopefully this is the right section to post my question in. I’m looking at helping out a friend who is working on a server solution for his small business (about 25 employees). He is currently looking at a Dell PowerEdge T430 server, and I am trying to come up with an alternative that doesn’t cost like $4000 USD. It seems that Windows Server 2016 charges by Cores and CALs? What are CALs? We’re looking to install it onto bare-metal, meaning it’s not running in a VM, windows server is going to be installed directly onto it. I was also looking at Windows Server 2012 R2 because it seems a lot cheaper and doesn’t do stupid shit like charging per core. Is Windows Server 2012 R2 still a decent option?
I think his main goal is to have people log onto the server as a domain and share files off of it, and save his archives to it. This was going to be my recommended build:
System Builder — Ryzen 7 1700 3 GHz 8-Core, HAF X ATX Full Tower — PCPartPickerAgain, I’m trying to figure out about Windows Server 2016 vs 2012 R2 and what version of 2016 to get if he decides to go that route. For a raid card since I want to be running those two 6tb hitachi drives in raid 1, I figured something like this LSI card would suffice:
https://www.ebay.com/itm/LSI-9267-8…987173?hash=item21175e7565:gNIAAOSwAuZX5C28
Any thoughts and suggestions? Really could use help with the OS side of things, I think that the hardware I selected is pretty good. I already have a HAF X case I’d just throw in for like $100, which will suffice for a case. Thanks for all your guys’ thoughts and suggestions.
Edit: Just to explain why I am so desperately trying to help him get away from Dell, I took a screenshot of the hard drive selection for the customizing Dell Server. They want $163.17 USD per 1TB 7.2K RPM Sata Drive, which is not just ridiculous but it’s highway robbery.
Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting
-
Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting — Similar Threads — Server 2016 unable
-
unable to add IIS roles on Windows server 2016
in Windows 10 Installation and Upgrade
unable to add IIS roles on Windows server 2016: the request to add or remove features on the specified server failed.installation of one or more roles ,role services or features failed.the parameter is incorrect .error:0x80070057… -
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder — Windows 11
in Windows 10 Gaming
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder — Windows 11: Hi, Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder crashes when opening in windows 11. I have tried re installing and on another windows 11 machine.Can’t find a way to report this bug other than here?… -
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder — Windows 11
in Windows 10 Software and Apps
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder — Windows 11: Hi, Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Report Builder crashes when opening in windows 11. I have tried re installing and on another windows 11 machine.Can’t find a way to report this bug other than here?… -
Windows Server 2016
in Windows 10 Customization
Windows Server 2016: DearHow you hide windows updates on the Windows server 2016. I tried downloading WUSHOWHIDE.DIAGCAD from Microsoft site download link broken.
Can someone please assist.
Thank You…
-
Windows Error Reporting High CPU load, unable to disable WER.
in Windows 10 Customization
Windows Error Reporting High CPU load, unable to disable WER.: The following steps were used to disable the service, however it continues to run after restart.Disabled in Windows Service Manager
Disabled in Group Policy Manager
Disabled in Control Panel, Security and Maintenance
msconfig DISABLE on startup
msconfig
UNCHECK the…
-
Windows Server 2016
in Windows 10 Ask Insider
Windows Server 2016: I’ve inherited some problems at a new employer related to Windows Server 2016. I know Server 2012 and older pretty well, but not 2016.The problem is that something is killing Admin Control. Admins can still log in, but things that require Admin Elevation or just admin…
-
Windows server 2016
in Windows 10 Installation and Upgrade
Windows server 2016: Hi,Please can you help me to understand if Windows server 2016 required MS17-010 patch.
https://answers.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/forum/all/windows-server-2016/8b50913e-b88d-4a84-9e93-a49a15baa37f
-
WIndow server 2016 error
in Windows 10 BSOD Crashes and Debugging
WIndow server 2016 error: Dear Microsoft Team,We finded the problem on our server, the error is:
The application-specific permission settings do not grant Local Activation permission for the COM Server application with CLSID
{D63B10C5-BB46-4990-A94F-E40B9D520160}
and APPID… -
Disable Windows Error Reporting
in Windows 10 Performance & Maintenance
Disable Windows Error Reporting: When a program crashes, how do you disable the menu that pops up that ask if you want to fix it and then attempts to send data?9719
Users found this page by searching for:
-
how to stop windows error reporting windows server 2016
,
-
windows problem reporting 2016
,
-
server 2016 disable windows error reporting
,
- disable windows error reporting Server 2016,
- Disable error reporting dumps Server 2016,
- disable windows error reporting in server 2016,
- windows server 2016 configure windows error reporting,
- disable windows error reporting windows 2016,
- how to stop windows error reporting service windows 2016,
- disable windows problem reporting server 2016

Содержание
- Для чего нужна служба «Windows Error Reporting» и как отключить ее в Windows 7, 8.1 и 10
- Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 7 и 8.1
- Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 10
- Универсальный способ отключения Error Reporting
- Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting
- Enabling event channels
- Gathering Logs
- Gathering Windows Error Reporting reports
- Troubleshooting using Windows Error Reporting reports
- Physical disk failed to come online
- Physical disk timed out
- Microsoft Windows 7: рекомендации по улучшению стабильности приложений
- Механизм Windows Error Reporting
- Использование механизма Windows Error Reporting
- Заключение
Для чего нужна служба «Windows Error Reporting» и как отключить ее в Windows 7, 8.1 и 10
Когда в работе какой-то программы происходит ошибка, Windows автоматически регистрирует это событие и запускает штатную утилиту Windows Error Reporting, которая формирует отчет и предлагает отправить его на сервера Microsoft. Отправка лога не осуществляется автоматически, более того, большинство пользователей предпочитают не делиться информацией о программных ошибках и были бы не прочь отключить эту функцию вообще.
В Windows 7 и 8.1 это можно сделать через графический интерфейс системы, если же вы хотите отключить Windows Error Reporting в Windows 10, нужно отредактировать один ключ в реестре или изменить значение соответствующей ему политики в редакторе gpedit.msc . Существует и универсальный способ, одинаково подходящий для всех версий Windows, но о нём будет сказано ниже.
Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 7 и 8.1
Откройте через окошко «Выполнить» ( Win + R ) Центр поддержки командой wscui.cpl апплет «Центр поддержки».
Нажмите в меню справа ссылку «Параметры центра поддержки».
На следующей странице нажмите ссылку «Параметры отчета о неполадках».
И активируйте радиокнопку «Не проверять на наличие новых решений».
Отключение Error Reporting в Windows 10
В Windows 10 опция «Параметры отчета о неполадках» была удалена из окна параметров центра поддержки, поэтому для отключения формирования отчетов о программных ошибках в этой версии системы придется действовать в обход.
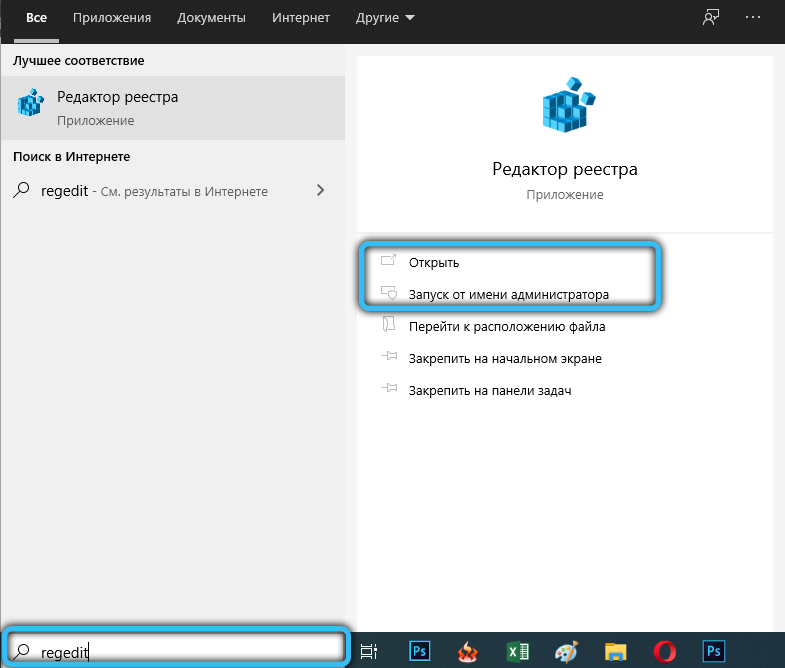
Откройте через окошко «Выполнить» одноименной командой редактор реестра Regedit и раскройте ключ:
HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting
Справа создайте новый DWORD -параметр.
Назовите его Disabled и задайте в качестве его значения единицу.
Сохраните настройки, закройте редактор реестра и перезагрузите компьютер.
Описание примера отключения функции Error Reporting через редактор групповых политик мы опускаем, поскольку его результат является эквивалентным применяемому твику реестра, к тому же редактор gpedit.msc доступен не всех редакциях Windows.
Универсальный способ отключения Error Reporting
Предложенный ниже способ является универсальным и одинаково работает в Windows 7, 8.1 и Windows 10.
Вызовите окошко «Выполнить» и выполните в нём команду services.msc , чтобы открыть оснастку управления службами.
Отыщите справа службу «Служба регистрации ошибок Windows», откройте ее свойства и выставьте параметры так, как показано на скриншоте после чего сохраните настройки.
Любители командной строки могут отключить ее через консоль.
Запустив командную строку или PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните в ней команду:
sc config wersvc start=disabled
gpupdate /force
Чтобы обновить политику без перезагрузки компьютера.
Источник
Troubleshooting a Failover Cluster using Windows Error Reporting
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server, Azure Stack HCI, versions 21H2 and 20H2
Windows Error Reporting (WER) is a flexible event-based feedback infrastructure designed to help advanced administrators or Tier 3 support gather information about the hardware and software problems that Windows can detect, report the information to Microsoft, and provide users with any available solutions. This reference provides descriptions and syntax for all WindowsErrorReporting cmdlets.
The information on troubleshooting presented below will be helpful for troubleshooting advanced issues that have been escalated and that may require data to be sent to Microsoft for triaging.
Enabling event channels
When Windows Server is installed, many event channels are enabled by default. But sometimes when diagnosing an issue, we want to be able to enable some of these event channels since it will help in triaging and diagnosing system issues.
You could enable additional event channels on each server node in your cluster as needed; however, this approach presents two problems:
- You have to remember to enable the same event channels on every new server node that you add to your cluster.
- When diagnosing, it can be tedious to enable specific event channels, reproduce the error, and repeat this process until you root cause.
To avoid these issues, you can enable event channels on cluster startup. The list of enabled event channels on your cluster can be configured using the public property EnabledEventLogs. By default, the following event channels are enabled:
Here’s an example of the output:
The EnabledEventLogs property is a multistring, where each string is in the form: channel-name, log-level, keyword-mask. The keyword-mask can be a hexadecimal (prefix 0x), octal (prefix 0), or decimal number (no prefix) number. For instance, to add a new event channel to the list and to configure both log-level and keyword-mask you can run:
If you want to set the log-level but keep the keyword-mask at its default value, you can use either of the following commands:
If you want to keep the log-level at its default value, but set the keyword-mask you can run the following command:
If you want to keep both the log-level and the keyword-mask at their default values, you can run any of the following commands:
These event channels will be enabled on every cluster node when the cluster service starts or whenever the EnabledEventLogs property is changed.
Gathering Logs
After you have enabled event channels, you can use the DumpLogQuery to gather logs. The public resource type property DumpLogQuery is a mutistring value. Each string is an XPATH query as described here.
When troubleshooting, if you need to collect additional event channels, you can a modify the DumpLogQuery property by adding additional queries or modifying the list.
To do this, first test your XPATH query using the get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet:
Next, append your query to the DumpLogQuery property of the resource:
And if you want to get a list of queries to use, run:
Gathering Windows Error Reporting reports
Windows Error Reporting Reports are stored in %ProgramData%MicrosoftWindowsWER
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsQueue folder contains reports that are waiting to be uploaded to Watson.
Here’s an example of the output:
Inside the WER folder, the ReportsArchive folder contains reports that have already been uploaded to Watson. Data in these reports is deleted, but the Report.wer file persists.
Here’s an example of the output:
Windows Error Reporting provides many settings to customize the problem reporting experience. For further information, please refer to the Windows Error Reporting documentation.
Troubleshooting using Windows Error Reporting reports
Physical disk failed to come online
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder:
Here’s an example of the output:
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what failed.
Since the resource failed to come online, no dumps were collected, but the Windows Error Reporting report did collect logs. If you open all .evtx files using Microsoft Message Analyzer, you will see all of the information that was collected using the following queries through the system channel, application channel, failover cluster diagnostic channels, and a few other generic channels.
Here’s an example of the output:
Message Analyzer enables you to capture, display, and analyze protocol messaging traffic. It also lets you trace and assess system events and other messages from Windows components. You can download Microsoft Message Analyzer from here. When you load the logs into Message Analyzer, you will see the following providers and messages from the log channels.
You can also group by providers to get the following view:
To identify why the disk failed, navigate to the events under FailoverClustering/Diagnostic and FailoverClustering/DiagnosticVerbose. Then run the following query: EventLog.EventData[«LogString»] contains «Cluster Disk 10». This will give you give you the following output:
Physical disk timed out
To diagnose this issue, navigate to the WER report folder. The folder contains log files and dump files for RHS, clussvc.exe, and of the process that hosts the «smphost» service, as shown below:
Here’s an example of the output:
Next, start triaging from the Report.wer file — this will tell you what call or resource is hanging.
The list of services and processes that we collect in a dump is controlled by the following property: PS C:Windowssystem32> (Get-ClusterResourceType -Name «Physical Disk»).DumpServicesSmphost
Источник
Microsoft Windows 7: рекомендации по улучшению стабильности приложений
В предыдущей статье данного цикла, посвященной механизму Application Restart and Recovery, мы упомянули механизм Windows Error Reporting (WER). О нем и пойдет речь в настоящей статье данного цикла
В предыдущей статье данного цикла, посвященной механизму Application Restart and Recovery, мы упомянули механизм Windows Error Reporting (WER). О нем и пойдет речь в настоящей статье данного цикла.
Механизм Windows Error Reporting
С помощью механизма Windows Error Reporting (WER) можно собирать данные об ошибках, происходящих в приложениях, и либо отсылать эту информацию на специальный сайт Microsoft (сайт http://winqal.microsoft.com), либо сохранять ее локально. Сбор детальной информации об ошибках и сбоях помогает в устранении недостатков приложений, коррекции ошибок, упрощает выпуск пакетов обновлений и новых версий приложений, обеспечивает общую стабильность и надежность как самих приложений, так и операционной системы.
Отметим, что компания Microsoft сама активно использует механизм Windows Error Reporting как в процессе разработки, так и после выпуска продуктов на рынок. Так, продуктовая группа Microsoft Office исправила 50% ошибок в Office Service Pacl 2, продуктовая группа Visual Studio — 74% ошибок в Beta 1 Visual Studio 2005, 29% ошибок в Windows XP было исправлено в Windows XP Service Pack 1. В настоящее время более 2 тыс. компаний применяют сервисы Windows Error Reporting для улучшения качества своих приложений.
Механизм Windows Error Reporting впервые появился в Windows XP, был существенно расширен в Windows Vista и получил дальнейшее развитие в Windows Server 2008, Vista Service Pack 1 и Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2. Так, на уровне Windows Vista у разработчиков появилась возможность не только получать информацию о сбоях, произошедших в приложениях, но и данные о производительности. Теперь можно более гибко создавать, настраивать и отсылать отчеты о проблемах, улучшились средства онлайнового анализа данных и упростился механизм коммуникаций с пользователями — через механизм Problem Reports and Solutions (в Windows Vista — Start —> Control Panel —> System and Maintenance —> Problem Reports and Solutions —> View Problem History) и Action Center (в Windows 7). Затем в Windows Server 2008 и Vista Service Pack 1 появилась возможность создания локальных дампов, а в Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2 добавлена возможность генерации исключений, которые не будут обрабатываться традиционными обработчиками и будут приводить к немедленному завершению приложения и автоматическому запуску механизма Windows Error Reporting, а также возможность задания внешнего процесса — обработчика исключений, который будет вызываться для получения названия события, параметров отчета об ошибке и опционального запуска отладчика.
Использование механизма Windows Error Reporting
Давайте кратко рассмотрим, как разработчики могут применять механизм Windows Error Reporting для получения информации о сбоях и других проблемах со своими приложениями. Начиная с Windows Vista Windows по умолчанию предоставляет отчет о сбоях, зависаниях и ошибках уровня ядра операционной системы (kernel faults) для всех приложений — внесения изменений в код приложений не требуется. При необходимости отчет включает мини-дамп памяти и дамп «кучи» приложения, приложениям требуется использование программных интерфейсов в тех случаях, когда необходима отсылка какойто специфической для приложения дополнительной информации. Поскольку ядро Windows автоматически собирает в отчет информацию о необработанных исключениях, приложениям не нужно обрабатывать исключения, приводящие к фатальным ошибкам.
В случае возникновения сбоев, зависаний или ошибок уровня ядра операционной системы механизм Windows Error Reporting выполняет следующую последовательность действий:
- Возникновение проблемы.
- Ядро операционной системы вызывает WER.
- WER собирает данные, создает отчет и, при необходимости, запрашивает от пользователя подтверждение на отсылку отчета.
- При получении подтверждения WER отсылает отчет в Microsoft (так называемый Watson Server).
- Если серверу требуются дополнительные данные, WER собирает их и, при необходимости, запрашивает от пользователя подтверждение на отсылку.
- Если приложение зарегистрировано для перезапуска (эту тему мы обсуждали ранее), то WER выполняет соответствующую косвенно вызываемую функцию приложения.
- Если существует решение проблемы, приведшей к сбою, пользователь получает уведомление с помощью соответствующих средств операционной системы.
В зависимости от ситуации в CAB-файле могут присутствовать различные типы дампов, которые можно различать по расширению имени файла (табл. 1).
В приложении могут использоваться перечисленные ниже функции для настройки содержимого отчета, посылаемого в Microsoft, — регистрационная функция указывает Web на необходимость включения в создаваемый отчет указанных файлов и блоков памяти.
Для включения в состав отчета файла применяется функция WerRegisterFile(), которой в качестве параметров передаются: полное имя файла, его тип (одно из значений WER_REGISTER_FILE_TYPE) и два флага: WER_DELETE_FILE_WHEN_DONE, указывающий на то, что файл должен быть удален после отсылки отчета, и WER_ANONYMOUS_ DATA, указывающий на то, что в файле не содержатся приватные данные. Возможные значения параметра WER_REGISTER_FILE_ TYPE приведены в табл. 2.
Отметим, что задача генерации дампа памяти возлагается на разработчика приложения — для ее решения можно применять, например, отладочные механизмы, описанные в Windows SDK (см. функцию MiniDumpWriteDump()).
Для исключения файла из отчета следует использовать функцию WerUnRegisterFile(), указав ей в качестве параметра имя исключаемого файла.
В большинстве сценариев отсылка дополнительных файлов происходит только при получении от сервера соответствующего запроса. В случае отсылки дополнительных файлов необходимо применять флаг WER_ADD_ REGISTERED_DATA при вызове функции WerReportSubmit() — о ней мы расскажем далее.
Для включения в состав отчета копии области памяти применяется функция WerRegisterMemoryBlock(), в качестве параметров которой передаются адрес начала включаемого блока памяти и размер этого блока в байтах (максимальный размер блока памяти — WER_MAX_MEM_BLOCK_SIZE). Для отмены включения копии области памяти в отчет следует применять функцию WerUnRegisterMemoryBlock(). В случае отсылки данных из памяти необходимо использовать флаг WER_ADD_REGISTERED_DATA при вызове функции WerReportSubmit().
Функции WerSetFlags() и WerGetFlags() могут применяться соответственно для управления состоянием процесса в момент генерации отчета об ошибках и получения информации о настройках.
Процесс генерации и отсылки отчета состоит из нескольких шагов. Инициализация отчета выполняется вызовом функции WerReportCreate(), с помощью которой указывается тип события, для которого создается отчет, тип отчета (WerReportNonCritical — для сбоев с возможностью восстановления и WerReportCritical — для сбоев, повлекших аварийное завершение приложения), ссылка на информацию, включаемую в отчет (см. структуру WER_REPORT_INFORMATION), и переменная, которая будет содержать ссылку на созданный отчет, — ReportHandle.
После того как отчет успешно инициализирован, необходимо добавить в него параметры первой и второй групп. Параметры первой группы задаются с помощью функции WerReport-Set-Parameter(), которой передается ссылка на созданный отчет (результат успешного выполнения функции WerReportCreate), набор флагов, имя параметра и его значение (16-битная строка в Unicode, заканчивающаяся нулем).
Для включения в состав отчета дополнительных параметров применяется функция WerReportAddSecondaryParameter(), которой передается ссылка на отчет, имя параметра и его значение.
Помимо возможности включения в состав отчетов файлов и снимков областей памяти, предусмотрена передача в составе отчета и дампов памяти — для этого можно использовать функцию WerReportAddDump(), в качестве параметров которой указываются ссылка на отчет, ссылки на процесс и поток, для которых был создан дамп, тип дампа (одно из значений WER_DUMP_TYPE), информация об исключении (указатель на структуру типа WER_EXCEPTION_INFORMATION), дополнительные опции (тип данных WER_DUMP_CUSTOM_OPTIONS) и флаги. Отметим, что процесс, для которого создается дамп, должен иметь права доступа STANDARD_RIGHTS_READ и PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION.
Для включения в состав отчета файлов мы применяем функцию WerReportAddFile(), которой передаем ссылку на отчет, полное имя файла, тип файла (WER_FILE_ TYPE) и дополнительные флаги.
Помимо этого разработчикам предоставляется возможность настройки пользовательского интерфейса — выбора информации, отображаемой в системной диалоговой панели. Для этих целей служит функция WerReportSetUI Option(), которой передается ссылка на отчет, тип интерфейса отчета (WER_REPORT_UI) и значение отображаемой строки. Приложение может модифицировать любое из полей интерфейсного элемента, заданного параметром WER_REPORT_UI; каждый вызов функции позволяет модифицировать только одно поле. Функция WerReportSetUIOption() может вызываться в любой момент работы приложения до непосредственной отсылки отчета.
После того как отчет сформирован и настроен, мы используем функцию WerReportSubmit() для отсылки отчета. В качестве параметров этой функции передаются ссылка на отчет, тип пользовательского интерфейса (наличие прав администратора, подтверждение отсылки и т.п.) и набор флагов. После того как отчет послан, следует закрыть ссылку на него, используя функцию WerReportCloseHandle().
Для отключения приложения от механизма Windows Error Reporting следует использовать функцию WerAddExcludedApplication(), а для повторного подключения — функцию WerRemoveExcludedApplication().
Настройки Windows Error Reporting располагаются в двух ветвях реестра:
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting;
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting.
Наиболее полезные настройки показаны в табл. 3.
Заключение
В данном цикле статей мы обсудили различные вопросы улучшения стабильности работы приложений. Мы рассмотрели технику, позволяющую избежать утечки памяти, предотвратить зависание приложений, обсудили использование механизма Application Restart and Recovery, позволяющего перезапускать приложения, которые либо заблокировали какието ресурсы, либо перестали реагировать на сообщения системы, и механизма Windows Error Reporting, который дает возможность собирать данные о сбоях, происходящих в приложениях.
В следующих статьях, посвященных операционной системе Windows 7 для разработчиков, мы рассмотрим ряд изменений на уровне ядра операционной системы, которые могут представлять интерес для разработчиков приложений.
Источник
Служба WER (Windows Error Reporting) служит для сбора и отправки отладочной информации о падении системных и сторонних приложений в Windows на сервера Microsoft. По задумке Microsoft, эта информация должна анализироваться и при наличии решения, вариант исправления проблемы должен отправляется пользователю через Windows Error Reporting Response. Но по факту мало кто пользуется этим функционалом, хотя Microsoft настойчиво оставляет службу сбора ошибок WER включенной по умолчанию во всех последних версиях Windows. В большинстве случае о службе WER вспоминают, когда каталог C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue начинает занимать на системном диске довольно много места (вплоть до нескольких десятков Гб).
Служба Windows Error Reporting
Служба Windows Error Reporting представляет собой отдельный сервис Windows, который можно легко отключить командой:
net stop WerSvc
Внутри каталога WERReportQueue содержится множество каталогов, с именами в формате:
- Critical_6.3.9600.18384_{ID}_00000000_cab_3222bf78
- Critical_powershell.exe_{ID}_cab_271e13c0
- Critical_sqlservr.exe__{ID}_cab_b3a19651
- NonCritical_7.9.9600.18235__{ID}_0bfcb07a
- AppCrash_cmd.exe_{ID}_bda769bf_37d3b403
Как вы видите, имя каталога содержит степень критичности события и имя конкретного exe файла, который завершился аварийно. Во всех каталогах обязательно имеется файл Report.wer, который содержит описание ошибок и несколько файлов с дополнительной информацией.
Очистка папки WERReportQueue в Windows
Как правило, размер каждой папки незначителен, но в некоторых случаях для проблемного процесса генерируется дамп памяти, который занимает довольно много места. На скриншоте ниже видно, что размер файла дампа memory.hdmp составляет около 610 Мб. Парочка таким дампов – и на диске исчезло несколько свободных гигибайт.
Чтобы очистить все эти ошибки и журналы штатными средствами, откройте панель управления и перейдите в раздел ControlPanel -> System and Security -> Action Center -> Maintenance -> View reliability history -> View all problem reports и нажмите на кнопку Clear all problem reports.
Для быстрого освобождения места на диске от файлов отладки, сгенерированных службой WER, содержимое следующих каталогов можно безболезненно удалить и руками.
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive
- C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue
Отключение Window Error Reporting в Windows Server 2012 R2 / 2008 R2
Отключить запись информации об ошибках Windows Error Reporting в серверных редакция Windows можно следующим образом:
Отключение функции сбора и отправки отчетов в Windows 10
В Windows 10 возможность отключить Error Reporting через GUI отсутствует. Проверить статус компонента можно в панели управления Система и безопасность ->Центр безопасности и обслуживания -> секция Обслуживание. Как вы видите, по умолчанию параметр Поиск решения для указанных в отчетах проблем включен (Control Panel -> System and Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance -> Check for solutions to problem reports).
Отключить Windows Error Reporting в Windows 10 можно через реестр. Для этого в ветке HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting нужно создать новый параметр типа DWORD (32 бита) с именем Disabled и значением 1.
Теперь еще раз проверим статус параметра Поиск решения для указанных в отчетах проблем в панели управления. Его статус должен изменится на Отключено.
Отключение Windows Error Reporting через групповые политики
Ведение журналов службой Windows Error Reporting можно отключить и через групповую политику. Она находится в разделе Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Windows Error Reporting (Компоненты Windows -> Отчеты об ошибках Windows). Для отключения сбора и отправки данных включите политику Disable Windows Error Reporting (Отключить отчеты об ошибках Windows).
В результате сообщения об ошибках приложений в Windows перестанут формироваться и автоматически отправляться в Microsoft.
С ошибками в Windows знакомо большинство пользователей. Разработчики предусмотрели реакцию операционной системы на такие события, которая заключается в отсылке отчёта о неполадке на сервере Microsoft с целью её анализа и устранения в будущих обновлениях. Насколько хорошо программисты справляются с этой задачей, мы обсуждать не берёмся, но и сама эта служба далеко не безупречна, иногда приводя к зависаниям компьютера. Сегодня мы рассмотрим, как работает Windows Error Reporting и что делать, если она начинает грузить CPU и диск.
Тот факт, что служба WER может грузить компьютер, не удивителен – это достаточно сложный механизм, который должен уметь правильно реагировать на все возникающие проблемы, независимо от того, являются ли они системным сбоем или произошли во время работы пользовательских процессов.
Принцип действия службы можно описать следующим образом: когда возникает системный сбой, срабатывает специальный механизм, отлавливающий такие случаи (на техническом языке они называются необработанными исключениями). В этом случае записываются все возможные сопутствующие факторы (например, значения стека и регистров в момент возникновения исключения), после чего запускается компонента WER, занимающаяся анализом состояния аварийно завершившегося приложения. В её функции входит также и оповещение пользователя о проблеме. Обычно это процесс WerFault.exe, который запускается с полномочиями пользователя компьютера, и по настройкам по умолчанию именно он и выводит окно, сообщающее о возникновении сбоя.
Если дефолтные настройки не менялись (а такая возможность для этой службы имеется), то созданный в результате работы анализирующего модуля отчёт с включёнными в него данными об ошибке (дамп памяти и небольшой файл в формате XML, в котором содержатся некоторые подробности типа версий DLL-библиотек, используемых аварийно завершившимся процессом) отправляется на сервера Microsoft.
После этого пользователь уведомляется о проблеме и ему предлагаются варианты действий, который можно предпринять для попытки решить эту проблему. Что, конечно же, не гарантирует нужный результат. Это же сообщение дублируется в Центре поддержки Windows. Наконец, записываются все необходимые данные о состоянии приложения и операционной системы в службу Reliability Monitor (переводится как «Монитор стабильности системы»).
ВНИМАНИЕ. Windows Error Reporting срабатывает не всегда. Обязательное условие – наличие хотя бы одного активного окна приложения, в котором произошёл сбой. Вернее, окно не обязательно должно быть активным, но должно реагировать на системные запросы, что не всегда возможно. Если интерактивности по отношению к ОС нет, сбой всё равно будет отображён в журнале, но пользователь никаких сообщений не получит. Чтобы просмотреть сведения об ошибке, ему придётся вручную его искать в Центре поддержки. Это сделано для того, чтобы не вводить в заблуждение пользователя при возникновении аварийных ситуаций, не связанных с работой приложения, то есть это могут быть фоновые системные процессы.
Как отключить Windows problem reporting
Нередко сбои в работе приложений приводят к его аварийному завершению, но, когда в дело вступает Служба оповещений об ошибках, она сама становится источником проблем. Если такие случаи возникают часто при выполнении однотипных задач (например, при вставке большого массива данных в документ), самое простое решение – отключить службу WER, раз уж она не справляется со своими прямыми обязанностями.
Рассмотрим основные способы отключения Windows problem reporting, если служба грузит диск, процессор и систему в целом.
Очистка папок службы WER
Дампы с описанием ошибок обычно небольшие, но иногда дамп памяти, который обязательно включается в файл memory.hdmp, может достигать значительных размеров, порядка многих сотен мегабайт. Если на системном диске не так много места, с десяток таких дампов могут попросту исчерпать свободное пространство, и очередному отчёту уже не будет места – вот вам и проблемы, и зависания.
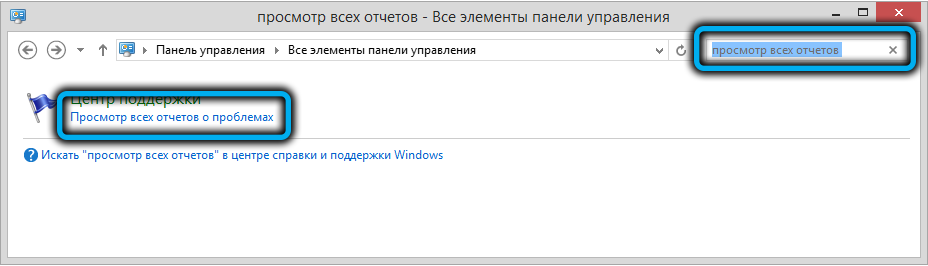
Для очистки логов службы запускаем Панель управления и набираем в строке поиска текст «Просмотр всех отчетов», выбираем из списка пункт с соответствующим названием, и в новом окне жмём кнопку «Очистить все отчёты о проблемах».
Ту же операцию можно выполнить вручную, очистив две папки, WERReportArchive и WERReportQueue, находящиеся в каталоге ProgramDataMicrosoftWindows, от всего содержимого (там могут быть сотни подкаталогов).
Наконец, имеется альтернативный вариант, позволяющий удалять только старые файлы из каталогов Windows Error Reporting, причём интервал в днях, задаётся пользователем. Это команды, выполняемые через PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportArchive' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30) | Remove-Item -force -Recurse
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsWERReportQueue' -Recurse | Where-Object CreationTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30) | Remove-Item -force –Recurse
В данном примере будут удалены все логи старше одного месяца.
Отключение WER в Windows 7/8
Но очистка логов службы – это не совсем правильное решение, ведь со временем ситуация может повториться. Проще отключить службу, ведь толку от неё мало. Делается это следующим образом:
Точно таким же образом, используя Панель управления, можно отключить службу WER в серверных версиях Windows (2019/2016/2012R2).
Отключение вывода отчётов об ошибках через системный реестр
К сожалению, в «десятке» этот простой способ не работает. Здесь имеется возможность только проверить статус службы (вкладка «Система и безопасность», переход в пункт «Центр безопасности и обслуживания», выбор подпункта «Обслуживание»). Хотя сам параметр «Отчёта о проблемах» здесь имеется, и он находится во включённом состоянии, кнопка отключения службы здесь не предусмотрена – очевидно, намеренно, чтобы иметь возможность всегда получать отчёты об ошибках.
Тем не менее, если Windows Error Reporting время от времени грузит компьютер, нужное решение имеется – для отключения службы придётся править системный реестр.
Для этого заходим в ветку HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting.
Кликаем по пустому месту в правом окне и создаём новый параметр (выбираем тип DWORD 32-битный), присваиваем этому параметру тип Disabled, а в поле «Значение» вбиваем 1.
Следующими командами можно отключить сбор и отправку логов об ошибках для некоторых или всех пользователей:
reg add "HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
reg add "HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsWindows Error Reporting" /v "Disabled" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f
Теперь, если вы зайдёте в Панель управления для проверки статуса службы, вместо On вы увидите Off, то есть у нас получилось отключить службу, призванную решать проблемы, но иногда создающую их.
При желании этот статус можно продублировать на всех компьютерах в рамках одного домена, используя GPO.
Отключение вывода отчётов об ошибках через редактор групповой политики
Действительно, если у вас есть сеть с несколькими компьютерами (а в среднем офисе их может быть десяток-другой), вместо того, чтобы выполнять все эти манипуляции энное количество раз, можно воспользоваться проверенным средством – редактором групповых политик.
Используя консоль «Выполнить», набираем команду gpmc.msc или gpedit.msc (первая – для редактора доменной GPO, вторая – для локальной). Ищем и открываем ветку Computer Configuration, затем выбираем подпункт Administrative Templates, заходим в ветку Windows Components, и наконец, кликаем по строке Windows Error Reporting.
Если в правом окне напротив параметра Disable Windows Error Reporting стоит значение Disabled, кликаем по этому параметру и в открывшемся окне изменяем его значение на Enable (Включено).
Вот и всё, теперь это правило будет действовать на все компьютерах в рамках домена. Кстати, точно такая же политика имеется в разделе User Configuration.
Как видим, для отключения службы Windows problem reporting требуется выполнить минимальное количество манипуляций, и только в Windows 10 придётся править реестр.

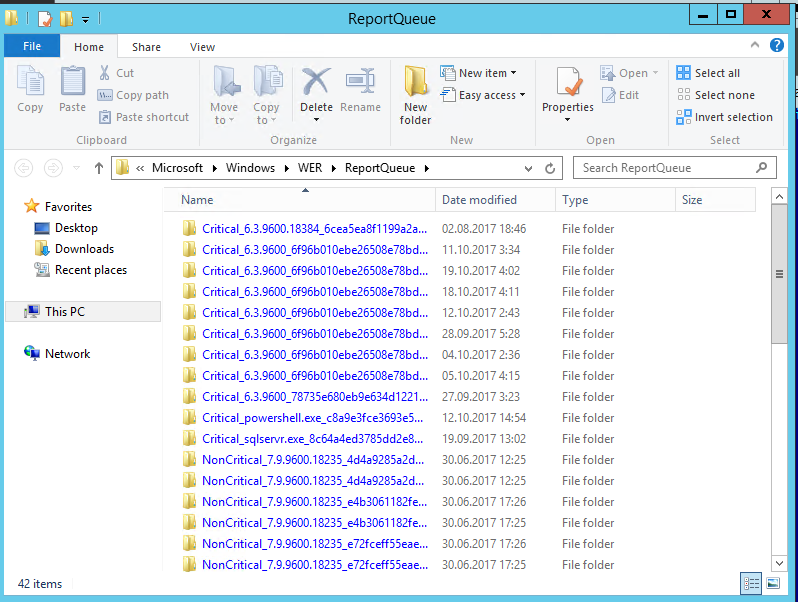
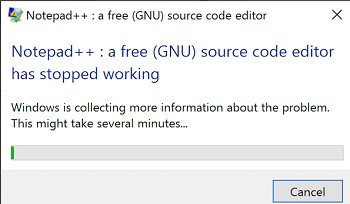
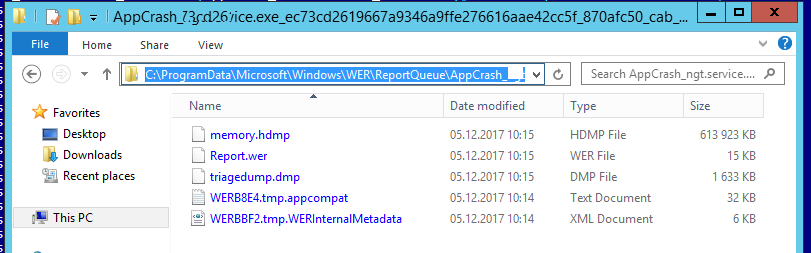
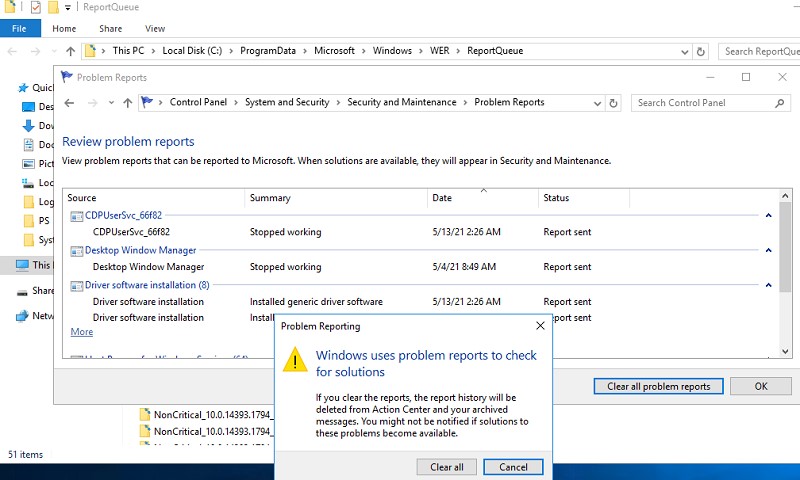
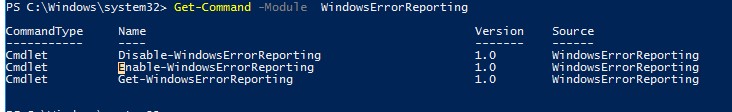
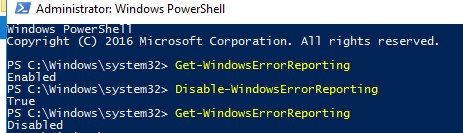
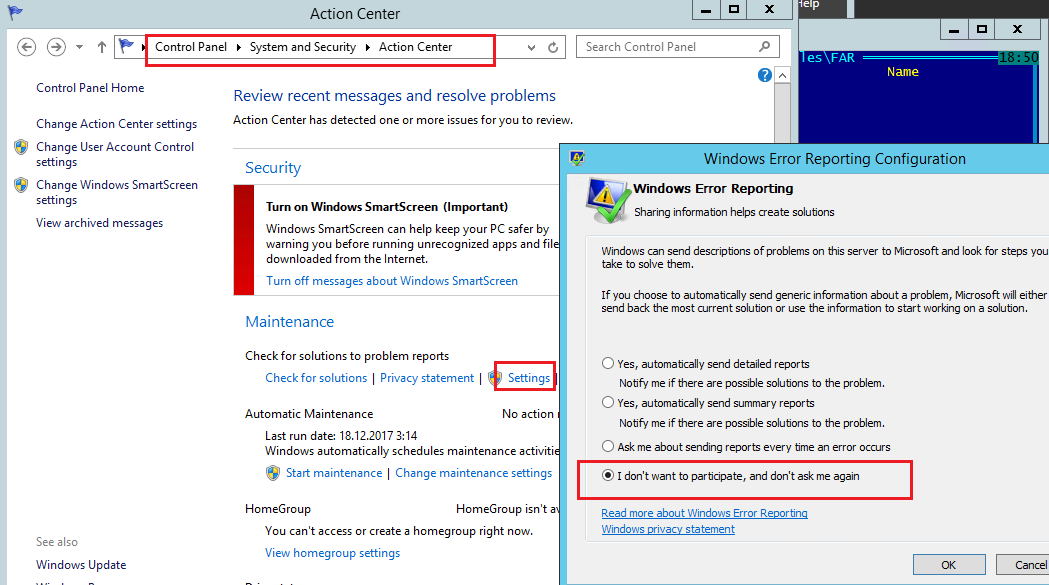
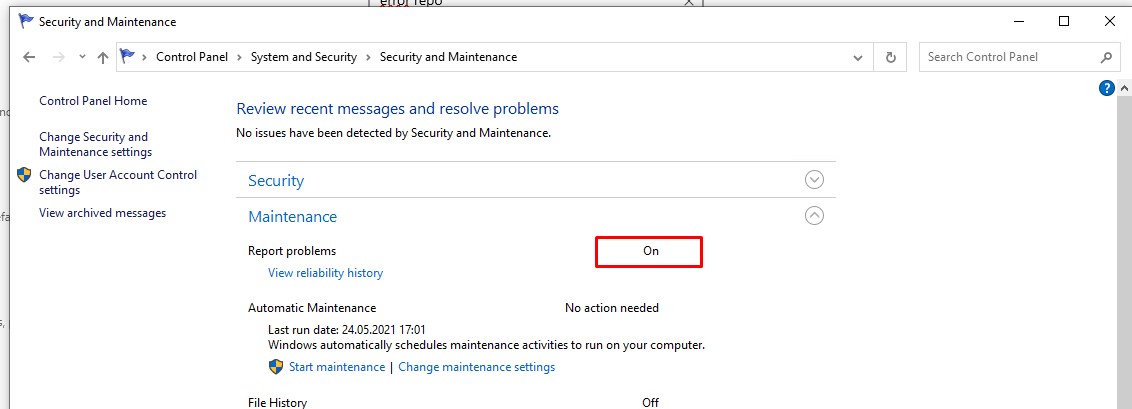
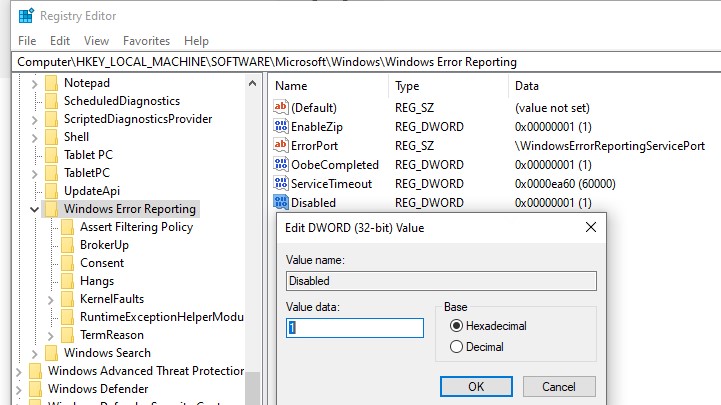

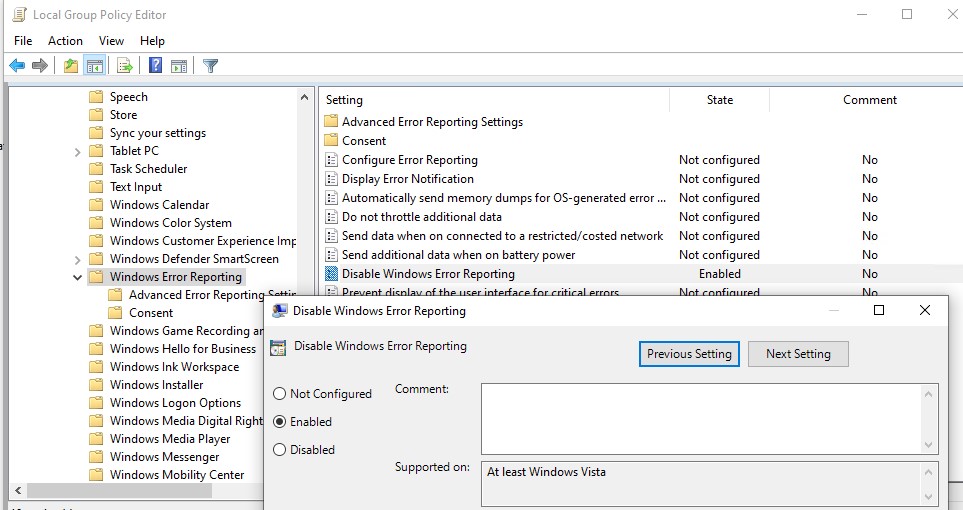




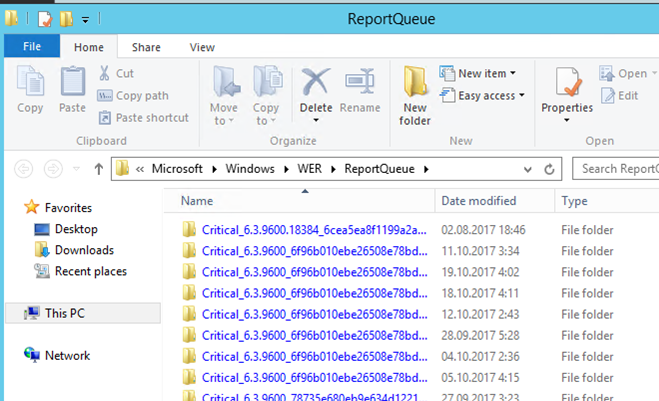
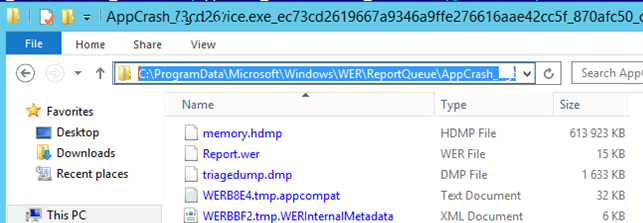
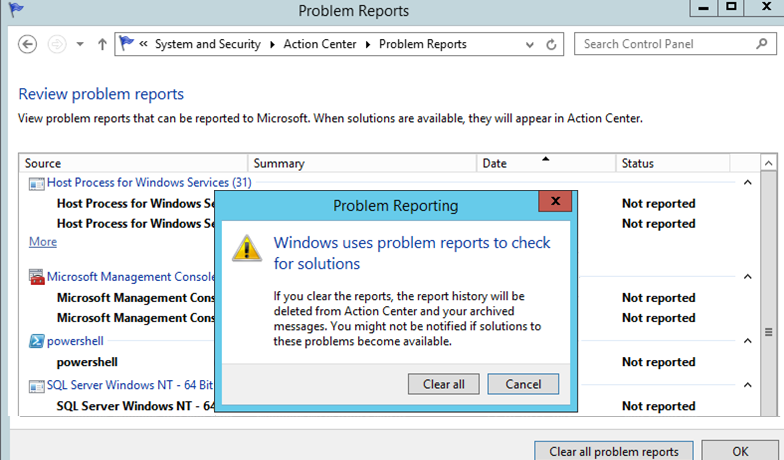
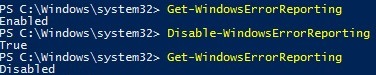
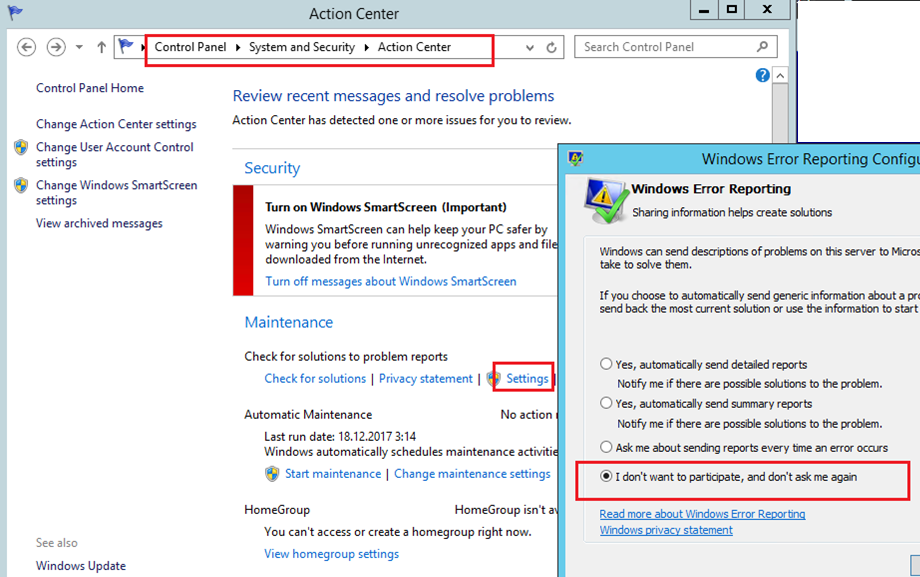
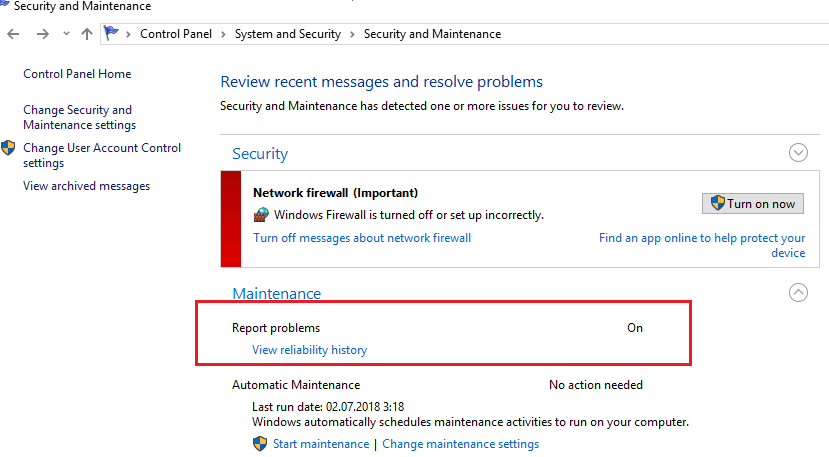
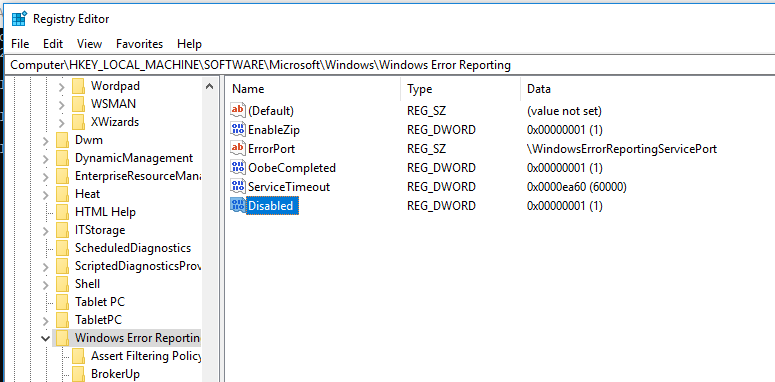
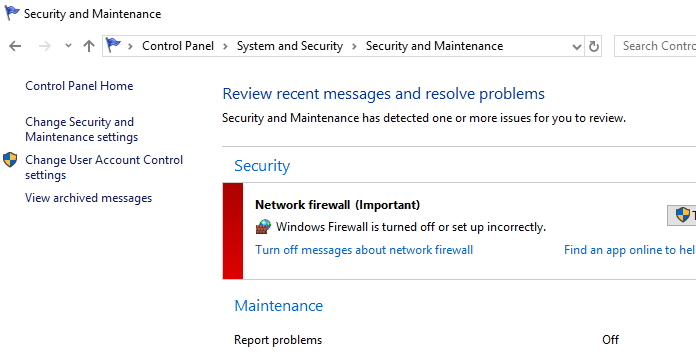
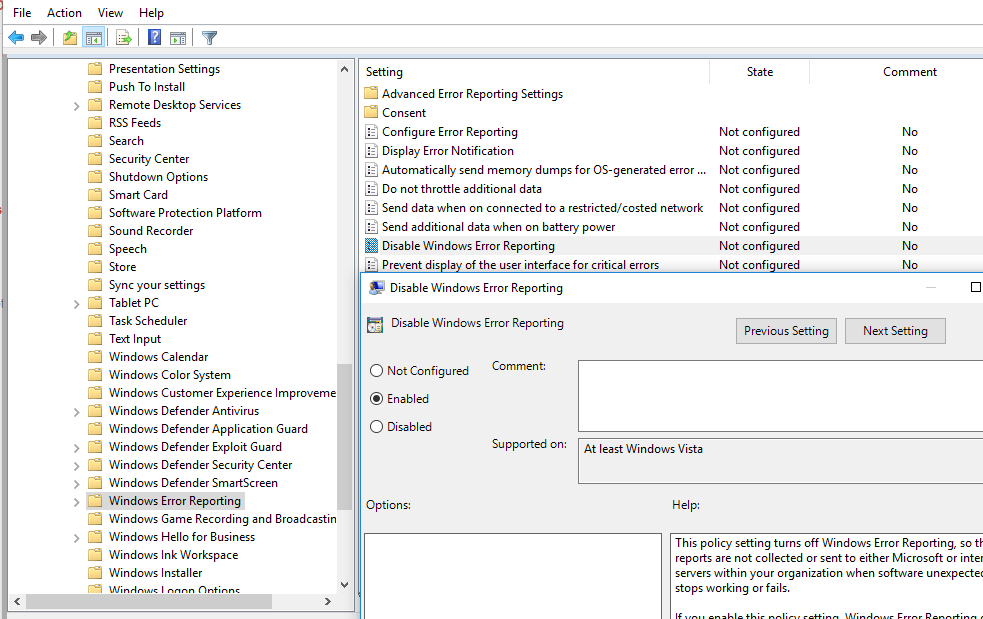

 NIAAOSwAuZX5C28
NIAAOSwAuZX5C28![Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting Windows Server 2016 unable to disable windows error reporting [IMG]](https://www.windowsphoneinfo.com/threads/windows-server-2016-unable-to-disable-windows-error-reporting.131628/proxy.php?image=https%3A%2F%2Fimgur.com%2Fa%2FRbJ7y&hash=86f3bf3cf835de3538e7cabc1b8d08ea)